Virtual Tools for Testing Autonomous Driving: A Survey and Benchmark of Simulators, Datasets, and Competitions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Related Works
1.2. Motivations and Contributions
- This survey is the first to systematically investigate autonomous driving simulators by providing a deep analysis of their physics and rendering engines to support informed simulator selection.
- This survey provides an in-depth analysis of three key functions in autonomous driving simulators: scenario simulation, sensor simulation, and the implementation of vehicle dynamics simulation.
- This survey is the first to systematically review virtual autonomous driving competitions that are valuable for virtually testing autonomous driving systems.
1.3. Organizations
2. Autonomous Driving Simulators
2.1. Open Source Simulators
- AirSim
- Autoware
- Baidu Apollo
- CARLA
- Gazebo
- 51Sim-One
- LGSVL
- Waymax
2.2. Non-Open-Source Simulators
- Ansys Autonomy

- CarCraft
- Cognata
- CarSim
- CarMaker
- HUAWEI Octopus
- Matlab
- NVIDIA DRIVE Constellation
- Oasis Sim
- PanoSim
- PreScan
- PDGaiA
- SCANeR Studio
- TAD Sim 2.0
2.3. Discussions of Autonomous Driving Simulators
2.3.1. Accessibility
2.3.2. Physics Engines
- ODE
- Bullet
- DART
- PhysX
- Unigine Engine
- Chaos Physics
- Selection of Physics Engines
2.3.3. Rendering Engines
- Unigine Engine
- Unreal Engine
- Unity Engine
- OGRE
- OptiX
- Selection of Rendering Engines
2.3.4. Critical Functions
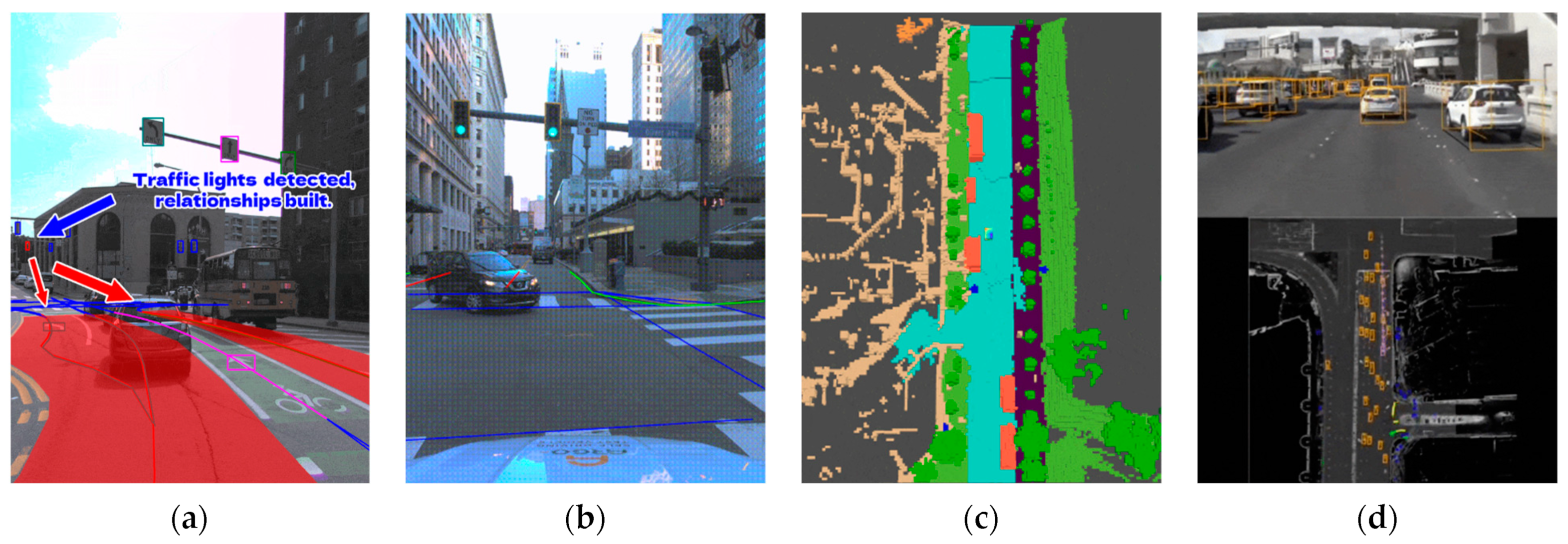
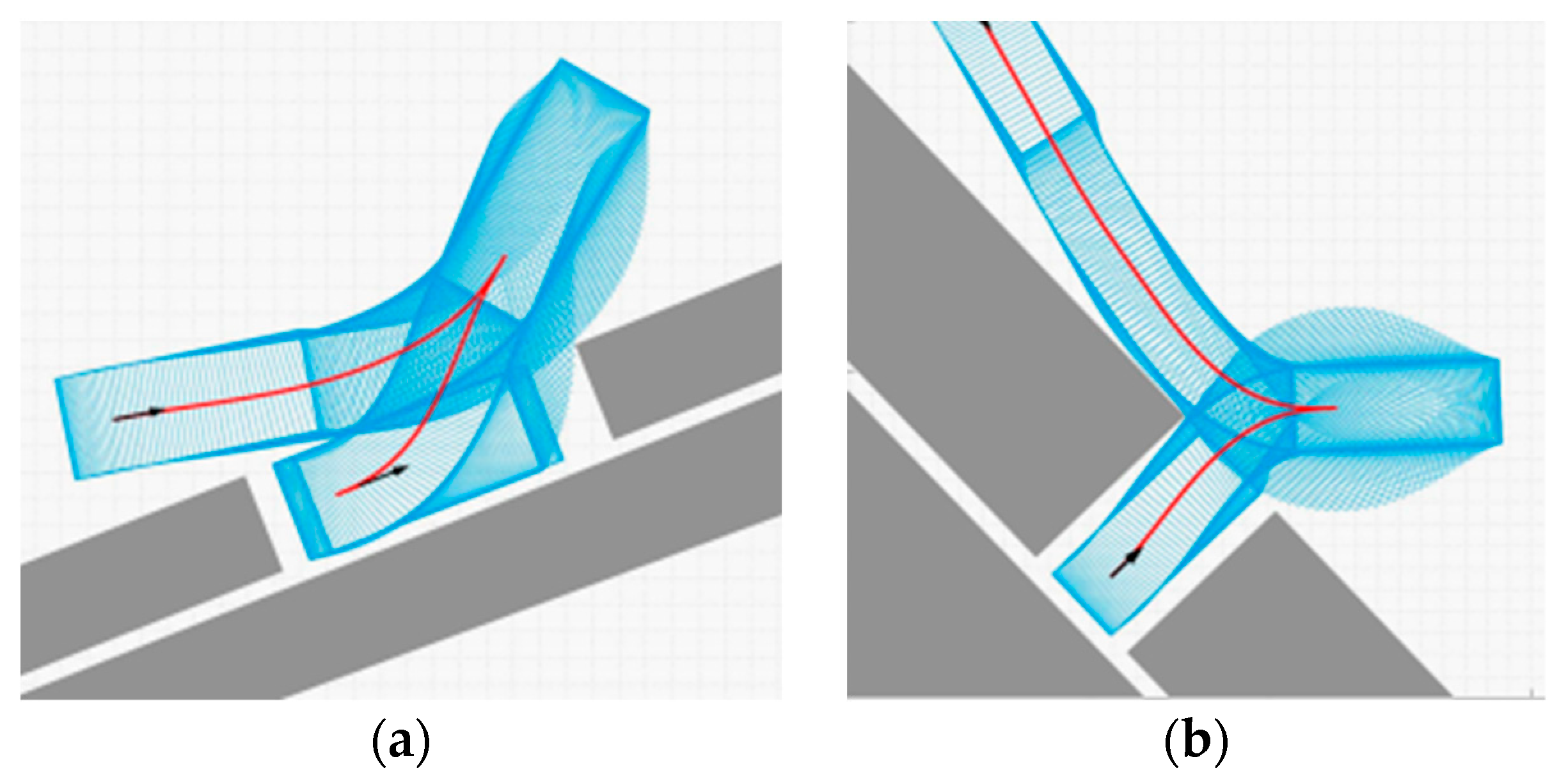
- Scenario Simulation
- Sensor Simulation
- Implementation of Vehicle Dynamics Simulation
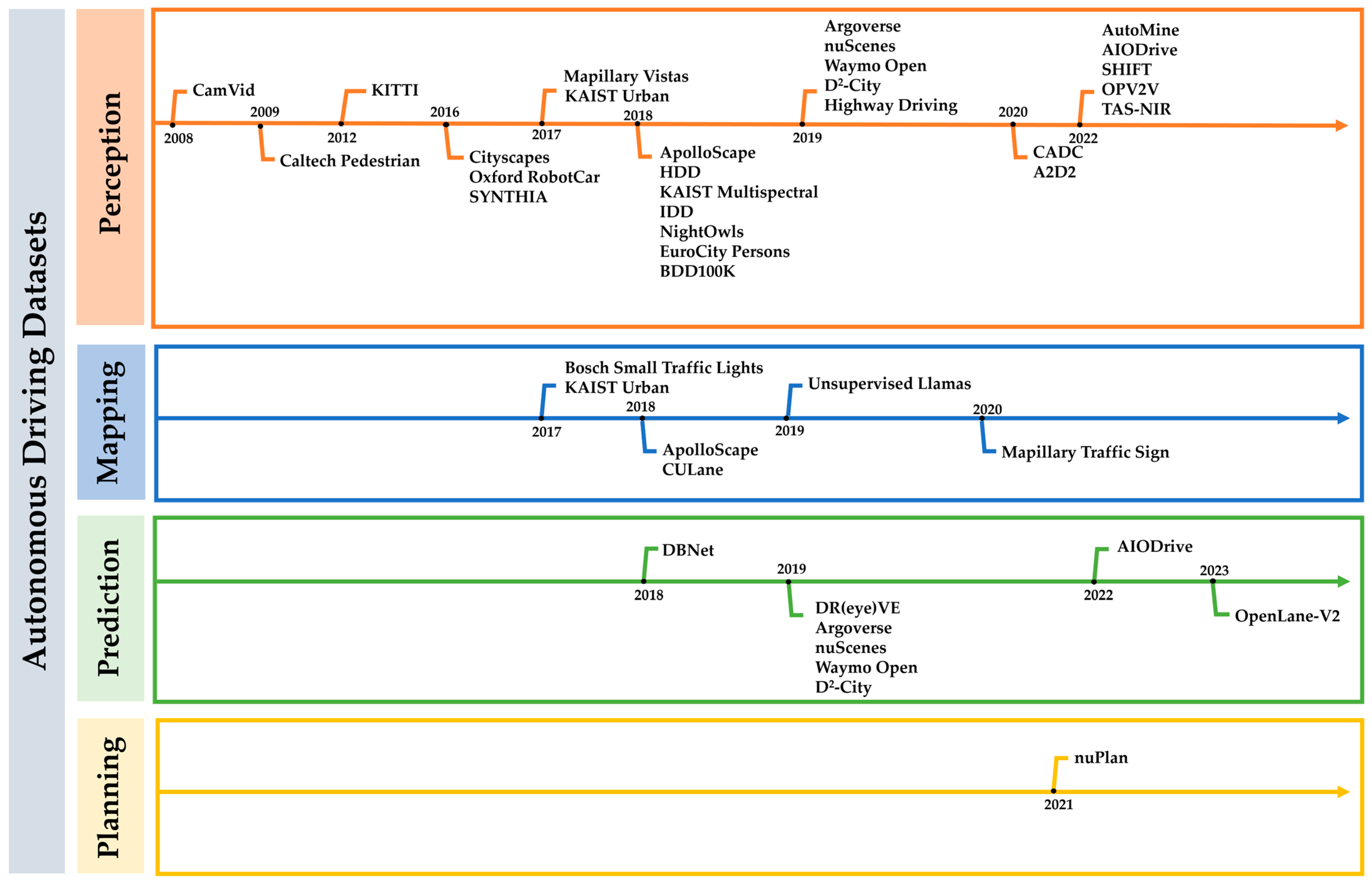
3. Autonomous Driving Datasets
3.1. Datasets
- CamVid Dataset
- Caltech Pedestrian Dataset
- KITTI Dataset
- Cityscapes Dataset
- Oxford RobotCar Dataset
- SYNTHIA Dataset
- Mapillary Vistas Dataset
- Bosch Small Traffic Lights Dataset
- KAIST Urban Dataset
- ApolloScape Dataset
- CULane Dataset
- DBNet Dataset
- HDD Dataset
- KAIST Multispectral Dataset
- IDD Dataset
- NightOwls Dataset
- EuroCity Persons Dataset
- BDD100K Dataset
- DR(eye)VE Dataset
- Argoverse Dataset
- nuScenes Dataset
- Waymo Open Dataset
- Unsupervised Llamas Dataset
- D2-City Dataset
- Highway Driving Dataset
- CADC Dataset
- Mapillary Traffic Sign Dataset
- A2D2 Dataset
- nuPlan Dataset
- AutoMine Dataset
- AIODrive Dataset
- SHIFT Dataset
- OPV2V Dataset
- TAS-NIR Dataset
- OpenLane-V2 Dataset
3.2. Discussions of Autonomous Driving Datasets
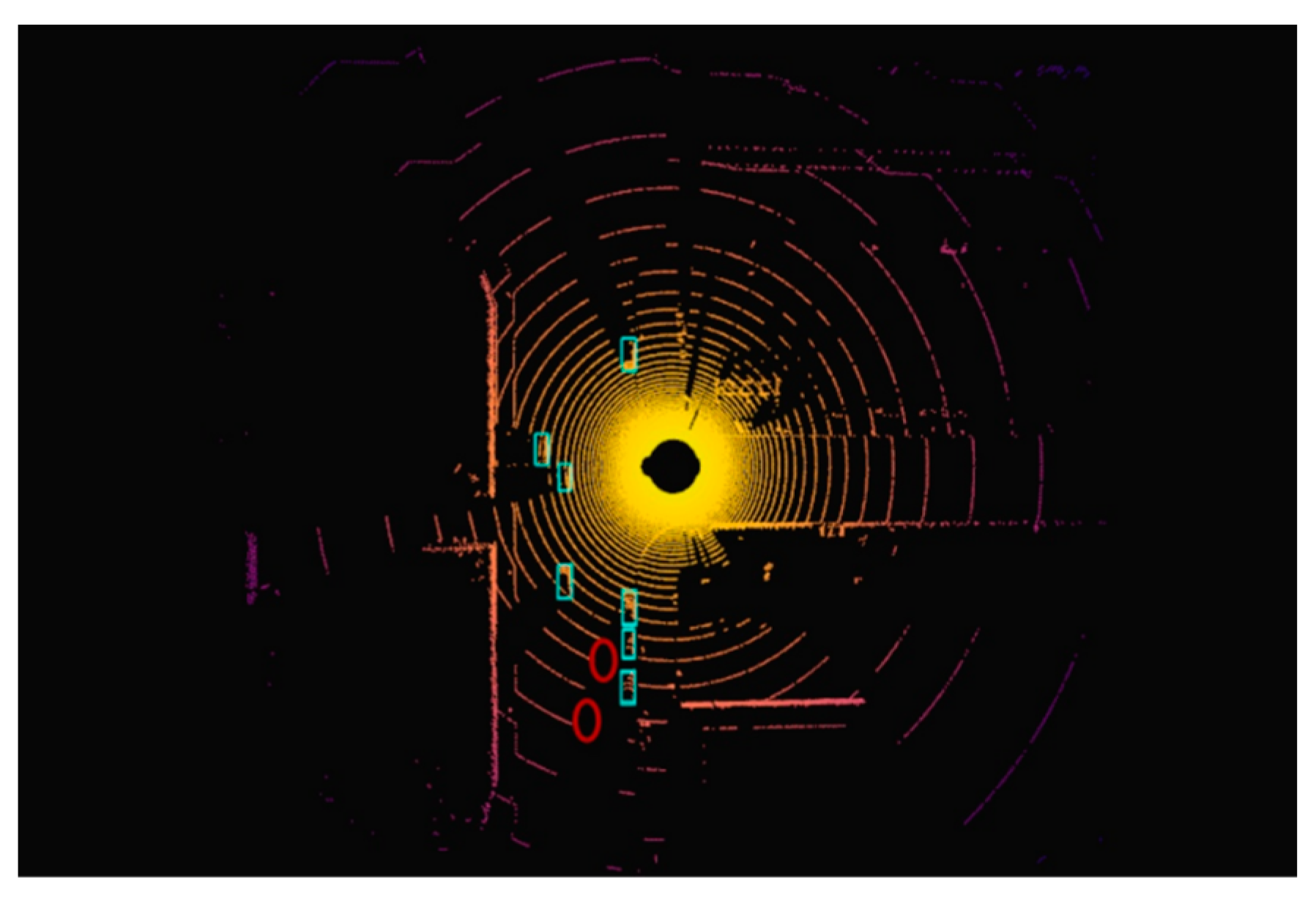
- The CADC dataset focuses on autonomous driving in adverse weather conditions.
- The CULane dataset is designed for road detection.
- The KAIST multispectral dataset is suitable for low-light environments.
- The DR(eye)VE dataset addresses driver attention prediction.
- The Caltech Pedestrian, NightOwls, and EuroCity Persons datasets focus on pedestrian detection.
- The HDD and DBNet datasets are centered on human driver behavior.
- The Oxford RobotCar dataset emphasizes long-term autonomous driving.
- The Complex Urban, D2-City, and Cityscapes datasets are aimed at urban scenarios.
- The KAIST Urban dataset is mainly for SLAM tasks.
- The Argoverse dataset targets 3D tracking and motion prediction.
- The Mapillary Traffic Sign dataset focuses on traffic signs.
- The SYNTHIA, SHIFT, and OPV2V datasets originate from virtual worlds.
4. Virtual Autonomous Driving Competitions
4.1. Virtual Competitions
- Baidu Apollo Starfire Autonomous Driving Competition
- China Intelligent and Connected Vehicle Algorithm Competition
- CVPR Autonomous Driving Challenge
- Waymo Open Dataset Challenge
- Argoverse Challenge
- BDD100K Challenge
- CARLA Autonomous Driving Challenge
- CARSMOS International Autonomous Driving Algorithm Challenge
- The Competition of Trajectory Planning for Automated Parking
- OnSite Autonomous Driving Challenge
4.2. Discussions of Virtual Autonomous Driving Competitions
5. Perspectives of Simulators, Datasets, and Competitions
- Closing the Gap Between Simulators and the Real World
- Modeling Sensors Accurately
- Generating Critical Scenarios
- Enhancing Data Diversity
- Enhancing Privacy Protection
- Enhancing Competitiveness in Competitions
- Optimizing Algorithm Reliability Verification
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, B.; Ouyang, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y. Autonomous Driving on Curvy Roads without Reliance on Frenet Frame: A Cartesian-Based Trajectory Planning Method. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 23, 15729–15741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bimbraw, K. Autonomous Cars: Past, Present and Future a Review of the Developments in the Last Century, the Present Scenario and the Expected Future of Autonomous Vehicle Technology. In Proceedings of the 2015 12th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics (ICINCO), Colmar, France, 21–23 July 2015; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2015; Volume 1, pp. 191–198. [Google Scholar]
- Bathla, G.; Bhadane, K.; Singh, R.K.; Kumar, R.; Aluvalu, R.; Krishnamurthi, R.; Kumar, A.; Thakur, R.N.; Basheer, S. Autonomous Vehicles and Intelligent Automation: Applications, Challenges, and Opportunities. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2022, 2022, 7632892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, J. Safety of Autonomous Vehicles. J. Adv. Transp. 2020, 2020, 8867757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghodhaifi, H.; Lakshmanan, S. Autonomous Vehicle Evaluation: A Comprehensive Survey on Modeling and Simulation Approaches. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 151531–151566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, N.; Paddock, S.M. Driving to Safety: How Many Miles of Driving Would It Take to Demonstrate Autonomous Vehicle Reliability? Transp. Res. Part A Policy Pract. 2016, 94, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Sun, H.; Yan, X.; Zhu, H.; Zou, Z.; Shen, S.; Liu, H.X. Dense Reinforcement Learning for Safety Validation of Autonomous Vehicles. Nature 2023, 615, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Arief, M.; Lam, H.; Zhao, D. Synthesis of Different Autonomous Vehicles Test Approaches. In Proceedings of the 2018 21st International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Maui, HI, USA, 4–7 November 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 2000–2005. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.; Wang, K.; Lv, Y.; Zhu, F. Autonomous Vehicles Testing Methods Review. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 19th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1–4 November 2016; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 163–168. [Google Scholar]
