Graphical Design Approach for UWB Stacked CG LNA Using Inversion Coefficient
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Design Methodology
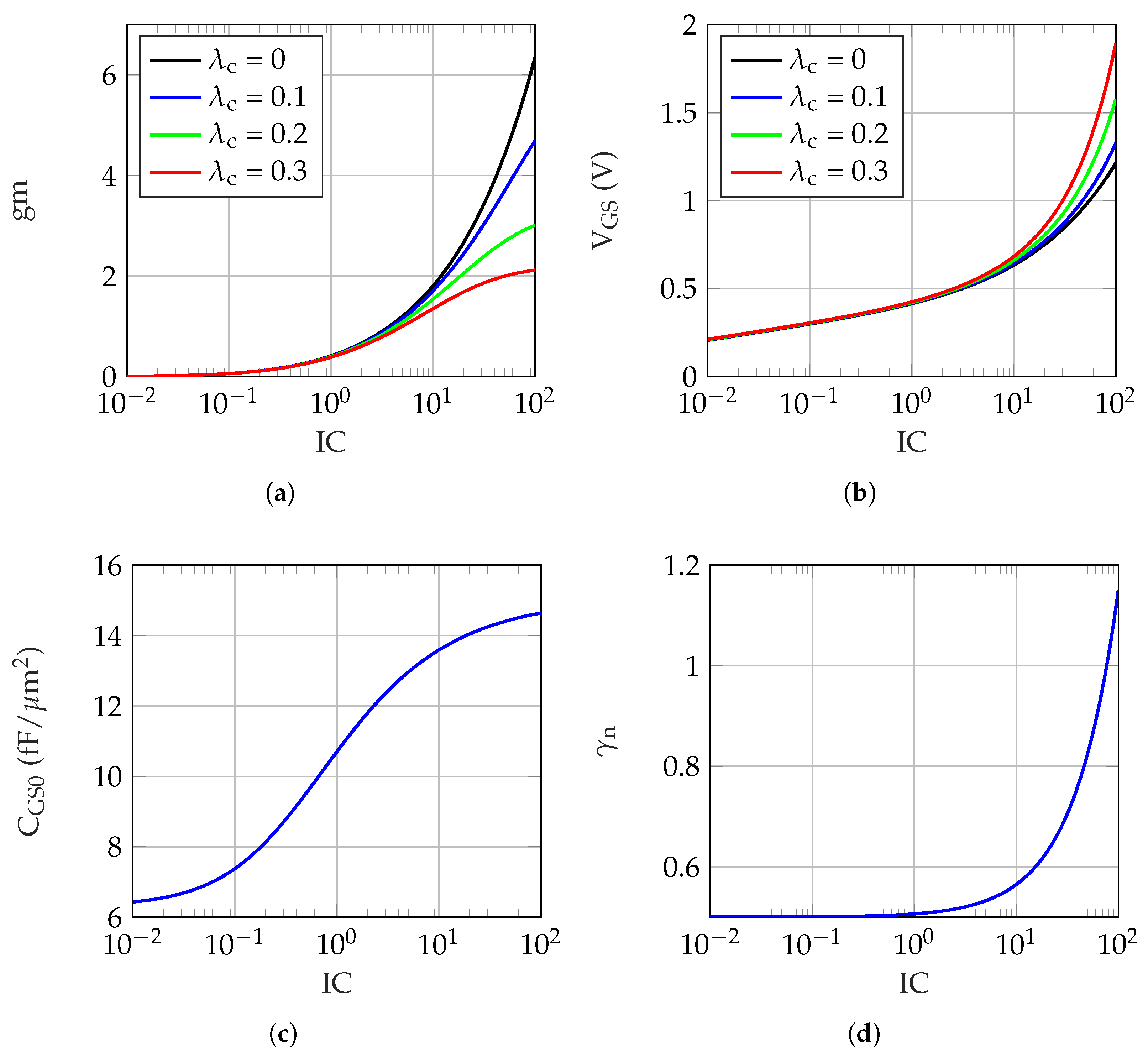
3. Charge-Based Transistor Model
4. Analysis of the Stacked CG Topology
4.1. PMOS-to-NMOS Sizing Ratio
4.1.1. Strong Inversion Approximation
4.1.2. Weak Inversion Approximation
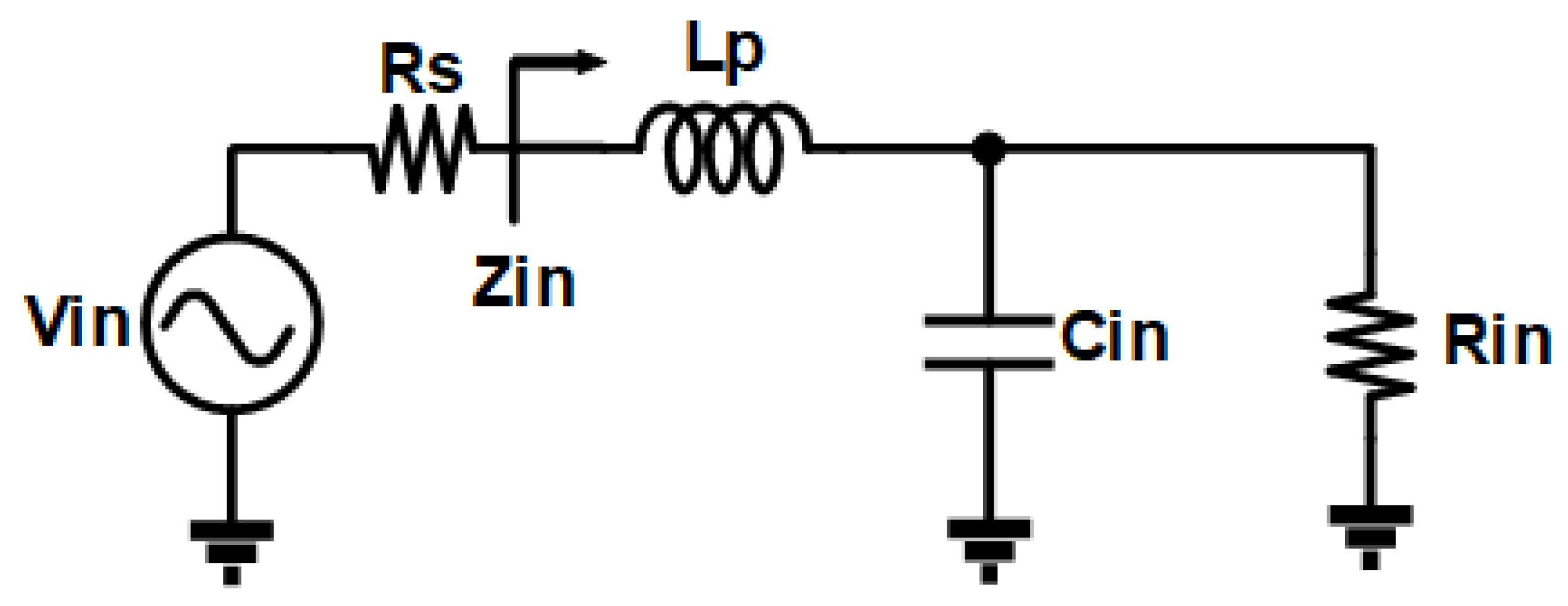
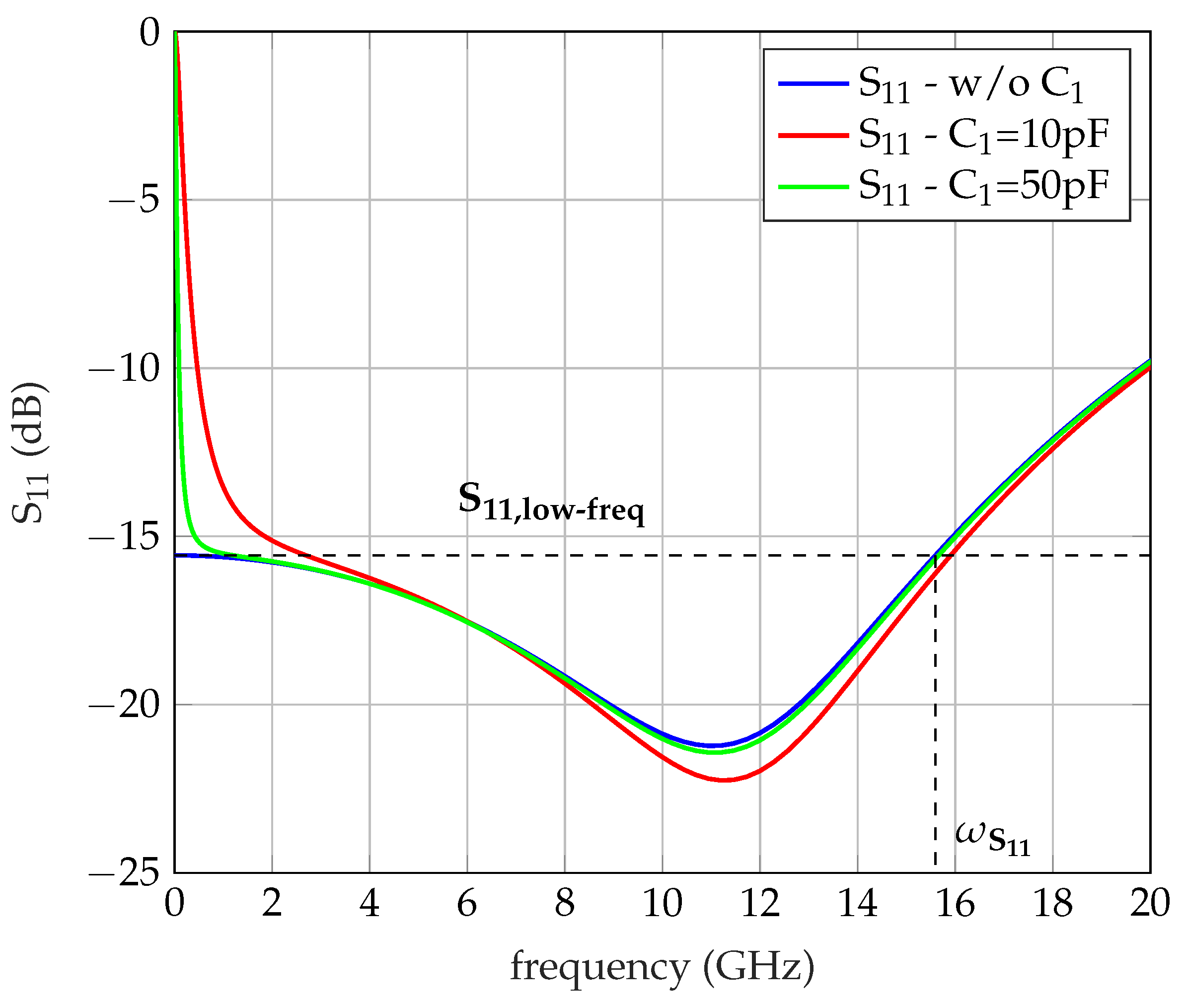
4.2. Input Matching
4.3. Gain
4.4. Bandwidth
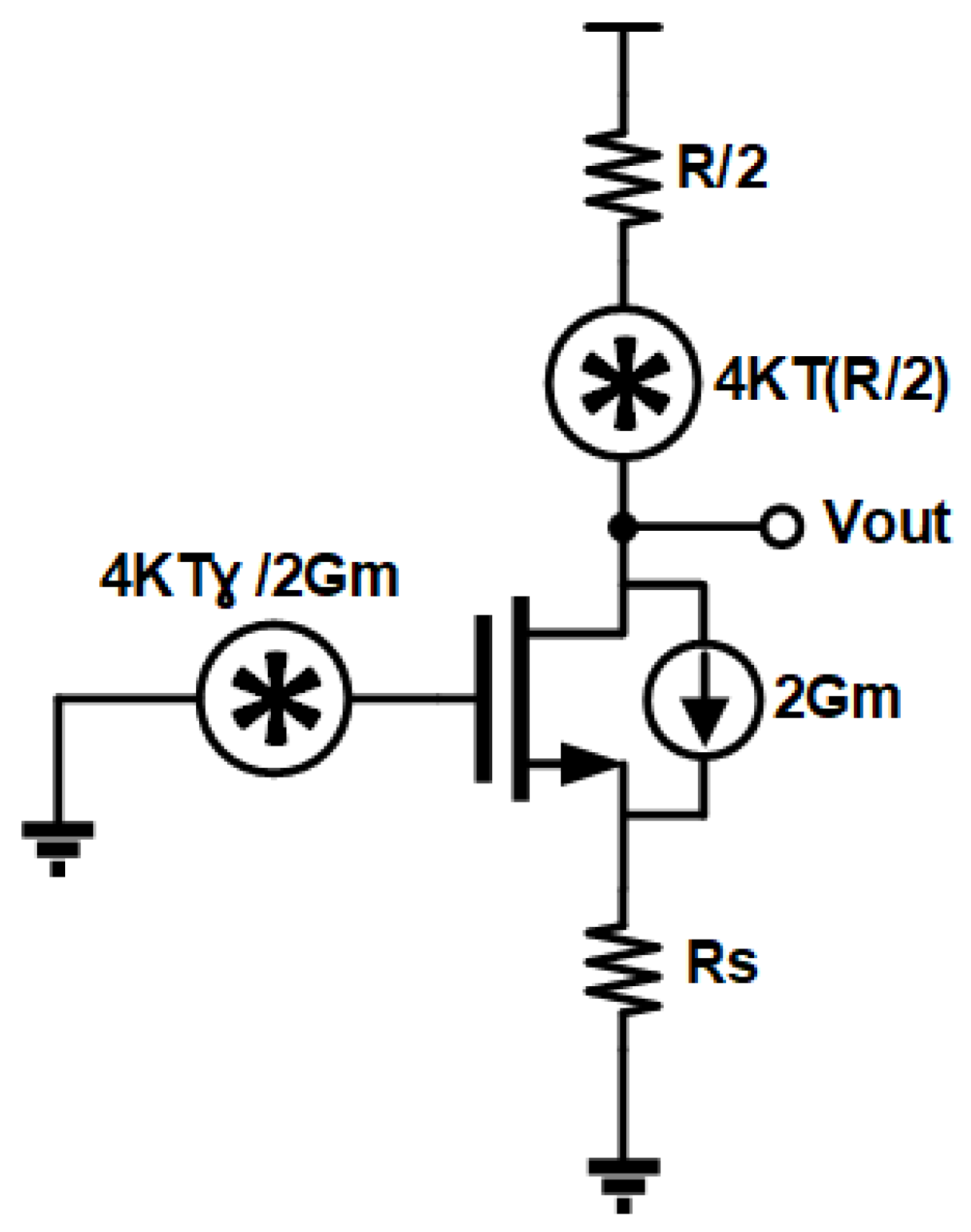
4.5. Noise
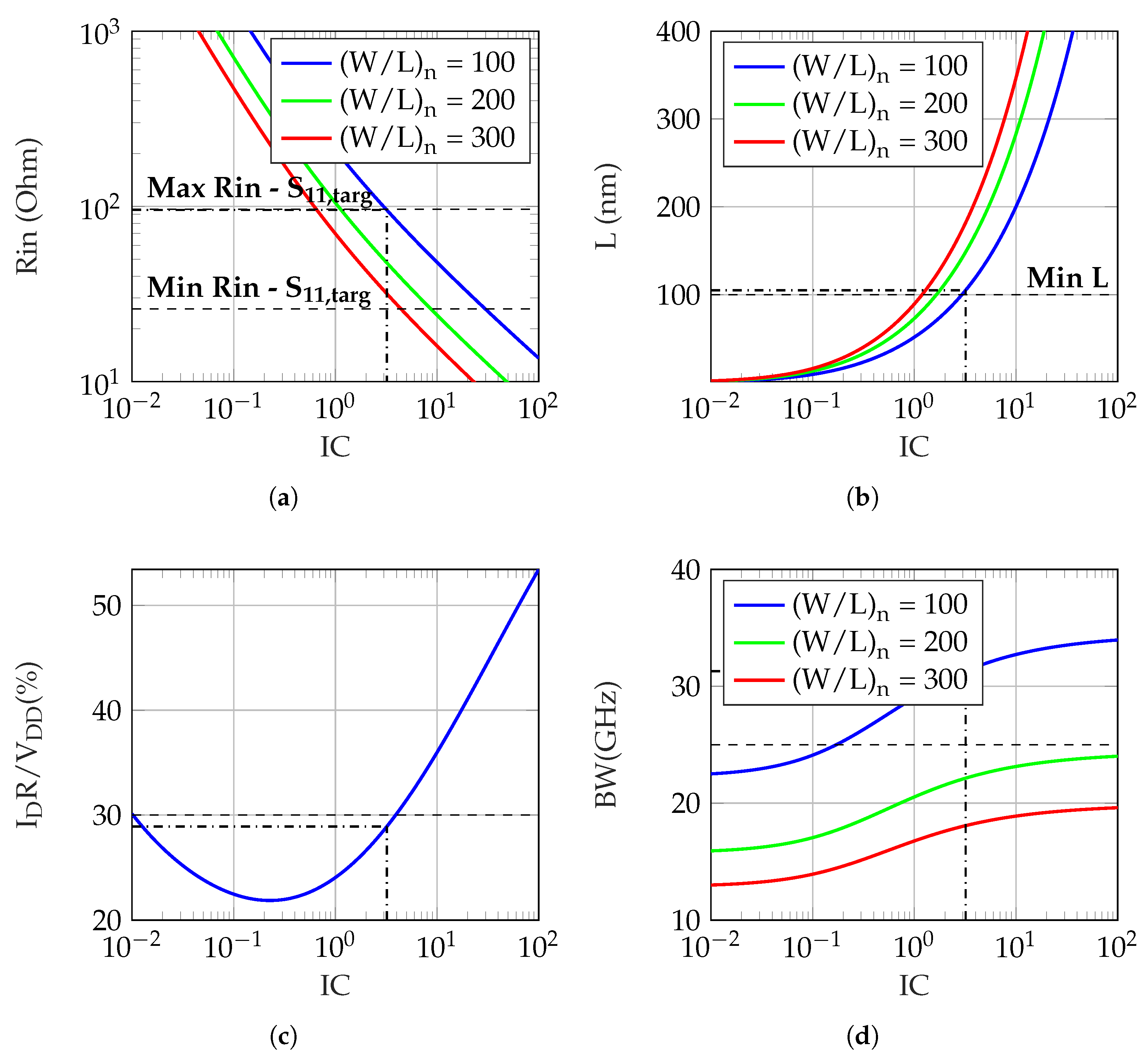
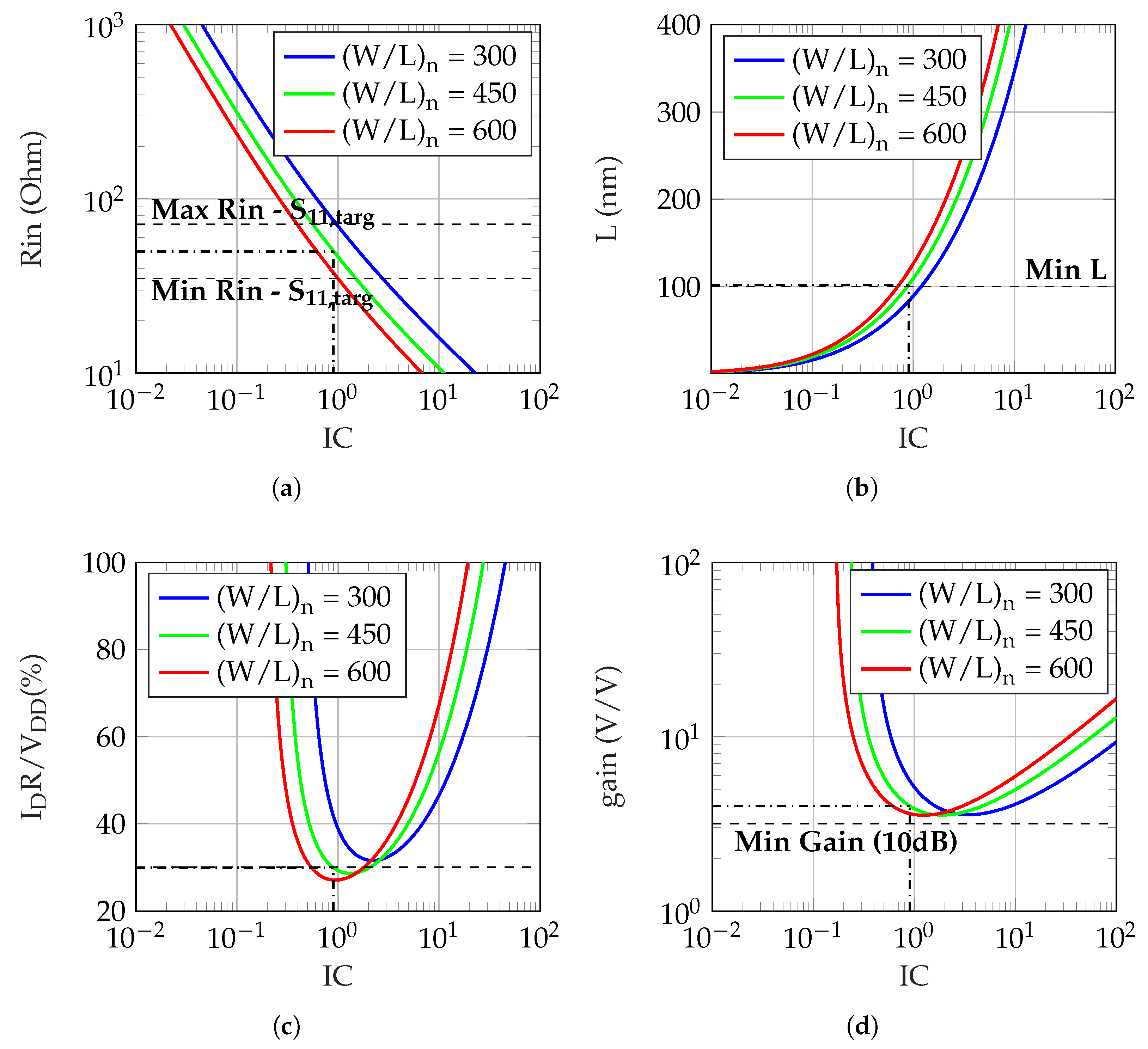
5. Graph-Based Design
5.1. Design Constraints
5.1.1. Minimum Gain Constraint
5.1.2. Maximum Constraint
5.1.3. Input Matching Constraint
5.1.4. Headroom Constraint
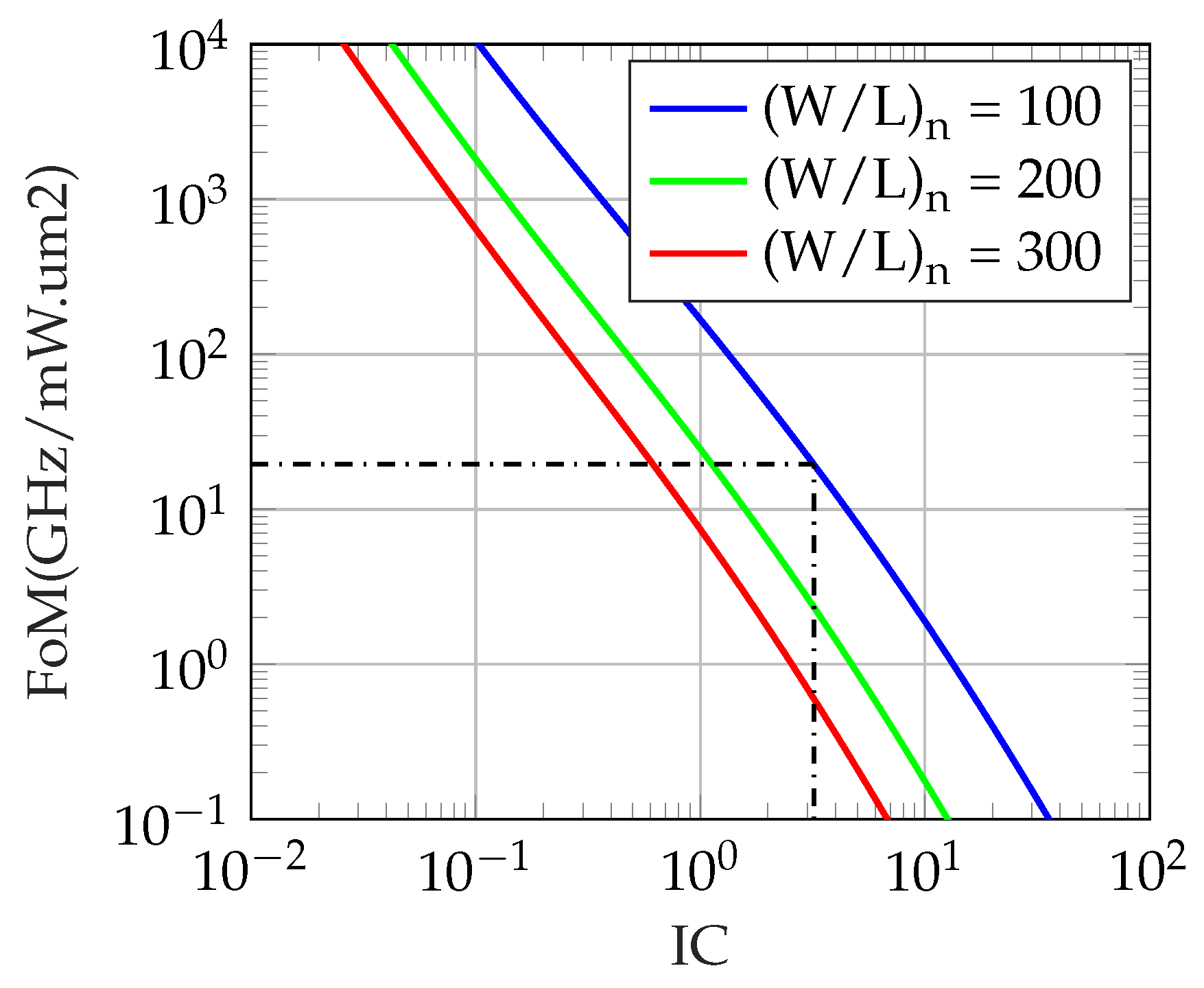
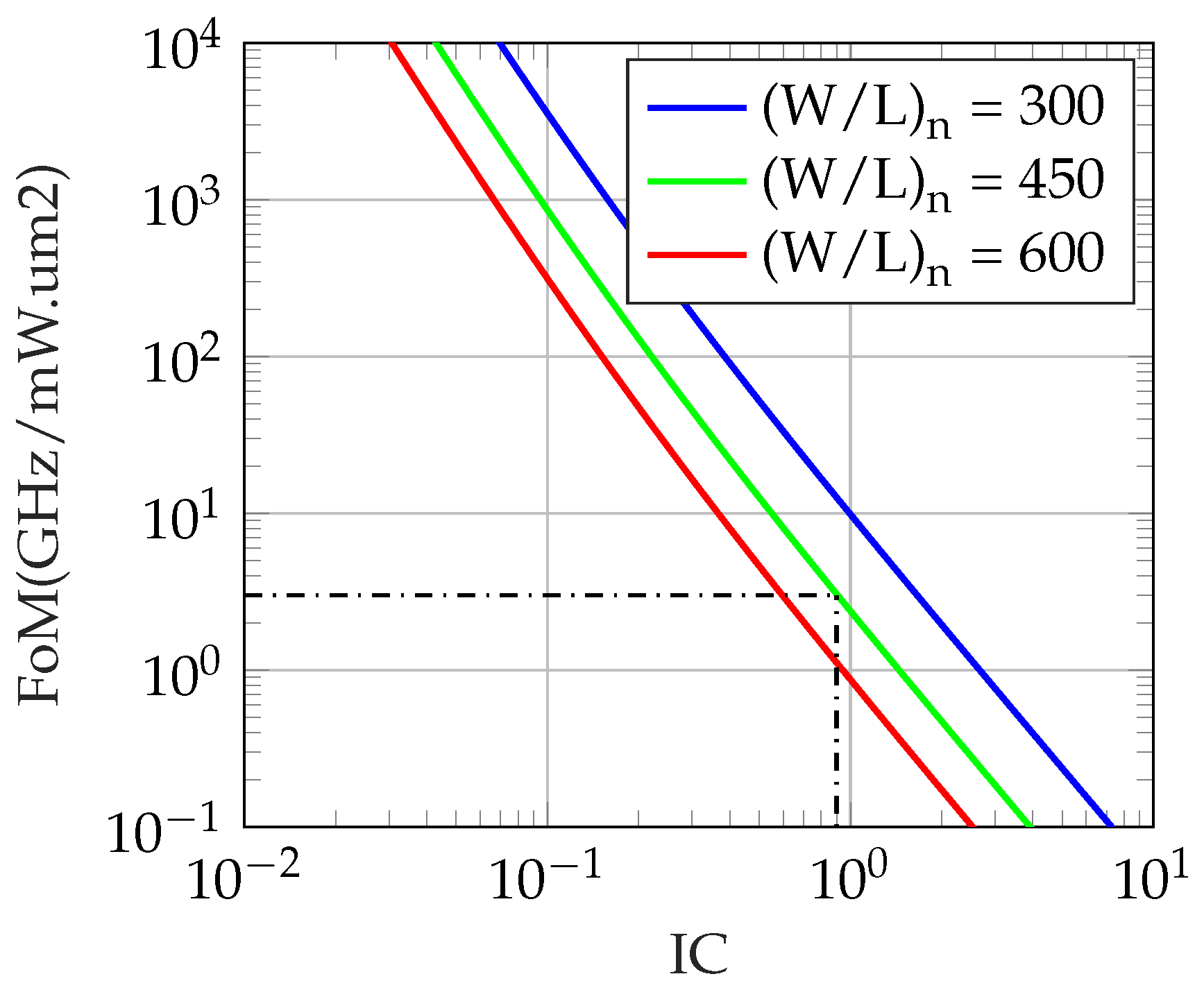
5.2. Figure of Merit
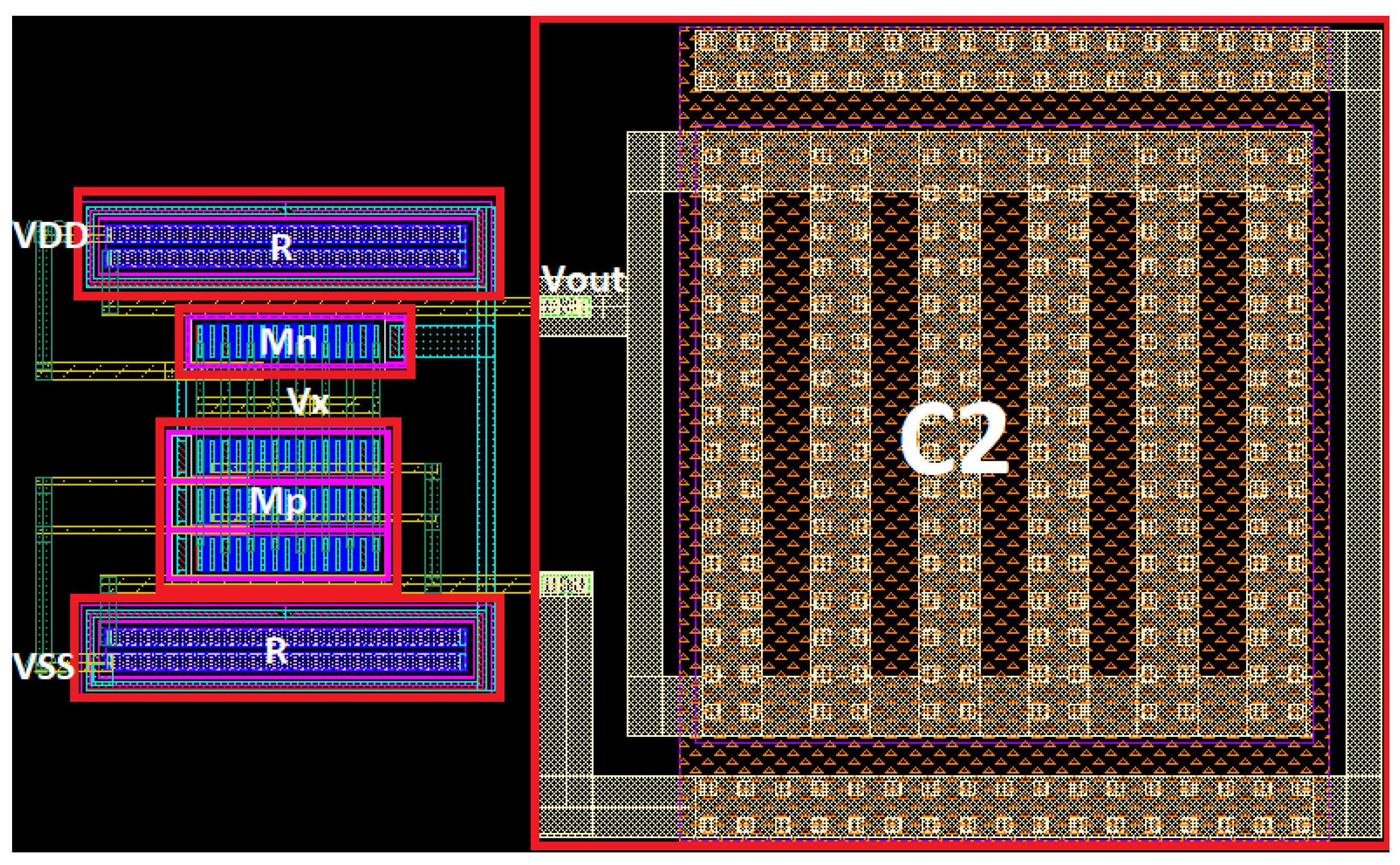
5.3. Sizing/Bias Point Selection
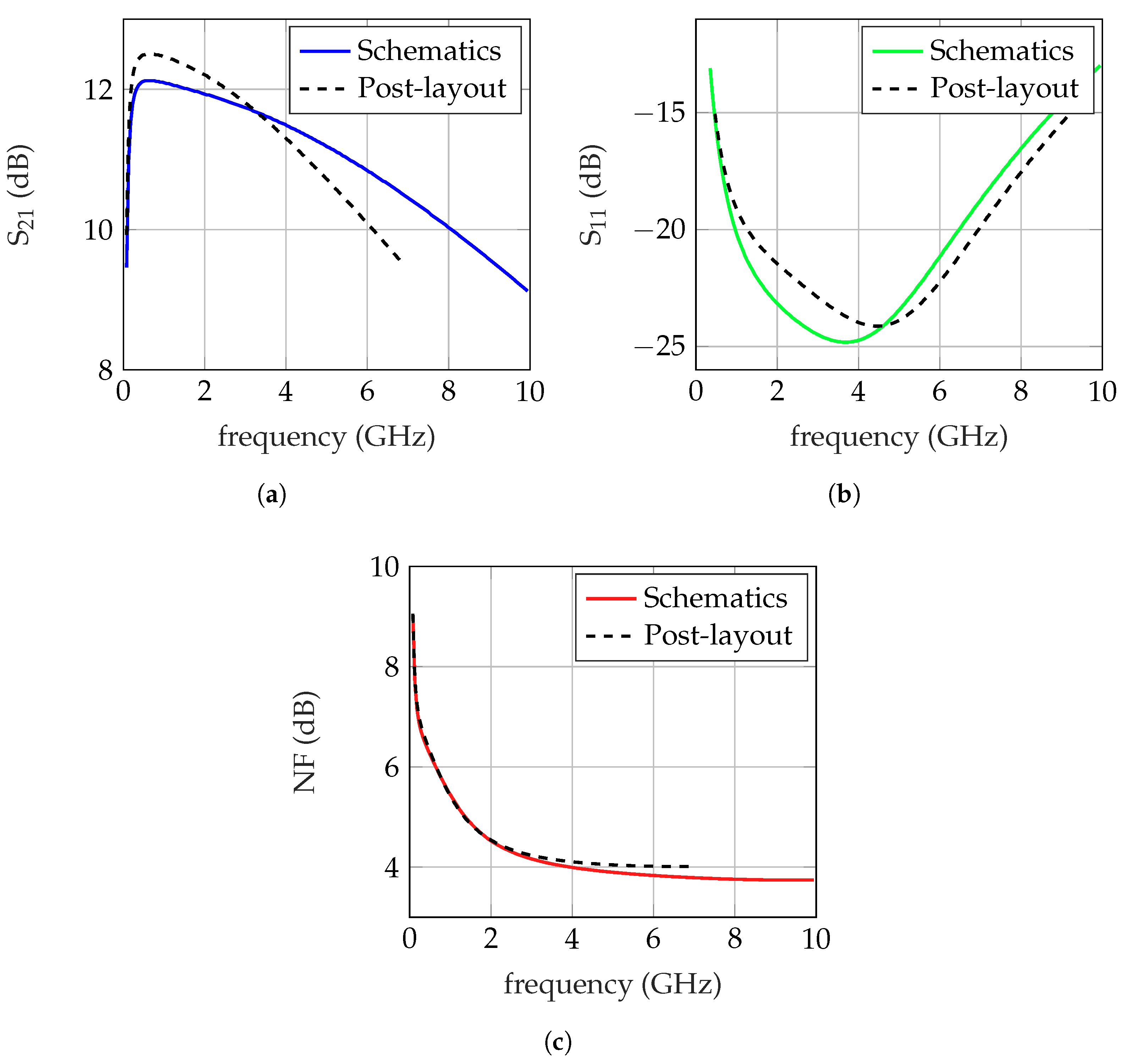
5.3.1. High-Bandwidth LNA
5.3.2. Low-Noise LNA
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACM | Advanced Compact MOSFET |
| BW | Bandwidth |
| FCC | Federal Communications Commission |
| IC | Inversion Coefficient |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| IR | Impulse radio |
| LNA | Low-noise amplifier |
| LUT | Lookup table |
