Diamond FET Biosensor Fabrication and Application
Abstract
:1. Background
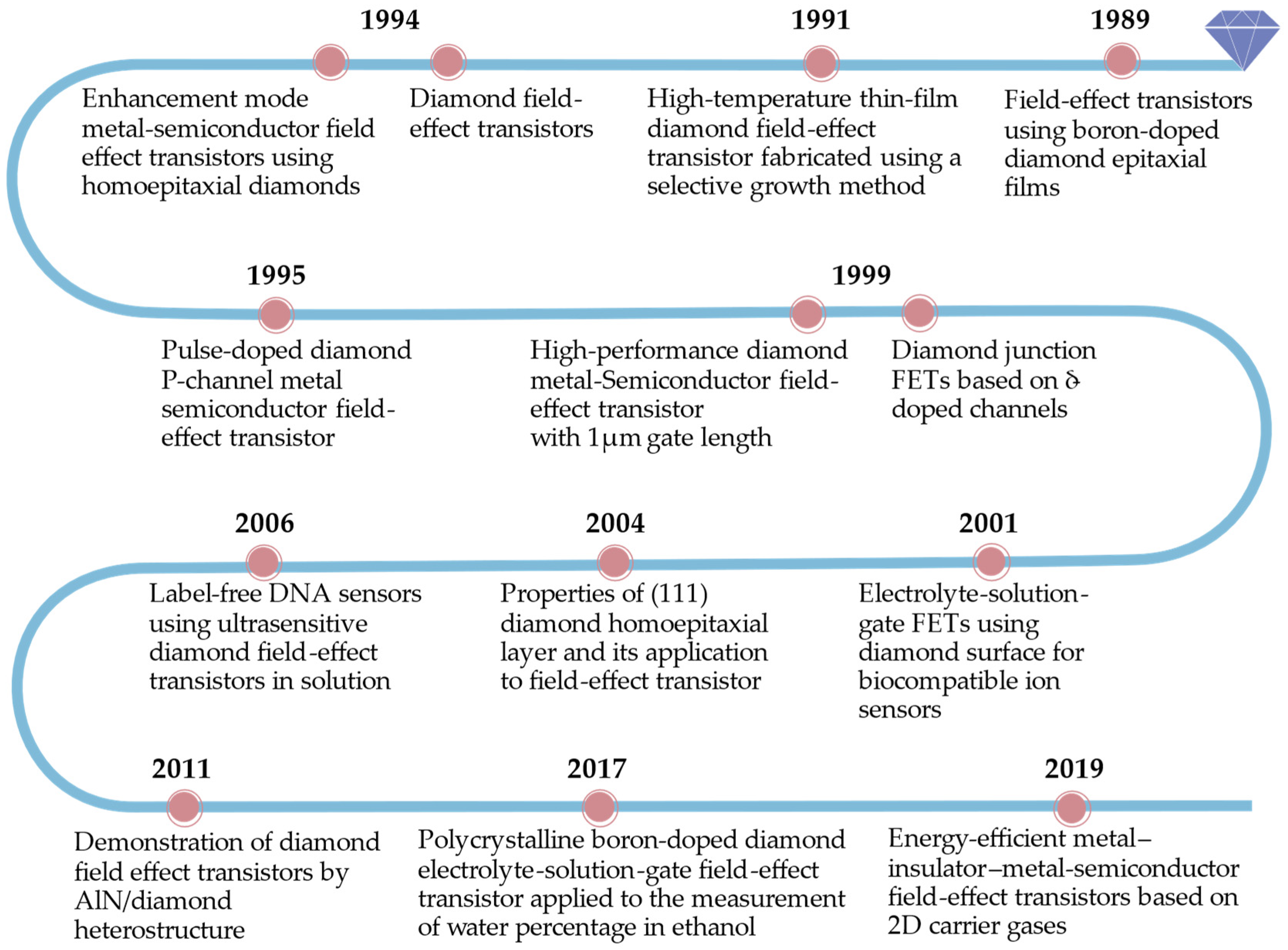
2. Development History of Diamond FET
3. Diamond SGFET
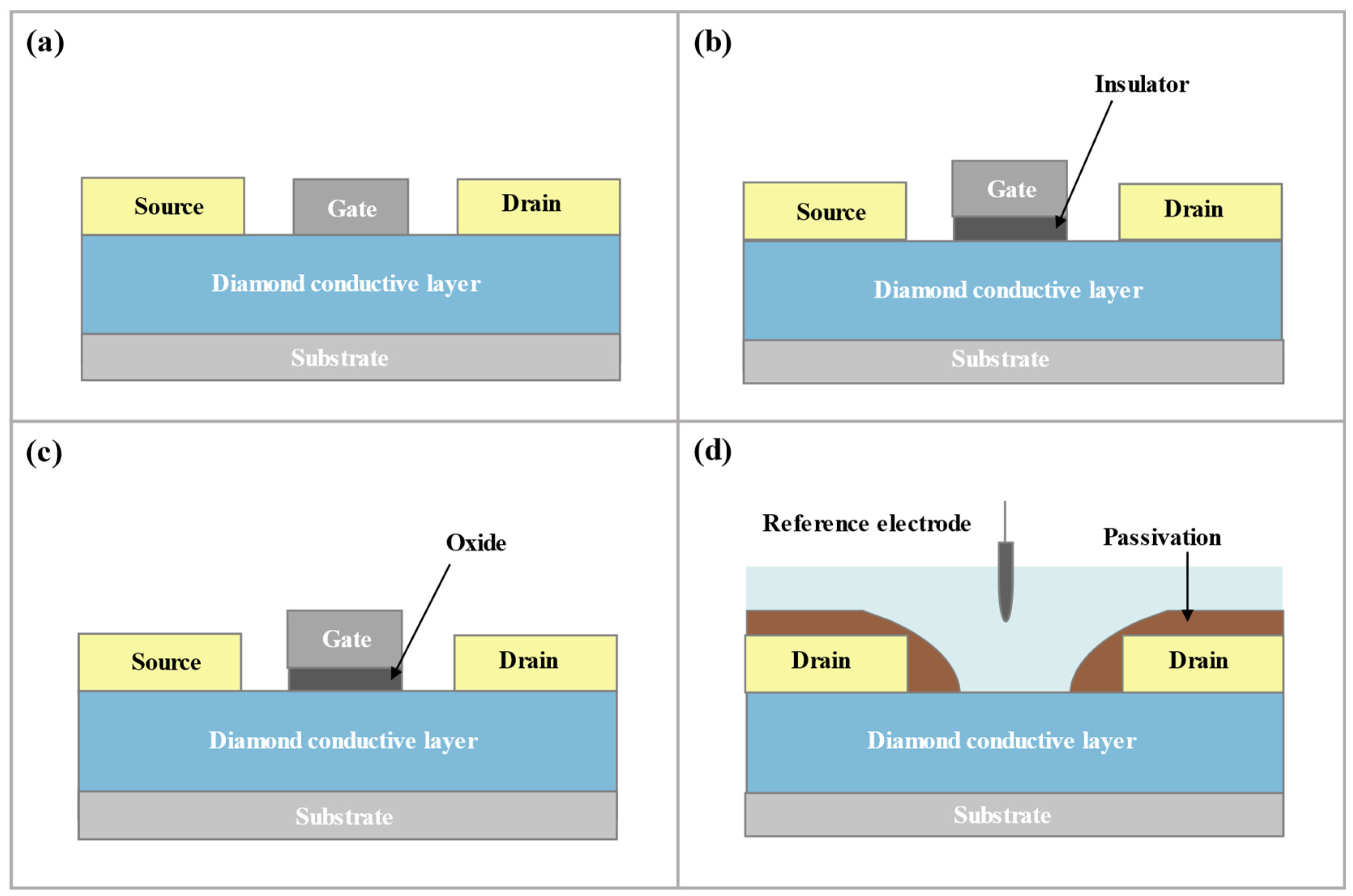
3.1. Introduction of D-SGFET
3.2. D-SGFET Fabrication Process
3.2.1. Diamond Film Synthesis
3.2.2. Diamond Semiconductor Manufacturing
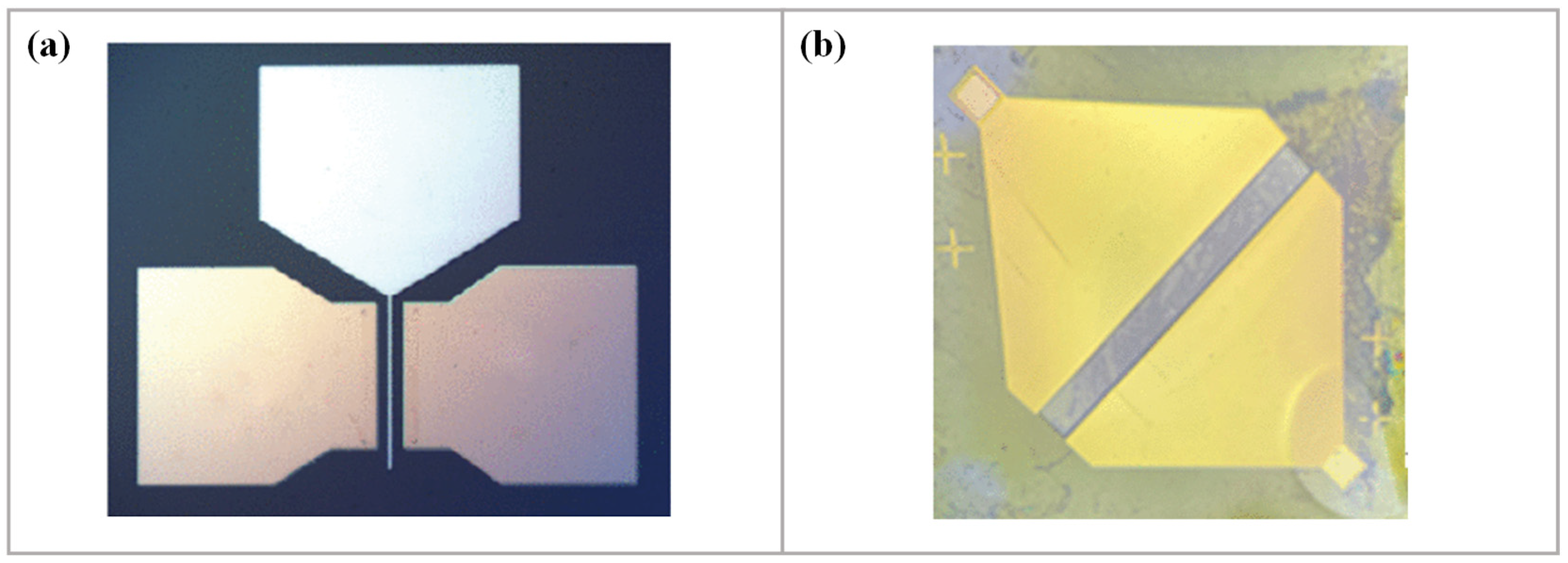
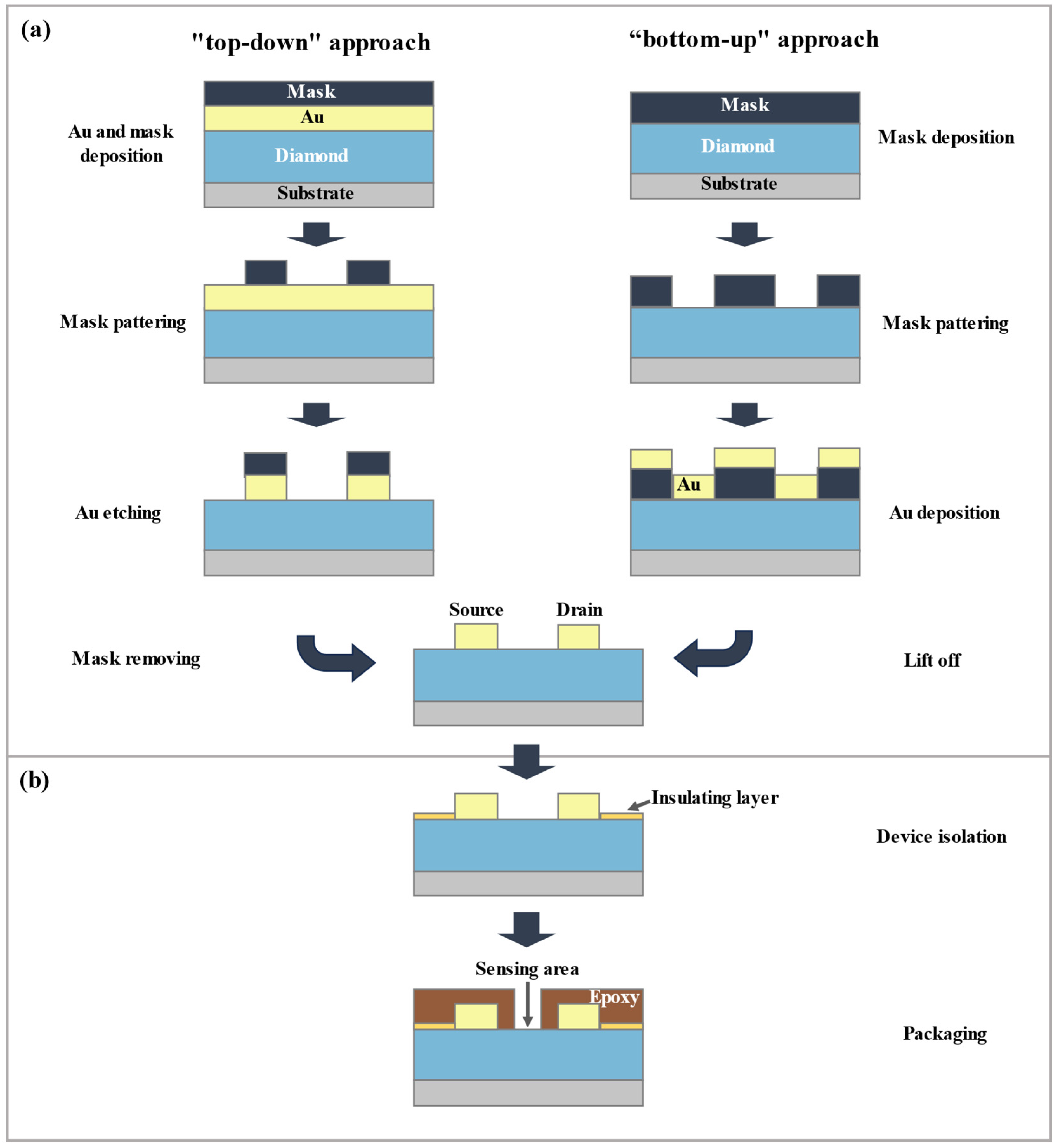
3.2.3. D-SGFET Source/Drain Fabrication
3.2.4. D-SGFET Packaging
3.3. D-SGFET Surface Functionalization and Application
3.3.1. Diamond Surface Functionalization
3.3.2. D-SGFET Application
4. Discussion and Prospect
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kawarada, H.; Araki, Y.; Sakai, T.; Ogawa, T.; Umezawa, H. Electrolyte-solution-gate FETs using diamond surface for biocompatible ion sensors. Phys. Status Solidi A-Appl. Mater. Sci. 2001, 185, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, P.J.F. Carbon nanotube composites. Int. Mater. Rev. 2004, 49, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Xiao, L.; Sushko, M.; Wang, W.; Schwenzer, B.; Xiao, J.; Nie, Z.; Saraf, L.V.; Yang, Z.; Liu, J. Sodium Ion Insertion in Hollow Carbon Nanowires for Battery Applications. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 3783–3787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, D.-S.; Zhou, T.-X.; Zhou, S.-L.; Zou, W.-J.; Mo, S.-S.; Xia, N.-N. Nitrogen-enriched carbon nanowires from the direct carbonization of polyaniline nanowires and its electrochemical properties. Electrochem. Commun. 2011, 13, 242–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Yin, X.; Xue, J.; Cheng, L.; Zhang, L. In-situ synthesis of hierarchically porous and polycrystalline carbon nanowires with excellent microwave absorption performance. Carbon 2016, 107, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saleh, M.H.; Sundararaj, U. A review of vapor grown carbon nanofiber/polymer conductive composites. Carbon 2009, 47, 2–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto-Márquez, A.; Romero, R.; Romero, A.; Valverde, J.L. Carbon nanospheres: Synthesis, physicochemical properties and applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 1664–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wort, C.J.H.; Balmer, R.S. Diamond as an electronic material. Mater. Today 2008, 11, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S. Biomedical Applications of Carbon Nanomaterial Modified Sensors: A Promising Future. ECS Meet. Abstr. 2019, MA2019-01, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, T.K.; Budarapu, P.R.; Chappidi, S.R.; YB, S.S.; Paggi, M.; Bordas, S.P. Advances in Carbon Based Nanomaterials for Bio-Medical Applications. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 6851–6877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Zhang, M.; Du, Y.; Xu, B.; Chen, G.; He, S.; Zhang, D.; Li, Q.; Wang, H. Trace detection of SARS-CoV-2 N-protein by diamond solution-gate field-effect transistor. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2023, 134, 109775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.S.; Auciello, O.; Butler, J.E.; Cai, W.; Carlisle, J.A.; Gerbi, J.E.; Gruen, D.M.; Knickerbocker, T.; Lasseter, T.L.; Russell, J.N., Jr.; et al. DNA-modified nanocrystalline diamond thin-films as stable, biologically active substrates. Nat. Mater. 