A 3GSps 12-bit Four-Channel Time-Interleaved Pipelined ADC in 40 nm CMOS Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
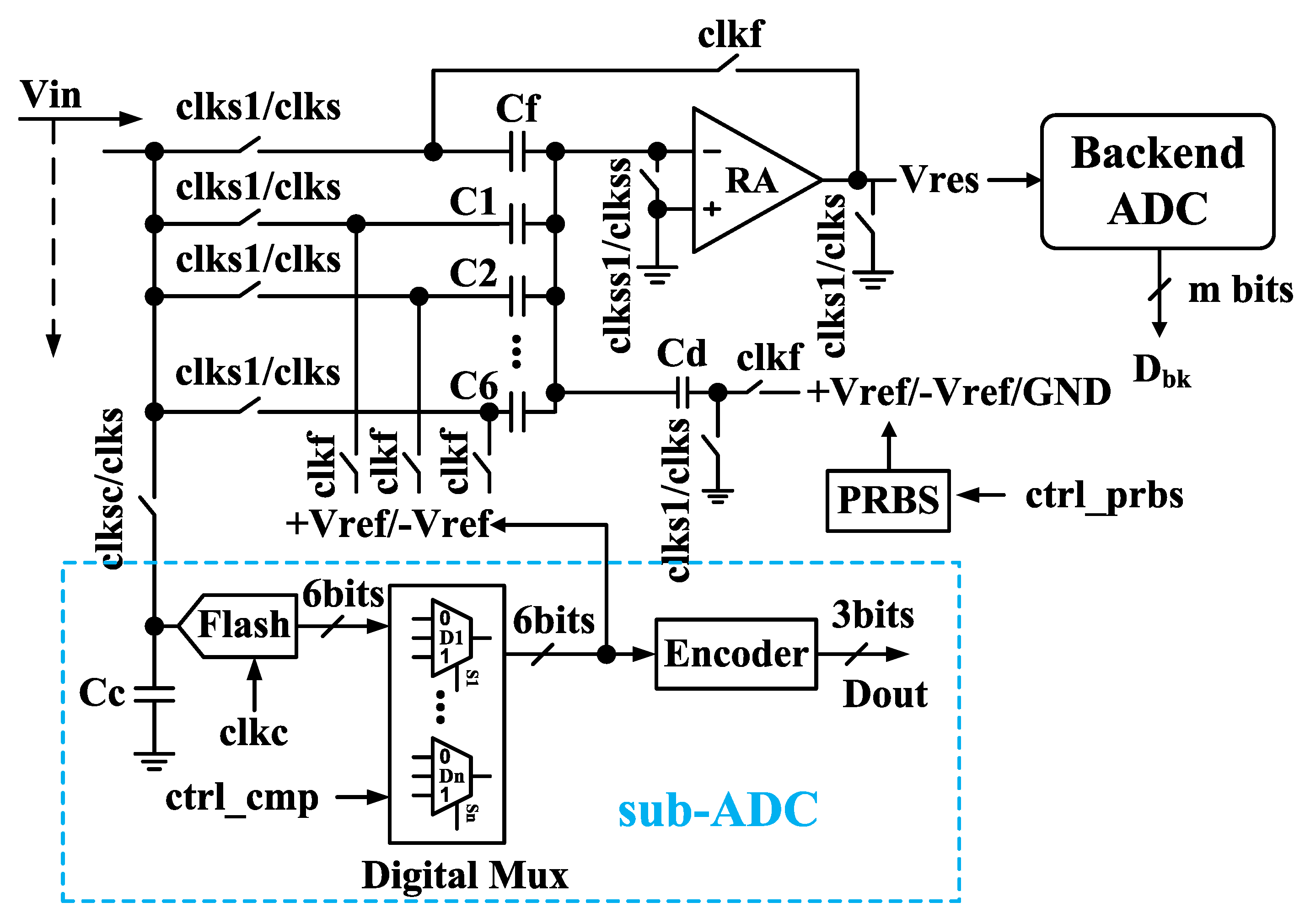
2. Proposed ADC Architecture
3. Circuits Implementation and Calibration
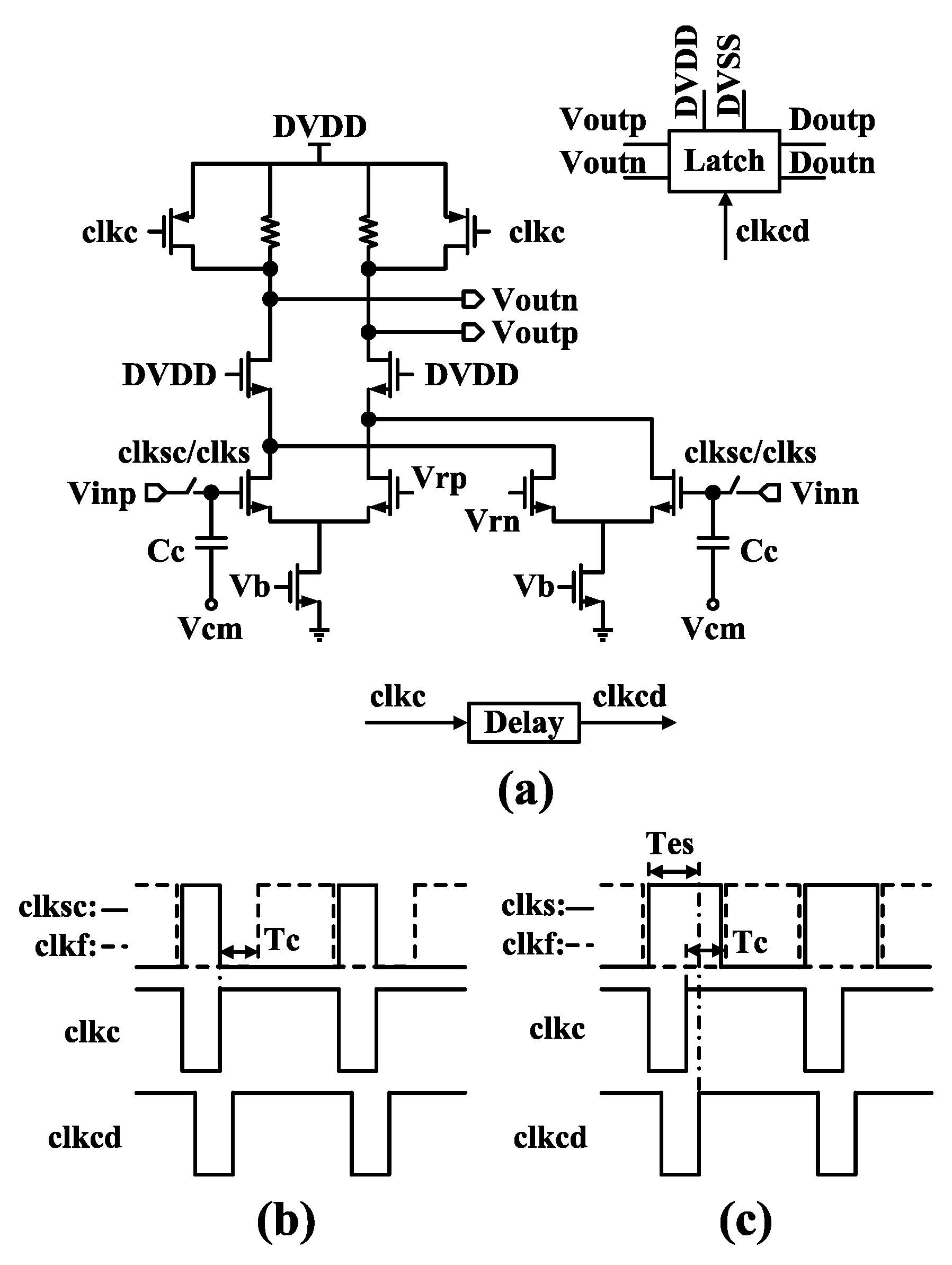
3.1. The Combination of Retiming and Delay-Adjusting
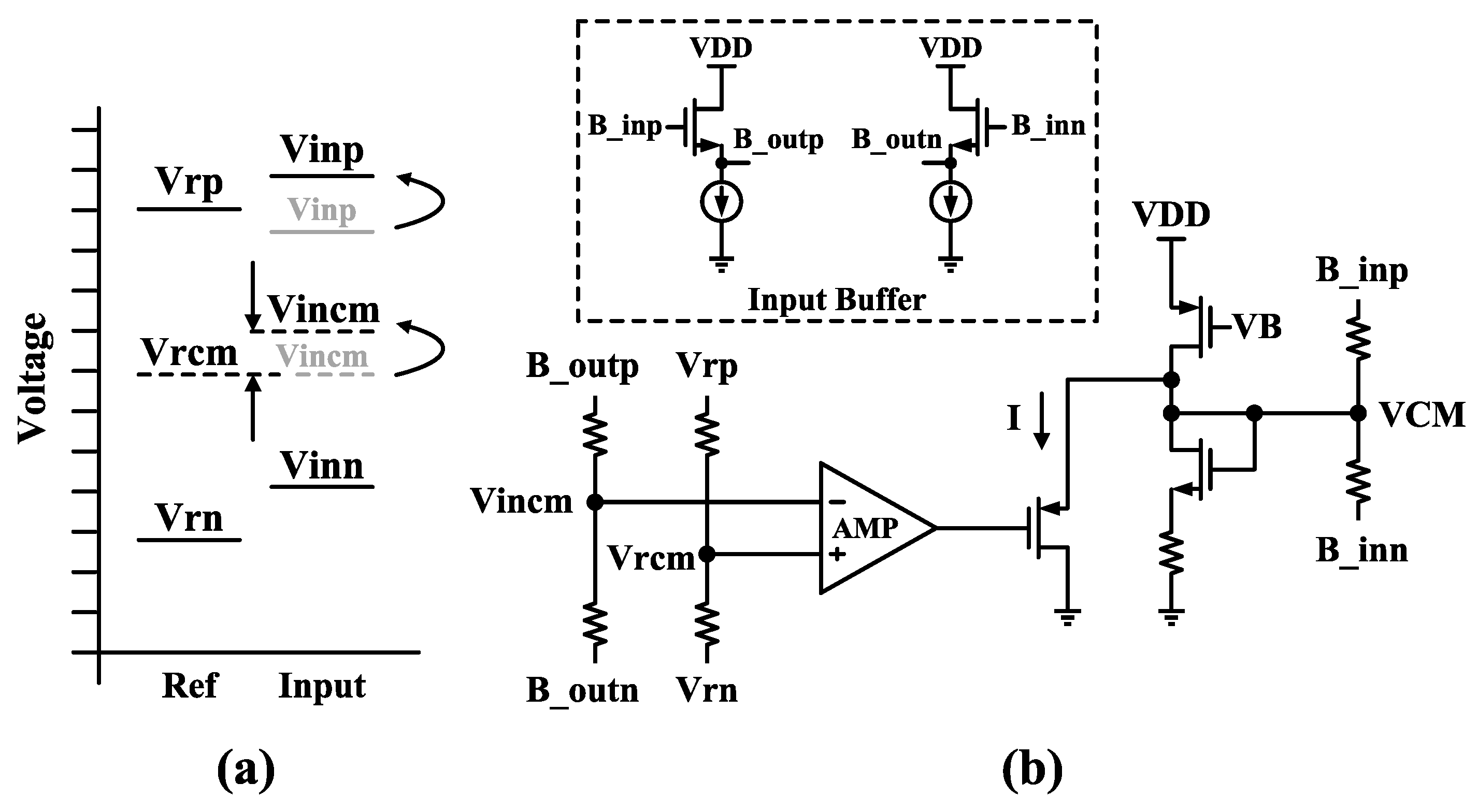
3.2. Early Comparison Scheme
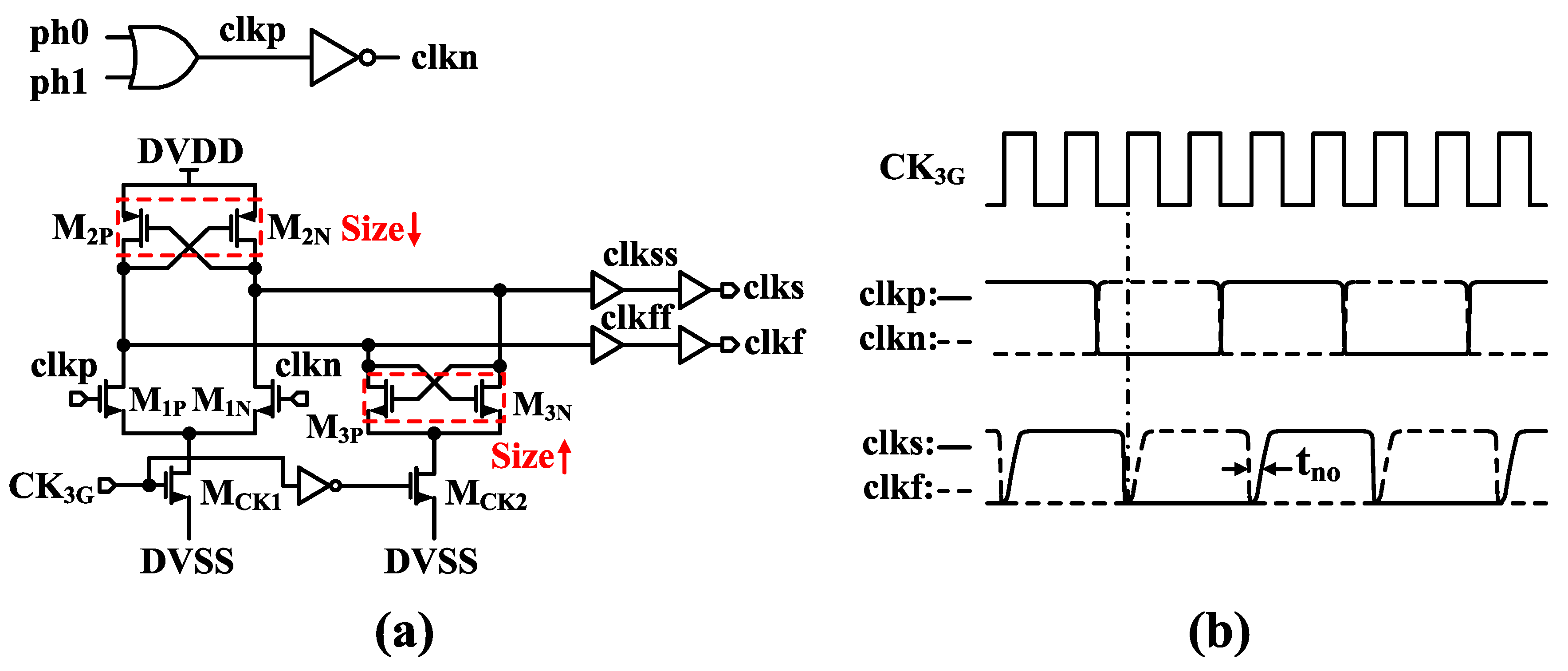
3.3. The Implementation of CLNC
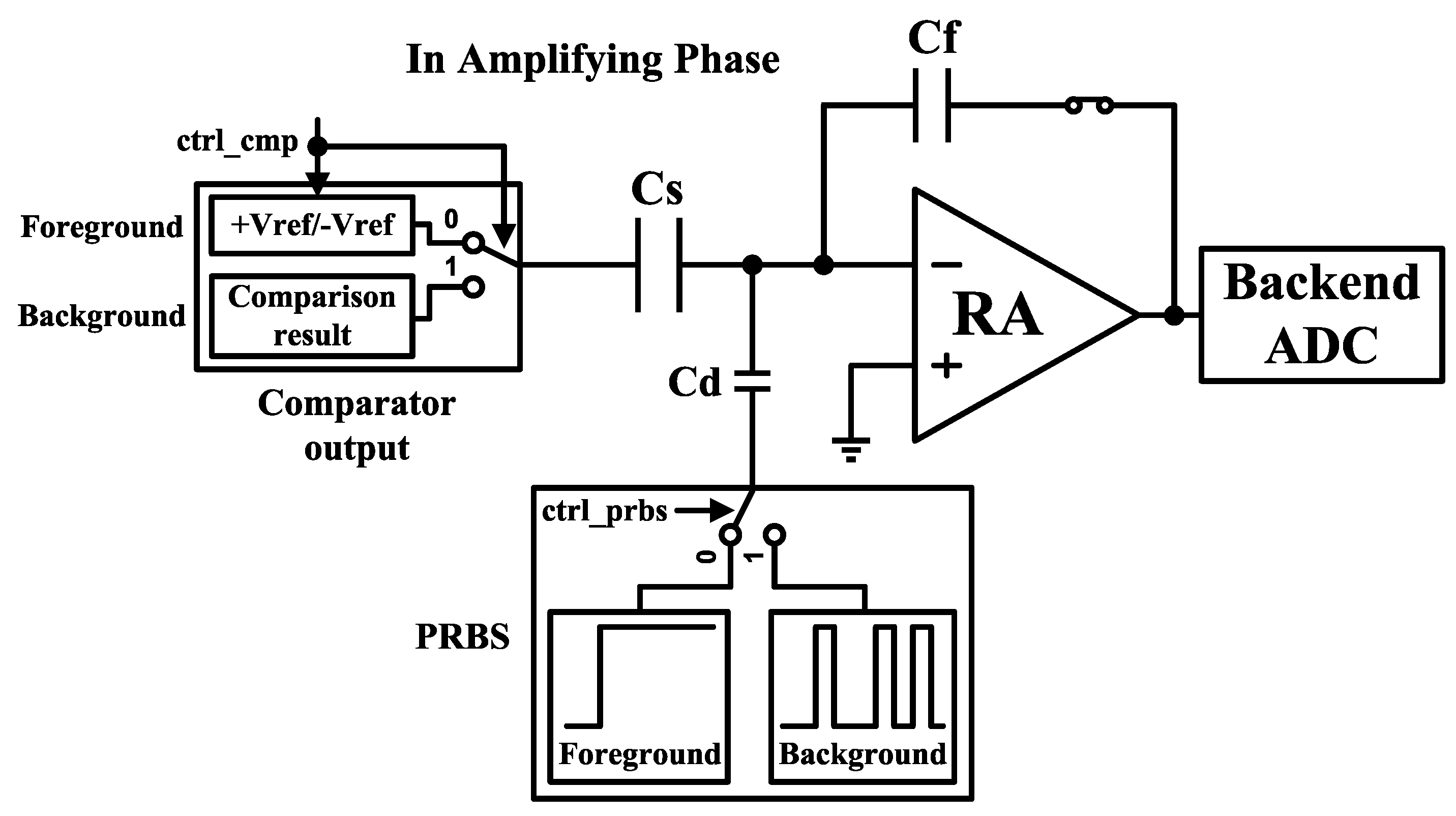
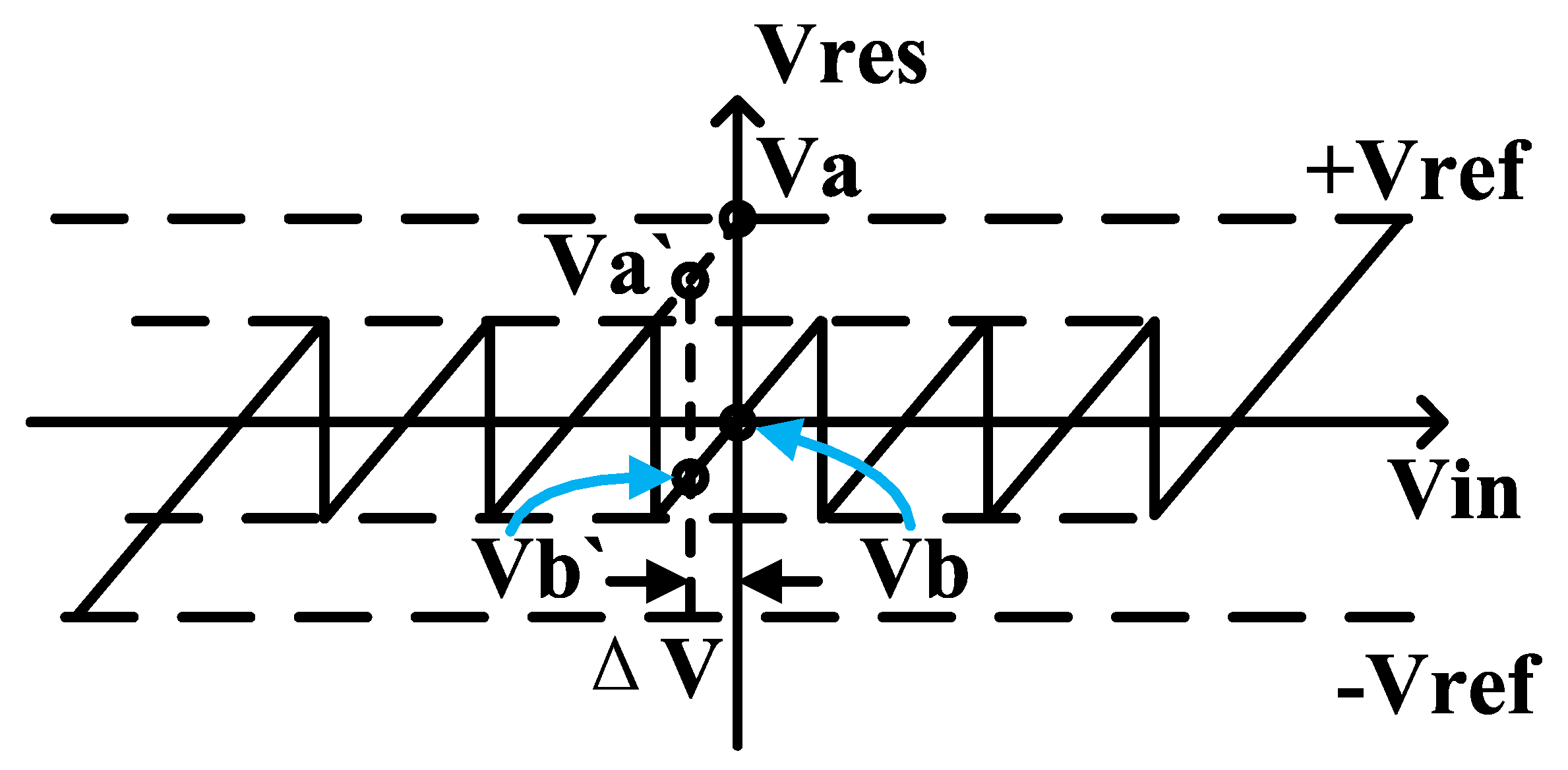
3.4. Zero-input-based calibration
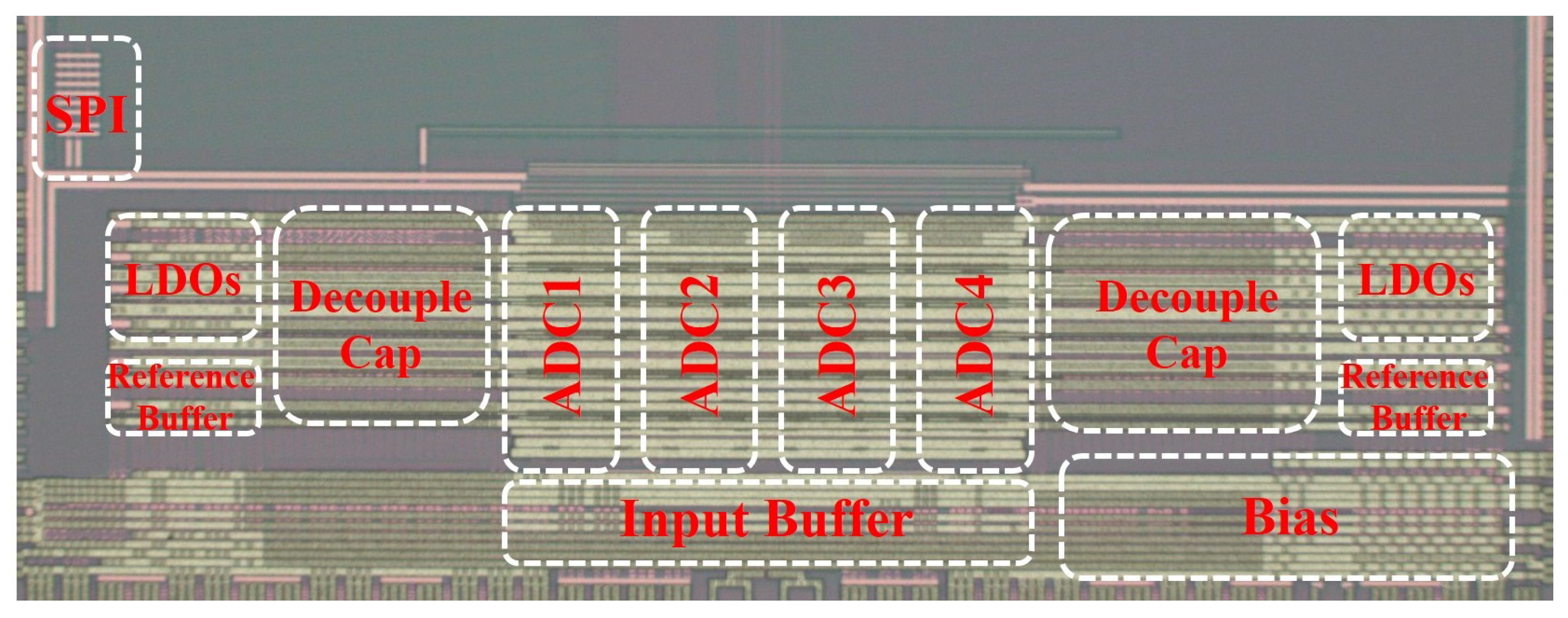
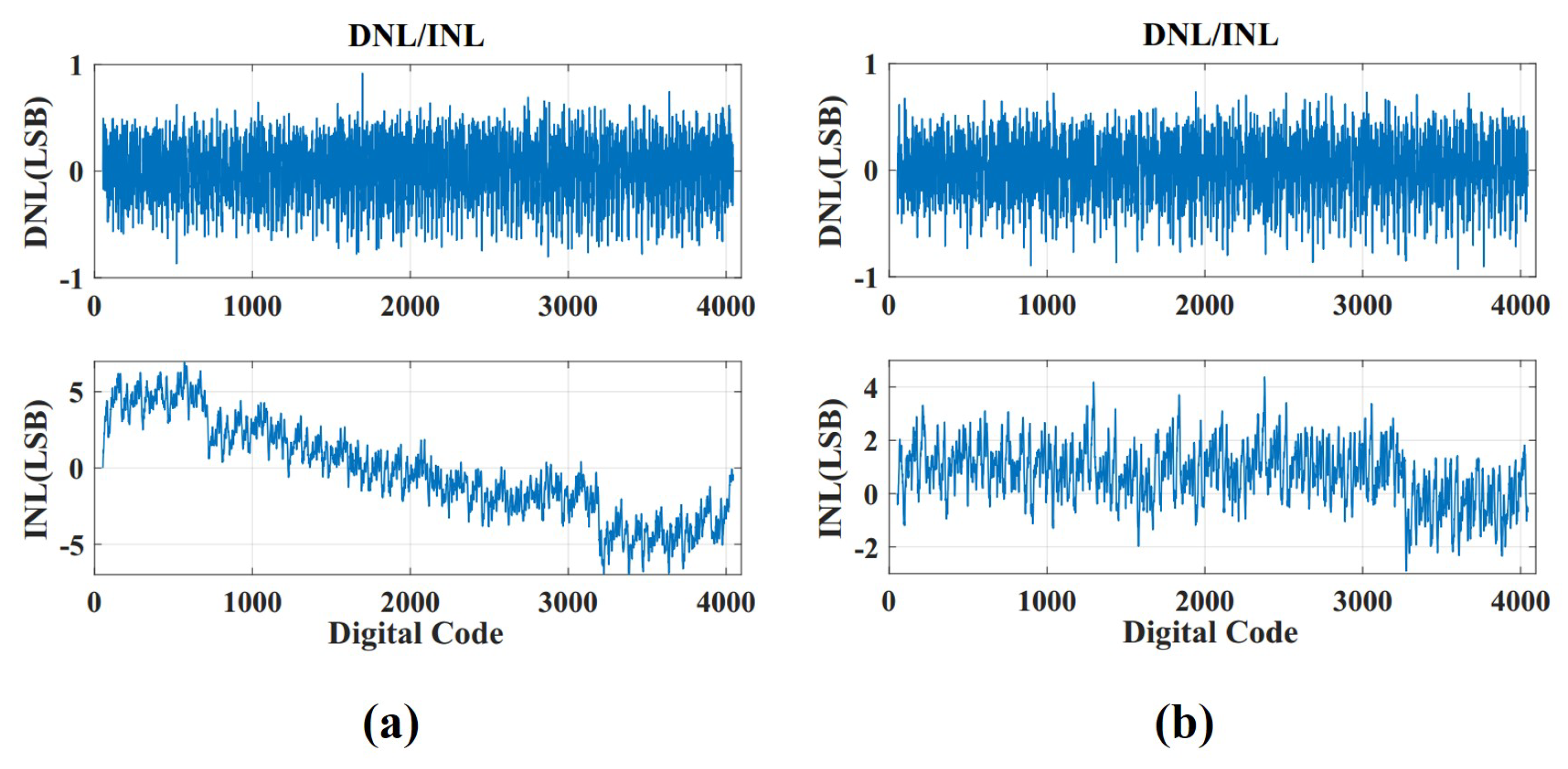
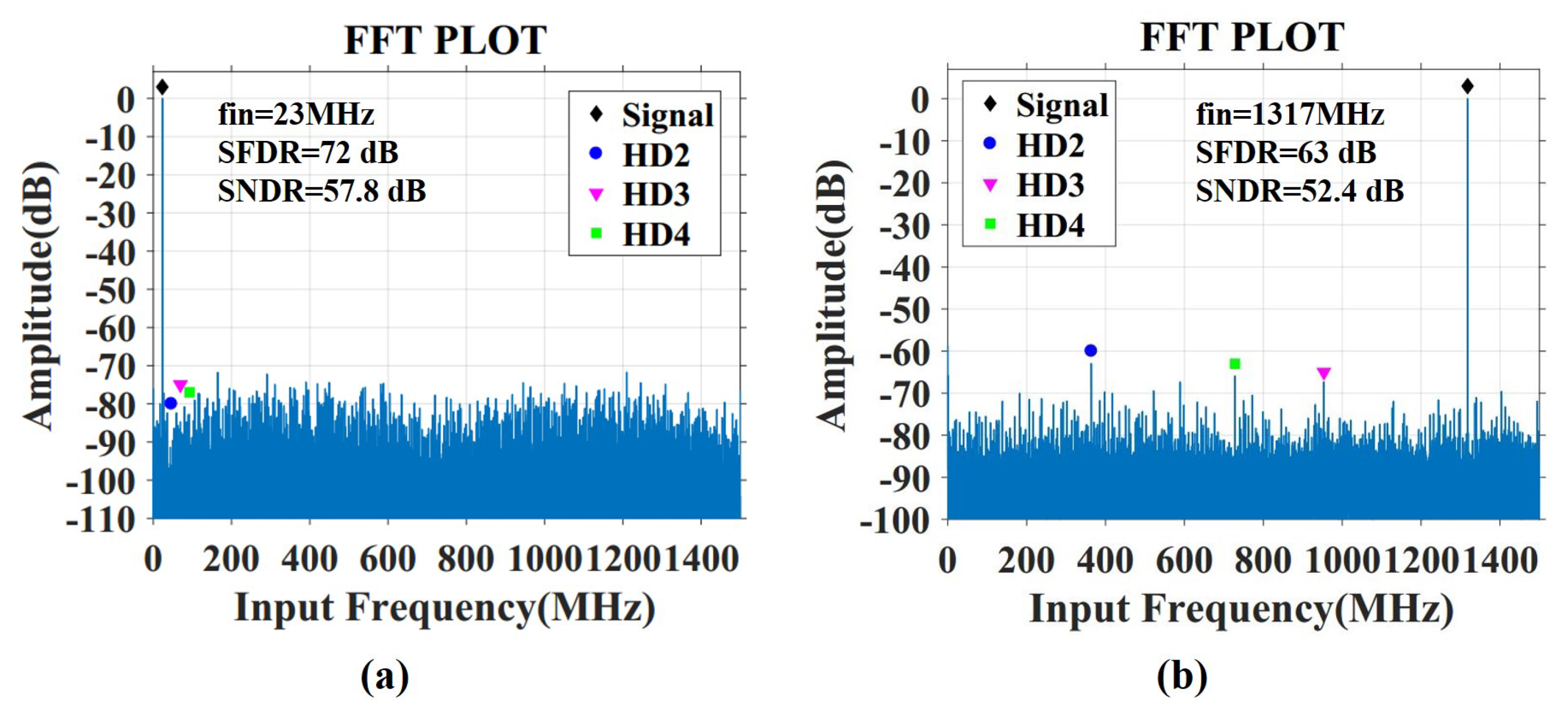
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADC | Analog-to-digital converter | The system that converts an analog signal into a digital signal. |
| CLNC | Custom-designed latch for non-overlapping clock | The circuit that replaces NCG to generate the non-overlapping clock. |
| CMOS | Complementary metal oxide silicon | The basic component of integrated circuits. |
| DAC | Digital-to-analog converter | The system that converts a digital signal into an analog signal. |
| DNL | Differential nonlinearity | A term describing the deviation between two analog values corresponding to adjacent input digital values. |
| FFT | Fast Fourier transform | It converts a signal from time domain to a representation in the frequency domain. |
| FIR | Finite impulse response | The impulse response (or response to any finite length input) is of finite duration, because it settles to zero in finite time. |
| FOM | Figure of merit | A numerical expression representing the performance or efficiency of a given ADC. |
| GSps | Giga samples per second | The unit of sampling rate. |
| HD | Harmonic distortion | The distortion due to the signal whose frequency is an integral multiple of the frequency of the fundamental signal. |
