Abstract
Wearable electronics is a rapidly growing field that recently started to introduce successful commercial products into the consumer electronics market. Employment of biopotential signals in wearable systems as either biofeedbacks or control commands are expected to revolutionize many technologies including point of care health monitoring systems, rehabilitation devices, human–computer/machine interfaces (HCI/HMIs), and brain–computer interfaces (BCIs). Since electrodes are regarded as a decisive part of such products, they have been studied for almost a decade now, resulting in the emergence of textile electrodes. This study presents a systematic review of wearable textile electrodes in physiological signal monitoring, with discussions on the manufacturing of conductive textiles, metrics to assess their performance as electrodes, and an investigation of their application in the acquisition of critical biopotential signals for routine monitoring, assessment, and exploitation of cardiac (electrocardiography, ECG), neural (electroencephalography, EEG), muscular (electromyography, EMG), and ocular (electrooculography, EOG) functions.
Keywords:
biopotential monitoring; biosignal acquisition; conductive textile; eHealth; e-textile; IoT; long-term monitoring; health monitoring; mHealth; smart textile; textile electrodes; dry electrode; Ag/AgCl electrode; wearable computing; wearable electronics; flexible electronics; vital signs; electrocardiography; electroencephalography; electromyography; electrooculography; ECG; EEG; EMG; EOG; assistive devices; neural monitoring; cardiac monitoring; rehabilitation; eye tracking; sleep monitoring; muscular monitoring; prosthetics; gesture; human computer interaction; human machine interface; personalized healthcare 1. Introduction
A new trend in electronics is towards the miniaturization and integration of devices into wearable formats such as smart watches, garments, and goggles, where the technology is collectively referred to as wearable electronics or wearable computing [1]. The emerging wearable electronics market is expected to grow 15.5% annually from 2016 to 2022 [2]. This has created a new venue for researchers to investigate novel approaches and develop robust, compact, reliable, and cost-effective solutions to meet the growing demand for wearable devices. Hence, a thorough investigation of suitable materials, fabrication methodologies, and sensing elements needs to be carried out.
Electronic textile (e-textile) or “smart textile” is an evolving technological platform in the field of wearable electronics that studies the integration of functional materials with ordinary clothing to realize devices including sensors, energy harvesters (e.g., photovoltaic cells [3] or piezoelectric materials [4]), antennas [5], advanced textiles for self-heating and cooling [6], and even fashion applications [7]. These are achieved by embedding materials with electrical, mechanical, and/or thermal properties into textiles to add desired functionalities for a given application. For instance, materials with unique properties have been used for chemical sensing of sweat [8,9], temperature [10], and pressure and strain [11,12]. Moreover, internet of things (IoT)-friendly applications are also possible by the integration of wireless transmission modules into textiles to allow continuous transfer of physiological information to a remote medical unit or to the cloud [13,14]. The usage of electroconductive textiles promises to add several other advantages including flexibility, permeability to air and moisture, and easy integration to daily clothing [15]. Flexibility is important primarily to enable skin-compatible devices by matching with the natural contours of the body, to provide wearability, and to achieve better skin–electrode coupling, whereas permeability to air and moisture alleviates the possibility of skin irritations.
One important application of e-textiles within the sensor domain is in the acquisition of biopotential signals for personal and routine health monitoring. Conventionally, biopotential signals are measured by disposable, “wet” silver/silver chloride (Ag/AgCl) electrodes [16]. Wet electrodes are comprised of a gel layer to reduce the skin–electrode contact impedance and adhesive padding to improve contact with the skin. The performance of wet electrodes, however, degrades with time as the gel layer dries, which further results in degradation of the signal fidelity. In addition, wet electrodes usually require skin preparation, which can involve abrasion of the outer skin layer [17]. On the other hand, the gel can cause allergic reactions and irritation, while the adhesive layer causes added discomfort both while wearing the electrode and at the time of removal, due to the need for mechanical peeling for electrode detachment [18,19].
Although wet electrodes are standard in clinical environments, gel-free, “dry” electrodes can serve as good candidates for wearable, long-term, point-of-care personal health monitoring applications and many other similar systems. To this end, wearable conductive textiles provide a viable alternative. Therefore, it is the aim of this study to survey and critically review the state-of-art wearable textile technologies, with a specific focus on the acquisition of biopotentials including cardiac, neural, muscular, and ocular signals, and to discuss some of the emerging applications enabled by their detection and processing.
In alignment with this goal, this paper is organized in three main sections: first, manufacturing technology for e-textiles is presented, followed by a discussion on the critical performance metrics of textile electrodes. The acquisition of various biopotentials with e-textiles is then discussed, along with the different wearable electronics applications. The challenges from fundamental material development to high-level integration are emphasized to highlight areas that need development and suggest future directions.