| MOSFET | Metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor |
| NF | Noise figure |
| PAN | Personal area network |
| SAR | Synthetic aperture radar |
| TOA | Time of arrival |
| TOF | Time of flight |
| UWB | Ultra-wide band |
| WBAN | Wireless body area network |
References
- Chandrakasan, A.; Lee, F.; Wentzloff, D.; Sze, V.; Ginsburg, B.; Mercier, P.; Daly, D.; Blazquez, R. Low-Power Impulse UWB Architectures and Circuits. Proc. IEEE 2009, 97, 332–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigraham, B.; Kinget, P.R. A Self-Duty-Cycled and Synchronized UWB Pulse-Radio Receiver SoC with Automatic Threshold-Recovery Based Demodulation. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2014, 49, 581–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Diao, S.; Toh, W.; Ang, C.; Je, M.; Heng, C. Low-Power Ultrawideband Wireless Telemetry Transceiver for Medical Sensor Applications. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 58, 768–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gezici, S.; Tian, Z.; Giannakis, G.; Kobayashi, H.; Molisch, A.; Poor, H.; Sahinoglu, Z. Localization via ultra-wideband radios: A look at positioning aspects for future sensor networks. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2005, 22, 70–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Lauga-Larroze, E.; Subias, S.; Fournier, J.; Bourdel, S.; Galup, C.; Hameau, F. A Methodology for the