Abstract
Human motion prediction is critical for applications such as autonomous driving and healthcare. However, existing methods struggle to balance diversity (varied motion patterns), fidelity (realistic and accurate motion), and computational efficiency. Traditional variational autoencoders (VAEs) and generative adversarial networks (GANs) often fail to simultaneously achieve both diversity and fidelity, while diffusion-based approaches suffer from high computational costs. In this paper, we propose a novel sparse spatiotemporal diffusion model that integrates the parallel enhanced attention (PEA) module and spatiotemporal sparse self-attention (STSSA). The PEA module enhances attention to important joints and key motion frames via a dual-branch structure, whereas STSSA reduces redundancy through adaptive sparsification and single-head compression, and exploits spatiotemporal structure to reduce accuracy loss. Experimental results show that the proposed model achieves competitive performance on three benchmark datasets: Human3.6M, HumanEva-I, and AMASS. Compared to the best existing diffusion-based methods, our model significantly enhances efficiency while maintaining similar prediction accuracy. Specifically, the model reduces the number of parameters by 45.7% and shortens the single-sample inference time by 63.0% (from 1.1 s to 0.4 s). Through the joint design of the PEA module and STSSA, the model achieves a balance between efficiency, diversity, and fidelity. The lightweight design and end-to-end framework of the model provide a practical solution for real-time human motion prediction.
1. Introduction
Human motion prediction involves analyzing a sequence of past movements to forecast future human motion. This field has attracted significant attention in recent years due to its critical role in applications such as autonomous driving [1], motion tracking [2], and healthcare [3]. Advances in deep learning have led to significant advancements in this area; however, predicting human motion in complex scenarios remains challenging due to behavioral uncertainty [4]. Existing methods face two main challenges. First, balancing the diversity and fidelity of generated motion is difficult [5,6]. Second, there exists a trade-off between model complexity and the requirement for real-time inference [7,8,9]. Here, diversity refers to the model’s ability to generate multiple distinct motion hypotheses that reflect the stochastic nature of human behavior, while fidelity measures how closely the predicted motion matches the ground truth trajectory in terms of spatial accuracy, temporal consistency, and physical plausibility.
To better understand the nature of human motion prediction, it is important to clarify the typical input representation and data acquisition process. Most existing works, including ours, use a sequence of 3D joint coordinates as model input, which captures the spatial configuration of key human joints (typically 15, 17, or 22 joints) over time. These data are usually obtained in laboratory environments using synchronized multi-camera systems and depth sensors. Through precise calibration, all captured data are transformed into a unified global coordinate system, ensuring spatial consistency between the observer and the subject. This setup allows models to leverage consistent spatial references and rich motion information for learning. Furthermore, the complexity and high dimensionality of such temporally evolving joint data have motivated the widespread use of multi-head attention mechanisms in prior works, which enable the model to capture diverse spatiotemporal dependencies across different body parts and motion phases.
Traditional human motion prediction methods commonly employ variational autoencoders (VAEs) [10] to model the stochastic nature of human movement by sampling from a latent space. While these approaches introduce motion diversity through stochastic encoding and decoding, they often suffer from error accumulation in latent representations, leading to joint misalignment and degraded fidelity, particularly in long-term predictions. At the same time, generative adversarial networks (GANs) [11] improve diversity by leveraging adversarial training, often in combination with auxiliary objectives, such as temporal smoothness and physical plausibility. However, GAN-based models are typically sensitive to hyperparameter tuning and require the careful balancing of multiple loss terms to ensure training stability [12]. Furthermore, both VAEs and GANs tend to rely on complex multi-stage sampling pipelines, which increase computational overhead and hinder real-time applicability.
Recently, denoising probabilistic diffusion models (DDPMs) [13] have been widely used in generative tasks. These models iteratively refine noisy input signals to produce high-quality outputs, making them effective for various applications. In the context of human motion prediction, however, the term “noise” refers to intentional perturbations added to motion sequences during training. This strategy enables the model to learn to reconstruct the original clean motion from corrupted data. While diffusion models have been primarily applied to image generation tasks, their underlying denoising process can also be adapted for predicting future human motion sequences by treating the missing parts of a sequence as “noise” that needs to be denoised. However, the computational cost of DDPMs increases linearly with the number of denoising steps, which poses a challenge for real-time inference.
In motion prediction, traditional denoising models [14,15,16] generate predictions by removing noise but rely solely on the denoising process, making them unable to effectively utilize observed information. This increases the unpredictability of the generated results. To address this, HumanMAC [17] was the first to integrate diffusion models with the discrete cosine transform (DCT) and introduce a frequency domain mask completion method for end-to-end prediction, improving result controllability.
However, current methods have several limitations. First, the conditional fusion module depends on a complex cross-attention mechanism, leading to a quadratic increase in computational complexity as the sequence length grows. Second, the temporal utilization of features is insufficient, limiting the model’s ability to capture temporal dependencies effectively. Lastly, traditional multi-attention mechanisms suffer from redundant computations, reducing the efficiency of real-time inference.
To tackle these issues, we propose a new parallel enhanced attention with sparse spatiotemporal diffusion modeling (PEA-STDiff). Specifically, we designed a parallel enhanced attention module to account for the varying importance of different stages in the human motion prediction process. This module enhances feature perception by identifying important joints in the channel dimension and capturing key motion frames in the temporal dimension, enabling fine-grained feature selection and reconstruction, and improving the model’s ability to capture key motion information. Additionally, we propose using spatiotemporal sparse self-attention to reduce the computational redundancy of traditional multi-head attention. By leveraging single-head attention with adaptive sparsification, our approach enhances efficiency without compromising performance.
To summarize, the main contributions of this paper are as follows:
- We propose a novel PEA module with a dual-branch channel and temporal architecture. It dynamically perceives joint importance by integrating soft pooling and depthwise separable convolution, enhancing key-frame localization while preserving sensitivity to multi-scale spatiotemporal features.
- We designed an STSSA module that combines single-head compression architecture with adaptive sparsification. This reduces model parameters and triples the inference speed with only minimal accuracy loss.
- We propose an efficient, lightweight, and end-to-end diffusion model for HMC, achieving competitive results on the Human3.6M, HumanEva-I, and AMASS datasets, providing a practical solution for real-world applications.
2. Related Works
2.1. Diffusion Models
The denoising diffusion probabilistic model is an important breakthrough in the field of deep generative models in recent years, capable of generating high-quality images through straightforward training procedures. The model consists of two processes—forward diffusion and backward denoising—in which the data distribution is gradually transformed into pure Gaussian noise in the forward process, and then the noise is removed during the reverse process to reconstruct the target image. The forward process gradually transforms the original data into pure noise in T steps through predefined noise scheduling, and its single-step transfer can be expressed as:
where is the noise attenuation coefficient. With the reparameterization trick, the state at any moment t can be sampled directly from the initial data by a closed-form solution written as:
where .
In the backward process, the objective is to recover clean data from noise. To this end, the trained neural network, designated as , is employed to predict the injected noise. Thereafter, the original data distribution is gradually recovered through a single-step transfer, which is defined as follows:
In the context of DDPM, and denote the mean and the covariance of the inverse distribution, respectively. The DDPM does not directly predict from ; instead, it learns to predict the added noise through a neural network . This direct prediction of the noise, as opposed to the behavior of the data itself, serves to decouple the mean and the noise prediction network, thereby simplifying the optimization objective. The parameterization of the mean is as follows:
where is the noise prediction network with a simple loss function. The optimization objective function is as follows:
where N (0,I).
