Dual-Task Learning for Long-Range Classification in Single-Pixel Imaging Under Atmospheric Turbulence
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theory
2.1. SPI for Atmospheric Turbulence
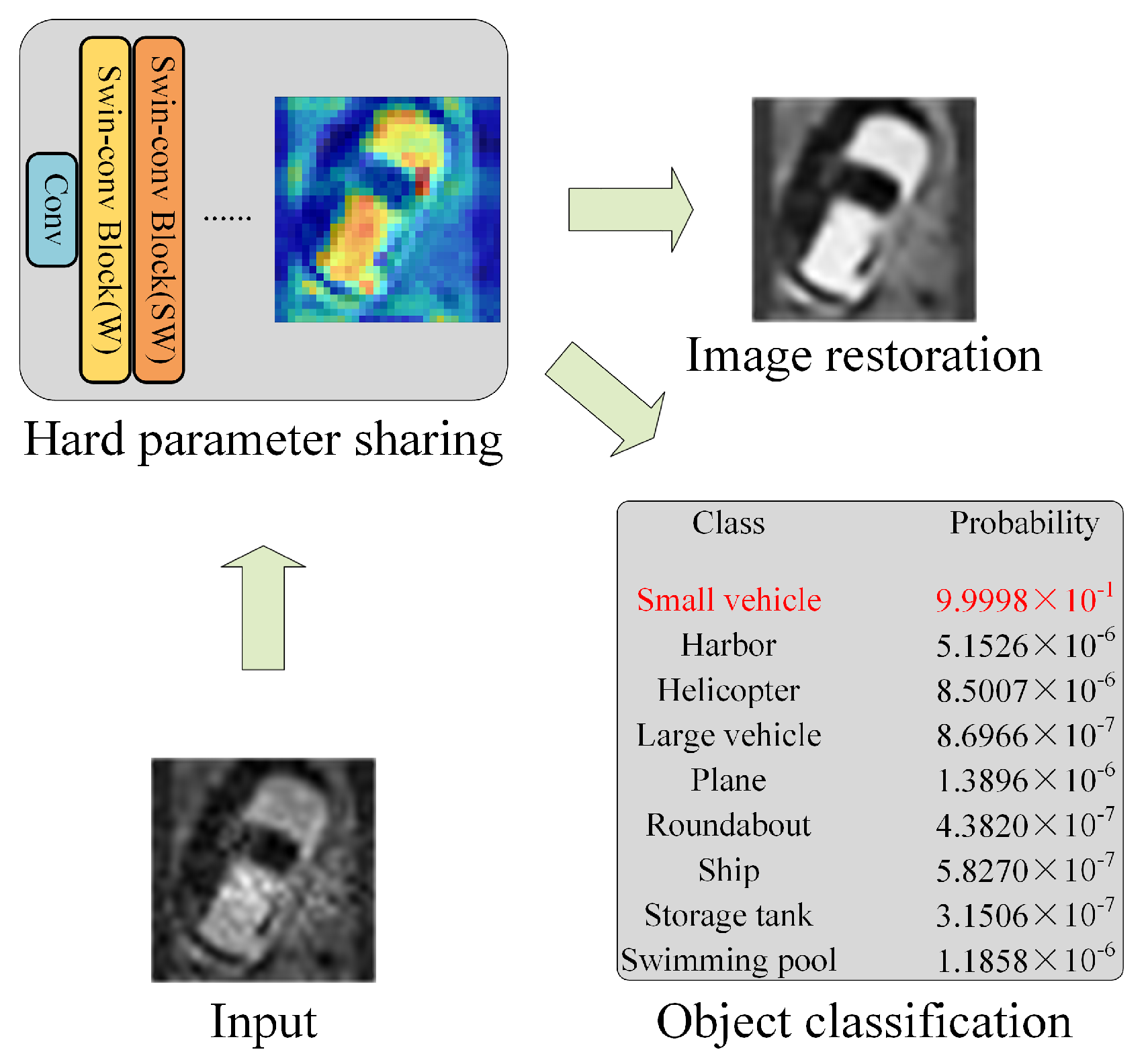
2.2. LR-DTSPNet for Dual-Task Learning
2.2.1. Dual-Task Learning
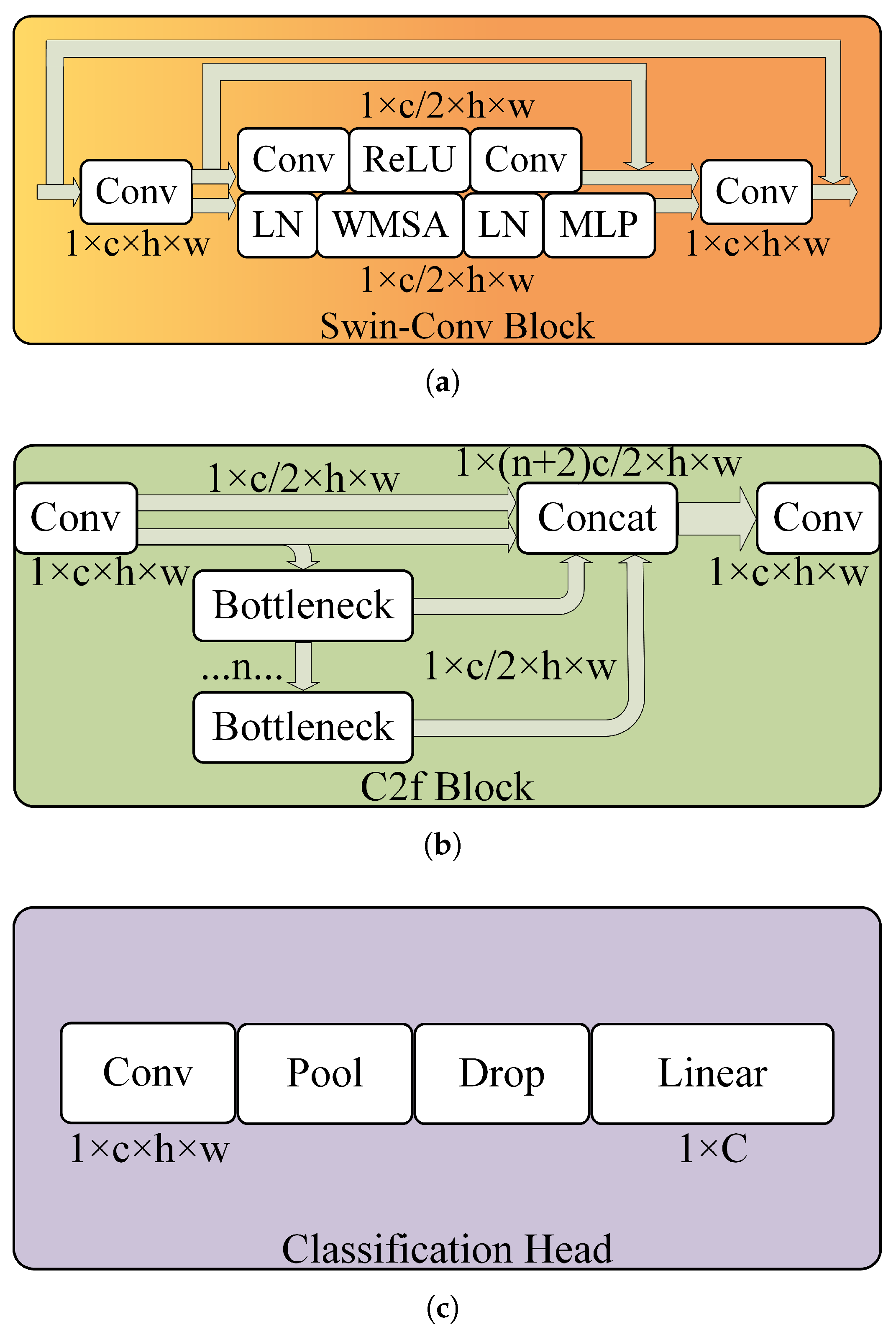
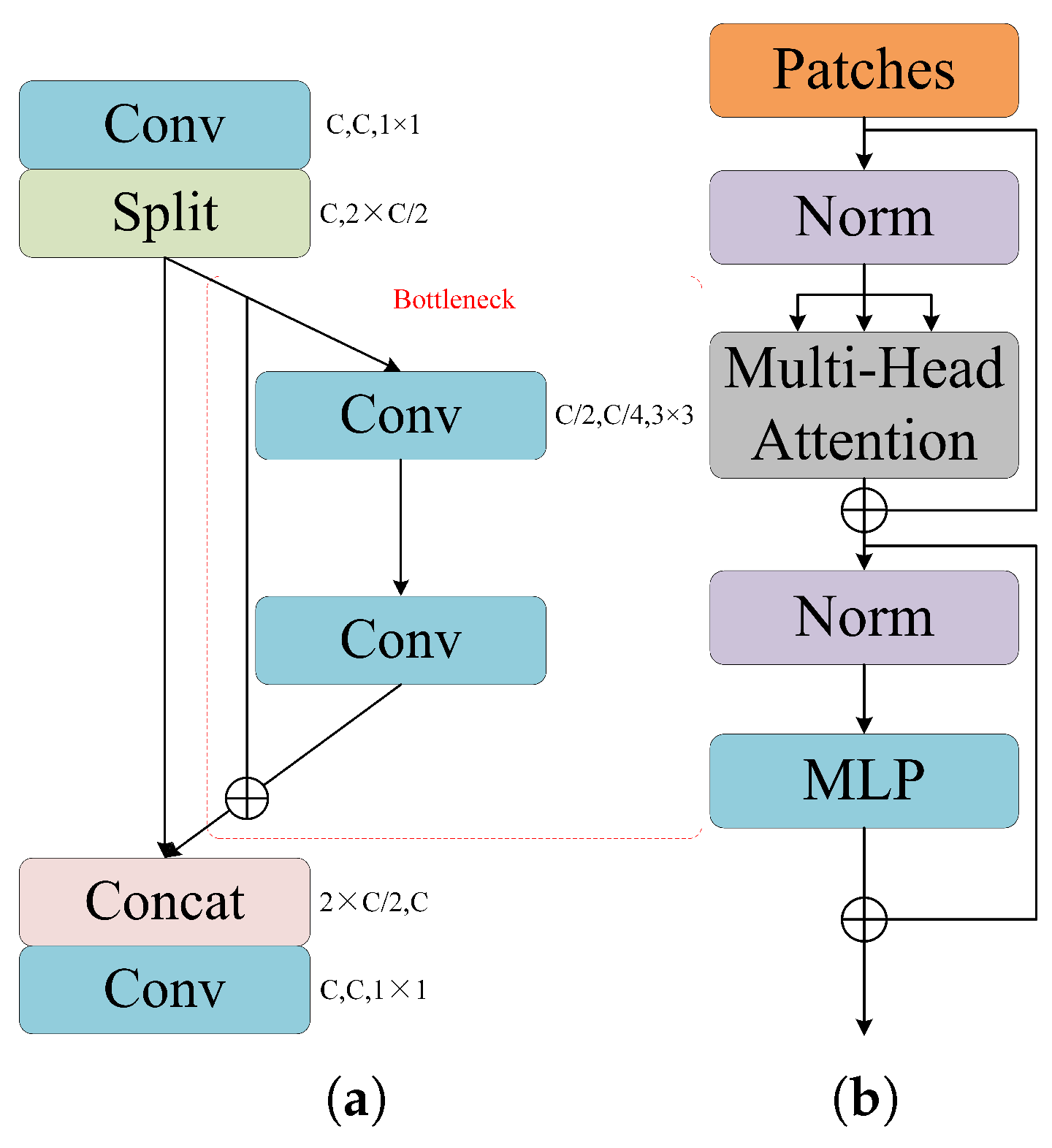
2.2.2. LR-DTSPNet Architecture
2.2.3. Cost Function for LR-DTSPNet
3. Simulation Experiments
3.1. Dataset
3.2. Object Classification
3.2.1. Recent Classification Network for Comparison
3.2.2. Classification Results
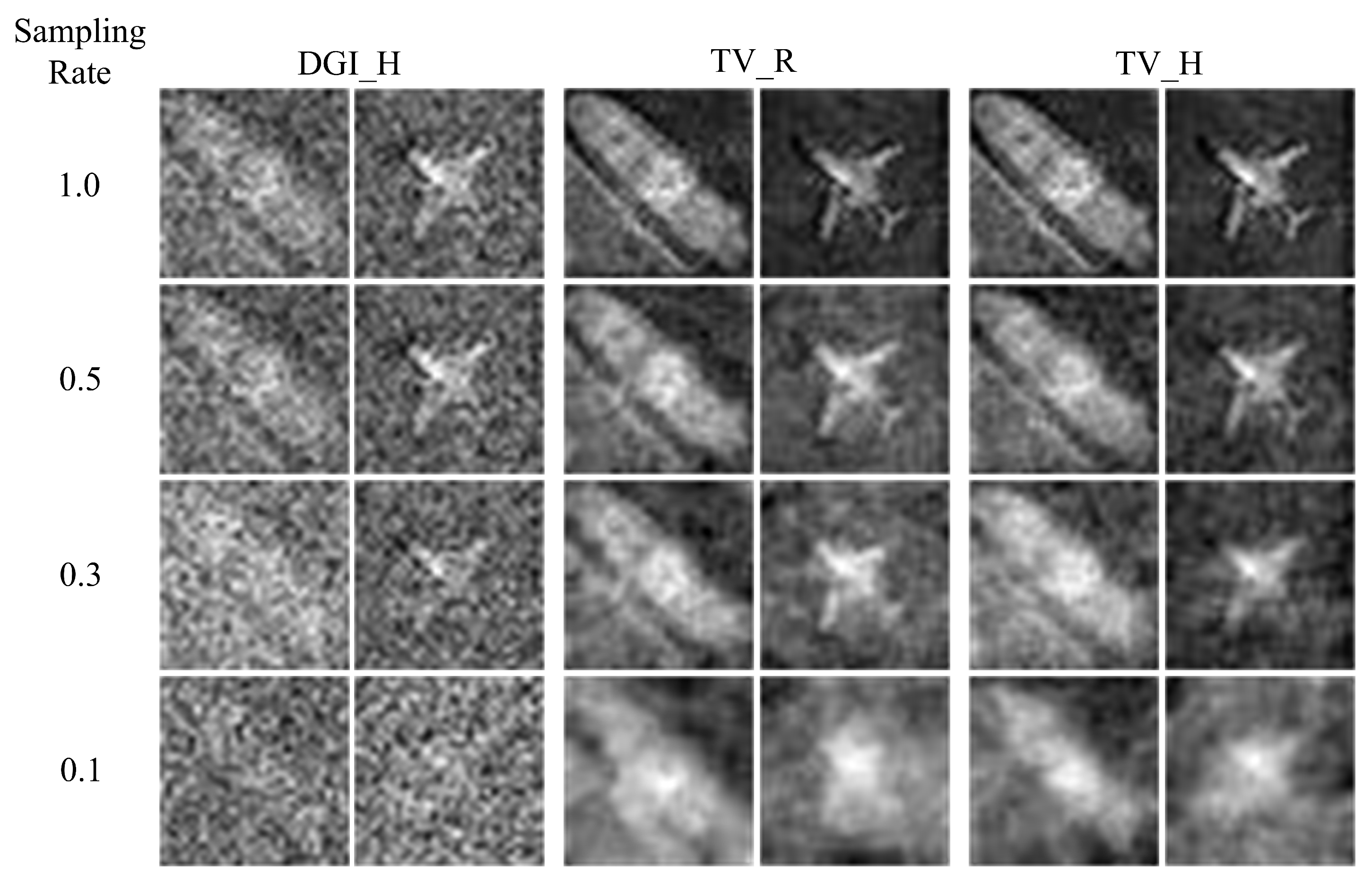
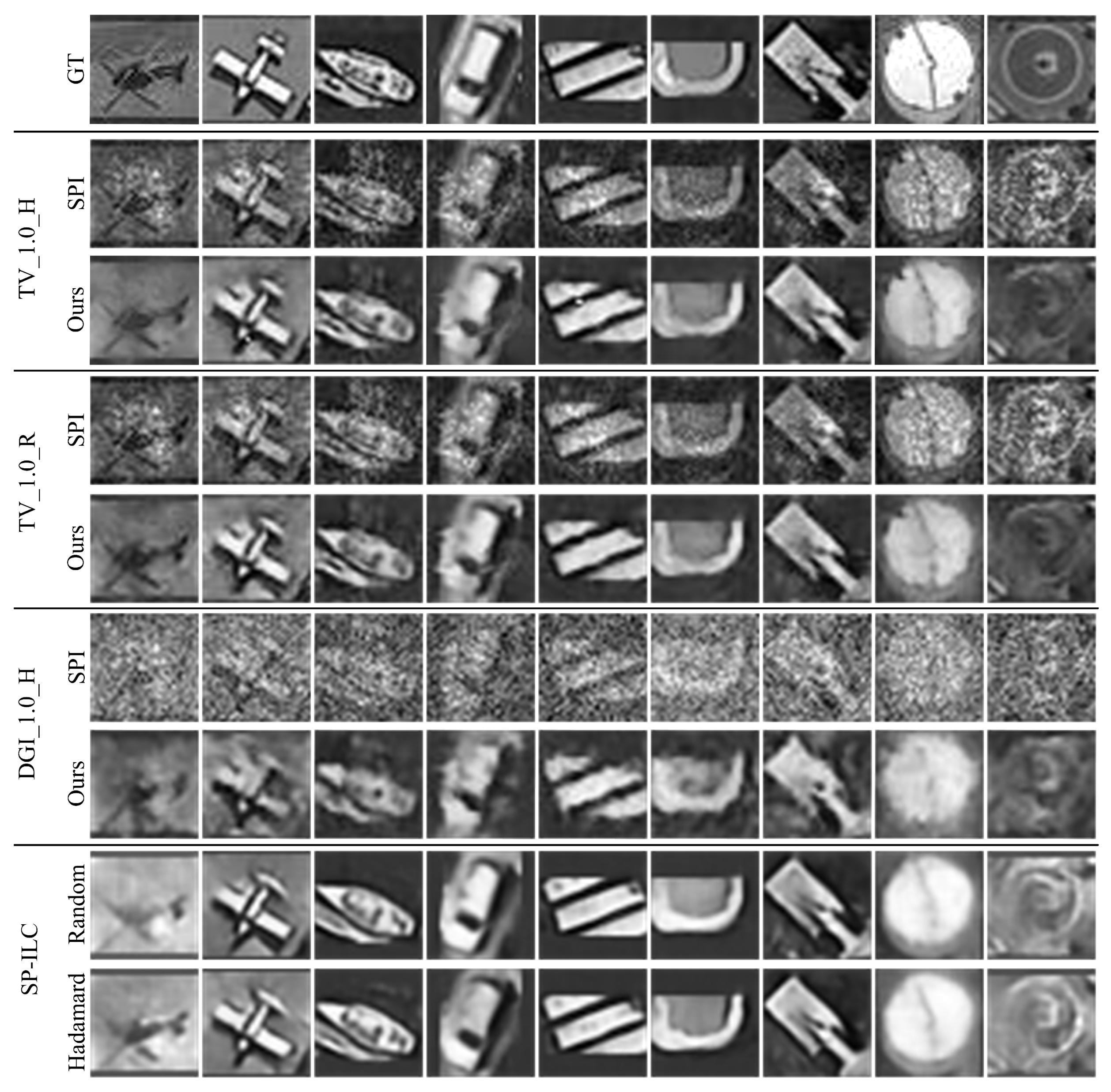
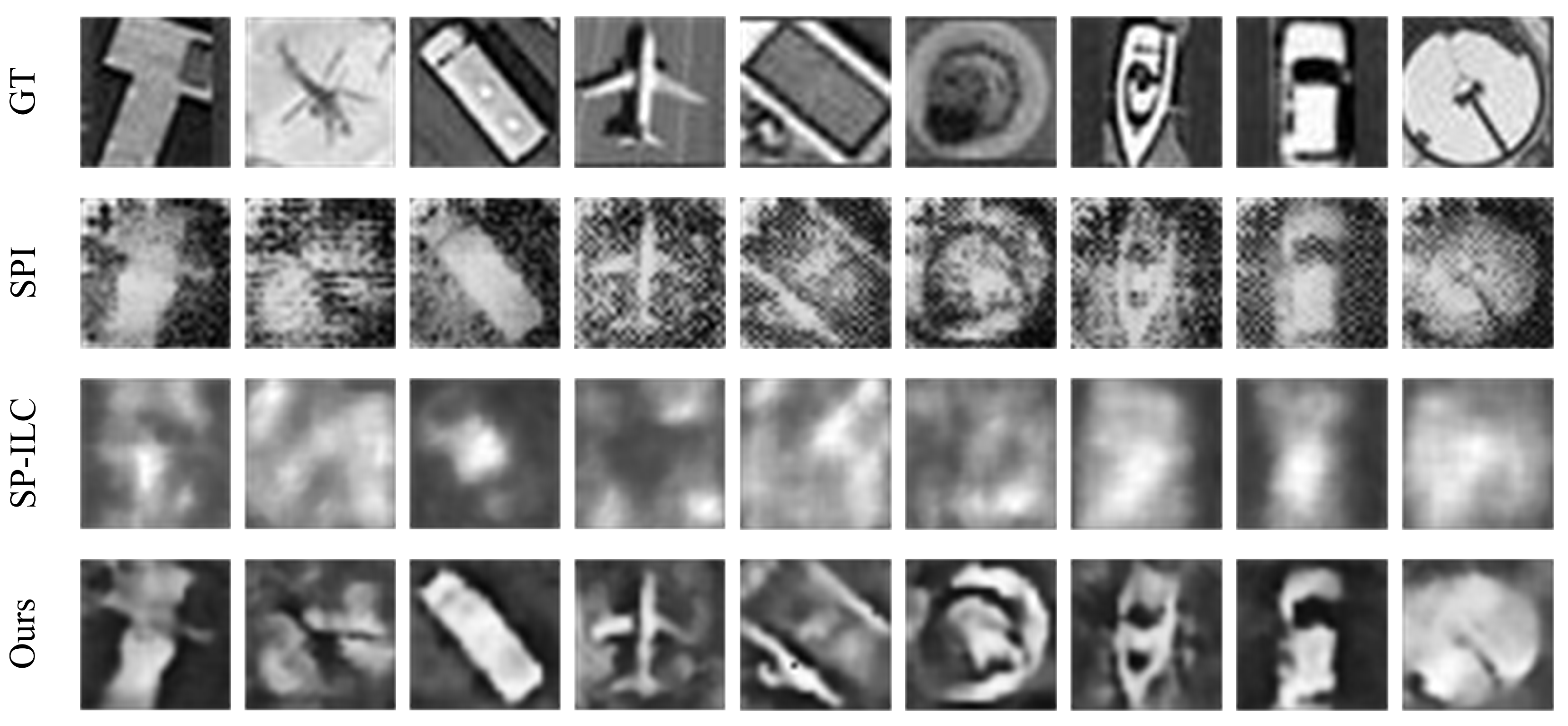
3.3. Image Quality Enhancement
4. Ablation Study
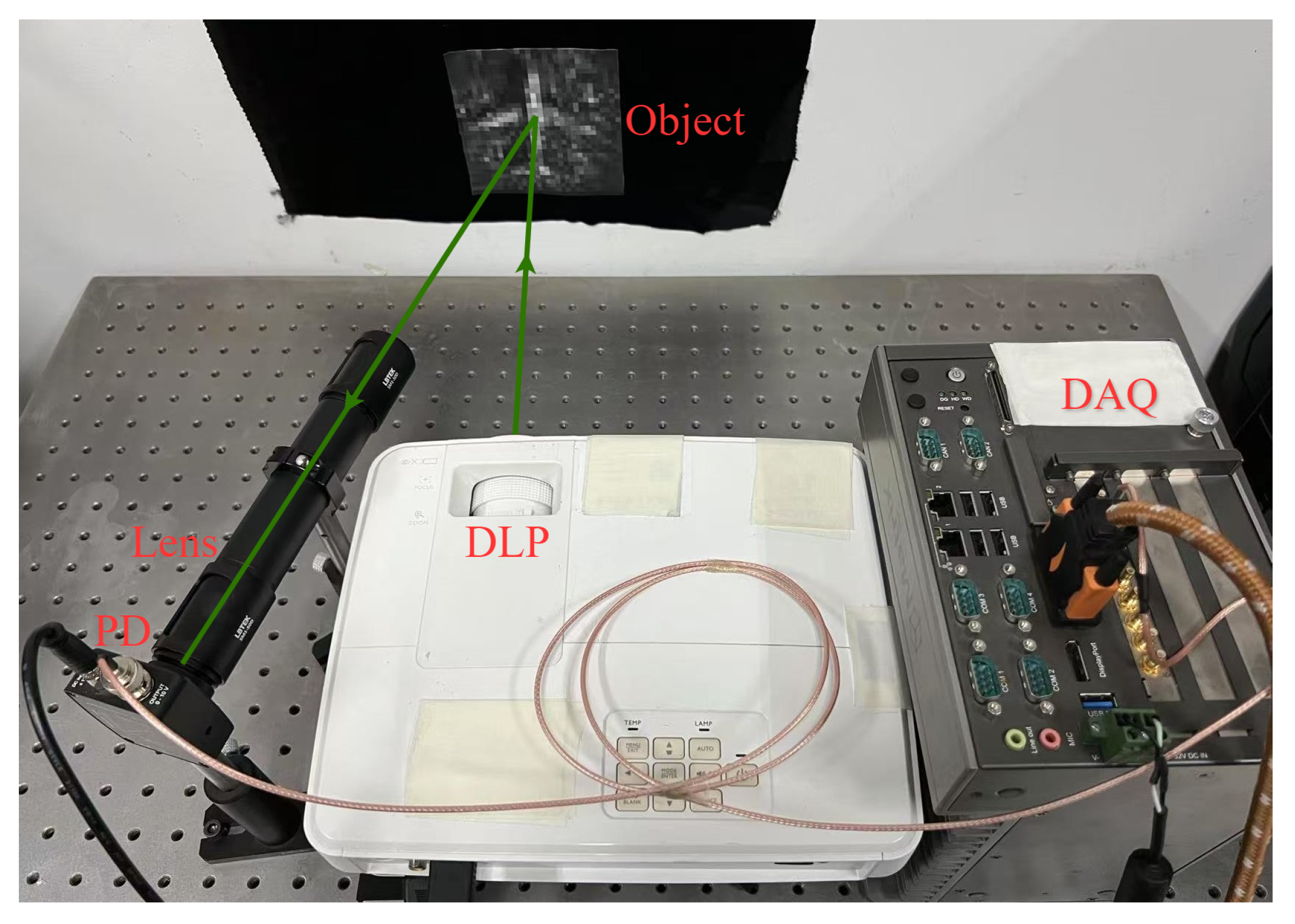
5. Optical Experiments
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kechagias-Stamatis, O.; Aouf, N. Automatic target recognition on synthetic aperture radar imagery: A survey. IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 2021, 36, 56–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huizing, A.; Heiligers, M.; Dekker, B.; De Wit, J.; Cifola, L.; Harmanny, R. Deep learning for classification of mini-UAVs using micro-Doppler spectrograms in cognitive radar. IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 2019, 34, 46–56. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, H.; Diao, Z.; Shi, T.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, F.; Hu, W.; Zhu, X.; Luo, S.; Tong, G.; Yao, Y.D. A review of deep learning-based multiple-lesion recognition from medical images: Classification, detection and segmentation. Comput. Biol. Med. 2023, 157, 106726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penumuru, D.P.; Muthuswamy, S.; Karumbu, P. Identification and classification of materials using machine vision and machine learning in the context of industry 4.0. J. Intell. Manuf. 