Evaluating the Application of Electrical Resistivity Tomography for Investigating Seawater Intrusion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review and Research Method
2.1. Electrical Resistivity Tomography
2.2. Time-Lapse Resistivity Detection
2.3. Impact of Tidal Action on Underground Water
2.4. Research Method
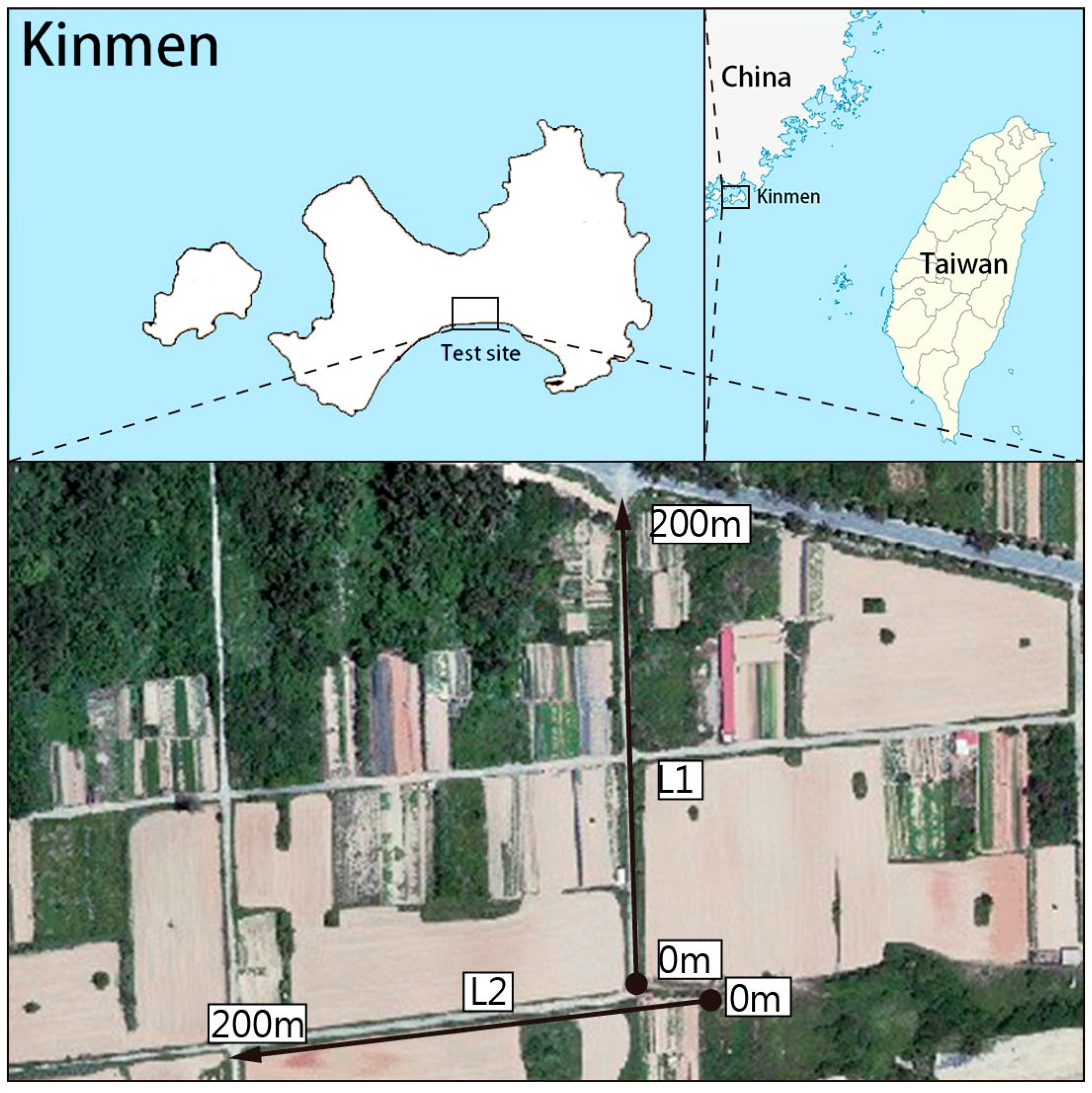
3. Introduction to Test Site
4. Test Results
4.1. ERT Field Acquisiton and Data Analysis
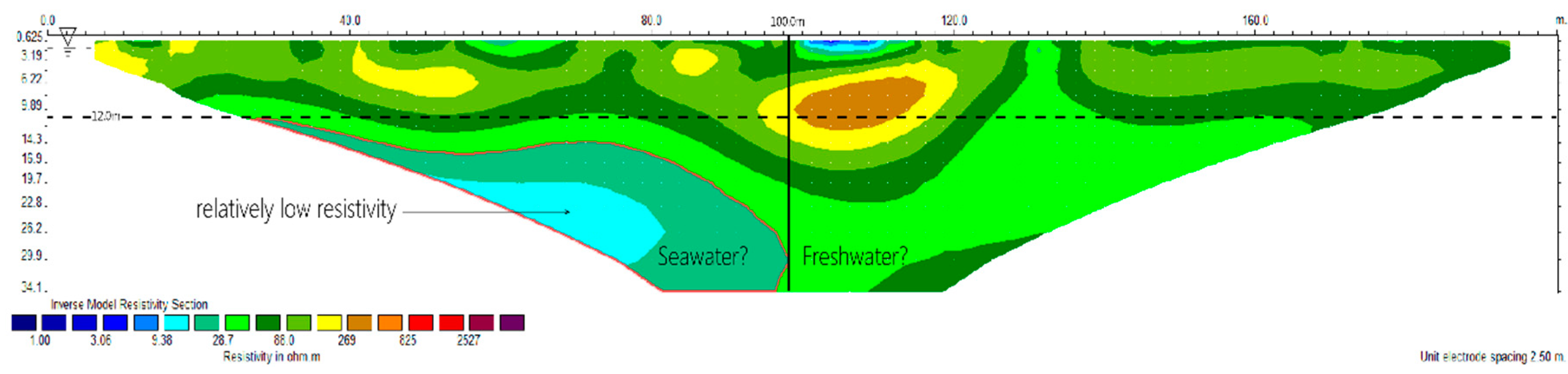
4.1.1. L1 Measuring Line
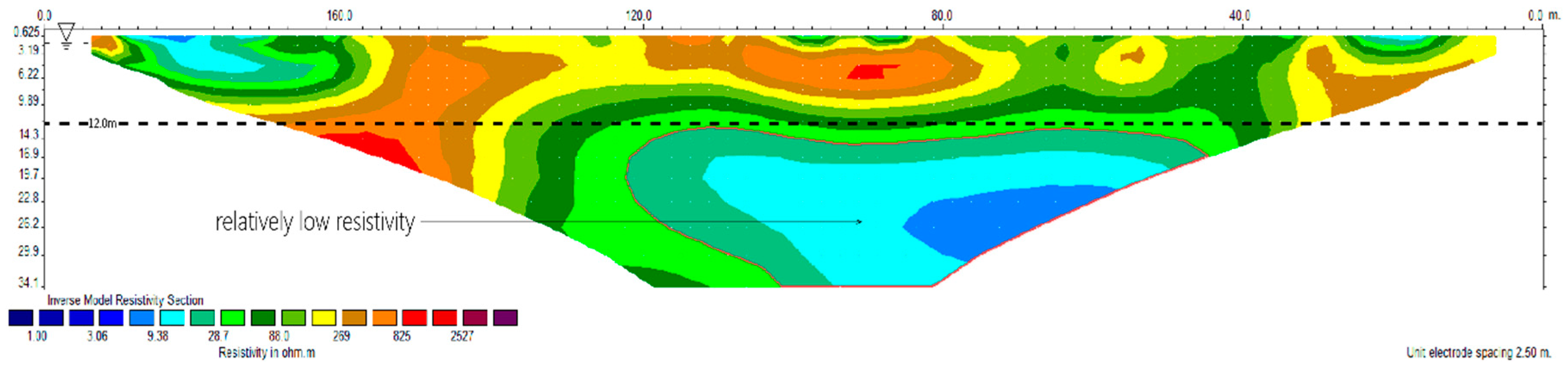
4.1.2. L2 Measuring Line
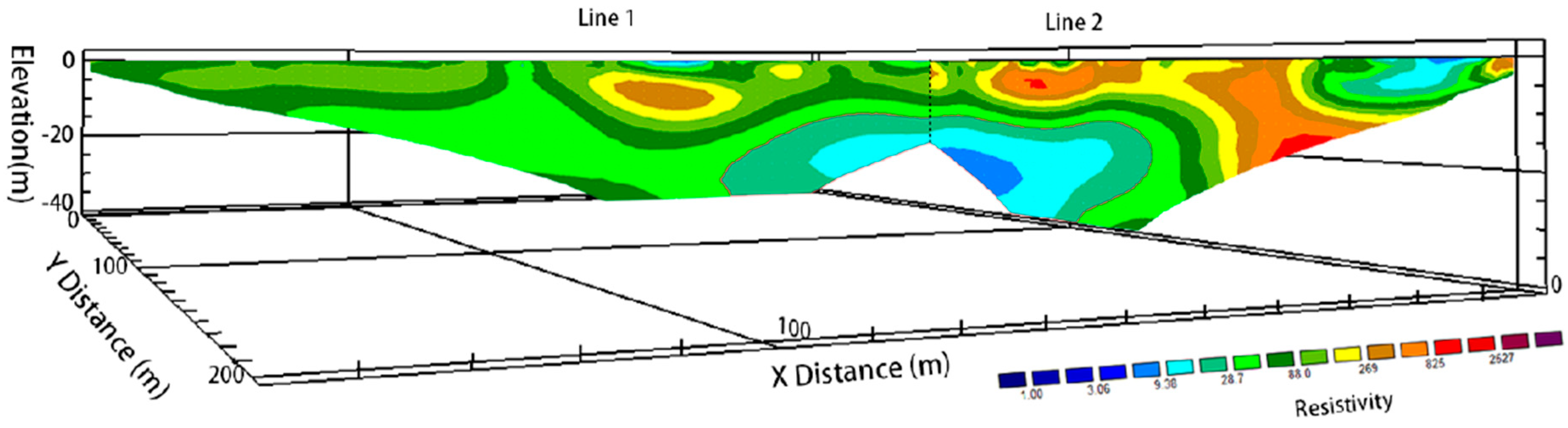
4.1.3. Comprehensive Interpretation
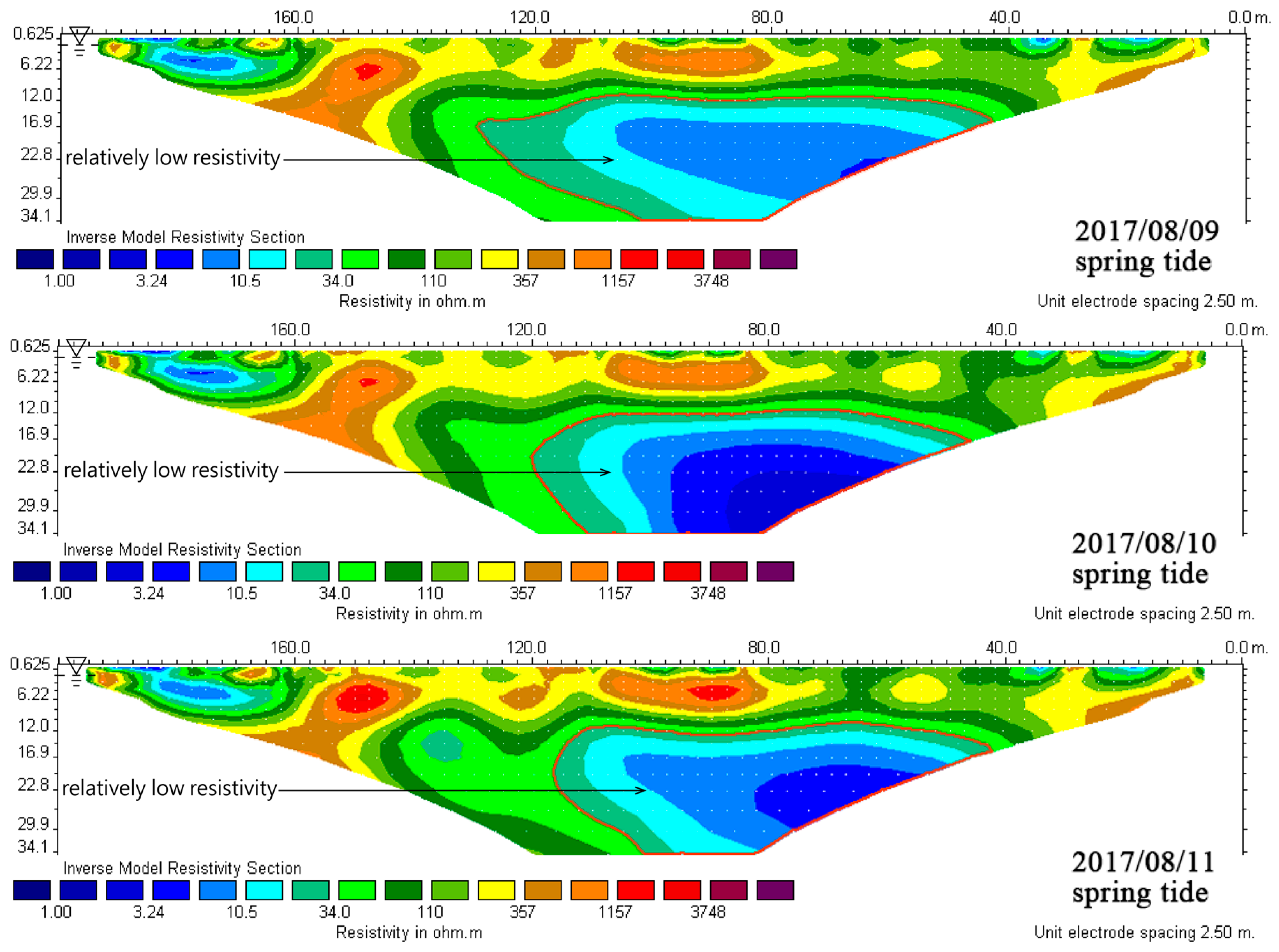
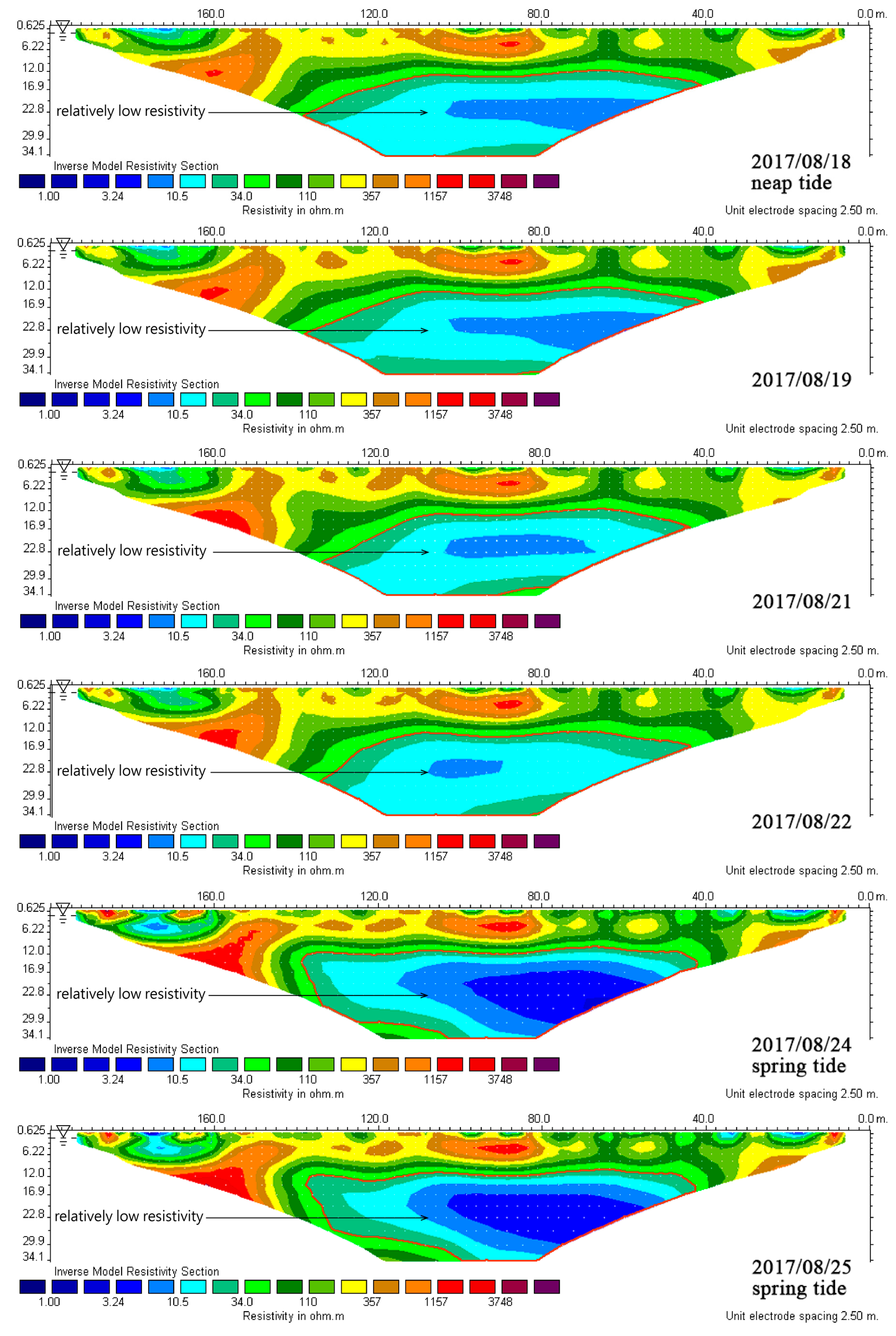
4.2. Time-Lapse
4.2.1. L1 Measuring Line
4.2.2. L2 Measuring Line
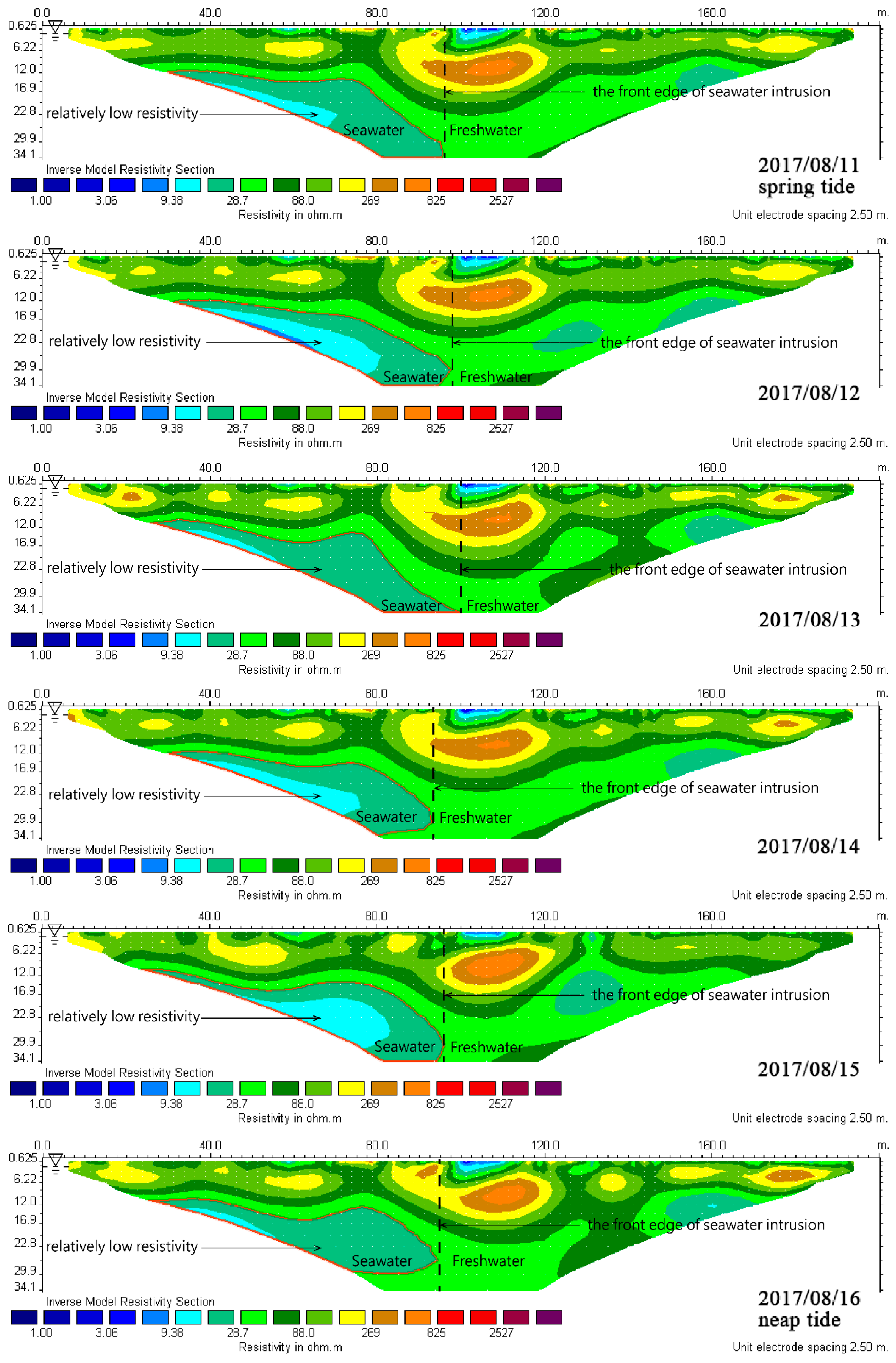
4.3. Tidal Action
4.3.1. L1 Measuring Line of Tide Rise and Tide Ebb
4.3.2. L2 Measuring Line of Tide Rise and Tide Ebb
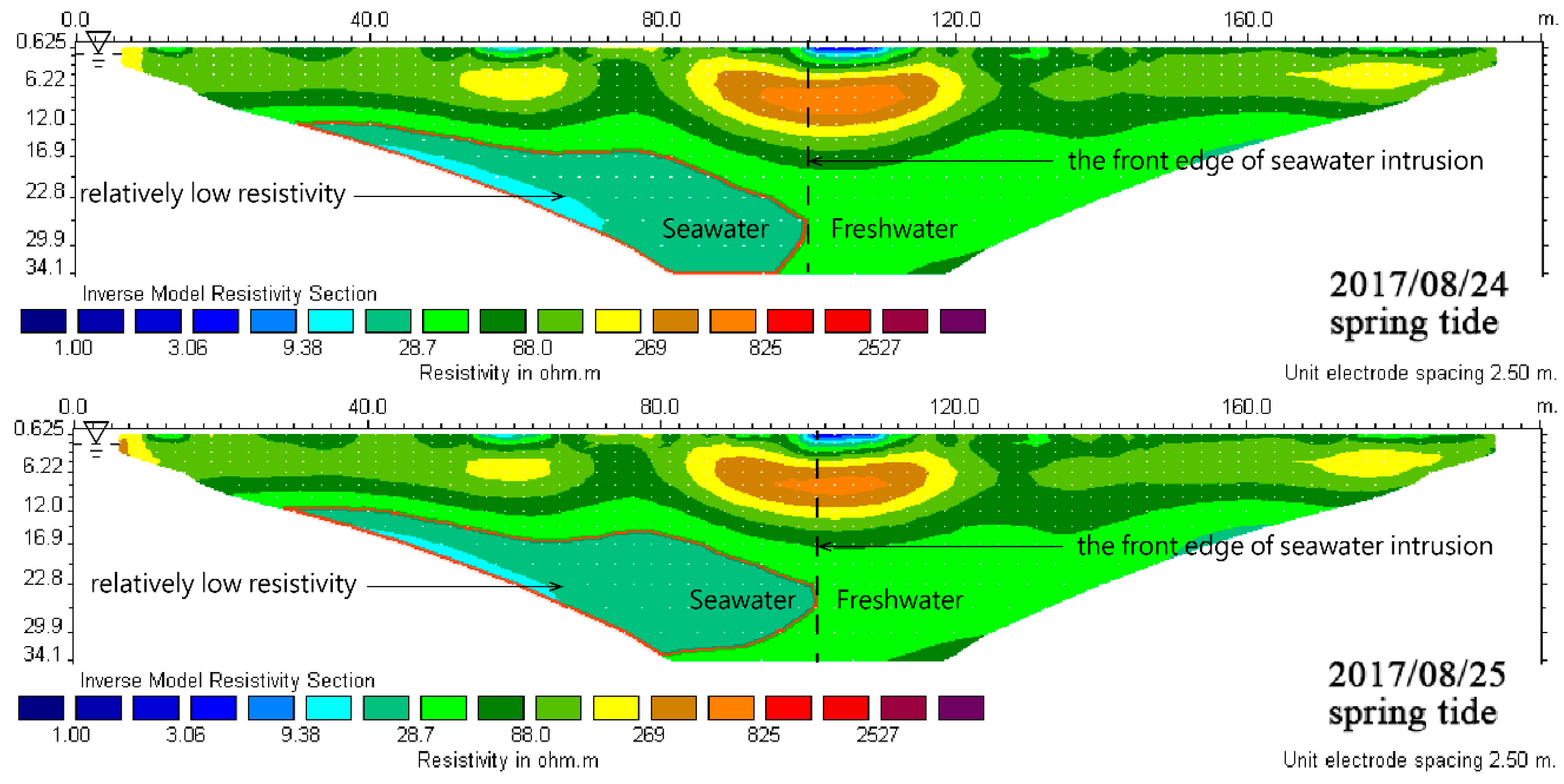
4.3.3. L1 Measuring Line of Spring Tide and Neap Tide
4.3.4. L2 Measuring Line of Spring Tide and Neap Tide
4.3.5. Comprehensive Interpretation
5. Conclusions and Suggestions
5.1. Conclusions
