A Dual-Mode Clock Enhancement Technology N-Path Notch Filter with High Linearity
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Mode 1 clock boost: improved linearity and large operating bandwidth with no additional power consumption.
- (2)
- Mode 2 clock boost + bootstrap: dramatically improves small-signal performance and boosts blocking power capacity, sacrificing power consumption and operating bandwidth.
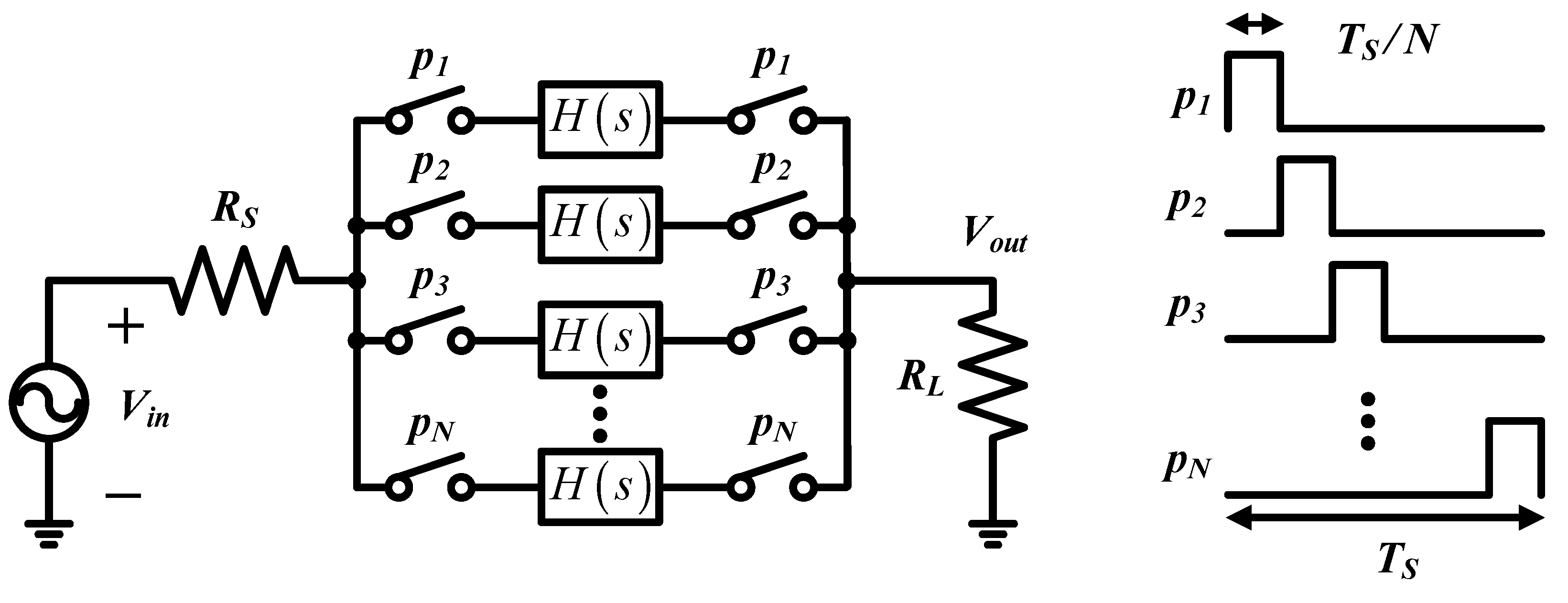
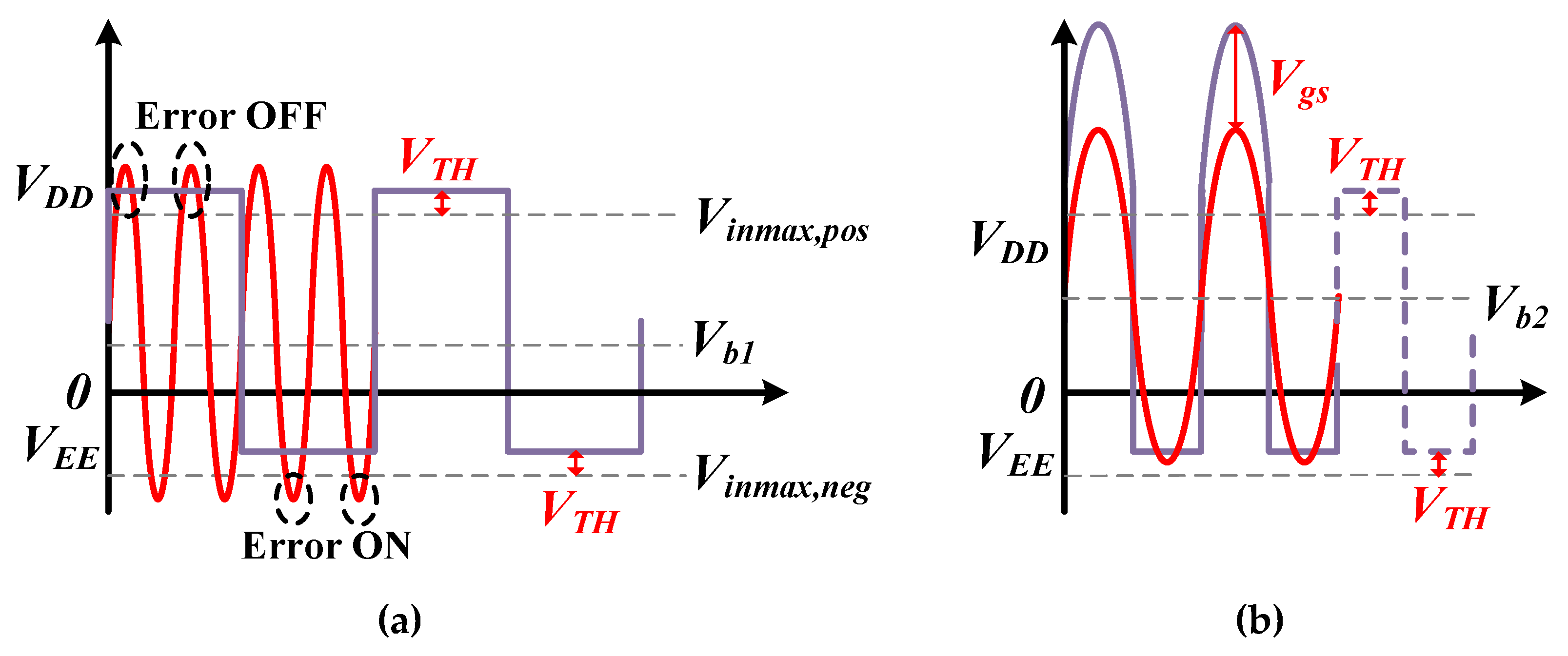
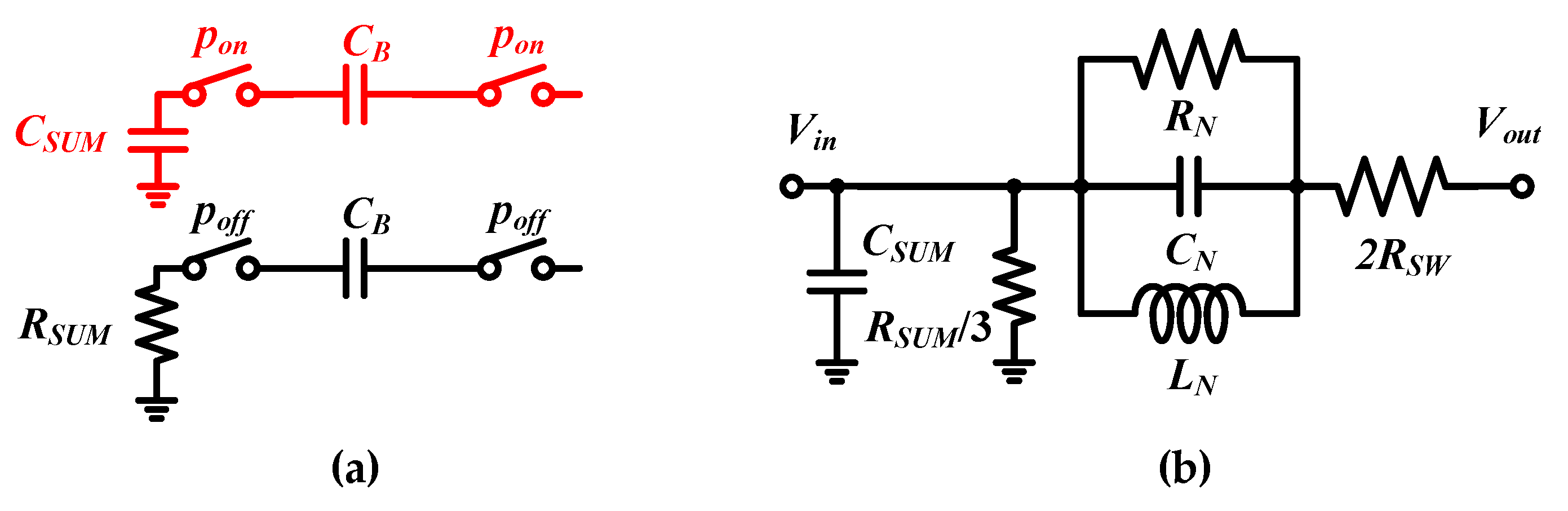
2. N-Path Notch Filter with Clock Swing Enhance
2.1. Mode 1: Clock Swing Enhance Module
2.1.1. Level Shifter Circuit
2.1.2. Clock Boost Circuit
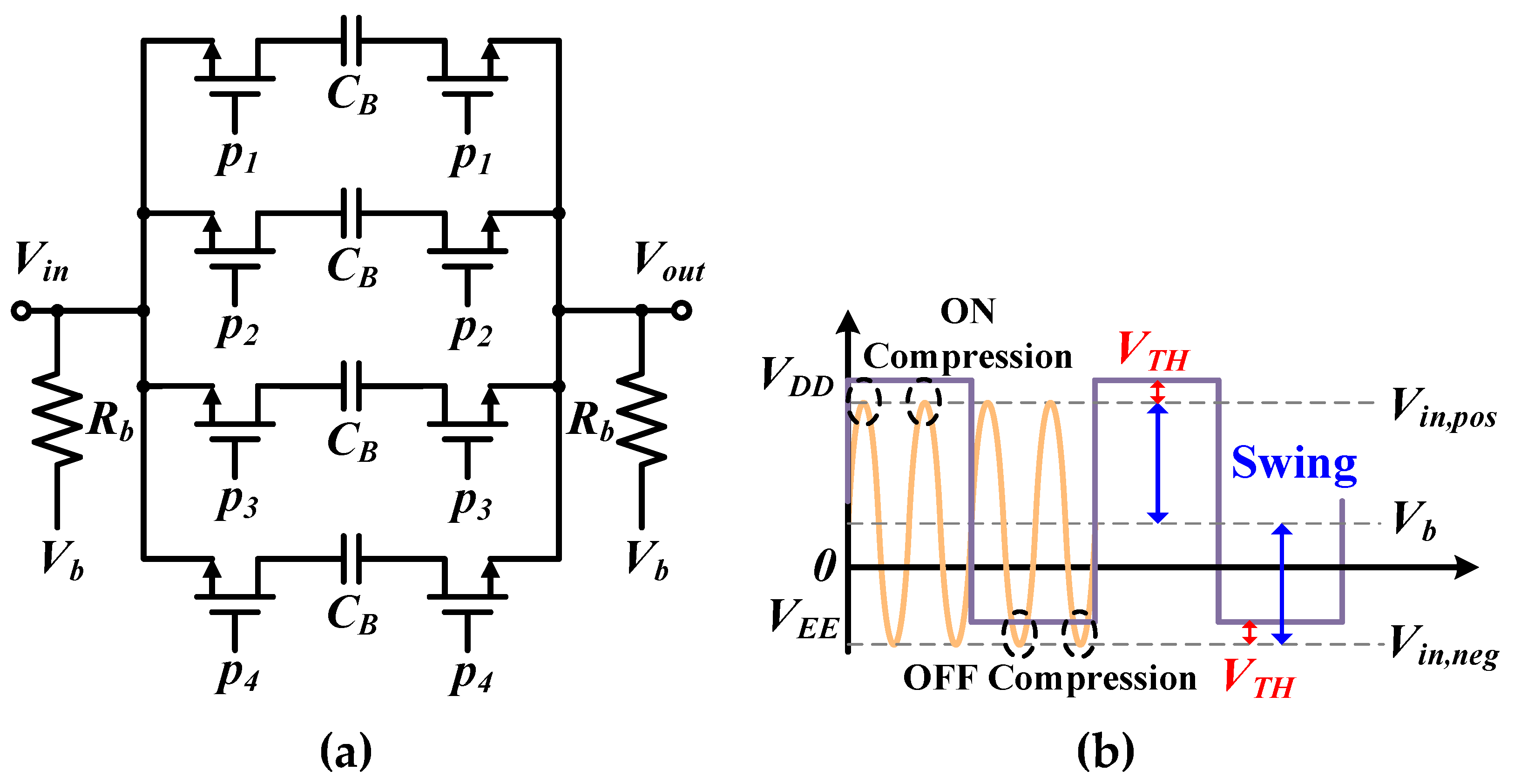
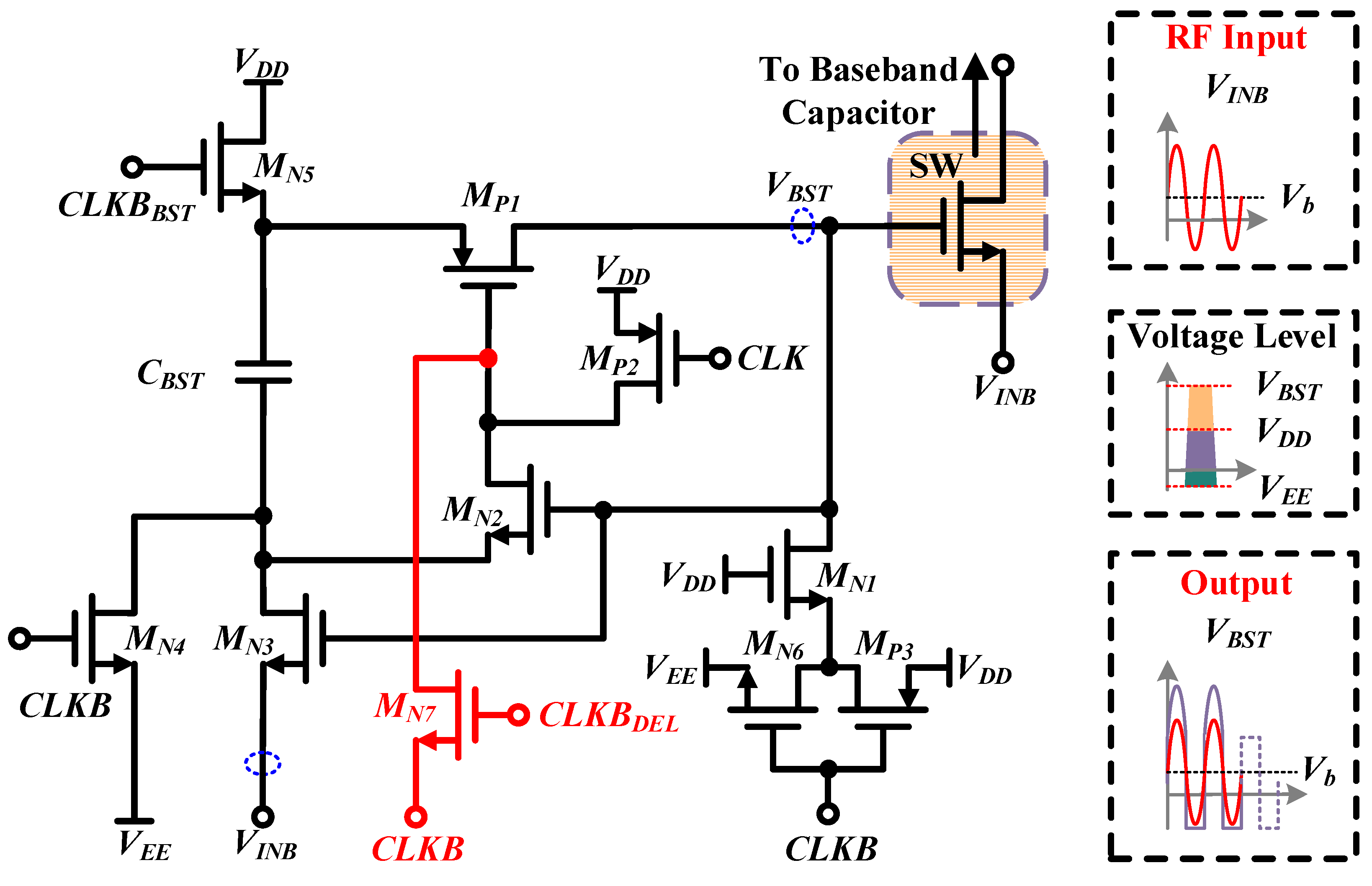
2.2. Mode 2: Clock Bootstrap Module
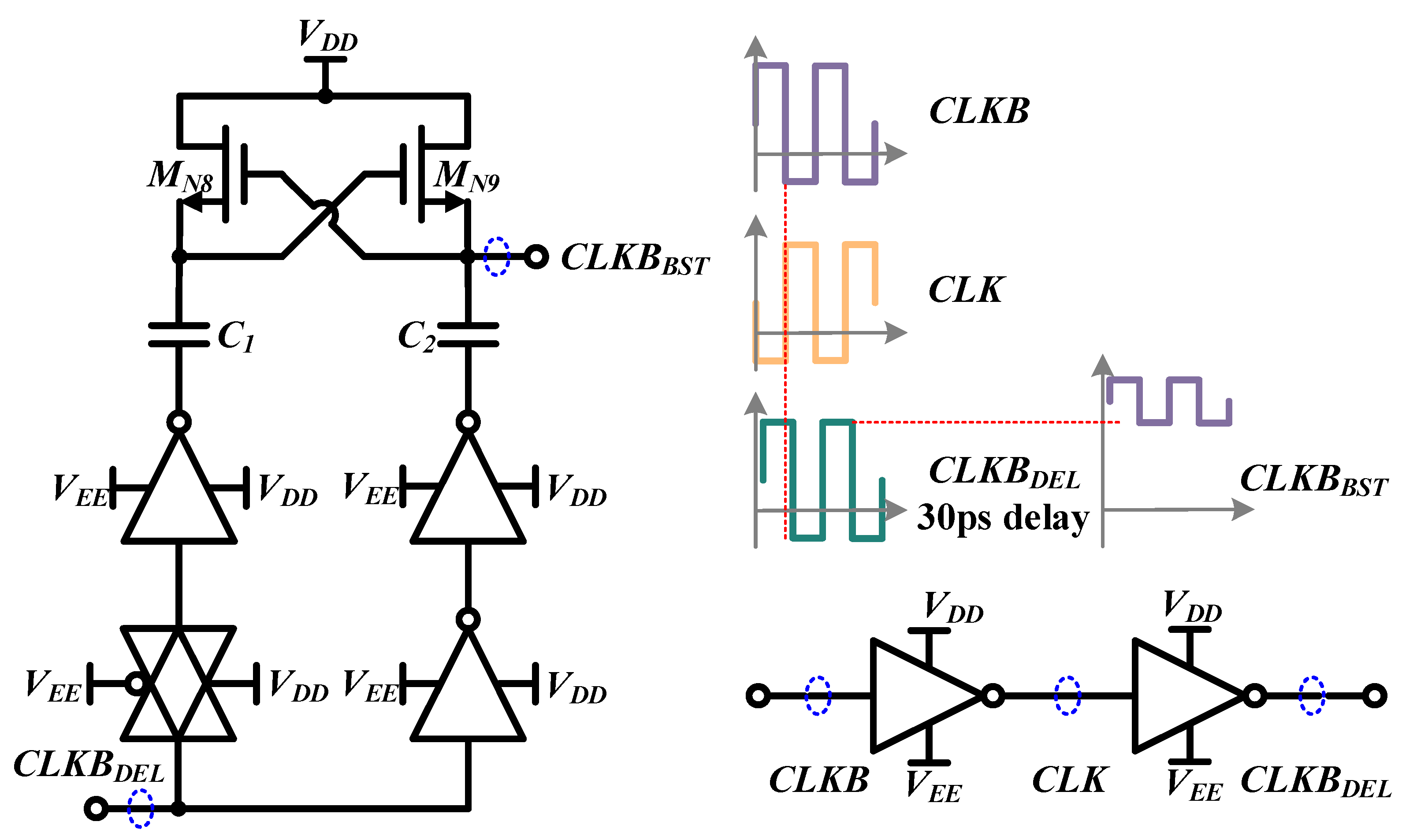
2.3. Frequency Divider
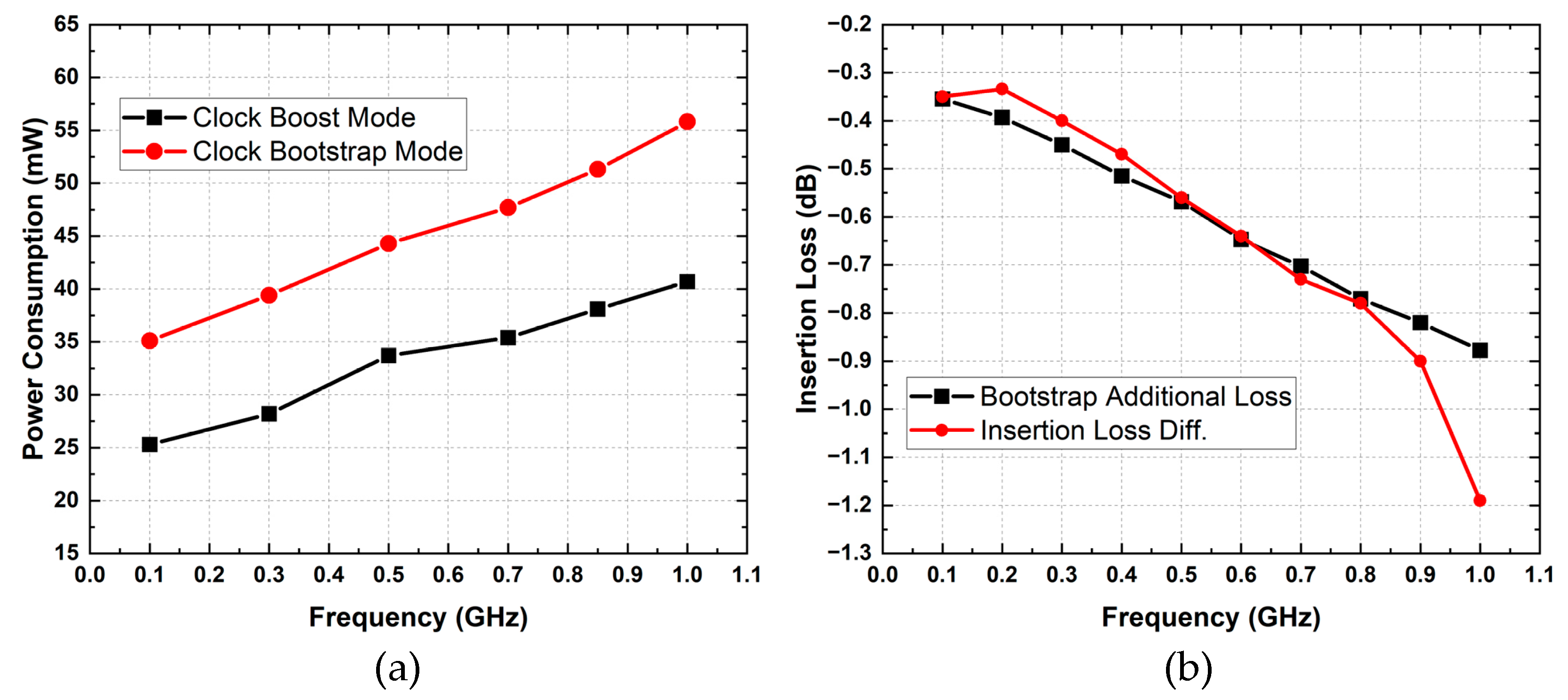
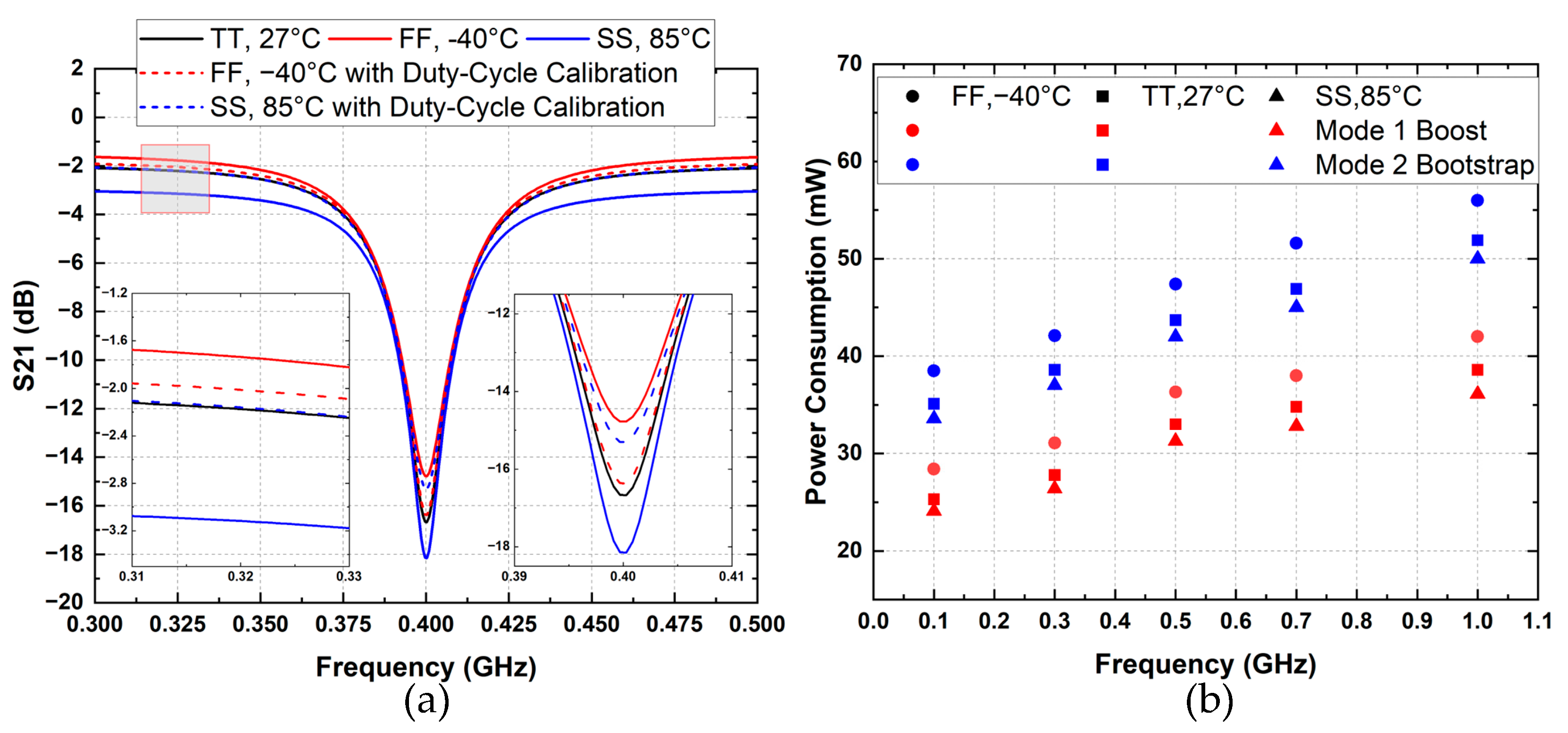
3. Post-Layout Simulation Results
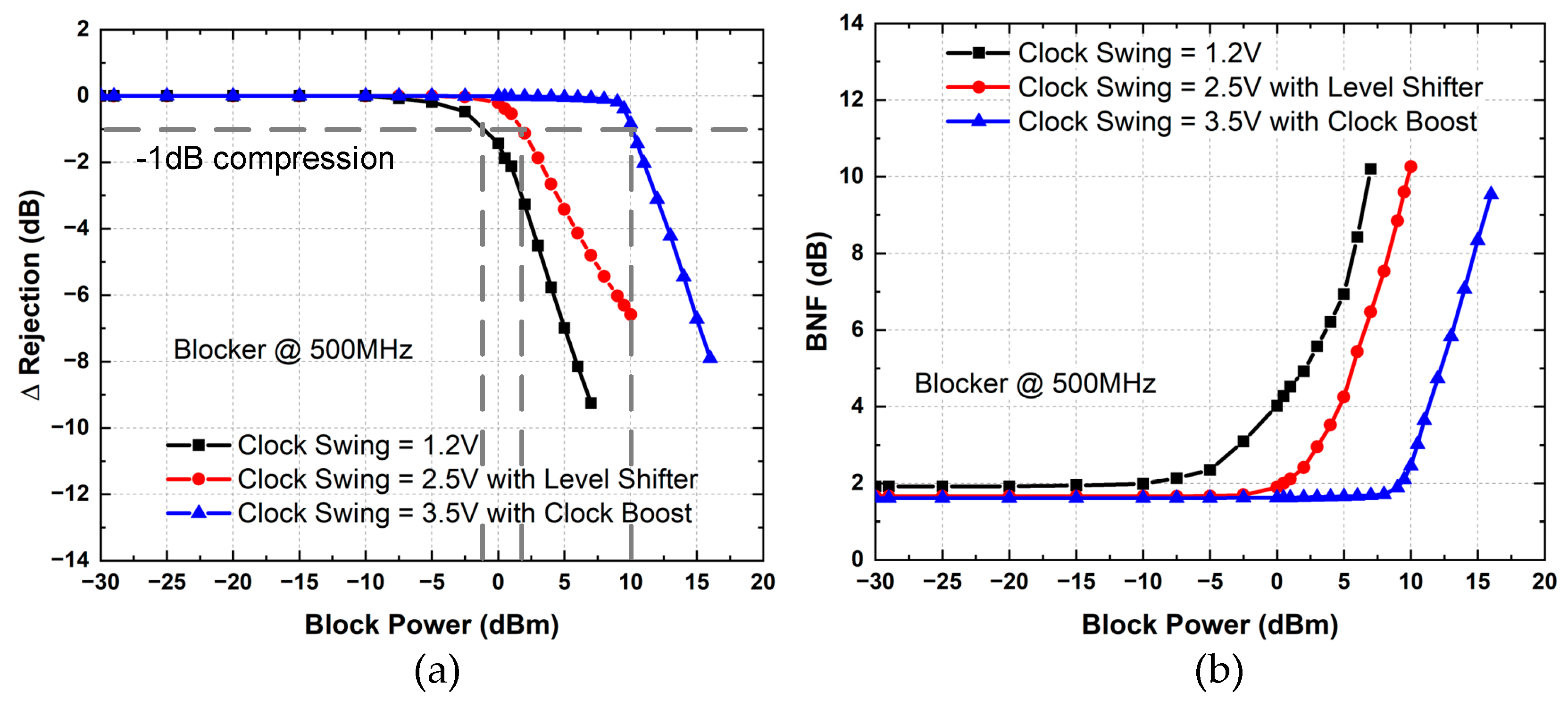
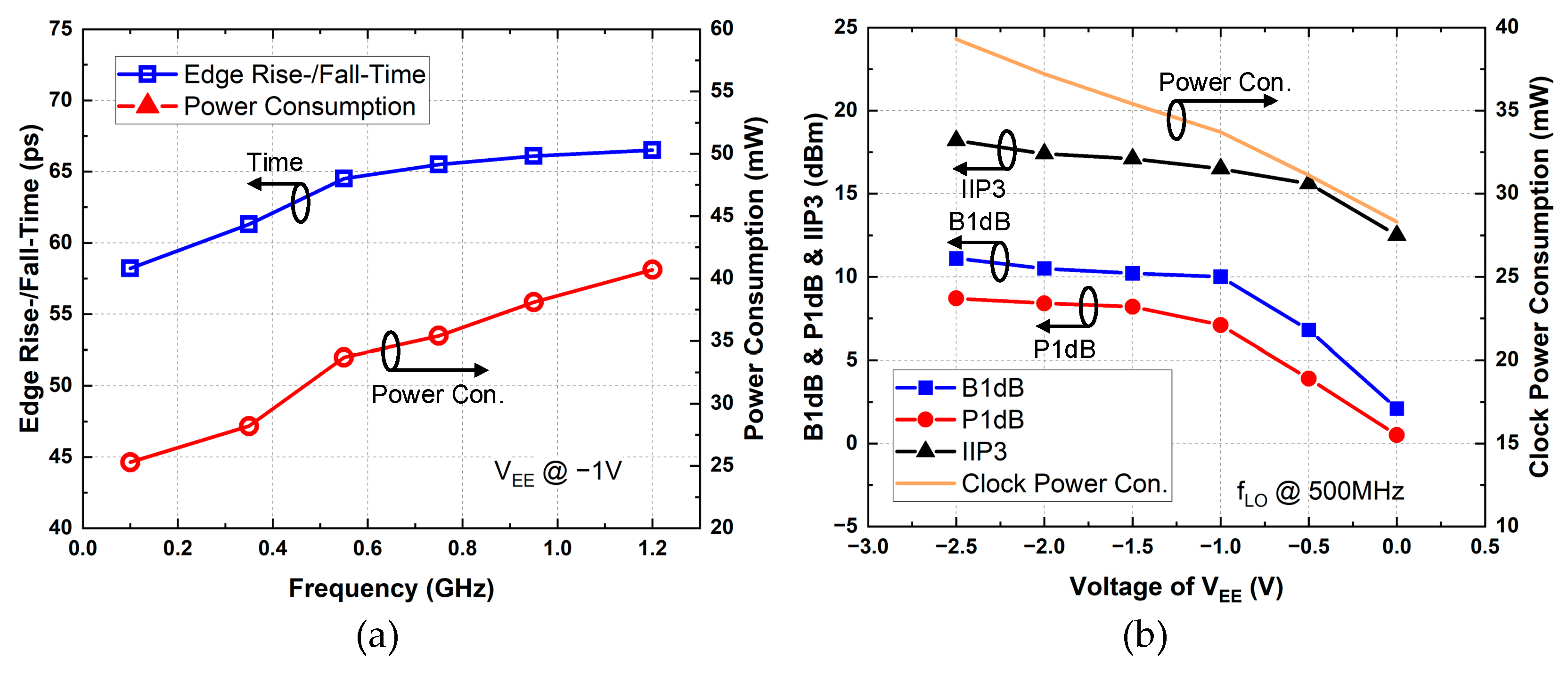
3.1. S-Parameters
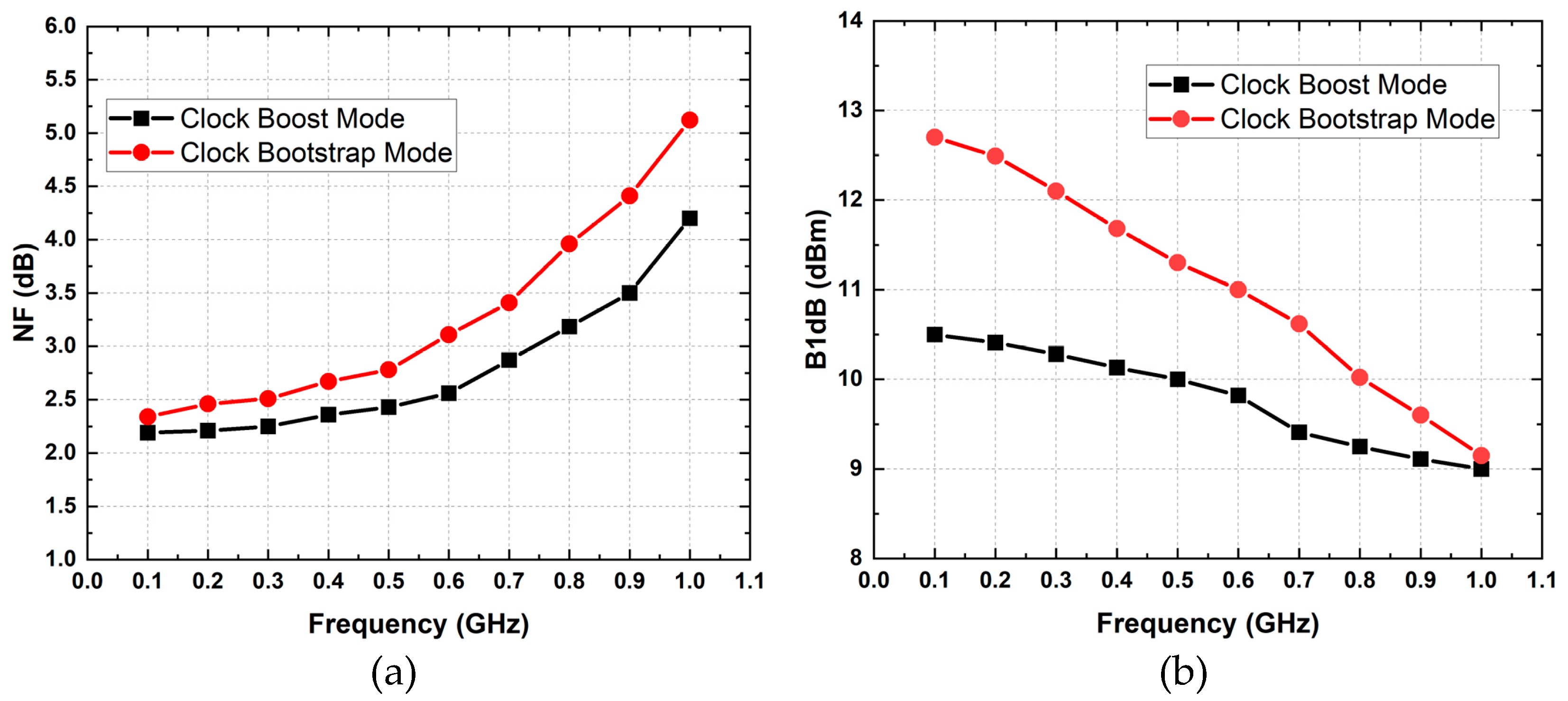
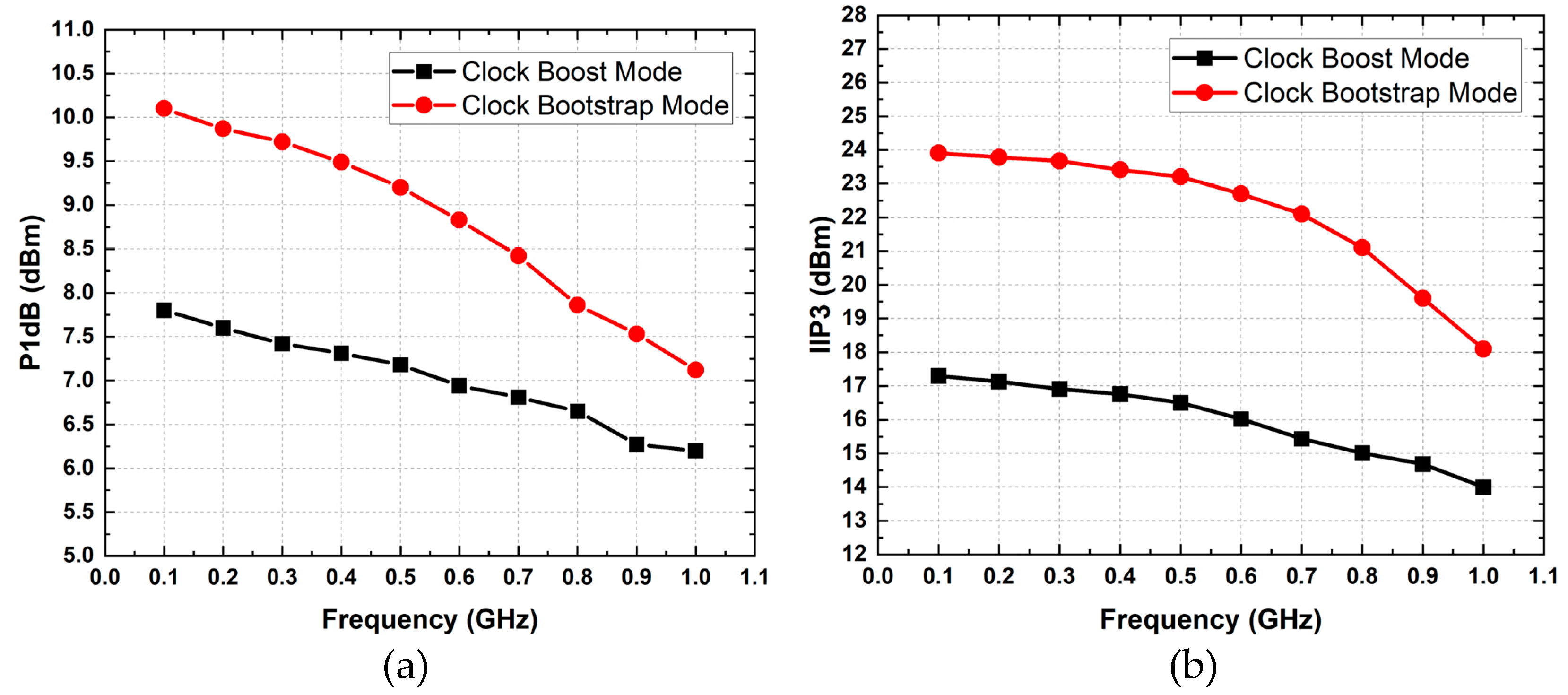
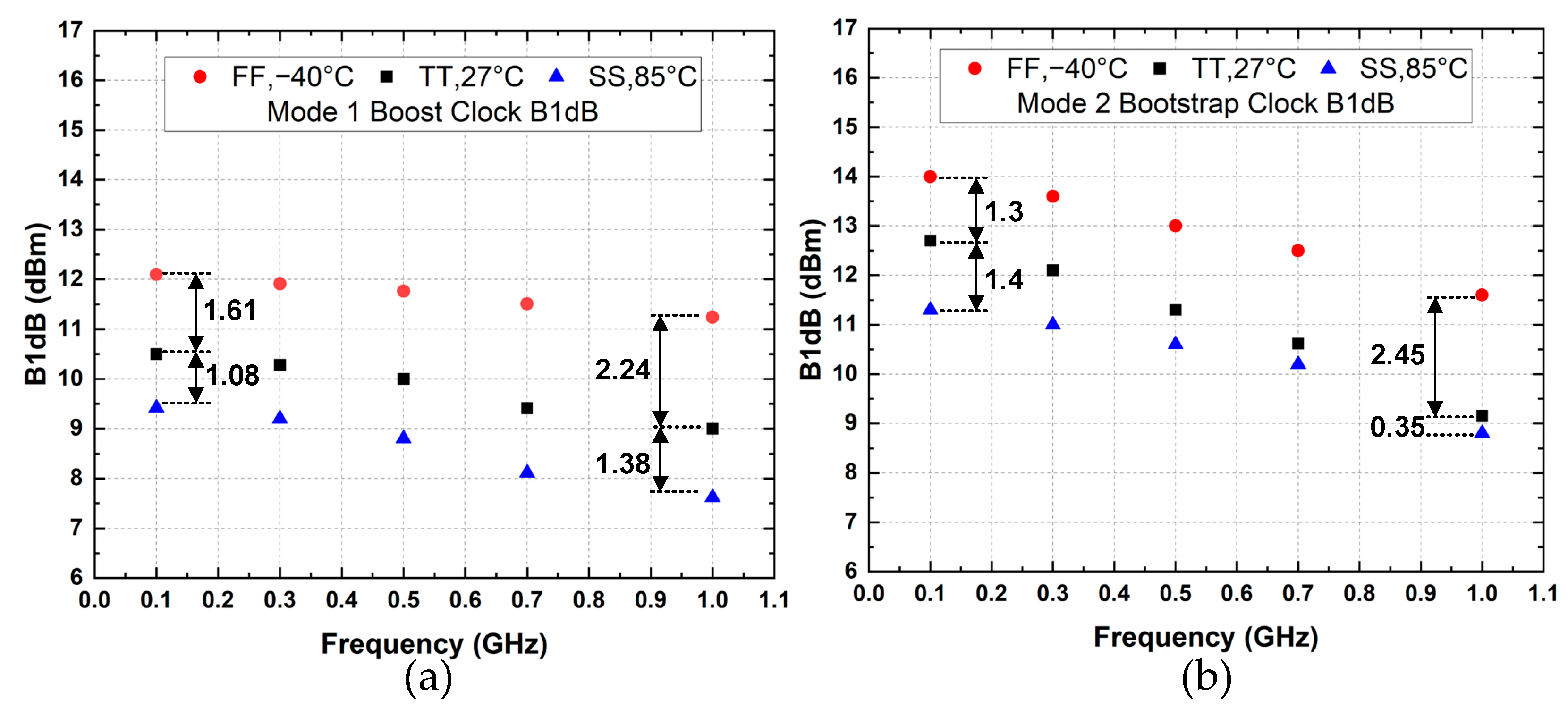
3.2. Linearity and NF
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| TX | Transmitter |
| RX | Receiver |
| LNA | Low noise amplifier |
| B1dB | Blocker 1-dB compression point |
| P1dB | 1-dB compression point |
| IIP3 | Third-order input-intercept-point |
| SNR | Signal-to-noise ratio |
| LTI | Linear time-invariant |
| SC | Switched capacitor |
| SAW | Surface acoustic wave |
| BRF | Band reject filters |
| BPF | Bandpass filter |
| LO | Local oscillator |
| Vgs | Gate-to-source voltage |
| NF | Noise figure |
| BNF | Blocker noise figure |
References
