Abstract
To avoid degradation of navigation performance in the navigation warfare environment, the multi-radio integrated navigation system can be used, in which all available radio navigation systems are integrated to back up Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) when the GNSS is not available. Before real-time multi-radio integrated navigation systems are deployed, time and cost can be saved when the modeling and simulation (M&S) software is used in the performance evaluation. When the multi-radio integrated navigation system M&S is comprised of independent function modules, it is easy to modify and/or to replace the function modules. In this paper, the M&S software design method was proposed for multi-radio integrated navigation systems as a GNSS backup under the navigation warfare. The M&S software in the proposed design method consists of a message broker and function modules. All the messages were transferred through the message broker in order to be exchanged between the function modules. The function modules in the M&S software were independently operated due to the message broker. A message broker-based M&S software was designed for a multi-radio integrated navigation system. In order to show the feasibility of the proposed design method, the M&S software was implemented for Global Positioning System (GPS), Korean Navigation Satellite System (KNSS), enhanced Long range navigation (eLoran), Loran-C, and Distance Measuring Equipment/Very high-frequency Omnidirectional Radio range (DME/VOR). The usefulness of the proposed design method was shown by checking the accuracy and availability of the GPS only navigation and the multi-radio integrated navigation system under the attack of jamming to GPS.
1. Introduction
The simulation is defined as the imitative representation of the functioning of one system or process by means of the function of another and the modeling is defined as producing a representation or simulation [1]. Navigation warfare is defined as protecting the use of PNT (position, navigation and timing) information by friendly forces against the hostile attack with the electronic warfare method [2]. Since the received Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) signal strength is very weak and the signal structure of GNSS for civil use is open to the public, GNSS