Next-Gen Dynamic Hand Gesture Recognition: MediaPipe, Inception-v3 and LSTM-Based Enhanced Deep Learning Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Extending the work conducted by authors [3], we reduce the dimensionality of the 3D feature map to 1D while retaining the temporal aspects of the data.
- Temporal data that is present in the sequence of frames are utilized efficiently by the proposed hybrid model at a lower computational cost than existing methods.
- A lightweight model is proposed, reducing the computation complexity.
- The performance is improved compared to the baseline algorithm [3].
2. Related Work
2.1. Dynamic Hand Gesture Classification
2.2. Classification with Hybrid Deep Learning
3. Methodology
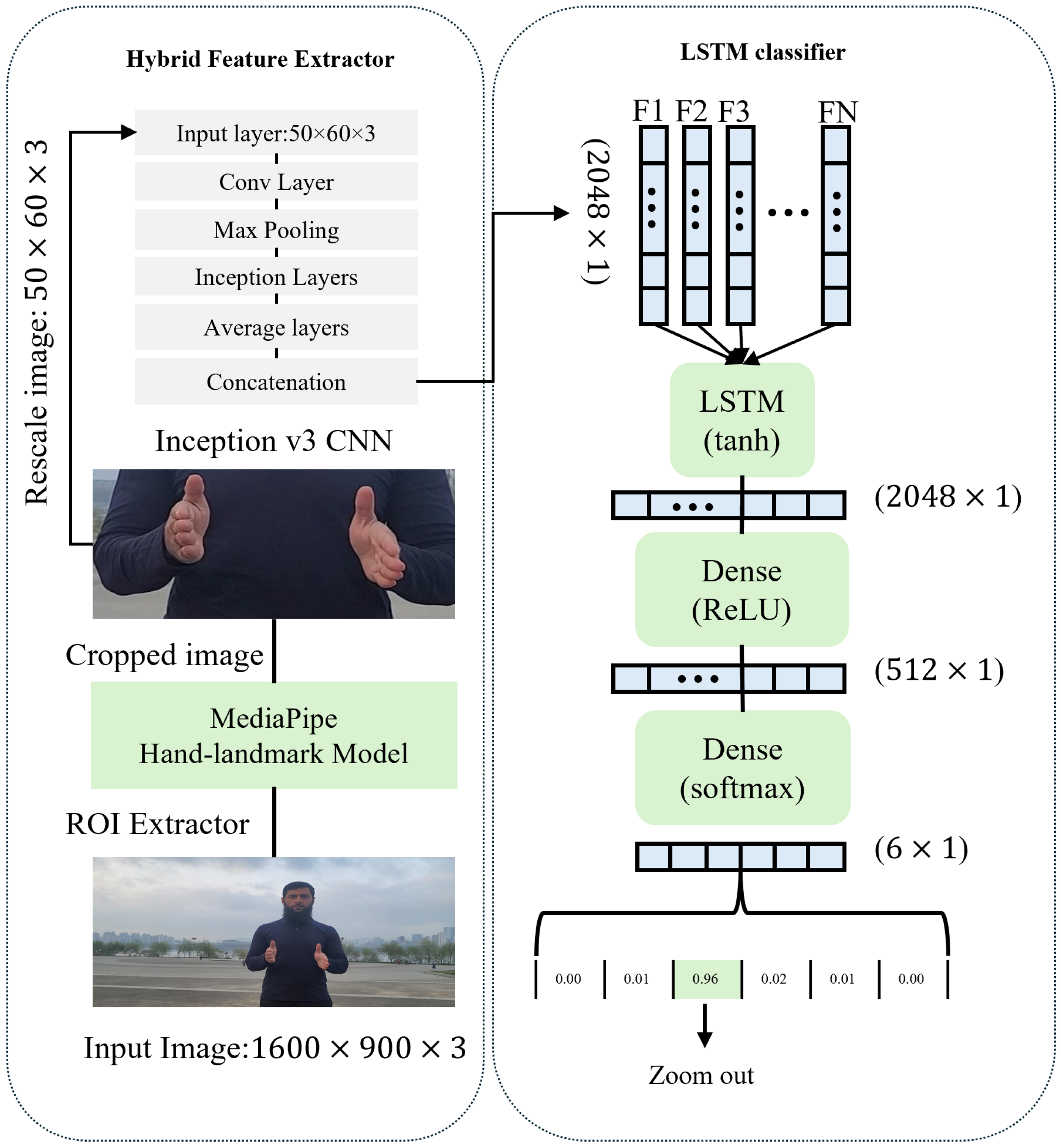
- The use of MediaPipe as an ROI extractor effectively locates the ROI, reducing the image dimension and computational cost.
- It also offers improved efficiency for hand landmark detection compared to Inception v3 alone.
