Active EMI Reduction Using Chaotic Modulation in a Buck Converter with Relaxed Output LC Filter
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Proposed Chaos-Based EMI Reduction with On-Chip Chaotic Ramp Generator
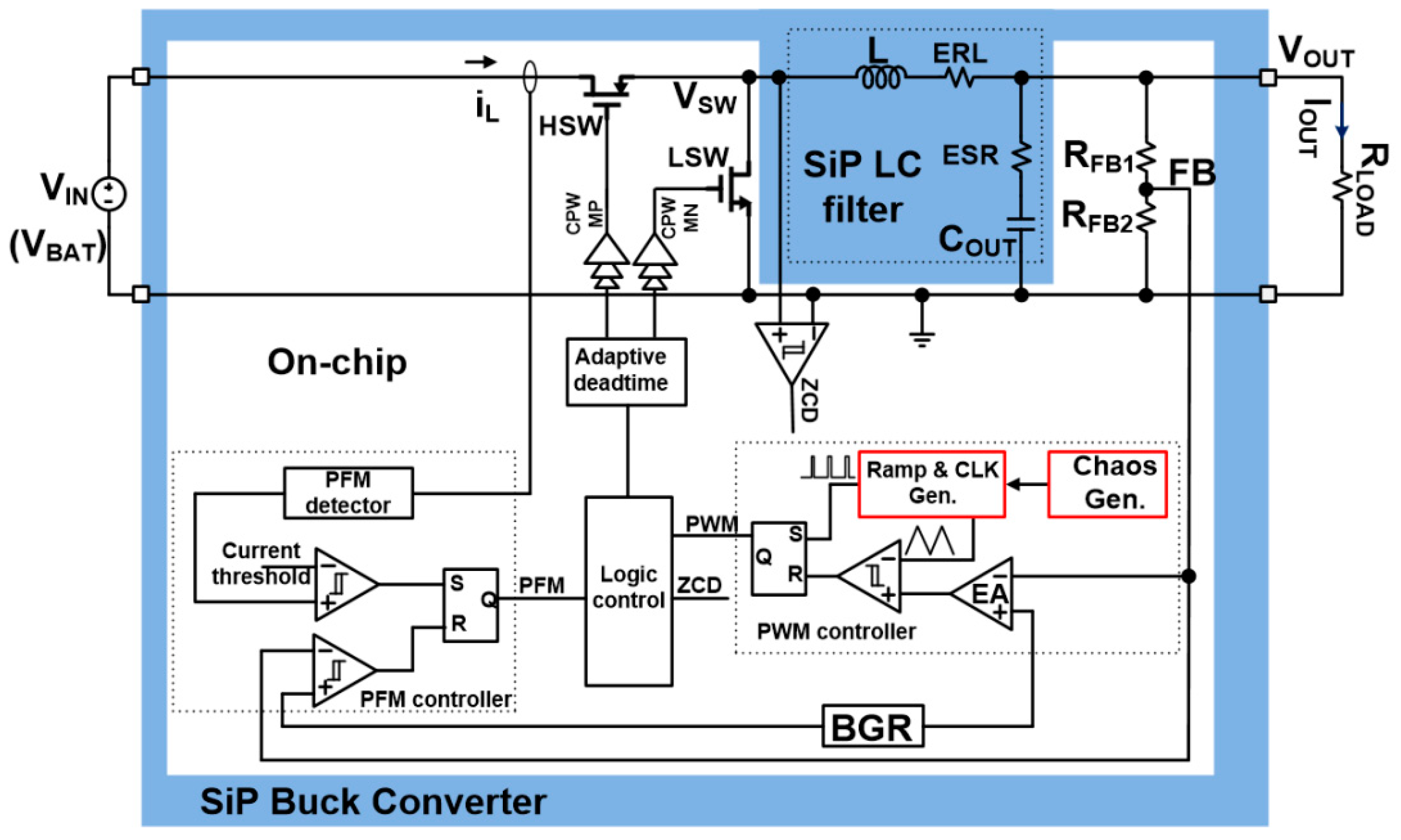
2.1. SiP Dual-Mode PWM/PFM Buck Converter with Chaos-Based EMI Reduction Scheme
2.2. Fully Integrated On-Chip Chaos Generator with N-Shaped Map
2.2.1. N-Shaped Chaos Generator
- Sub space R1: At tk, if Vk < Vb1, the capacitor will continue charging on the next clock cycle as shown in Figure 4b, corresponding to FSM S1. However, if Vk > Vb1, the subspace higher than Vb1 can be divided into 2 other sub spaces, R2 and R3, depending on a second boundary condition, Vb2.