2.2. Diffusion-Based Human Motion Prediction
Previous motion prediction methods based on generative adversarial networks (GANs) [11] and variational auto-encoders (VAEs) [10,18] have been demonstrated to achieve basic motion generation; however, they are prone to joint misalignment and late-stage motion drift in long-term predictions. To enhance prediction accuracy, STARS [19] proposed a spatiotemporal anchor mechanism to achieve multi-scale motion modeling through decoupled graph convolutional networks, and designed a handcrafted constraint module to enhance the generation diversity. However, complex multi-stage training processes significantly increase the difficulty of engineering implementation. These limitations highlight the inherent constraints of the pure VAE framework in balancing prediction accuracy and motion realism.
The advent of diffusion modeling has precipitated a paradigm shift in the field of human motion prediction. In this context, MotionDiffusion (MotionDiff) [20] introduced a diffusion model based on an encoder–decoder architecture. The model’s encoder amalgamates historical motion sequences with diffusion time-step coding into a conditional signal, thereby facilitating multi-scale feature interactions through a gated linear transform module. In the decoding stage, the method employs a spatial time transformer [21] for implicit feature extraction of noise sequences, and a cascaded transformer block for noise prediction. It is important to note that MotionDiff introduces a graph convolutional network for post-processing optimization of the output. This non-end-to-end design increases the model complexity and may hinder training convergence. TCD [22] adopts a staged prediction strategy. Its short-term diffusion module first generates the initial frames, and the long-term diffusion module iteratively generates the complete sequence conditional on the short-term prediction. Despite the absence of an additional post-processing stage, the model requires two forward propagations during inference, thereby indicating potential avenues for optimization concerning real-time performance.
Recent research has focused on end-to-end architecture optimization. HumanMAC proposes a mask completion strategy to address the prediction task, which involves splicing the noise spectrum generated by the forward diffusion process with the DCT spectrum of the observed sequence, and jointly denoising the noise in the reverse process via U-Net. This approach achieves end-to-end training; however, its conditional fusion module relies on a complex channel attention mechanism, resulting in quadratic computational overhead concerning sequence length. To address this issue, TransFusion [23] has introduced a redesigned architectural paradigm for diffusion modeling, with its core innovation lying in the unified mapping of time-step coding of the diffusion process and frequency domain motion features into the transformer’s hidden space. Specifically, the method inputs the discrete cosine-transformed motion sequence spectrum, together with the diffusion step embedding vectors, into a multilayer self-attention module, and directly predicts the noise residuals through the interaction of features across steps. This method maintains the simplicity of the model structure. Experiments show that it not only requires fewer parameters and achieves faster inference but also attains state-of-the-art performance. Unfortunately, however, its over-reliance on the SE channel leads to poor feature extraction and a lack of attention to keyframes in long-term prediction.
2.3. Attention Mechanisms in Human Motion Analysis
Recent advancements in attention mechanisms have shown significant promise for spatiotemporal modeling in human motion analysis. The adaptive spatiotemporal graph transformer network for action quality assessment [24] introduces a tailored attention mechanism that adaptively learns the spatial graph structure and combines it with a hierarchical spatiotemporal transformer framework. Specifically, it employs an adaptive graph attention module to dynamically infer the importance of joint connections based on the input data, replacing static skeletal topologies. This allows the network to focus on more informative joint interactions. Additionally, the model incorporates spatial and temporal self-attention layers, which separately capture intra-frame joint dependencies and inter-frame motion dynamics. This design facilitates fine-grained motion understanding and improves the alignment between predicted actions and ground truth quality scores.
Similarly, TCN-attention-HAR [25] introduces a hybrid architecture that embeds attention modules within temporal convolutional networks. By utilizing depthwise separable convolutions alongside channel-wise attention recalibration, this approach efficiently models long-range temporal dependencies while maintaining computational efficiency. These studies underscore the adaptability and effectiveness of attention mechanisms in diverse motion analysis scenarios, highlighting their potential for enhancing both spatial and temporal feature extraction.