Design of Capacitive Feedback LNAs based on the gm/ID Characteristic. In Proceedings of the 2018 16th IEEE International New Circuits And Systems Conference (NEWCAS), Montreal, QC, Canada, 24–27 June 2018; pp. 178–181. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez-Perez, A.D.; Aznar, F.; Flandre, D.; Celma, S. Design-Window Methodology for Inductorless Noise-Cancelling CMOS LNAs. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 29482–29492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enz, C.; Vittoz, E. Charge-Based MOS Transistor Modeling; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Guitton, G.; Souza, M.; Mariano, A.; Taris, T. Design Methodology Based on the Inversion Coefficient and its Application to Inductorless LNA Implementations. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2019, 66, 3653–3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadhuile, F.; Taris, T.; Deval, Y.; De Matos, M.; Belot, D.; Enz, C. Design methodology for low power RF LNA based on the figure of merit and the inversion coefficient. Analog. Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 2016, 87, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchoucha, M.K.; Pino-Monroy, D.A.; Scheer, P.; Cathelin, P.; Fournier, J.M.; Barragan, M.J.; Cathelin, A.; Bourdel, S. Resistive Feedback LNA design using a 7-parameter design-oriented model for advanced technologies. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Monterey, CA, USA, 21–25 May 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Thangavelu, L.; Ramakrishna, P. Design Space Exploration and Synthesis of CMOS Low Noise Amplifiers. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Symposium on Electronic System Design (ISED), Kolkata, India, 19–22 December 2012; pp. 38–42. [Google Scholar]
- Mangla, A.; Enz, C.; Sallese, J. Figure-of-merit for optimizing the current-efficiency of low-power RF circuits. In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference—Mixed Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems, MIXDES 2011, Gliwice, Poland, 16–18 June 2011; pp. 85–89. [Google Scholar]
- Binkley, D. Tradeoffs and Optimization in Analog CMOS Design; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Machado, G.A.S.; Enz, C.C.; Bucher, M. Estimating key parameters in the EKV MOST model for analogue design and simulation. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Seattle, WA, USA, 30 April–3 May 1995; Volume 3, pp. 1588–1591. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Feng, W.; Li, X. A CMOS 3–12-GHz Ultrawideband Low Noise Amplifier by Dual-Resonance Network. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Components Lett. 2017, 27, 383–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmas, F.; Hameau, F.; Fournier, J. A Low Power Inductorless LNA with Double Gm Enhancement in 130 nm CMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2012, 47, 1094–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Chen, Y.; Boon, C.; Mak, P.; Martins, R. A 0.096-mm2 1–20-GHz Triple-Path Noise- Canceling Common-Gate Common-Source LNA with Dual Complementary pMOS–nMOS Configuration. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2020, 68, 144–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, X.; Huang, Z.; Tan, T.; Chen, D.; Cao, C.; Qi, Z. A Novel Low-Power Notch-Enhanced Active Filter for Ultrawideband Interferer Rejected LNA. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2021, 69, 1684–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Boon, C.; Yu, X.; Li, C.; Yang, K.; Liang, Y. A 0.061-mm2 1–11-GHz Noise-Canceling Low-Noise Amplifier Employing Active Feedforward with Simultaneous Current and Noise Reduction. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2021, 69, 3093–3106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozorg, A.; Staszewski, R. A 0.02–4.5-GHz LN(T)A in 28-nm CMOS for 5G Exploiting Noise Reduction and Current Reuse. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2021, 56, 404–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Wang, C.; Lee, G.; Chen, C. High-Performance Wideband Low-Noise Amplifier Using Enhanced π-Match Input Network. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Components Lett. 2014, 24, 200–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Parameter Name | Value for NMOS | Value for PMOS |