2003, 2, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuga, S.; Yang, J.-H.; Takahashi, H.; Hirama, K.; Iwasaki, T.; Kawarada, H. Detection of Mismatched DNA on Partially Negatively Charged Diamond Surfaces by Optical and Potentiometric Methods. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 13251–13263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauss, A.R.; Auciello, O.; Gruen, D.M.; Jayatissa, A.; Sumant, A.; Tucek, J.; Mancini, D.C.; Moldovan, N.; Erdemir, A.; Ersoy, D. Ultrananocrystalline diamond thin films for MEMS and moving mechanical assembly devices. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2001, 10, 1952–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gracio, J.J.; Fan, Q.H.; Madaleno, J.C. Diamond growth by chemical vapour deposition. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2010, 43, 374017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawarada, H.; Ruslinda, A.R. Diamond electrolyte solution gate FETs for DNA and protein sensors using DNA/RNA aptamers. Phys. Status Solidi A-Appl. Mater. Sci. 2011, 208, 2005–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isberg, J.; Hammersberg, J.; Johansson, E.; Wikström, T.; Twitchen, D.J.; Whitehead, A.J.; Coe, S.E.; Scarsbrook, G.A. High Carrier Mobility in Single-Crystal Plasma-Deposited Diamond. Science 2002, 297, 1670–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Ruotolo, A. Photo-induced Hall effect in metals. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, F.Z.; Li, D.J. A review of investigations on biocompatibility of diamond-like carbon and carbon nitride films. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2000, 131, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Tsai, C.; Gerberich, W.W.; Kruckeberg, L.; Kania, D.R. Biocompatibility of chemical-vapour-deposited diamond. Biomaterials 1995, 16, 483–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smentkowski, V.S.; Yates, J.T. Fluorination of Diamond Surfaces by Irradiation of Perfluorinated Alkyl Iodides. Science 1996, 271, 193–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ando, T.; Nishitani-Gamo, M.R.; Rawles, E.; Yamamoto, K.; Kamo, M.; Sato, Y. Chemical modification of diamond surfaces using a chlorinated surface as an intermediate state. Diam. Relat. Mater. 1996, 5, 1136–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.B.; Brown, D.W. Properties of photochemically modified diamond films. Diam. Relat. Mater. 1995, 4, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.-S.; Hiraki, T.; Umezawa, H.; Kawarada, H. Miniaturized diamond field-effect transistors for application in biosensors in electrolyte solution. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2007, 90, 063901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, Y.; Kawarada, H. Low drift and small hysteresis characteristics of diamond electrolyte-solution-gate FET. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2010, 43, 374020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-H.; Song, K.-S.; Kuga, S.; Kawarada, H. Characterization of Direct Immobilized Probe DNA on Partially Functionalized Diamond Solution-Gate Field-Effect Transistors. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2006, 45, L1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Härtl, A.; Baur, B.; Stutzmann, M.; Garrido, J.A. Enzyme-Modified Field Effect Transistors Based on Surface-Conductive Single-Crystalline Diamond. Langmuir 2008, 24, 9898–9906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-H.; Kuga, S.; Song, K.