2. Materials and Methods
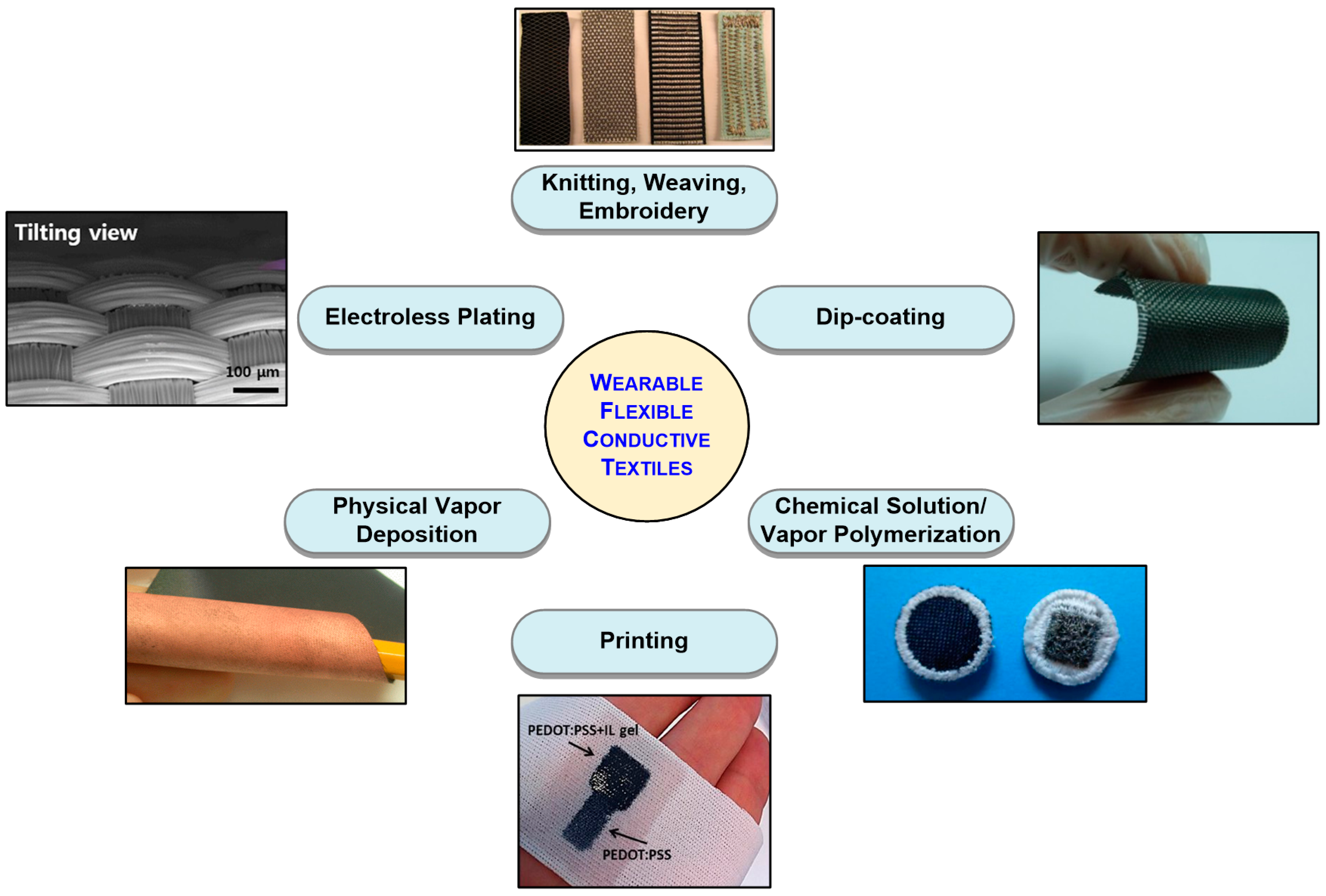
While the materials and methods to realize conductive textiles do not directly affect the performance of the textile electrode, they are among the most important, if not the primary, aspects of e-textile technology since manufacturing cost and reliability tend to be a direct function of the manufacturing technology. In this section, a comprehensive survey of the various techniques and materials used to realize electroconductive textiles is provided. Fabrication of e-textiles essentially relies on the stable integration of conductive materials with fabrics and fibers. Commonly used conductive materials include metals, conductive polymers, and carbon allotropes (i.e., graphene and carbon nanotubes). These materials can be used either with mainstream fabric manufacturing/decoration approaches (e.g., knitting, weaving, embroidery) [20], or can be applied onto finished textiles with various techniques like electroplating [21,22], physical vapor deposition (PVD) [23,24], chemical polymerization [25], dip-coating [26], and printing methods [27] to coat the surface of the textile (Figure 1).
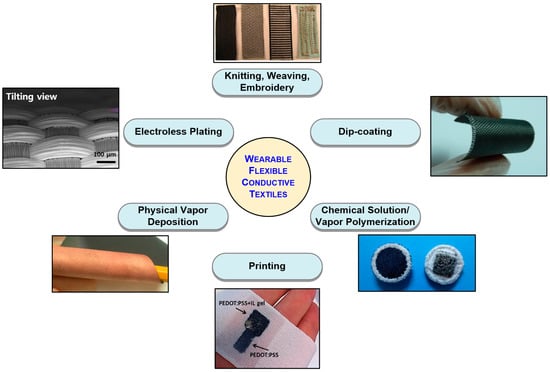
Figure 1.
Primary methods of realizing conductive textiles [3,26,27,28,29,30].
2.1. Knitting, Weaving, and Embroidery
Knitting, weaving, and embroidery are well-established techniques in textile manufacturing and decoration. By using various conductive fibers and yarns, e-textiles can be directly produced through knitting or weaving, while embroidery could be used to create conductive patterns on finished textile surfaces. Woven textiles are produced by interlacing two perpendicular sets of yarns. In contrast, knitting uses a needle to continuously connect a series of chains of yarn together. Embroidery is a decoration method for a finished fabric surface involving different forms of stitches. Knitted textiles provide skin comfort, low weight, and high elasticity for users [31]. Since it is a well-established traditional method, with knitting, an entire garment can be formed on one machine.
Meanwhile, knitting enables the processing of a wide variety of natural yarns and filaments. For this reason, it has been considered the most suitable method for preparing an unobtrusive, compatible fabric for a garment [32]. On the other hand, knitted structures exhibit many intermittent contacts in between the yarns, which leads to fluctuations in electrical resistivity especially in dynamic conditions [33]. Although resistance variation is undesirable for biopotential measurements as it causes larger signal artifacts, it is preferable in sensor applications such as pressure and strain monitoring.
Since conductive yarns are placed above the fabric surface, it was suggested that embroidery offers better electrode contact with the skin [28]. For the positioning of textile electrodes on garments, it can be argued that embroidery is an ideal choice for prototyping. In contrast, weaving and knitting become more useful when mass production of a smart garment is desired.
2.1.1. Metallic Fibers
An effective way to impart conductivity to fabrics for biopotential measurements is by adding conductive “elements” inside them. A common strategy is based on combining metallic fibers with regular yarns or fibers by following established textile manufacturing processes like knitting [34], weaving [35] or embroidery [28,36]. Metallic fibers can be realized by creating fine metal wires [20] or through the deposition of metals on regular yarns via methods like physical vapor deposition (PVD) [37] and electrodeposition [22].
Among metals, silver provides the highest conductivity and is one of the most preferred materials due to its biocompatibility and stability [38]. In a number of different studies, silver was incorporated into fabrics made out of cotton [39], nylon [40], or polyester threads [41]. Another metal that is used for producing conductive textiles is stainless steel [42]. Likewise, copper is a good candidate due to its high electrical conductivity; however, especially in contact with water, it is prone to corrosion. To address this issue, the coating of copper surfaces with silver has been suggested [32].
