On the Prediction of the Threshold Voltage Degradation in CMOS Technology Due to Bias-Temperature Instability
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Bias-Temperature Instability
2.1. Silicon-Based Technology
2.2. NBTI and PBTI in CMOS Technology
3. BTI Models
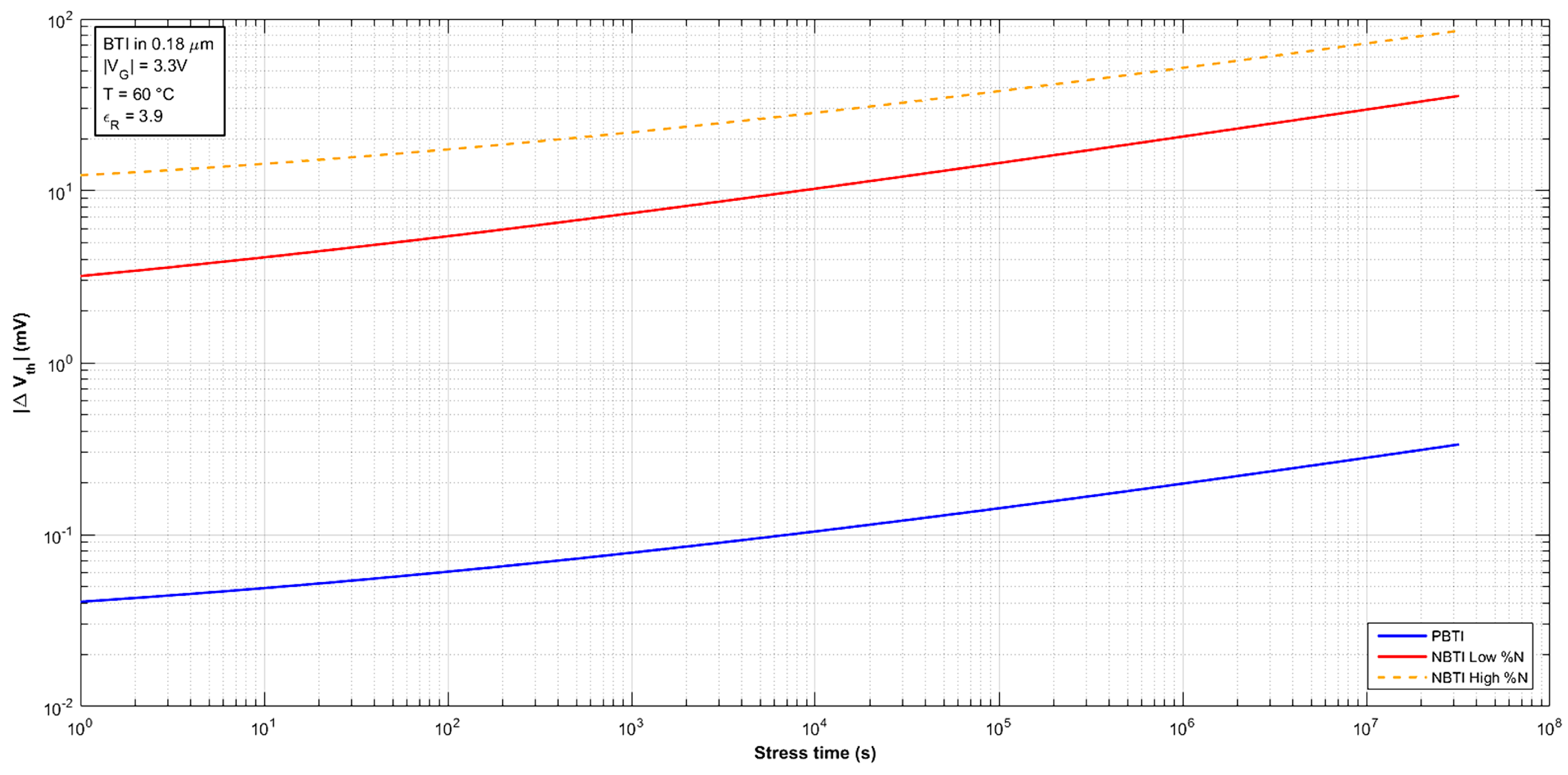
4. BTI Simulation and Discussion of the Results
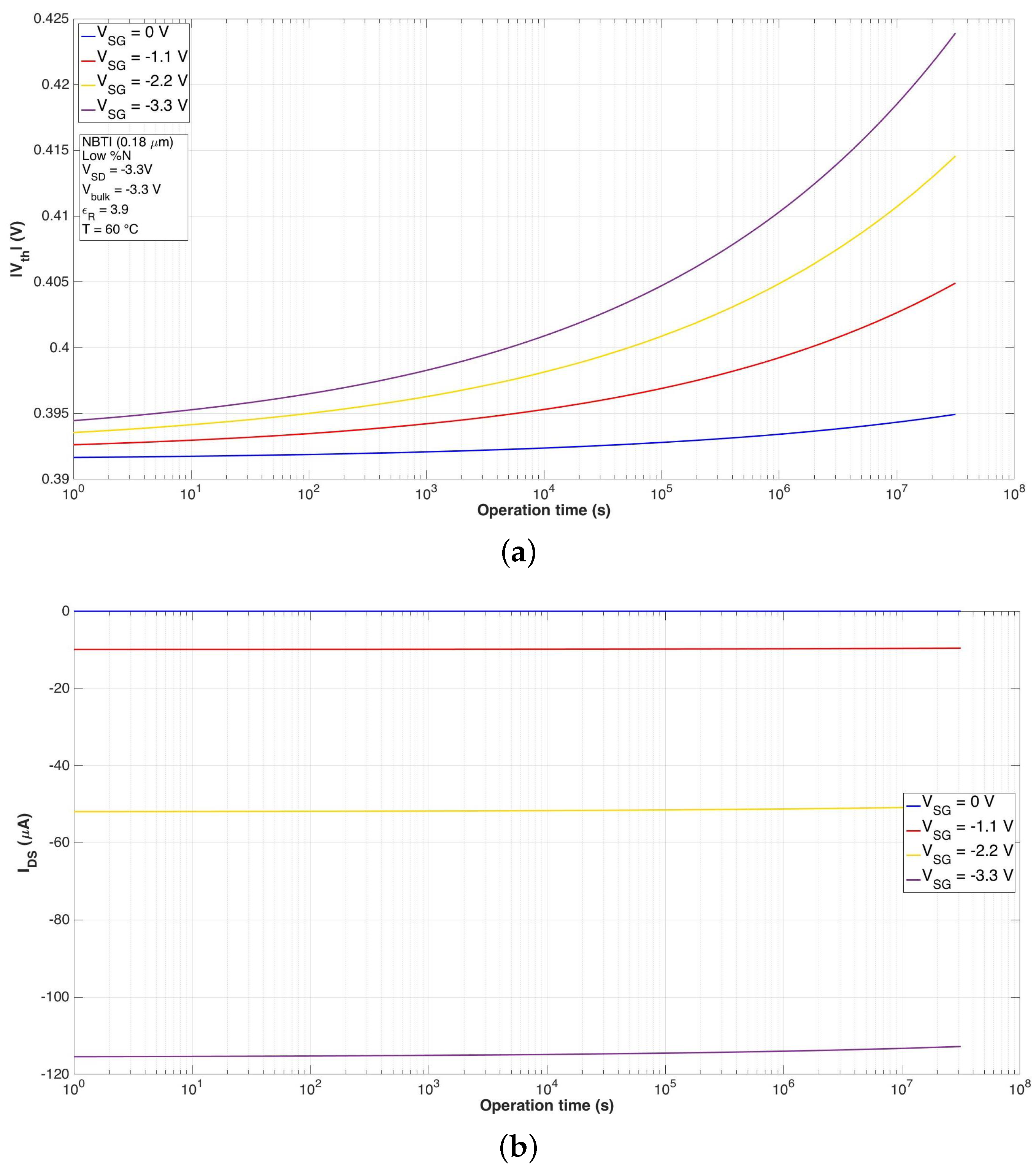
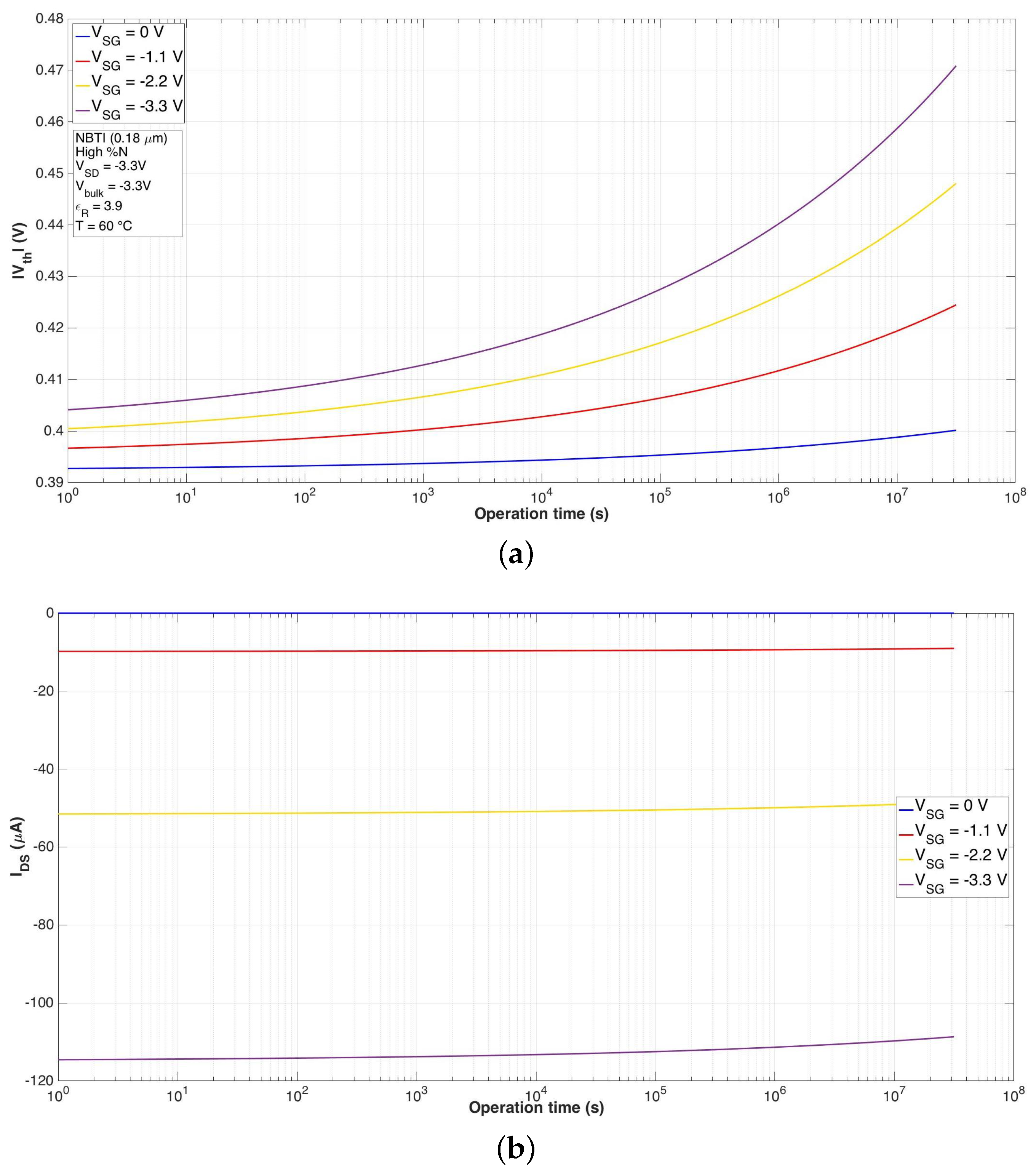
4.1. Physics-Based Model for NBTI
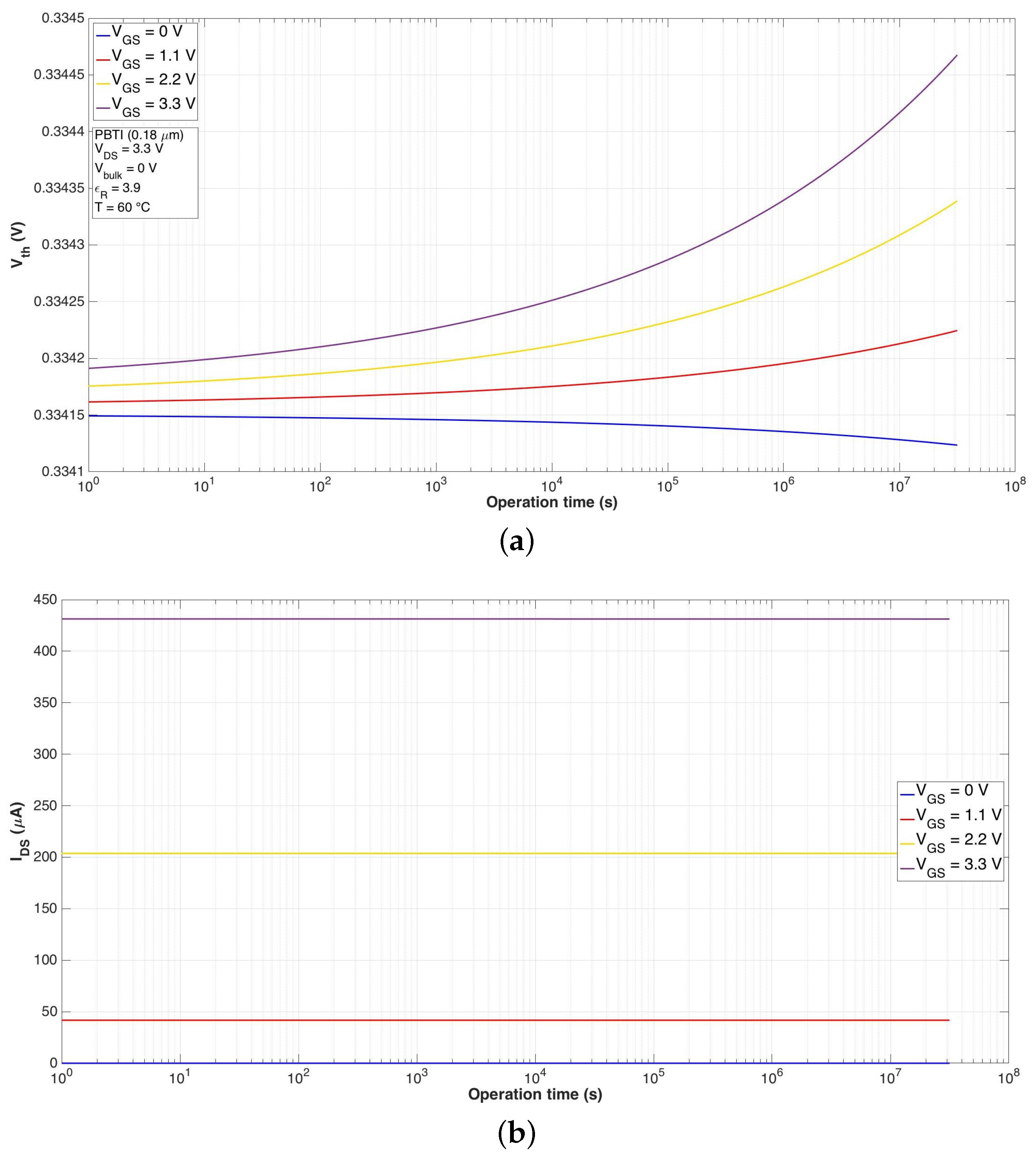
4.2. Physics-Based Model for PBTI
4.3. BTI Evaluation for Extending Aging Ranges and Inclusion of the BTI Physics-Based Model into BSIM3v3
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Both, T.H.; Furtado, G.F.; Wirth, G.I. Modeling and simulation of the charge trapping component of BTI and RTS. Microelectron. Reliab. 2018, 80, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajmi, R.; Cacho, F.; Larroze, E.L.; Bourdel, S.; Benech, P.; Huard, V.; Federspiel, X. Characterization of Low Drop-Out during ageing and design for yield. Microelectron. Reliab. 