2020, 31, 1229–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yan, L.; Qi, P.; Zhang, L.; Goudail, F.; Liu, T.; Zhai, J.; Hu, H. Polarimetric imaging via deep learning: A review. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Li, X.; Zhai, J.; Hu, H. PODB: A learning-based polarimetric object detection benchmark for road scenes in adverse weather conditions. Inf. Fusion 2024, 108, 102385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Chen, Z.; Lu, L.; Qi, P.; Zhang, L.; Ma, Q.; Hu, H.; Zhai, J.; Li, X. Cascaded frameworks in underwater optical image restoration. Inf. Fusion 2025, 117, 102809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, C.; Deng, C.; Han, S.; Situ, G. Single-pixel imaging using physics enhanced deep learning. Photonics Res. 2021, 10, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Huang, J.; Shi, D.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, K.; Hu, S.; Wang, Y. Single-pixel imaging with untrained convolutional autoencoder network. Opt. Laser Technol. 2023, 167, 109710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Li, Z.; Shi, D.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, K.; Hu, S.; Wang, Y. Scanning single-pixel imaging lidar. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 37484–37492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Gong, W.; Shen, X.; Han, S. Correlated imaging through atmospheric turbulence. Phys. Rev. A—Atomic Mol. Opt. Phys. 2010, 82, 033817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.K.; Liu, W.T.; Zhang, E.F.; Li, Q.; Dai, H.Y.; Chen, P.X. Is ghost imaging intrinsically more powerful against scattering? Opt. Express 2015, 23, 32993–33000. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Mathai, A.; Lau, S.L.; Yam, J.W.; Xu, X.; Wang, X. Underwater object detection and reconstruction based on active single-pixel imaging and super-resolution convolutional neural network. Sensors 2021, 21, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Dai, S.; Huang, L. Research on single-pixel imaging method in the complex environment. Optik 2022, 271, 170153. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, J.; Nie, W.; Zhou, M. A high-resolution and low-cost entangled photon quantum imaging framework for marine turbulence environment. IEEE Netw. 2022, 36, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Xiong, S.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, G.; Chang, H.; Zhong, J. Seeing through fire with one pixel. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2024, 183, 108540. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, W. Single-pixel microscopic imaging through complex scattering media. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2025, 126, 031106. [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro, J.H. Computational ghost imaging. Phys. Rev. A—Atomic Mol. Opt. Phys. 2008, 78, 061802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Q.; Bai, Y.; Tan, W.; Huang, X.; Nan, S.; Fu, X. Principle of subtraction ghost imaging in scattering medium. Chin. Phys. B 2023, 32, 064203. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Jiang, P.; Gao, W.; Liu, Z.; Li, L.; Liu, J. Long-distance ghost imaging with incoherent four-petal Gaussian sources in atmospheric turbulence. Laser Phys. 2023, 33, 096003. [Google Scholar]