can be easily attacked by jamming, meaconing, and spoofing under the navigation warfare [3,4]. In order to overcome this weak point of the GNSS, other radio navigation systems can be integrated with the GNSS [3,5,6]. The FAA (Federal Aviation Administration) in the U.S. has announced a plan to use ground-based radio navigation systems when the GPS (Global Positioning System) is attacked by jamming and/or spoofing [6,7]. An alternative navigation system with enhanced Long-range navigation (eLoran) and the GNSS for marine navigation was proposed by the GLA (General Lighthouse Authority) in the U.K. [8]. Research on the multi-radio integrated navigation system has been conducted in Korea [9,10,11,12,13]. A regional satellite navigation system and ground-based radio navigation systems are additionally used with GPS in order to have a continuous navigation solution [9,10,14]. The regional satellite navigation system with seven satellites, called the KNSS (Korean Navigation Satellite System), will be deployed by the Korean government. Ground-based radio navigation systems include DME (Distance Measuring Equipment), Loran-C (Long-range navigation), e-Loran, and VOR (Very high-frequency Omnidirectional Radio range). Even though the KNSS and ground-based radio navigation systems are used with GPS, navigation performance can be unsatisfactory. In this case, fixed and/or moving pseudo-satellites (pseudolites) will be additionally integrated.
Before real-time radio navigation systems are deployed, lots of tests and performance evaluations should be carried out. The M&S (modeling and simulation) software can be used for performance evaluation in order to save cost and time [9,15]. When the software is not complicated, it may be efficient to design the software in one module. However, when the software is sophisticated, it is more efficient to design a modularized software. By modularizing, it is easy to modify and/or to replace the software [16,17,18,19,20].
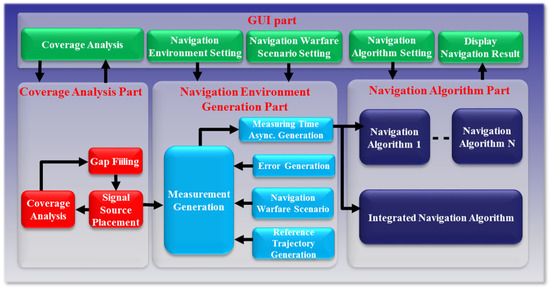
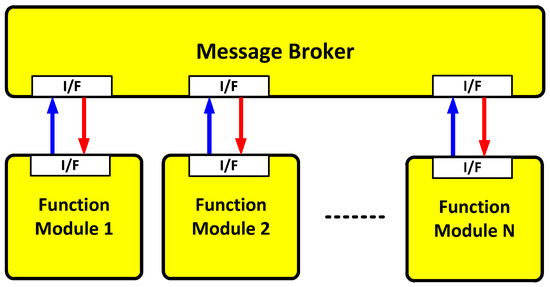
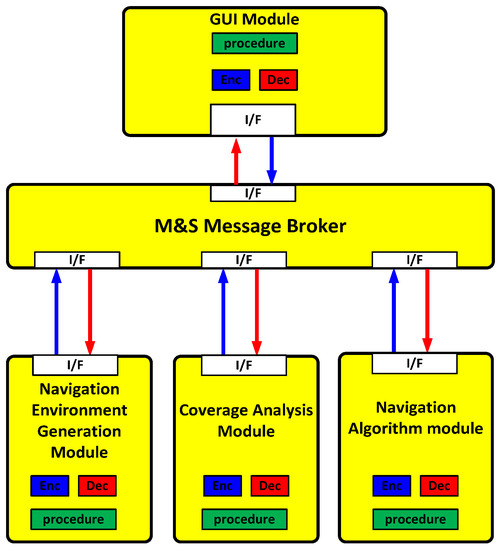
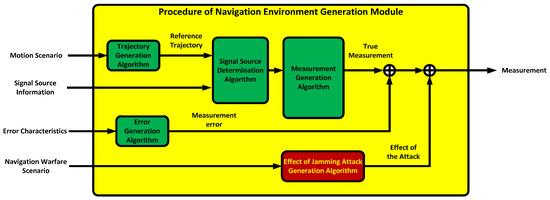
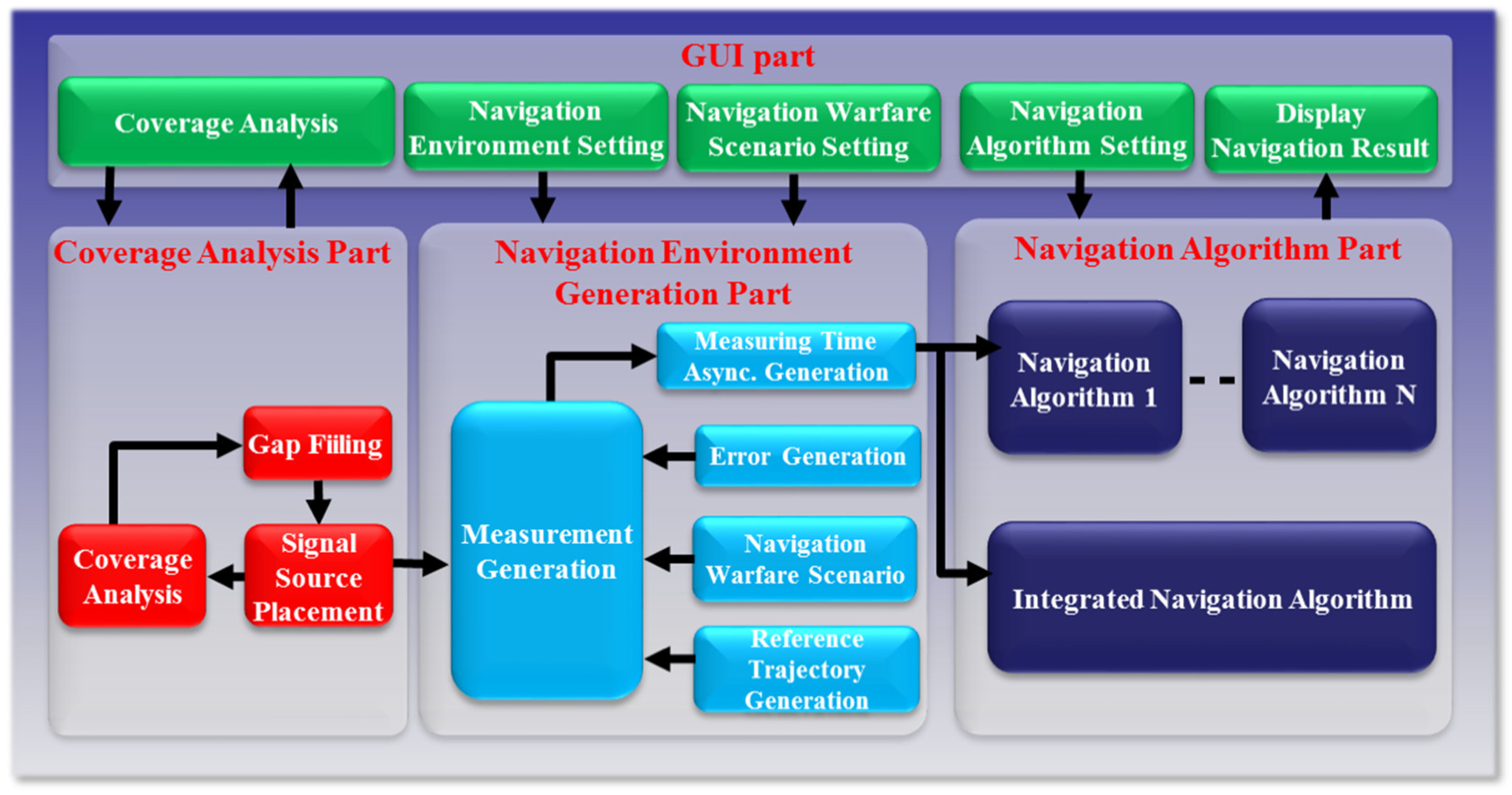
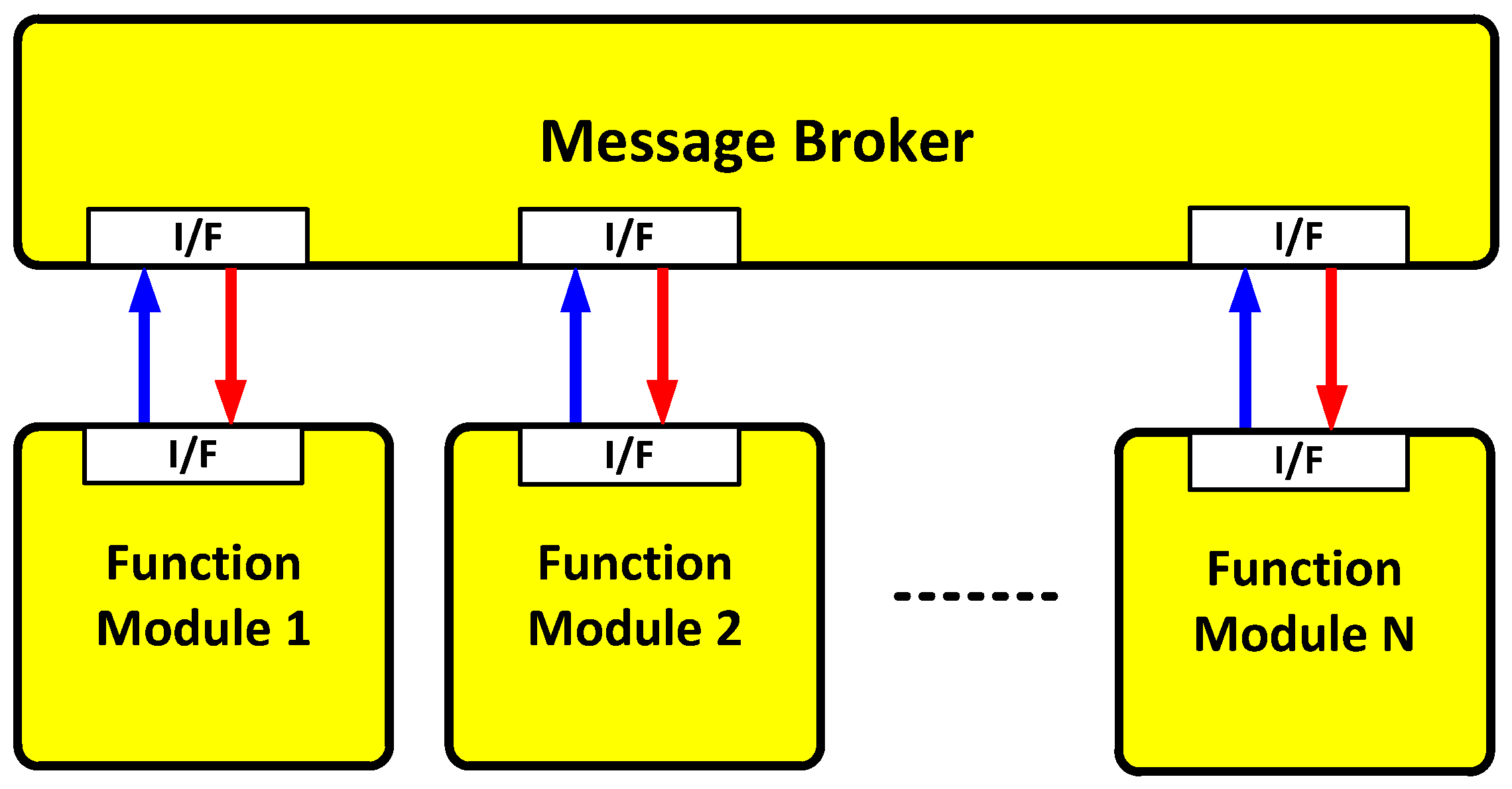
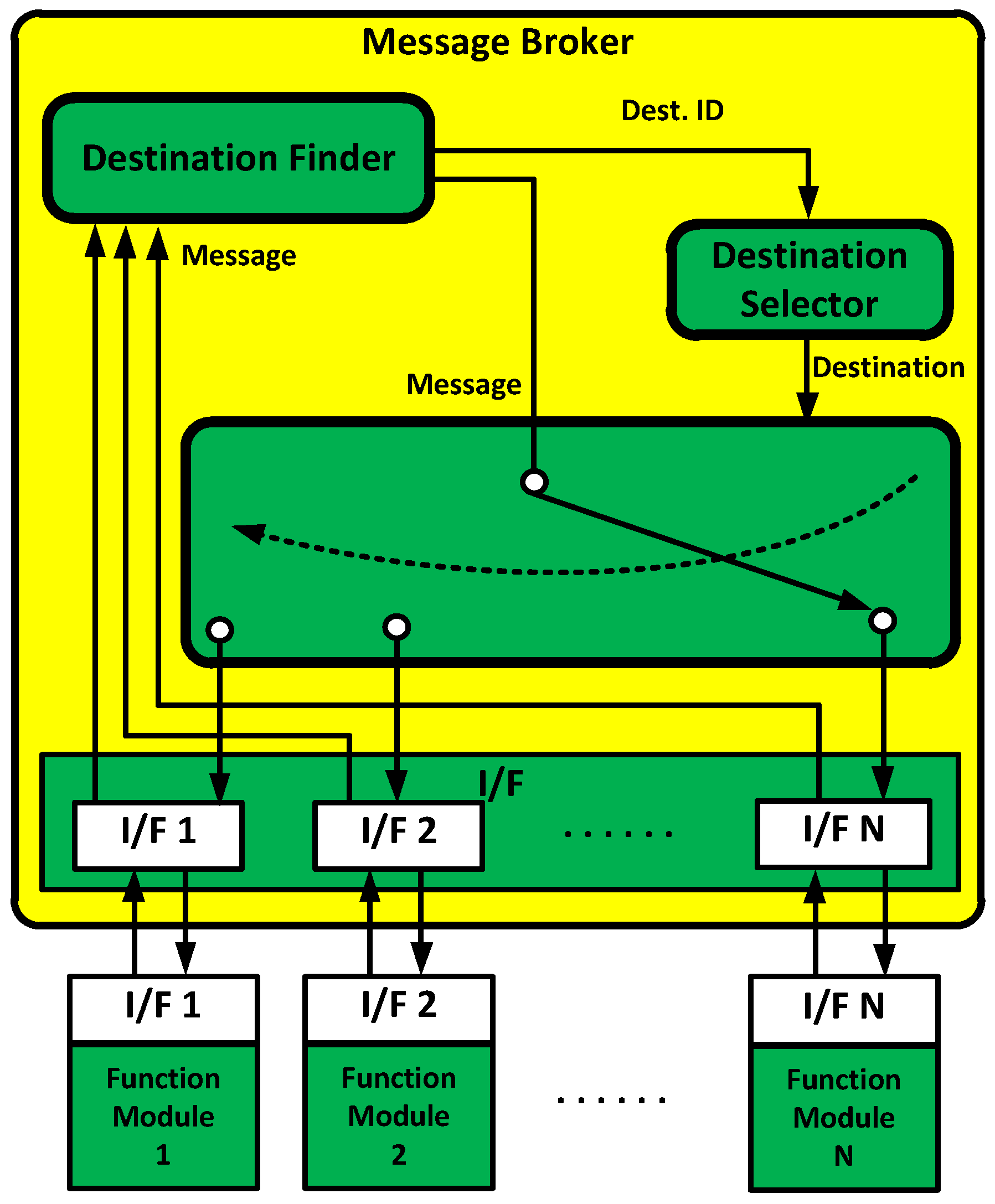
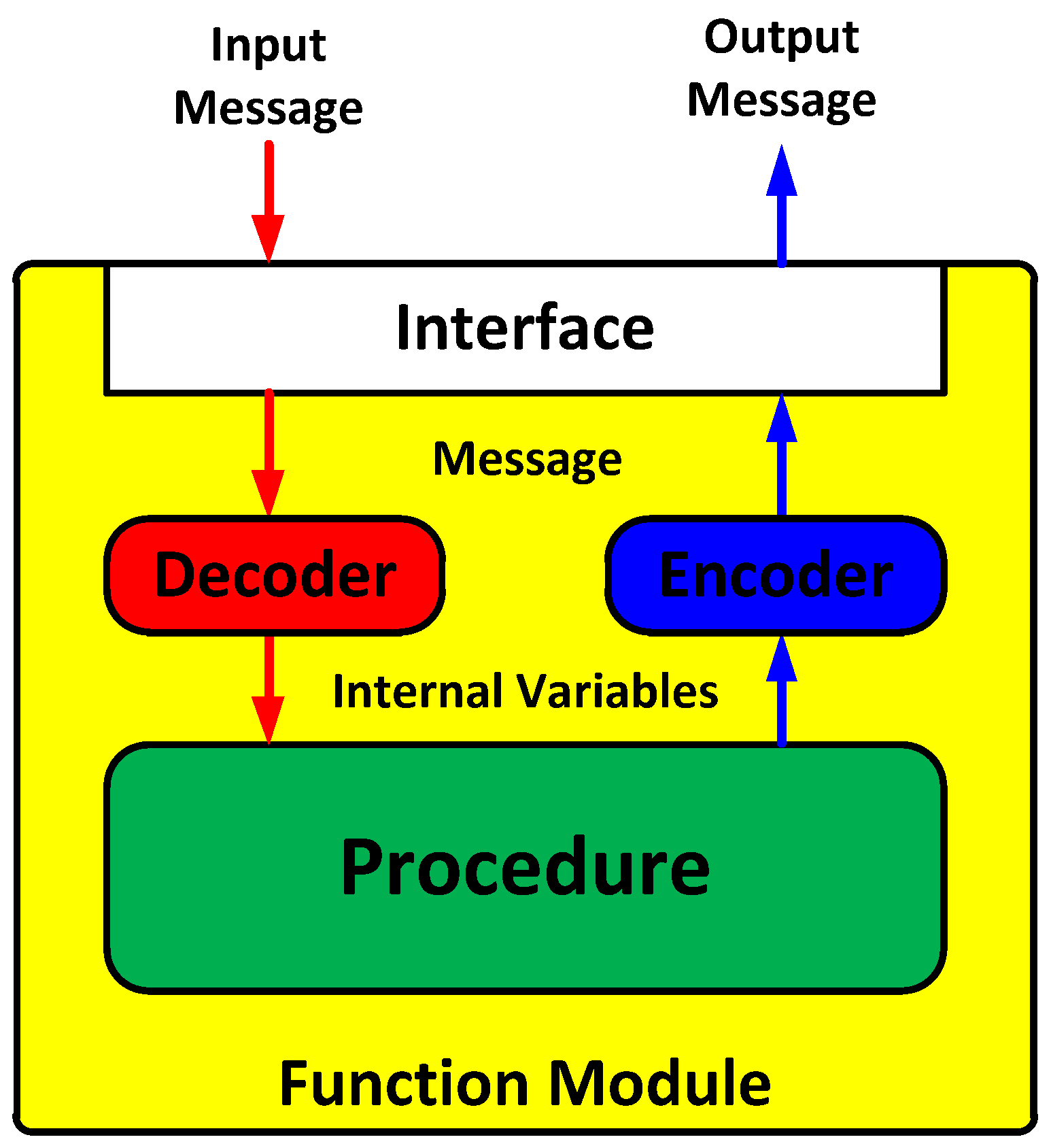
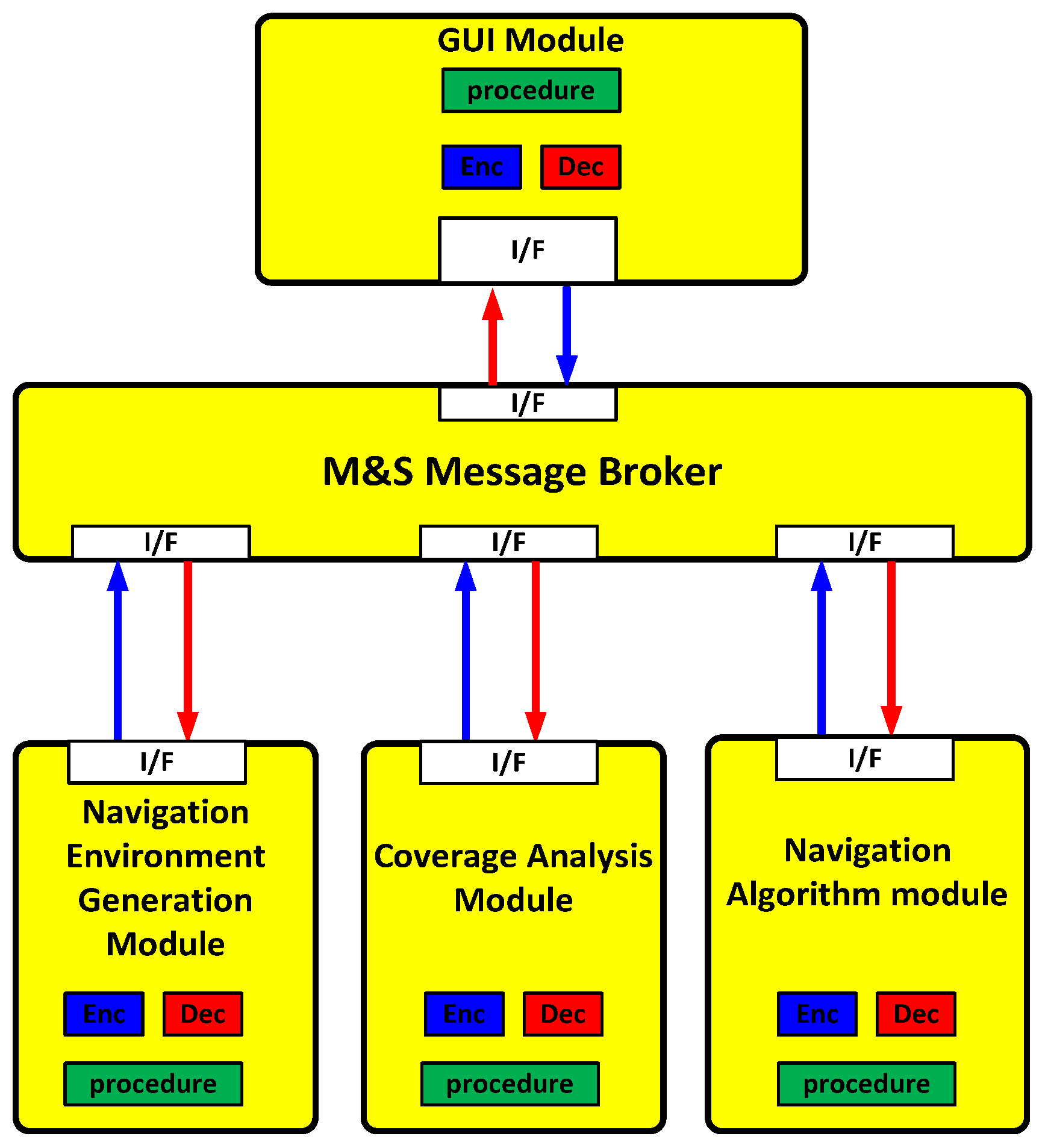