Apart from the choice of metal, the type of yarn (e.g., cotton, polyester, and lycra) and fiber styles (either single filament or multifilament) along with the structure of the textile can also affect the functionality of the electrodes. Textiles comprised of metallic yarns are relatively easy to manufacture, are flexible, and are adaptable to existing textile manufacturing environments. Nevertheless, they usually compromise the texture and natural feel of the textile, which causes discomfort especially when the percentage of metallic fiber is above a certain level [43]. This inherent trade-off between the conductivity of the textile versus the texture and wearability, therefore, requires careful balance in design.
2.1.2. Conductive Polymer Fibers
Another way of realizing conductive fibers is by creating polymer fibers that possess bulk conductivity. It is possible to categorize these as intrinsic conductive polymer fibers and extrinsic conductive polymer fibers [44].
Intrinsic conductive polymer fibers are produced by spinning conjugated polymers, also known as intrinsic conductive polymers (ICPs), such as polyaniline (PANI) [45], polypyrrole (PPy) [46], and poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT) [47]. Techniques such as melt spinning, wet spinning, and electrospinning are used to produce conductive polymer fibers. Most of the ICPs start to decay in temperatures lower than their melting point, which makes the use of melt spinning unfavorable [48]. In addition, the relative characteristics of ICPs such as poor solubility, rigid backbone structure, and low molecular weight makes them harder to electrospin [48]. To increase processability, blending with a polymer with good spinnability is suggested, but this decreases the conductivity of the polymer fibers [49]. Thus, wet spinning turns out to be the most suitable method for fiber fabrication from ICPs.
Extrinsically conductive polymers (ECPs), or conductive polymer composites, can be obtained by blending insulating polymers with conductive fillers [44]. Melt and wet spinning are common methods to produce composite polymer fibers. Wet spinning can produce fibers with better electrical and mechanical properties, whereas melt spinning is faster and free of chemical solvents [44]. As in the case of metallic fibers, conductive polymer fibers can be used to create textile electrodes with weaving, knitting, and embroidery.
Even though creating conductive fibers with electrospinning is challenging, decreasing the polymer fiber diameter down to nanometers results in a high surface area and advantageous mechanical behaviors [50]. Additionally, electrospinning is regarded as the most reliable method to create continuous polymer nanofibers [49]. It is possible to use these fibers to produce conductive nonwoven textiles, which are a good candidate for biopotential electrodes since a large contact area is a desired. Nonetheless, it is not necessary to first create conductive nanofibers and then produce a nonwoven textile to take advantage of the large surface area. It is simpler and more efficient to first fabricate a nonwoven textile with electrospinning and bestow conductivity on it with conductive fillers afterwards [51]. With this approach, researchers were able to fabricate textile electrodes and validate their performance in biopotential recordings against Ag/AgCl electrodes.
2.2. Electrodeposition
Electroless plating is a technique that involves spontaneous reactions in an aqueous solution without requiring the application of an external electric field [52], unlike electroplating, which uses an electrode current to reduce the metal cations for the coating. Electrodeposition techniques along with physical vapor deposition are the most prominent techniques to perform metal coating on non-conductive yarns and textiles.
Electroless plating on polymer fibers is an appealing choice to realize conductive fibers since it enables conductivity in all surface directions and is an acceptable way to obtain the uniform deposition of metals on complex geometries [3]. Usually, metal coating on synthetic fibers is preferred rather than natural fibers. This trend is mostly because of the low cost of synthetic yarns. The preferred metals in electroless plating are usually silver, copper, and nickel [21,22,53].
Despite the various fabric–metal combinations, metal-plated fabrics face durability issues when worn or washed since they can be easily peeled off from regions exposed to air or water. One of the methods that are practiced to enhance the adhesion of metals to polymeric fibers is increasing the surface roughness either with mechanical abrasion or chemical etching [54]. Performing electroless plating followed by electroplating is an appealing coating method where electroless plating allows deposition of a more uniform coating between the starting yarn/fiber, whereas electroplating provides a larger window for thickness control [55]. To prevent wearing out of the surface coating, lamination of metal-coated polyester fabrics with a polyurethane sealing layer was also suggested [15].
2.3. Physical Vapor Deposition
PVD techniques such as thermal/e-beam evaporation and sputtering are well-established in the microelectronics process industry [56]. Similar to electrodeposition, the performance of a PVD-deposited conductive layer depends both on the nature of the textile and on the deposited layer. Its conductivity can be controlled by selection of the thin-film coating material and film thickness. So far, there have been several attempts that utilized PVD to evaporate metals and deposit thin conductive films on a variety of textiles [57,58]. Sputtering has been used to deposit layers of silver [23,59] and copper [24,29] on textiles made from polyethylene terephthalate (PET) yarns and polyurethane (PU)-coated nylon fabrics.
For PVD, like other coating techniques, adhesion of the conductive materials on the surface of the fibers is critical. Removal of potential residues like oil from fiber surfaces can promote adhesion, which can be achieved by plasma cleaning or chemical treatments [60]. Metals like chromium [23] and titanium [59] have also been sputtered onto fabrics to either improve the adhesion of silver or passivate it to limit potential cytotoxicity when used in direct contact with the skin in low humidity conditions. As for the film thickness, it was shown that sputtered fibers generally require a smaller thickness of metal deposition compared to electroless-plated ones, due to the greater adhesion and smoother coating of metals via PVD [37,54].
On the other hand, a disadvantage is that during PVD, a significant portion of the source material is lost in spots other than the desired substrate. This issue, combined with the need for dedicated equipment and a vacuum deposition environment, potentially increases the cost of the conductive textile. While there have been few attempts to produce e-textiles based on PVD, this approach is still among the less preferred techniques, fundamentally due to the elevated cost and limited or non-trivial scalability of vacuum processing.
2.4. Dip Coating
Dip coating is one of the simplest methods to coat yarns or fabrics, and it is still used in the textile industry [61]. The process consists of the immersion of the substrate in a solution containing conductive materials such as metallic particles [62], conductive polymers [63], or carbon derivatives such as graphene [26] and carbon nanotubes (CNTs) [64]. Upon application of a conductive solution to textiles, excess material is removed [65] and a drying step, known as curing, is performed to evaporate the solvent and fixate the conductive particles on fiber surfaces. To realize a stable coating, surface properties of the textile such as wettability and hydrophilicity are important [65]. Care should also be taken to limit the drying/curing temperatures to avoid potential damage to the textile [66].
