Multi-Agent Collaborative Path Planning Algorithm with Multiple Meeting Points
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Related Work
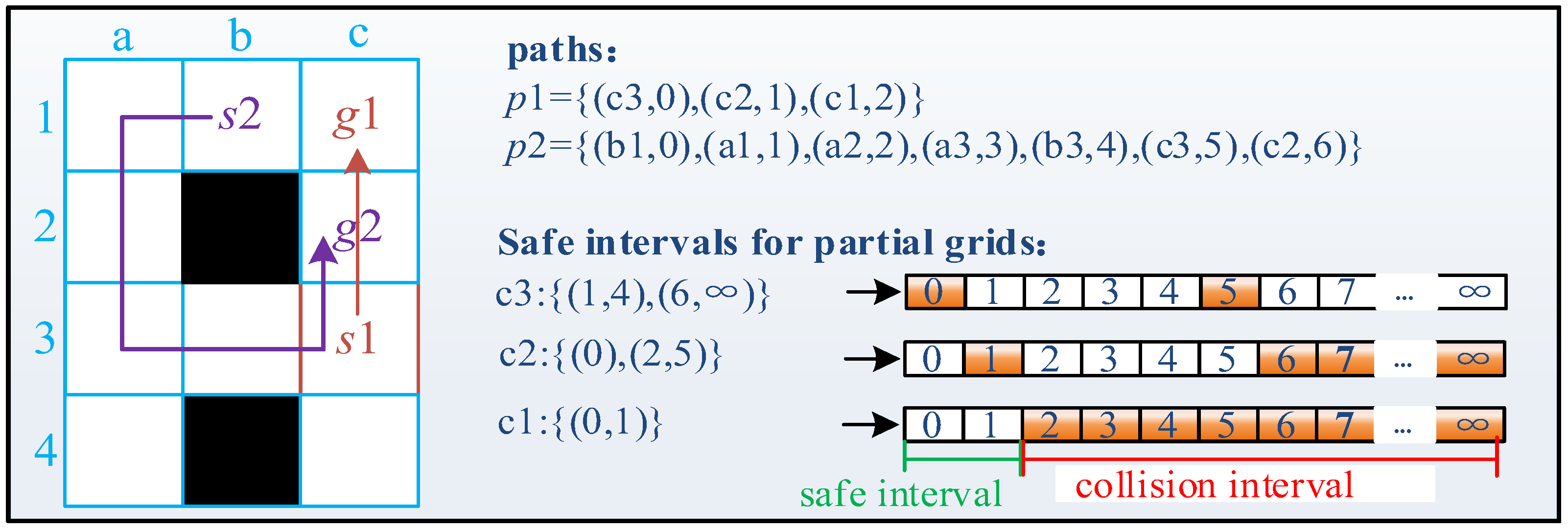
2.1. Basic Principles of the SIPP and CBS Algorithms
2.2. Research Progress on Multi-Agent Collaboration
3. Problem Description
3.1. MAPF Definition
3.2. Co-MAPF Description
3.2.1. Co-MAPF Definition
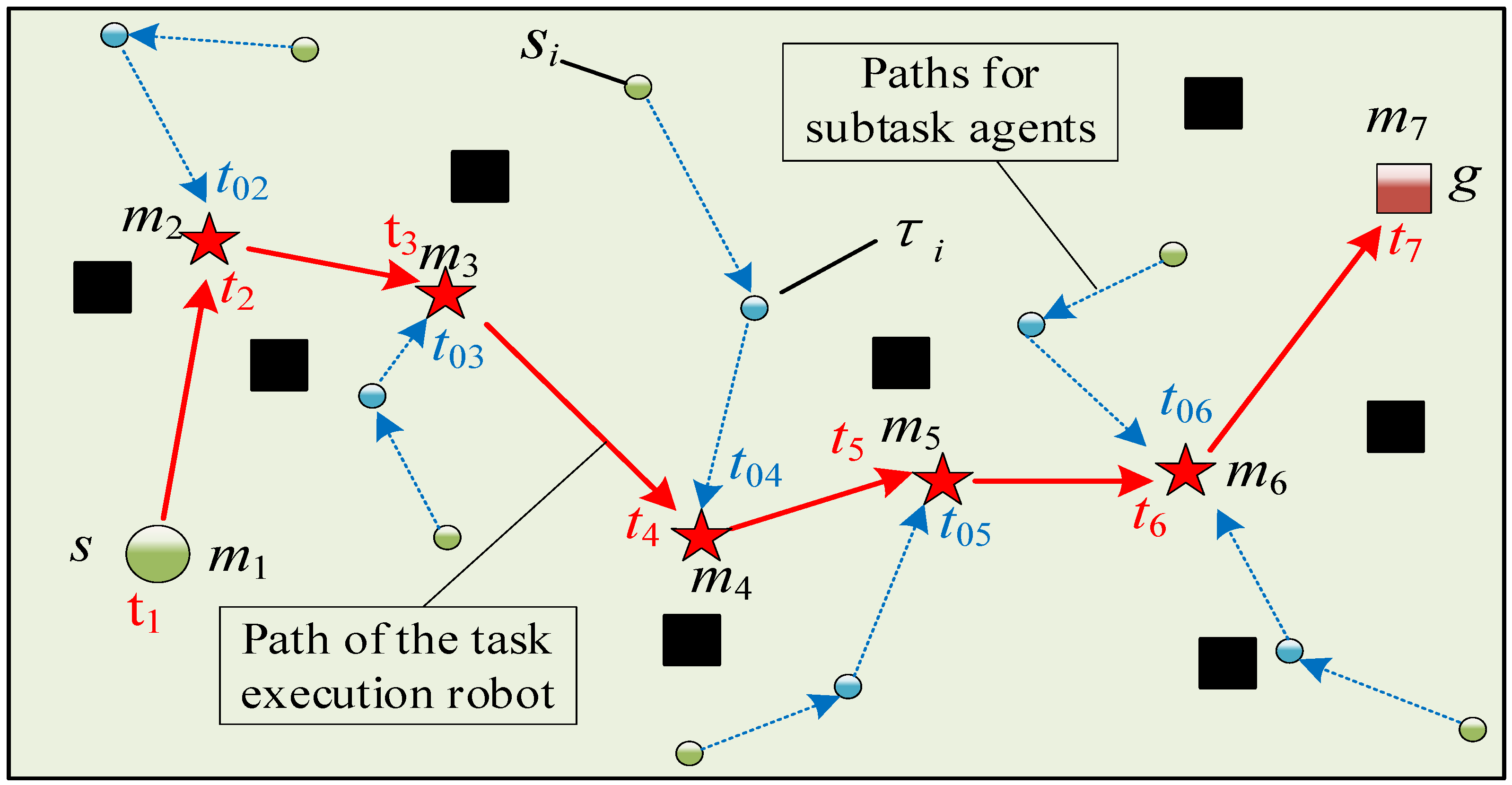
3.2.2. Two Forms of Collaborative Task Handover
4. Co-DP Algorithm
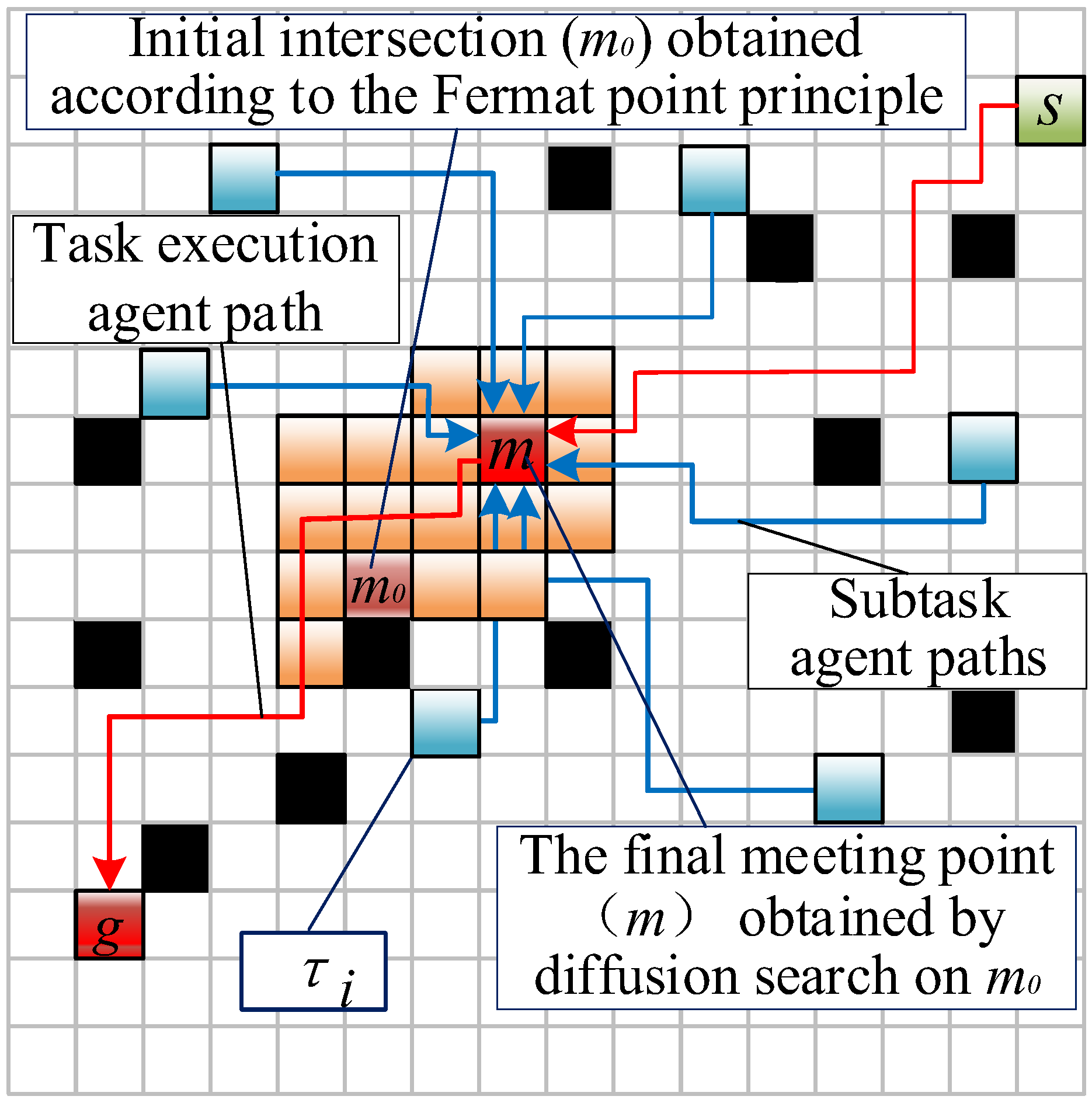
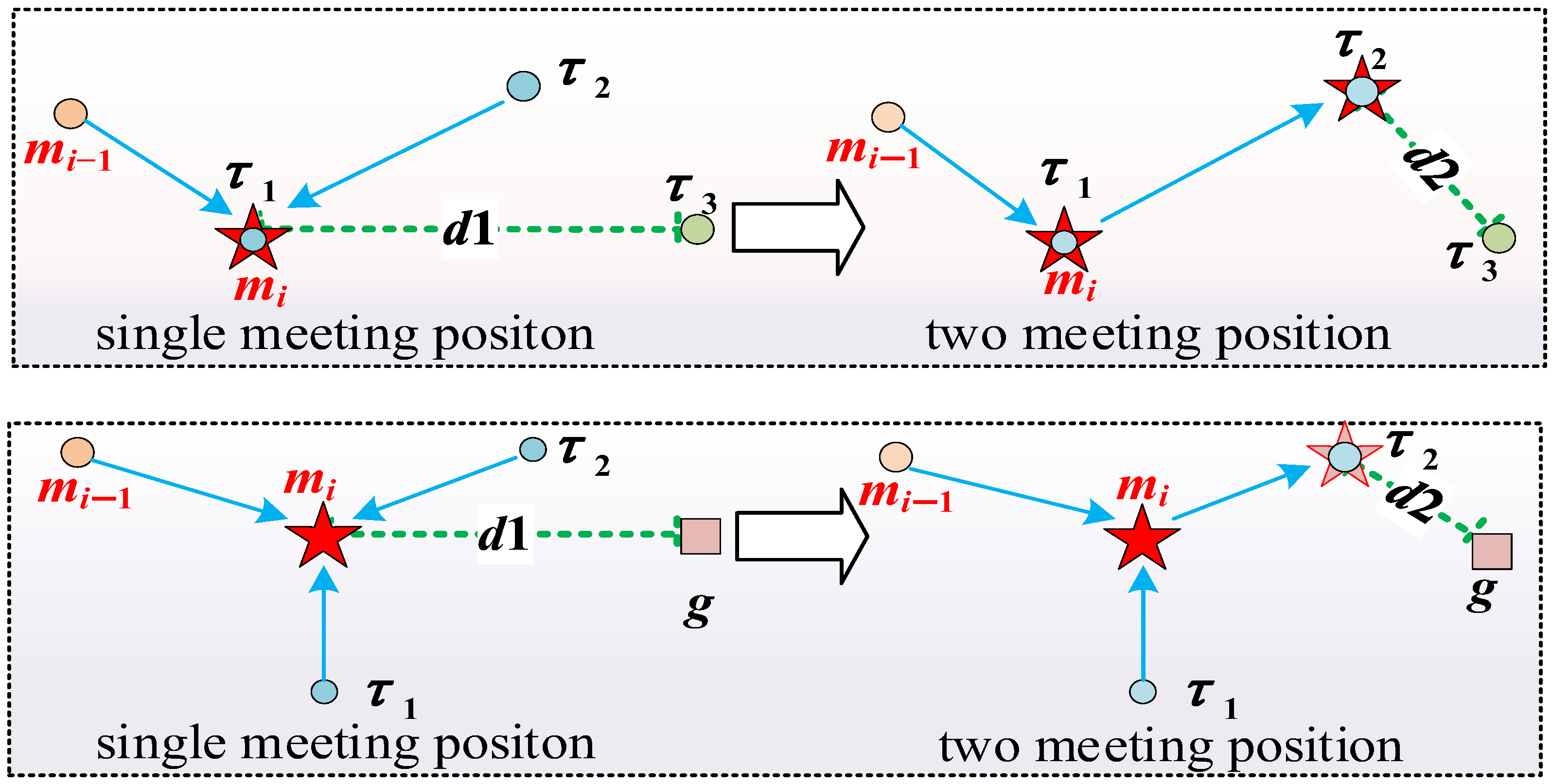
4.1. Multiple Meeting Points Solution Method Considering Obstacles
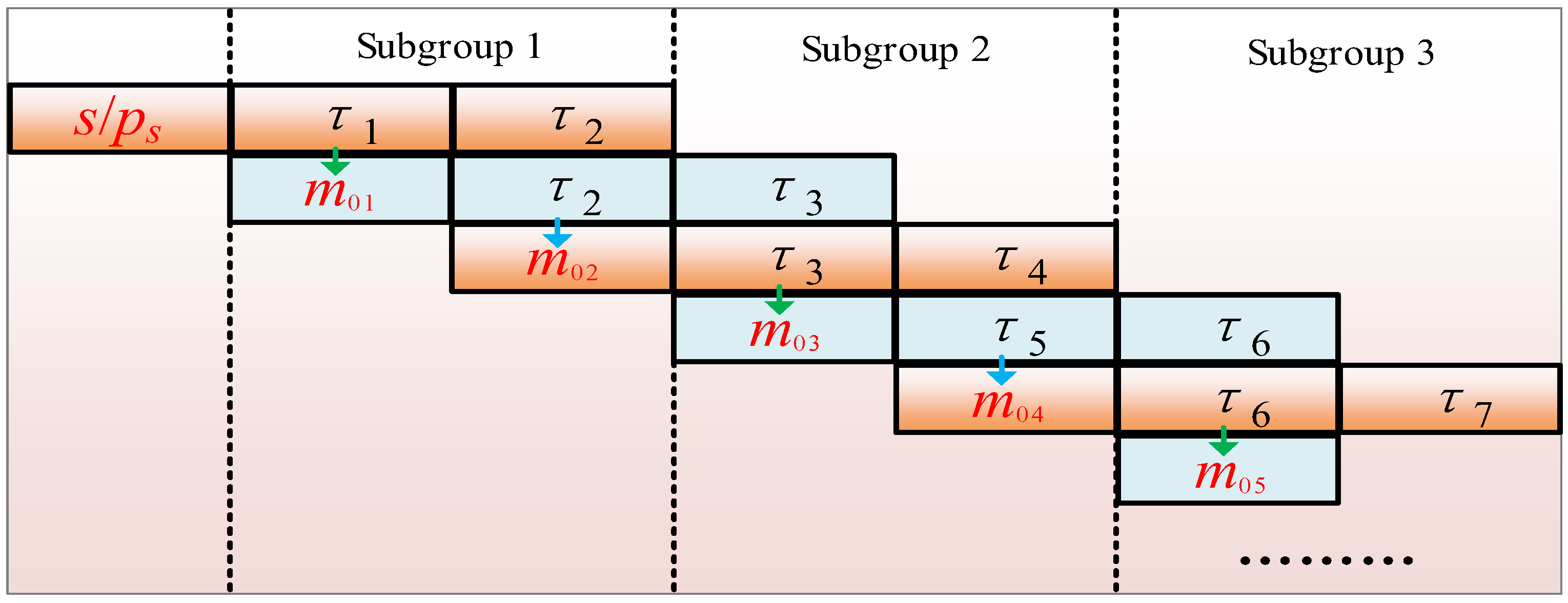
4.2. Segmented Path Planning Strategy
4.3. Hybrid Solution Mode Switching Mechanism
4.4. Pseudocode and Flowchart of the Co- Algorithm
| Algorithm 1: Co- algorithm |
| input: %, initial use of multi-meeting-point solving mode |
| output: |
| 1: while < do |
| 2: for in Group do |
| 3: if = then |
| 4: ←CalMultipleMeetingPoints() %Solving for multiple meeting points |
| 5: end if |
| 6: if = then |
| 7: ←CalSingleMeetingPoint() %Solving for single meeting point |
| 8: end if |
| 9: for in do |
| 10: ←( |
| 11: if then |
| 12: insert , update %Update safe intervals to avoid future conflicts |
| 13: end if |
| 14: if then |
| 15: if = P and ≥ 1/6∙ then |
| 16: =SP |
| 17: end if |
| 18: ←DeterReScheduling() %Set the priority of failed groups to the highest |
| 19: ← |
| 20: ←,← |
| 21: end if |
| 22: end for |
| 23: end for |
| 24: return , |
| 25: end while |
| 26: return |
| Algorithm 2: iSIPP algorithm |
| input:,= |
| output: |
| 1: while do |
| 2: expand nodes using A* |
| 3: if OPEN = then |
| 4: return |
| 5: end if |
| 6: if not then |
| 7: if then |
| 8: if is then |
| 9: Perform the wait operation according to Equation (11) |
| 10: end if |
| 11: %A unvisited meeting location as new goal point |
| 12: if is then |
| 13: %Plan to the ultimate goal |
| 14: end if |
| 15: end if |
| 16: end if |
| 17: if then |
| 18: if then |
| 19: return |
| 20: end if |
| 21: end if |
| 22: end while |
5. Simulation Experimental Analysis