| INL | Integral nonlinearity | A term describing the deviation between the ideal output value and the actual measured output value for a certain input code. |
| LDO | Low dropout regulator | A DC linear voltage regulator that can regulate the output voltage. |
| MDAC | Multiplying digital-to-analog converter | The cascaded coarse digitization stage which mainly consist of a sampling switch, a coarse ADC, a digital-to-analog converter (DAC), and a residue amplifier. |
| MIMO | Multiple-input, multiple-output | A method for multiplying the capacity of a radio link using multiple transmission and receiving antennas to exploit multipath propagation. |
| NCG | Non-overlapping clock generator | The circuit that generates the non-overlapping clock. |
| PRBS | Pseudorandom bit sequence | A binary sequence that, while generated with a deterministic algorithm, is difficult to predict and exhibits statistical behavior similar to a truly random sequence. |
| RA | Residue amplifier | The circuit that amplifies the residue signal to full scale. |
| SFDR | Spurious free dynamic range | Strength ratio of the fundamental signal to the strongest spurious signal in the output, which is measured with the unit of dB scale. |
| SHA | Sample and hold amplifier | The circuit that is used to sample an analog signal and to store its value for some length of time. |
| SPI | Serial peripheral interface | A synchronous serial communication interface specification used for short-distance communication. |
| SNDR | Signal-to-noise-and-distortion ratio | It stands for the ratio of the signal power to all the unwanted components, which is measured with the unit of dB scale. |
| SL | Sampling latch | The sampling clock is retimed by this circuit with master clock. |
| UCP | Unit conversion period | The time that ADC converts an analog signal to a digital signal once. |