Conductive solutions or pastes are the only feasible way to utilize graphene/CNTs in textile coating. Although multiple techniques such as chemical vapor deposition (CVD), mechanical exfoliation, epitaxial growth on silicon carbide, and chemical reduction of graphene oxide (GO) exist for preparing graphene [67], the latter approach (i.e., chemical reduction) is the most suitable and applicable for textile surfaces due to low-temperature processing and scalability [68]. In graphene-coated textile preparation, the desired piece of textile is dipped in a GO solution, and subsequent drying provides fixation on fiber surfaces. As for post-processing, a chemical reduction procedure is performed to convert GO flakes into graphene, allowing electrical conductivity to be imparted [26,69]. Carbon nanotube (CNT) powders have also been used to create conductive fabrics [70]. For instance, textile electrodes were fabricated by cladding cotton fabrics with multi-walled CNTs (MWNT). To ensure their adhesion, a conductive paste made from tapioca starch and MWNT powder was applied to the surface and cured afterward [71]. Another aspect of wearable monitoring was looked into with the creation of conductive cotton yarns to use in biosignal transmission [64]. Regular cotton yarns became conductive with dipping in a single-walled carbon nanotube (SWNT) solution and drying afterward, which fixated SWNTs to cotton microfibrils.
Regarding the biocompatibility of CNTs, while there is some concern regarding their cytotoxicity, the purity of the carbon nanotube (i.e., elimination of trace metals such as iron that get incorporated into CNTs during manufacturing) has been shown to be a critical factor, especially for the case of dermal administration and exposure to CNTs [72]. Arguably, with better control of purity, it may be possible to reduce or eliminate the potential toxicity of CNTs when used as part of conductive textile electrodes placed in direct contact with the skin. Graphene, on the other hand, has been shown to have minimal effects on skin as long as the concentration and exposure duration is moderate [73].
The simple and scalable nature of dip-coating allows the manufacturing of rolls of conductive fabrics with lower fabrication cost, and after cutting and sewing of the desired patch, it is also possible to attach textile electrodes onto an existing garment [74].
2.5. Printing
Printing techniques such as ink-jet and screen printing are widely used to create conductive patterns on textile substrates, and these are already used on a large scale to print decals/images onto textiles [75]. Some advantages of printing techniques include: (a) site-specific, localized, and direct deposition of conductive materials on finished roll-to-roll (R2R) fabrication textiles; (b) reduced consumption of chemicals/inks; (c) ability for adaptation to both desktop scale R&D and commercial manufacturing environments with the potential to be combined into or allow further reduction of e-textile production costs.
Screen printing uses a fine mesh or stencil with openings to enable preferential passage of viscous, conductive inks/pastes, while ink-jet printing is a well-known maskless technology that can interface with numerous ink–substrate combinations to address both daily applications as well as advanced areas such as biomolecular patterning [76]. In a single pass, screen printing can deliver higher amounts of ink compared to ink-jet printing. Therefore, screen printing requires fewer printing cycles to achieve a stable conductive pattern on textile surfaces. Another aspect is regarding the contact and non-contact nature of the printings. Applied pressure in screen printing promotes adhesion, penetration of the ink to the substrate, and facilitates the formation of connected patterns. Conversely, non-contact ink-jet printing relies on the spread of the ink to achieve the merging of successive ink droplets and form electrically-connected structures, which requires careful engineering of the ink diffusion and printing process, especially on rough textiles where yarn-to-yarn spacing may be on the order of tens of microns [77]. Inkjet printing’s flexibility in pattern creation and available materials makes it versatile for e-textile research [78]. On the other hand, screen printing seems to be ahead of ink-jet printing for the creation of e-textiles for consumer products. It is faster since it allows the transfer of larger amounts of ink at one time, and it is a mature technology already used in industry, which makes screen printing a cheaper alternative.
Printing technique, nonetheless, is not the only consideration for achieving optimal conductive pattern transfer. Ink properties such as viscosity and curing temperature, and surface properties such as surface roughness and surface energy, affect the accuracy of pattern transfer [79]. Using an ink with high enough viscosity is important to contain the ink on the desirable pattern after deposition. This calls for the addition of binders to engineer the ink viscosity, which often affect the conductivity negatively.
It is not easy to control the surface properties of woven fabrics; the resolution achievable by printing on them depends on both the yarn diameter and inter-yarn distance. As an alternative, the surface texture, density, porosity, and thickness of nonwoven fabrics can be controlled during fabrication. They are also cheaper and faster to fabricate, which makes them better substrates on which to print [79]. Nevertheless, woven textiles are known to be more flexible and breathable than nonwoven ones, which makes them more comfortable to wear. Moreover, it was suggested that the creation of a high surface energy interface layer on top of the fabric can provide a desired substrate on which to print, while conserving the comfortable wear of the woven fabrics [80]. The extra interface layer is not expected to affect comfort since it can also be printed on only the desired areas, such as electrodes and their interconnections.
Metallic inks/pastes can be produced by using metallic nanoparticles, metallo-organic complexes, or metallic salts as precursors [81]. Even though there are commercial metallic inks (mostly silver-based), their curing temperatures should be lowered to be compatible with textile substrates, and their cost should be decreased so that they can be used in the mass fabrication of textile electrodes. Conductive polymers are also studied to create alternative conductive solutions. Their conductivity is typically lower than their metallic counterparts, but their adhesion and mechanical stability are better, and they do not usually require post-treatment steps. To this end, poly (3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-poly(styrenesulfonate) (PEDOT:PSS)-based solutions are regarded as the most promising material to enter the market, due to their flexible processing and durable electrical conductivity [82,83]. Dispersions of graphene or CNTs can also be used in printing to create conductive patterns [84,85]. The effect of pretreating the fabric to increase its printability was also shown with ink-jet printing a hydrophobic layer prior to application of GO solution [85]. This helped to improve the continuity of the conductive layer by three orders of magnitude compared with untreated coating.
2.6. Chemical Solution/Vapor Polymerization
Vapor deposition, electrochemical deposition, and in situ solution polymerizations are techniques that allow the formation and deposition of intrinsically conductive polymers in a single step.