-S.; Kawarada, H. Characterization of Hybridization on Diamond Solution-Gate Field-Effect Transistors for Detecting Single Mismatched Oligonucleotides. Appl. Phys. Express 2008, 1, 118001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notsu, H.; Yagi, I.; Tatsuma, T.; Tryk, D.A.; Fujishima, A. Surface carbonyl groups on oxidized diamond electrodes. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2000, 492, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruslinda, A.R.; Tajima, S.; Ishii, Y.; Ishiyama, Y.; Edgington, R.; Kawarada, H. Aptamer-based biosensor for sensitive PDGF detection using diamond transistor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 1599–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, K.; Björkman, H.; Hjort, K. Role of water and oxygen in wet and dry oxidation of diamond. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 90, 1026–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.W.; Moon, M.W.; Ahmed, S.F.; Kim, H.; Cha, T.G.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, S.S.; Lee, K.R. Long-Lasting Hydrophilicity on Nanostructured Si-Incorporated Diamond-Like Carbon Films. Langmuir 2010, 26, 17203–17209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, S.; Sun, W.; Hu, Z.; Quan, B.; Xia, X.; Li, Y.; Han, D.; Li, J.; Gu, C. Morphology Modulating the Wettability of a Diamond Film. Langmuir 2014, 30, 12647–12653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kriele, A.; Williams, O.A.; Wolfer, M.; Hees, J.J.; Smirnov, W.; Nebel, C.E. Formation of nano-pores in nano-crystalline diamond films. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2011, 507, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dearnaley, G.; Arps, J.H. Biomedical applications of diamond-like carbon (DLC) coatings: A review. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 200, 2518–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nistor, P.A.; May, P.W. Diamond thin films: Giving biomedical applications a new shine. J. R. Soc. Interface 2017, 14, 20170382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radeka, V. The field-effect transistor-its characteristics and applications. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 1964, 11, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, B.; Ma, X.; Wang, Y. Highly sensitive gas sensing platforms based on field effect Transistor-A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1172, 338575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirleto, L. Micro and Nano Raman Lasers. Micromachines 2021, 12, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.-X.; Tsai, Y.C.; Lee, C.Y.; Wu, C.C.; Dai, C.L. Thermoelectric Energy Micro Harvesters with Temperature Sensors Manufactured Utilizing the CMOS-MEMS Technique. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Qian, C.; Chahal, P.; Cao, C. Printed Diodes: Materials Processing, Fabrication, and Applications. Adv. Sci. 2019, 6, 1801653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiomi, H.; Nishibayashi, Y.; Fujimori, N. Field-Effect Transistors using Boron-Doped Diamond Epitaxial Films. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1989, 28, L2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denisenko, A.; Aleksov, A.; Daumiller, I.; Kohn, E. pH sensors based on wide bandgap semiconductors. In Proceedings of the 58th DRC. Device Research Conference, Conference Digest (Cat. No.00TH8526), Denver, CO, USA, 19–21 June 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.-H.; Degawa, M.; Song, K.-S.; Wang, C.; Kawarada, H. Fabrication of calcium ion sensitive diamond field effect transistors (FETs) based on immobilized calmodulin. Mater. Lett. 2010, 64, 2321–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.-S.; Sakai, T.; Kanazawa, H.; Araki, Y.; Umezawa, H.; Tachik, M.; Kawarada, H. Cl− sensitive biosensor used electrolyte-solution-gate diamond FETs. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2003, 19, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, N.A.; Rahim, R.A.; Rezek, B.; Kromka, A.; Ismail, N.S.B.; Gopinath, S.; Izsák, T.; Procházka, V.; Faudzi, F.N.M.; Abidin, A.S.Z.; et al. Nanocrystalline Diamond Electrolyte-Gates in Field Effect Transistor for a Prolific Aptasensing HIV-1 Tat on Hydrogen-terminated Surface. Int. J. Nanoelectron. Mater. 2020, 13, 295–306. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Hamers, R.J. Fabrication and characterization of a biologically sensitive field-effect transistor using a nanocrystalline diamond thin film. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 85, 3626–3628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim Ruslinda, A.; Tanabe, K.; Ibori, S.; Wang, X.; Kawarada, H. Effects of diamond-FET-based RNA aptamer sensing for detection of real sample of HIV-1 Tat protein. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 40, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shintani, Y.; Ibori, S.; Kawarada, H. Deoxyribonucleic-acid-sensitive Polycrystalline Diamond Solutiongate Field-effect Transistor with a Carboxyl-terminated Borondoped Channel. Anal. Sci. 2019, 35, 923–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, K.S.; Zhang, G.-J.; Nakamura, Y.; Furukawa, K.; Hiraki, T.; Yang, J.-H.; Funatsu, T.; Ohdomari, I.; Kawarada, H. Label-free DNA sensors using ultrasensitive diamond field-effect transistors in solution. Phys. Rev. E 2006, 74, 041919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.-S.; Degawa, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Kanazawa, H.; Umezawa, H.; Kawarada, H. Surface-modified Diamond Field-effect Transistors for Enzyme-immobilized Biosensors. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 43, L814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Du, Y.; Chang, X.; Xu, B.; Chen, G.; He, S.; Zhang, D.; Li, Q.; Wang, J.; Wang, R. Partly-O-Diamond Solution-Gate Field-Effect Transistor as an Efficient Biosensor of Glucose. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2023, 170, 037507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shintani, Y.; Kawarada, H. Polycrystalline Boron-doped Diamond Electrolyte-solution-gate Field-effect Transistor Applied to the Measurement of Water Percentage in Ethanol. Anal. Sci. 2017, 33, 1193–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, R.; Chen, G.; Chang, X.; Lin, F.; Wen, F.; Jia, K.; Wang, H. An Enhancement-Mode Hydrogen-Terminated Diamond Field-Effect Transistor With Lanthanum Hexaboride Gate Material. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2020, 41, 585–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Chang, X.; Xu, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Feng, Y.; He, S.; Chen, G.; Li, Q.; Wang, J.; et al. Detection of Glucose Using Diamond Solution-Gate Field-Effect Transistor. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2022, 69, 4534–4539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gildenblat, G.S.; Grot, S.A.; Hatfield, C.W.; Badzian, A.R. High-temperature thin-film diamond field-effect transistor fabricated using a selective growth method. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 1991, 12, 37–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreifus, D.L.; Tessmer, A.J.; Holmes, J.S.; Kao, C.-T.; Malta, D.M.; Plano, L.S.; Stoner, B.R. Diamond Field-Effect Transistors. MRS Online Proc. Libr. 1994, 339, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, T.; Song, K.-S.; Kanazawa, H.; Nakamura, Y.; Umezawa, H.; Tachiki, M.; Kawarada, H. Ozone-treated channel diamond field-effect transistors. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2003, 12, 1971–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, J.A.; Härtl, A.; Kuch, S.; Stutzmann, M.; Williams, O.A.; Jackmann, R.B. pH sensors based on hydrogenated diamond surfaces. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 073504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denisenko, A.; Jamornmarn, G.; El-Hajj, H.; Kohn, E. pH sensor on O-terminated diamond using boron-doped channel. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2007, 16, 905–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezek, B.; Shin, D.; Watanabe, H.; Nebel, C.E. Intrinsic hydrogen-terminated diamond as ion-sensitive field effect transistor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 122, 596–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falina, S.; Tanabe, K.; Iyama, Y.; Tadenuma, K.; Bi, T.; Chang, Y.; Manaf, A.A.; Syamsul, M.; Kawarada, H. Feasibility Study of TiOx Encapsulation of Diamond Solution-Gate Field-Effect Transistor Metal Contacts for Miniature Biosensor Applications. Phys. Status Solidi (A) 2020, 217, 2000634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgington, R.; Ruslinda, R.; Sato, S.; Ishiyama, Y.; Tsuge, K.; Ono, T.; Kawarada, H.; Jackman, R.B. Boron δ-doped (111) diamond solution gate field effect transistors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 33, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawaguchi, S.; Nomoto, R.; Sato, H.; Takarada, T.; Chang, Y.H.; Kawarada, H. pH Measurement at Elevated Temperature with Vessel Gate and Oxygen-Terminated Diamond Solution Gate Field Effect Transistors. Sensors 2022, 22, 1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleksov, A.; Vescan, A.; Kunze, M.; Gluche, P.; Ebert, W.; Kohn, E.; Bergmeier, A.; Dollinger, G. Diamond junction FETs based on δ-doped channels. Diam. Relat. Mater. 1999, 8, 941–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, T.; Hoshino, Y.; Tsuzuki, K.; Kato, H.; Makino, T.; Ogura, M.; Takeuchi, D.; Matsumoto, T.; Okushi, H.; Yamasaki, S. Diamond Junction Field-Effect Transistors with Selectively Grown n+-Side Gates. Appl. Phys. Express 2012, 5, 091301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imura, M.; Hayakawa, R.; Watanabe, E.; Liao, M.; Koide, Y.; Amano, H. Demonstration of diamond field effect transistors by AlN/diamond heterostructure. Phys. Status Solidi (RRL)—Rapid Res. Lett. 2011, 5, 125–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, M.; Sang, L.; Shimaoka, T.; Imura, M.; Koizumi, S.; Koide, Y. Energy-Efficient Metal–Insulator–Metal-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors Based on 2D Carrier Gases. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2019, 5, 1800832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Umezawa, H.; Kawashima, H.; Makino, T.; Hoshikawa, N.; Kaneko, J.H. Exploring diamond multigate FET for next generation three-phase CCD. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2024, 144, 111012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yugo, S.; Kanai, T.; Kimura, T.; Muto, T. Generation of diamond nuclei by electric field in plasma chemical vapor deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1991, 58, 1036–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Wei, J.; Chen, L.; An, K.; Zhang, X.; Ye, H.; Zhou, H.; et al. Vertically Aligned Boron-Doped Diamond Hollow Nanoneedle Arrays for Enhanced Field Emission. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 10878–10889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Gao, Y.; Hu, W.; Xu, B.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Ge, B.; Yang, Z.; et al. Hierarchically structured diamond composite with exceptional toughness. Nature 2020, 582, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evtimova, J.; Kulisch, W.; Petkov, C.; Petkov, E.; Schnabel, F.; Reithmaier, J.P.; Popov, C. Reactive ion etching of nanocrystalline diamond for the fabrication of one-dimensional nanopillars. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2013, 36, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, Y.; Mutsukura, N.M.N.; Machi, Y.M.Y. Synthesis of Diamond Using Fe Catalysts by RF Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition Method. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1992, 31, 1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Kandasami, A.; Ramachandra Rao, M.S. Realization of highly conducting n-type diamond by phosphorus ion implantation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2021, 118, 102102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, H.; Ogura, M.; Makino, T.; Takeuchi, D.; Yamasaki, S. N-type control of single-crystal diamond films by ultra-lightly phosphorus doping. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 109, 142102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakano, Y.; Zhang, X.; Kobayashi, K.; Matsumoto, T.; Inokuma, T.; Yamasaki, S.; Nebel, C.E.; Tokuda, N. Impact of nitrogen doping on homoepitaxial diamond (111) growth. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2022, 125, 108997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nebel, C.E.; Yang, N.; Uetsuka, H.; Osawa, E.; Tokuda, N.; Williams, O. Diamond nano-wires, a new approach towards next generation electrochemical gene sensor platforms. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2009, 18, 910–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Ariki, T.; Iwabuchi, M.; Maki, T.; Shikama, S.; Suzuki, S. Analytical studies on multiple delta doping in diamond thin films for efficient hole excitation and conductivity enhancement. J. Appl. Phys. 1994, 76, 1977–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasu, M.; Saha, N.C.; Oishi, T.; Kim, S. Fabrication of diamond modulation-doped FETs by NO2 delta doping in an Al2O3 gate