2017, 76–77, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halak, B.; Tenentes, V.; Rossi, D. The impact of BTI ageing on the reliability of level shifters in nano-scale CMOS technology. Microelectron. Reliab. 2016, 67, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasser, T. Bias Temperature Instability for Devices and Circuits; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, J.E.; Jeng, M.C.; Moon, J.E.; Ko, P.K.; Hu, C. Performance and reliability design issues for deep-submicrometer MOSFETs. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 1991, 38, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppson, K.O.; Svensson, C.M. Negative bias stress of MOS devices at high electric fields and degradation of MNOS devices. J. Appl. Phys. 1977, 48, 2004–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroder, D.K. Negative bias temperature instability: What do we understand? Microelectron. Reliab. 2007, 47, 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.A.; Mahapatra, S. A comprehensive model of PMOS NBTI degradation. Microelectron. Reliab. 2005, 45, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahapatra, S.; Goel, N.; Desai, S.; Gupta, S.; Jose, B.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Joshi, K.; Jain, A.; Islam, A.; Alam, M. A comparative study of different physics-based NBTI models. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2013, 60, 901–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J.; Xiong, K.; Tse, K.Y. Importance of Oxygen Vacancies in High K Gate Dielectrics. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Integrated Circuit Design and Technology (ICICDT’07), Austin, TX, USA, 30 May–1 June 2007; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Cartier, E.; Linder, B.; Narayanan, V.; Paruchuri, V. Fundamental understanding and optimization of PBTI in nFETs with SiO2/HfO2 gate stack. In Proceedings of the International IEEE Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM’06), San Francisco, CA, USA, 11–13 December 2006; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Huard, V. Two independent components modeling for Negative Bias Temperature Instability. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Reliability Physics Symposium (IRPS), Anaheim, CA, USA, 2–6 May 2010; pp. 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasser, T.; Kaczer, B.; Goes, W.; Reisinger, H.; Aichinger, T.; Hehenberger, P.; Wagner, P.J.; Schanovsky, F.; Franco, J.; Luque, M.; et al. The Paradigm Shift in Understanding the Bias Temperature Instability: From Reaction-Diffusion to Switching Oxide Traps. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2011, 58, 3652–3666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudor, B.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Tan, R.; Liu, W.; Lee, F. An accurate and scalable MOSFET aging model for circuit simulation. In Proceedings of the 2011 12th International Symposium on Quality Electronic Design (ISQED), Santa Clara, CA, USA, 14–16 March 2011; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudor, B.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Tan, R.; Liu, W.; Lee, F. An accurate MOSFET aging model for 28 nm integrated circuit simulation. Microelectron. Reliab. 2012, 52, 1565–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Joshi, K.; Chaudhary, V.; Goel, N.; De, S.; Pandey, R.K.; Murali, K.V.R.M.; Mahapatra, S. Trap Generation in IL and HK layers during BTI/TDDB stress in scaled HKMG N and P MOSFETs. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Reliability Physics Symposium, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 1–5 June 2014; pp. GD.3.1–GD.3.11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasser, T.; Rott, K.; Reisinger, H.; Waltl, M.; Schanovsky, F.; Kaczer, B. NBTI in Nanoscale MOSFETs—The Ultimate Modeling Benchmark. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2014, 61, 3586–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maricau, E.; Zhang, L.; Franco, J.; Roussel, P.; Groeseneken, G.; Gielen, G. A compact NBTI model for accurate analog integrated circuit reliability simulation. In Proceedings of the 2011 European Solid-State Device Research Conference (ESSDERC), Helsinki, Finland, 12–16 September 2011; pp. 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, K.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Goel, N.; Nanware, N.; Mahapatra, S. A Detailed Study of Gate Insulator Process Dependence of NBTI Using a Compact Model. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2014, 61, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, K.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Goel, N.; Mahapatra, S. A consistent physical framework for N and P BTI in HKMG MOSFETs. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Reliability Physics Symposium (IRPS), Anaheim, CA, USA, 15–19 April 2012; pp. 5A.3.1–5A.3.10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, K.; Hung, S.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Chaudhary, V.; Nanaware, N.; Rajamohnan, B.; Sato, T.; Bevan, M.; Wei, A.; Noori, A.; et al. HKMG process impact on N, P BTI: Role of thermal IL scaling, IL/HK integration and post HK nitridation. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Reliability Physics Symposium (IRPS), Anaheim, CA, USA, 14–18 April 2013; pp. 4C.2.1–4C.2.10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattangady, S.; Kraft, R.; Grider, D.; Douglas, M.; Brown, G.; Tiner, P.; Kuehne, J.; Nicollian, P.; Pas, M. Ultrathin nitrogen-profile engineered gate dielectric films. In Proceedings of the International IEEE Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM’96), San Francisco, CA, USA, 8–11 December 1996; pp. 495–498. [Google Scholar]

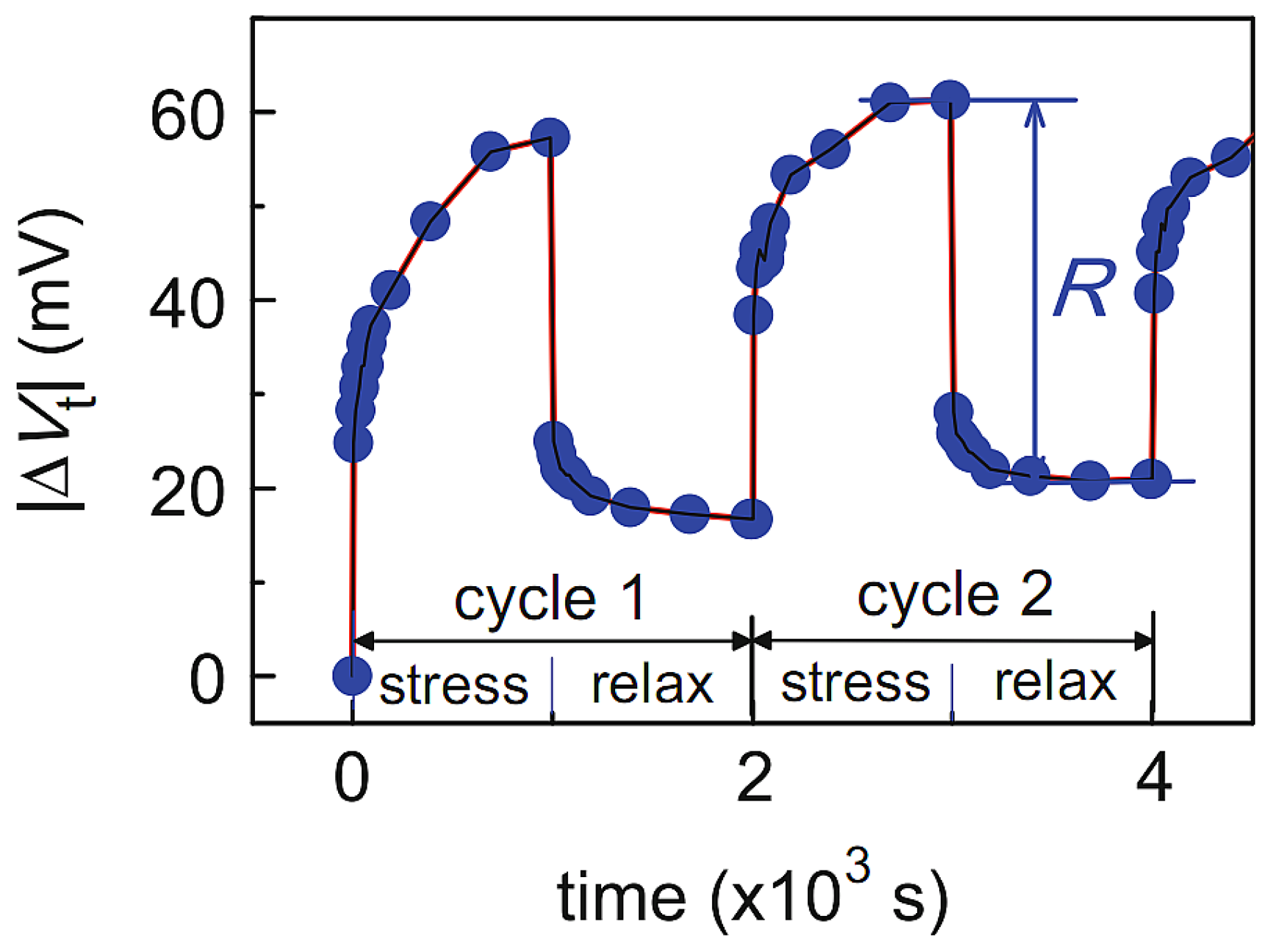
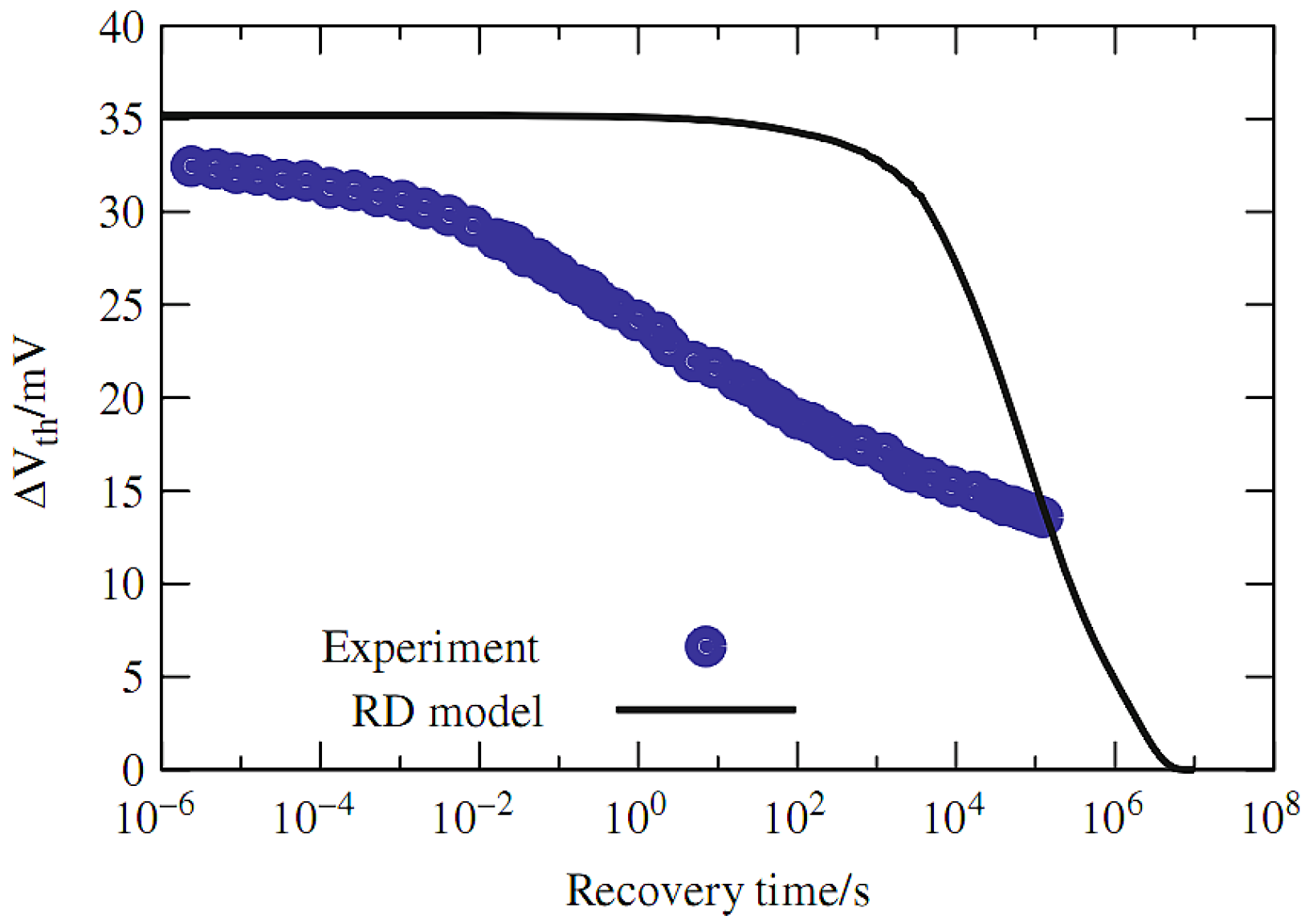
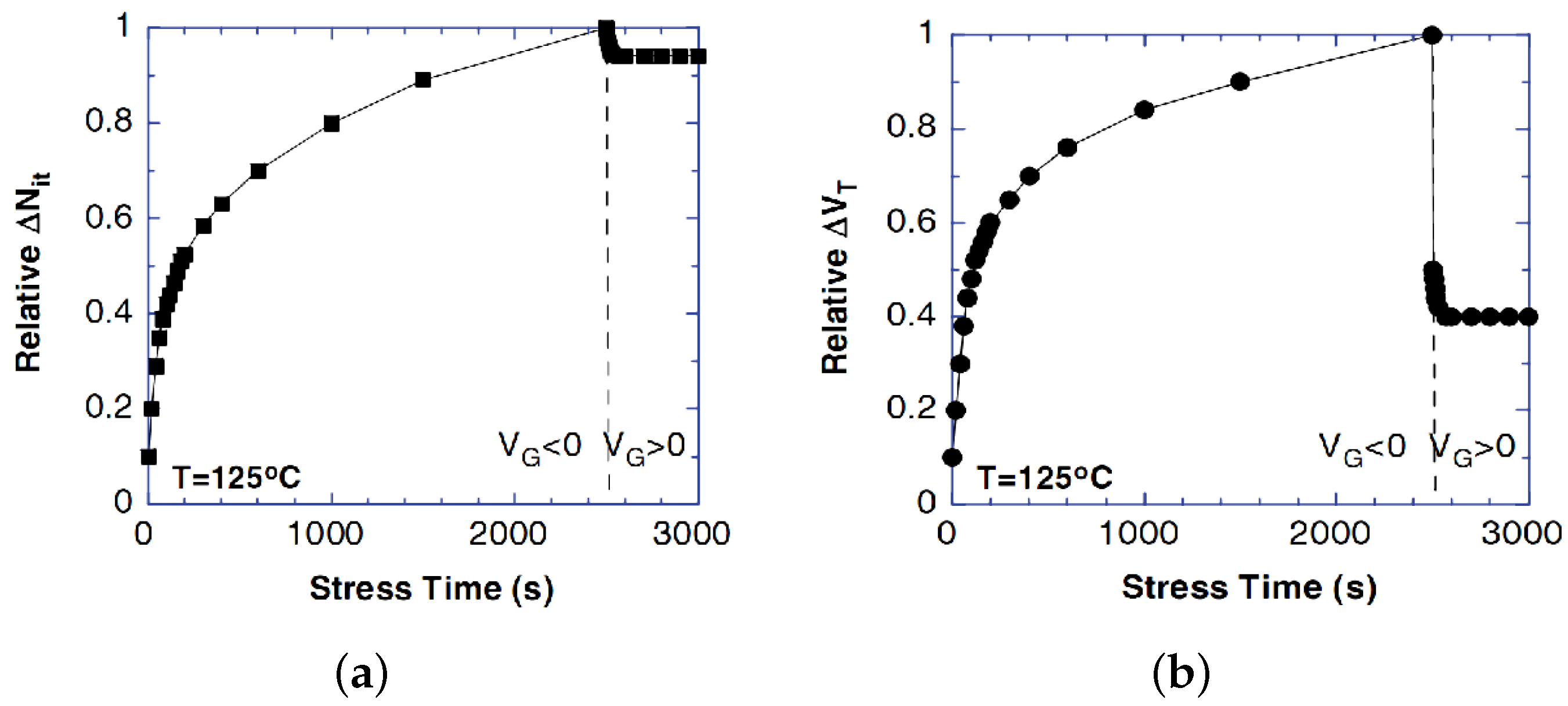
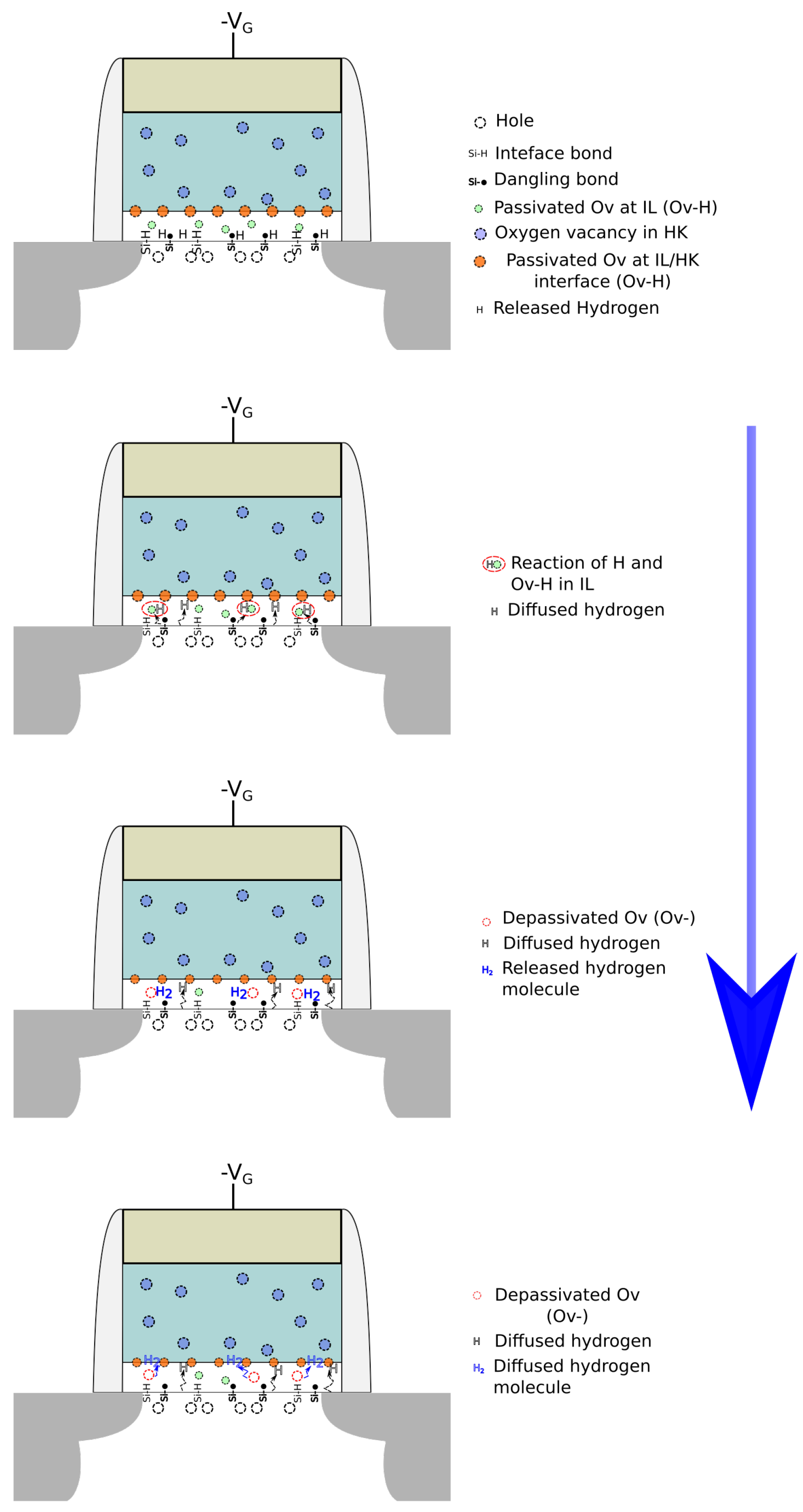



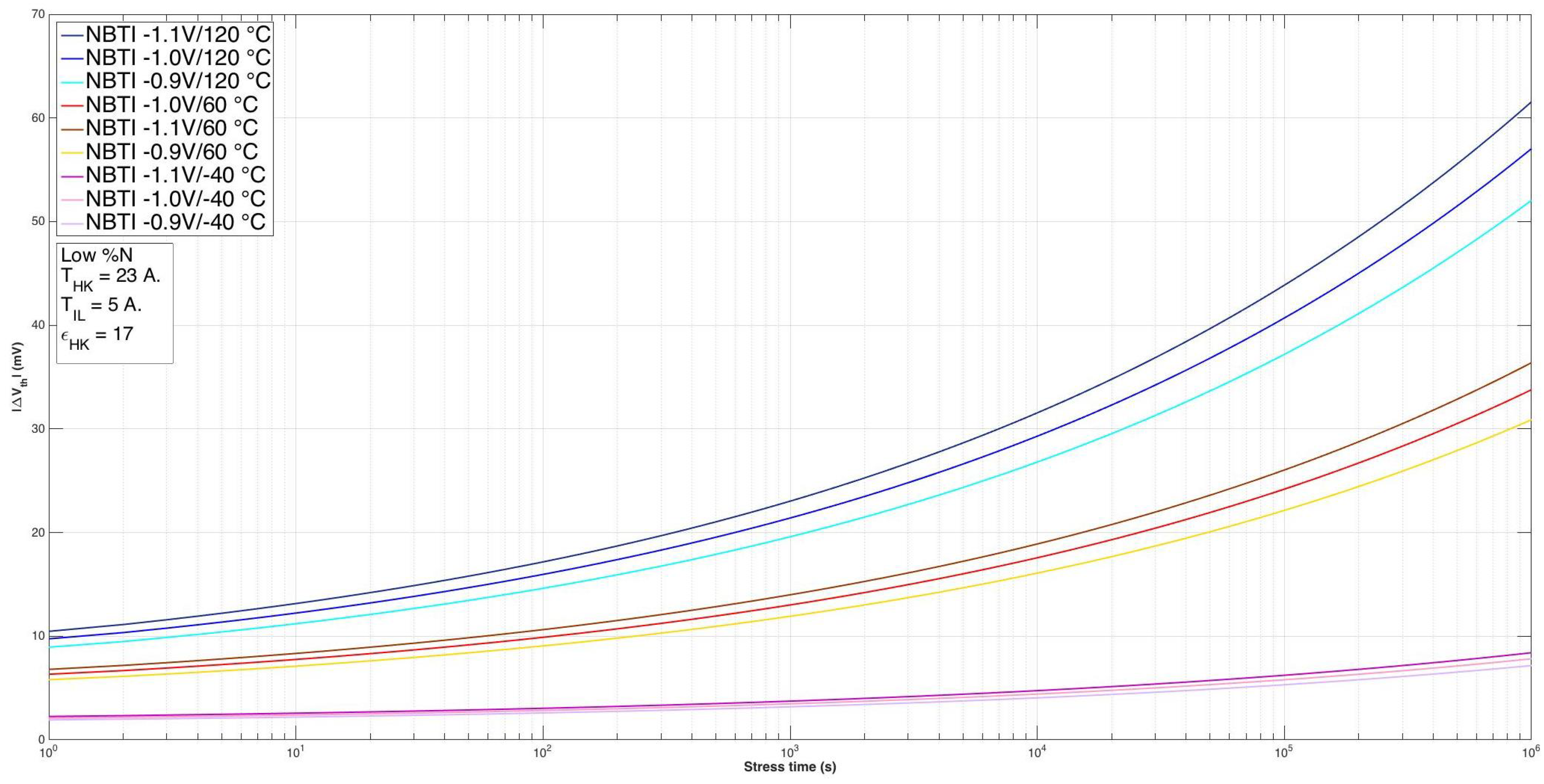
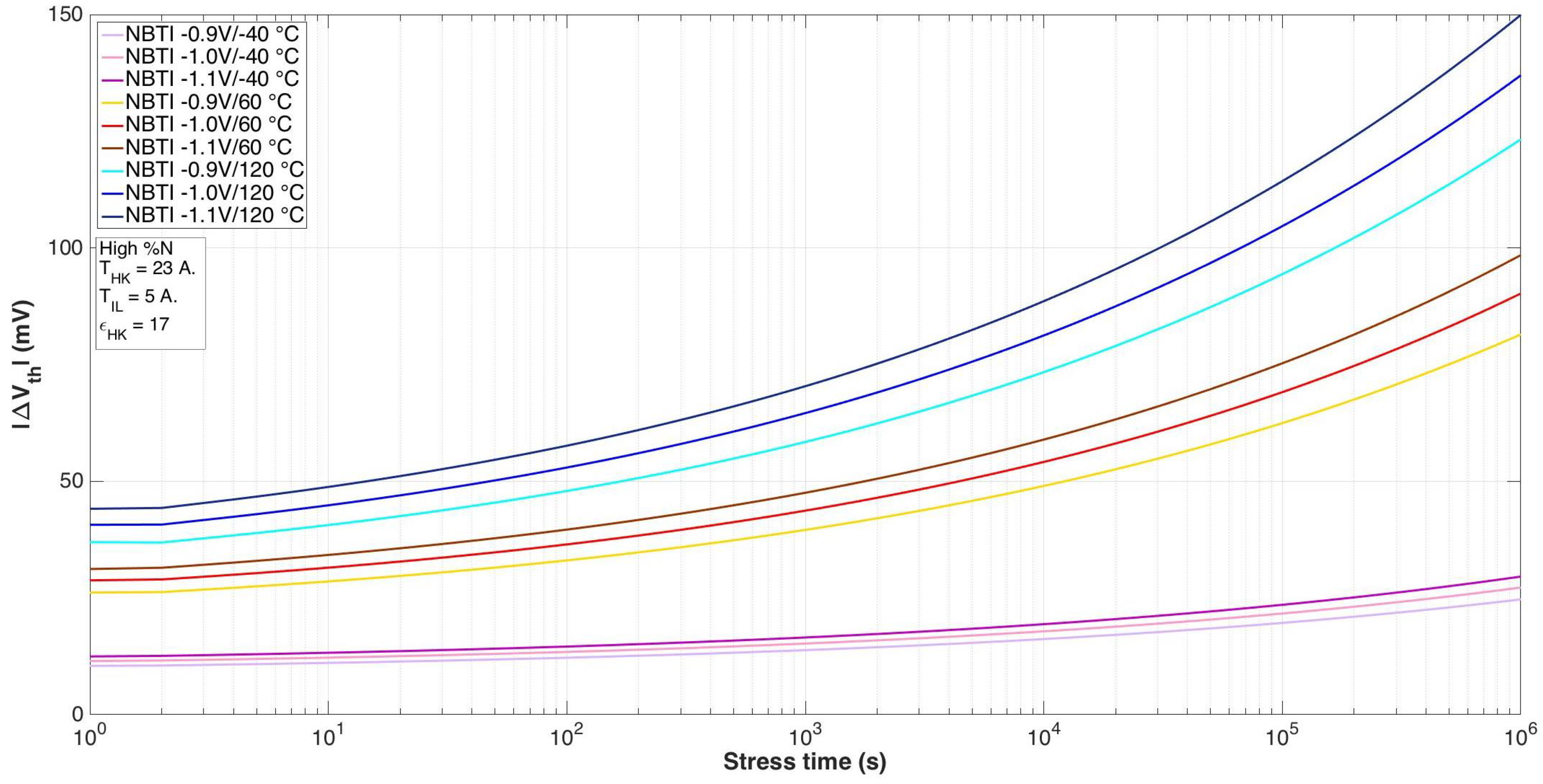