Vapor deposition allows uniform coating for any surface morphology or roughness, and coating can be thin enough to not change the mechanical properties of the fibers. Two main ingredients used in vapor polymerization are conjugated monomers and iron salts as oxidant agents [86]. They are used to create conductive polymers in two distinct ways: impregnation of the oxidant solvent to textile with dipping/printing followed by monomer vapor feeding, and the simultaneous application of both the oxidant and conjugated monomer vapor. A closed chamber is required for the application of vapors. This process, however, is not solvent-free since oxidant residues need to be rinsed after vapor deposition, and they require vapor chambers, which limit the scalability of the process. Nonetheless, with the advancements made in the past, the textile industry recently started to adopt this technique [86] because vapor-deposited films inherently show wash and wear resistance, as opposed to the need for binders in the dip-coating method. Additionally, vapor-deposited textiles show higher conductivity compared to the conductive textiles created with commercial polymer inks [86]. For instance, coating of polyester fabrics with PEDOT by vapor polymerization revealed a sheet conductivity as low as 10 Ω/sq, which is claimed to be among the best in any kind of synthesis of PEDOT and its dispersions [30].
Polymerization can also be done by placing the textile substrate in a solution containing the monomer and adding an oxidant to the solution, which starts the deposition; this is called in situ solution polymerization. Even though it is a relatively simple process, polymerization is hard to control. It is possible to degrade the textile substrate with acidic reaction conditions, which can harm the mechanical characteristics of the textile [86].
Electrochemical polymerization happens with an application of varying voltage on an electrode in a solution including a monomer and electrolyte salt; polymer coating occurs on the electrode. Textile fibers are natural insulators, and to be able to use electrochemical deposition for coating, it is first necessary to create a conductive seed layer on the fibers with other polymer deposition techniques. Not surprisingly, the final morphology of the coating is mainly determined by the previously coated seed layer. Electrochemical polymerization can be regarded as a technique to increase the thickness of the polymer coating in a more controllable fashion [87]. For example, textile electrodes were created by coating PPy on cotton fabrics via initial in situ solution polymerization followed by electrochemical polymerization [25].
Like the rest of the fabrication methods, the choice of technique for conductive polymer coating boils down to a trade-off between desired quality and cost. Vapor polymerization is an apparent example, which promises the best quality with possibly the highest cost. Optimization can be achieved by improving existing techniques or using them in combination, which requires knowledge of the whole palette of techniques.
3. Performance Characteristics
Understanding the major performance characteristics for wearable biopotential monitoring system is important to assess their utility in recording and for the development of electrodes with better performance. Some key performance metrics include skin–electrode contact impedance, noise immunity or susceptibility to motion artifacts, stability, and lifetime of the electrodes. Even though the system’s “wearability”, user comfort, and seamless integration are not numerical metrics, they are some of the most important points to be considered in system-level development.
3.1. Skin–Electrode Contact Impedance
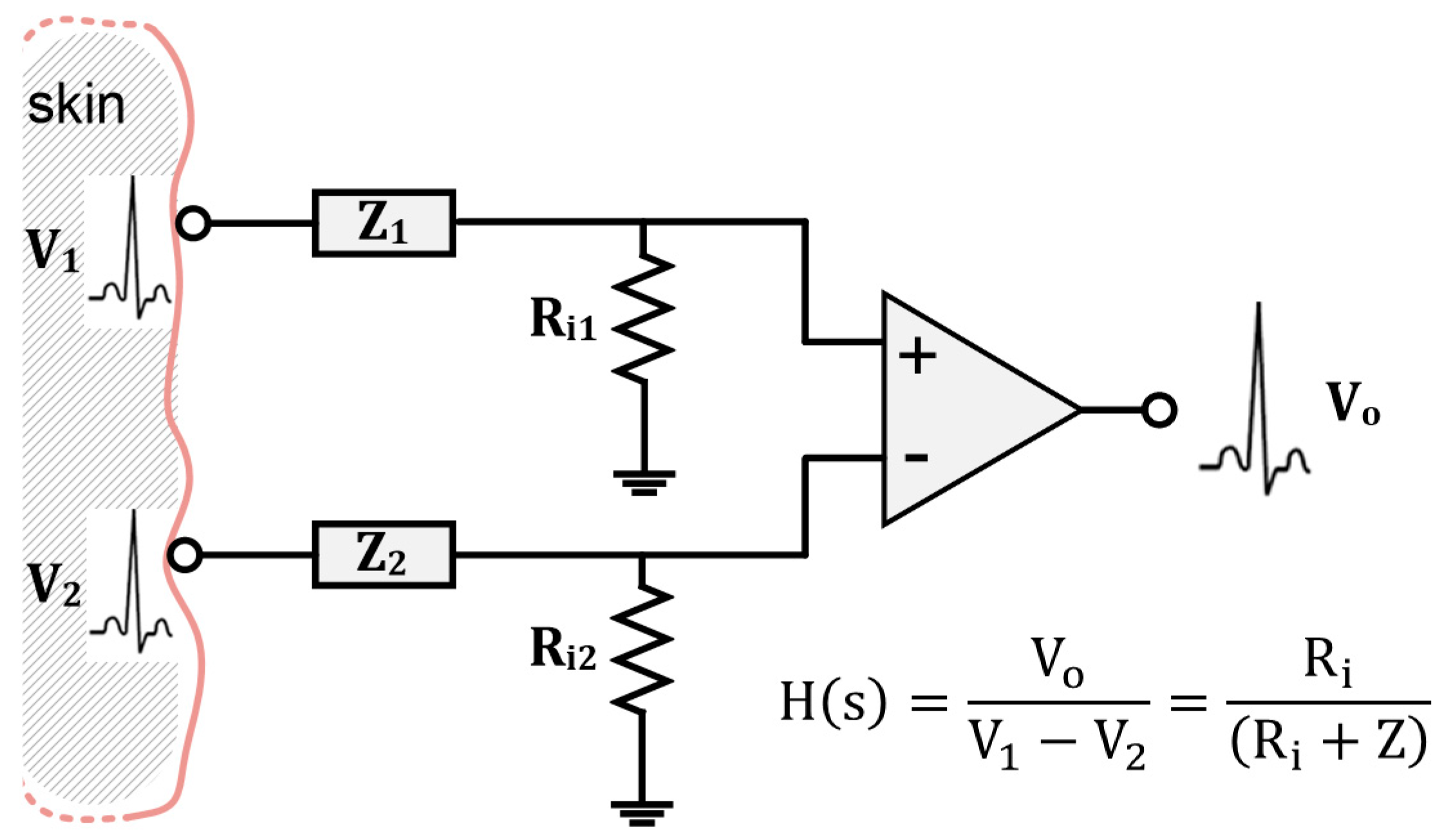
In biopotential recordings, skin–electrode contact impedance is critical as it directly affects the received signal at the amplifier output. The effect is analogous to the filtering of the actual biopotentials emanating from the body [88]. If we assume the skin–electrode contact impedance of both electrodes to be equal (Z1 (w) = Z2 (w)) and name it as Z (w), and similarly, the amplifier input impedance is seen by each electrode to be the same (Ri1 = Ri2), then the transfer function of the system H(s) can be expressed as the ratio of the amplifier output (Vo) to the biosignals V1 and V2 emanating from the body, as shown in Figure 2.