- Schöner, H.-P. Simulation in Development and Testing of Autonomous Vehicles. In 18 Internationales Stuttgarter Symposium; Bargende, M., Reuss, H.-C., Wiedemann, J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 1083–1095. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, T.; Acarman, T.; Ouyang, Y.; Li, L.; Dong, H.; Cao, D. Embodied Footprints: A Safety-Guaranteed Collision-Avoidance Model for Numerical Optimization-Based Trajectory Planning. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 25, 2046–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadler, C.; Montanari, F.; Baron, W.; Sippl, C.; Djanatliev, A. A Credibility Assessment Approach for Scenario-Based Virtual Testing of Automated Driving Functions. IEEE Open J. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 3, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yuan, W.; Zhang, S.; Yan, W.; Shen, Q.; Wang, C.; Yang, M. Choose Your Simulator Wisely: A Review on Open-Source Simulators for Autonomous Driving. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2024, 9, 4861–4876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chance, G.; Ghobrial, A.; Lemaignan, S.; Pipe, T.; Eder, K. An Agency-Directed Approach to Test Generation for Simulation-Based Autonomous Vehicle Verification. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Artificial Intelligence Testing (AITest), Oxford, UK, 3–6 August 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 31–38. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Huang, W.-L.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, N.-N.; Wang, F.-Y. Intelligence Testing for Autonomous Vehicles: A New Approach. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2016, 1, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Huang, C.; Li, B.; Xing, Y.; Tian, D.; Li, L.; Hu, Z.; Na, X.; Li, Z. Milestones in Autonomous Driving and Intelligent Vehicles: Survey of Surveys. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2022, 8, 1046–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Shen, T.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Tian, Y.; Yu, H.; Chen, L.; Xin, J.; Wu, X. Parallel Vision for Long-Tail Regularization: Initial Results from IVFC Autonomous Driving Testing. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2022, 7, 286–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Han, Z.; Xing, Y.; Xu, S.; Wang, J. A Survey on Datasets for the Decision Making of Autonomous Vehicles. IEEE Intell. Transp. Syst. Mag. 2024, 16, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Tian, Y.; Wang, F.-Y. A Survey of Vehicle Dynamics Modeling Methods for Autonomous Racing: Theoretical Models, Physical/Virtual Platforms, and Perspectives. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2024, 9, 4312–4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosero, L.A.; Gomes, I.P.; da Silva, J.A.R.; dos Santos, T.C.; Nakamura, A.T.M.; Amaro, J.; Wolf, D.F.; Osório, F.S. A Software Architecture for Autonomous Vehicles: Team Lrm-b Entry in the First Carla Autonomous Driving Challenge. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.12598. [Google Scholar]
- Leathrum, J.F.; Mielke, R.R.; Shen, Y.; Johnson, H. Academic/Industry Educational Lab for Simulation-Based Test & Evaluation of Autonomous Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2018 Winter Simulation Conference (WSC), Gothenburg, Sweden, 9–12 December 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 4026–4037. [Google Scholar]
- Rosique, F.; Navarro, P.J.; Fernández, C.; Padilla, A. A Systematic Review of Perception System and Simulators for Autonomous Vehicles Research. Sensors 2019, 19, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Xue, Y.; Meng, L.; Wang, P.; Shi, Y.; Yang, Q.; Dong, Q. Survey on Autonomous Vehicle Simulation Platforms. In Proceedings of the 2021 8th International Conference on Dependable Systems and Their Applications (DSA), Yinchuan, China, 11–12 September 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 692–699. [Google Scholar]
- Kaur, P.; Taghavi, S.; Tian, Z.; Shi, W. A Survey on Simulators for Testing Self-Driving Cars. In Proceedings of the 2021 Fourth International Conference on Connected and Autonomous Driving (MetroCAD), Detroit, MI, USA, 28–29 April 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 62–70. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, S.; Guo, Y. A Survey on Autonomous Driving System Simulators. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Symposium on Software Reliability Engineering Workshops (ISSREW), Charlotte, NC, USA, 31 October–3 November 2022; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 301–306. [Google Scholar]
- Janai, J.; Güney, F.; Behl, A.; Geiger, A. Computer Vision for Autonomous Vehicles: Problems, Datasets and State of the Art. Found. Trends® Comput. Graph. Vis. 2020, 12, 1–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Berger, C. When to Use What Data Set for Your Self-Driving Car Algorithm: An Overview of Publicly Available Driving Datasets. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE 20th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Yokohama, Japan, 16–19 October 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Y.; Yin, H.; Berger, C. Test Your Self-Driving Algorithm: An Overview of Publicly Available Driving Datasets and Virtual Testing Environments. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2019, 4, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Kurup, U.; Shah, M. Is It Safe to Drive? An Overview of Factors, Metrics, and Datasets for Driveability Assessment in Autonomous Driving. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2019, 21, 3135–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Yurtsever, E.; Zhou, X.; Fossaert, J.; Cui, Y.; Zagar, B.L.; Knoll, A.C. A Survey on Autonomous Driving Datasets: Data Statistic, Annotation, and Outlook. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.01454. [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Fang, Y.; Ma, S.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, T.; Bian, X.; Wang, F.-Y. Toward Fair and Thrilling Autonomous Racing: Governance Rules and Performance Metrics for Autonomous One. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2023, 8, 3974–3982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betz, J.; Zheng, H.; Liniger, A.; Rosolia, U.; Karle, P.; Behl, M.; Krovi, V.; Mangharam, R. Autonomous Vehicles on the Edge: A Survey on Autonomous Vehicle Racing. IEEE Open J. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2022, 3, 458–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.; Dey, D.; Lovett, C.; Kapoor, A. Airsim: High-Fidelity Visual and Physical Simulation for Autonomous Vehicles. In Proceedings of the Field and Service Robotics: Results of the 11th International Conference, Zurich, Switzerland, 12–15 September 2017; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018; pp. 621–635. [Google Scholar]
- Autoware—The World’s Leading Open-Source Software Project for Autonomous Driving. Available online: https://github.com/autowarefoundation/autoware (accessed on 2 July 2024).