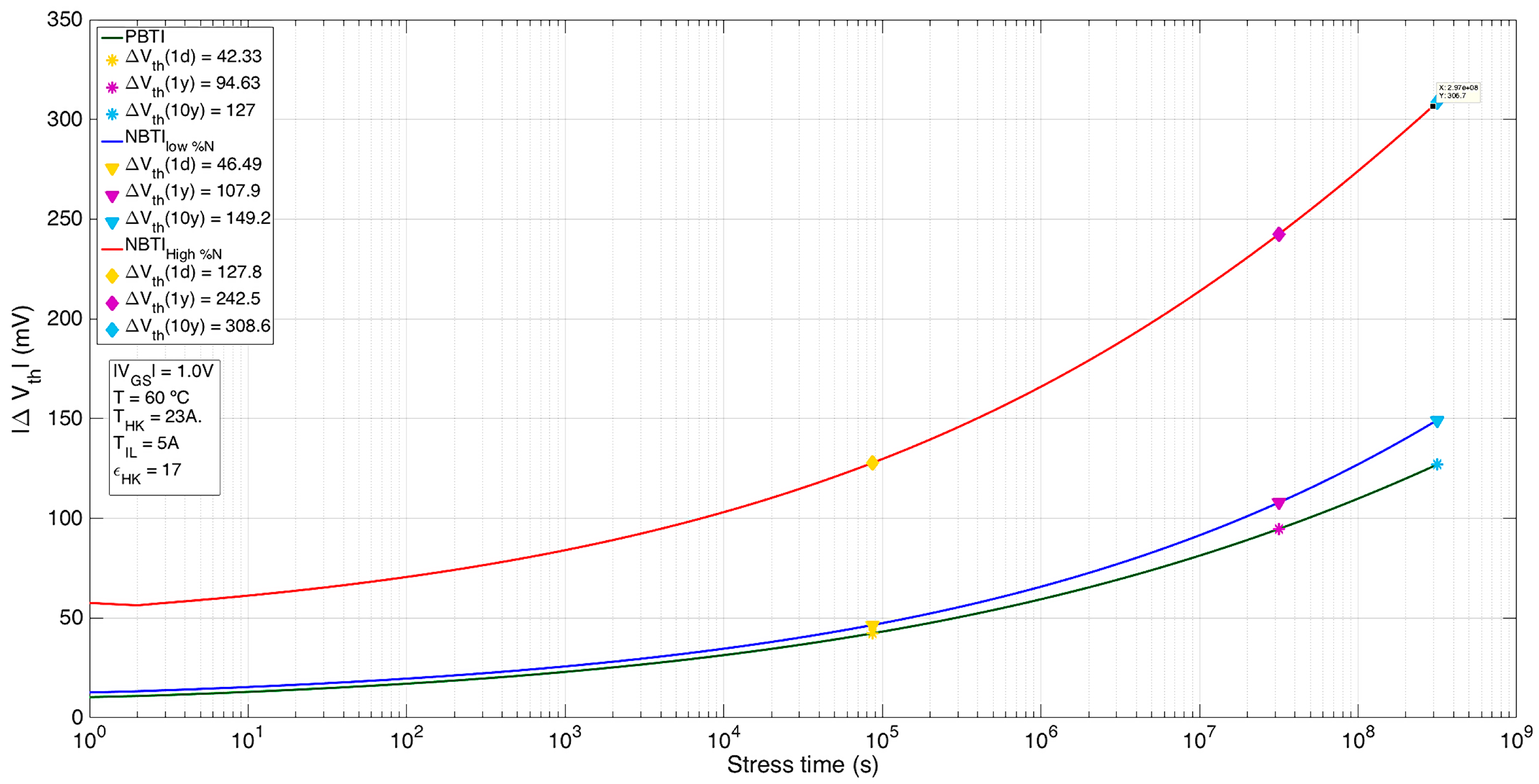

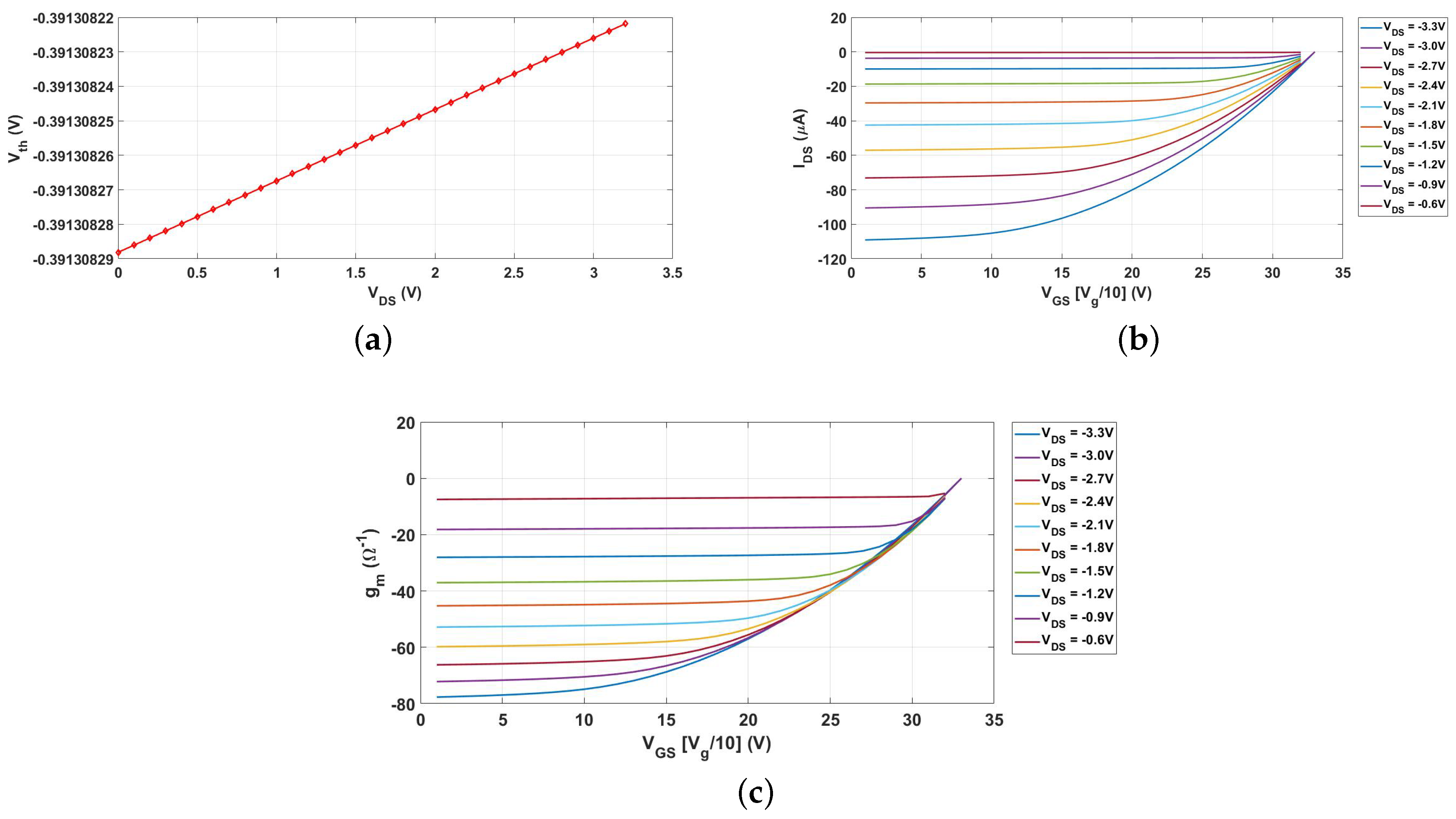

| Parameter | nMOS | pMOS |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature (C) | 60 | 60 |
| Channel’s width (m) | 1.8 | 1.8 |
| Channel’s length (m) | 1.8 | 1.8 |
| Gate voltage (V) | 3.3 | 0 |
| Drain voltage (V) | 3.3 | 0 |
| Source voltage (V) | 0 | 3.3 |
| Bulk voltage (V) | 0 | 3.3 |
| PBTI | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 V | 1.1 V | 2.2 V | 3.3 V | |
| (mV) | 0 | 0 | 0.1 | 0.3 |
| (nA) | 0 | −6.8 | −37.5 | −89.4 |
| (m) | 0 | −8.7 | −21.1 | −33.3 |
| (m) | 0 | 0.6 | 1.7 | 2.8 |
| NBTI Low %N | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 V | −1.1 V | −2.2 V | −3.3 V | |
| (mV) | −3.5 | −12.3 | −21 | −29.4 |
| (A) | 0 | −0.3445 | −1.3141 | −2.6377 |
| () | 0 | −0.4957 | −0.7954 | −1.0207 |
| () | 0 | 0.2416 | 0.413 | 0.5788 |
| NBTI High %N | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 V | −1.1 V | −2.2 V | −3.3 V | |
| (mV) | −7.4 | −27.8 | −47.5 | −66.7 |
| (A) | 0 | −0.765 | −2.9314 | −5.8941 |
| () | 0 | −1.1176 | −1.7922 | −2.3011 |