5.2. Suggestions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dahlin, T. The development of DC resistivity imaging techniques. Comput. Geosci. 2001, 27, 1019–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipfert, G.; Sandberg, S.; Slater, L.; Reeve, A.; Loiselle, M. The Temporal Variation of a Saltwater Contaminant Plume as Evidenced through Long-Term Resistivity Monitoring. In Symposium on the Application of Geophysics to Engineering and Environmental Problems; Environment and Engineering Geophysical Society: Denver, CO, USA, 1999; pp. 497–506. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, D.; Abbey, D.; Mackie, D.; Luzitano, R.; Cleary, M. Investigation of Potential Saltwater Intrusion Pathways in a Fractured Aquifer using an Integrated Geophysical, Geological and Geochemical Approach. J. Environ. Eng. Geophys. 2002, 7, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodlur, G.; Dhakate, R.; Andrade, R. Correlation of vertical electrical sounding and borehole-log data for delineation of saltwater and freshwater aquifers. Geophysics 2006, 71, G11–G20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Franco, R.; Biella, G.; Tosi, L.; Teatini, P.; Lozej, A.; Chiozzotto, B.; Giada, M.; Rizzetto, F.; Claude, C.; Mayer, A.; et al. Monitoring the saltwater intrusion by time lapse electrical resistivity tomography: The Chioggia test site (Venice Lagoon, Italy). J. Appl. Geophys. 