- Sub space R2: The capacitor continues charging until v(t) reaches VHC and then discharge for the time durations ta and tb, respectively. Figure 4c shows the representative waveform for this case with the charging period ta and discharging period tb, which can be deduced from Equations (1) and (2): ta = I1/C × (VHC − Vk); tb = T − ta =T −I1/C × (VHC − Vk). For this case, ta + tb = T.
- Sub space R3: The capacitor continues charging until v(t) reaches VHC, then it discharges to VLC for the periods ta, tb, and tc, as shown in Figure 4d. In this case, ta + tb < T; therefore, tc can be calculated as tc = T − ta − tb = T − I1/C × (VHC − Vk) − C/I2 (VHC − VLC). In this case, tb is different from before and can be calculated using the discharging equation VLC = VHC − I2/C × tb. The second boundary condition can be derived by the setup tc = 0:
2.2.2. Dynamical Analysis of the Chaos Map
2.3. Design of Chaotic Triangular Ramp Generator
3. Simulation Results
4. Experimental Results and Discussion
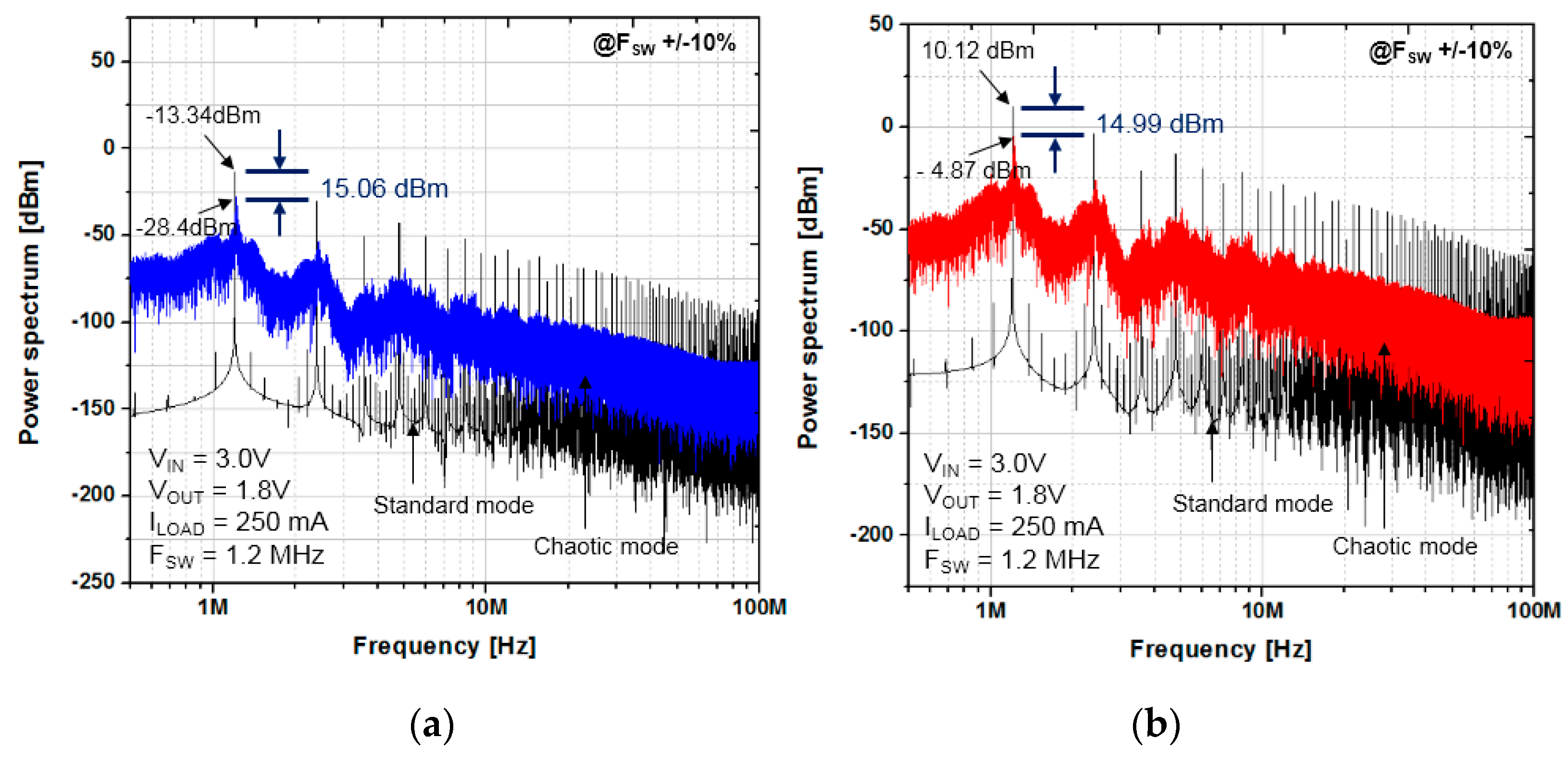
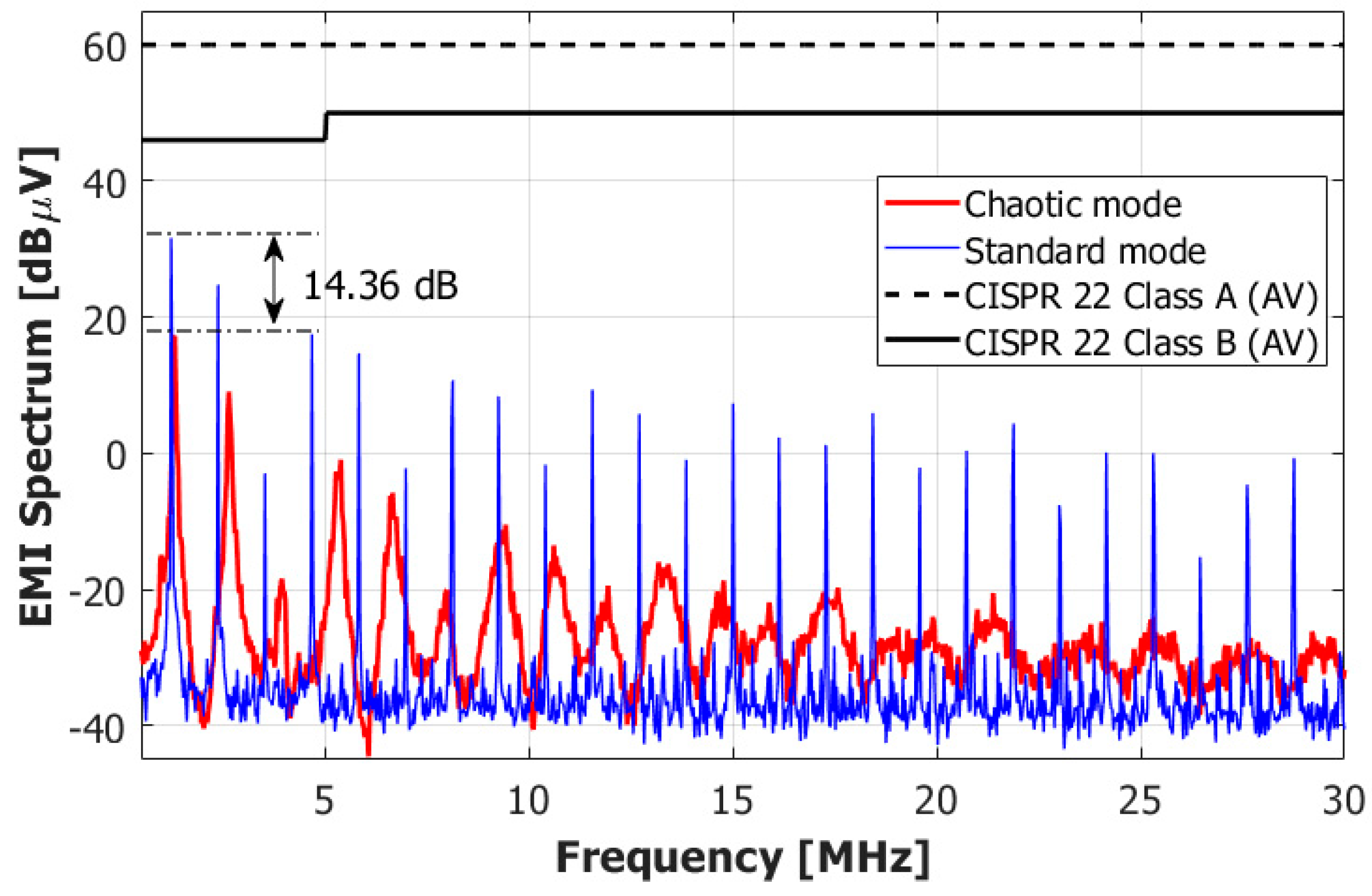
4.1. EMI Reduction Performance of the Proposed Scheme
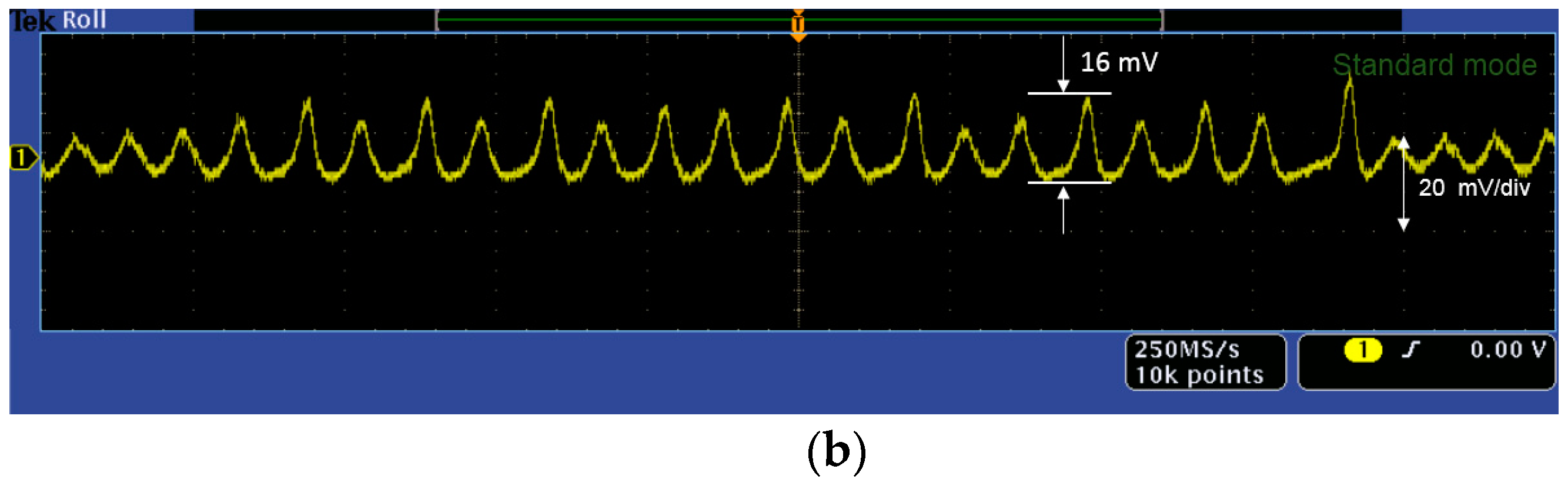
4.2. Reducing the Side Effects of the Proposed EMI-Improvement Scheme
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Disney, D.; Shen, Z.J. Review of silicon power semiconductor technologies for power supply on chip and power supply in package applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 28, 4168–4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Ho, M.; Guo, J.; Leung, K.N. A Single-Inductor Multiple-Output Auto-Buck–Boost DC–DC Converter with Tail-Current Control. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 7857–7875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, J.; Hwang, J.; Song, E.; Kim, S.Y. On-chip layout optimization of synchronous DC-DC buck converter for EMI reduction. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Electrical Design of Advanced Packaging and Systems Symposium (EDAPS), Haining, China, 14–16 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Edward, N.Y.H.; Philip, K.T.M. Design of PWM ramp signal in voltage-mode CCM random switching frequency buck converter for conductive EMI reduction. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. I Reg. Pap. 2013, 60, 505–515. [Google Scholar]
- Bhargava, A.; Pommerenke, D.; Kam, K.W.; Centola, F.; Lam, C.W. DC-DC buck converter EMI reduction using PCB layout modification. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2011, 53, 806–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.J.; Chen, C.L. A passive lossless snubber cell for non-isolated PWM DC/DC converters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 1998, 45, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, Q. Modeling and stability analysis of active/hybrid common-mode EMI filters for DC/DC power converters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 6254–6263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pareschi, F.; Rovatti, R.; Setti, G. EMI reduction via spread-spectrum in DC/DC converters: State of the art, optimization, and tradeoffs. IEEE Access. 2015, 3, 2857–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Chen, D.Y. Reduction of power supply EMI emission by switching frequency modulation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 1994, 9, 132–137. [Google Scholar]