In this paper, a message broker-based M&S software design method was proposed. The whole M&S software was divided into function modules in the proposed design method. All the messages were transferred through the message broker in order to be exchanged between the function modules. Due to the message broker, each function module could be independently operated. A message broker-based multi-radio integrated navigation M&S software was designed using the proposed method. The M&S software was comprised of a GUI module, a navigation environment generation module, a navigation algorithm module, a coverage analysis module, and an M&S message broker. In order to show the feasibility of the proposed design method, the M&S software was implemented for GPS, KNSS, eLoran, Loran-C, and DME/VOR. The M&S software was programmed in Visual C++ under a Windows 10 operating system. The performance of the multi-radio integrated navigation system was evaluated under the navigation warfare environment through the M&S software. The results of the multi-radio integrated navigation system were compared with those of GPS only navigation when the GPS was attacked by a jammer. This is an extension of the authors’ conference paper [21]. The effect of the jammer power to GPS measurements was modeled and included in the navigation environment generation module of the implemented M&S software. The navigation warfare scenario editor was added in the graphical user interface (GUI) for the M&S parameter setting.
In Section 2, the scheme of the M&S software is described for the performance evaluation of the multi-radio integrated navigation system. A message broker-based software design method is proposed. A message broker-based multi-radio integrated navigation M&S software was designed using the proposed method. In Section 3, the M&S software is implemented. In Section 4, the performance of the navigation systems in the M&S software is evaluated. Finally concluding remarks and further studies are presented in Section 5.
3. Implementation of the M&S Software
The feasibility of the proposed design method is shown through implementation of the message broker-based multi-radio integrated navigation system M&S software for GPS, KNSS, eLoran, Loran-C and DME/VOR [9,10,26,27,28]. MFC library and sockets were used in the implementation [29,30].