2009, 69, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kura, N.U.; Ramli, M.F.; Ibrahim, S.; Sulaiman, W.N.A.; Zaudi, M.A.; Aris, A.Z. A Preliminary Appraisal of the Effect of Pumping on Seawater Intrusion and Upconing in a Small Tropical Island Using 2D Resistivity Technique. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 796425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oueuemi, K.D.; Aizebeokhai, A.P.; Oladunjoye, M.A. Integrated Geophysical and Geochemical Investigations of Saline Water Intrusion in a Coastal Alluvial Terrain, Southwestern Nigeria. Int. J. Appl. Environ. Sci. 2015, 10, 1275–1288. [Google Scholar]
- Pidlisecky, A.; Moran, T.; Hansen, B.; Knight, R. Electrical resistivity imaging of seawater intrusion into the monterey bay aquifer system. Groundwater 2015, 54, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashim, M.M.M.; Samuding, K.; Zawawi, M.H.; Daung, J.A.D.; Zulkurnain, M.H.; Mohamad, K. Application of Geophysical Method for Determining Seawater Intrusion in Coastal Aquifer. INIS 2017, 48, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Goebel, M.; Pidlisecky, A. Rosemary Knight, Resistivity imaging reveals complex pattern of saltwater intrusion along Monterey coast. J. Hydrol. 2017, 551, 746–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-P.; Hung, Y.-C.; Yu, Z.-H.; Wu, P.-L. Investigation of Abnormal Seepages in an Earth Dam Using Resistivity Tomography. J. GeoEng. 2013, 8, 61–70. [Google Scholar]