- Leihong, Z.; Zhixiang, B.; Hualong, Y.; Zhaorui, W.; Kaimin, W.; Dawei, Z. Restoration of single pixel imaging in atmospheric turbulence by Fourier filter and CGAN. Appl. Phys. B 2021, 127, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Duan, D. Turbulence-immune computational ghost imaging based on a multi-scale generative adversarial network. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 43929–43937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhai, Y.; Xu, R.; Wang, K.; Zhang, D. End-to-end computational ghost imaging method that suppresses atmospheric turbulence. Appl. Opt. 2023, 62, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Liao, Y.; Zhou, S.; Chen, J.; Ke, J. Enhanced Single Pixel Imaging in Atmospheric Turbulence. In Proceedings of the Computational Optical Sensing and Imaging, Toulouse, France, 15–19 July 2024; CF1B. 5. Optica Publishing Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Li, G.; Situ, G. Learning from simulation: An end-to-end deep-learning approach for computational ghost imaging. Opt. Express 2019, 27, 25560–25572. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Song, K.; Bian, Y.; Wu, K.; Liu, H.; Han, S.; Li, J.; Tian, J.; Qin, C.; Hu, J.; Xiao, L. Single-pixel imaging based on deep learning. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2310.16869. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Le, M.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Li, B.; Peng, J. Object identification in computational ghost imaging based on deep learning. Appl. Phys. B 2020, 126, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Zheng, S.; Yao, M.; Zheng, G.; Zhong, J. Image-free classification of fast-moving objects using “learned” structured illumination and single-pixel detection. Opt. Express 2020, 28, 13269–13278. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Bai, Y.M.; Sun, L.D.; Huang, K.X.; Liu, J.; Ruan, D.; Li, J.L. SP-ILC: Concurrent single-pixel imaging, object location, and classification by deep learning. Photonics 2021, 8, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Xie, S.; Qin, T.; Cao, L.; Bian, L. Image-free single-pixel object detection. Opt. Lett. 2023, 48, 2527–2530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.D. Numerical Simulation of Optical Wave Propagation with Examples in MATLAB; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, L.C. An analytical model for the refractive index power spectrum and its application to optical scintillations in the atmosphere. J. Mod. Opt. 1992, 39, 1849–1853. [Google Scholar]
- Ferri, F.; Magatti, D.; Lugiato, L.A.; Gatti, A. Differential ghost imaging. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010, 104, 253603. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, C. An Efficient Algorithm for Total Variation Regularization with Applications to the Single Pixel Camera and Compressive Sensing. Master’s Thesis, Rice University, Houston, TX, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, L.; Suo, J.; Dai, Q.; Chen, F. Experimental comparison of single-pixel imaging algorithms. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2017, 35, 78–87. [Google Scholar]