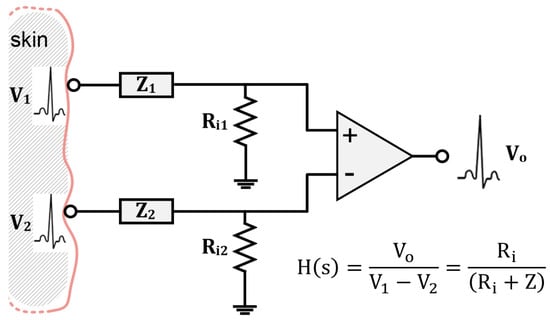
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the path of biopotential signals starting from the skin surface until acquisition and display at the circuit output (adapted from [88]).
An electrode–electrolyte interface can be modeled by a parallel RC network [89]. However, skin is more complex; understanding skin–electrode impedance and its frequency-dependent characteristics requires investigation of the skin itself, which consists of three main layers: epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis or subcutaneous tissue.
The outermost layer, the epidermis, plays a significant role in the skin–electrode interface since it has direct contact with the electrode, besides the fact that it constantly renews itself. The deeper layers involve the vascular tissues and the nerves along with sweat glands, sweat ducts, and hair follicles [90].
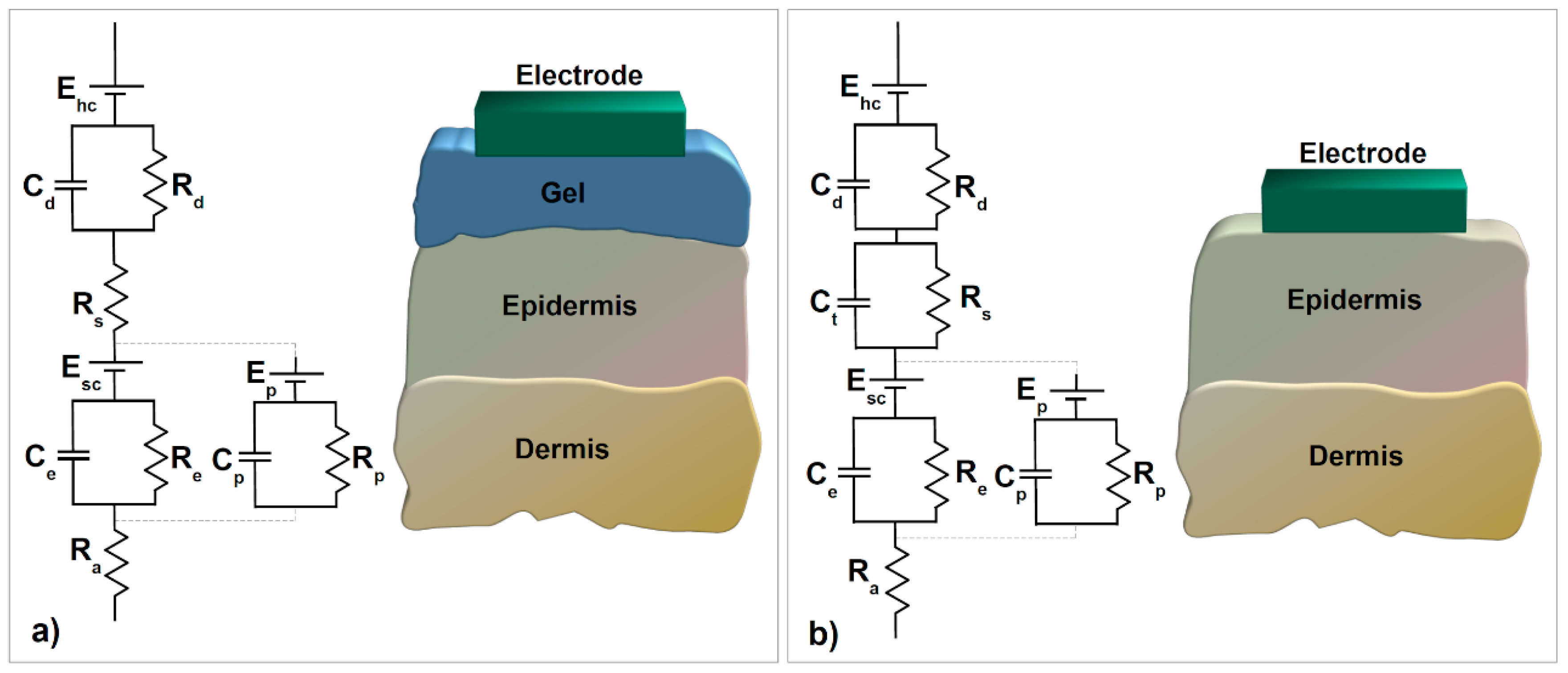
The equivalent circuit of the skin–electrode interface (Figure 3a) starts with an electrode half-cell potential Ehc followed by the electrode–electrolyte interface between the electrode and the gel, which is represented by capacitance due to electrical double layer formation Cd and charge transfer resistance Rd. The gel medium is modeled by a series resistance Rs. The upper layer of the epidermis behaves as a semipermeable membrane that causes the difference in ion concentration and a potential difference, which is shown with Ehc. Ce and Re model the impedance of the epidermal layer and Ra models the dermis, which behaves as a pure resistance.
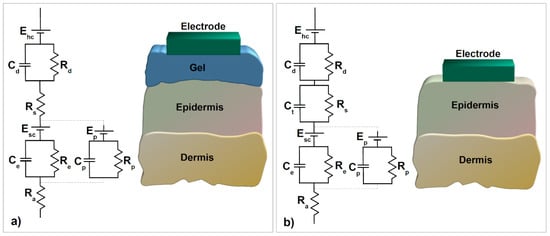
Figure 3.