|---|---|---|
| 1.5 A | 0.5 A | |
| n | 1.5 | 1.5 |
| 380 mV | 390 mV | |
| −0.3 m | −0.3 m | |
| 19.8 m | 19.8 m | |
| 0.4 fF/m | 0.4 fF/m | |
| 0.5 | 0.5 | |
| 10 m | 3 m |
| Circuit Components | Transistor Constraints | Specifications | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | Bandwidth | ||||||
| Value | 0.5 nH | 30% | 100 nm | 10 dB | −10 dB | 25 GHz | |
| Analytical Value | Schematics (No Body Effect) | Schematics (Body Effect) | Post-Layout (Body Effect) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transistor Parameters | 3.2 | 3.26 | 3.21 | 3.18 | |
| (A) | 480 | 489 | 482 | 478 | |
| L (nm) | 105 | 105 | 105 | 105 | |
| 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | ||
| 300 | 300 | 300 | 300 | ||
| Circuit Parameters | 605 | 606 | 606 | 606 | |
| (V) | 1 | 0.98 | 1.1 | 1.12 | |
| (fF) | 55 | 60.3 | 58.7 | N/A | |
| (fF) | 16.8 | 20.2 | 19.2 | N/A | |
| () | 95.4 | 127.2 | 106.7 | 111.9 | |
| Circuit Performance Metrics | (dB) | 10 | 10.8 | 11.9 | 12.4 |
| (GHz) | 31.3 | 32.9 | 25.6 | 16.5 | |
| (%) | 28.9 | 30.4 | 26.7 | 27.6 | |
| (dB) | ≤−10 | −7.1 | −8.6 | −8.2 | |
| (GHz) | N/A | 34.7 | 27.2 | 27.6 | |
| (mW) | 0.48 | 0.48 | 0.53 | 0.53 | |