- Carter, A.R.J. Investigation into the Use of Resistivity Profiling in the Detection of the Fresh/Saline Water Interface within Coastal Settings. Bachelor’s Thesis, University of Lancaster, Lancaster, UK, 2002; p. 71. [Google Scholar]
- Singha, K.; Gorelick, S.M. Saline tracer visualized with three dimensional electrical resistivity tomography: Field-scale spatial moment analysis. Water Resour. Res. 2005, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swarzenski, P.W.; Burnett, W.C.; Greenwood, W.J.; Herut, B.; Peterson, R.; Dimova, N.; Shalem, Y.; Yechieli, Y.; Weinstein, Y. Combined time-series resistivity and geochemical tracer techniques to examine submarine groundwater discharge at Dor Beach, Israel. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kazakis, N.; Pavlou, A.; Vargemezis, G.; Voudouris, K.S.; Soulios, G.; Pliakas, F.; Tsokas, G. Seawater intrusion mapping using electrical resistivity tomography and hydrochemical data. An application in the coastal area of eastern Thermaikos Gulf, Greece. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 543, 373–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutter, E.; Ingham, M. Seasonal saline intrusion monitoring of a shallow coastal aquifer using time-lapse DC resistivity traversing. Near Surf. Geophys. 2017, 15, 59–73. [Google Scholar]