- Feng, M.; Zhang, H. Application of Baidu Apollo Open Platform in a Course of Control Simulation Experiments. Comput. Appl. Eng. Educ. 2022, 30, 892–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CARLA Simulator. Available online: https://carla.org/ (accessed on 2 July 2024).
- Cook, D.; Vardy, A.; Lewis, R. A Survey of AUV and Robot Simulators for Multi-Vehicle Operations. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE/OES Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUV), Oxford, MS, USA, 6–9 October 2014; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- 51Sim-One. Available online: https://wdp.51aes.com/news/27 (accessed on 2 June 2024).
- Rong, G.; Shin, B.H.; Tabatabaee, H.; Lu, Q.; Lemke, S.; Možeiko, M.; Boise, E.; Uhm, G.; Gerow, M.; Mehta, S. Lgsvl Simulator: A High Fidelity Simulator for Autonomous Driving. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 23rd International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC), Rhodes, Greece, 20–23 September 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Gulino, C.; Fu, J.; Luo, W.; Tucker, G.; Bronstein, E.; Lu, Y.; Harb, J.; Pan, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, X. Waymax: An Accelerated, Data-Driven Simulator for Large-Scale Autonomous Driving Research. In Proceedings of the 37th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems Track on Datasets and Benchmarks, New Orleans, LA, USA, 10–16 December 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Autoware. Available online: https://autoware.org/ (accessed on 2 June 2024).
- Baidu Apollo. Available online: https://apollo.baidu.com/ (accessed on 2 June 2024).
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Ros, G.; Codevilla, F.; Lopez, A.; Koltun, V. CARLA: An Open Urban Driving Simulator. In Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning; Proceedings of Machine Learning Research, 2017, Mountain View, CA, USA, 13–15 November 2017; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Koenig, N.; Howard, A. Design and Use Paradigms for Gazebo, an Open-Source Multi-Robot Simulator. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS) (IEEE Cat. No. 04CH37566), Sendai, Japan, 28 September–2 October 2004; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2004; Volume 3, pp. 2149–2154. [Google Scholar]
- DART. Available online: https://dartsim.github.io./ (accessed on 2 July 2024).
- Smith, R. Open Dynamics Engine. 2005. Available online: https://ode.org/ode-latest-userguide.pdf (accessed on 28 August 2024).
- Bullet. Available online: https://github.com/bulletphysics/bullet3 (accessed on 2 July 2024).
- Sovani, S. Simulation Accelerates Development of Autonomous Driving. ATZ Worldw. 2017, 119, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ANSYS Autonomous Driving Simulation Verification Platform. Available online: http://www.app17.com/supply/offerdetail/9574940.html (accessed on 22 June 2024).
- Ansys Autonomy: Designing and Validating Safe Automated Driving Systems. Available online: https://www.ansys.com/products/av-simulation/ansys-avxcelerate-autonomy (accessed on 2 July 2024).
- Welcome to Simulation City, the Virtual World Where Waymo Tests Its Autonomous Vehicles. Available online: https://www.theverge.com/2021/7/6/22565448/waymo-simulation-city-autonomous-vehicle-testing-virtual (accessed on 23 June 2024).
- Autonomous and ADAS Vehicles Simulation Software. Available online: https://www.cognata.com/simulation/ (accessed on 23 June 2024).
- CarSim Overview. Available online: https://www.carsim.com/products/carsim/ (accessed on 23 June 2024).
- CarMaker. Available online: https://www.ipg-automotive.com/cn/products-solutions/software/carmaker/ (accessed on 2 July 2024).
- Why Is Huawei’s Autonomous Driving Cloud Service Named “Huawei Octopus”? Available online: https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1660135510834912717&wfr=spider&for=pc (accessed on 23 June 2024).
- Automated Driving Toolbox. Available online: https://ww2.mathworks.cn/products/automated-driving.html (accessed on 13 August 2024).
- NVIDIA DRIVE Constellation. Available online: https://www.nvidia.com/content/dam/en-zz/Solutions/self-driving-cars/drive-constellation/nvidia-drive-constellation-datasheet-2019-oct.pdf (accessed on 23 June 2024).
- OASIS SIM Simulation Platform. Available online: https://www.synkrotron.ai/sim.html (accessed on 23 June 2024).
- PanoSim. Available online: https://www.panosim.com/ (accessed on 30 June 2024).
- Simcenter Prescan Software Simulation Platform. Available online: https://plm.sw.siemens.com/en-US/simcenter/autonomous-vehicle-solutions/prescan/ (accessed on 30 June 2024).
- PDGaiA. Available online: http://www.pd-automotive.com/pc/#/ (accessed on 30 June 2024).
- SCANeR Studio. Available online: https://www.avsimulation.com/scaner/ (accessed on 30 June 2024).
- TAD Sim 2.0. Available online: https://tadsim.com/ (accessed on 30 June 2024).
- Li, W.; Pan, C.W.; Zhang, R.; Ren, J.P.; Ma, Y.X.; Fang, J.; Yan, F.L.; Geng, Q.C.; Huang, X.Y.; Gong, H.J. AADS: Augmented Autonomous Driving Simulation Using Data-Driven Algorithms. Sci. Robot 2019, 4, eaaw0863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Zhang, J.; Hu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, X. Autonomous-driving Vehicle Test Technology Based on Virtual Reality. J. Eng. 2018, 2018, 1768–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, G.; Wang, L. Trajectory Tracking Control of Driverless Racing Car under Extreme Conditions. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 36778–36790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, C.J.; Aparow, V.R. System Configuration of Human-in-the-Loop Simulation for Level 3 Autonomous Vehicle Using IPG CarMaker. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE International Conference on Internet of Things and Intelligence Systems (IoTaIS), Bandung, Indonesia, 23–24 November 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 215–221. [Google Scholar]
- HUAWEI Octopus. Available online: https://developer.huaweicloud.com/techfield/car/oct.html (accessed on 30 June 2024).
- Matlab, S. Matlab. MathWorks Natick MA 2012, 9. Available online: https://itb.biologie.hu-berlin.de/~kempter/Teaching/2003_SS/gettingstarted.pdf (accessed on 27 August 2024).
- Vergara, P.F.E.; Malla, E.E.G.; Paillacho, E.X.M.; Arévalo, F.D.M. Object Detection in a Virtual Simulation Environment with Automated Driving Toolbox. In Proceedings of the 2021 16th Iberian Conference on Information Systems and Technologies (CISTI), Chaves, Portugal, 23–26 June 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Beale, M.H.; Hagan, M.T.; Demuth, H.B. Deep Learning Toolbox. In R2018b User’s Guide; The MathWorks, Inc.: Natick, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Vukić, M.; Grgić, B.; Dinčir, D.; Kostelac, L.; Marković, I. Unity Based Urban Environment Simulation for Autonomous Vehicle Stereo Vision Evaluation. In Proceedings of the 2019 42nd International Convention on Information and Communication Technology, Electronics and Microelectronics (MIPRO), Opatija, Croatia, 20–24 May 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 949–954. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Du, Z.; Zhao, S.; Zhai, Y.; Shen, Y. Development and Verification of Traffic Confrontation Simulation Test Platform Based on PanoSim. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 4th Information Technology, Networking, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (ITNEC), Chongqing, China, 12–14 June 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; Volume 1, pp. 1814–1818. [Google Scholar]
- Ortega, J.; Lengyel, H.; Szalay, Z. Overtaking Maneuver Scenario Building for Autonomous Vehicles with PreScan Software. Transp. Eng. 2020, 2, 100029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusari, A.; Li, P.; Yang, H.; Punshi, N.; Rasulis, M.; Bogard, S.; LeBlanc, D.J. Enhancing SUMO Simulator for Simulation Based Testing and Validation of Autonomous Vehicles. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Aachen, Germany, 5–9 June 2022; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 829–835. [Google Scholar]
- Barbour, E.; McFall, K. Autonomous Vehicle Simulation Using Open Source Software Carla. J. UAB ECTC 2019, 18, 51–57. [Google Scholar]
- Staranowicz, A.; Mariottini, G.L. A Survey and Comparison of Commercial and Open-Source Robotic Simulator Software. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on PErvasive Technologies Related to Assistive Environments, Crete, Greece, 25–27 May 2011; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Leading by Example. Available online: https://autoware.org/case-studies/ (accessed on 2 July 2024).
- Arslan, E.; Yıldırım, Ş. ODE (Open Dynamics Engine) Based Walking Control Algorithm for Six Legged Robot. J. New Results Sci. 2018, 7, 35–46. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, J.M.; Peters, S.C. Extending Open Dynamics Engine for the DARPA Virtual Robotics Challenge. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Simulation, Modeling, and Programming for Autonomous Robots, Bergamo, Italy, 20–23 October 2014; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 37–48. [Google Scholar]
- Drumwright, E.; Shell, D.A. Extensive Analysis of Linear Complementarity Problem (Lcp) Solver Performance on Randomly Generated Rigid Body Contact Problems. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, Vilamoura-Algarve, Portugal, 7–12 October 2012; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 5034–5039. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, T.; Wang, M.Y. Computation of Three-Dimensional Rigid-Body Dynamics with Multiple Unilateral Contacts Using Time-Stepping and Gauss-Seidel Methods. IEEE Trans. Autom. Sci. Eng. 2005, 2, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapley, L.S. A Note on the Lemke-Howson Algorithm. In Pivoting and Extension: In Honor of AW Tucker; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 175–189. [Google Scholar]
- Izadi, E.; Bezuijen, A. Simulating Direct Shear Tests with the Bullet Physics Library: A Validation Study. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catto, E. Fast and Simple Physics Using Sequential Impulses. In Proceedings of the Game Developer Conference, San Jose, CA, USA, 20–24 March 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Cottle, R.W.; Dantzig, G.B. Complementary Pivot Theory of Mathematical Programming. Linear Algebra Its Appl. 1968, 1, 103–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NVIDIA PhysX. Available online: https://developer.nvidia.com/physx-sdk (accessed on 2 July 2024).