5.1. Experimental Parameter Settings
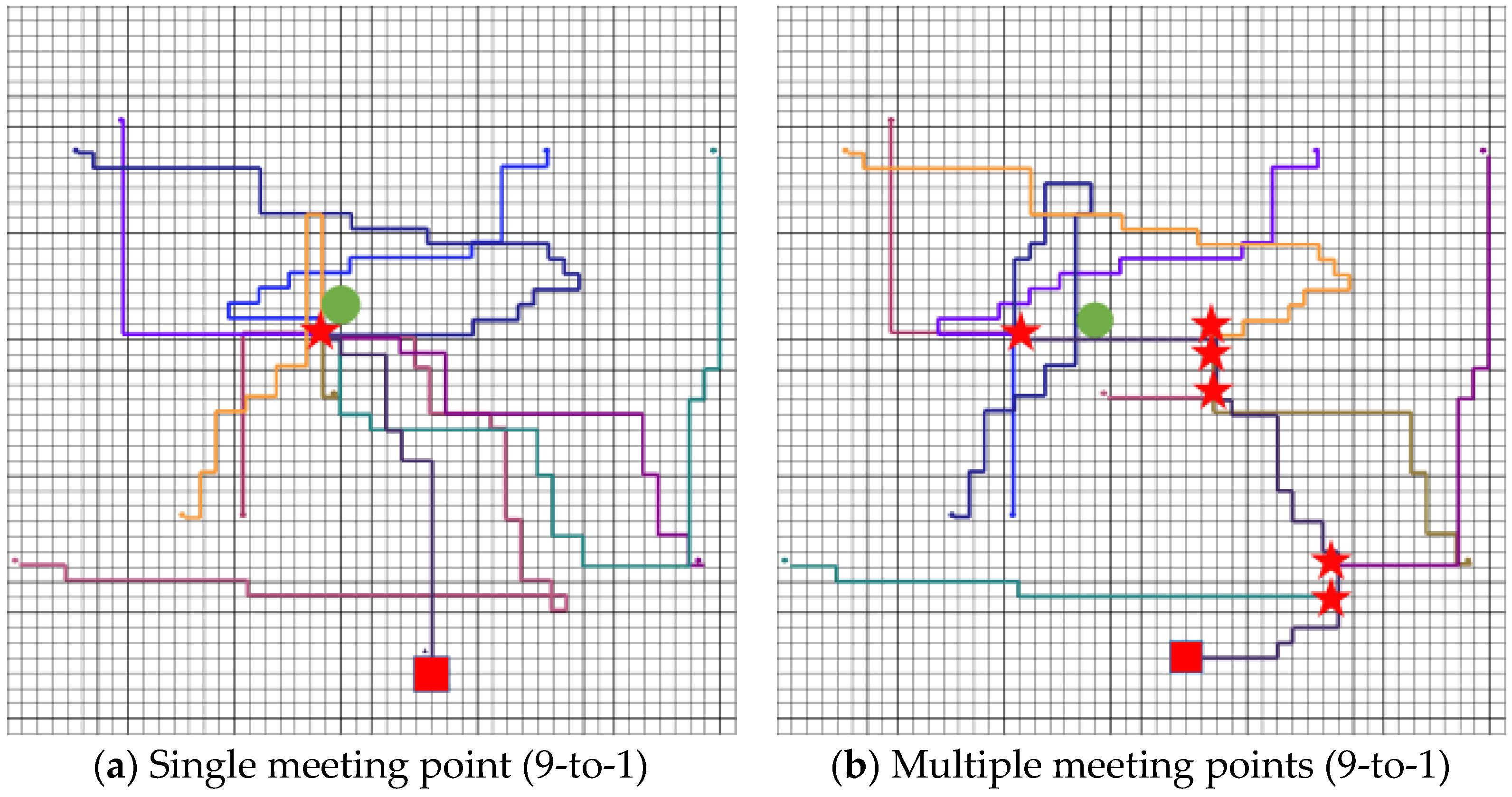
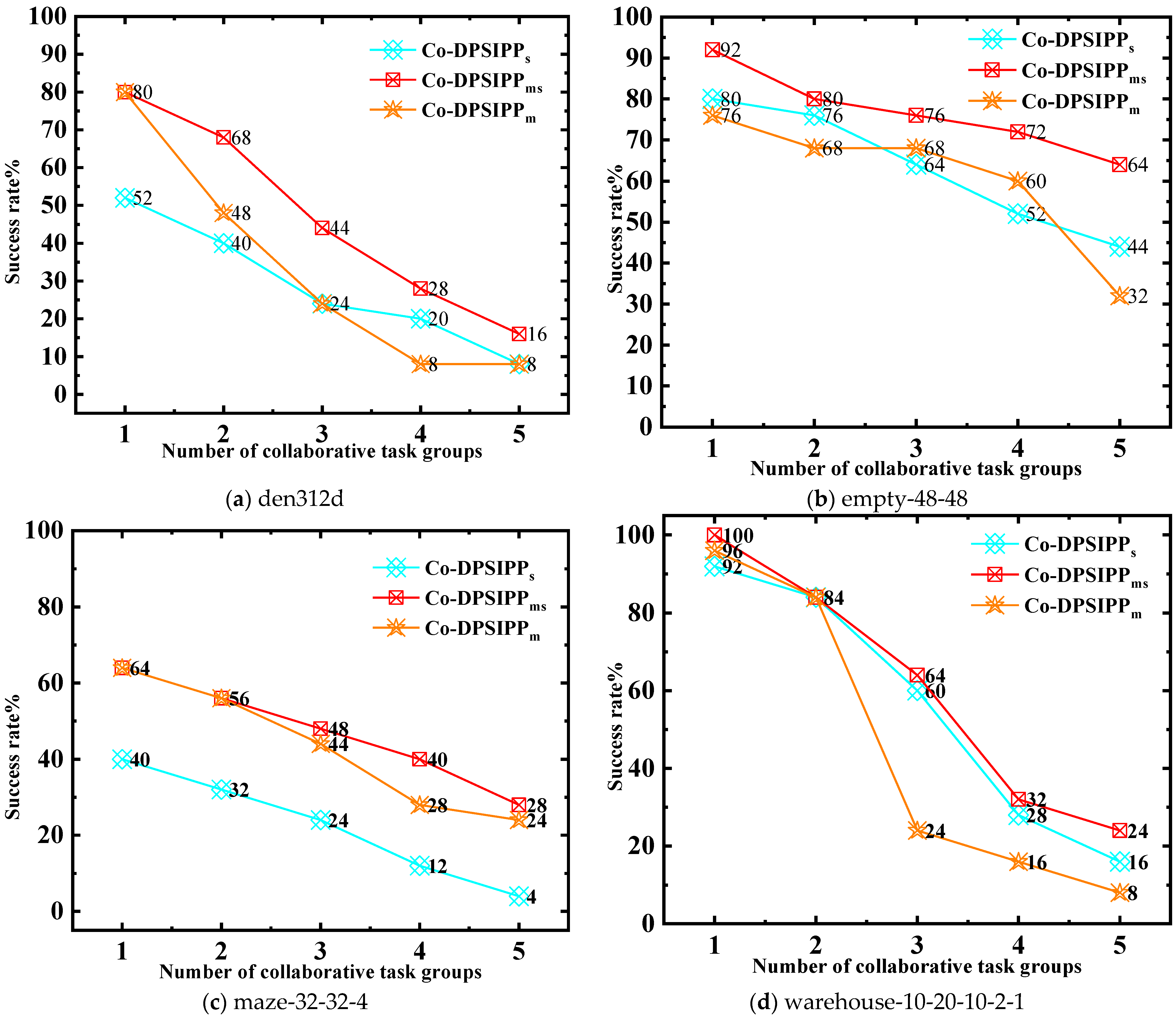
5.2. Simulation Experiment 1
5.3. Simulation Experiment 2
5.4. Simulation Experiment 3
6. Experimental Verification
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Stern, R.; Sturtevant, N.; Felner, A.; Koenig, S.; Ma, H.; Walker, T.T.; Li, J.; Atzmon, D.; Cohen, L.; Satish Kumar, T.K.; et al. Multi-agent pathfinding: Definitions, variants, and benchmarks. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Combinatorial Search, Napa, CA, USA, 16–17 July 2019; Volume 10, pp. 151–158. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Z.; Rathinam, S.; Choset, H. A conflict-based search framework for multiobjective multiagent path finding. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2022, 20, 1262–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, Z.A.; Yakovlev, K. Safe Interval Path Planning with Kinodynamic Constraints. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Washington, DC, USA, 7–14 February 2023; Volume 37, pp. 12330–12337. [Google Scholar]
- Cohen, L.; Wagner, G.; Chan, D.; Choset, H.; Sturtevant, N.; Koenig, S.; Satish Kumar, T.K. Rapid randomized restarts for multi-agent path finding solvers. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Combinatorial Search, Stockholm, Sweden, 14–15 July 2018; Volume 9, pp. 148–152. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.; Han, G.; Du, J.; Xu, T.; Lv, Z. Spatiotemporal congestion-aware path planning toward intelligent transportation systems in software-defined smart city IoT. Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 8012–8024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Jia-Qiang, E.; Hao, Z.; Yuan-Wang, D. Driving-Record-Based Distributed Path-Planning for Autonomous Vehicle. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Transportation, Big Data and Smart City, Xi’an, China, 19–20 December 2015; pp. 320–323. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, N.; Shi, H.; Han, G.; Wang, B.; Shu, L. Dynamic path planning algorithms with load balancing based on data prediction for smart transportation systems. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 15907–15922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Li, C.; Hui, Y.; Hui, Y.; Yang, J. Space-Time Map Based Path Planning solution in Large-Scale Intelligent Warehouse System. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems, Rhodes, Greece, 20–23 September 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Hu, B.; Huang, R. Task allocation and path planning of many robots with motion uncertainty in a warehouse environment. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Real-Time Computing and Robotics, Xining, China, 15–19 July 2021; pp. 776–781. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, L. A coordinated path planning algorithm for multi-robot in intelligent warehouse. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics, Dali, China, 6–8 December 2019; pp. 2945–2950. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, H.; Lin, Y.; Wu, J.B. Co-evolutionary optimization algorithm based on the future traffic environment for emergency rescue path planning. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 148125–148135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dresner, K.; Stone, P. A multiagent approach to autonomous handover point management. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2008, 31, 591–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, C.; Pham, H.X.; La, H.M. A Multi-Robotic System for Environmental Cleaning. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1811.00690. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, M.; Likhachev, M. Sipp: Safe interval path planning for dynamic environments. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Shanghai, China, 9–13 May 2011; pp. 5628–5635. [Google Scholar]
- Silver, D. Cooperative pathfinding. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Interactive Digital Entertainment, Marina Del Rey, CA, USA, 1–3 June 2005; Volume 1, pp. 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Sharon, G.; Stern, R.; Felner, A.; Sturtevant, N.R. Conflict-based search for optimal multi-agent pathfinding. Artif. Intell. 2015, 219, 40–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, G.; Choset, H. M*: A complete multirobot path planning algorithm with performance bounds. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, San Francisco, CA, USA, 25–30 September 2011; pp. 3260–3267. [Google Scholar]
- Lan, X.; Lv, X.; Liu, W.; He, Y.; Zhang, X. Research on robot global path planning based on improved A-star ant colony algorithm. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 5th Advanced Information Technology, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (IAEAC), Xi’an, China, 12–14 March 2021; Volume 5, pp. 613–617. [Google Scholar]
- Narayanan, V.; Phillips, M.; Likhachev, M. Anytime safe interval path planning for dynamic environments. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Algarve, Portugal, 7–12 October 2012; pp. 4708–4715. [Google Scholar]
- Yakovlev, K.; Andreychuk, A.; Stern, R. Revisiting bounded-suboptimal safe interval path planning. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Automated Planning and Scheduling, Nancy, France, 26–30 October 2020; Volume 30, pp. 300–304. [Google Scholar]
- Barer, M.; Sharon, G.; Stern, R.; Felner, A. Suboptimal variants of the conflict-based search algorithm for the multi-agent pathfinding problem. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Combinatorial Search, Prague, Czech Republic, 15–17 August 2014; Volume 5, pp. 19–27. [Google Scholar]
- Boyarski, E.; Felner, A.; Stern, R.; Sharon, G.; Betzalel, O.; Tolpin, D.; Shimony, E. Icbs: The improved conflict-based search algorithm for multi-agent path finding. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Combinatorial Search, Jerusalem, Israel, 11–13 June 2015; Volume 6, pp. 223–225. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Ruml, W.; Koenig, S. EECBS: A bounded-suboptimal search for multi-agent path finding. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 2–9 February 2021; Volume 35, pp. 12353–12362. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.; Li, J.; Kumar, T.K.; Koenig, S. Lifelong multi-agent path finding for online pickup and delivery tasks. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1705.10868. [Google Scholar]