- García-Menéndez, O.; Ballesteros, B.J.; Renau-Pruñonosa, A.; Morell, I.; Mochales, T.; Ibarra, P.I.; Rubio, F.M. Using electrical resistivity tomography to assess the effectiveness of managed aquifer recharge in a salinized coastal aquifer. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2018, 190, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, I.R.; Eyre, B.D.; Huettel, M. The driving forces of porewater and groundwater flow in permeable coastal sediments: A review. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 98, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Q.; Xu, X.; Chen, G.; Fu, T.; Liu, W. Study on the Impact of Tides on Groundwater Table Fluctuation in Coastal Aquifer. Adv. Mar. Sci. 2017, 35, 568–578. [Google Scholar]
- Inouchi, K.; Kishi, Y.; Kakinuma, T. The motion of coastal groundwater in response to the tide. J. Hydrol. 1990, 115, 165–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, P. Tide dynamics of the water table in beaches. Water Resour. Res. 1990, 26, 2127–2134. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Barry, D.A.; Pattiaratchi, C.B. Numerical modeling of tide-induced beach water table fluctuations. Coast. Eng. 1997, 30, 105–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, P. Groundwater Dynamics and Salinity in Coastal Barriers. J. Coast. Res. 1999, 15, 732–740. [Google Scholar]
- Koefoed, O. Geosounding Principles; Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1979. [Google Scholar]







| AUG | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tide Time | Tide Height | Tide Time | Tide Height | Tide Time | Tide Height | |||||||||
| 9 | 1:04 | 222 | 507 | H | 15 | 4:52 | 205 | 490 | H | 21 | 5:18 | −171 | 115 | L |
| 7:00 | −190 | 96 | L | 11:10 | −209 | 76 | L | 11:19 | 224 | 509 | H | |||
| 12:53 | 216 | 501 | H | 17:29 | 174 | 459 | H | 17:41 | −274 | 11 | L | |||
| 19:15 | −257 | 28 | L | 23:32 | −159 | 126 | L | |||||||
| 10 | 1:37 | 227 | 512 | H | 16 | 5:47 | 193 | 478 | H | 22 | 0:12 | 248 | 533 | H |
| 7:35 | −195 | 90 | L | 12:11 | −212 | 73 | L | 6:06 | −188 | 97 | L | |||
| 13:30 | 220 | 505 | H | 18:40 | 163 | 448 | H | 12:08 | 242 | 527 | H | |||
| 19:48 | −252 | 33 | L | 18:28 | −277 | 8 | L | |||||||
| 11 | 2:10 | 228 | 513 | H | 17 | 0:44 | −136 | 149 | L | 23 | 0:53 | 257 | 542 | H |
| 8:10 | −198 | 87 | L | 6:51 | 182 | 467 | H | 6:49 | −202 | 84 | L | |||
| 14:08 | 218 | 503 | H | 13:19 | −218 | 67 | L | 12:52 | 252 | 537 | H | |||