However, existing methods often process spatial and temporal features sequentially or rely on dense attention computations, which introduce redundancy in long-sequence motion prediction. In contrast, our work introduces a PEA mechanism that simultaneously models joint importance and key-frame localization through dual-branch processing, enabling efficient fine-grained feature selection. Furthermore, we address the computational bottlenecks of traditional multi-head attention by proposing STSSA. This method leverages adaptive sparsification and single-head compression to reduce redundancy while preserving essential motion dynamics. By integrating these innovations into a diffusion framework, our approach achieves an optimal balance between prediction diversity and fidelity, and real-time inference efficiency. These advancements differentiate our work from prior attention-based motion analysis approaches.
3. Methodology
3.1. Problem Definition and Notations
We note that the complete coordinate sequence of human motion can be expressed as , where the motion data for the first time steps represent the observed historical data, and the motion data for the subsequent time steps denote the future motion data to be predicted. As well, denotes the Cartesian coordinates of the human skeleton at this point, and denotes the number of human joints. The goal of the human motion prediction problem, given the observed human motion sequences , is to predict the motion sequences in the future time steps. The work [26] proposes using the discrete cosine transform because it is beneficial in obtaining continuous motion, which we adopt, and denote as the result after the DCT of .
3.2. Transformer-Based Diffusion Model
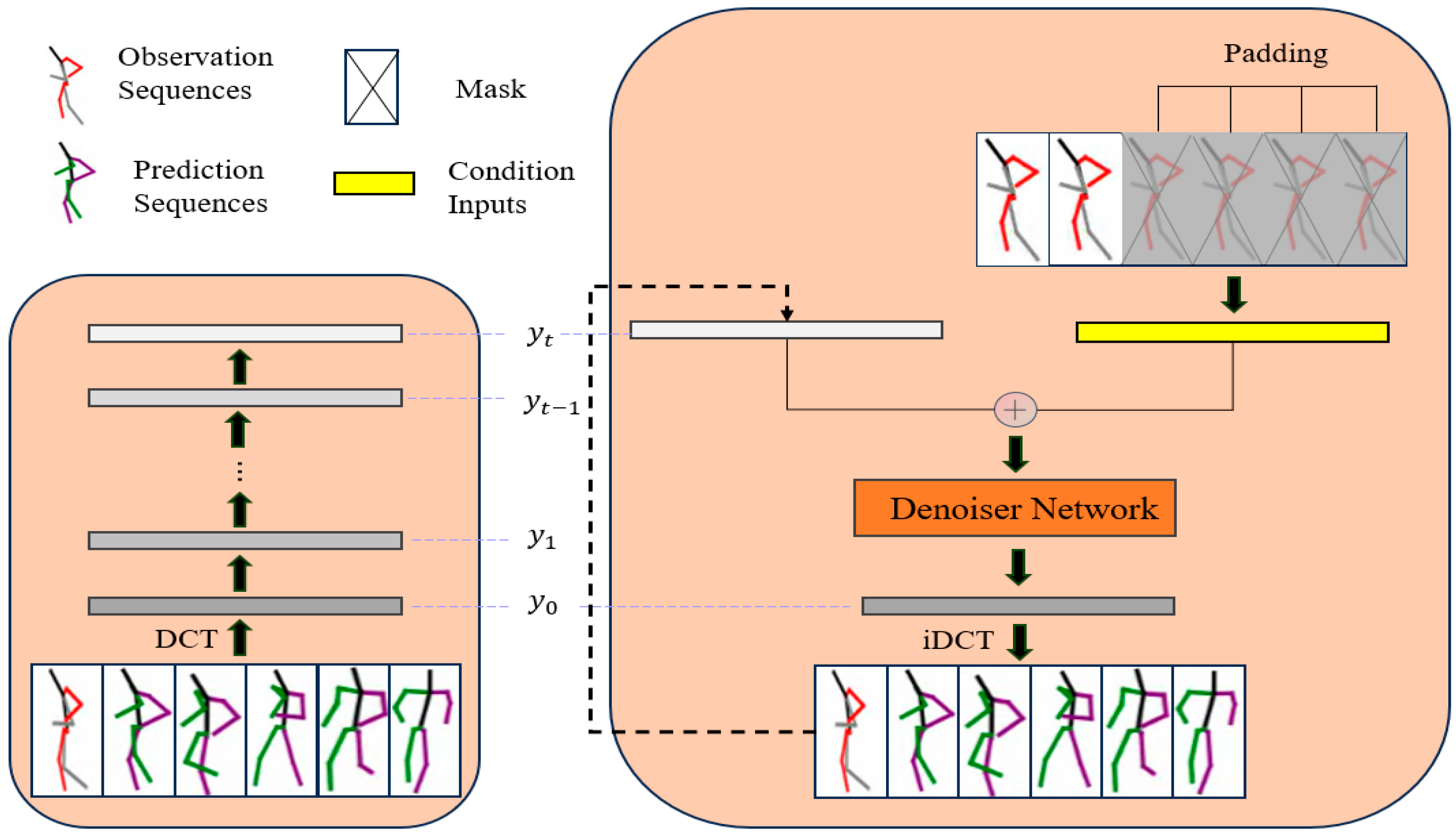
In our work, the diffusion model is used to process the frequency domain representation of the human motion data, and the overall flow of generation using the trained model is shown in Figure 1. In the forward process, the input motion data is first DCT varied so that it is projected into the frequency domain = DCT() = Dx, D ∈ R(H+F)×(H+F), where D is the bias of . Also, since the DCT operation is an orthogonal transformation, we can recover the original motion sequence from the frequency coefficient by applying the inverse discrete cosine transform (idct), = IDCT() = DT. We note that the important joint information of human motion is mainly retained in the low frequencies, while the high frequencies contain more irrelevant noise information. Therefore, we retain only the first L rows of D and discard the remaining rows, effectively reducing the dimensionality of the data. Subsequently, we apply the reparameterization trick to sample the noisy DCT coefficients at any diffusion step . Let be the original DCT coefficients and be the coefficients at the time step, where the noise gradually increases with time step .
where , is a predefined variance and parameter, N (0,I).
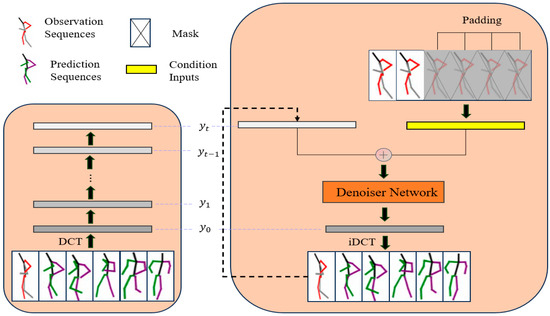
Figure 1.
An overview of the modeling approach. The proposed method consists of a training process (left) and an inference process (right). In the inference phase, the observed sequence (filled) is summed with the sequence generated by the diffusion model to generate the complete observed sequence. The gray-filled area represents the occluded part of the input sequence.
By controlling the increase in noise, we can simulate a gradual transition from clear motion data to completely random noise. The backward process, on the other hand, learns the gradual recovery of motion data from random noise through a neural network model, which is essentially a denoising process. To improve the effectiveness of the denoising process, we incorporate temporal embeddings, positional codings, and historical information at each diffusion step to capture the temporal and spatial information of the motion data. Meanwhile, we adopt the strategy from TransFusion, where we reduce the computational complexity by summing the historical information and the encoded diffusion time step before entering the denoising network. Finally, we optimize the parameter using the noise prediction loss formula as follows:
Finally, we recover the denoised DCT coefficients as motion data in the time domain by using an inverse DCT transform to generate high-quality future human motion sequences.
3.3. Model Structure
In the backward denoising process of noise prediction for human motion prediction, we replaced the use of the U-Net structure in DDPM with transformer-based architecture by a TransFusion design based on HumanMAC, and represented it with . The specific structure is shown in Figure 2.
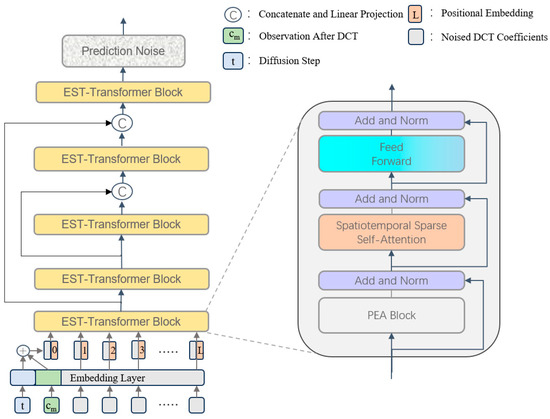
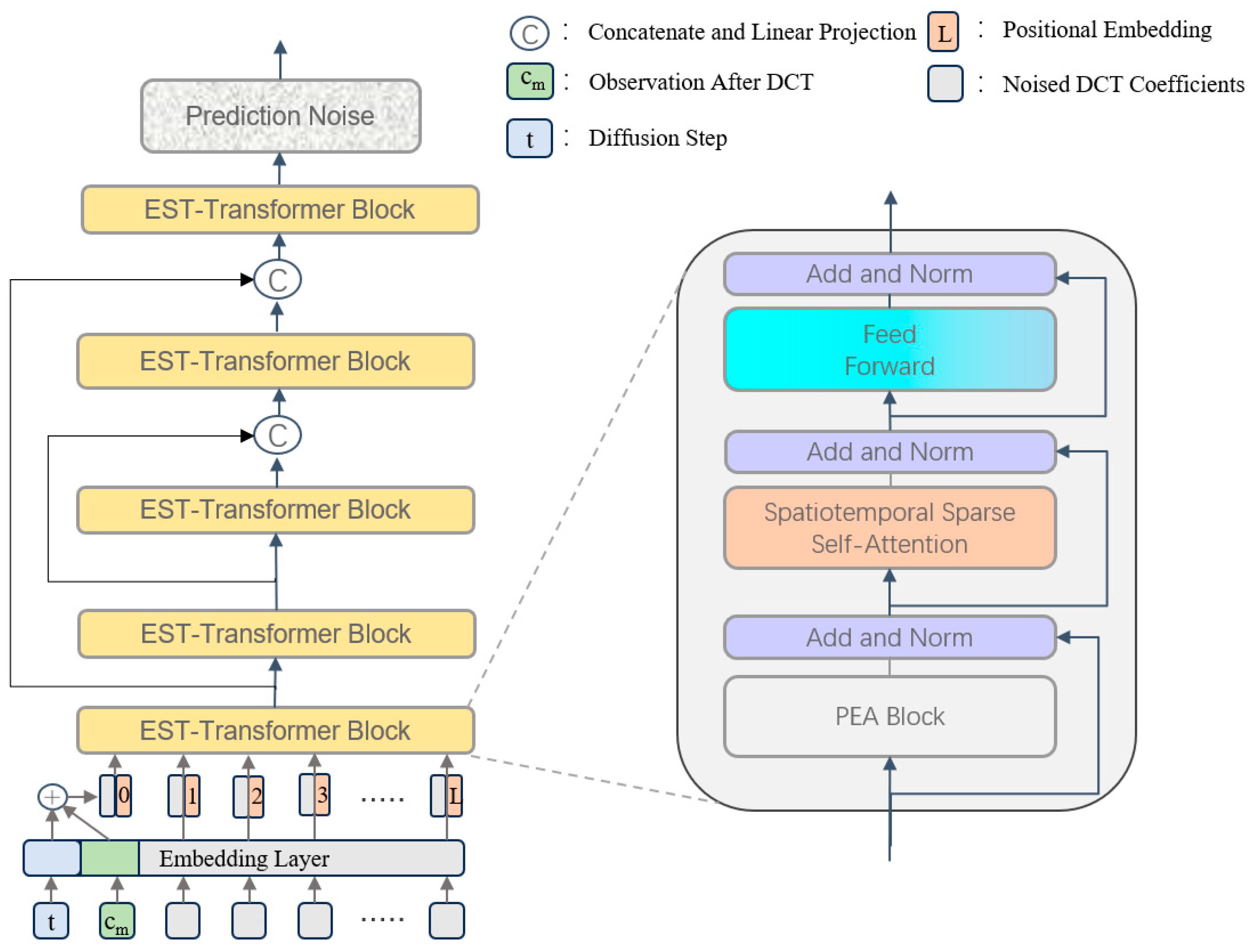
Figure 2.