- Greshler, N.; Gordon, O.; Salzman, O.; Shimkin, N. Cooperative multi-agent path finding: Beyond path planning and collision avoidance. In Proceedings of the 2021 International Symposium on Multi-Robot and Multi-Agent Systems (MRS), Cambridge, UK, 4–5 November 2021; pp. 20–28. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, S.; Gu, C.; Wan, Q.; Huang, H.; Jia, X. CROTPN based collision-free and deadlock-free path planning of AGVs in logistic center. In Proceedings of the 2018 15th International Conference on Control, Automation, Robotics and Vision (ICARCV), Singapore, 18–21 November 2018; pp. 1685–1691. [Google Scholar]
- Salzman, O.; Stern, R. Research challenges and opportunities in multi-agent path finding and multi-agent pickup and delivery problems. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and MultiAgent Systems, Auckland, New Zealand, 9–13 May 2020; pp. 1711–1715. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, N.; Yang, X.; Wang, T.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, M.; Wang, H.; Li, H. Collaborative path planning and task allocation for multiple agricultural machines. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 213, 108218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yang, L.; Huang, Z.; Ji, Z.; He, Y. Collaborative path planning for agricultural mobile robots: A review. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Autonomous Unmanned Systems, Beijing, China, 24–26 September 2021; pp. 2942–2952. [Google Scholar]
- Alshammrei, S.; Boubaker, S.; Kolsi, L. Improved Dijkstra algorithm for mobile robot path planning and obstacle avoidance. Comput. Mater. Contin. 2022, 72, 5939–5954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Zhao, Q.; Zou, Z. Threat-oriented collaborative path planning of unmanned reconnaissance mission for the target group. Aerospace 2022, 9, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, L.; Zuo, Y. Collaborative Path Planning of Multiple AUVs Based on Adaptive Multi-Population PSO. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xia, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, T. Multi-objective particle swarm optimization with multi-mode collaboration based on reinforcement learning for path planning of unmanned air vehicles. Knowl. Based Syst. 2022, 250, 109075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atia MG, B.; El-Hussieny, H.; Salah, O. A supervisory-based collaborative obstacle-guided path refinement algorithm for path planning in wide terrains. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 214672–214684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenouilleau, F.; Van Hoeve, W.J.; Hooker, J.N. A multi-label A* algorithm for multi-agent pathfinding. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Automated Planning and Scheduling, Berkeley, CA, USA, 11–15 July 2019; Volume 29, pp. 181–185. [Google Scholar]
- Atzmon, D.; Felner, A.; Li, J.; Shperberg, S.; Sturtevant, N.; Koenig, S. Conflict-tolerant and conflict-free multi-agent meeting. Artif. Intell. 2023, 322, 103950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motes, J.; Sandström, R.; Lee, H.; Thomas, S.; Amato, N.M. Multi-robot task and motion planning with sub-task dependencies. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2020, 5, 3338–3345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tinka, A.; Kiesel, S.; Durham, J.W.; Kumar, T.S.; Koenig, S. Lifelong multi-agent path finding in large-scale warehouses. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 2–9 February 2021; Volume 35, pp. 11272–11281. [Google Scholar]
- Teichteil-Koenigsbuch, F.; Poveda, G. Collaborative common path planning in large graphs. Aerosp. Lab 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Li, M. Path planning for collaborative robot under complex biomedical lab environment. In Proceedings of the 2022 7th International Conference on Control, Robotics and Cybernetics (CRC), Zhanjiang, China, 15–17 December 2022; pp. 