| VDL | Variable delay line | The circuit that adjusts the delay time of sampling clock. |
| DC | Direct current | |
| IF | Intermediate frequency | |
| RF | Radio frequency | |
| LSB | Least significant bit | |
| MSB | Most significant bit | |
| nMOS | n-type metal oxide silicon | |
| pMOS | p-type metal oxide silicon | |
| PCB | Printed circuit board |
References
- Kumar, A.; Ganti, R.K.; Aniruddhan, S. A Same-Channel Full-Duplex Receiver Using Direct RF Sampling. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS), Florence, Italy, 27–30 May 2018; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Haberl, M.; Sanftl, B.; Trautmann, M.; Weigel, R.; Koelpin, A. A direct RF-to-baseband quadrature subsampling receiver using a low cost ADC. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Radio and Wireless Symposium (RWS), Phoenix, AZ, USA, 15–18 January 2017; pp. 144–146. [Google Scholar]
- Psiaki, M.L.; Powell, S.P.; Hee, J.; Kintner, P.M. Design and practical implementation of multifrequency RF front ends using direct RF sampling. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2005, 53, 3082–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thor, J.; Akos, D.M. A direct RF sampling multifrequency GPS receiver. In Proceedings of the 2002 IEEE Position Location and Navigation Symposium, Palms Springs, CA, USA, 15–18 April 2002; pp. 44–51. [Google Scholar]
- Doris, K.; Janssen, E.; Nani, C.; Zanikopoulos, A.; Van der Weide, G. A 480 mW 2.6GS/s 10b 65 nm CMOS time-interleaved ADC with 48.5 dB SNDR up to Nyquist. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 20–24 February 2011; pp. 180–182. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, S.; Choi, M.; Inerfield, M.; Wang, J. A 1GS/s 11b Time-Interleaved ADC in 0.13 um. In Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Solid State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 6–9 February 2006; pp. 2360–2369. [Google Scholar]