- Caruana, R. Multitask learning. Mach. Learn. 1997, 28, 41–75. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Li, Y.; Liang, J.; Cao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, H.; Fan, D.P.; Timofte, R.; Gool, L.V. Practical blind image denoising via Swin-Conv-UNet and data synthesis. Mach. Intell. Res. 2023, 20, 822–836. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, G.S.; Bai, X.; Ding, J.; Zhu, Z.; Belongie, S.; Luo, J.; Datcu, M.; Pelillo, M.; Zhang, L. DOTA: A large-scale dataset for object detection in aerial images. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–22 June 2018; pp. 3974–3983. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.; Sandler, M.; Chu, G.; Chen, L.C.; Chen, B.; Tan, M.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Pang, R.; Vasudevan, V.; et al. Searching for mobilenetv3. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 1314–1324. [Google Scholar]
- Woo, S.; Debnath, S.; Hu, R.; Chen, X.; Liu, Z.; Kweon, I.S.; Xie, S. Convnext v2: Co-designing and scaling convnets with masked autoencoders. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 16133–16142. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q. Efficientnetv2: Smaller models and faster training. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 18–24 July 2021; PMLR: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; pp. 10096–10106. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16 × 16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Y.; Liao, H.Y.M.; Wu, Y.H.; Chen, P.Y.; Hsieh, J.W.; Yeh, I.H. CSPNet: A new backbone that can enhance learning capability of CNN. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 390–391. [Google Scholar]

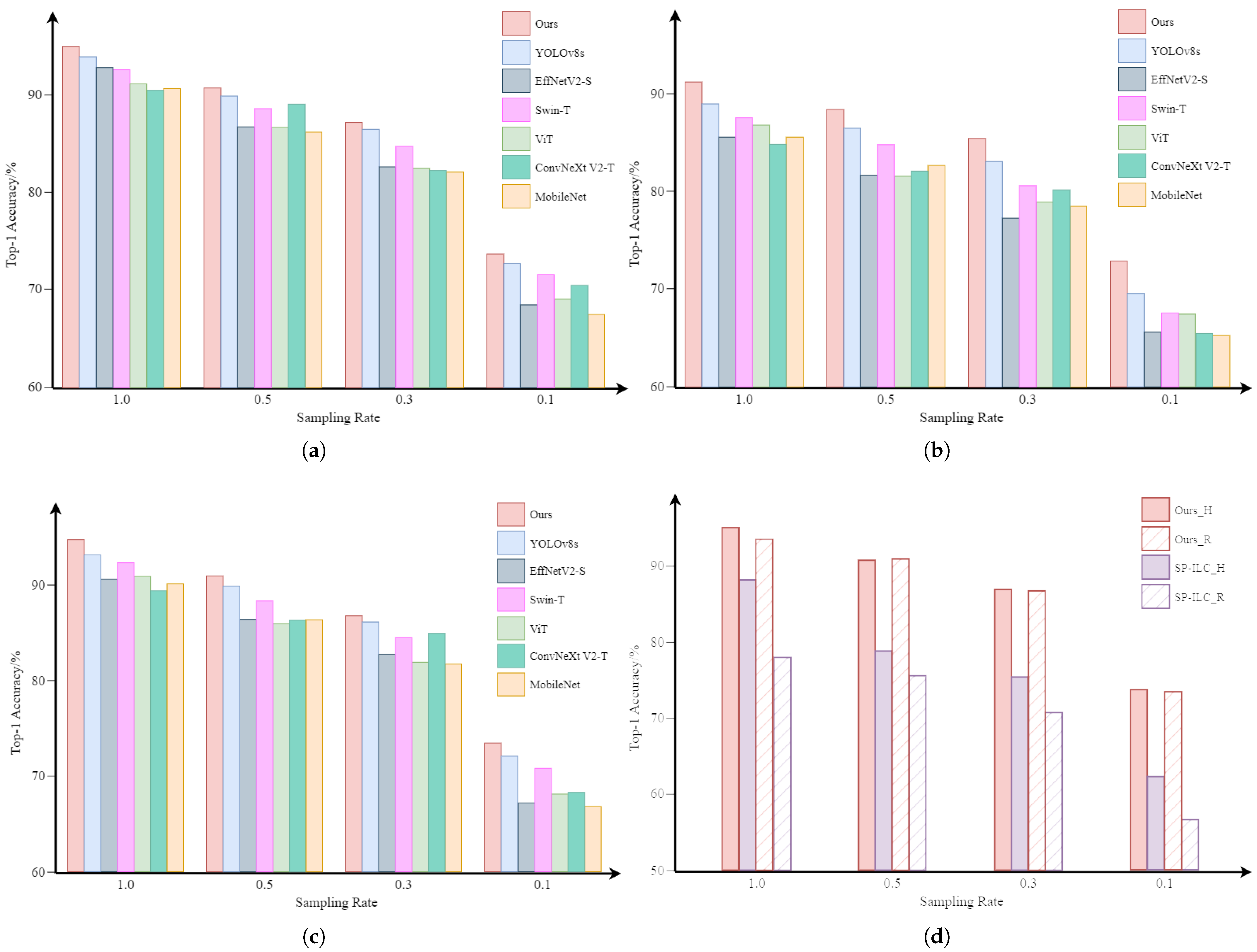