Architecture of the denoising network. The noise prediction network consists of several EST-transformer modules. At each diffusion step t, tokens are embedded and combined in conjunction with historical information. These tokens are then processed through the EST-transformer modules along with the positional embeddings to obtain the predicted noise for a given input.
We generated predictions by capturing information on the noise distribution in the training phase; however, since this approach does not incorporate the observed human pose information, we decided to adopt conditional DDPM to generate human pose sequences and accelerate them with DDIM. Specifically, we fill in the sequence length of the observation sequence xO by end replication to make it match the normal motion sequence—and let it go through the processing of the DCT operator to get the compact history information cm that we need—and then let it and the diffusion step encoding t construct the spatiotemporal conditional vector by direct addition, which, together with the noisy DCT coefficients, form the token sequence input denoising network. Meanwhile, to address the computational efficiency bottleneck and insufficient feature fusion in the original framework, we propose an improved efficient spatiotemporal transformer (EST-transformer) architecture. The denoising network consists of multiple EST-transformer layers and introduces long jump connections between the shallow and deep layers. Each EST-transformer layer contains a PEA module, a STSSA module, and a feedforward neural network.
3.3.1. PEA
Existing studies have shown that there are two major problems with the traditional channel attention mechanism in modeling time-series data: Firstly, the lack of spatial information—the traditional method only focuses on the weights of the channel dimensions and ignores the spatiotemporal positional information of the keyframes in the motion sequences. Secondly, the receptive field is limited—the fixed-scale feature pooling fails to adapt to dynamic human motion patterns [19,27].
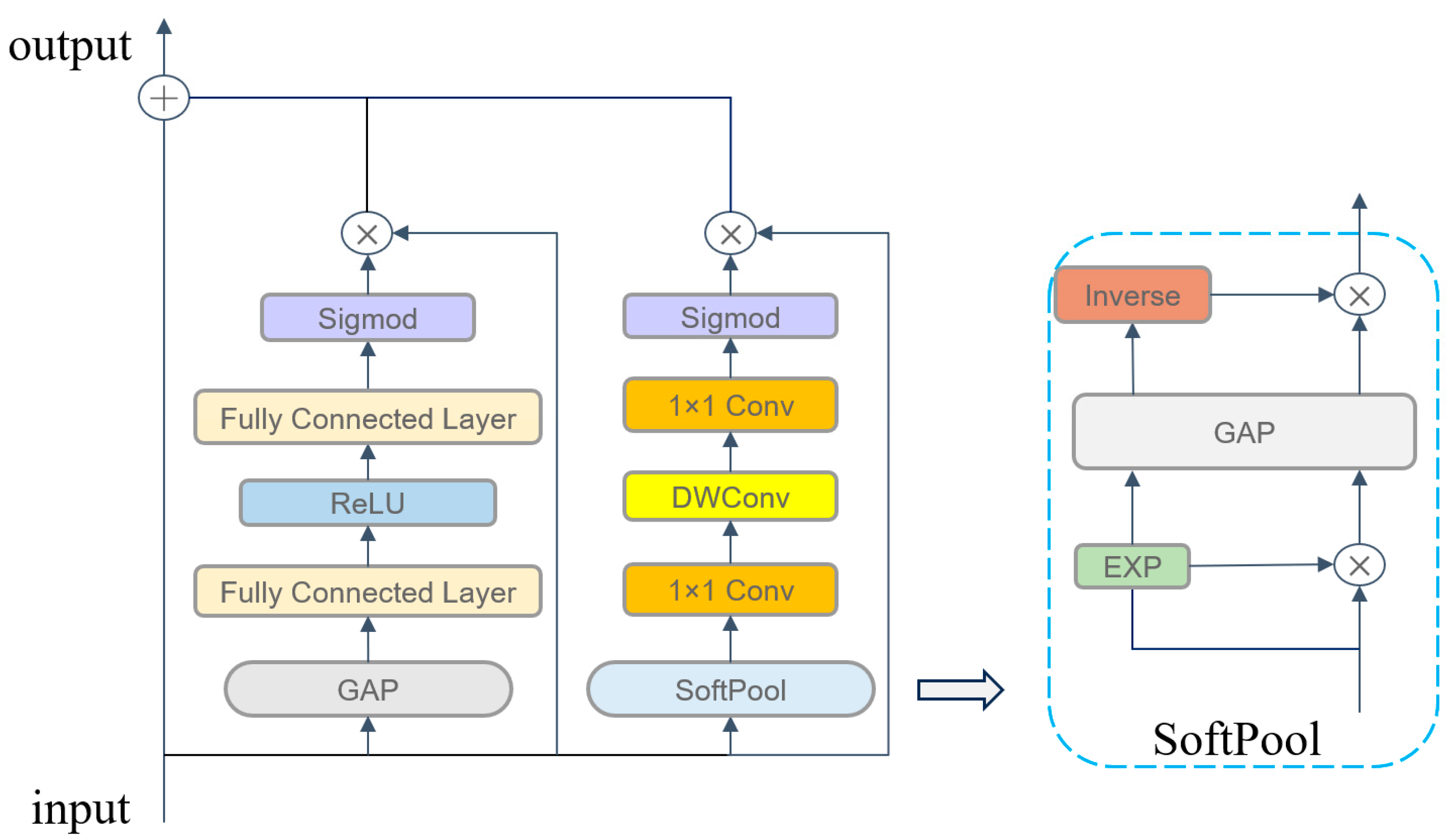
Based on this, we propose a PEA mechanism to enhance the characterization of dynamic features of the model joints and enhance the model’s ability to capture key frames; the specific structure is shown in Figure 3. For channel attention, we employ the classic squeeze-and-excitation (SE) module, which can explicitly model the dependencies between channels and is very lightweight. For temporal dimension feature extraction, we designed a spatiotemporal attention branch that includes soft pooling [28] and dynamic convolution: Firstly, we use exponentially weighted soft pooling instead of maximal pooling. This approach reduces information loss while preserving peak features. The learnable parameter β is initialized to 1, and the spatial features of the keyframes are reinforced through exponential weighting.