- Hardin, K.B.; Fessler, J.T.; Bush, R. Spread spectrum clock generation for the reduction of radiated emissions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Symposium on Electromagnetic Compatibility, Chicago, IL, USA, 22–26 August 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, S.; Zane, R. custom spectral shaping for EMI reduction in high-frequency inverters and ballasts. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2005, 20, 1499–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elrayyah, A.; Namburi, K.M.P.K.; Sozer, Y.; Husain, I. An effective dithering method for electromagnetic interference (EMI) reduction in single-phase DC/AC inverters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 2798–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davari, P.; Hoene, E.; Zare, F.; Blaabjerg, F. Improving 9–150 kHz performance of single-phase PFC rectifier. In Proceedings of the 10th International conference on integrated power electronics systems (CIPS), Stuttgart, Germany, 20–22 March 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ming, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, Z.-K.; Zhang, B. An advanced spread spectrum architecture using pseudorandom modulation to improve EMI in class D amplifier. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2011, 26, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morcillo, J.D.; Burbano, D.; Angulo, F. Adaptive ramp technique for controlling chaos and subharmonic oscillations in DC-DC power converters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 5330–5343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, B.; Wang, F.; Tan, N.; Halang, W.A. Design of analogue chaotic PWM for EMI suppression. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2010, 52, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.G.; Gong, S.D.; Liu, J.W.; Su, D.L. CMOS-based chaotic PWM generator for EMI reduction. IEEE Trans. Electromagn. Compat. 2017, 59, 1224–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, H.A.; Han, Y.; Park, S.; Hwang, J.; Song, E.; Kim, S. Design and analysis of the DC-DC converter with a frequency hopping technique for EMI reduction. IEEE Trans. Compon. Packag. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 8, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, J.; Huang, T.; Lai, W.; Chen, K. Dual modulation technique for high efficiency in high-switching buck converters over a wide load range. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2011, 58, 1671–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.F.; Chen, W.Z.; Wu, J.C. A monolithic current-mode buck converter with advanced control and protection circuits. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2007, 22, 1836–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattingly, D. Designing Stable Compensation Networks for Single Phase Voltage Mode Buck Regulators. Available online: www.intersil.com/data/tb/tb417.pdf (accessed on 11 October 2018).