| Network | Parameter Count (M) | FLOPs (G) | Inference Speed (FPS) | Restoration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv8s | 5 | 0.016 | 555 | × |
| ViT | 85 | 5.6 | 208 | × |
| Swin-T | 28 | 4.5 | 83 | × |
| ConvNeXt V2-T | 28.6 | 4.47 | 144 | × |
| EffNetV2-S | 21.5 | 8.4 | 100 | × |
| MobileNetV3 | 4.2 | 0.0072 | 104 | × |
| SP-ILC | 2.3 | 0.12 | 225 | √ |
| Ours | 4.1 | 0.17 | 48 | √ |
| Object | PSNR | SSIM | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Degraded | Restored | Degraded | Restored | |
| Swimming pool | 13.67 | 16.35 | 0.25 | 0.34 |
| Ship | 16.98 | 21.14 | 0.66 | 0.79 |
| Helicopter | 12.80 | 14.97 | 0.11 | 0.18 |
| Storage tank | 12.80 | 20.86 | 0.39 | 0.65 |
| Small vehicle | 17.02 | 21.92 | 0.61 | 0.76 |
| Roundabout | 14.50 | 19.66 | 0.10 | 0.24 |
| Harbor | 17.86 | 21.57 | 0.52 | 0.63 |
| Plane | 15.64 | 20.91 | 0.61 | 0.73 |
| Large vehicle | 15.78 | 20.43 | 0.69 | 0.82 |
| Object | PSNR | SSIM | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Degraded | Restored | Degraded | Restored | |
| Swimming pool | 12.61 | 15.72 | 0.17 | 0.30 |
| Ship | 13.03 | 17.94 | 0.39 | 0.63 |
| Helicopter | 12.66 | 14.87 | 0.11 | 0.17 |
| Storage tank | 13.27 | 18.97 | 0.22 | 0.57 |
| Small vehicle | 12.60 | 18.94 | 0.35 | 0.61 |
| Roundabout | 14.38 | 19.24 | 0.10 | 0.23 |
| Harbor | 13.14 | 19.28 | 0.31 | 0.50 |
| Plane | 14.54 | 17.80 | 0.38 | 0.56 |
| Large vehicle | 12.43 | 17.37 | 0.40 | 0.69 |
| Dataset | PSNR | SSIM | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Degraded | Restored | Degraded | Restored | |
| TV_1.0_H | 15.99 | 20.57 | 0.55 | 0.68 |
| TV_0.5_H | 15.44 | 18.84 | 0.50 | 0.60 |
| TV_0.3_H | 14.55 | 16.69 | 0.45 | 0.51 |
| TV_0.1_H | 12.43 | 14.78 | 0.32 | 0.35 |
| TV_1.0_R | 16.11 | 20.26 | 0.54 | 0.67 |