- Rieffel, J.; Saunders, F.; Nadimpalli, S.; Zhou, H.; Hassoun, S.; Rife, J.; Trimmer, B. Evolving Soft Robotic Locomotion in PhysX. In Proceedings of the 11th Annual Conference Companion on Genetic and Evolutionary Computation Conference: Late Breaking Papers, Montreal, QC, Canada, 8–12 July 2009; pp. 2499–2504. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, A.; Shakeel, H.; Hussain, F.; Uddin, N.; Ghouri, T.L. Unity Game Development Engine: A Technical Survey. Univ. Sindh J. Inf. Commun. Technol. 2020, 4, 73–81. [Google Scholar]
- UNIGINE: Real-Time 3D Engine. Available online: https://unigine.com/ (accessed on 2 July 2024).
- Unigine Physic. Available online: https://developer.unigine.com/ch/docs/latest/ (accessed on 2 July 2024).
- Overview of Chaos Physics. Available online: https://docs.unrealengine.com/4.27/zh-CN/InteractiveExperiences/Physics/ChaosPhysics/Overview/ (accessed on 2 July 2024).
- Yoon, J.; Son, B.; Lee, D. Comparative Study of Physics Engines for Robot Simulation with Mechanical Interaction. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erez, T.; Tassa, Y.; Todorov, E. Simulation Tools for Model-Based Robotics: Comparison of Bullet, Havok, Mujoco, Ode and Physx. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Seattle, WA, USA, 26–30 May 2015; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 4397–4404. [Google Scholar]
- Shafikov, A.; Tsoy, T.; Lavrenov, R.; Magid, E.; Li, H.; Maslak, E.; Schiefermeier-Mach, N. Medical Palpation Autonomous Robotic System Modeling and Simulation in Ros/Gazebo. In Proceedings of the 2020 13th International Conference on Developments in eSystems Engineering (DeSE), Virtual, 14–17 December 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 200–205. [Google Scholar]
- Fields, M.; Brewer, R.; Edge, H.L.; Pusey, J.L.; Weller, E.; Patel, D.G.; DiBerardino, C.A. Simulation Tools for Robotics Research and Assessment. In Proceedings of the Unmanned Systems Technology XVIII, Baltimore, MD, USA, 20–21 April 2016; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2016; Volume 9837, pp. 156–171. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, K. Learning Physics Modeling with PhysX; Packt Publishing: Birmingham, UK, 2013; ISBN 1849698147. [Google Scholar]
- Maciel, A.; Halic, T.; Lu, Z.; Nedel, L.P.; De, S. Using the PhysX Engine for Physics-based Virtual Surgery with Force Feedback. Int. J. Med. Robot. Comput. Assist. Surg. 2009, 5, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- CarMaker 10.0 Release By IPG Automotive. Available online: https://unigine.com/news/2021/carmaker-10-0-release-by-ipg-automotive (accessed on 2 July 2024).
- Šmíd, A. Comparison of Unity and Unreal Engine. Czech Tech. Univ. Prague 2017, 41–61. Available online: https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/84832291.pdf (accessed on 27 August 2024).
- Unreal Engine: The Most Powerful Real-Time 3D Creation Tool. Available online: https://www.unrealengine.com/zh-CN (accessed on 2 July 2024).
- What Is Real-Time Ray Tracing, and Why Should You Care? Available online: https://www.unrealengine.com/en-US/explainers/ray-tracing/what-is-real-time-ray-tracing (accessed on 2 July 2024).
- Unity Real-Time Development Platform. Available online: https://unity.com/cn (accessed on 2 July 2024).
- OGRE—Open Source 3D Graphics Engine. Available online: https://www.ogre3d.org/ (accessed on 2 July 2024).
- NVIDIA OptiX Ray Tracing Engine. Available online: https://developer.nvidia.com/rtx/ray-tracing/optix (accessed on 2 July 2024).
- Shergin, D. Unigine Engine Render: Flexible Cross-Api Technologies. In ACM SIGGRAPH 2012 Computer Animation Festival; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2012; p. 85. [Google Scholar]
- Sanders, A. An Introduction to Unreal Engine 4; AK Peters/CRC Press: Natick, MA, USA, 2016; ISBN 1315382555. [Google Scholar]
- Haas, J. A History of the Unity Game Engine. 2014. Available online: http://www.daelab.cn/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/A_History_of_the_Unity_Game_Engine.pdf (accessed on 27 August 2024).
- Feng, Y.; Xia, Z.; Guo, A.; Chen, Z. Survey of Testing Techniques of Autonomous Driving Software. J. Image Graph. 2021, 26, 13–27. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Z.; Tang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Neves, V.D.O.; Liu, Y.; Ray, B. A Survey on Scenario-Based Testing for Automated Driving Systems in High-Fidelity Simulation. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.00964. [Google Scholar]
- Tancik, M.; Casser, V.; Yan, X.; Pradhan, S.; Mildenhall, B.; Srinivasan, P.P.; Barron, J.T.; Kretzschmar, H. Block-Nerf: Scalable Large Scene Neural View Synthesis. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 17–20 June 2022; pp. 8248–8258. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Guan, H.; Jia, X.; Duan, C. Decision-Making Model for Dynamic Scenario Vehicles in Autonomous Driving Simulations. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 8515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, M.; Park, J.; Sung, Y.; Park, Y.W.; Cho, K. Virtual Scenario Simulation and Modeling Framework in Autonomous Driving Simulators. Electronics 2021, 10, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wang, Y.; Ma, S.; Bian, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, T.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y. Adaptive Pure Pursuit: A Real-Time Path Planner Using Tracking Controllers to Plan Safe and Kinematically Feasible Paths. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2023, 8, 4155–4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, J.; Yu, S.; Tan, H.L.; Zhu, H.; Tan, C. A Survey of Embodied Ai: From Simulators to Research Tasks. IEEE Trans. Emerg. Top Comput. Intell. 2022, 6, 230–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- How Tencent TAD Sim Can Improve Gaming Productivity. Available online: https://www.leiphone.com/category/transportation/QyMdqw9BMeQdAvwN.html (accessed on 13 August 2024).
- Deng, W.; Zeng, S.; Zhao, Q.; Dai, J. Modelling and Simulation of Sensor-Guided Autonomous Driving. Int. J. Veh. Des. 2011, 56, 341–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negrut, D.; Serban, R.; Elmquist, A. Physics-Based Sensor Models for Virtual Simulation of Connected and Autonomous Vehicles. 2020. Available online: https://rosap.ntl.bts.gov/view/dot/60196 (accessed on 27 August 2024).
- Blasband, C.; Bleak, J.; Schultz, G. High Fidelity, Physics-based Sensor Simulation for Military and Civil Applications. Sens. Rev. 2004, 24, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PilotD Automotive Provides Sensor Physical Level Simulation for Autonomous Driving. Available online: https://letschuhai.com/automated-driving-system-development-and-validation-services (accessed on 14 August 2024).
- Ansys AVxcelerate Sensors Test and Validate Sensor Perception for Autonomous Vehicles. Available online: https://www.ansys.com/products/av-simulation/ansys-avxcelerate-sensors#tab1-2 (accessed on 14 August 2024).
- Autonomous Driving Sensor Development. Available online: https://www.ansys.com/zh-cn/applications/autonomous-sensor-development (accessed on 14 August 2024).
- Lindenmaier, L.; Aradi, S.; Bécsi, T.; Törő, O.; Gáspár, P. Object-Level Data-Driven Sensor Simulation for Automotive Environment Perception. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2023, 8, 4341–4356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schramm, D.; Hiller, M.; Bardini, R. Vehicle Dynamics. Model. Simulation. Berl. Heidelb. 2018, 6–11. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Dogara, B.T.; He, M. The Research of Dynamic Stability Control System for Passenger Cars Using CarSim and Matlab-Simulink. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Advanced Electronic Science and Technology (AEST 2016), Shenzhen, China, 19–21 August 2016; Atlantis Press: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 706–710. [Google Scholar]
- VehicleSim Dynamics. Available online: https://www.unrealengine.com/marketplace/en-US/product/carsim-vehicle-dynamics (accessed on 15 August 2024).
- VehicleSim Dynamics Plugin for Unreal Engine. Available online: https://www.carsim.com/products/supporting/unreal/index.php (accessed on 16 August 2024).
- Brostow, G.J.; Shotton, J.; Fauqueur, J.; Cipolla, R. Segmentation and Recognition Using Structure from Motion Point Clouds. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ECCV 2008: 10th European Conference on Computer Vision, Part I 10, Marseille, France, 12–18 October 2008; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 44–57. Available online: http://mi.eng.cam.ac.uk/research/projects/VideoRec/CamVid (accessed on 14 August 2024).
- Dollár, P.; Wojek, C.; Schiele, B.; Perona, P. Pedestrian Detection: A Benchmark. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Miami, FL, USA, 20–25 June 2009; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 304–311. Available online: https://data.caltech.edu/records/f6rph-90m20 (accessed on 14 August 2024).
- Geiger, A.; Lenz, P.; Stiller, C.; Urtasun, R. Vision Meets Robotics: The Kitti Dataset. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2013, 32, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordts, M.; Omran, M.; Ramos, S.; Rehfeld, T.; Enzweiler, M.; Benenson, R.; Franke, U.; Roth, S.; Schiele, B. The Cityscapes Dataset for Semantic Urban Scene Understanding. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 3213–3223. Available online: https://www.cityscapes-dataset.com/ (accessed on 14 August 2024).
- Maddern, W.; Pascoe, G.; Linegar, C.; Newman, P. 1 Year, 1000 Km: The Oxford Robotcar Dataset. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2017, 36, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ros, G.; Sellart, L.; Materzynska, J.; Vazquez, D.; Lopez, A.M. The Synthia Dataset: A Large Collection of Synthetic Images for Semantic Segmentation of Urban Scenes. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 3234–3243. Available online: https://synthia-dataset.net/ (accessed on 14 August 2024).
- Neuhold, G.; Ollmann, T.; Rota Bulo, S.; Kontschieder, P. The Mapillary Vistas Dataset for Semantic Understanding of Street Scenes. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 4990–4999. Available online: https://www.mapillary.com/dataset/vistas (accessed on 16 August 2024).
- Behrendt, K.; Novak, L.; Botros, R. A Deep Learning Approach to Traffic Lights: Detection, Tracking, and Classification. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Singapore, 29 May–3 June 2017; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 1370–1377. Available online: https://zenodo.org/records/12706046 (accessed on 16 August 2024).
- Jeong, J.; Cho, Y.; Shin, Y.-S.; Roh, H.; Kim, A. Complex Urban Dataset with Multi-Level Sensors from Highly Diverse Urban Environments. Int. J. Robot. Res. 2019, 38, 642–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Cheng, X.; Geng, Q.; Cao, B.; Zhou, D.; Wang, P.; Lin, Y.; Yang, R. The Apolloscape Dataset for Autonomous Driving. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 954–960. Available online: https://apolloscape.auto/ (accessed on 16 August 2024).
- Pan, X.; Shi, J.; Luo, P.; Wang, X.; Tang, X. Spatial as Deep: Spatial Cnn for Traffic Scene Understanding. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New Orleans, LA, USA, 2–7 February 2018; Volume 32. Available online: https://xingangpan.github.io/projects/CULane.html (accessed on 16 August 2024).
- Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Lu, C.; Luo, Z.; Xue, H.; Wang, C. Lidar-Video Driving Dataset: Learning Driving Policies Effectively. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 5870–5878. Available online: https://github.com/driving-behavior/DBNet. (accessed on 16 August 2024).
- Ramanishka, V.; Chen, Y.-T.; Misu, T.; Saenko, K. Toward Driving Scene Understanding: A Dataset for Learning Driver Behavior and Causal Reasoning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7699–7707. Available online: https://usa.honda-ri.com/hdd (accessed on 16 August 2024).
- Choi, Y.; Kim, N.; Hwang, S.; Park, K.; Yoon, J.S.; An, K.; Kweon, I.S. KAIST Multi-Spectral Day/Night Data Set for Autonomous and Assisted Driving. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2018, 19, 934–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, G.; Subramanian, A.; Namboodiri, A.; Chandraker, M.; Jawahar, C. V IDD: A Dataset for Exploring Problems of Autonomous Navigation in Unconstrained Environments. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), Waikoloa Village, HI, USA, 7–11 January 2019; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 1743–1751. Available online: https://idd.insaan.iiit.ac.in/ (accessed on 16 August 2024).
- Neumann, L.; Karg, M.; Zhang, S.; Scharfenberger, C.; Piegert, E.; Mistr, S.; Prokofyeva, O.; Thiel, R.; Vedaldi, A.; Zisserman, A. Nightowls: A Pedestrians at Night Dataset. In Proceedings of the Computer Vision–ACCV 2018: 14th Asian Conference on Computer Vision, Revised Selected Papers, Part I 14, Perth, Australia, 2–6 December 2018; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 691–705. Available online: https://www.nightowls-dataset.org/ (accessed on 16 August 2024).
- Braun, M.; Krebs, S.; Flohr, F.; Gavrila, D.M. Eurocity Persons: A Novel Benchmark for Person Detection in Traffic Scenes. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2019, 41, 1844–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, F.; Chen, H.; Wang, X.; Xian, W.; Chen, Y.; Liu, F.; Madhavan, V.; Darrell, T. Bdd100k: A Diverse Driving Dataset for Heterogeneous Multitask Learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 2636–2645. Available online: https://dl.cv.ethz.ch/bdd100k/data/ (accessed on 16 August 2024).
- Palazzi, A.; Abati, D.; Solera, F.; Cucchiara, R. Predicting the Driver’s Focus of Attention: The Dr (Eye) ve Project. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2018, 41, 1720–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.-F.; Lambert, J.; Sangkloy, P.; Singh, J.; Bak, S.; Hartnett, A.; Wang, D.; Carr, P.; Lucey, S.; Ramanan, D. Argoverse: 3d Tracking and Forecasting with Rich Maps. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 8748–8757. Available online: https://www.argoverse.org/av1.html (accessed on 16 August 2024).
- Caesar, H.; Bankiti, V.; Lang, A.H.; Vora, S.; Liong, V.E.; Xu, Q.; Krishnan, A.; Pan, Y.; Baldan, G.; Beijbom, O. Nuscenes: A Multimodal Dataset for Autonomous Driving. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 11621–11631. Available online: https://www.nuscenes.org/nuscenes (accessed on 16 August 2024).
- Sun, P.; Kretzschmar, H.; Dotiwalla, X.; Chouard, A.; Patnaik, V.; Tsui, P.; Guo, J.; Zhou, Y.; Chai, Y.; Caine, B. Scalability in Perception for Autonomous Driving: Waymo Open Dataset. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 2446–2454. Available online: https://waymo.com/open/ (accessed on 16 August 2024).
- Behrendt, K.; Soussan, R. Unsupervised Labeled Lane Markers Using Maps. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27–28 October 2019; Available online: https://unsupervised-llamas.com/llamas/ (accessed on 16 August 2024).
- Che, Z.; Li, G.; Li, T.; Jiang, B.; Shi, X.; Zhang, X.; Lu, Y.; Wu, G.; Liu, Y.; Ye, J. D2-City: A Large-Scale Dashcam Video Dataset of Diverse Traffic Scenarios. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.01975. Available online: https://www.scidb.cn/en/detail?dataSetId=804399692560465920 (accessed on 16 August 2024).
- Kim, B.; Yim, J.; Kim, J. Highway Driving Dataset for Semantic Video Segmentation. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2011.00674. Available online: https://arxiv.org/abs/2011.00674 (accessed on 16 August 2024).
- Pitropov, M.; Garcia, D.E.; Rebello, J.; Smart, M.; Wang, C.; Czarnecki, K.; Waslander, S. Canadian Adverse Driving Conditions Dataset. Int. J. Rob. Res. 2021, 40, 681–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ertler, C.; Mislej, J.; Ollmann, T.; Porzi, L.; Neuhold, G.; Kuang, Y. The Mapillary Traffic Sign Dataset for Detection and Classification on a Global Scale. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 68–84. Available online: https://www.mapillary.com/dataset/trafficsign (accessed on 16 August 2024).
- Geyer, J.; Kassahun, Y.; Mahmudi, M.; Ricou, X.; Durgesh, R.; Chung, A.S.; Hauswald, L.; Pham, V.H.; Mühlegg, M.; Dorn, S. A2d2: Audi Autonomous Driving Dataset. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.06320. Available online: https://a2d2.audi/a2d2/en.html (accessed on 16 August 2024).
- Caesar, H.; Kabzan, J.; Tan, K.S.; Fong, W.K.; Wolff, E.; Lang, A.; Fletcher, L.; Beijbom, O.; Omari, S. Nuplan: A Closed-Loop Ml-Based Planning Benchmark for Autonomous Vehicles. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.11810. Available online: https://www.nuscenes.org/nuplan (accessed on 16 August 2024).
- Li, Y.; Li, Z.; Teng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Cao, D.; Tian, B.; Ai, Y.; Xuanyuan, Z. AutoMine: An Unmanned Mine Dataset. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 21308–21317. Available online: https://automine.cc/ (accessed on 16 August 2024).
- Weng, X.; Man, Y.; Park, J.; Yuan, Y.; O’Toole, M.; Kitani, K.M. All-in-One Drive: A Comprehensive Perception Dataset with High-Density Long-Range Point Clouds. 2021. Available online: https://opendatalab.com/OpenDataLab/AIOdrive (accessed on 16 August 2024).
- Sun, T.; Segu, M.; Postels, J.; Wang, Y.; Van Gool, L.; Schiele, B.; Tombari, F.; Yu, F. SHIFT: A Synthetic Driving Dataset for Continuous Multi-Task Domain Adaptation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 21371–21382. Available online: https://www.vis.xyz/shift/ (accessed on 16 August 2024).
- Xu, R.; Xiang, H.; Xia, X.; Han, X.; Li, J.; Ma, J. Opv2v: An Open Benchmark Dataset and Fusion Pipeline for Perception with Vehicle-to-Vehicle Communication. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Philadelphia, PA, USA, 23–27 May 2022; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 2583–2589. Available online: https://mobility-lab.seas.ucla.edu/opv2v/ (accessed on 16 August 2024).
- Mortimer, P.; Wuensche, H.-J. TAS-NIR: A VIS+ NIR Dataset for Fine-Grained Semantic Segmentation in Unstructured Outdoor Environments. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2212.09368. Available online: https://mucar3.de/iros2022-ppniv-tas-nir/ (accessed on 16 August 2024).
- Wang, H.; Li, T.; Li, Y.; Chen, L.; Sima, C.; Liu, Z.; Wang, B.; Jia, P.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, S. Openlane-v2: A Topology Reasoning Benchmark for Unified 3d Hd Mapping. In Proceedings of the Thirty-Seventh Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems Datasets and Benchmarks Track, New Orleans, LA, USA, 10–16 December 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, B.; Qi, W.; Agarwal, T.; Lambert, J.; Singh, J.; Khandelwal, S.; Pan, B.; Kumar, R.; Hartnett, A.; Pontes, J.K. Argoverse 2: Next Generation Datasets for Self-Driving Perception and Forecasting. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.00493. [Google Scholar]
- Baidu Apollo Starfire Autonomous Driving Competition. Available online: https://apollo.baidu.com/community/competition/13 (accessed on 2 July 2024).
- China Intelligent and Connected Vehicle Algorithm Competition. Available online: https://www.panosim.com/h-col-188.html (accessed on 2 July 2024).
- CVPR Autonomous Driving Challenge. Available online: https://www.shlab.org.cn/news/5443385 (accessed on 2 July 2024).
- Waymo Open Dataset Challenge. Available online: https://waymo.com/open/challenges/ (accessed on 2 July 2024).
- Workshop on Autonomous Driving. Available online: https://cvpr2023.wad.vision/ (accessed on 2 July 2024).
- Argoverse Challenge. Available online: https://www.argoverse.org/tasks.html (accessed on 2 July 2024).
- BDD100K Challenge. Available online: https://www.vis.xyz/bdd100k/challenges/ (accessed on 2 July 2024).
- CARSMOS International Autonomous Driving Algorithm Challenge. Available online: https://www.carsmos.cn/Race2023/ (accessed on 2 July 2024).
- Li, B.; Fan, L.; Ouyang, Y.; Tang, S.; Wang, X.; Cao, D.; Wang, F.-Y. Online Competition of Trajectory Planning for Automated Parking: Benchmarks, Achievements, Learned Lessons, and Future Perspectives. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2022, 8, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OnSite Autonomous Driving Algorithm Challenge. Available online: https://www.onsite.com.cn/#/dist/home (accessed on 2 July 2024).
- Li, B.; Ouyang, Y.; Li, X.; Cao, D.; Zhang, T.; Wang, Y. Mixed-Integer and Conditional Trajectory Planning for an Autonomous Mining Truck in Loading/Dumping Scenarios: A Global Optimization Approach. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2022, 8, 1512–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- What Is so Difficult about Sensor Simulation. Available online: https://www.51fusa.com/client/knowledge/knowledgedetail/id/3168.html (accessed on 16 August 2024).