- Brandolini, M.; Shin, Y.J.; Raviprakash, K.; Wang, T.; Wu, R.; Geddada, H.M.; Ko, Y.; Ding, Y.; Huang, C.; Shih, W.; et al. A 5 GS/s 150 mW 10 b SHA-Less Pipelined/SAR Hybrid ADC for Direct-Sampling Systems in 28 nm CMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuit 2015, 50, 2922–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, E.; Doris, K.; Zanikopoulos, A.; Murroni, A.; Weide, G.; Lin, Y.; Alvado, L.; Darthenay, F.; Fregeais, Y. An 11b 3.6 GS/s time-interleaved SAR ADC in 65 nm CMOS. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 17–21 February 2013; pp. 464–465. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, H.; Zhang, P.; Sahoo, B.D.; Razavi, B. An 8 Bit 4 GS/s 120 mW CMOS ADC. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuit 2014, 49, 1751–1761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, B. Design Considerations for Interleaved ADCs. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuit 2013, 48, 1806–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jamal, S.M.; Fu, D.; Hurst, P.J.; Lewis, S.H. A 10b 120 MSample/s time-interleaved analog-to-digital converter with digital background calibration. In Proceedings of the 2002 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 7 February 2002; pp. 172–457. [Google Scholar]
- El-Chammas, M.; Murmann, B. A 12-GS/s 81-mW 5-bit Time-Interleaved Flash ADC With Background Timing Skew Calibration. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuit 2011, 46, 838–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcneil, J.A.; David, C.; Coin, M.; Croughwell, R. “Split ADC” Calibration for All-Digital Correction of Time-Interleaved ADC Errors. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2009, 56, 344–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haftbaradaran, A.; Martin, K.W. A Sample-Time Error Compensation Technique for Time-Interleaved ADC Systems. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference, San Jose, CA, USA, 16–19 September 2007; pp. 341–344. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Levy, B.C. Adaptive blind calibration of timing offset and gain mismatch for two-channel time-interleaved ADCs. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2006, 53, 1278–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanovic, D.; Nikolic, B. A 2.8 GS/s 44.6 mW Time-Interleaved ADC Achieving 50.9 dB SNDR and 3 dB Effective Resolution Bandwidth of 1.5 GHz in 65 nm CMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuit 2013, 48, 971–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, R.; Louerat, M.M.; Petigny, R.; Gicquel, H. Background offset and gain calibration for time-interleaved ADC using digital sinusoidal calibration signal. In Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Synthesis, Modeling, Analysis and Simulation Methods and Applications to Circuit Design (SMACD), Seville, Spain, 19–21 September 2012; pp. 273–276. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, F.; Zhao, F.; Yue, S.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z. A 14-bit 250 MS/s IF Sampling Pipelined ADC in 180 nm CMOS Process. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2016, 63, 1381–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, A.M.A.; Dinc, H.; Bhoraskar, P.; Dillon, C.; Puckett, S.; Gray, B.; Speir, C.; Lanford, J.; Brunsilius, J.; Derounian, P.R.; et al. A 14 Bit 1 GS/s RF Sampling Pipelined ADC With Background Calibration. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuit 2014, 49, 2857–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, Y.; Tsang, C.W.; Nikolic, B.; Gray, P.R. Least mean square adaptive digital background calibration of pipelined analog-to-digital converters. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I-Regul. Pap. 2004, 51, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, U.