| TV_0.5_R | 15.43 | 18.76 | 0.50 | 0.59 |
| TV_0.3_R | 14.52 | 17.04 | 0.45 | 0.51 |
| TV_0.1_R | 12.39 | 14.77 | 0.32 | 0.35 |
| DGI_1.0_H | 13.03 | 18.01 | 0.32 | 0.56 |
| DGI_0.5_H | 13.01 | 16.40 | 0.35 | 0.56 |
| DGI_0.3_H | 11.74 | 14.46 | 0.24 | 0.43 |
| DGI_0.1_H | 10.68 | 13.85 | 0.14 | 0.32 |
| Dataset | PSNR/SSIM | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Full Model | w/o Swin–Conv Block | w/o C2f Block | |
| TV_1.0_H | 20.57/0.68 | 19.16/0.66 | 20.40/0.68 |
| TV_0.5_H | 18.84/0.60 | 15.22/0.56 | 17.29/0.57 |
| TV_0.3_H | 16.69/0.51 | 13.93/0.48 | 16.28/0.51 |
| TV_0.1_H | 14.78/0.35 | 14.07/0.35 | 13.00/0.33 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liao, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Ke, J. Dual-Task Learning for Long-Range Classification in Single-Pixel Imaging Under Atmospheric Turbulence. Electronics 2025, 14, 1355. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14071355
Liao Y, Cheng Y, Ke J. Dual-Task Learning for Long-Range Classification in Single-Pixel Imaging Under Atmospheric Turbulence. Electronics. 2025; 14(7):1355. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14071355
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiao, Yusen, Yin Cheng, and Jun Ke. 2025. "Dual-Task Learning for Long-Range Classification in Single-Pixel Imaging Under Atmospheric Turbulence" Electronics 14, no. 7: 1355. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14071355
APA StyleLiao, Y., Cheng, Y., & Ke, J. (2025). Dual-Task Learning for Long-Range Classification in Single-Pixel Imaging Under Atmospheric Turbulence. Electronics, 14(7), 1355. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics14071355