- Wang, P.-H.P.; Mercier, P.P. A Dual-Mode Wi-Fi/BLE Wake-Up Receiver. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2021, 56, 1288–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.; Gaba, G.S.; Kansal, L.; Ngo, S. 5G and Beyond. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Communication and Signal Processing (ICCSP), Chennai, India, 3–5 April 2018; pp. 0878–0882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mugerwa, D.; Nam, Y.; Choi, H.; Shin, Y.; Lee, E. Adaptive Mobility-Based IoT LoRa Clustering Communication Scheme. Electronics 2024, 13, 2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Chen, D.; Wang, Q.; Lei, C.; Wang, M.; Li, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Liu, J. Key Issues on Integrating 5G into Industrial Systems. Electronics 2024, 13, 2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atzori, L.; Iera, A.; Morabito, G. The internet of things: A survey. Comput. Netw. 2010, 54, 2787–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, N.; Aneja, S. Internet of Things: Vision, application areas and research challenges. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on I-SMAC (IoT in Social, Mobile, Analytics and Cloud) (I-SMAC), Palladam, India, 10–11 February 2017; Volume 10, pp. 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Fumagalli, A. Internet of Things Security—Multilayered Method For End to End Data Communications Over Cellular Networks. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 5th World Forum on Internet of Things (WF-IoT), Limerick, Ireland, 15–18 April 2019; pp. 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortino, G.; Russo, W.; Savaglio, C.; Viroli, M.; Zhou, M. Opportunistic cyberphysical services: A novel paradigm for the future Internet of Things. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 4th World Forum on Internet of Things (WF-IoT), Singapore, 5–8 May 2018; pp. 488–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Heo, J.; Hong, D. A New GNSS-based Channel Estimation Strategy for LEO Satellite Communication Systems. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 97th Vehicular Technology Conference (VTC2023-Spring), Florence, Italy, 20–23 June 2023; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, Z.; Zhou, H.; Chen, X.; Peng, Y.; Yu, P.; Wang, Y.; Feng, X. A System of Power Emergency Communication System Based BDS and LEO Satellite. In Proceedings of the 2021 Computing, Communications and IoT Applications (ComComAp), Shenzhen, China, 26–28 November 2021; pp. 286–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filjar, R.; Huljenic, D. Positioning augmentation using synergy between telecommunications networks and satellite positioning methods. In Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Applied Electromagnetics and Communications, 2003. ICECom 2003, Dubrovnik, Croatia, 1–3 October 2003; pp. 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egea-Roca, D.; Arizabaleta-Diez, M.; Pany, T.; Antreich, F.; Lopez-Salcedo, J.A.; Paonni, M.; Seco-Granados, G. GNSS User Technology: State-of-the-Art and Future Trends. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 39939–39968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, B.-Y.; Park, J.-H.; Yang, J.-R. Quasi-Circulator Using an Asymmetric Coupler for Tx Leakage Cancellation. Electronics 2018, 7, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emon, M.Z.A.; Salim, K.M.; Chowdhury, M.I.B. Design and Analysis of a High-Gain, Low-Noise, and Low-Power Analog Front End for Electrocardiogram Acquisition in 45 nm Technology Using gm/ID Method. Electronics 2024, 13, 