- Heiden, E.; Liu, Z.; Ramachandran, R.K.; Sukhatme, G.S. Physics-Based Simulation of Continuous-Wave Lidar for Localization, Calibration and Tracking. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Virtual, 31 May–1 August 2020; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 2595–2601. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, K.; Fu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, J. Physics-Based Noise Modeling for Extreme Low-Light Photography. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 44, 8520–8537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Z.; Cai, Z.; Han, Q.; Alrawais, A.; Li, W. ADGAN: Protect Your Location Privacy in Camera Data of Auto-Driving Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2020, 17, 6200–6210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Gao, T.; Ma, S.; Zhang, Y.; Acarman, T.; Cao, K.; Zhang, T.; Wang, F.-Y. From Formula One to Autonomous One: History, Achievements, and Future Perspectives. IEEE Trans. Intell. Veh. 2023, 8, 3217–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
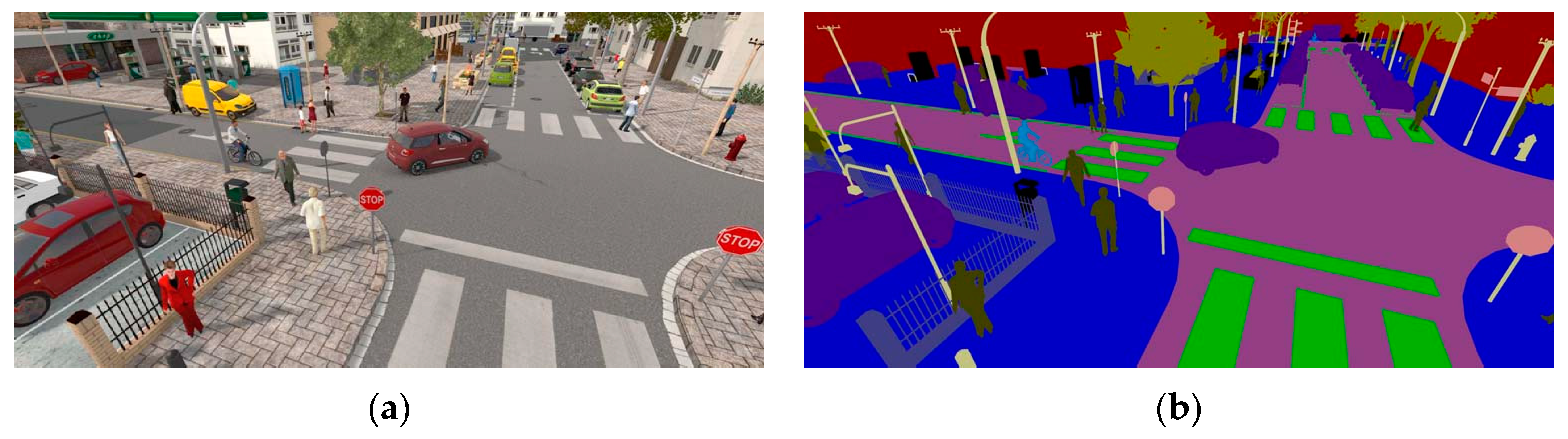
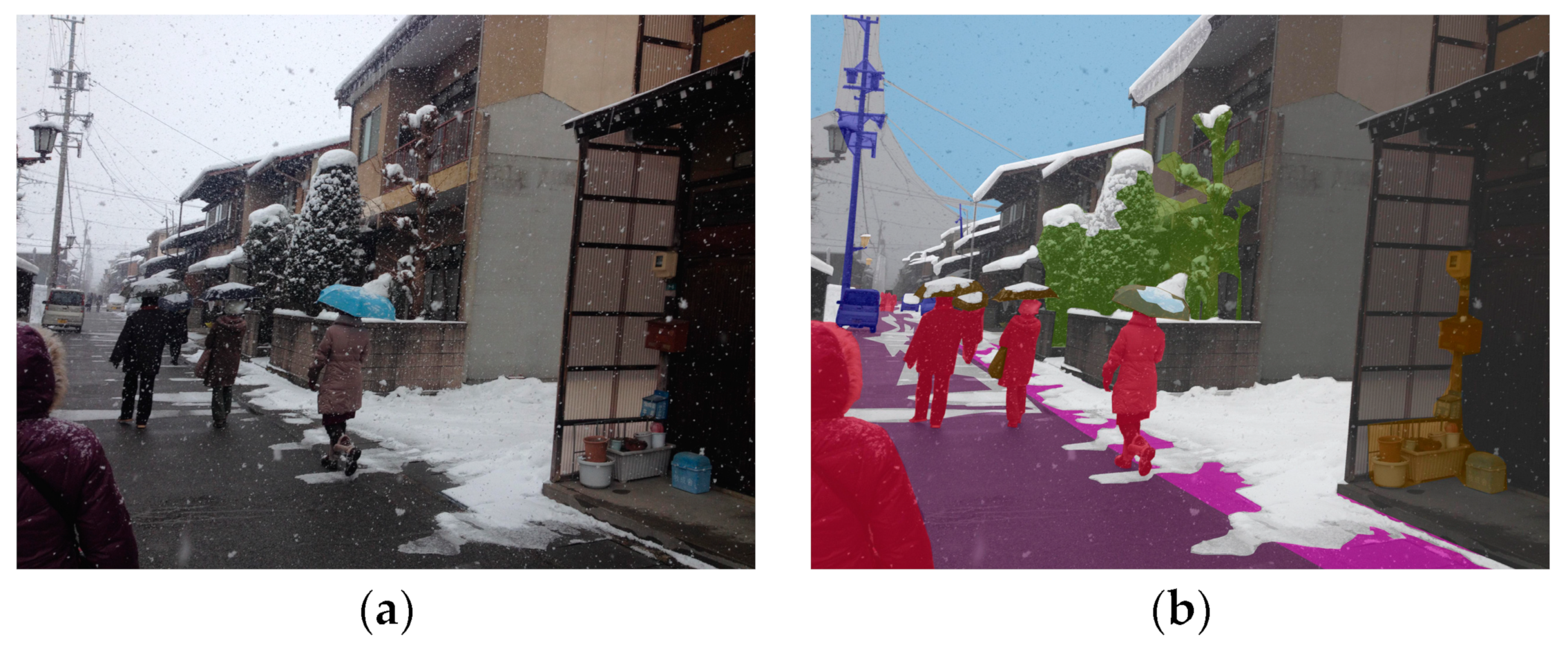
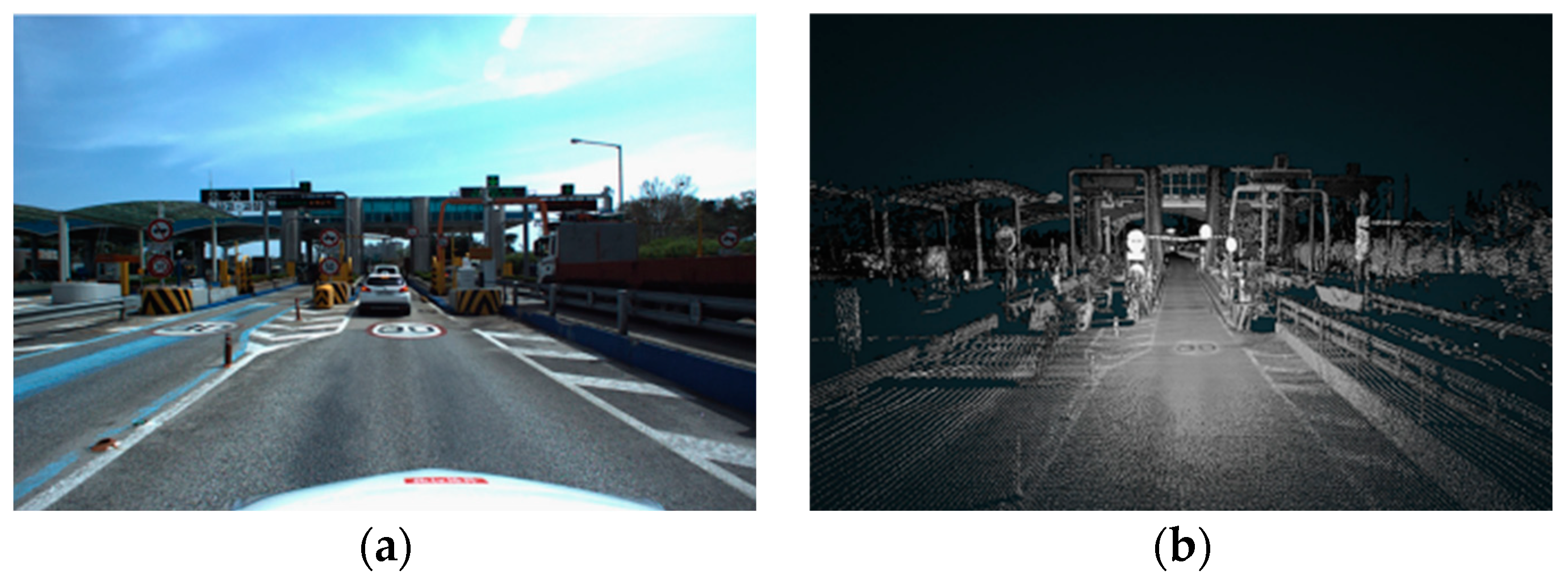
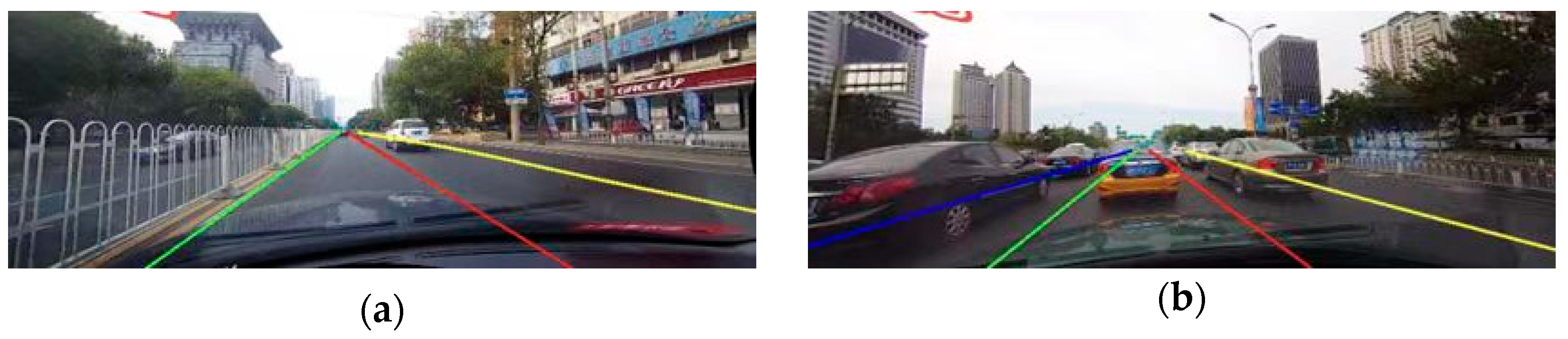
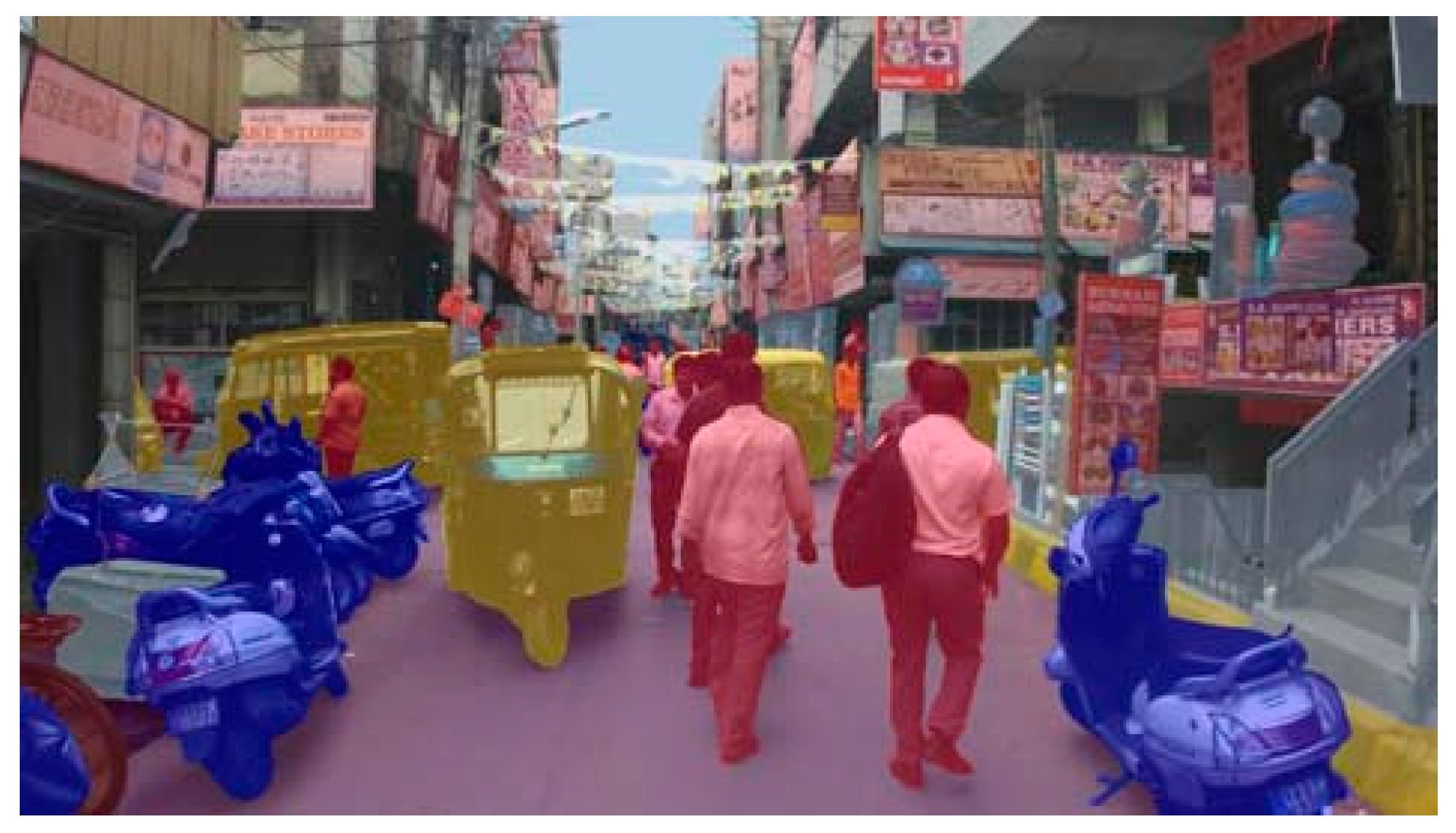
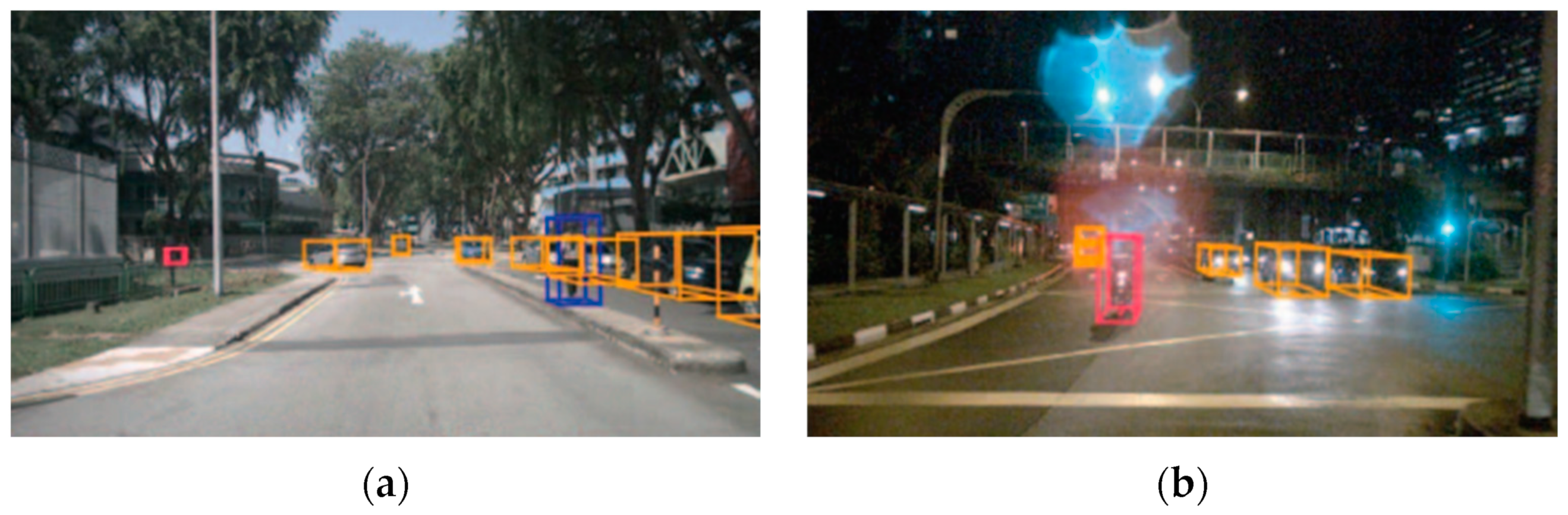
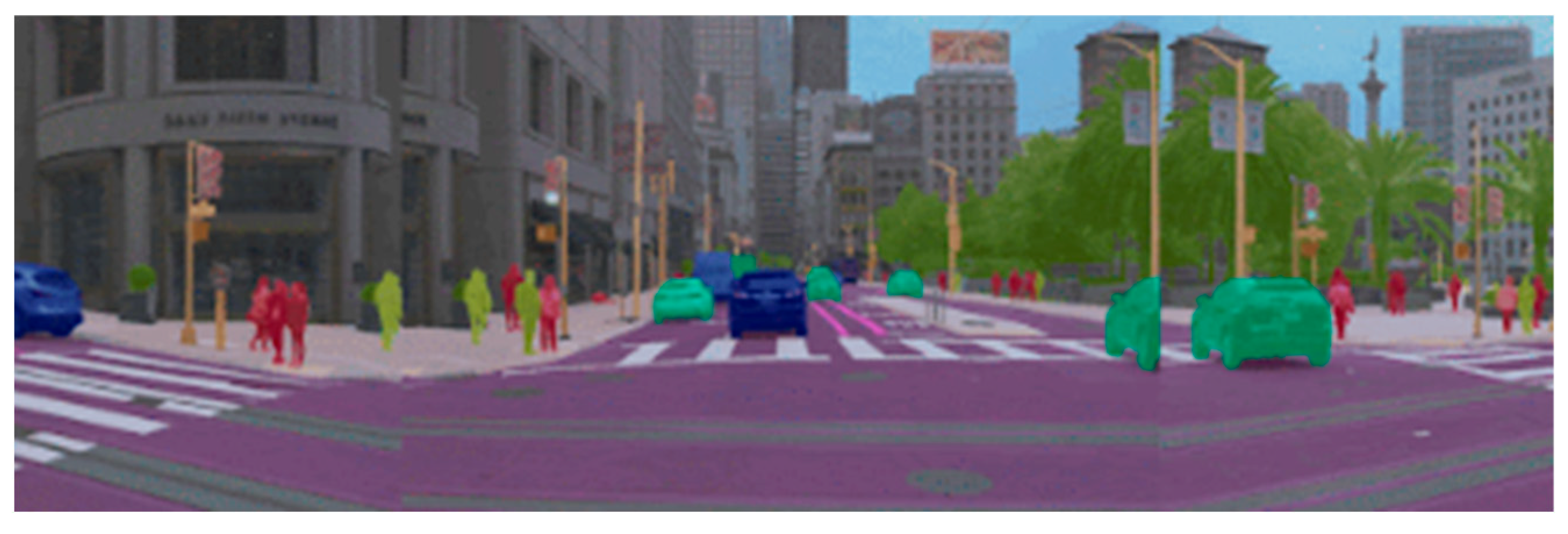
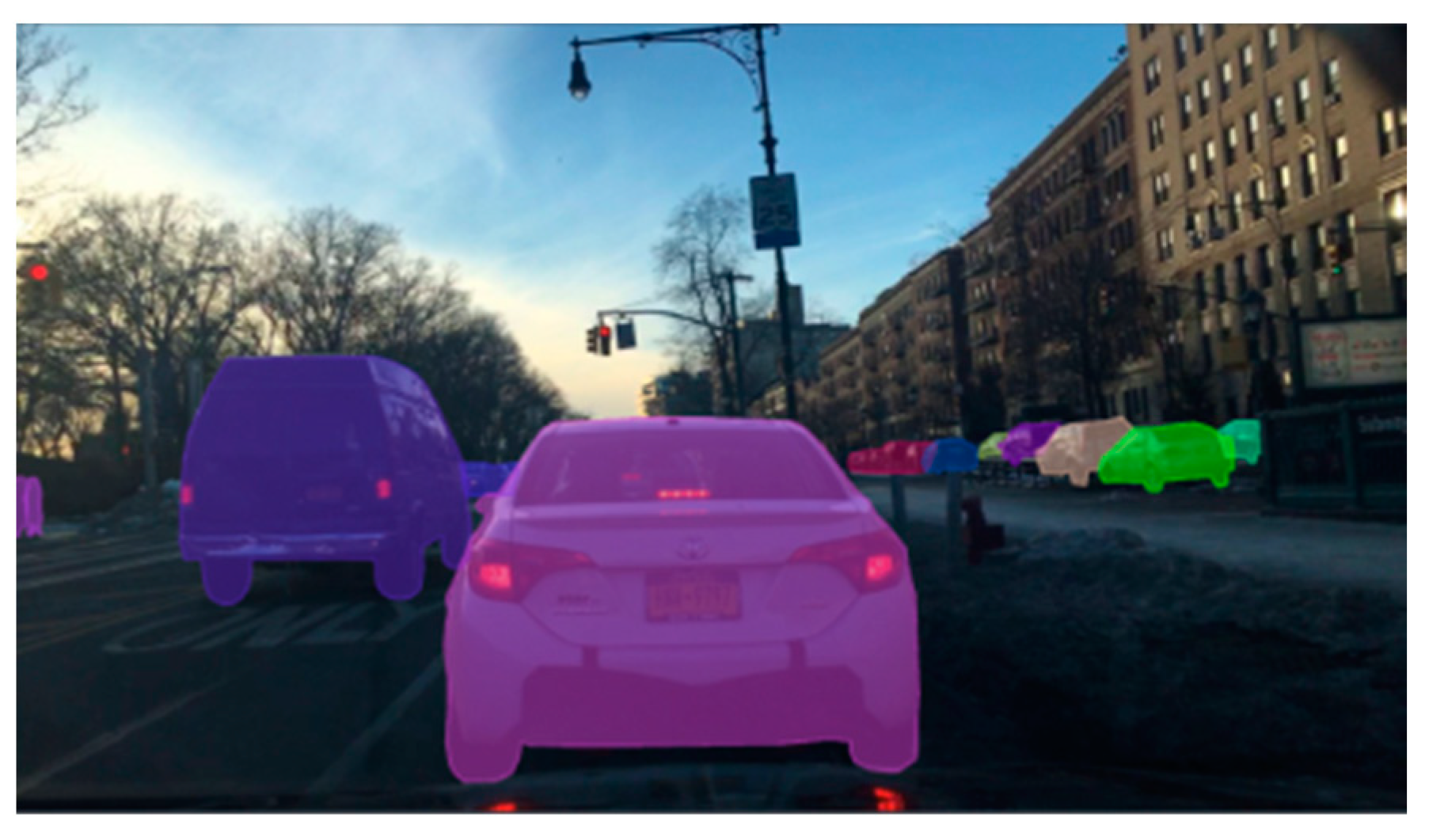





















| Simulator | Accessibility | Operating Systems | Languages | Engines | Sensor Models Included |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AirSim [33] | Open-Source | Windows, Linux, macOS | C++, Python, C#, Java, Matlab | Unreal Engine | Accelerometer, gyroscope, barometer, magnetometer, GPS |
| Autoware [34] | Open-Source | Linux | C++, Python | Unity Engine | Camera, LiDAR, IMU, GPS |
| Baidu Apollo [42] | Open-Source | Linux | C++ | Unity Engine | Camera, LiDAR, GNSS, radar |
| CARLA [43] | Open-Source | Windows, Linux, macOS | C++, Python | Unreal Engine | IDARs, multiple camera, depth sensor, GPS |
| Gazebo [44] | Open-Source | Linux, macOS | C++, Python | ODE, Bullet, DART, OGRE, OptiX | Monocular camera, depth camera, LiDAR, IMU, contact, altimeter, magnetometer sensors |
| 51Sim-One [38] | Open-Source | Windows, Linux | C++, Python | Unreal Engine | Physical-level camera, LiDAR, mmWave radar |
| LGSVL [39] | Open-Source | Windows, Linux | Python, C# | Unity Engine | Camera, LiDAR, radar, GPS, IMU |
| Waymax [40] | Open-Source | Windows, Linux, macOS | Python | N/A | N/A |
| Ansys Autonomy [48] | Commercial | Windows, Linux, macOS | C++, Python | Self-developed | Physical-level Camera, LiDAR, mmWave radar |
| CarCraft [64] | Private | N/A | N/A | Self-developed | N/A |
| Cognata [52] | Commercial | N/A | N/A | Self-developed | RGB HD Camera, LiDAR, mmWave radar |
| CarSim [66] | Commercial | Windows | C++, Matlab | Self-developed | N/A |
| CarMaker [67] | Commercial | Windows, Linux | C, C++, Python, Matlab | Unigine Engine | Camera, LiDAR, radar, GPS |
| HUAWEI Octopus [68] | Commercial | N/A | C++, Python | N/A | N/A |
| Matlab [56] | Commercial | Windows, Linux, macOS | Matlab, C++, Python, Java | Unreal Engine | Camera, LiDAR, radar |
| NVIDIA DRIVE Constellation [72] | Commercial | Linux | C++, Python | Self-developed | N/A |
| Oasis Sim [58] | Commercial | Windows, Linux | C++, Simulink, Python | Unreal Engine | Object-level Camera, LiDAR, Ultrasonic, mmWave radar, GNSS, IMU |
| PanoSim [73] | Commercial | Windows | C++, Simulink, Python | Unity Engine | Camera, LiDAR, Ultrasonic, mmWave radar, GNSS, IMU |
| PreScan [74] | Commercial | Windows | C++, Simulink, Python | Self-developed | Camera, LiDAR, Ultrasonic radar |
| PDGaiA [61] | Commercial | N/A | C++, Python | Unity Engine | Camera, LiDAR, mmWave radar, GPS |
