Simple Torque Control Method for Hybrid Stepper Motors Implemented in FPGA
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
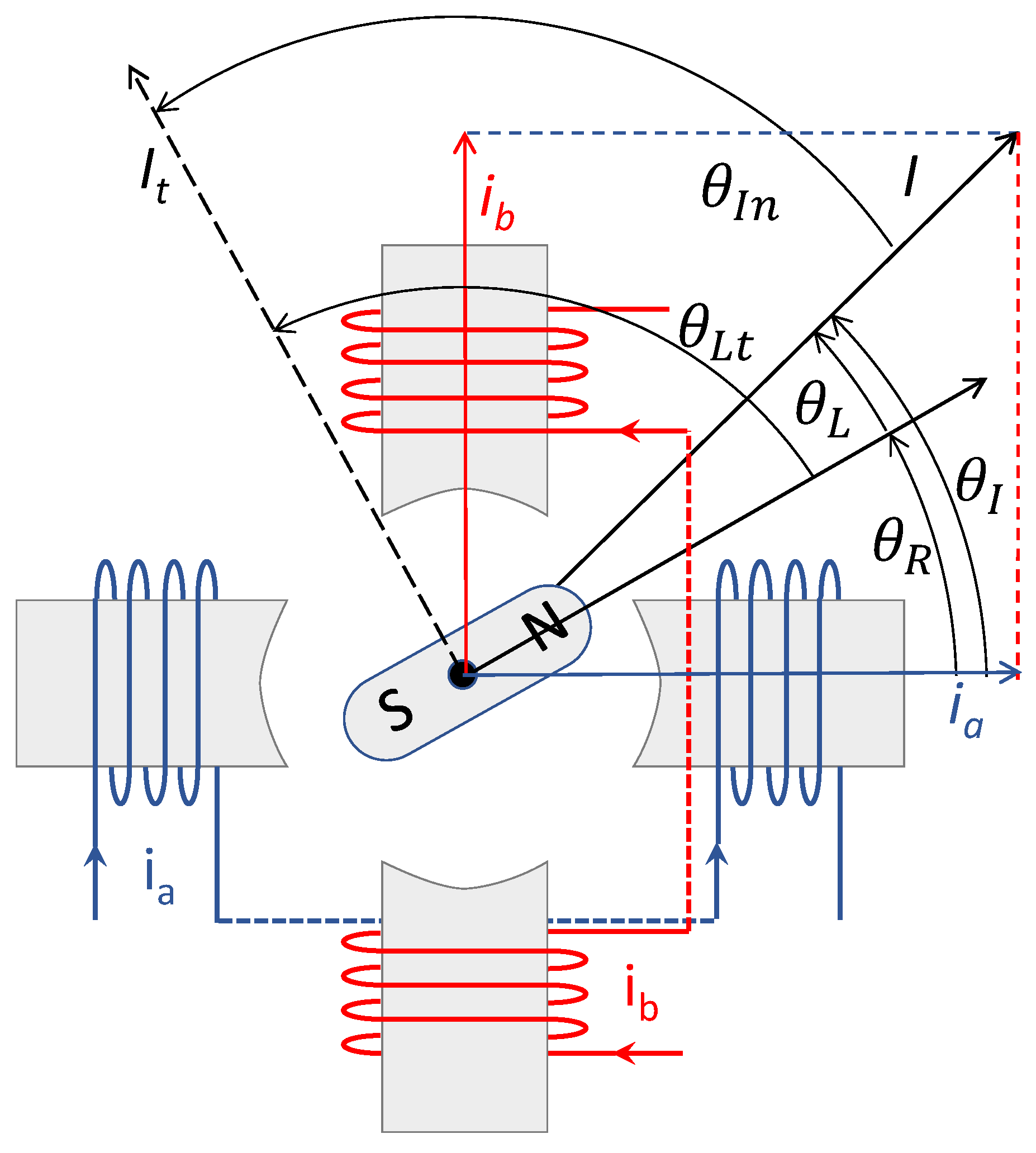
2.1. Torque Generation and Step Movement
2.2. Torque Modulation
3. Method Implementation
3.1. The Electronics
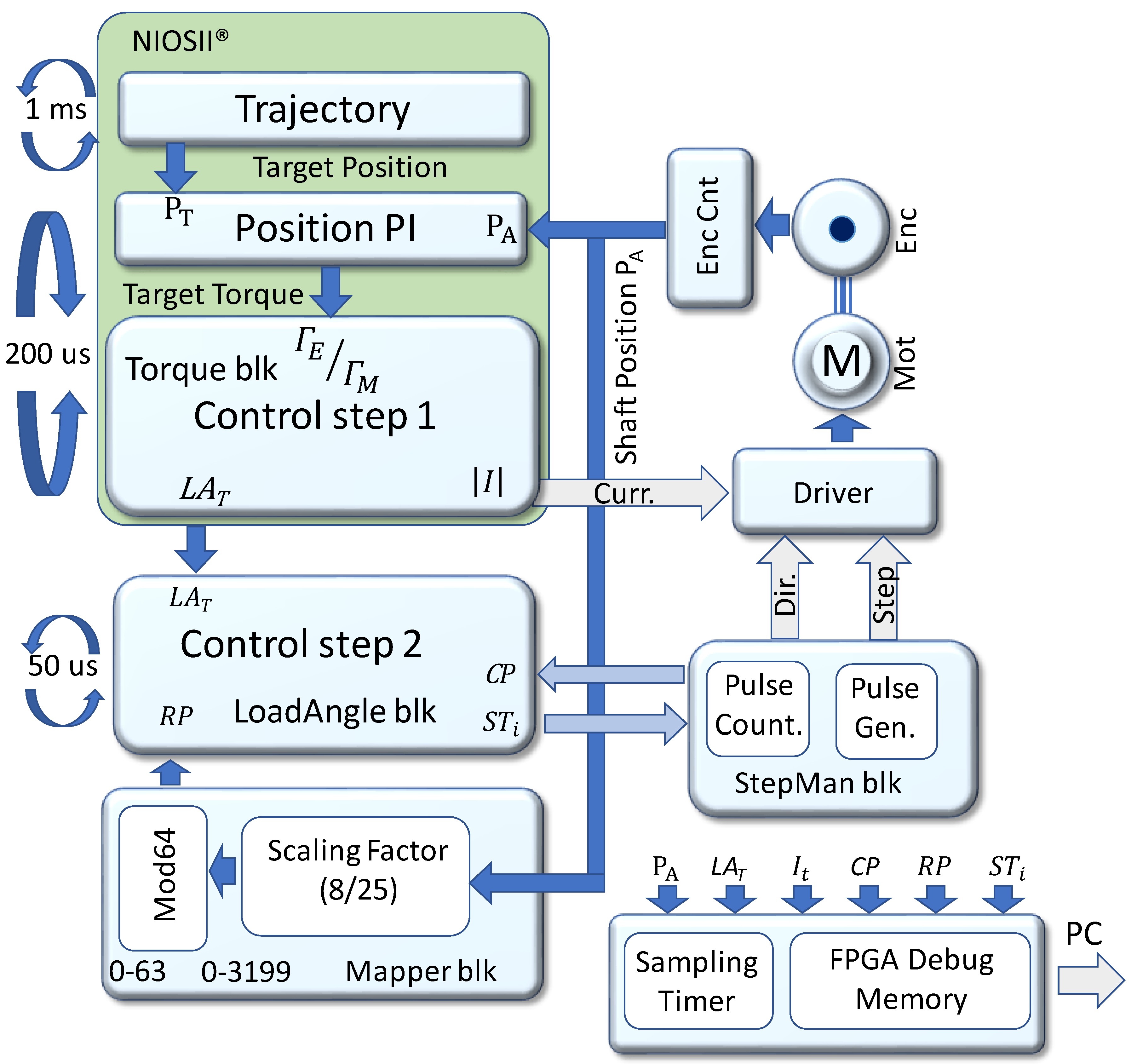
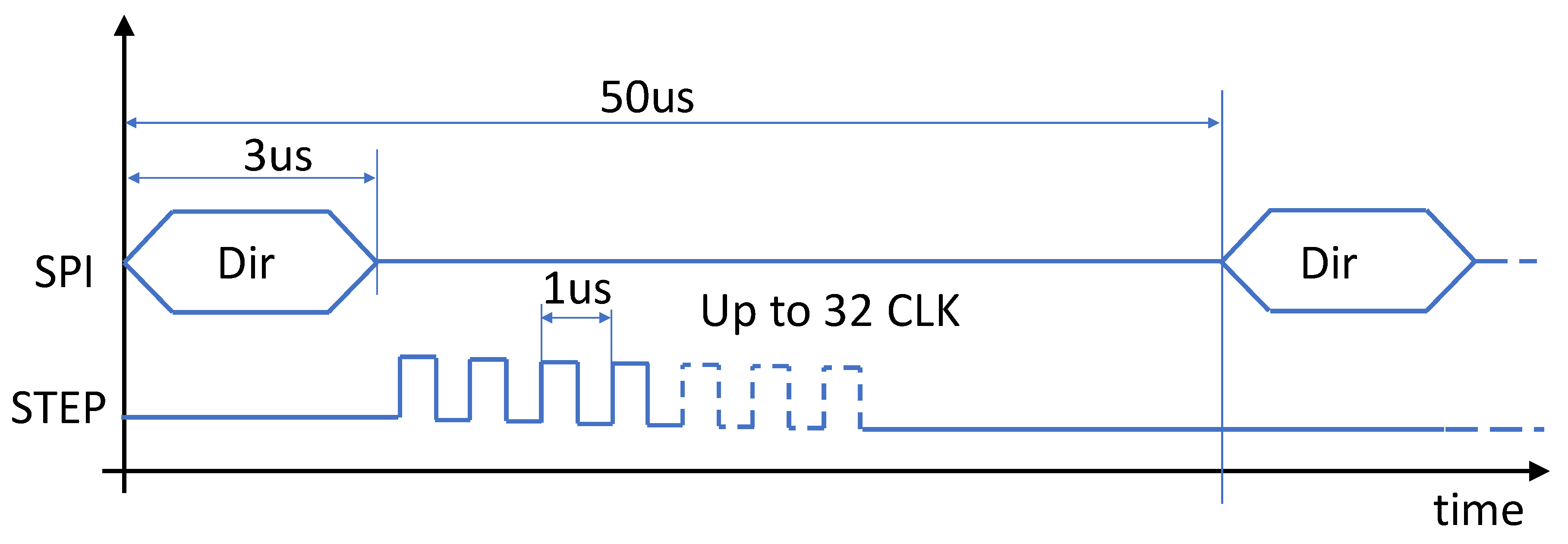
3.2. FPGA Implementation
3.3. Debug Memory
3.4. Timings and Resources
4. Experiments
4.1. Experimental Set-Ups
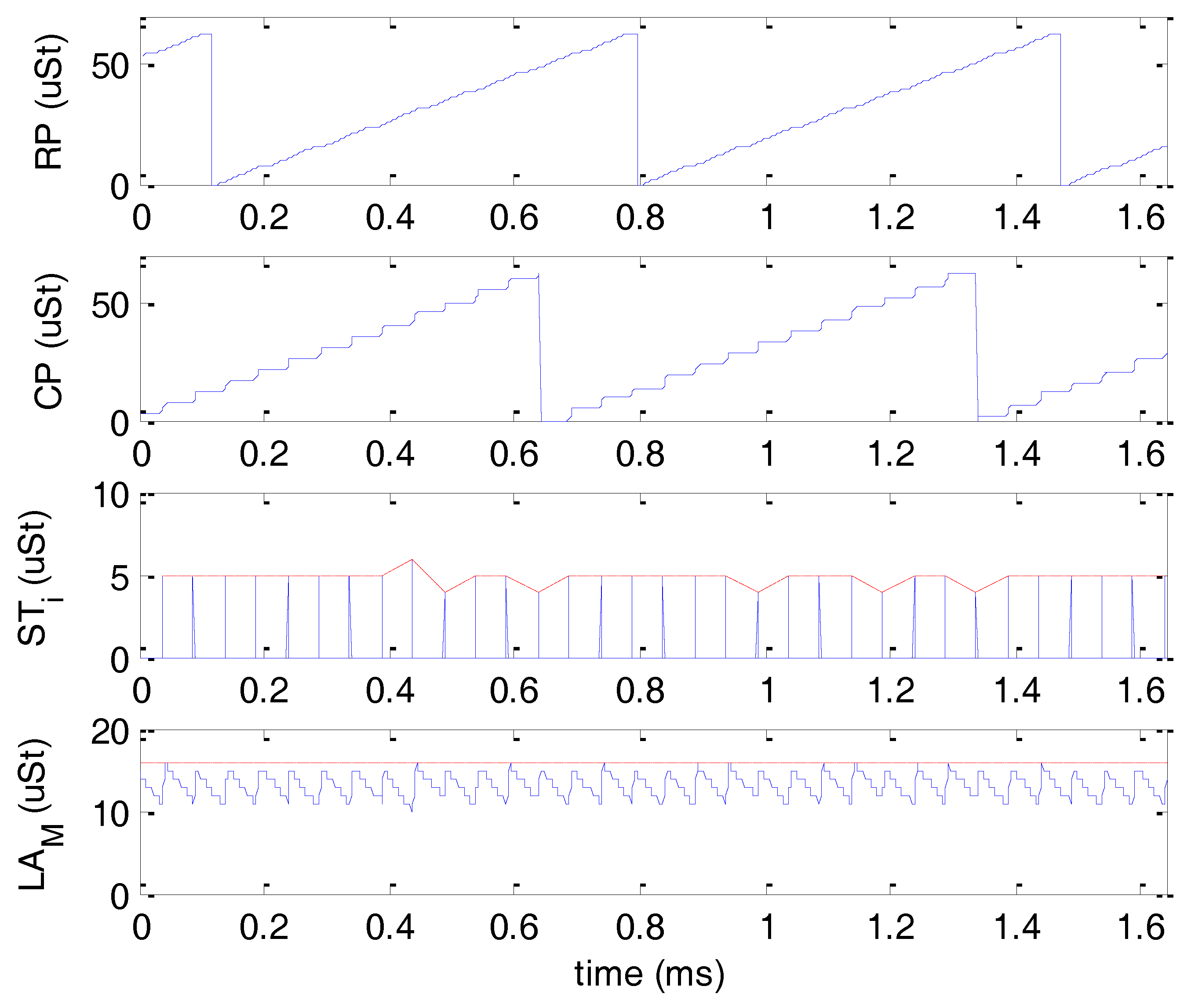
4.2. Control Procedure Test
4.3. Torque Load Disturbance Test
4.4. Trajectory Test in Different Load Conditions
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Athani, V.V. Stepper Motors: Fundamentals, Applications and Design; New Age International: New Delhi, India, 2005; ISBN 81-224-1006-5. [Google Scholar]
- Robert, B.; Feki, M. Control of the stepping motor. In Control of Non-Con- Conventional Synchronous Motors; Louis, J.P., Ed.; Wiley-ISTE: London, UK, 2012; ISBN 978-1-848-21331-9. [Google Scholar]
- Gaan, D.R.; Kumar, M.; Sudhakar, S. Real-time precise position tracking with stepper motor using frequency modulation based microstepping. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2018, 54, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derammelaere, S.; Vervisch, B.; Cottyn, J.; Vanwalleghem, B.; Cox, P.; De Belie, F.; Stockman, K.; Vandevelde, L.; Van Den Abeele, G. The efficiency of hybrid stepping motors. IEEE Ind. Appl. Mag. 2014, 20, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krause, P.; Wasynczuk, O.; Sudhoff, S.; Pekarek, S. Analysis of Electric Machinery and Drive Systems; IEEE Press Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-1-118-02429-4. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, Z.; Mei, X.; Rodríguez, J.; Kennel, R. Advanced control strategies of induction machine: Field oriented control, direct torque control and model predictive control. Energies 2018, 11, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackburn, J.L. Symmetrical Components for Power Systems Engineering; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Monmasson, E.; Cirstea, M.N. FPGA design methodology for industrial control systems—A review. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2007, 54, 1824–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, S.; Meacci, V.; Birkhofer, B.; Wiklund, J. FPGA-based system for in-line measurement of velocity profiles of fluids in industrial pipe flow. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 3997–4005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astrom, K.J.; Hagglund, T. Advanced PID Control; ISA-The Instrumentation, Systems, and Automation Society: Research Triangle Park, CA, USA, 2006; ISBN 13: 978-1556179426. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, W.; Yang, C.; Chung, C.C. Design and implementation of simple field-oriented control for permanent magnet stepper motors without DQ transformation. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2011, 47, 4231–4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, K.M.; Hoang, H.V.; Jeon, J.W. An advanced closed-loop control to improve the performance of hybrid stepper motors. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 32, 7244–7255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Fernandez, A.; Jimenez-Moreno, G.; Linares-Barranco, A.; Dominguez-Morales, M.J.; Paz-Vicente, R.; Civit-Balcells, A. A neuro-inspired spike-based PID motor controller for multi-motor robots with low cost FPGAs. Sensors 2012, 12, 3831–3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, Q.N.; Jeon, J.W. Neural-network-based low-speed-damping controller for stepper motor with an FPGA. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 57, 3167–3180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, N.; Nakamura, M.; Kosaka, T. Instantaneous torque analysis of hybrid stepping motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 1996, 32, 1176–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, E.; Daldaban, F. Analyzing the profile effects of the various magnet shapes in axial flux PM motors by means of 3D-FEA. Electronics 2018, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazmierkowski, M.P.; Malesani, L. Current control techniques for three-phase voltage-source PWM converters: A survey. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 1998, 45, 691–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, S.; Meacci, V.; Russo, D.; Matera, R. Encoder-Motor Misalignment Compensation for Closed-Loop Hybrid Stepper Motor Control. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference Applications in Electronics Pervading Industry Environment Society (APPLEPIES 2018), Pisa, Italy, 26–27 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, W.; Wang, Q.; Ji, K.; Dong, H.; Lin, J.; Qian, J. Research on closed-loop drive system of two-phase hybrid step motor based on SVPWM. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Vehicle Power and Propulsion Conference (VPPC), Hangzhou, China, 17–20 October 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.F.; Li, H.W. Design of stepper motor position control system based on DSP. In Proceedings of the 2017 2nd International Conference on Machinery, Electronics and Control Simulation (MECS 2017), Dubai, UAE, 24–25 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Crnosija, P.; Kuzmanovic, B.; Ajdukovic, S. Microcomputer implementation of optimal algorithms for closed-loop control of hybrid stepper motor drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2000, 47, 1319–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsui, K.W.H.; Cheung, N.C.; Yuen, K.C.W. Novel modeling and damping technique for hybrid stepper motor. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derammelaere, S.; Vervisch, B.; De Viaene, J.; Stockman, K. Sensorless load angle control for two-phase hybrid stepper motors. Mechatronics 2017, 43, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Villalobos, J.M.; Rodriguez-Resendiz, J.; Rivas-Araiza, E.A.; Martínez-Hernández, M.A. Sensorless FOC performance improved with on-line speed and rotor resistance estimator based on an artificial neural network for an induction motor drive. Sensors 2015, 15, 15311–15325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez-Espinosa, A.; Hernández-Guzmán, V.M.; Bandala-Sánchez, M.; Jiménez-Hernández, H.; Rivas-Araiza, E.A.; Rodríguez-Reséndiz, J.; Herrera-Ruíz, G. A new adaptive self-tuning Fourier coefficients algorithm for periodic torque ripple minimization in permanent magnet synchronous motors (PMSM). Sensors 2013, 13, 3831–3847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Condition | Control Strategy | Angle | Current | Torque | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Angle fixed, modulated by | (2a) | ||||
| Current fixed controlled by | (2b) |