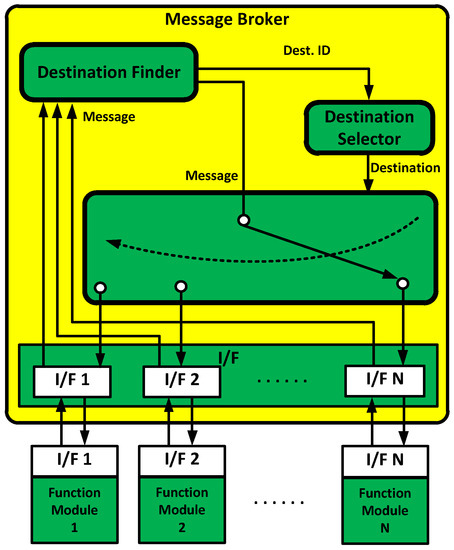
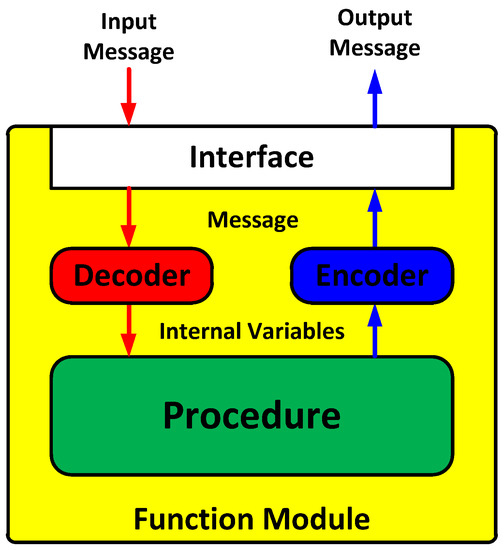
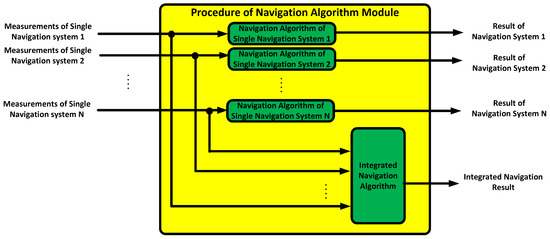
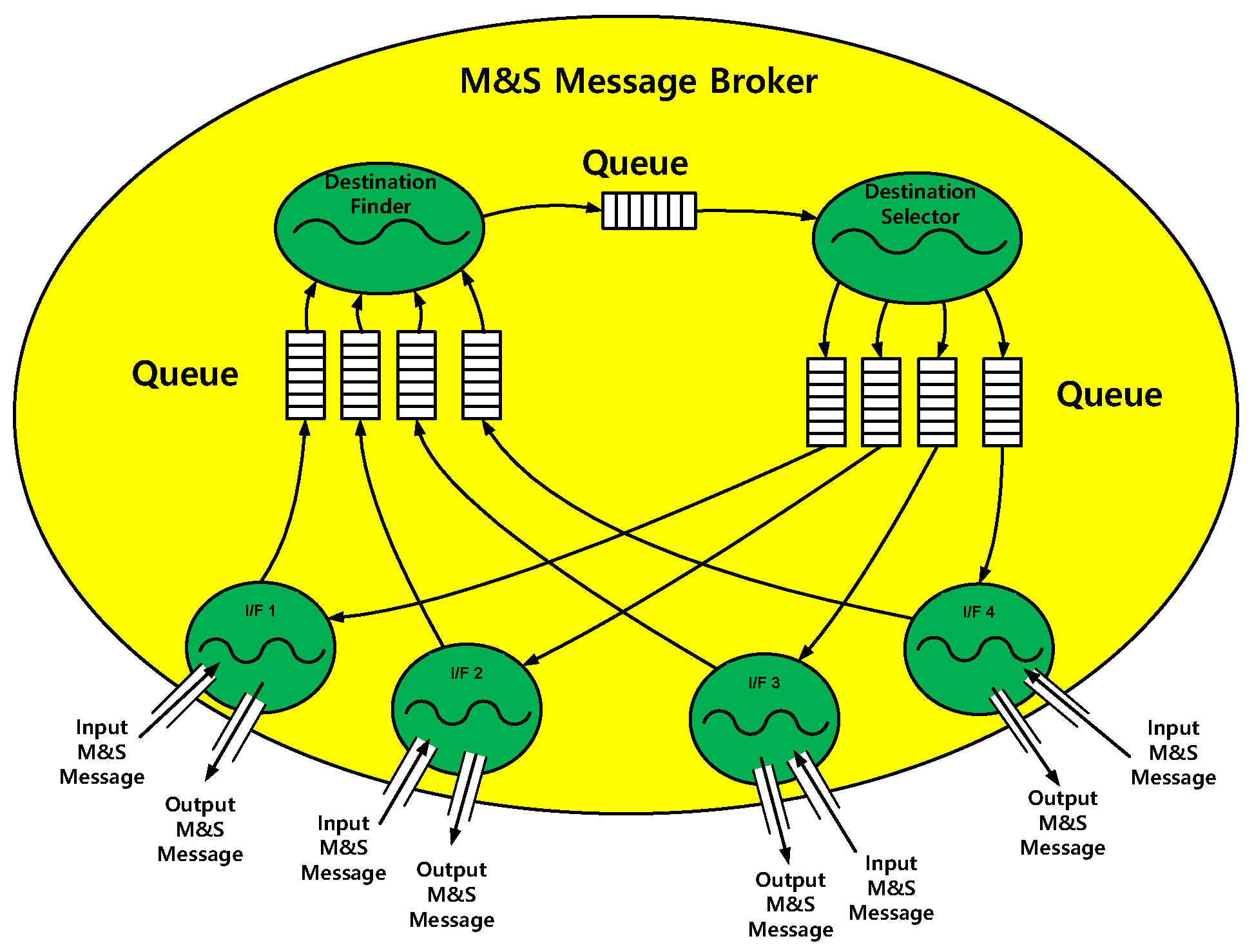
The M&S message broker and function modules were implemented in the tasks. All the tasks included threads and queues, as shown in Table 4. The M&S message broker could be represented in the task, as shown in Figure 10. The function modules could be similarly represented.

Table 4.
Task, thread, and queue in the implementation.
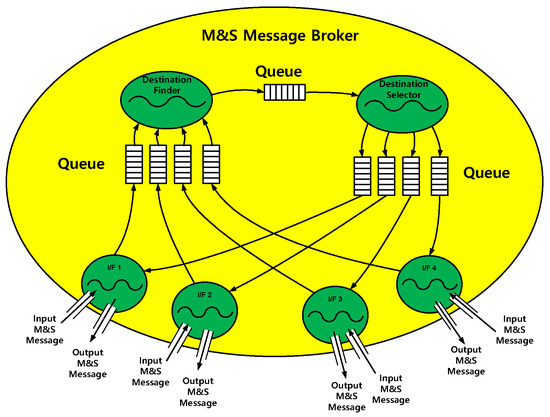
Figure 10.
M&S message broker task.
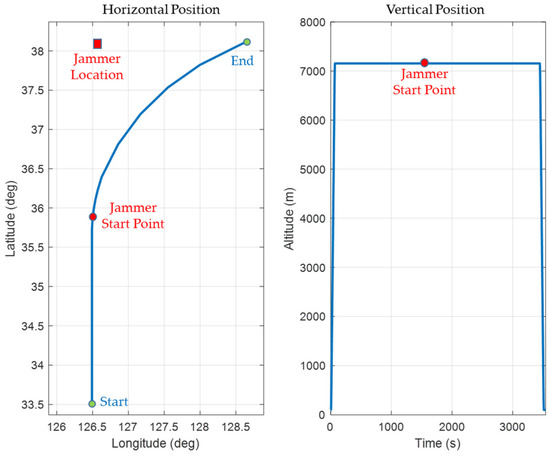
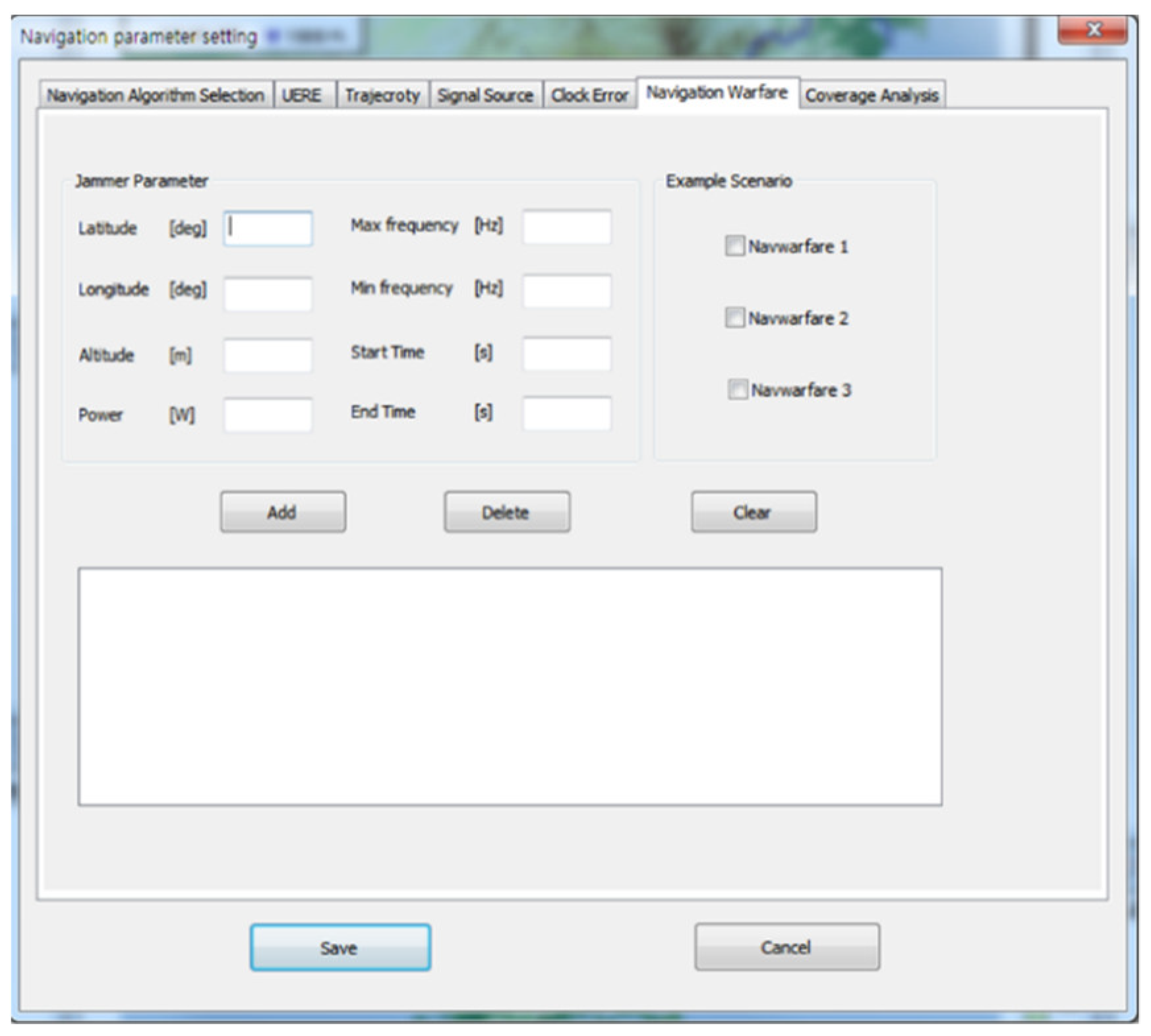
Figure 11 shows the GUI for navigation warfare scenario parameters setting. Initial values and motion types were set. If the load button was clicked, the receiver independent exchange format (RINEX) files of the GPS and the files of the location data of the ground-based navigation system stations were loaded. If the navigation warfare scenario was edited, the location, operating time and power of jammer could be set as in Figure 11.