2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, T.; Koziel, S.; Pietrenko-Dabrowska, A. Resonator-Loaded Waveguide Notch Filters with Broad Tuning Range and Additive-Manufacturing-Based Operating Frequency Adjustment Procedure. Electronics 2023, 12, 4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soorapanth, T.; Wong, S. A 0-dB IL 2140 ± 30 MHz bandpass filter utilizing Q-enhanced spiral inductors in standard CMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2002, 37, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franks, L.E.; Sandberg, I.W. An alternative approach to the realization of network transfer functions: The N-path filter. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1960, 39, 1321–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Mak, P.-I.; Martins, R.P. Analysis and Modeling of a Gain-Boosted N-Path Switched-Capacitor Bandpass Filter. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I: Regul. Pap. 2014, 61, 2560–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, G.; Mak, P.-I. A 0.5-to-1.5GHz BW-Extended Gain-Boosted N-Path Filter Using a Switched gm−C Network Achieving 50 MHz BW and 18.2 dBm OB-IIP3. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE Asian Solid-State Circuits Conference (A-SSCC), Haikou, China, 5–8 November 2023; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, C.-K.; Gudem, P.S.; Buckwalter, J.F. A 0.2–3.6-GHz 10-dBm B1dB 29-dBm IIP3 Tunable Filter for Transmit Leakage Suppression in SAW-Less 3G/4G FDD Receivers. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2015, 63, 3514–3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffari, A.; Klumperink, E.A.M.; Nauta, B. Tunable N-Path Notch Filters for Blocker Suppression: Modeling and Verification. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2013, 48, 1370–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagulu, A.; Yi, M.; Zhuang, Y.; Garikapati, S.; Krishnaswamy, H. A 1-to-5GHz All-Passive Frequency-Translational 4th-Order N-path Filter with Low-Power Clock Boosting for High Linearity and Relaxed Pdc-Frequency Trade-Off. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 19–23 February 2023; pp. 378–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desta, N.; Cohen, E. A 0.15 um Depletion Mode GaN Bootstrapped N-path Filter with 23dBm Inband Blocker Handling. In Proceedings of the 2022 Asia-Pacific Microwave Conference (APMC), Yokohama, Japan, 29 November–2 December 2022; pp. 746–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khorshidian, M.; Reiskarimian, N.; Krishnaswamy, H. 29.4 High-Performance Isolators and Notch Filters Based on N-Path Negative Transresistance. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference—(ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 16–20 February 2020; pp. 446–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devarajan, S.; Singer, L.; Kelly, D.; Pan, T.; Silva, J.; Brunsilius, J.; Rey-Losada, D.; Murden, F.; Speir, C.; Bray, J.; et al. A 12-b 10-GS/s Interleaved Pipeline ADC in 28-nm CMOS Technology. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2017, 52, 3204–3218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Dai, F.F. A 7.27 GHz Q-Enhanced Low Noise Amplifier RFIC with 70 dB Image Rejection Ratio. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Compon. Lett. 2010, 20, 456–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulaziz, M.; Klumperink, E.A.M.; Nauta, B.; Sjoland, H. Improving Receiver Close-In Blocker Tolerance by Baseband Gm−C Notch Filtering. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2019, 66, 885–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, Y.; Klumperink, E.; Tenbroek, B.; Strange, J.; Nauta, B. 24.3 A high-linearity CMOS receiver achieving +44 dBm IIP3 and +13 dBm B1dB for SAW-less LTE radio. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 5–9 February 2017; pp. 412–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purushothaman, V.K.; Klumperink, E.A.M.; Clavera, B.T.; Nauta, B. A Fully Passive RF Front End with 13-dB Gain Exploiting Implicit Capacitive Stacking in a Bottom-Plate N-Path Filter/Mixer. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2020, 55, 1139–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






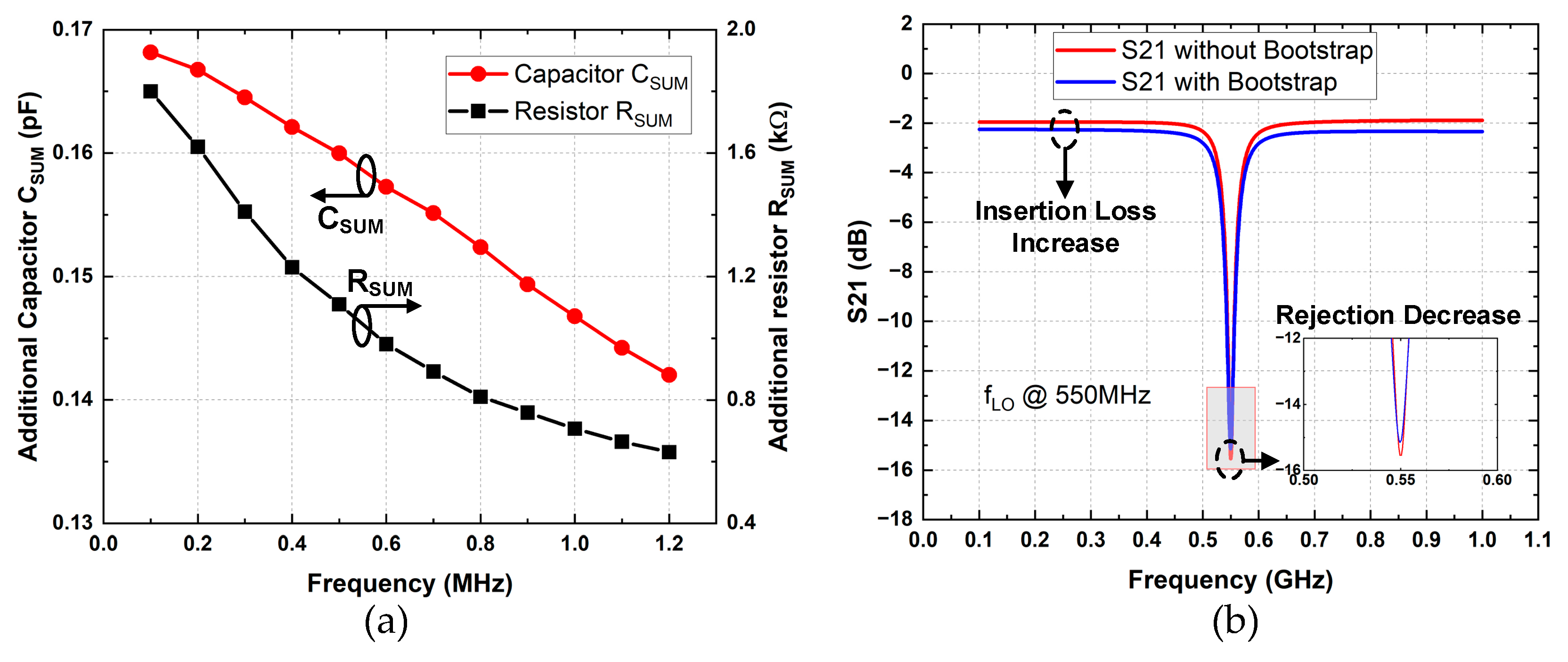
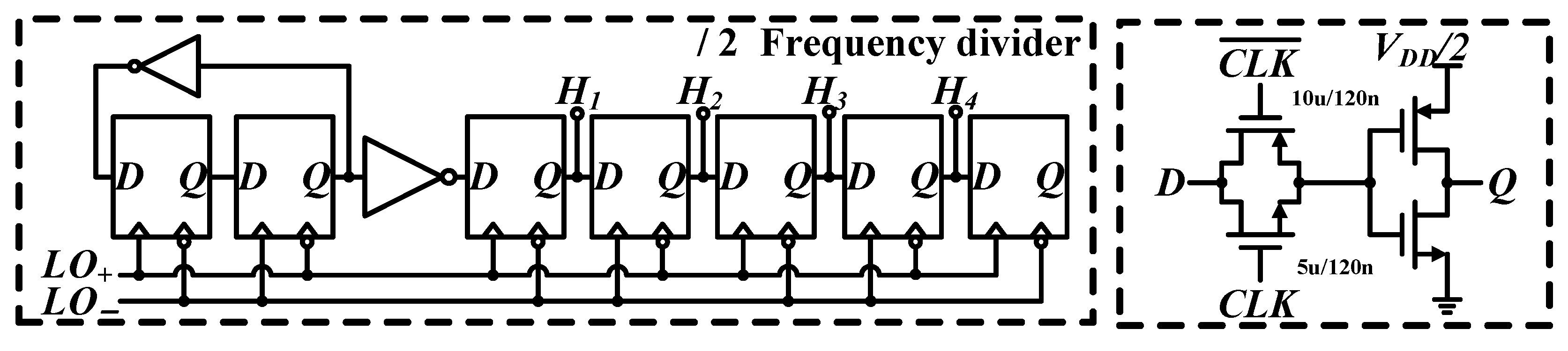
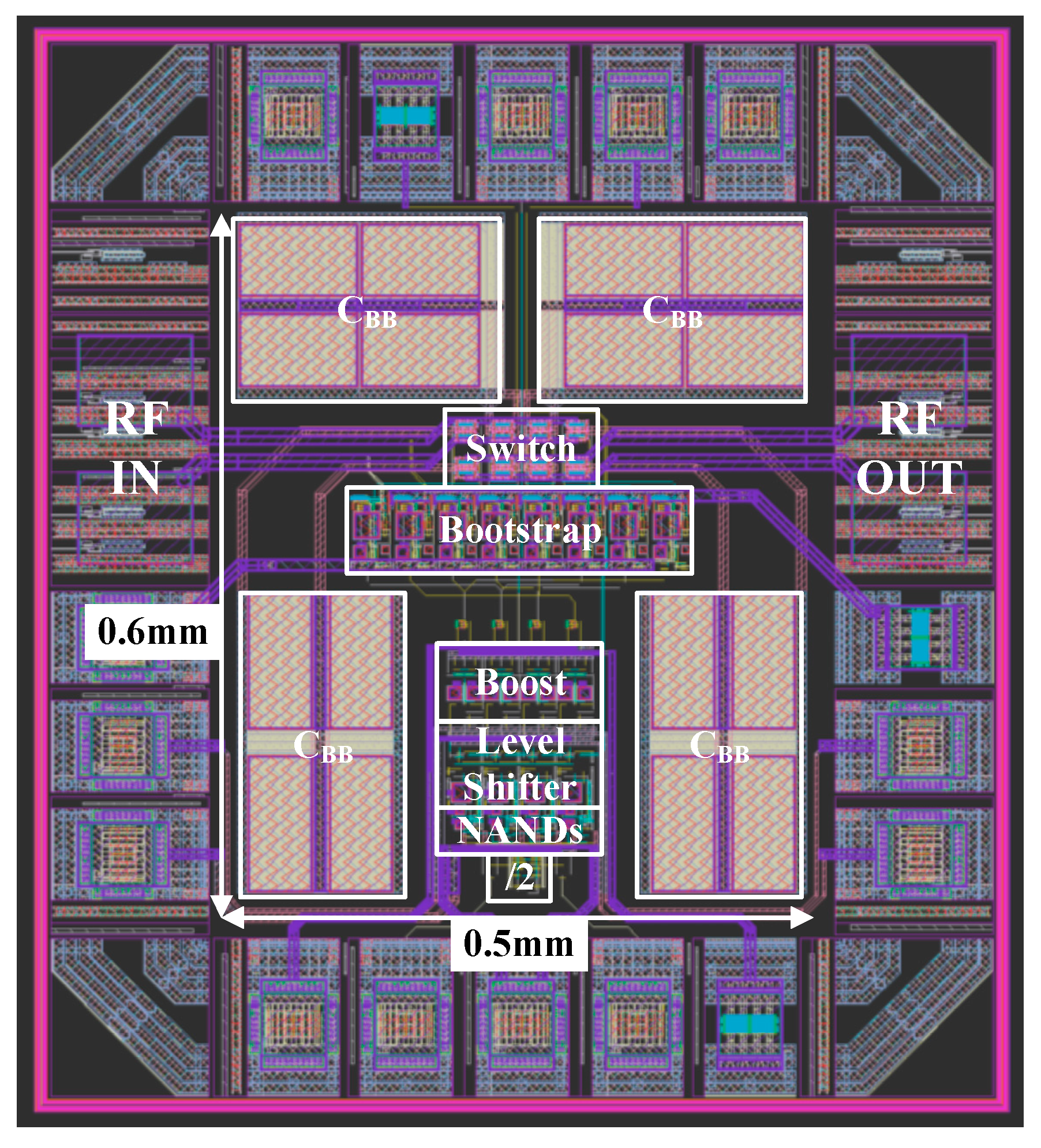
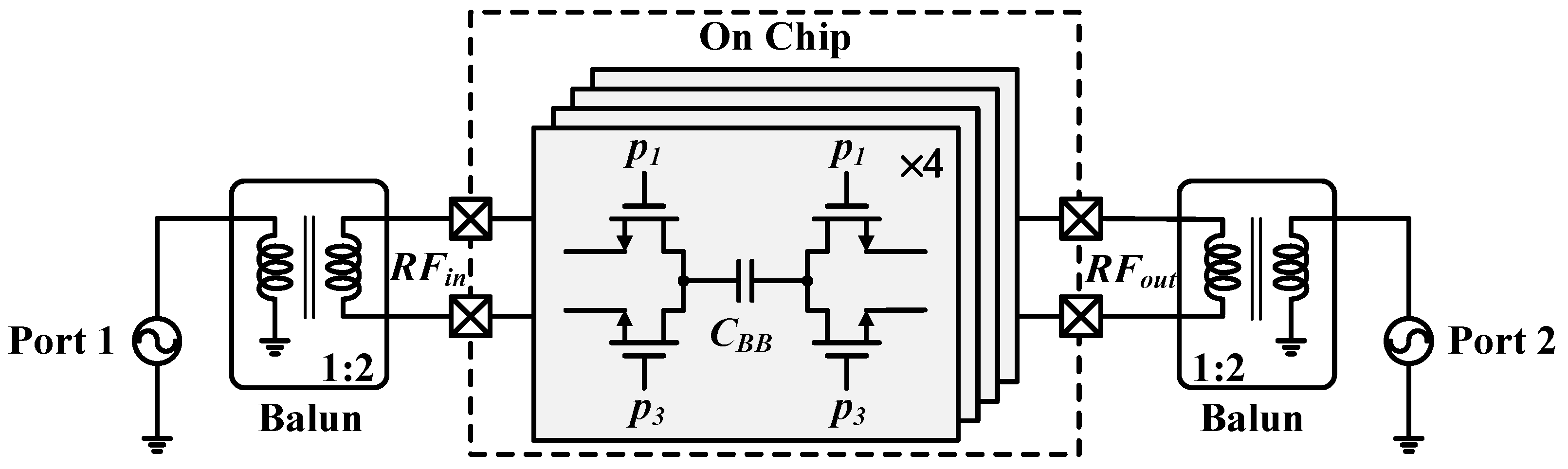


| Transistors | Vsource,ON | Vdrain,ON | Vsource,OFF | Vdrain,OFF | Vgate Level | Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MN1 | VDD/2 | VDD/2 | VDD | VDD/2 | VDD − VDD/2 | 0.5u/120n |
| MN2 | VDD/2 | VDD/2 | VDD | VDD/2 | VDD − VDD/2 | 0.5u/120n |
| MN3 | VDD/2 | VDD/2 | VDD | VDD/2 | VDD/2 − VDD | 10u/120n |
| MP1 | VDD | VDD | VDD/2 | 0 | VDD − 0 | 20u/120n |
| MN4 | 0 | 0 | VDD/2 | VDD | VDD − VDD/2 | 40u/120n |
| 1.2 V Divider 1.2 V Switch | 2.5 V Divider 2.5 V Switch | 1.2 V Divider + 2.5 V Switch with Level Shifter | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Divider/mW | 4.2 | 14.9 | 4.3 |
| NAND/mW | 4.8 | 8.5 | 4.8 |
| Level Shifter/mW | / | / | 1.9 |
| Buffer/mW | 6 | 10.5 | 10.5 |
| Total Power/mW | 15 | 33.9 | 21.5 |
| Bias Voltage/V | 0.2 | 0.5 | 0.5 |
| B1dB/dBm | −1.3 | 2.1 | 2.1 |
| BNF @ 0dBm Blocker | 4.1 | 1.9 | 1.9 |