| () | 0 | 0.5466 | 0.935 | 1.3112 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Campos-Cruz, A.; Espinosa-Flores-Verdad, G.; Torres-Jacome, A.; Tlelo-Cuautle, E. On the Prediction of the Threshold Voltage Degradation in CMOS Technology Due to Bias-Temperature Instability. Electronics 2018, 7, 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7120427
Campos-Cruz A, Espinosa-Flores-Verdad G, Torres-Jacome A, Tlelo-Cuautle E. On the Prediction of the Threshold Voltage Degradation in CMOS Technology Due to Bias-Temperature Instability. Electronics. 2018; 7(12):427. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7120427
Chicago/Turabian StyleCampos-Cruz, Alejandro, Guillermo Espinosa-Flores-Verdad, Alfonso Torres-Jacome, and Esteban Tlelo-Cuautle. 2018. "On the Prediction of the Threshold Voltage Degradation in CMOS Technology Due to Bias-Temperature Instability" Electronics 7, no. 12: 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7120427
APA StyleCampos-Cruz, A., Espinosa-Flores-Verdad, G., Torres-Jacome, A., & Tlelo-Cuautle, E. (2018). On the Prediction of the Threshold Voltage Degradation in CMOS Technology Due to Bias-Temperature Instability. Electronics, 7(12), 427. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7120427