| (dB) | 5.3 | 4.5 → 6.2 | 4.3 → 6 | 4.5 → 5.8 | |
| (dBm) | N/A | −5.5 | −4.3 | −5.2 | |
| 19.6 | 29.6 | 25.5 | 16.2 |
| Circuit Components | Transistor Constraints | Specifications | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameter | |||||||
| Value | 0.5 nH | 30% | 100 nm | 10 dB | −15 dB | 4 dB | |
| Analytical Value | Schematics (No Body Effect) | Schematics (Body Effect) | Post-Layout (Body Effect) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transistor Parameters | 0.9 | 0.9 | 0.92 | 0.92 | |
| (A) | 608 | 607 | 618 | 605 | |
| L (nm) | 102 | 100 | 100 | 100 | |
| 450 | 450 | 450 | 450 | ||
| 1350 | 1350 | 1350 | 1350 | ||
| Circuit Parameters | 400 | 400 | 400 | 400 | |
| (V) | 0.82 | 0.79 | 0.9 | 0.91 | |
| (fF) | 197.8 | 214.7 | 210.3 | N/A | |
| (fF) | 73.6 | 83.5 | 81 | N/A | |
| () | 50 | 64.6 | 54.4 | 57 | |
| Circuit Performance Metrics | 12 | 11.1 | 12.1 | 12.5 | |
| (GHz) | 10.8 | 13.8 | 9.9 | 6.8 | |
| (%) | 29.9 | 30.9 | 27.6 | 27.6 | |
| (dB) | ≤−15 | −15 | −13 | −15 | |
| (GHz) | N/A | 13.4 | 9.6 | 8.8 | |
| (mW) | 0.5 | 0.48 | 0.56 | 0.55 | |
| (dB) | 4 | 4 → 7.8 | 3.7 → 7 | 4 → 7 | |
| (dBm) | N/A | −7 | −4.1 | −4.3 | |
| 3.1 | 3.8 | 3 | 1.9 |
| Design | Tech | Gain | Bandwidth | NF | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (nm) | (dB) | (dB) | (GHz) | (dBm) | (mW) | (dB) | (GHz) | |
| [6] | 65 | 17 | 7 | 0.7 | 5.5 | 3.7 | 7.9 | |