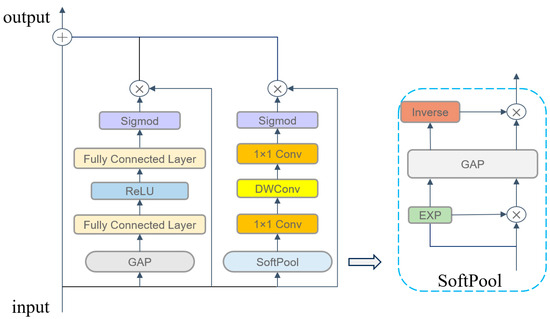
Figure 3.
The structure of parallel enhanced attention (PEA).
Secondly, a dynamic scaling mechanism for constructing depthwise, separable convolutional kernels with kernel sizes that follow an incremental rule of k = 11 + 2n (where n is the number of network layers) so that the shallow network captures fine action patterns and the deep network integrates global motion trends.
3.3.2. STSSA
In the original self-attention layer, we redesigned the structure to align with temporal data characteristics. To balance spatiotemporal dependency modeling and computational efficiency for human motion prediction, this paper proposes the STSSA mechanism. The STSSA achieves efficient modeling through the synergistic design of single-head compression architecture and adaptive sparsification [29], as shown in Figure 4.
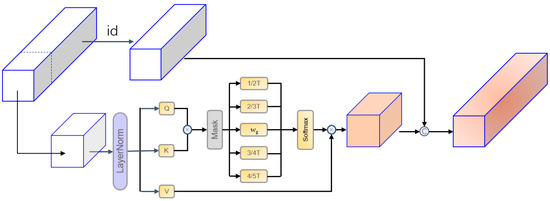
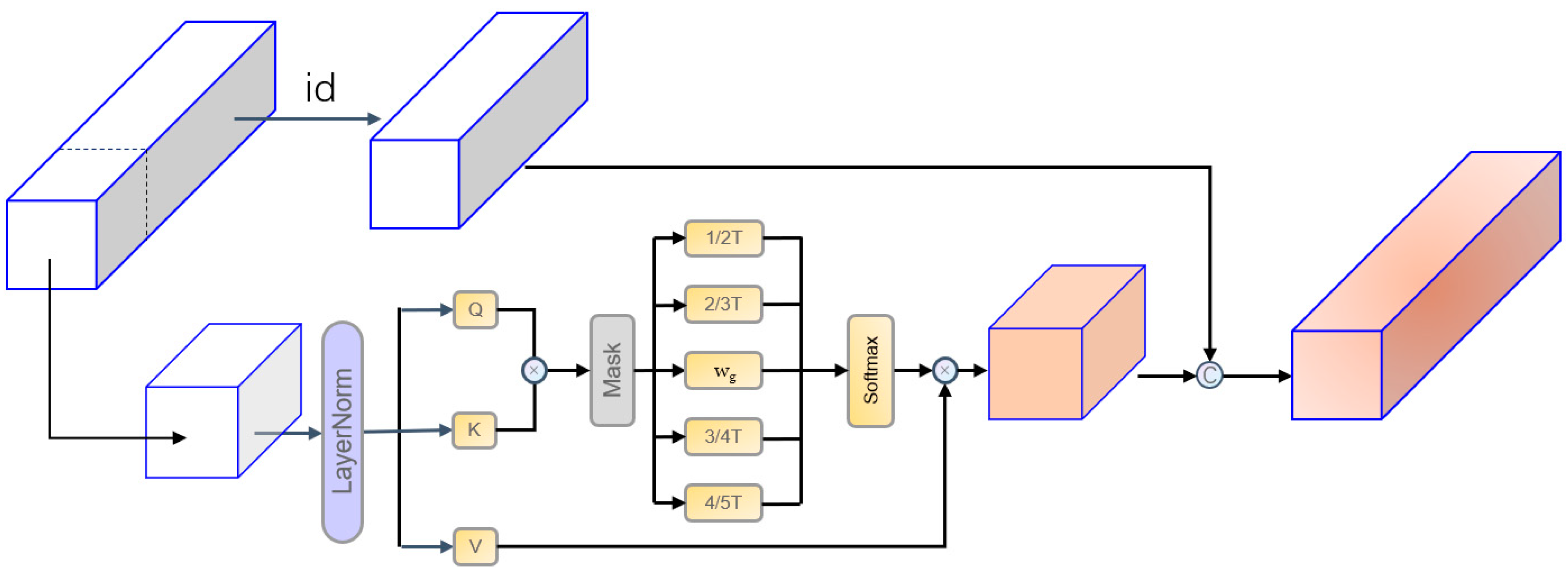
Figure 4.
Structure of a spatiotemporal sparse self-attention (STSSA); id refers to the portion of the original inputs that remains after the channel-wise segmentation.
Traditional methods for sequential motion frames face two key limitations. First, the multi-head attention mechanism generates redundant temporal computations, significantly increasing memory overhead. This is particularly pronounced when processing extensive video sequences, as the QK computations executed independently by multiple heads result in the redundant modeling of motion joint points, leading to a significant wastage of computational resources. Furthermore, the fixed sparse model is difficult to adapt to the dynamic characteristics of human motion, and in the fast motion phase, this model is prone to losing correlation information between keyframes, thus affecting the complete understanding of the pose sequence. To overcome the aforementioned problems, the STSSA adopts a channel decoupling strategy to divide the feature stream into a dynamic attention area and a static memory area. The dynamic attention region is responsible for the efficient capture of cross-frame joint motion patterns through lightweight single-head QK compression computations, while the static memory region is responsible for maintaining the continuity of the pose basis vector representation.
To enhance the model’s capacity to adapt to dynamic changes, STSSA proposes a multi-scale sparse gating mechanism. This mechanism initially generates a base attention mask, utilizing a learnable sparsity parameter to dynamically regulate the number of associated nodes at each moment. The model incorporates four parallel mask branches with predefined sparsity ratios (1/2T, 2/3T, 3/4T, 4/5T) to achieve multi-scale fusion through adaptive weighting driven by the mean of the temporal features. This design enables the model to accurately capture both short-time joint micro-movements and long-time behavioral patterns, which significantly improves the processing of continuous frame pose sequences. However, it was observed that sparse self-attention was susceptible to violating normal human motion posture during the late stage of long-time prediction. To address this issue, human kinematic constraints were incorporated into the late stage of the time-series prediction. This ensured the stability and accuracy of the final posture of the model.
3.3.3. Historical Information Guiding Mechanisms
In the inference stage, we introduce a noise observation bootstrap mechanism that leverages historical motion information at the beginning of each denoising step. This is formulated as follows:
Specifically, the trained DDPM generates an initial prediction, after which the observed human motions are encoded with DCT. The missing parts are then filled in by adding noise. Using the invertibility of DCT, we perform the inverse DCT (iDCT) on both the DDPM prediction and the noise spectrum generated by the observed motion data xO. These components are then mixed together by a masking operation, where the mask M is defined as M = [1, 1, …, 1, 0, 0, …0]. The first H elements of the mask M are set to 1 to represent the noisy observation and the remaining elements are set to 0 to represent the denoised motion. Finally, the final motion sequence prediction is generated using this mixed data. The workflow of the proposed model training and inference is delineated in Algorithms 1 and 2.
| Algorithm 1: Training Procedure |
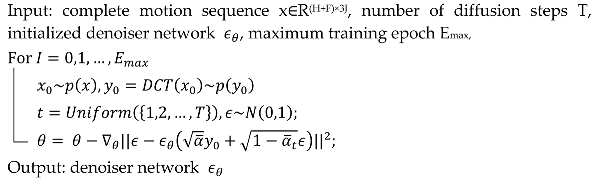 |
| Algorithm 2: Inference Procedure |
 |
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Datasets and Evaluation Metrics
(1) Datasets: The evaluation of the model was conducted on three benchmark datasets: Human3.6M [30], HumanEva-I [31], and AMASS [32].