Equivalent circuit of skin–electrode interface for (a) traditional wet electrodes and (b) textile electrodes (adapted from [90]).
Moreover, Ep, Cp, and Rp stand for the effect of sweat glands as a parallel conduction path through the epidermis [36]. The half-cell potential appears as a DC baseline on the biopotential signals and is a particularly important factor in design decisions for any physiological signal acquisition unit development. This is due to its fluctuation, as it varies even with a relatively insignificant movement in between the electrode and the skin, which is interpreted as a noise-like artifact.
Textile electrodes were believed to show a strong capacitive behavior compared to conventional electrodes, owing to the absence of electrolytes. Figure 3b illustrates this effect with capacitance Ct parallel to Rs, herein which Ct is in inverse proportion with sweat and the moisture over the skin [90]. Additionally, ambient humidity or applied pressure can be used to change moisture intensity [91]. Parallel RC blocks on the equivalent circuit imply that skin–electrode impedance decreases with increased frequency. The relation between acquired output signal and in-body biosignal means that lower frequency components of the biosignal will deviate more than the original. Decreasing the skin–electrode impedance, therefore, improves the signal quality.
One way to decrease the skin–electrode impedance is by moisturizing the interface either with a hydrogel membrane or salty water. Since a membrane interface improves the comfortability of the electrode, instead of salty water, a hydrogel membrane seems more preferable. The only drawback of such a technique, however, is the bactericide/fungicide effect, which causes skin irritation, but by optimizing a hydrogel membrane’s pH value to between 3.5 and 9, this issue could be avoided [92]. The other ingredient that affects the skin–electrode interface is the electrode’s overall size, which presents an inverse relation with skin–electrode impedance [80]. In this manner, different sewing patterns affect skin–electrode impedance since they result in diverse contact areas. A comparison of knitted and woven textile electrodes showed that knitted textiles express lower impedance. Since sewing patterns directly affect density, their thread diameter ought to change the skin–electrode interface impedance [80]. Research has illustrated this fact, finding that in knitted structures, electrodes produced with a plain stitch had less impedance than electrodes produced with a honeycomb stitch since pits existing in honeycomb patterns represent non-contact areas [93]. In addition, studies have suggested that the pressure applied to the skin leads to lower skin–electrode impedance by providing better skin–electrode coupling [94].
It is, however, not an easy task to accurately compare skin–electrode impedance for different electrodes since people’s skin characteristics vary and can change with time [89]. Repeatable measurement setups are therefore desirable. It was suggested that the skin’s electrolytes can be simulated with an electrolyte cell, and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy can be used in electrode characterization [95]. A more comprehensive setup was suggested that uses a skin dummy made out of agar-agar [90]. It enabled contact impedance analysis at different frequencies and at different pressure levels.
3.2. Susceptibility to Motion Artifacts
Motion artifacts, identified as an undesirable signal in biopotential monitoring systems, occurs by any sort of motion due to movement of one part of a section with respect to another (e.g., movement of connecting cables, a patient’s head) and can be categorized in relation to five different sources [94]:
- Measurement of an unrelated biopotential signal, for instance, electromyography (EMG) interferences in an electrocardiography (ECG) recording. Proper electrode placement can usually avoid such interference [96].
- Stretching of the skin leading to variations in the skin potential. In the textile electrode-based system, fixation of the electrodes relies on the applied pressure, which is in direct translation to the skin stretch. To reduce such motion artifacts, the applied force could be distributed to a bigger area than the electrode through the use of a supporting structure surrounding the electrode [97].
- Motion between the electrical double layer of metal and electrolyte, which causes a voltage difference in its electrochemical cell. Reducing the electrolyte resistance, polarization potential, and the movement of the electrode are believed to decrease such motion artifacts.
- Cable bending generating friction and deformation on the cable isolator, resulting in triboelectric noise [98]. To reduce this effect, a wearable garment or clothing could be designed in such a way as to secure cables and the acquisition system into the garment and provide wireless streaming of information.
- Static electricity storage and discharge caused by patient or nurse-staff localization and/or movement [99].
Besides all of this, placing preamplifiers subsequently after the electrodes (i.e., active electrodes) is a recommended technique for reducing motion artifacts. A preamplifier block functions as an impedance converter that converts the high-impedance signal to a low-impedance one, lowering noise susceptibility and impedance mismatch before differential amplifiers [100]. Additionally, it is possible to use digital signal processing (DSP) algorithms for motion artifact reduction, including blind source separation and adaptive filters [94,95]. Similarly, a multiscale mathematical morphology and finite impulse response bandpass filters were also shown to reduce the effects of motion artifacts [93].
3.3. Stability and Lifetime
The other expected requirement from textile electrodes is their stability and reusability, which directly affect their lifetime. In the literature, a few studies have looked into this issue and characterize stability by subjecting their textile electrodes to “wash tests” with detergent, either by using a washing machine with respect to the ISO 6330 standard [101] or simply them dipping into detergent.
One of the factors that the washability of textile electrodes depends on is the adhesion of conductive material is on textile fibers. This issue will not occur for bulk conductive fibers like metal wires; however, they eventually create unwanted wrinkles and loops after cleaning in a washing machine [54]. Washing temperature, speed, and time are thought to have an effect on the adhesion of the conductive material. Therefore, an optimal washing range needed to be determined for the reusability of a textile electrode. Different groups have reported washing tests on textile electrodes, such as ones coated with Cu/Ni plating [15], PEDOT:PSS [77], graphene [26], and silver-based ink [102], which were reported to maintain their optimum stability even after multiple washing cycles.
4. Conductive e-Textiles for the Acquisition of Biopotentials
Among the various applications of e-textiles, biopotential monitoring (cardiac, muscular, neural, and ocular biopotentials) is growing steadily and shows large parallelism to the developments in wearable technologies and the internet of things (IoT) [103,104]. Applications from mobile health monitoring (mHealth) to brain–computer interfaces (BCI) and human–machine/computer interaction (HMI/HCI) are greatly facilitated by developments in wearable technologies, and in this respect, textile electronics is a key technology enabler. Since a critical signal “source” in wearable applications is the human body itself, in this section, we focus on providing an overview of the different biopotentials that have been acquired by conductive textiles and discuss the relevant applications (Table 1).