| 20:23 | −243 | 43 | L | 20:01 | 162 | 447 | H | 19:11 | −271 | 14 | L | |||
| 12 | 2:44 | 227 | 512 | H | 18 | 2:03 | −126 | 159 | L | 24 | 1:31 | 259 | 544 | H |
| 8:48 | −201 | 84 | L | 8:02 | 178 | 463 | H | 7:29 | −210 | 75 | L | |||
| 14:49 | 212 | 497 | H | 14:34 | −230 | 55 | L | 13:33 | 254 | 539 | H | |||
| 21:01 | −229 | 56 | L | 21:23 | 178 | 463 | H | 19:50 | −258 | 27 | L | |||
| 13 | 3:22 | 222 | 507 | H | 19 | 3:18 | −133 | 152 | L | 25 | 2:06 | 255 | 540 | H |
| 9:30 | −203 | 82 | L | 9:15 | 185 | 470 | H | 8:08 | −214 | 72 | L | |||
| 15:35 | 202 | 487 | H | 15:45 | −248 | 38 | L | 14:13 | 247 | 532 | H | |||
| 21:43 | −210 | 75 | L | 22:31 | 204 | 489 | H | 20:26 | −239 | 46 | L | |||
| 14 | 4:04 | 215 | 500 | H | 20 | 4:22 | −150 | 135 | L | |||||
| 10:17 | −206 | 79 | L | 10:22 | 203 | 488 | H | |||||||
| 16:27 | 188 | 473 | H | 16:47 | −264 | 21 | L | |||||||
| 22:33 | −186 | 99 | L | 23:26 | 229 | 514 | H | |||||||
| Depth (m) | Thickness (m) | Rock or Soil Properties Description |
|---|---|---|
| 0–0.5 | 0.5 | Concrete and Granite Blocks |
| 0.5–4.5 | 4 | Brown crude sand, Granite Blocks, clay |
| 4.5–20 | 15.5 | Brown crude sand, Granite Blocks, clay |
| Sample | Sample 1 (On the L1 Line at 100 m) | Sample 2 (On the L1 Line at 125 m) | Freshwater |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electrical conductivity(μS/cm) | 1455 | 898 | <1200 |
| Chlorine salt value (ppm) | 440 | 268 | <250 |
| Total dissolved solids (ppm) | 724 | 440 | <500 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, T.-T.; Hung, Y.-C.; Hsueh, M.-W.; Yeh, Y.-H.; Weng, K.-W. Evaluating the Application of Electrical Resistivity Tomography for Investigating Seawater Intrusion. Electronics 2018, 7, 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7070107
Chen T-T, Hung Y-C, Hsueh M-W, Yeh Y-H, Weng K-W. Evaluating the Application of Electrical Resistivity Tomography for Investigating Seawater Intrusion. Electronics. 2018; 7(7):107. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7070107
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Tung-Tsan, Yin-Chun Hung, Ming-Wei Hsueh, Yung-Hsin Yeh, and Ko-Wei Weng. 2018. "Evaluating the Application of Electrical Resistivity Tomography for Investigating Seawater Intrusion" Electronics 7, no. 7: 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7070107
APA StyleChen, T.-T., Hung, Y.-C., Hsueh, M.-W., Yeh, Y.-H., & Weng, K.-W. (2018). Evaluating the Application of Electrical Resistivity Tomography for Investigating Seawater Intrusion. Electronics, 7(7), 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics7070107