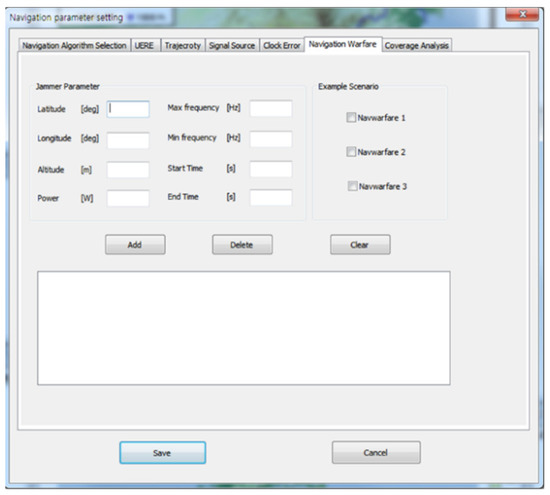
Figure 11.
Graphical user interface (GUI) for navigation warfare scenario parameter setting.
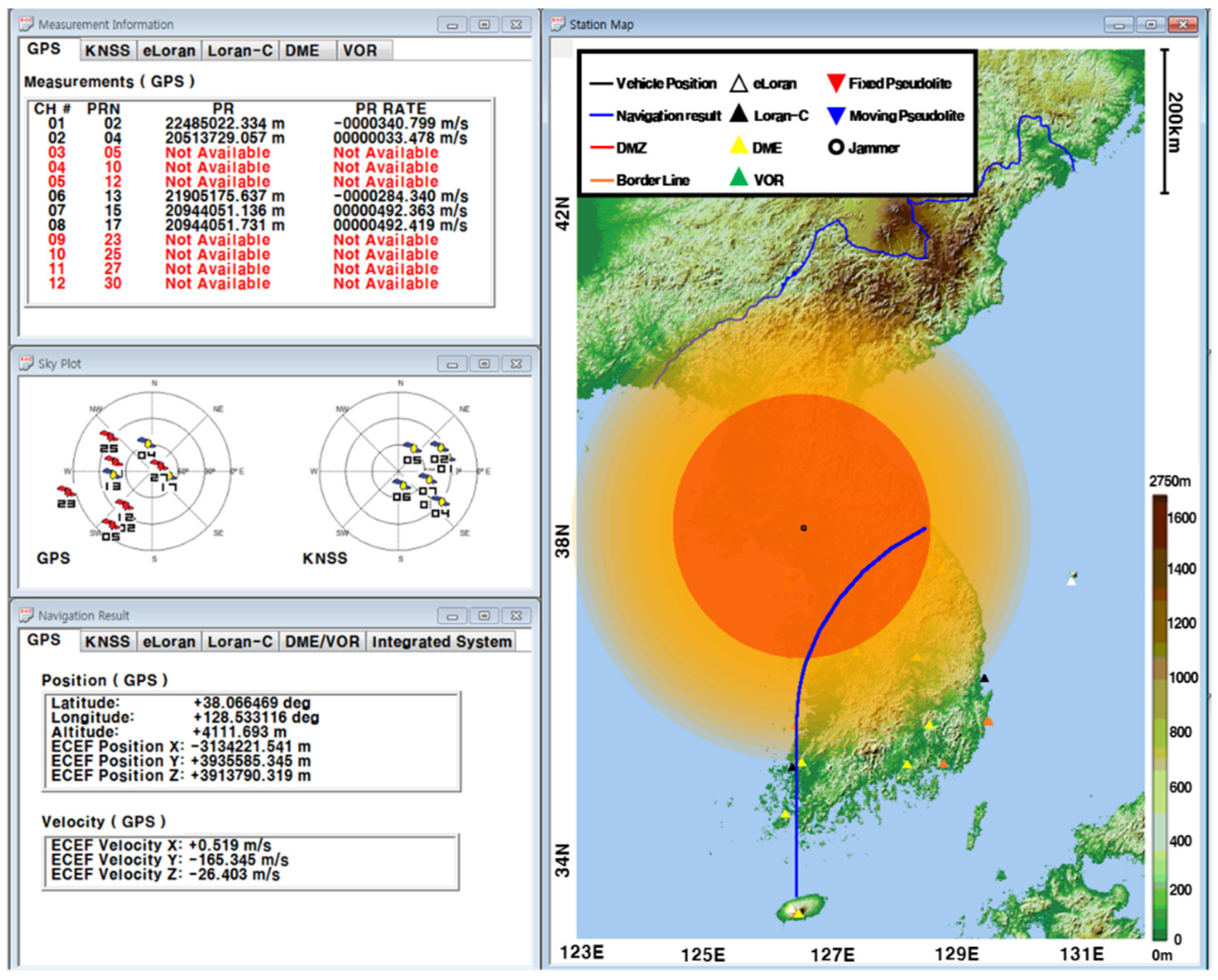
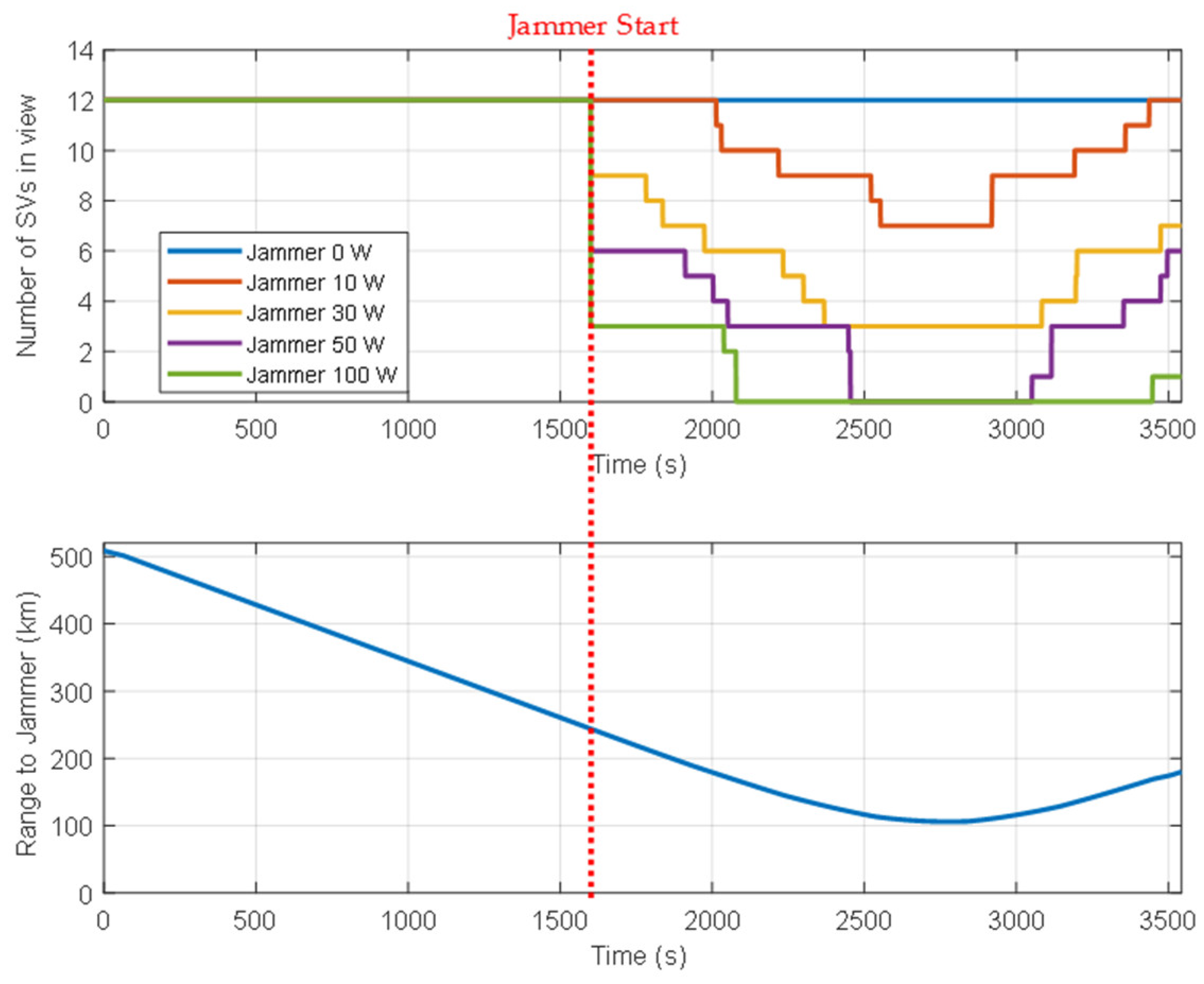
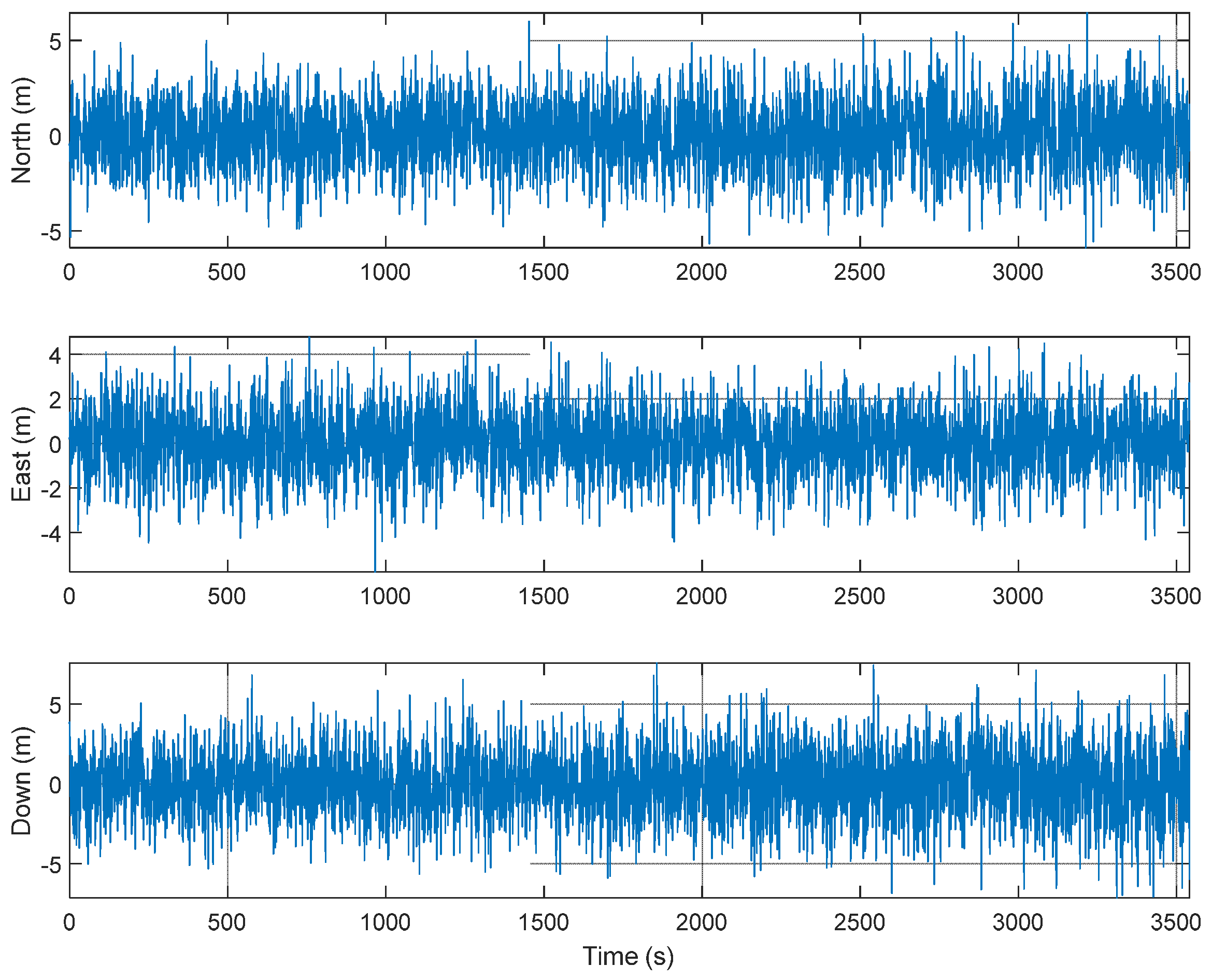
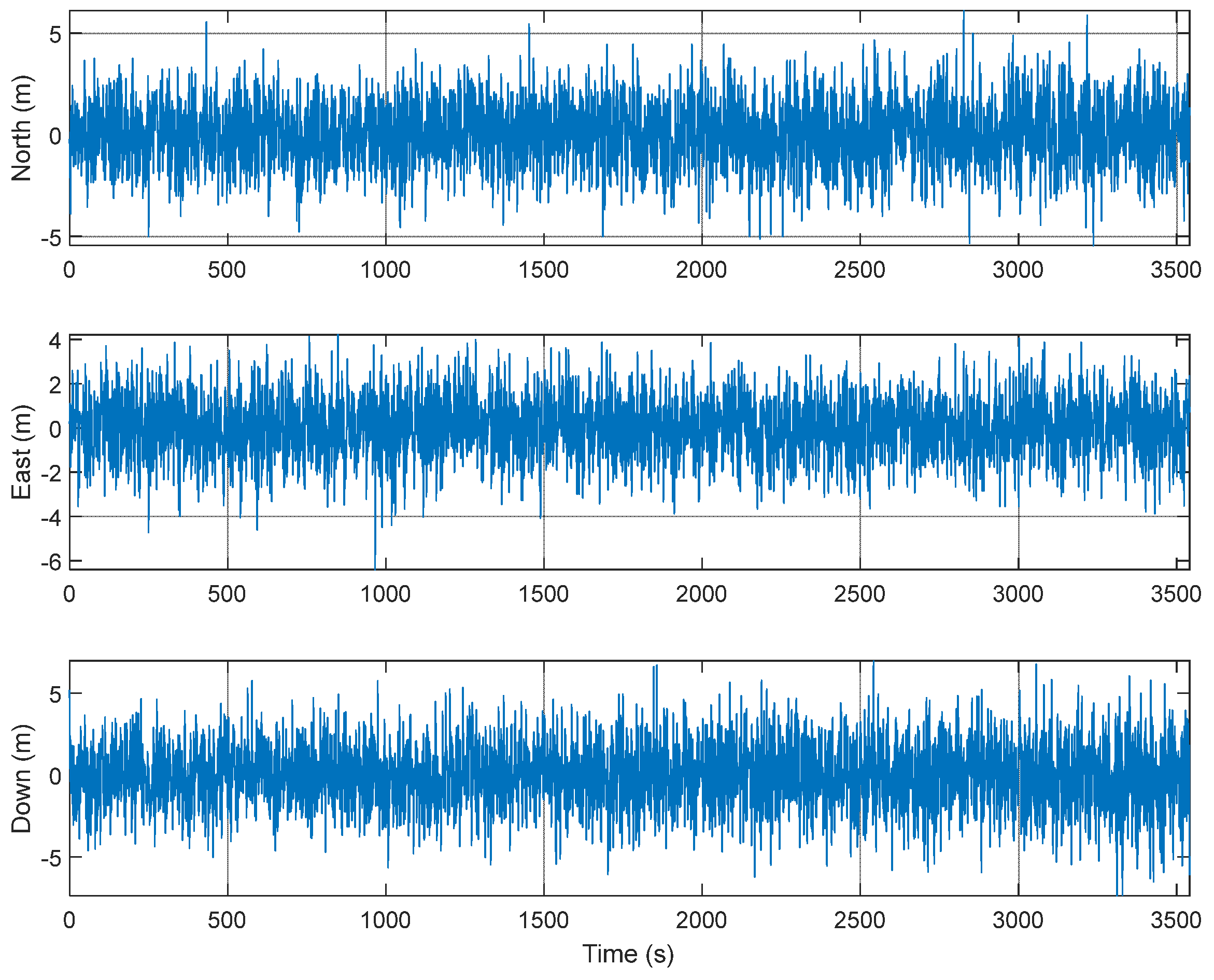
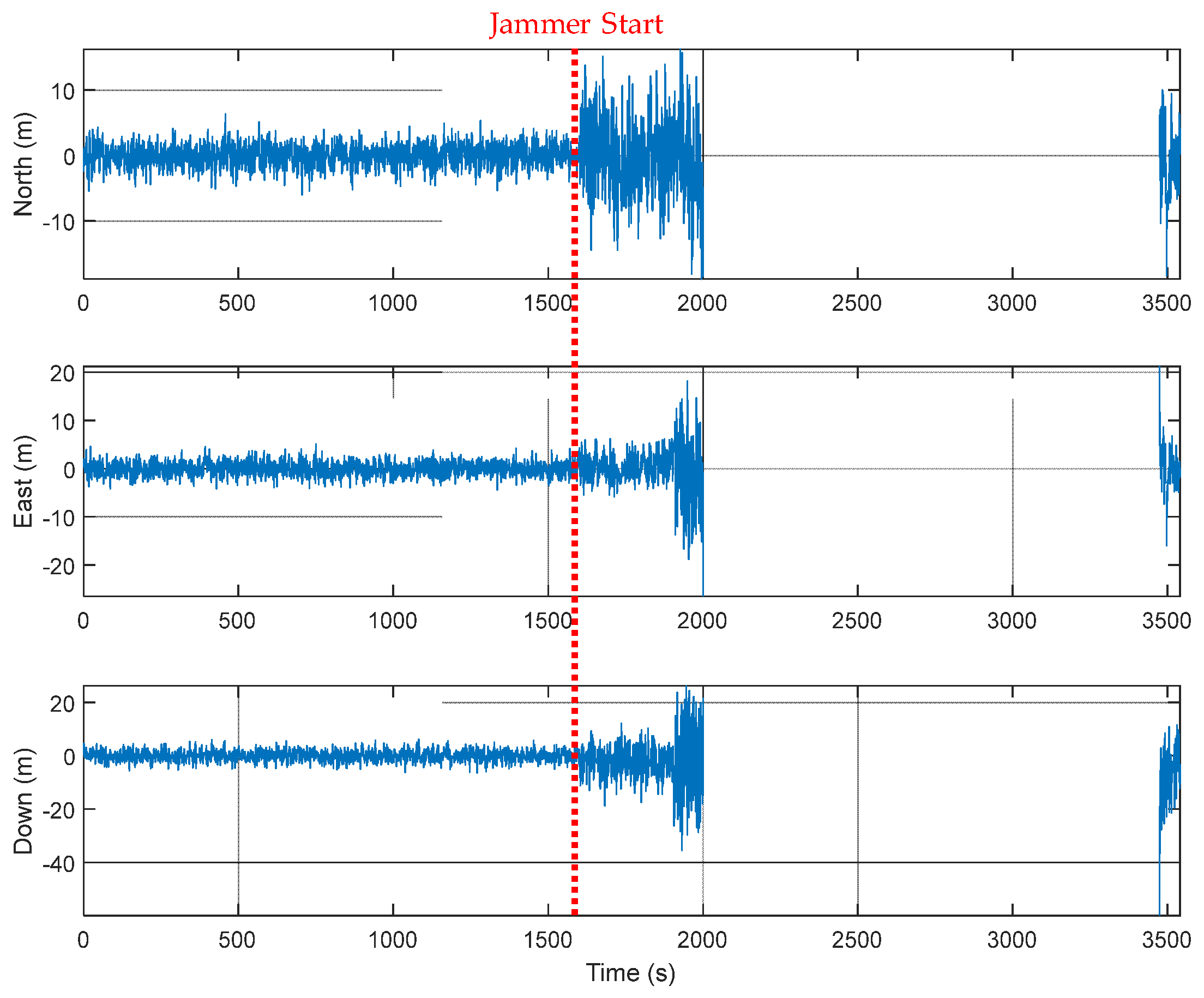
The GUI for measurements, signal sources, navigation results, and navigation warfare situation is shown in Figure 12. The measurements of the navigation systems are shown in the left upper window. The sky plots of the GPS and KNSS satellites are shown in the left middle window. The navigation result of the GPS is shown in the left lower window. The horizontal path of the vehicle, the locations of the ground-based navigation system stations, and the jamming area are shown in the right window.