- Kim, E.J.; Cho, C.H.; Kim, W.; Lee, C.H.; Laskar, J. Spurious noise reduction by modulating switching frequency in dc-to-dc converter for RF power amplifier. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits Symposium, Anaheim, CA, USA, 23–25 May 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Juncu, V.D. Integrated circuit implementation of a compact discrete-time chaos generator. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 2006, 46, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Wang, C. Current-mode multi-scroll chaos generator employing CCCII. Electron. Lett. 2016, 52, 1295–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.L.; Yang, C.H.; Wu, C.H. Chip implementation of a new hyperchaotic oscillator. Electron. Lett. 2017, 53, 226–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, M.; Sawada, Y. Measurement of the Lyapunov spectrum from a chaotic time series. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1985, 55, 1082–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, V.H.; Kumar, S.; Song, H.J. A family of fully integrated CMOS chaos generators with strictly 1-D linear-piecewise chaos maps. J. Comput. Electron. 2018, 17, 1343–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nashed, M.; Fayed, A.A. Current-mode hysteretic buck converter with spur-free control for variable switching noise mitigation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 650–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Liu, Y.; Wing-Hung, K. A 10/30 MHz fast reference-tracking buck converter with DDA-based type-III compensator. IEEE J. Solid-State Circ. 2014, 9, 2788–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aruna, P.; Premalatha, L. Investigation of EMI reduction in buck converter by using external chaos generator. In Proceedings of the 2011 International conference on recent advancements in electrical, electronics and control engineering, Sivakasi, India, 15–17 December 2011. [Google Scholar]


















| Parameter | Description | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| VIN | Input voltage range (Battery) | 2.7–4.2 V |
| VOUT | Output voltage range | 1.0–1.8 V |
| IOUT,max | Maximum load current | 500 mA |
| Vrip,(max) | Maximum output ripple | 50 mV |
| FSW | Switching frequency | 1–2 MHz |
| LOUT | Inductor (in package) | 2.2 μH |
| COUT | Output capacitor (in package) | 2.2 μF |
| Parameter | Quantity |
|---|---|
| CIN | 10 μF |
| LOUT | 2.2 μH |
| COUT | 2.2 μF |
| RFB1 | 4.3 kΩ |
| (*) RFB2 | 9.47 kΩ |
| C1 | 15 pF |
| C2 | 1 nF |
| C3 | 470 pF |
| R1 | 4.7 kΩ |
| R2 | 560 Ω |
| Ref. | Implementation Method | Modulation Technique | EMI Reduction | Switching Frequency | Compatibility for On-Chip Integration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [17] | CMOS @ 0.35 μm | Random PWM | 12.85 dB | 0.89–1.44 MHz | Suitable |
| [18] | CMOS @ 0.18 μm | Random PWM (Frequency hopping) | 12.6 dB | 1.4–2.1 MHz | Suitable |
| [19] | Hybrid | Chaotic PWM | 10 dB 1 | 60 +/− Δf 2 | No |
| This work | CMOS @ 0.18 μm | Chaotic PWM | 14.53 dB | 1.04–1.31 MHz | Suitable |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nguyen, V.H.; Huynh, H.A.; Kim, S.; Song, H. Active EMI Reduction Using Chaotic Modulation in a Buck Converter with Relaxed Output LC Filter. Electronics 2018, 7, 254. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7100254
Nguyen VH, Huynh HA, Kim S, Song H. Active EMI Reduction Using Chaotic Modulation in a Buck Converter with Relaxed Output LC Filter. Electronics. 2018; 7(10):254. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7100254
Chicago/Turabian StyleNguyen, Van Ha, Hai Au Huynh, SoYoung Kim, and Hanjung Song. 2018. "Active EMI Reduction Using Chaotic Modulation in a Buck Converter with Relaxed Output LC Filter" Electronics 7, no. 10: 254. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7100254
APA StyleNguyen, V. H., Huynh, H. A., Kim, S., & Song, H. (2018). Active EMI Reduction Using Chaotic Modulation in a Buck Converter with Relaxed Output LC Filter. Electronics, 7(10), 254. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7100254