Human3.6M is a widely utilized 3D human motion dataset that contains 17 body key points derived from recordings of five daily activities from 11 professional actors who were recorded at 50 Hz. To ensure a fair comparison with existing work, we followed the dataset partitioning approach that has been widely used in previous studies [12]. In our experiments, we utilized a 25-frame (0.5 s) observation window to predict the subsequent 100 frames (2 s) of the human gesture sequence.
HumanEva-I is a comparatively limited human gesture dataset, comprising movement data from three subjects recorded at a substantially higher frequency of 60 Hz. The data from each subject contained 15 body key points. In our experiments, we utilized 15 frames (0.25 s) as the observation window to predict the human motion sequence for the subsequent 60 frames (1 s).
AMASS is a large-scale and diverse motion capture dataset that includes data from 344 subjects with various body sizes and motion styles, covering a wide range of scenarios, from daily activities to complex movements. Rather than being a single homogeneous dataset, AMASS unifies over 15 publicly available motion capture datasets (e.g., CMU, HDM05, BMLmovi) using the MoSh++ framework (a model designed by the authors of the AMASS dataset, available at https://amass.is.tue.mpg.de/, accessed on 5 March 2025), resulting in significant variability in motion types, capture conditions, and subject demographics across its sub-datasets. To evaluate the generalization ability of the model, we adopted a cross-sub-dataset validation strategy, where the training (eleven sub-datasets), validation (four sub-datasets), and test sets (seven sub-datasets) come from different source datasets within AMASS. This design mimics a cross-dataset setting while ensuring compatibility in skeleton structure and annotation format. In our experiments, the model uses 30 frames (0.5 s) as the observation input window and predicts the subsequent 120 frames (2 s) of motion sequences.
(2) Evaluation metrics: To comprehensively evaluate the performance of our model, following previous work, we employ five key metrics for quantitative analysis [15]. (1) Average pairwise distance (APD) is the L2 distance between all motion examples. (2) Average displacement error (ADE) is defined as the average L2 distance between the ground truth and the predicted motions and thus serves as a metric to evaluate the accuracy of the entire sequence. (3) Final displacement error (FDE) is the L2 distance between the prediction and the ground truth in the last prediction frame. (4) MMADE is a multimodal version of ADE, where the average of the ADEs is computed over all the predictions instead of selecting only the best one. (5) Similarly, MMFDE is a multimodal version of FDE.
4.2. Baselines
To evaluate the validity of the proposed model, a full-scale comparison was performed with several state-of-the-art models, including DeLIGAN [11], DLOW [12], DivSamp [5], BoM [33], DSF [34], MOJO [35], GSPS [10], Motron [27], MotionDiff [20], HumanMAC [17], and TransFusion [23]. Detailed results are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Model results for multiple metrics on Human3.6M, HumanEva-I, and AMASS.
4.3. Mathematical Model Validation
To validate the effectiveness of the proposed mathematical model, we conducted comprehensive experimental setups and analyses. Specifically, the model was trained for 1500 epochs on the Human3.6M dataset, 100 epochs on the HumanEva-I dataset, and 3200 epochs on the AMASS dataset. During training, a dropout rate of 0.2 was used, and the initial learning rate was set to 3 × 10−4. For the noise prediction network, different numbers of EST-transformer blocks were used for each dataset: seven layers for Human3.6M, five layers for HumanEva-I, and eleven layers for AMASS. Additionally, the first 20 DCT coefficients were used for all datasets, and the hidden state dimension was set to 512, as is customary. All experiments were performed using the PyTorch (1.8.1) framework, with training conducted on A800 GPUs, and the Adam optimizer was employed.
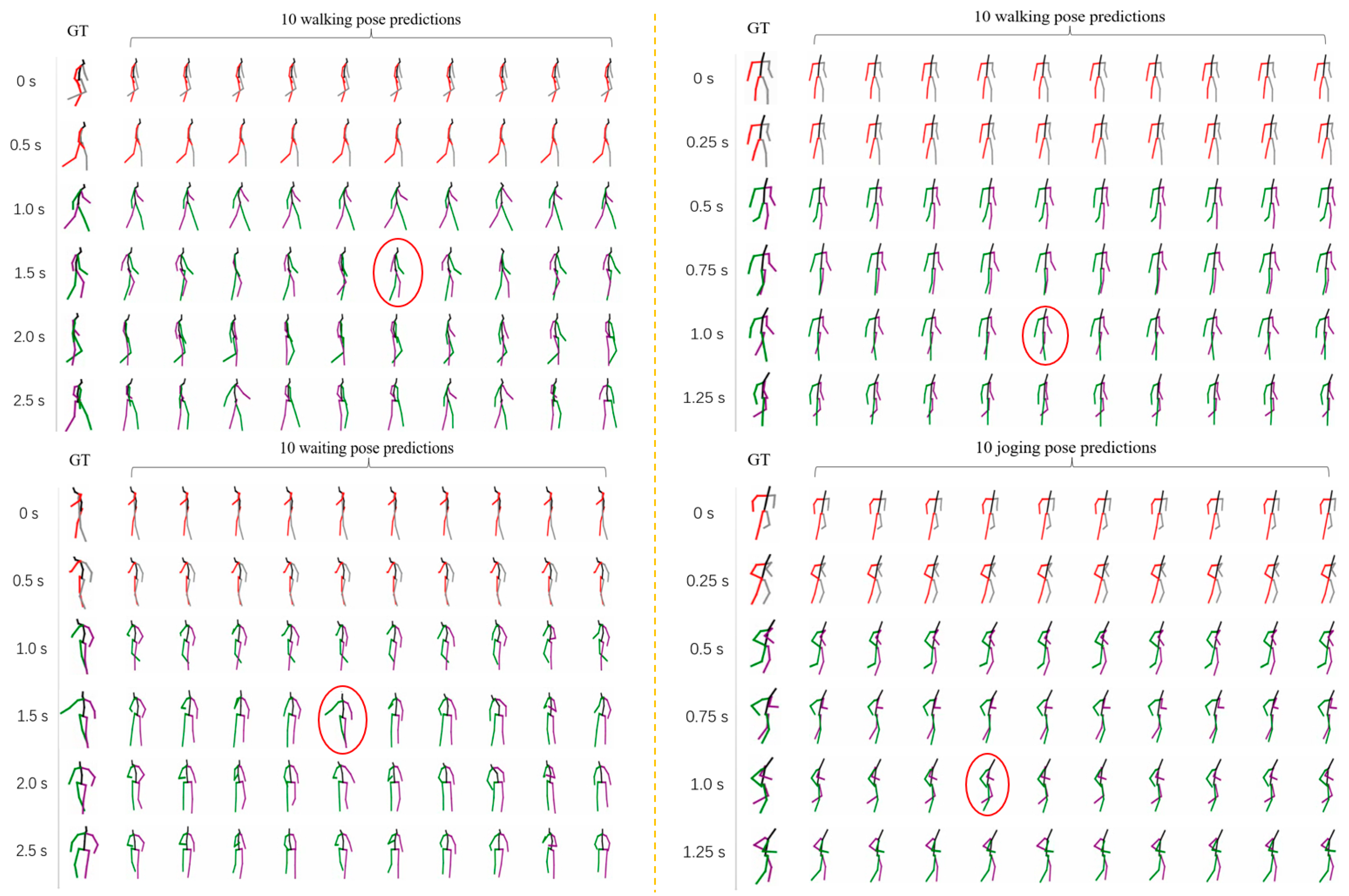
To quantify the consistency between the model’s predictions and the experimental data, we assessed the model’s performance by comparing the predicted results with the ground truth data. For example, in the Human3.6M dataset, key frames of the actions were marked (indicated by red circles), providing a clear visual representation that the predicted values closely align with the ground truth, as shown in Figure 5. This demonstrates the model’s ability to generate high-quality predictions and further confirms the accuracy of its mathematical framework. In addition, quantitative metrics, such as ADE and FDE, were employed to further demonstrate the model’s proximity to the ground truth data.