- Time complexity is low, and real-time performance is highly durable compared to Inception v3 without MediaPipe.
- MediaPipe, when employed as an ROI extractor on the input layer in a hybrid architecture alongside an LSTM layer, as shown in Figure 1, exhibits a significant enhancement in terms of classification accuracy.
- The frame dimensions are lowered from (1600 × 900 × 3) to (50 × 60 × 3).
- In the case of baseline architecture, ten frames are processed per sequence, and the proposed architecture can process variable-length sequences.
3.1. Dynamic Hand Gesture Dataset
3.2. Data Processing Pipeline
3.3. Evaluating Criteria
- Accuracy: Reflects the model’s performance regarding the overall correctness for the given number of test instances (1).
- Recall: Also called true positive rate as it measures the model’s ability regarding true positives (2).
- F1-score: Reflects the model’s ability concerning false positives and negatives (3).
- Specificity: Reflects the model’s ability to correctly identify true negative instances (4).
4. Results
4.1. Experimental Setup
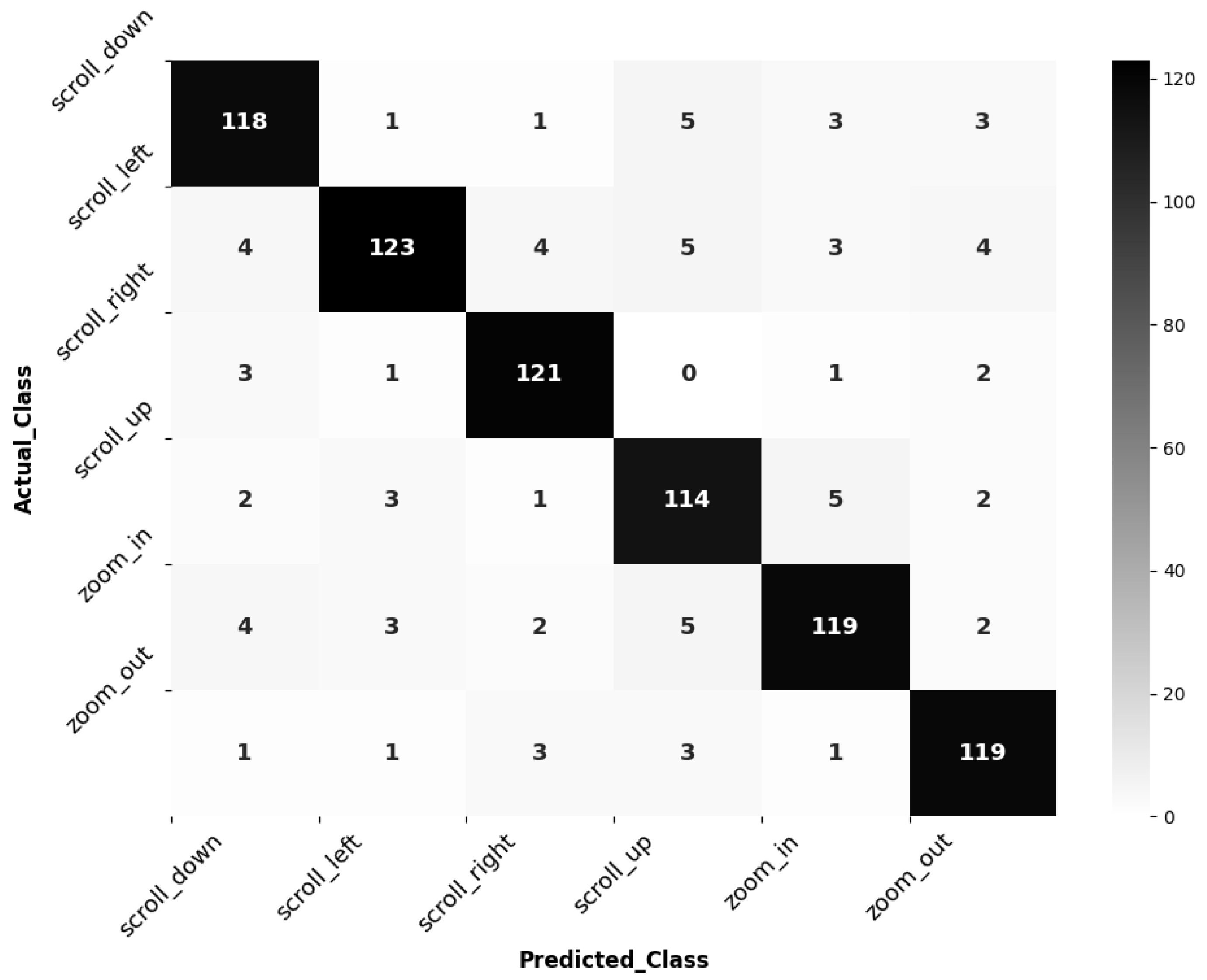
4.2. Performance Metrics and Visualizations
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HGR | Hand Gesture Recognition |
| CNN | Convolutional Neural Networks |
| RNN | Recurrent Neural Networks |
| GRU | Gated Recurrent Unit |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| ROI | Region of Interest |
References
- Rastgoo, R.; Kiani, K.; Escalera, S.; Sabokrou, M. Multi-modal zero-shot dynamic hand gesture recognition. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 247, 123349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaji, P.; Prusty, M.R. Multimodal fusion hierarchical self-attention network for dynamic hand gesture recognition. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2024, 98, 104019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hax, D.R.T.; Penava, P.; Krodel, S.; Razova, L.; Buettner, R. A Novel Hybrid Deep Learning Architecture for Dynamic Hand Gesture Recognition. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 28761–28774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karsh, B.; Laskar, R.H.; Karsh, R.K. mXception and dynamic image for hand gesture recognition. Neural Comput. Appl. 2024, 36, 8281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunanda; Balmik, A.; Nandy, A. A novel feature fusion technique for robust hand gesture recognition. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2024, 83, 65815–65831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Li, Y.; Fu, X.; Miao, K.; Miao, Q. Review of dynamic gesture recognition. Virtual Real. Intell. Hardw. 2021, 3, 183–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.; Karsh, R.K.; Barbhuiya, A.A. Literature review of vision-based dynamic gesture recognition using deep learning techniques. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2022, 34, e7159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapuscinski, T.; Inglot, K. Vision-based gesture modeling for signed expressions recognition. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2022, 207, 1007–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaseen; Kwon, O.J.; Lee, J.; Ullah, F.; Jamil, S.; Kim, J.S. Automatic Sequential Stitching of High-Resolution Panorama for Android Devices Using Precapture Feature Detection and the Orientation Sensor. Sensors 2023, 23, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullahi, S.B.; Chamnongthai, K. American sign language words recognition of skeletal videos using processed video driven multi-stacked deep LSTM. Sensors 2022, 22, 1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxe, A.; Nelli, S.; Summerfield, C. If deep learning is the answer, what is the question? Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2021, 22, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Liu, W.; Jia, Y.; Sermanet, P.; Reed, S.