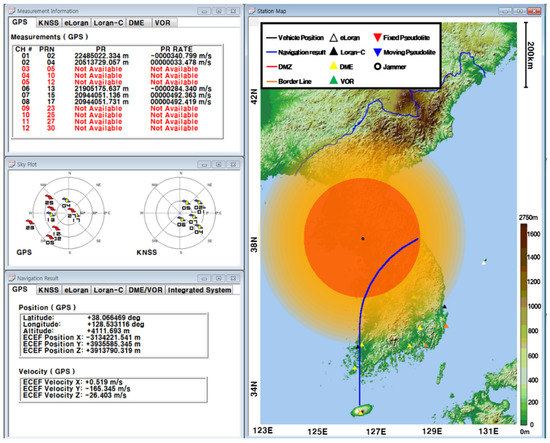
Figure 12.
GUI for measurements, signal sources, navigation results and navigation warfare situation.
5. Concluding Remarks and Further Studies
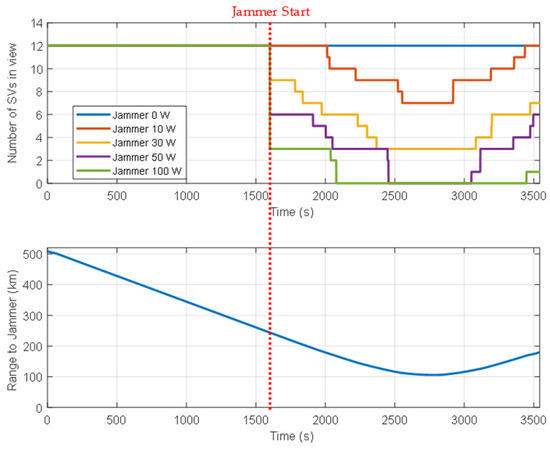
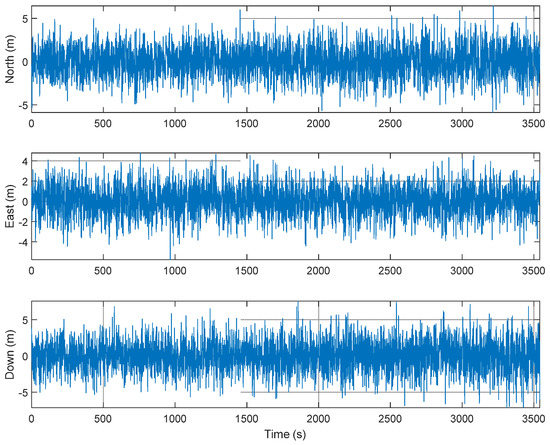
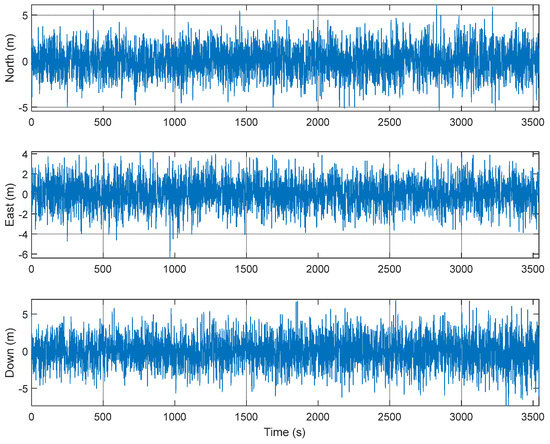
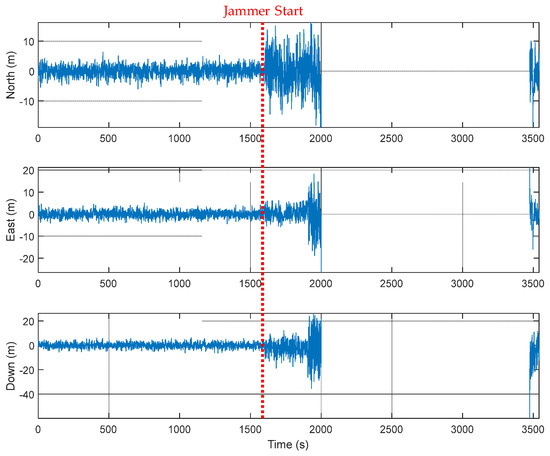
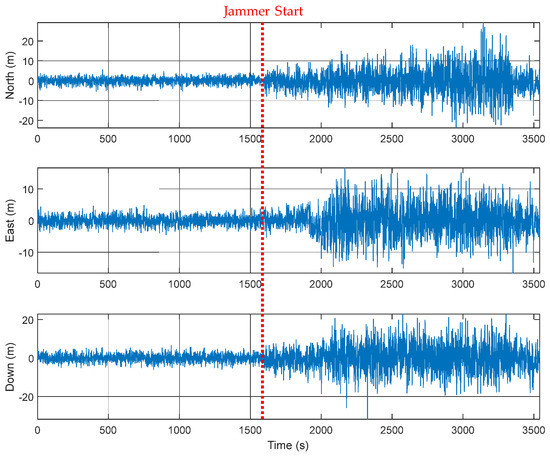
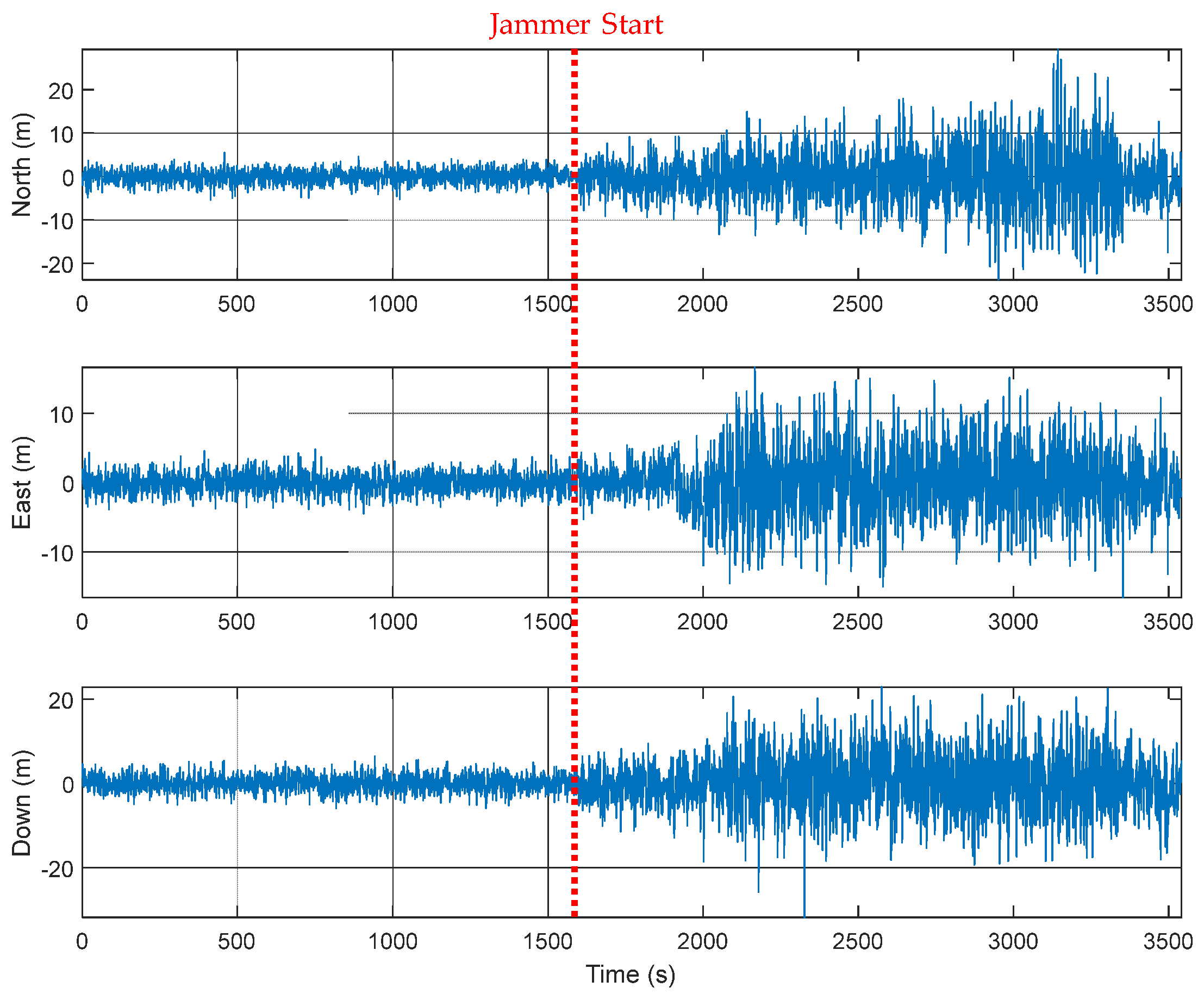
An M&S software design method was proposed for multi-radio integrated navigation systems as a GNSS backup under navigation warfare. The M&S software in the proposed design method consisted of a message broker and function modules. A message broker-based M&S software was designed for a multi-radio integrated navigation system. In order to show the feasibility of the proposed design method, the M&S software was implemented for GPS, KNSS, eLoran, Loran-C, and DME/VOR and the performance evaluation was carried out. The results showed that the multi-radio integrated navigation system provides navigation results continuously, even when the GPS only navigation system cannot provide navigation results, due to the jamming under a navigation warfare environment.