-K.; Song, B.-S. Background digital calibration techniques for pipelined ADCs. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II 1997, 44, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grace, C.R.; Hurst, P.J.; Lewis, S.H. A 12-bit 80-MSample/s pipelined ADC with bootstrapped digital calibration. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuit 2005, 40, 1038–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ali, A.M.A.; Nagaraj, K. Background calibration of operational amplifier gain error in pipelined A/D converters. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II 2003, 50, 631–634. [Google Scholar]
- Jalali-Farahani, B.; Meruva, A. A 14-b 32 MS/s pipelined ADC with fast convergence comprehensive background calibration. Analog Integr. Circuits Process. 2009, 61, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, S.W.; Sun, H.; Razavi, B. A 10-Bit 800-MHz 19-mW CMOS ADC. In Proceedings of the 2013 Symposium on VLSI Circuits, Kyoto, Japan, 12–14 June 2013; pp. C100–C101. [Google Scholar]
- Min, B.M.; Kim, P.; Bowman, F.W.; Boisvert, D.M.; Aude, A.J. A 69-mW 10-bit 80-MSample/s Pipelined CMOS ADC. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuit 2003, 38, 2031–2039. [Google Scholar]
- Lien, Y.C. A 14.6 mW 12b 800MS/s 4× time-interleaved pipelined SAR ADC achieving 60.8 dB SNDR with Nyquist input and sampling timing skew of 60fsrms without calibration. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Symposium on VLSI Circuits (VLSI-Circuits), Honolulu, HI, USA, 15–17 June 2016; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, J.; Shen, X.; Huang, X.; Fu, D.; Zhang, R. A 14-bit 500 MS/s low power time-interleaved analog-to-digital converter in 0.18-uM CMOS technology with background calibration. In Proceedings of the 2014 12th IEEE International Conference on Solid-State and Integrated Circuit Technology (ICSICT), Guilin, China, 28–31 October 2014; pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, T.B.; Gray, P.R. A 10 b, 20 Msample/s, 35 mW pipeline A/D converter. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuit 1995, 30, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, S.H.; Fetterman, H.S.; Gross, G.F.; Ramachandran, R.; Viswanathan, T.R. A 10-b 20-Msample/s analog-to-digital converter. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuit 1992, 27, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsu, C.; Huang, F.; Shih, C.; Huang, C.; Lin, Y.; Lee, C.; Razavi, B. An 11b 800MS/s Time-Interleaved ADC with Digital Background Calibration. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 11–15 February 2007; pp. 464–615. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, Y.; Li, S.; Tang, X.; Shen, L.; Zhao, W.; Wu, S.; Sun, N. A Second-Order Purely VCO-Based CT ΔΣ ADC Using a Modified DPLL Structure in 40-nm CMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuit 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Tang, X.; Shen, L.; Zhao, W.; Xin, X.; Liu, S.; Zhu, Z.; Sathe, V.S.; Sun, N. A 10-bit 120-MS/s SAR ADC With Reference Ripple Cancellation Technique. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuit 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.; Lee, C.; Lee, S.; Ryu, S.R. A Two-Channel Asynchronous SAR ADC With Metastable-Then-Set Algorithm. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2012, 20, 765–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, K.; Jo, D.; Kim, W.; Choi, M.; Ko, H.; Ryu, S. A 9.1-ENOB 6-mW 10-Bit 500-MS/s Pipelined-SAR ADC With Current-Mode Residue Processing in 28-nm CMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuit 2019, 54, 2532–2542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, M.; Kim, Y.; Chung, J.; Ryu, S. A 40nm CMOS 12b 200 MS/s Single-amplifier Dual-residue Pipelined-SAR ADC. In Proceedings of the 2019 Symposium on VLSI Circuits, Kyoto, Japan, 9–14 June 2019; pp. C72–C73. [Google Scholar]