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Vanhoucke, V.; Rabinovich, A. Going deeper with convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Boston, MA, USA, 7–12 June 2015; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Liu, F.; Yang, W.; Peng, S.; Zhou, J. A survey of convolutional neural networks: Analysis, applications, and prospects. IEEE Trans. Neural Networks Learn. Syst. 2021, 33, 6999–7019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Cao, J.; Philip, S.Y. Deep learning for spatio-temporal data mining: A survey. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2020, 34, 3681–3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ur Rehman, A.; Belhaouari, S.B.; Kabir, M.A.; Khan, A. On the use of deep learning for video classification. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adithya, V.; Rajesh, R. A deep convolutional neural network approach for static hand gesture recognition. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2020, 171, 2353–2361. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, C.; Saito, A.; Sugiura, Y. Using the virtual data-driven measurement to support the prototyping of hand gesture recognition interface with distance sensor. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2022, 338, 113463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, T.L.; Tran, S.D.; Nguyen, T.H.; Kim, S.; Monet, N. An improved hand gesture recognition system using keypoints and hand bounding boxes. Array 2022, 16, 100251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rautaray, S.S.; Agrawal, A. Real time gesture recognition system for interaction in dynamic environment. Procedia Technol. 2012, 4, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naguri, C.R.; Bunescu, R.C. Recognition of dynamic hand gestures from 3D motion data using LSTM and CNN architectures. In Proceedings of the 2017 16th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA), Cancun, Mexico, 18–21 December 2017; pp. 1130–1133. [Google Scholar]
- Huu, P.N.; Ngoc, T.L. Two-stream convolutional network for dynamic hand gesture recognition using convolutional long short-term memory networks. Vietnam J. Sci. Technol. 2020, 58, 514–523. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, J. Dynamic hand gesture recognition based on 3D convolutional neural network models. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 16th International Conference on Networking, Sensing and Control (ICNSC), Banff, AB, Canada, 9–11 May 2019; pp. 224–229. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Lafreniere, B.; Zhao, J. Exploring Visualizations for Precisely Guiding Bare Hand Gestures in Virtual Reality. In Proceedings of the CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Honolulu, HI, USA, 11–14 May 2024; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, W.; Cheng, J.; Yang, F.; Xu, Y. Two-stream convolutional network for improving activity recognition using convolutional long short-term memory networks. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 67772–67780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.Y.; Chen, M.H.; Kira, Z.; AlRegib, G. TS-LSTM and temporal-inception: Exploiting spatiotemporal dynamics for activity recognition. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2019, 71, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullahi, S.B.; Bature, Z.A.; Gabralla, L.A.; Chiroma, H. Lie recognition with multi-modal spatial–temporal state transition patterns based on hybrid convolutional neural network–bidirectional long short-term memory. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durstewitz, D.; Koppe, G.; Thurm, M.I. Reconstructing computational system dynamics from neural data with recurrent neural networks. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2023, 24, 693–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendrikx, N.; Barhmi, K.; Visser, L.; de Bruin, T.; Pó, M.; Salah, A.; van Sark, W. All sky imaging-based short-term solar irradiance forecasting with Long Short-Term Memory networks. Sol. Energy 2024, 272, 112463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiq, I.; Mahmood, A.; Ahmed, U.; Khan, A.R.; Arshad, K.; Assaleh, K.; Ratyal, N.I.; Zoha, A. A Hybrid Approach for Forecasting Occupancy of Building’s Multiple Space Types. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 50202–50216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Shang, Y.; Liu, T.; Shao, Z.; Guo, G.; Ding, H.; Hu, Q. Spatial–temporal attention network for depression recognition from facial videos. Expert Syst. Appl. 2024, 237, 121410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 2818–2826. [Google Scholar]
- Lugaresi, C.; Tang, J.; Nash, H.; McClanahan, C.; Uboweja, E.; Hays, M.; Zhang, F.; Chang, C.L.; Yong, M.; Lee, J.; et al. Mediapipe: A framework for perceiving and processing reality. In Proceedings of the Third Workshop on Computer Vision for AR/VR at IEEE Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) 2019, Long Beach, CA, USA, 17 June 2019; Volume 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Jeeru, S.; Sivapuram, A.K.; León, D.G.; Gröli, J.; Yeduri, S.R.; Cenkeramaddi, L.R. Depth camera based dataset of hand gestures. Data Brief 2022, 45, 108659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhingra, N.; Kunz, A. Res3atn-Deep 3D residual attention network for hand gesture recognition in videos. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Quebec City, QC, Canada, 16–19 September 2019; pp. 491–501. [Google Scholar]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Two-stream convolutional networks for action recognition in videos. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–13 December 2014; Volume 27. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, D.; Bourdev, L.; Fergus, R.; Torresani, L.; Paluri, M. Learning spatiotemporal features with 3D convolutional networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision 2015, Santiago, Chile, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 4489–4497. [Google Scholar]


| Data | Recall | F1-Score | Specificity | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Validation | 89.9% | 89.7% | 98.0% | 90.1% |
| Test | 91.5% | 90.0% | 97.9% | 89.7% |
| Architecture | Model | Data | Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hax et al. [3] | Inception-LSTM | Validation | 84.7% |
| Test | 83.6% | ||
| Res3-ATN [37] | Residual-Attention Network | Validation | 64.13% |
| Test | 62.70% | ||
| Spat. st. CNN [38] | Two Streams CNN | Validation | 55.79% |
| Test | 54.60% | ||
| C3D [39] | 3D CNNs | Validation | 64.90% |
| Test | 69.30% | ||
| Ours | ROI-Inception-LSTM | Validation | 90.1% |
| Test | 89.7% | ||
| ROI-Inception-GRU | Validation | 85.6% | |
| Test | 84.1% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yaseen; Kwon, O.-J.; Kim, J.; Jamil, S.; Lee, J.; Ullah, F. Next-Gen Dynamic Hand Gesture Recognition: MediaPipe, Inception-v3 and LSTM-Based Enhanced Deep Learning Model. Electronics 2024, 13, 3233. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13163233
Yaseen, Kwon O-J, Kim J, Jamil S, Lee J, Ullah F. Next-Gen Dynamic Hand Gesture Recognition: MediaPipe, Inception-v3 and LSTM-Based Enhanced Deep Learning Model. Electronics. 2024; 13(16):3233. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13163233
Chicago/Turabian StyleYaseen, Oh-Jin Kwon, Jaeho Kim, Sonain Jamil, Jinhee Lee, and Faiz Ullah. 2024. "Next-Gen Dynamic Hand Gesture Recognition: MediaPipe, Inception-v3 and LSTM-Based Enhanced Deep Learning Model" Electronics 13, no. 16: 3233. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13163233
APA StyleYaseen, Kwon, O.-J., Kim, J., Jamil, S., Lee, J., & Ullah, F. (2024). Next-Gen Dynamic Hand Gesture Recognition: MediaPipe, Inception-v3 and LSTM-Based Enhanced Deep Learning Model. Electronics, 13(16), 3233. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13163233