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Hegde, A.; Ghose, D. Multi-UAV collaborative transportation of payloads with obstacle avoidance. IEEE Control. Syst. Lett. 2021, 6, 926–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Tovey, C.; Sharon, G.; Kumar, T.K.; Koenig, S. Multi-agent path finding with payload transfers and the package-exchange robot-routing problem. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Phoenix, AZ, USA, 12–17 February 2016; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]







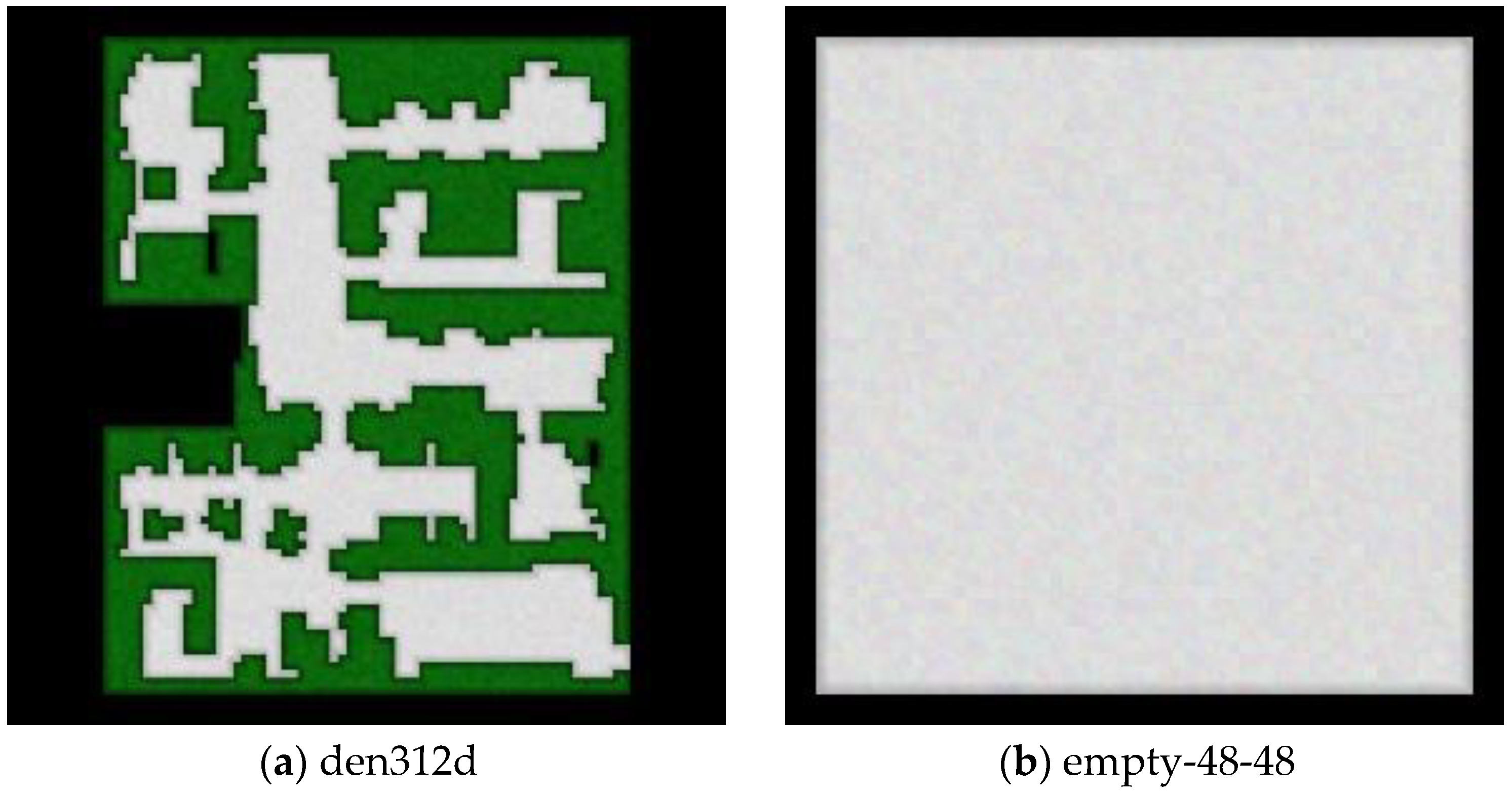
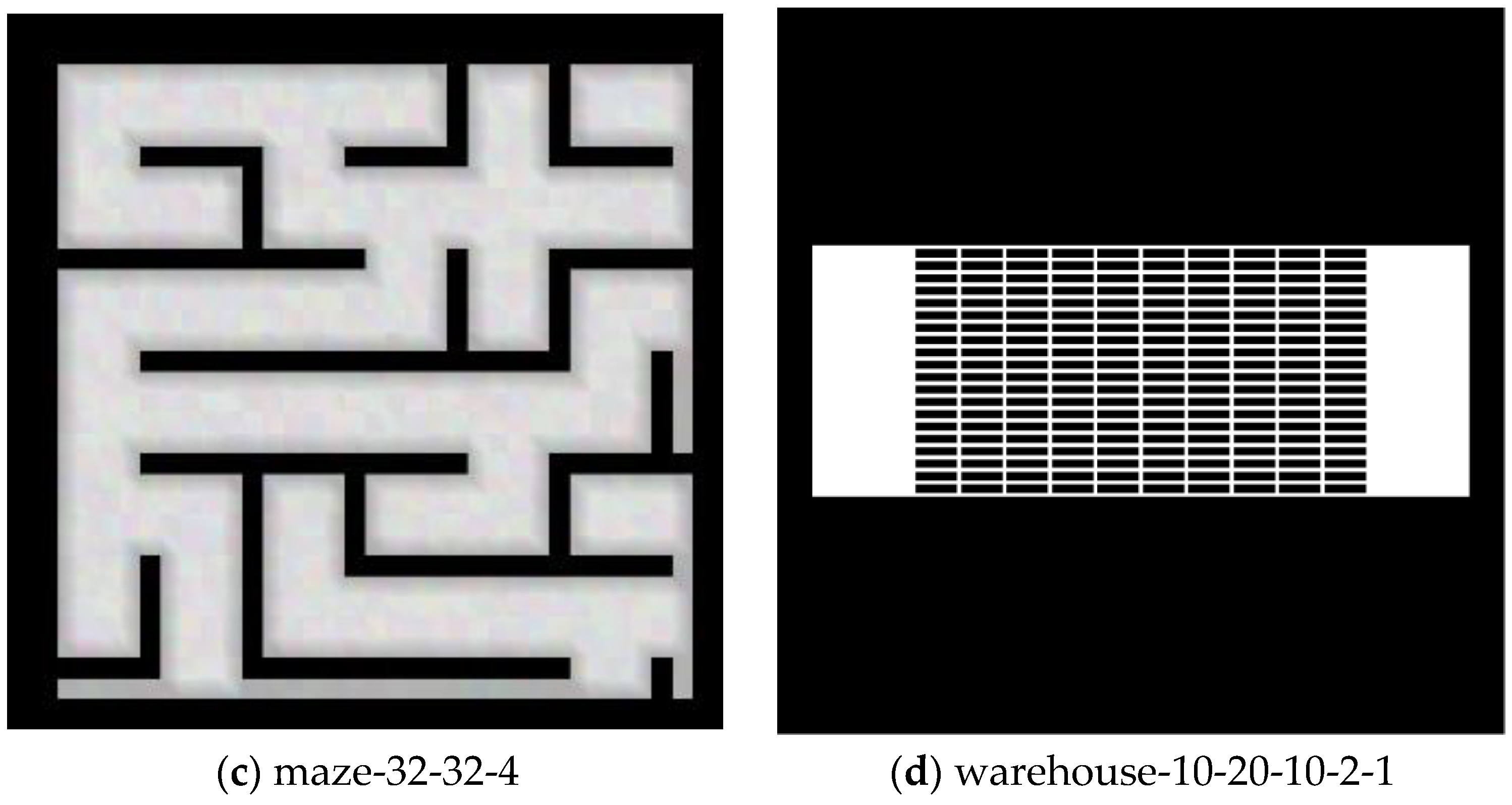



| Map | Ngroup | Length/Step | Flowtime/Step | Runtime/s | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co- | Co-CBS | Co- | Co-CBS | Co- | Co-CBS | ||
| den312d | 6 | 768.8 | 893.9 | 1014.2 | 972.7 | 16.12 | 43.42 |
| empty-48-48 | 6 | 467.88 | 536.12 | 665.52 | 592 | 4.63 | 8.47 |
| 12 | 950.72 | 1089.94 | 1253.72 | 1194.44 | 17.68 | 22.29 | |
| 18 | 1426.6 | 1607.8 | 1912.2 | 1777.2 | 54.29 | 128.65 | |
| maze-32-32-4 | 6 | 620.75 | 636.25 | 786.5 | 729.75 | 28.91 | 46.89 |
| warehouse-10-20-10-2-1 | 6 | 1254.4 | 1396.93 | 1630.86 | 1540.2 | 10.34 | 70.71 |
| 12 | 2379.33 | 2598.33 | 3096 | 2847.33 | 26.38 | 156.83 | |
| Map | Ngroup | Length/Step | Flowtime/Step | Runtime/s | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Co- | Co- | Co- | Co- | Co- | Co- | ||
| den312d | 1 | 760.38 | 806 | 852.84 | 929 | 21.18 | 7.86 |
| 2 | 1433.6 | 1638.6 | 1594.4 | 1860.6 | 121.37 | 73.37 | |
| 3 | 2262 | 2446 | 2567.5 | 2765.5 | 157.45 | 103.88 | |
| 4 | 2702 | 3307.5 | 2920.25 | 3793.25 | 233.2 | 283.64 | |
| 5 | 3190 | 4083 | 3433 | 4613 | 241.32 | 300 | |
| empty-48-48 | 1 | 454.25 | 495.85 | 506.15 | 565.85 | 2.64 | 3.05 |
| 2 | 855.66 | 1014.44 | 922.16 | 1153.33 | 35.71 | 26.92 | |
| 3 | 1253.53 | 1537.33 | 1363.6 | 1757.93 | 39.85 | 84.91 | |
| 4 | 1653 | 2076.63 | 1770.63 | 2356.81 | 116.41 | 213.75 | |
| 5 | 2108.1 | 2607.44 | 2284.67 | 2951.22 | 213.45 | 293.93 | |
| maze-32-32-4 | 1 | 604.9 | 637.7 | 727 | 757.8 | 19.76 | 8.92 |
| 2 | 1213.75 | 1404.87 | 1427 | 1695.87 | 42.35 | 25.61 | |
| 3 | 1797.5 | 2087.5 | 2152.5 | 2631.5 | 80.04 | 50.82 | |