| Reference | [8] | [5] | [6] | [31] | This Work |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Process | CMOS 65 nm | CMOS 65 nm | CMOS 0.13 m | CMOS 90 nm | CMOS 40 nm |
| Sampling rate(MSps) | 3600 | 2600 | 1000 | 800 | 3000 |
| Resolution(bits) | 11 | 10 | 11 | 11 | 12 |
| Supply(V) | 1.2/2.5 | 1.2/1.3/1.6 | 1.2/2.5 | 1.3/1.5 | 1.8 |
| SNDR@Nyquist(dB) | 42 | 48.5 | 52 | 54 | 52.3 |
| SFDR@Nyquist(dB) | 50 | 53.8 | 53.1 | 60 | 61.5 |
| Power(W) | 0.795 | 0.48 | 0.25 | 0.35 | 0.45 |
| FOM@Nyquist(pJ/step) | 2.15 | 0.85 | 0.5 | 1.1 | 0.44 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Guo, X.; Luan, J.; Wu, D.; Zhou, L.; Huang, Y.; Wu, N.; Jia, H.; Zheng, X.; Wu, J.; et al. A 3GSps 12-bit Four-Channel Time-Interleaved Pipelined ADC in 40 nm CMOS Process. Electronics 2019, 8, 1551. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8121551
Li J, Guo X, Luan J, Wu D, Zhou L, Huang Y, Wu N, Jia H, Zheng X, Wu J, et al. A 3GSps 12-bit Four-Channel Time-Interleaved Pipelined ADC in 40 nm CMOS Process. Electronics. 2019; 8(12):1551. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8121551
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jianwen, Xuan Guo, Jian Luan, Danyu Wu, Lei Zhou, Yinkun Huang, Nanxun Wu, Hanbo Jia, Xuqiang Zheng, Jin Wu, and et al. 2019. "A 3GSps 12-bit Four-Channel Time-Interleaved Pipelined ADC in 40 nm CMOS Process" Electronics 8, no. 12: 1551. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8121551
APA StyleLi, J., Guo, X., Luan, J., Wu, D., Zhou, L., Huang, Y., Wu, N., Jia, H., Zheng, X., Wu, J., & Liu, X. (2019). A 3GSps 12-bit Four-Channel Time-Interleaved Pipelined ADC in 40 nm CMOS Process. Electronics, 8(12), 1551. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8121551





