Multi-Channel Optoelectronic Measurement System for Soil Nutrients Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Sample Collection and Preparation
2.2. Measurement Principle
2.3. Principle Design
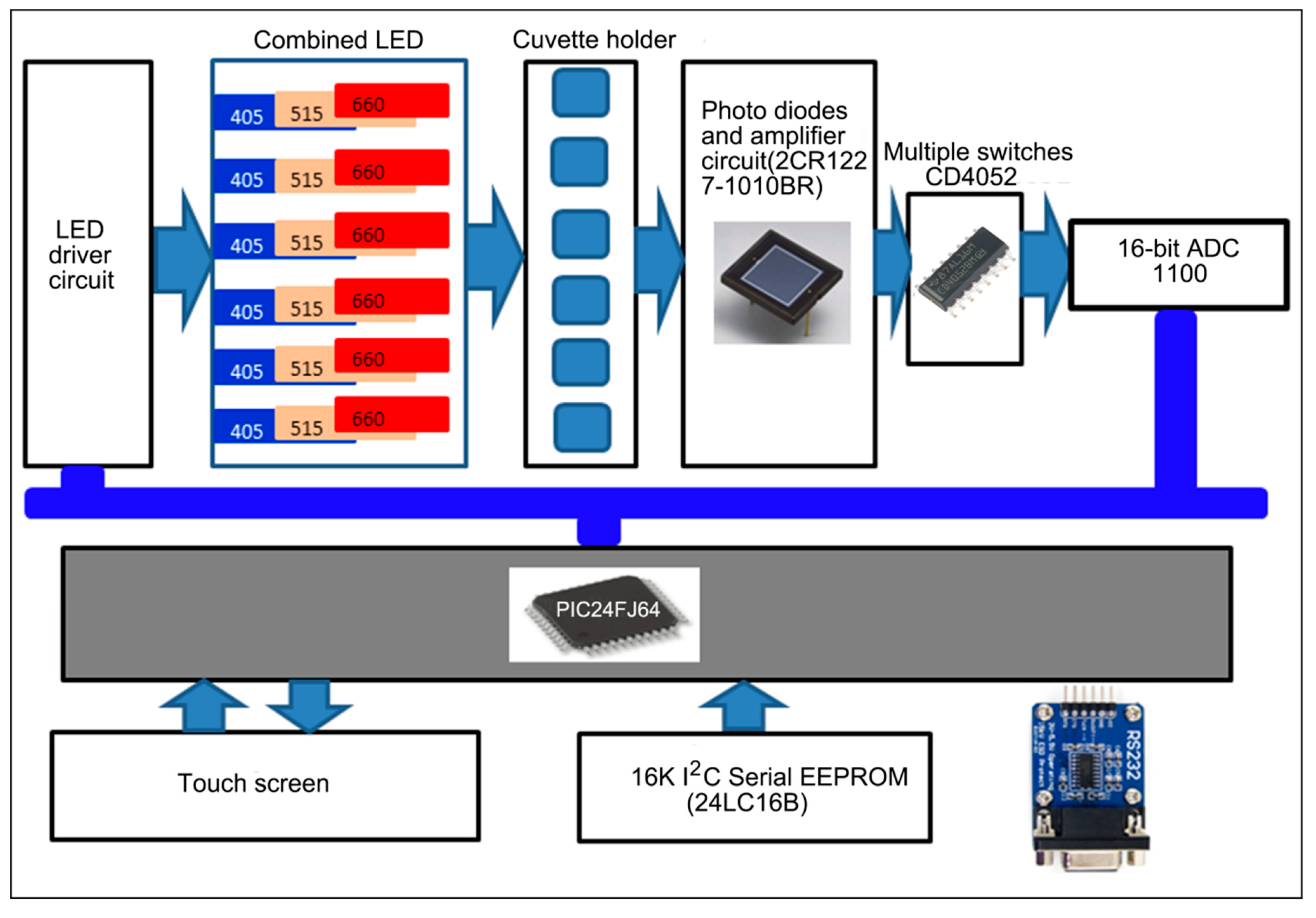
2.4. Construction of the Optoelectronic Measurement System
2.5. Absorbance Compensations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Establishment of the Calibration Curve
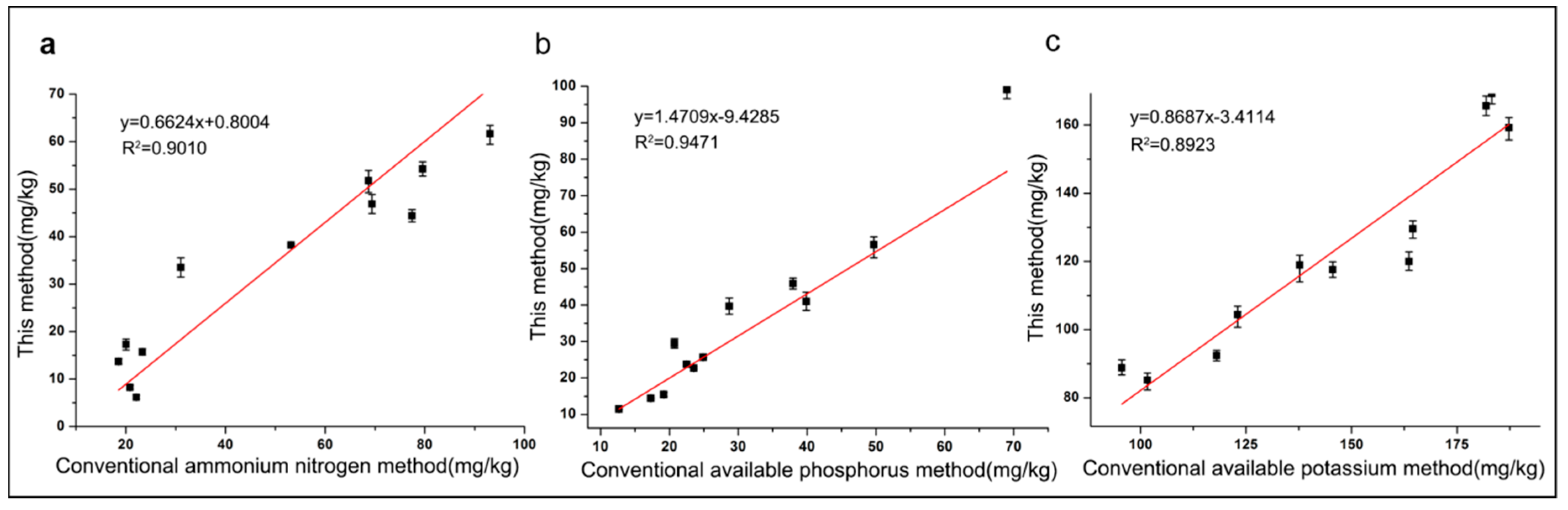
3.2. Sample Measurements
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cardoso, I.M.; Kuyper, T.W. Mycorrhizas and tropical soil fertility. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2006, 116, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.L.; Chen, D.L. Nitrogen fertilizer use in China-contributions to food production, impacts on the environment and best management strategies. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2002, 63, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, J.F.; Xu, M.J.; Zhang, B. The effect of climate changes on maize yield in a long-term fertilization experiment in the Huang-Huai-Hai Plain of China. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2010, 8, 754–758. [Google Scholar]
- Srivastava, P.K.; Gupta, M.; Upadhyay, R.K.; Sharma, S.; Shikha Singh, N.; Tewari, S.K.; Singh, B. Effects of combined application of vermicompost and mineral fertilizer on the growth of Allium cepa L. and soil fertility. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2012, 175, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yu, C.; Kong, X.; Hou, D.; Gu, J.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J. Progressive integrative crop managements increase grain yield, nitrogen use efficiency and irrigation water productivity in rice. Field Crops Res. 2018, 215, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-K.; Kwon, S.-I.; Jung, G.-B.; Kim, M.-Y.; Lee, S.-B.; Lee, D.-B. Phosphorus losses from agricultural soils to surface waters in a small agricultural watershed. Biosyst. Eng. 2011, 109, 10–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Delgado, M.S.; Sesmero, J.P. Dynamic adjustment in agricultural practices to economic incentives aiming to decrease fertilizer application. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 177, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, D.; Zhang, N. The role of agricultural training on fertilizer use knowledge: A randomized controlled experiment. Ecol. Econ. 2018, 148, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.; Siciliano, G.A. Comprehensive review of constraints to improved management of fertilizers in China and mitigation of diffuse water pollution from agriculture. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 11, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Kong, F.; Zhang, N.; Ying, R. Knowledge training and the change of fertilizer use intensity: Evidence from wheat farmers in china. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 197, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Cui, Z.; Chen, X.; Ju, X.; Shen, J.; Chen, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhang, W.; Mi, G.; Fan, M.; et al. Integrated nutrient management for food security and environmental quality in China. Adv. Agron. 2012, 116, 1–40. [Google Scholar]