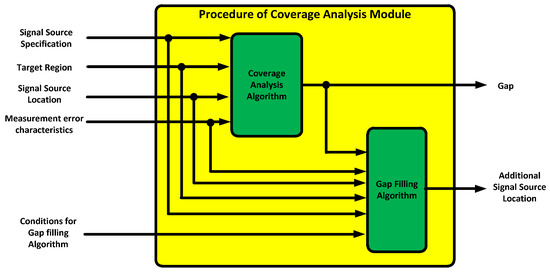
In further studies, additional ground stations and fixed/moving pseudolites will be included, which are newly assigned by the coverage analysis module in the M&S software. Performance evaluations of the M&S software based on integrity and continuity will be performed.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.H.O, H.S. and D.-H.H.; software, H.K. and J.L.; supervision, D.-H.H.; validation, H.S.; writing—original draft, H.K., J.L., S.H.O. and D.-H.H.; writing—review & editing, D.-H.H.
Funding
This research was funded by the National GNSS Research Center Program of Defense Acquisition Program Administration and Agency for Defense Development.
Acknowledgments
This work has been supported by the National GNSS Research Center Program of Defense Acquisition Program Administration and Agency for Defense Development.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Merriam Webster. The Merriam-Webster Dictionary, 11th ed.; Merriam Webster Inc.: Springfield, VR, USA, 2008; ISBN 978-0877792956. [Google Scholar]
- Department of Defense, Department of Homeland Security, and Department of Transportation. Federal Radio Navigation Plan 2017; National Technical Information Service: Springfield, VR, USA, 2017; pp. 16–217.
- Kaplan, E.D.; Hegarty, C.J. Understanding GPS/GNSS: Principles and Applications, 3rd ed.; Artech House: Boston, FL, USA, 2017; ISBN 978-1-63081-058-0. [Google Scholar]
- White, N.A.; Maybeck, P.S.; DeVilbiss, S.L. Detection of interference/jamming and spoofing in a DGPS-aided inertial system. IEEE Trans. AES 1998, 34, 1208–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grove, P.D. Principles of GNSS, Inertial, and Multisensor Integrated Navigation Systems, 2nd ed.; Artech House: Boston, FL, USA, 2013; ISBN 978-1-60807-005-3. [Google Scholar]
- Available online: http://www.dtic.mil/dtic/tr/fulltext/u2/a470386.pdf (accessed on 21 December 2018).
- Eldredge, L.; Enge, P.; Harrison, M.; Kenagy, R.; Lo, S.; Loh, R.; Lilly, R.; Narins, M.; Niles, R. Alternative positioning, navigation & timing (PNT) study. In Proceedings of the International Civil Aviation Organization Navigation Systems Panel (NSP) Working Group Meetings, Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–27 May 2010; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, S.; Enge, P.; Niles, F.; Loh, R.; Eldredge, L.; Narins, M. Preliminary assessment of alternative navigation means for civil aviation. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Technical Meeting of the Institute of Navigation, San Diego, CA, USA, 25–27 January 2010; Institute of Navigation: Manassas, VR, USA, 2010; pp. 314–322. [Google Scholar]
- Kee, C.; Lee, Y.J.; Hwang, D.-H. Final Report of National GNSS Research Center Satellite Navigation System Architecture Laboratory 2nd Phase; Agency for Defense Development: Daejeon, Korea, 2015; pp. 8–439. [Google Scholar]
- Kee, C.; Lee, Y.J.; Hwang, D.-H. Intermediate Report of National GNSS Research Center Satellite Navigation System Architecture Laboratory 3rd Phase; Agency for Defense Development: Daejeon, Korea, 2017; pp. 116–232. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, M.; Won, D.; Jeon, H.; Kim, D.; Sung, S.; Lee, Y.J. Navigation performance analysis according to the Korean navigation satellite system of bit design elements. In Proceedings of the 2012 KSASS Autumn Conference, Jeju, Korea, 14–16 November 2012; Korea Society for Aeronautical & Space Sciences: Seoul, Korea, 2012; pp. 626–630. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, M.; Won, D.; Sung, S.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.; Lee, Y.J. Korean navigation satellite system orbit design and navigation performance analysis. In Proceedings of the 2013 KSASS Spring Conference, Gangwon-do, Korea, 10–12 April 2013; Korea Society for Aeronautical & Space Sciences: Seoul, Korea, 2012; pp. 645–649. [Google Scholar]
- Koo, M.; Kim, Y.; Choi, K.H.; So, H.; Oh, S.H.; Kim, S.C.; Lee, H.-K.; Hwang, D.-H. M&S software design of multiple radio positioning integration system. J. Korea Inst. Mil. Sci. Technol. 2015, 18, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, M.; Kim, Y.; So, H.; Oh, S.H.; Kim, S.C.; Hwang, D.-H. Modeling & Simulation Software Design for Coverage Analysis of Multiple Radio Positioning Integration System. J. Position Navig. Timing 2016, 5, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J. The Theory and Practice for Modeling and Simulation as a Transformation Enabler for Efficient Defense Management; KRIMA: Seoul, Korea, 2008; pp. 150–185. ISBN 978-8-98764-741-8. [Google Scholar]
- Dalle, O.; Ribault, J.; Himmelspach, J. Design consideration for M&S software. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Winter Simulation Conference, Austin, TX, USA, 13–16 December 2009; Rossetti, M., Hill, R.R., Johansson, B., Eds.; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 944–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maria, A. Introduction to modeling and simulation. In Proceedings of the 1997 IEEE Winter Simulation Conference, Atlanta, GR, USA, 7–10 December 1997; Andradottir, S., Healy, K.J., Withers, D.H., Nelson, B.L., Eds.; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, R.J. CORBA and DCOM: Side by side. Distrib. Comput. 1998, 1, 41–45. [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan, K.J.; Griswold, W.G.; Cai, Y.; Hallen, B. The structure and value of modularity in software design. In Proceedings of the 8th European Software Engineering Conference, Vienna, Austria, 10–14 September 2010; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 99–108. [Google Scholar]
- Leye, S.; Himmelspach, J.; Uhrmacher, A.M. A discussion on experimental model validation. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE 11th International Conference on Computer Modelling and Simulation, Cambridge, UK, 25–27 March 2009; AI-Dabass, D., Orsoni, A., Brentnall, A., Abraham, A., Zobel, R., Eds.; IEEE Computer Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2009; pp. 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, H.; Hwang, D.-H.; Oh, S.H.; So, H. Multi-radio integrated navigation system M&S software design for GNSS back-up. In Proceedings of the Position, Location and Navigation Symposium 2018, Monterey, CA, USA, 23–26 April 2018; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E. Hybrid APNT architecture using DME/DME and multilateration. In Proceedings of the Digital Avionics Systems Conference (DASC) 2012, Indianapolis, IN, USA, 14–18 October 2012; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E. Investigation of APNT optimized DME/DME network using current state-of-the-art DMEs. In Proceedings of the Position, Location and Navigation Symposium 2012, Myrtle Beach, SC, USA, 23–26 April 2012; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeigler, B.P.; Sarjoughian, H.S. Creating distributed simulation using DEVS M&S environments. In Proceedings of the 2000 IEEE Winter simulation conference, Orlando, FL, USA, 10–13 December 2000; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 158–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kröner, A.; Holl, P.; Marquardt, W.; Gilles, E.D. DIVA-an open architecture for dynamic simulation. Comput. Chem. Eng. 1990, 14, 1289–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Maritime Positioning, Navigation, and Timing Office Home Page. Available online: http://www.ndgps.go.kr/ (accessed on 12 September 2018).
- Ministry of Science and ICT Home Page. Available online: http://www.msip.go.kr (accessed on 12 September 2018).
- GPS: The Global Positioning System Home Page. Available online: https://www.gps.gov/systems/gps/ (accessed on 12 September 2018).
- Forouzan, B.A. Data Communication and Networking, 5th ed.; McGraw-Hill: Boston, FL, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Hart, J.M. Windows System Programming, 4th ed.; Pearson Education: Boston, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).