| Transistors | Vsource,ON | Vdrain,ON | Vsource,OFF | Vdrain,OFF | Vgate Level | Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MN1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | VDD | 0 − VDD | 5u/220n |
| MP1 | VDD | VDD | VDD | 0 | VDD − 0 | 10u/220n |
| MN2 | VEE | VEE | 0 | VDD | 0 − VDD | 2.5u/220n |
| MP2 | VDD | VDD | 0 | VEE | 0 − VEE | 5u/220n |
| MN3 | VEE | VEE | VEE | 0 | VEE − 0 | 2.5u/220n |
| MP3 | VBN | VBN | VBN | VEE | VBN − VEE | 5u/220n |
| MN4 | VBN | VBN | VEE | VBN | VEE − VBN | 2.5u/220n |
| MN5 | VEE | VEE | VBN | VDD | VBN − VDD | 2.5u/220n |
| 2.5 V Divider 2.5 V Switch | 1.2 V Divider + 2.5 V Switch with Level Shifter | 2.5 V Switch with Level Shifter and Clock Boost | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Divider/mW | 14.9 | 4.3 | 4.3 |
| NAND/mW | 8.5 | 4.8 | 4.8 |
| Level Shifter/mW | / | 1.9 | 1.9 |
| Clock Boost/mW | / | / | 8.7 |
| Buffer/mW | 10.5 | 10.5 | 14 |
| Total Power/mW | 33.9 | 21.5 | 33.7 |
| Bias Voltage/V | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.55 |
| B1dB/dBm | 2.1 | 2.1 | 10 |
| BNF @ 0dBm Blocker | 1.9 | 1.9 | 1.63 |
| Transistors | Size |
|---|---|
| MN1 | 20u/220n |
| MN2 | 10u/220n |
| MN3 | 5u/220n |
| MN4 | 10u/220n |
| MN5 | 20u/220n |
| MP1 | 30u/220n |
| MP2 | 5u/220n |
| MP3 | 5u/220n |
| MN6 | 2.5u/220n |
| MN7 | 5u/220n |
| MN8 | 2u/220n |
| MN9 | 2u/220n |
| Inv. and Tran. NMOS | 5u/220n |
| Inv. and Tran. PMOS | 2.5u/220n |
| Reference | [25] | [26] | [29] | [24] | This Work # | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technology | 65 nm CMOS | 65 nm CMOS | 65 nm CMOS | 45 nm SOI | 130 nm SOI | |
| Filter Topology | N-path BRF with Neg. Tran. | N-path BRF | N-path BPF +Chip Inductor | N-path BPF +BRF | N-path BRF | N-path BRF |
| Clock Topology | Traditional | Traditional | Swing Boost | Swing Boost | Mode 1 Swing Boost | Mode 2 Bootstrap |