- Sinfield, J.V.; Fagerman, D.; Colic, O. Evaluation of sensing technologies for on-the-go detection of macro-nutrients in cultivated soils. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2010, 70, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Thomasson, J.A.; Sui, R. Remote sensing of soil properties in precision agriculture: A review. Front. Earth Sci. 2011, 5, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulder, V.L.; Bruin, S.D.; Schaepman, M.E.; Mayr, T.R. The use of remote sensing in soil and terrain mapping-a review. Geoderma 2011, 162, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruah, B.K.; Das, B.; Medhi, C.; Chitrani, M.; Abani, K.M. Fertility status of soil in the tea garden belts of Golaghat District, Assam, India. J. Chem. 2013, 1, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.; Sudduth, K.A.; Chung, S.O. Soil physical property estimation from soil strength and apparent electrical conductivity sensor data. Biosyst. Eng. 2016, 152, 68–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamchuk, V.I.; Lund, E.D.; Sethuramasamyraja, B.; Morgan, M.T.; Dobermann, A.; Marx, D.B. Direct measurement of soil chemical properties on-the-go using ion-selective electrodes. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2005, 48, 272–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, T.; Liu, J.; Lin, Z.; Li, S.; Wang, R.; Ge, Y. Soil pH value, organic matter and macronutrients contents prediction using optical diffuse reflectance spectroscopy. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2015, 111, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tully, K.L.; Weil, R. Ion-selective electrode offers accurate, inexpensive method for analyzing soil solution nitrate in remote regions. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2014, 45, 1974–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, M.; Chen, L.; Ang, S.S.; Nguyen, C.V.; Zhu, J. An automatic fluidic system for the rapid detection of soil nutrients. Autom. Logist. 2008, 1, 2742–2746. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.A.; Jiang, H.; Mahal, N.K.; Weber, R.J.; Kumar, R.; Castellano, M.J.; Dong, L. Microfluidic impedimetric sensor for soil nitrate detection using graphene oxide and conductive nanofibers enabled sensing interface. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 239, 1289–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iznaga, A.C.; Orozco, M.R.; Alcantara, E.A.; Pairol, M.C.; Sicilia, Y.E.D.; Baerdemaeker, J.D.; Saeys, W. Vis/NIR spectroscopic measurement of selected soil fertility parameters of cuban agricultural cambisols. Biosyst. Eng. 2014, 125, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.W.; Laird, D.A.; Mausbach, M.J.; Hurburgh, C.R. Near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy-principal components regression analyses of soil properties. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2001, 65, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.T.; Tao, L.Q.; Liu, B.; Tian, X.G.; Mohammad, M.; Yang, Y.; Ren, T.L. A miniaturized on-chip colorimeter for detecting NPK elements. Sensors 2016, 16, 1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Wavelength | Standard Concentration (μg/L) | Absorbance from 6 Channels | Mean | RSD (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CH1 | CH2 | CH3 | CH4 | CH5 | CH6 | ||||
| 405 nm | 30 (Nitrogen) | 0.1512 | 0.1563 | 0.1519 | 0.1548 | 0.1541 | 0.1535 | 0.1536 | 1.22 |
| 660 nm | 4000 (Phosphorus) | 0.1254 | 0.1278 | 0.1285 | 0.1276 | 0.1282 | 0.1246 | 0.1270 | 1.27 |
| 515 nm | 2000 (Potassium) | 0.1268 | 0.1289 | 0.1281 | 0.1267 | 0.1287 | 0.1257 | 0.1275 | 1.00 |
| Sample | Conventional Method (mg/kg) | This Method (mg/kg) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P2O5-P | K2O-K | NH4+-N | P2O5-P | K2O-K | NH4+-N | |
| 1 | 29.48 | 120.00 | 54.26 | 20.72 | 163.60 | 79.56 |
| 2 | 45.89 | 129.60 | 51.79 | 37.93 | 164.50 | 68.67 |
| 3 | 23.75 | 165.60 | 61.66 | 22.50 | 181.90 | 93.08 |
| 4 | 40.99 | 159.20 | 44.39 | 39.87 | 187.30 | 77.40 |
| 5 | 39.67 | 104.40 | 38.22 | 28.69 | 123.00 | 53.13 |
| 6 | 25.66 | 117.60 | 46.86 | 24.88 | 145.50 | 69.40 |
| 7 | 22.69 | 169.20 | 15.73 | 23.54 | 183.20 | 23.30 |
| 8 | 14.40 | 92.40 | 17.27 | 17.29 | 118.00 | 20.03 |
| 9 | 11.47 | 85.20 | 13.70 | 12.65 | 101.60 | 18.52 |
| 10 | 99.07 | 104.40 | 33.52 | 69.02 | 123.00 | 31.04 |
| 11 | 56.55 | 88.80 | 6.17 | 49.68 | 95.50 | 22.09 |
| 12 | 15.47 | 120.60 | 8.26 | 19.16 | 137.20 | 20.84 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, L.; Li, Z.; Birech, Z.; Li, S.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Hu, J. Multi-Channel Optoelectronic Measurement System for Soil Nutrients Analysis. Electronics 2019, 8, 451. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8040451
Ma L, Li Z, Birech Z, Li S, Yang Y, Zhang W, Hu J. Multi-Channel Optoelectronic Measurement System for Soil Nutrients Analysis. Electronics. 2019; 8(4):451. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8040451
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Liuzheng, Zhenfeng Li, Zephania Birech, Shixin Li, Yatao Yang, Wei Zhang, and Jiandong Hu. 2019. "Multi-Channel Optoelectronic Measurement System for Soil Nutrients Analysis" Electronics 8, no. 4: 451. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8040451
APA StyleMa, L., Li, Z., Birech, Z., Li, S., Yang, Y., Zhang, W., & Hu, J. (2019). Multi-Channel Optoelectronic Measurement System for Soil Nutrients Analysis. Electronics, 8(4), 451. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8040451