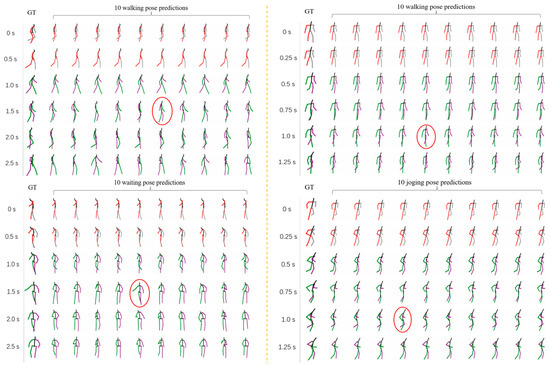
Figure 5.
Visualization results. The example movements for the Human3.6M dataset (left) are walking and waiting, whereas the example movements for the Humaneva-I dataset (right) are walking and running.
Furthermore, we compared additional performance metrics, such as the number of parameters and inference time, to demonstrate that the model achieves high accuracy while offering significant efficiency improvements. These experimental results provide a thorough validation of the proposed mathematical model, highlighting its effectiveness and advantages across different scenarios. These findings not only reinforce the model’s hypotheses but also offer strong evidence of its potential for practical applications.
4.4. Comparison with State-of-the-Art Models and Discussion
Our experimental results, as shown in Table 1, demonstrate that our model achieves the best performance in terms of FDE on both the AMASS and HumanEva-I datasets. Additionally, on the AMASS dataset, we obtain the lowest errors for MMADE, MMFDE, and FDE, indicating that our model excels in accurately predicting the final positions of future motion. While we do not achieve the best results on APD, it is important to note that a higher APD does not necessarily correlate with better model performance [26]. Excessively high APD often leads to generating motions that deviate significantly from expected trajectories, sometimes even violating fundamental human anatomical constraints. Our model on the Human3.6M dataset achieves a good balance between diversity and stability of predictions; we have marked the keyframes of the actions with red circles, and we can see that we are very close to the true values. The quality of the generated predictions can be seen in Figure 5.
In addition, our model achieves a significant improvement in computational complexity compared to HumanMAC. Compared to HumanMAC, the parameter quantity is reduced by 62.3% and the inference time is reduced by 67.6%. When comparing with the optimal model TransFusion, we reduced the number of parameters by 45.7% and the inference time by 63.0%, and our model is comparable with TransFusion, or even better, in several metrics on multiple datasets, as shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Comparison of the number of parameters and inference speeds of the models on the Human3.6M dataset.
4.5. Ablation Experiment
To comprehensively assess the effectiveness of our proposed modules, we conducted a series of ablation experiments, with the results summarized in Table 3. In these experiments, we adopt the original HumanMAC model as the baseline and systematically evaluate the contributions of our proposed PED and STSSA modules, as well as the effects of removing the dynamic and static attention areas in the sparse self-attention (SSA) design.

Table 3.
Comparison of different methods of combining modules under quantitative conditions.
Adding the PED module to the baseline (baseline + PED) leads to consistent improvements across most evaluation metrics. Compared to the baseline, it reduces ADE, FDE, MMADE, and MMFDE, with ADE decreasing from 0.369 to 0.362 on Human3.6M and from 0.511 to 0.505 on AMASS. These results indicate that PED effectively captures temporal dependencies, enabling more accurate motion trajectory prediction. The slight decrease in APD suggests a minor reduction in motion diversity; however, this trade-off enhances overall motion consistency, reinforcing the importance of PED in improving the continuity and robustness of human motion prediction.
Replacing the original self-attention mechanism with STSSA (baseline + STSSA) results in minor fluctuations in APD, ADE, and MMADE, while significantly optimizing FDE and MMFDE, along with a threefold improvement in inference speed. On Human3.6M, FDE is reduced from 0.480 to 0.472, and on AMASS, from 0.554 to 0.551. These improvements suggest that STSSA enhances endpoint precision by prioritizing keyframes and mitigating redundant attention computations. Additionally, its sparsification strategy and single-head compression substantially reduce computational overhead, demonstrating its practical advantages for real-time motion prediction.
To further examine the role of dynamic and static memory areas in SSA, we conducted an additional experiment by removing this design entirely (baseline + SSA). The results show a notable decline in performance across all metrics, particularly with ADE increasing from 0.371 to 0.385 and FDE rising from 0.472 to 0.494 on Human3.6M, as well as ADE increasing from 0.531 to 0.557 and FDE from 0.551 to 0.576 on AMASS. These findings highlight the effectiveness of the dynamic attention area in capturing temporal correlations, while the static memory retains non-time-sensitive information. The absence of this mechanism disrupts temporal consistency, leading to reduced accuracy in long-term motion prediction.
We also conducted a combined test by adding PED on top of SSA (baseline + SSA + PED) to further validate the individual and joint contributions of both components. Compared to using SSA alone, introducing PED helped recover a considerable portion of the lost performance, reducing ADE from 0.385 to 0.372 and FDE from 0.494 to 0.481 on Human3.6M, and lowering ADE from 0.557 to 0.533 and FDE from 0.576 to 0.562 on AMASS. This result reaffirms PED’s role in enhancing temporal modeling, and demonstrates its complementary effect when paired with SSA.
Although our model does not achieve the best performance on every individual metric, the full model (PEA-STDiff) demonstrates a balanced trade-off between prediction accuracy, computational efficiency, and generalization capability. The observed improvements in inference speed and FDE suggest that our design effectively prioritizes critical motion features while maintaining a lightweight computational cost, making it particularly well-suited for real-time motion prediction applications.
5. Conclusions
This paper presents PEA-STDiff, a lightweight diffusion model integrating the PEA and STSSA mechanisms for efficient yet accurate 3D human motion prediction. The PEA module, employing a dual-branch channel-temporal architecture, dynamically perceives key joints and essential motion frames while leveraging soft pooling and depthwise separable convolutions to enhance multi-scale spatiotemporal feature extraction. The STSSA module reduces the redundant computations of traditional multi-head attention through adaptive sparsification and a single-head compression design, significantly improving inference efficiency while maintaining prediction accuracy.
Experimental results demonstrate that on the Human3.6M dataset, PEA-STDiff achieves an FDE of 0.470, comparable to the state-of-the-art diffusion model TransFusion (0.468), while reducing the parameter count by 45.7% and accelerating the per-sample inference time from 1.1 s to 0.4 s. On the AMASS dataset, our model achieves the best performance across three key metrics: MMADE, FDE, and MMFDE. The lightweight design and end-to-end framework enable PEA-STDiff to balance prediction diversity, fidelity, and real-time requirements.