| RF Range/GHz | 0.2 to 1 | 0.1 to 1.2 | 1 to 5 | 0.2 to 3.6 | 0.1 to 1.0 | |
| Clock Swing/V | 2.5 | 2.5 | 3.36 | 3 | 3.5 | 3.5 + RFIN |
| B1dB/dBm | N/A | <0 | 9.3 | >10 | 9 to 10.5 | 9.2 to 12.7 |
| P1dB/dBm | 5 to 7 | 6 | 8.8 | N/A | 6.2 to 7.8 | 7.1 to 10.1 |
| IB IIP3/dBm | 17 to 21.5 | >17 | 23 | 22 | 14 to 17.3 | 18.1 to 23.9 |
| Max Rejection/dB | >50 | 24 | >24 | 41 | 15.8 to 23 | 15.5 to 24 |
| Insertion Loss/dB | 0.8 to 5 * | 1.4 to 2.8 | 4.9 to 8.4 * | 2.6 to 4.3 * | 1.9 to 3.8 | 1.95 to 4.8 |
| DSB NF/dB | 1 to 4 | 1.6 to 2.5 | 5 to 8.5 | 2.8 to 4.5 | 2.2 to 4.2 | 2.3 to 5.12 |
| Power/mW | 7.2 to 13.2 | 3.5 to 30 | 40 to 167 | 183.3 to 303.5 | 25.3 to 40.7 | 35.1 to 55.1 |
| PDC/fLO @ High Freq | 13.2 | 25 | 33.5 | 84.3 | 40.7 | 55.1 |
| Active Area/mm2 | 0.25 | 0.14 | 0.3 * | 0.21 | 0.08 | 0.12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, X.; Xu, S.; Zhang, H.; Wu, G.; Zhan, L. A Dual-Mode Clock Enhancement Technology N-Path Notch Filter with High Linearity. Electronics 2025, 14, 1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14051008
Luo X, Xu S, Zhang H, Wu G, Zhan L. A Dual-Mode Clock Enhancement Technology N-Path Notch Filter with High Linearity. Electronics. 2025; 14(5):1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14051008
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Xujia, Shang Xu, Haotian Zhang, Guoan Wu, and Lamin Zhan. 2025. "A Dual-Mode Clock Enhancement Technology N-Path Notch Filter with High Linearity" Electronics 14, no. 5: 1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14051008
APA StyleLuo, X., Xu, S., Zhang, H., Wu, G., & Zhan, L. (2025). A Dual-Mode Clock Enhancement Technology N-Path Notch Filter with High Linearity. Electronics, 14(5), 1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14051008