| SCANeR Studio [62] | Commercial | Windows, Linux | C++, Python | Unreal Engine | GPS, IMU, radar, LiDAR, Camera |
| TAD Sim 2.0 [23] | Commercial | N/A | N/A | Unreal Engine | Camera, LiDAR, mmWave radar |
| Dataset | Year | Area | Scenes | Sensors | Data Coverage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CamVid [128] | 2008 | Colombia | Daytime, dusk, urban, residential, mixed use roads | Camera | 86 min of video |
| Caltech Pedestrian [129] | 2009 | America | Urban | Camera | 350,000 labeled bounding boxes, 2300 unique pedestrians |
| KITTI [130] | 2012 | Germany | Daytime, urban, rural, highway | Camera, LiDAR, GPS/IMU | Images, LiDAR data, GPS/IMU data, bounding box label |
| Cityscapes [131] | 2016 | Primarily in Germany, neighboring countries | Urban street | Camera, GPS | 5000 images with high-quality pixel-level annotations, 20,000 images with coarse annotations |
| Oxford RobotCar [132] | 2016 | Oxford | All light condition, urban | Camera, LiDAR, GPS/IMU | Almost 20 million images, LiDAR data, GPS/IMU data |
| SYNTHIA [133] | 2016 | Virtual city | Urban | Camera, LiDAR | More than 213,400 composite images |
| Mapillary Vistas [134] | 2017 | Global | Daytime, urban, countryside, off-road | Camera | 25,000 high-resolution images, 66 object categories |
| Bosch Small Traffic Lights [135] | 2017 | America | N/A | N/A | 5000 images for training, a video sequence of 8334 frames for evaluation |
| KAIST Urban [136] | 2017 | Korea | Urban | Camera, LiDAR, GPS, IMU, FOG | 3D LiDAR data, 2D LiDAR data, GPS data, IMU data, stereo images, FOG data |
| ApolloScape [137] | 2018 | China | Daytime, urban | Camera, GPS, IMU/GNSS | Images, LiDAR data |
| CULane [138] | 2018 | Peking, China | Urban, rural, highway | Camera | 133,235 frames of images |
| DBNet [139] | 2018 | China | A variety of traffic conditions | Camera, LiDAR | Point cloud, videos |
| HDD [140] | 2018 | San Francisco | Suburban, urban, highway | Camera, LiDAR, GPS, IMU | 104 h of real human driving data |
| KAIST Multispectral [141] | 2018 | N/A | From urban to residential, campus, day to night | RGB/Thermal camera, RGB stereo, LiDAR, GPS/IMU | Images, GPS/IMU data |
| IDD [142] | 2018 | India | Residential areas, country roads, city roads | Camera | 10,004 images, 34 labels |
| NightOwls [143] | 2018 | England, Germany, The Netherlands | Dawn, night, various weather conditions, four seasons | Camera | 279,000 frame completely annotated data |
| EuroCity Persons [144] | 2018 | 12 European countries | Day to night, four seasons | Camera | 238,200 person instances manually labeled in over 47,300 images |
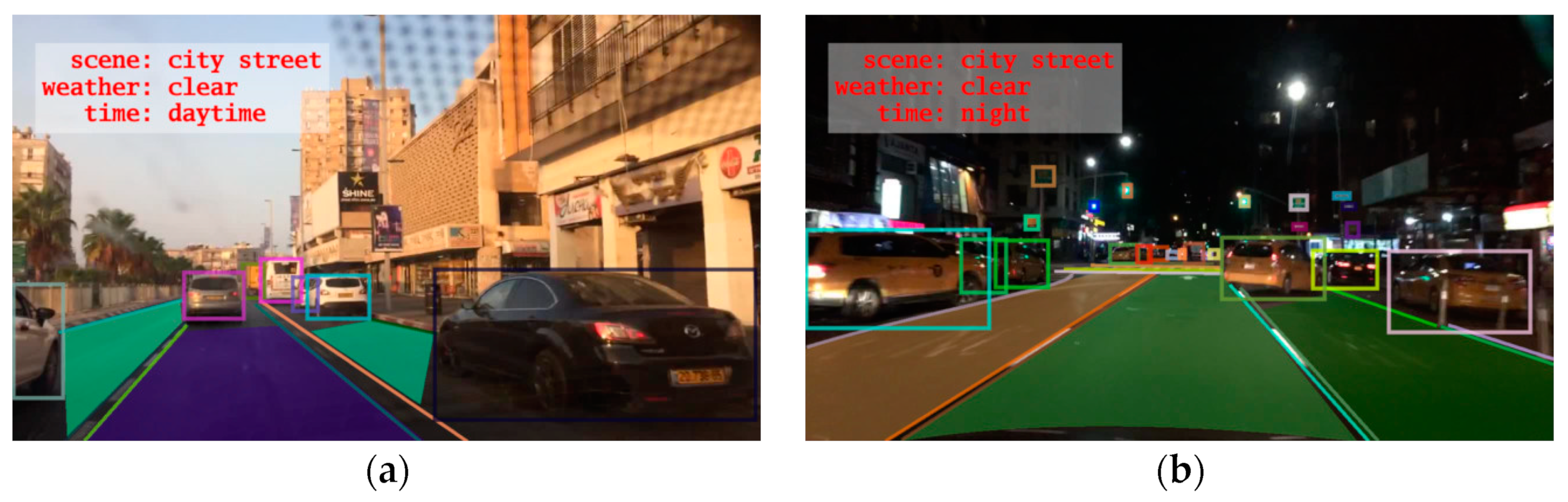
| BDD100K [145] | 2018 | New York, San Francisco Bay | Urban, suburban, highway | Camera, LiDAR, GPS/IMU | High-resolution images, high-frame rate images, GPS/IMU data |
| DR(eye)VE [146] | 2019 | N/A | Day to night, various weather, highway, downtown, countryside | Eye tracking glasses, camera, GPS/IMU | 555,000 frames annotated driving sequences |
| Argoverse [147] | 2019 | Pittsburgh, Miami | Urban | Camera, LiDAR, stereo camera, GNNS | Sensor data, 3D tracking annotations, 300k vehicle trajectories, rich semantic maps |
| nuScenes [148] | 2019 | Boston, Singapore | Urban, day to night | Camera, LiDAR, radar, GPS, IMU | 1000 scenes, 1.4 million images |
| Waymo Open [149] | 2019 | America | Urban, suburban | Camera, LiDAR | 1150 scenes that each span 20 s |
| Unsupervised Llamas [150] | 2019 | California | Highway | Camera | 100,042 labeled lane marker images |
| D2-City [151] | 2019 | China | Urban | Camera | More than 10,000 driving videos |
| Highway Driving [152] | 2019 | N/A | Highway | Camera | 20 video sequences with a 30 Hz frame rate |
| CADC [153] | 2020 | Waterloo, Canada | Urban, winter | Camera, LiDAR, GNSS/IMU | 7k frames of point clouds, 56k images |