| Condition | Control Strategy | Angle | Current | Torque | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Angle fixed, modulated by | (3a) | ||||
| Current fixed controlled by | (3b) |
| FPGA Blok | Logic Cell | Dedicated Reg | Memory Bits | DSP |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nios | 5017 | 3079 | 195,000 | 6 |
| StepManager | 45 | 30 | - | - |
| LoadAngle + Mapper Blk | 349 | 132 | - | - |
| Enc CNT | 167 | 67 | - | - |
| MOTOR | |
| Model | M1233041 |
| Manufacturer | Lam Technologies, Florence, Italy |
| Flange | NEMA23 |
| Step angle | 1.8° (200 step/rev) |
| Hold Torque | 1.1 N·m |
| Detent Torque | 0.035 N·m |
| Current | 4.2 A |
| Phase Resistance | 0.4 Ohm |
| Phase Inductance | 1.2 mH |
| Rotor Inertia | 0.280 kg·cm−2 |
| ENCODER | |
| Model | REV621 |
| Manufacturer | Elap, Milan, Italy |
| Zero reference | yes |
| Pulse/revolution | 10,000 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ricci, S.; Meacci, V. Simple Torque Control Method for Hybrid Stepper Motors Implemented in FPGA. Electronics 2018, 7, 242. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7100242
Ricci S, Meacci V. Simple Torque Control Method for Hybrid Stepper Motors Implemented in FPGA. Electronics. 2018; 7(10):242. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7100242
Chicago/Turabian StyleRicci, Stefano, and Valentino Meacci. 2018. "Simple Torque Control Method for Hybrid Stepper Motors Implemented in FPGA" Electronics 7, no. 10: 242. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7100242
APA StyleRicci, S., & Meacci, V. (2018). Simple Torque Control Method for Hybrid Stepper Motors Implemented in FPGA. Electronics, 7(10), 242. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7100242