Future work will focus on optimizing dynamic sparse mask generation strategies to further enhance the physical plausibility of long-term motion prediction. While our model has demonstrated strong performance on benchmark datasets, we recognize that real-world deployment presents additional challenges beyond the current scope. In particular, an end-to-end system would require integrating monocular 3D pose estimation. To address this, we plan to extend our framework by incorporating reliable pose estimation pipelines and alignment strategies, allowing our method to process video input from unconstrained environments more robustly, and effectively evaluate generalization performance under practical conditions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.H.; methodology, L.H.; software, M.J.; validation, M.J. and L.H.; formal analysis, M.J.; investigation, M.J.; resources, L.H.; data curation, M.J.; writing—original draft preparation, M.J.; writing—review and editing, M.J.; visualization, M.J.; supervision, L.H.; project administration, L.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in this article; further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zheng, W.; Song, R.; Guo, X.; Zhang, C.; Chen, L. Genad: Generative end-to-end autonomous driving. In European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV); Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; pp. 87–104. [Google Scholar]
- Bajcsy, A.; Siththaranjan, A.; Tomlin, C.J.; Dragan, A.D. Analyzing Human Models That Adapt Online. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Xi’an, China, 30 May–5 June 2021; pp. 2754–2760. [Google Scholar]
- Luber, M.; Stork, J.A.; Tipaldi, G.D.; Arras, K.O. People Tracking with Human Motion Predictions from Social Forces. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, Anchorage, AK, USA, 3–7 May 2010; pp. 464–469. [Google Scholar]
- Adeli, V.; Ehsanpour, M.; Reid, I.; Niebles, J.C.; Savarese, S.; Adeli, E.; Rezatofighi, H. Tripod: Human trajectory and pose dynamics forecasting in the wild. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 13390–13400. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, L.; Nie, Y.; Long, C.; Zhang, Q.; Li, G. Diverse Human Motion Prediction via Gumbel-Softmax Sampling from an Auxiliary Space. In Proceedings of the ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Lisboa, Portugal, 10–14 October 2022; pp. 5162–5171. [Google Scholar]
- Bouazizi, A.; Holzbock, A.; Kressel, U.; Dietmayer, K.; Belagiannis, V. Motionmixer: Mlp-based 3D human body pose forecasting. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2207.00499. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Z.; Jin, M.; Nie, H.; Shen, J.; Dong, A.; Zhang, Q. Towards Realistic Human Motion Prediction with Latent Diffusion and Physics-Based Models. Electronics 2025, 14, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Yoo, H.; Ryu, J.-H.; Lee, S.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, J. TransSMPL: Efficient Human Pose Estimation with Pruned and Quantized Transformer Networks. Electronics 2024, 13, 4980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barquero, G.; Escalera, S.; Palmero, C. BeLFusion: Latent Diffusion for Behavior-Driven Human Motion Prediction. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 2317–2327. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, W.; Liu, M.; Salzmann, M. Generating Smooth Pose Sequences for Diverse Human Motion Prediction. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 13309–13318. [Google Scholar]
- Gurumurthy, S.; Sarvadevabhatla, K.R.; Babu, V.R. DeLiGAN: Generative Adversarial Networks for Diverse and Limited Data. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 166–174. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Kitani, K. DLow: Diversifying Latent Flows for Diverse Human Motion Prediction. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Glasgow, UK, 23–28 August 2020; pp. 346–364. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, J.; Jain, A.; Abbeel, P. Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Virtual, 6–12 December 2020; Volume 33, pp. 6840–6851. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.; Zhou, Y.; Bao, F.; Chen, J.; Li, C.; Zhu, J. Dpm-solver: A fast ode solver for diffusion probabilistic model sampling in around 10 steps. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 5775–5787. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.; Zhou, Y.; Bao, F.; Chen, J.; Li, C.; Zhu, J. DPM-Solver++: Fast Solver for Guided Sampling of Diffusion Probabilistic Models. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2211.01095. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, X.; Zeng, A.; Zhao, C.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L.; Xu, Q. Humansd: A native skeleton-guided diffusion model for human image generation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 15988–15998. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.H.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Pang, Y.; Xia, X.; Liu, T. Humanmac: Masked motion completion for human motion prediction. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 2–6 October 2023; pp. 9544–9555. [Google Scholar]
- Blattmann, A.; Milbich, T.; Dorkenwald, M.; Ommer, B. Behavior-Driven Synthesis of Human Dynamics. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 12231–12241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Wang, Y.-X.; Gui, L.-Y. Diverse Human Motion Prediction Guided by Multi-Level Spatial-Temporal Anchors. In Proceedings of the Lecture Notes in Computer Science, Computer Vision (ECCV), Tel Aviv, Israel, 23–27 October 2022; pp. 251–269. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, D.; Sun, H.; Li, B.; Lu, J.; Li, W.; Sun, X.; Hu, S. Human Joint Kinematics Diffusion-Refinement for Stochastic Motion Prediction. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 25 February–4 March 2023; Volume 37, pp. 6110–6118. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, C.; Zhu, S.; Mendieta, M.; Yang, T.; Chen, C.; Ding, Z. 3D Human Pose Estimation with Spatial and Temporal Transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Montreal, QC, Canada, 10–17 October 2021; pp. 11636–11645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadatnejad, S.; Rasekh, A.; Mofayezi, M.; Medghalchi, Y.; Rajabzadeh, S.; Mordan, T.; Alahi, A. A generic diffusion-based approach for 3D human pose prediction in the wild. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), London, UK, 29 May–2 June 2023; pp. 8246–8253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, S.; Zheng, M.; Liang, X. TransFusion: A Practical and Effective Transformer-Based Diffusion Model for 3D Human Motion Prediction. IEEE Robot. Autom. Lett. 2024, 9, 6232–6239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Zhou, W.; Stawarz, K.; Corcoran, P.; Chen, Y.; Liu, H. Adaptive Spatiotemporal Graph Transformer Network for Action Quality Assessment. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2025. Early Access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Wang, Z. TCN-attention-HAR: Human activity recognition based on attention mechanism time convolutional network. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 7414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, W.; Liu, M.; Salzmann, M.; Li, H. Learning Trajectory Dependencies for Human Motion Prediction. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 9489–9497. [Google Scholar]
- Salzmann, T.; Pavone, M.; Ryll, M. Motron: Multimodal probabilistic human motion forecasting. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 6457–6466. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, G.; Liu, X. PlainUSR: Chasing Faster ConvNet for Efficient Super-Resolution. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2409.13435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Zhou, P.; Yan, S.; Wang, X. InceptionNeXt: When Inception Meets ConvNeXt. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 16–22 June 2024; pp. 5672–5683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ionescu, C.; Papava, D.; Olaru, V.; Sminchisescu, C. Human3. 6m: Large scale datasets and predictive methods for 3D human sensing in natural environments. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2013, 36, 1325–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigal, L.; Balan, A.O.; Black, M.J. Humaneva: Synchronized video and motion capture dataset and baseline algorithm for evaluation of articulated human motion. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2010, 87, 4–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, N.; Ghorbani, N.; Troje, N.F.; Pons-Moll, G.; Black, M.J. AMASS: Archive of motion capture as surface shapes. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic of Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 5442–5451. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharyya, A.; Schiele, B.; Fritz, M. Accurate and Diverse Sampling of Sequences Based on a “Best of Many” Sample Objective. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 8485–8493. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Kitani, K. Diverse Trajectory Forecasting with Determinantal Point Processes. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1907.04967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Black, M.J.; Tang, S. We Are More Than Our Joints: Predicting How 3D Bodies Move. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 3372–3382. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).