| Mapillary Traffic Sign [154] | 2020 | Global | City, countryside, diverse weather | Camera | 100,000 high-resolution images |
| A2D2 [155] | 2020 | Germany | Urban, highway, rural | Camera, LiDAR, GPS/IMU | Camera, LiDAR, vehicle bus data |
| nuPlan [156] | 2021 | Pittsburgh, Las Vegas, Singapore, Boston | Urban | Camera, LiDAR | LiDAR point clouds, images, localization information, steering inputs |
| AutoMine [157] | 2022 | 2 provinces in China | Mine | Camera, LiDAR, IMU/GPS | Over 18 h driving data, 18k annotated lidar data, 18k annotated image frames |
| AIODrive [158] | 2022 | CARLA simulator | Adverse weather, adverse lighting, crowded scenes, people running, etc. | RGB, stereo, depth camera, LiDAR, radar, IMU/GPS | 500,000 annotated images, 100,000 annotated frames |
| SHIFT [159] | 2022 | CARLA simulator | Diverse weather, day to night, urban, village | Comprehensive sensor suite | Rain intensity, fog intensity, vehicle density, pedestrian density |
| OPV2V [160] | 2022 | CARLA simulator, Los Angeles | 73 divergent scenes with various numbers of connected vehicles | LiDAR, GPS/IMU, RGB | LiDAR point clouds, RGB images, annotated 3D vehicle bounding boxes |
| TAS-NIR [161] | 2022 | N/A | Unstructured outdoor driving scenarios | Camera | 209 VIS+NIR image pairs |
| OpenLane-V2 [162] | 2023 | Global | Urban, suburban | N/A | 2k annotated road scenes, 2.1M instance-level annotations, 1.9M positive topology relationships |
| Competitions | Initial Year | Simulators | Datasets | Scenario |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baidu Apollo Starfire Autonomous Driving Competition [164] | 2020 | Apollo | - | Traffic light intersections with pedestrians, intersections, changing lanes due to road construction, etc. |
| CIAC [165] | 2022 | PanoSim | - | Highways, intersections, parking lots, etc. |
| CVPR Autonomous Driving Challenge [166] | 2023 | - | OpenLane-V2 dataset, nuPlan dataset | Urban traffic |
| Waymo Open Dataset Challenge [167] | 2020 | - | Waymo Open dataset | N/A |
| Argoverse Challenge [169] | 2020 | - | Argoverse dataset, Argoverse2 dataset | N/A |
| BDD100K Challenge [170] | 2022 | - | BDD100K dataset | N/A |
| CARLA Autonomous Driving Challenge [20] | 2019 | CARLA | - | Intersections, traffic congestion, highways, obstacle avoidance, etc. |
| CARSMOS International Autonomous Driving Algorithm Challenge [171] | 2023 | Oasis Sim | - | Foggy conditions, intersections, etc. |
| TPCAP [172] | 2022 | - | - | Parallel parking, perpendicular parking, angled parking, parking with multiple obstacles, etc. |
| OnSite Autonomous Driving Challenge [173] | 2023 | OnSite | - | Highways, entering, and exiting parking spaces in mining areas, parking in parking lots, etc. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, T.; Liu, H.; Wang, W.; Wang, X. Virtual Tools for Testing Autonomous Driving: A Survey and Benchmark of Simulators, Datasets, and Competitions. Electronics 2024, 13, 3486. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13173486
Zhang T, Liu H, Wang W, Wang X. Virtual Tools for Testing Autonomous Driving: A Survey and Benchmark of Simulators, Datasets, and Competitions. Electronics. 2024; 13(17):3486. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13173486
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Tantan, Haipeng Liu, Weijie Wang, and Xinwei Wang. 2024. "Virtual Tools for Testing Autonomous Driving: A Survey and Benchmark of Simulators, Datasets, and Competitions" Electronics 13, no. 17: 3486. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13173486
APA StyleZhang, T., Liu, H., Wang, W., & Wang, X. (2024). Virtual Tools for Testing Autonomous Driving: A Survey and Benchmark of Simulators, Datasets, and Competitions. Electronics, 13(17), 3486. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13173486