| 4 | 2612.66 | 2808 | 3475.66 | 3812 | 149.02 | 92.46 | |
| warehouse-10-20-10-2-1 | 1 | 951.3 | 1113.95 | 1035.08 | 1268.91 | 7.94 | 4.49 |
| 2 | 2185.68 | 2526.36 | 2373.89 | 2860.26 | 65.34 | 74.71 | |
| 3 | 3689.61 | 3813.53 | 4154.53 | 4295.53 | 131.82 | 118.85 | |
| 4 | 5373.2 | 5523.2 | 5984 | 6185.4 | 212.97 | 167.66 | |
| 5 | 6632.66 | 7100.66 | 7451 | 7969 | 259.82 | 229.61 | |
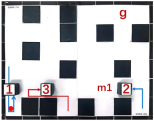
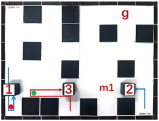
| Multiple Robot Positions Corresponding to Each Time Step | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
 | 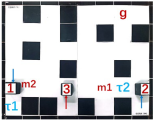 |  | 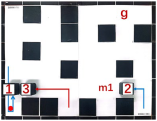 | 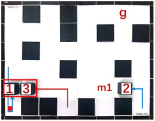 |
| 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
 |  |  | 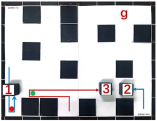 | 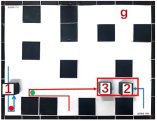 |
| 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 |
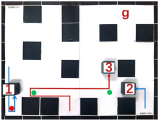 | 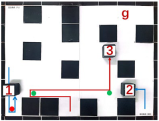 | 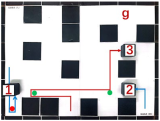 |  | 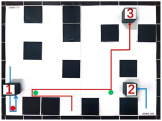 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mao, J.; He, Z.; Li, D.; Li, R.; Zhang, S.; Wang, N. Multi-Agent Collaborative Path Planning Algorithm with Multiple Meeting Points. Electronics 2024, 13, 3347. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13163347
Mao J, He Z, Li D, Li R, Zhang S, Wang N. Multi-Agent Collaborative Path Planning Algorithm with Multiple Meeting Points. Electronics. 2024; 13(16):3347. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13163347
Chicago/Turabian StyleMao, Jianlin, Zhigang He, Dayan Li, Ruiqi Li, Shufan Zhang, and Niya Wang. 2024. "Multi-Agent Collaborative Path Planning Algorithm with Multiple Meeting Points" Electronics 13, no. 16: 3347. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13163347
APA StyleMao, J., He, Z., Li, D., Li, R., Zhang, S., & Wang, N. (2024). Multi-Agent Collaborative Path Planning Algorithm with Multiple Meeting Points. Electronics, 13(16), 3347. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13163347