| [8] | 28 | 17 | 5.8 | 7.9 | 3.7 | 3 | 68.8 | |
| [10] | 28 | 25 | 3 | −9.6 | 0.9 | 1.5 | 15.8 | |
| [15] | 130 | 15 | 9.3 | −7 | 8.5 | 4 | 0.8 | |
| [17] | 65 | 12.8 | 19 | 5.8 | 20.3 | 3.3 | 13.6 | |
| [18] | 130 | 16.1 | 6.8 | 2.7 | 10.2 | 2.1 | 12.7 | |
| [19] | 40 | 17 | 10 | −2.8 | 9 | 3.5 | 3.3 | |
| [20] | 28 | 15.2 | 4.5 | −4.6 | 4.5 | 2.1 | 3.2 | |
| [21] | 180 | 15.2 | 11.5 | −0.2 | 18 | 2.2 | 5.3 | |
| High-BW LNA * | 65 | 12.4 | 16.5 | −5.2 | 0.53 | 4.5 | 21.5 | |
| Low-Noise LNA * | 65 | 12.5 | 6.8 | −4.3 | 0.55 | 4 | 12.8 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hamed, A.; Ismail, A. Graphical Design Approach for UWB Stacked CG LNA Using Inversion Coefficient. Electronics 2024, 13, 1602. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13091602
Hamed A, Ismail A. Graphical Design Approach for UWB Stacked CG LNA Using Inversion Coefficient. Electronics. 2024; 13(9):1602. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13091602
Chicago/Turabian StyleHamed, Ahmed, and Ayman Ismail. 2024. "Graphical Design Approach for UWB Stacked CG LNA Using Inversion Coefficient" Electronics 13, no. 9: 1602. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13091602
APA StyleHamed, A., & Ismail, A. (2024). Graphical Design Approach for UWB Stacked CG LNA Using Inversion Coefficient. Electronics, 13(9), 1602. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13091602