layer. Appl. Phys. Express 2021, 14, 051004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dergianlis, V.; Geller, M.; Oing, D.; Wöhrl, N.; Lorke, A. Patterning of diamond with 10 nm resolution by electron-beam-induced etching. Nanotechnology 2019, 30, 365302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivero, P.; Rubanov, S.; Reichart, P.; Gibson, B.C.; Huntington, S.T.; Rabeau, J.; Greentree, A.D.; Salzman, J.; Moore, D.; Jamieson, D.N.; et al. Ion-Beam-Assisted Lift-Off Technique for Three-Dimensional Micromachining of Freestanding Single-Crystal Diamond. Adv. Mater. 2005, 17, 2427–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, M.; Qi, F.; Lin, F.R.; Jen, A.K.-Y. Self-Assembled Monolayers for Interfacial Engineering in Solution-Processed Thin-Film Electronic Devices: Design, Fabrication, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2024, 124, 2138–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christiaens, P.; Vermeeren, V.; Wenmackers, S.; Daenen, M.; Haenen, K.; Nesládek, M.; van de Ven, M.; Ameloot, M.; Michiels, L.; Wagner, P. EDC-mediated DNA attachment to nanocrystalline CVD diamond films. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 22, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rietwyk, K.J.; Wong, S.L.; Cao, L.; O’Donnell, K.M.; Ley, L.; Wee, A.T.S.; Pakes, C.I. Work function and electron affinity of the fluorine-terminated (100) diamond surface. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 102, 091604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shintani, Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Kawarada, H. An All-Solid-State pH Sensor Employing Fluorine-Terminated Polycrystalline Boron-Doped Diamond as a pH-Insensitive Solution-Gate Field-Effect Transistor. Sensors 2017, 17, 1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shintani, Y.; Kawarada, H. Fluorine-Terminated Polycrystalline Diamond Solution-Gate Field-Effect Transistor Sensor with Smaller Amount of Unexpectedly Generated Fluorocarbon Film Fabricated by Fluorine Gas Treatment. Materials 2022, 15, 2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernando, J.; Pourrostami, T.; Garrido, J.A.; Williams, O.A.; Gruen, D.M.; Kromk, A.; Steinmüller, D.; Stutzmann, M. Immobilization of horseradish peroxidase via an amino silane on oxidized ultrananocrystalline diamond. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2007, 16, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Zhang, Q.; Chang, X.; Zhang, D.; Chen, G.; He, S.; Wang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Wang, H. Detection of carbohydrate antigen 19-9 by a diamond solution-gate field-effect transistor sensor. Mater. Lett. 2022, 318, 132116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzid, A.; Hayes, P.E.; Glennon, J.D.; Luong, J.H.T. Captavidin as a regenerable biorecognition element on boron-doped diamond for biotin sensing. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1059, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.H.; Iyama, Y.; Kawaguchi, S.; Takarada, T.; Sato, H.; Nomoto, R.; Tadenuma, K.; Falina, S.; Syamsul, M.; Shintani, Y.; et al. Ion-Sensitive Stainless Steel Vessel for All-Solid- State pH Sensing System Incorporating pH-Insensitive Diamond Solution Gate Field-Effect Transistors. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 9110–9119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suaebah, E.; Naramura, T.; Myodo, M.; Hasegawa, M.; Shoji, S.; Buendia, J.J.; Kawarada, H. Aptamer-Based Carboxyl-Terminated Nanocrystalline Diamond Sensing Arrays for Adenosine Triphosphate Detection. Sensors 2017, 17, 1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| SGFET | Band Gap (eV) | Thermal Conductivity (W/(m·K)) | Electron Mobility (cm2/V·s) | Hole Mobility (cm2/V·s) | Electron Mobility (cm/s) | Hole Mobility (cm/s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diamond | 5.5 | 2400 | 4500 | 3800 | ||
| Silicon | 1.1 | 150 | 1400 | 450 | ||
| SGFET | Johnson’s figure of merit | Keyes’ figure of merit | Baliga’s figure of merit | Hole surface density (/) | Relative dielectric constant | Critical breakdown field strength () |
| Diamond | 8200 | 32 | 17,200 | 1013 | 5.5 | 10 |
| Silicon | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1012 | 11.9 | 10 |
| Detection Principles | Application | Detection Range | Sensitivity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electrostatic interaction | ) [91] | Gate-source voltage | ||
| [45] | Threshold voltage | |||
| Non- covalent interaction | Non-covalent interaction | is one of the essential chemicals that regulate enzyme activity, neuronal activity, muscle contraction, and vesicle exocytosis [44] | Gate-source voltage | |
| Detection of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 trans activator transcription (HIV-1 Tat) protein [48] | Gate-source voltage | |||
| Detection of platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) [30] | Gate-source voltage | |||
| Detection of human immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibody [47] | --- | Concentration | ||
| Detection of carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (CA19-9) [89] | Gate-source voltage | |||
| Detection of the N protein of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) [11] | Drain-source current | |||
| Ligand interactions with non-protein receptor | Detection of biotin [90] | Concentration | ||
| DNA hybridization | Detection of DNA | --- | Gate-source voltage | |
| Non-covalent interaction | Detection of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) [92] | Gate-source voltage | ||
| Chemical reaction | Detection of glucose [52] | Gate-source voltage | ||
| Detection of urea [24] | Drain-source current | |||
| Detection of penicillin and acetylcholinesterase [27] | --- | Gate-source voltage | ||
| Detection of water content in ethanol solution [53] | --- | --- | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zou, F.; Wang, Z.; Lin, Z.; Wang, C.; Yuan, Z. Diamond FET Biosensor Fabrication and Application. Electronics 2024, 13, 3881. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13193881
Zou F, Wang Z, Lin Z, Wang C, Yuan Z. Diamond FET Biosensor Fabrication and Application. Electronics. 2024; 13(19):3881. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13193881
Chicago/Turabian StyleZou, Fengling, Zimin Wang, Zelong Lin, Chengyong Wang, and Zhishan Yuan. 2024. "Diamond FET Biosensor Fabrication and Application" Electronics 13, no. 19: 3881. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13193881
APA StyleZou, F., Wang, Z., Lin, Z., Wang, C., & Yuan, Z. (2024). Diamond FET Biosensor Fabrication and Application. Electronics, 13(19), 3881. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13193881