Table 1.
Summary of the various integrated textile system solutions categorized based on the acquired biopotentials to show the different manufacturing techniques and conductive materials used in their realization and the active sensing regions on the body.
4.1. Electrocardiography (ECG)
With the increase in cardiovascular diseases, there has been a growing interest in developing wearable devices that can continuously monitor cardiac activity. According to the World Health Organization, heart problems are the number one killer worldwide, accounting for 31% of total deaths each year (~17.9 million) [122]. Cardiovascular diseases assessed through abnormalities in heart rhythm such as atrial fibrillation, ventricular fibrillation, and atrioventricular block require long-term monitoring [123]. As people diagnosed with cardiovascular diseases have a higher rate of mortality in comparison with healthy people, the need for wearable devices that enable continuous heart monitoring is critical for a quick emergency response and earlier detection of heart malfunctioning [124].
ECG is a biopotential signal acquisition method by which the variation in heart potential is measured by utilizing surface electrodes across the body. It is a non-invasive method and gives a thorough indication of any abnormalities in heart rhythm. Its main components (i.e., P-QRS-T complex) can be used to diagnose various cardiac disorders. For instance, missing P-waves is an indication of atrial fibrillation and can lead to stroke; arterial diseases can be revealed by the morphology of the ST segment duration; variation in RR intervals leads to sleep apnea; abnormality of QT intervals is attributed to ventricular fibrillation and causes sudden cardiac arrest [125]. While some of these abnormalities are not immediately fatal and can be detected over longer diagnostic periods, others are characterized by sudden changes in ECG signal (e.g., ventricular fibrillation) and cannot be detected unless continuous monitoring is practiced [123]. A wearable routine monitoring system can help resolve this issue without restricting patients to a static ECG monitor.
From the perspective of wearability, textile substrates offer integration between various system modules such as electrodes, microprocessors, and transceivers. Therefore, they are helpful for offering a robust solution to realize smart clothing for personalized, point of care health monitoring. Textile platforms for wearable and continuous monitoring of ECG have been extensively studied [74,105,106,126,127]. Some of these wearable clothes are waterproof [107], while others were developed to encourage exercising and fitness through the routine monitoring of daily activities [128,129,130]. Among these projects, MagIC Space was a promising work designed to monitor heart activity and other vital signs while sleeping on space stations [131].
Moreover, conventional electrodes in a neonatal intensive care unit cause possible irritation and discomfort for neonates and requires separating them from their mother since they need to be connected to the monitoring system at all times.
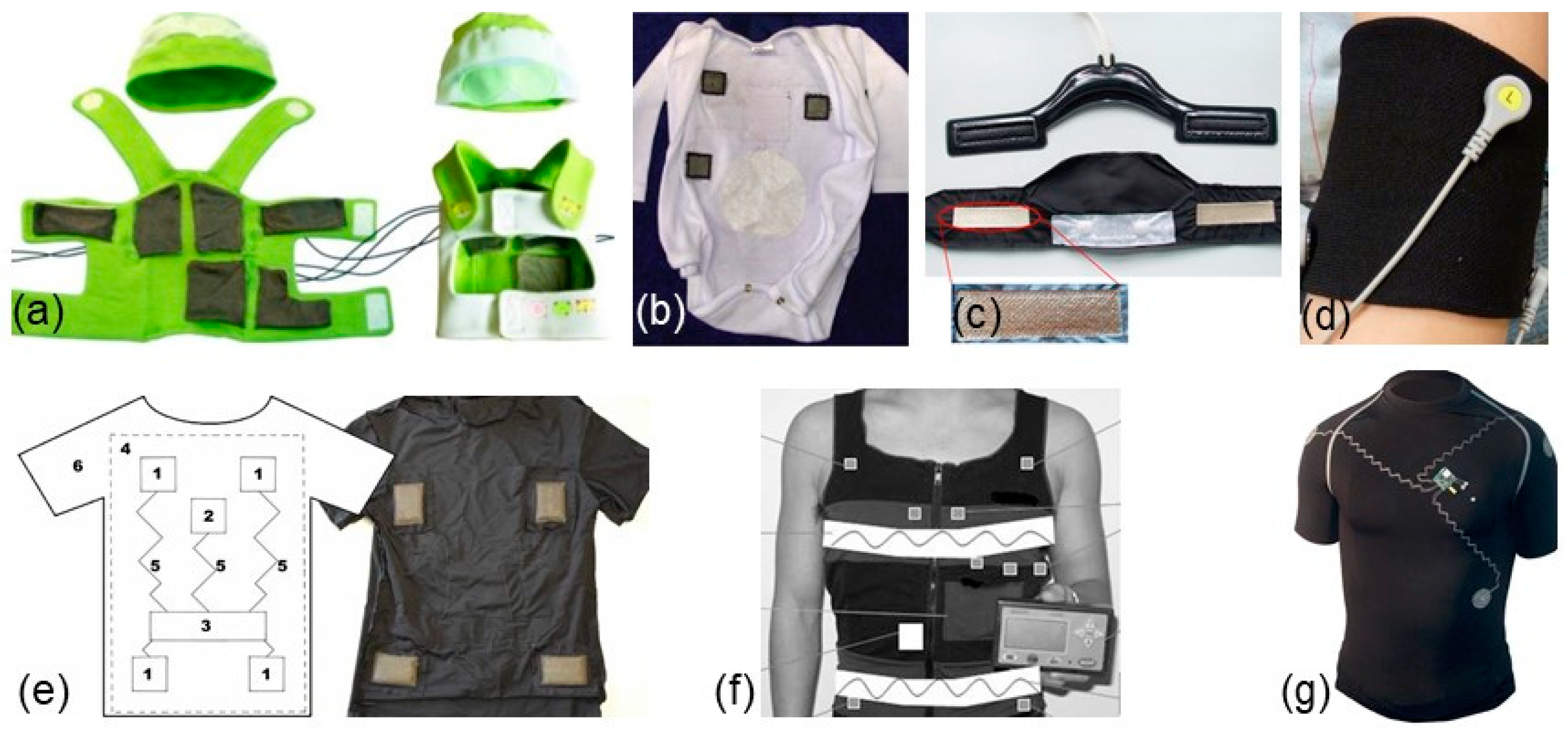
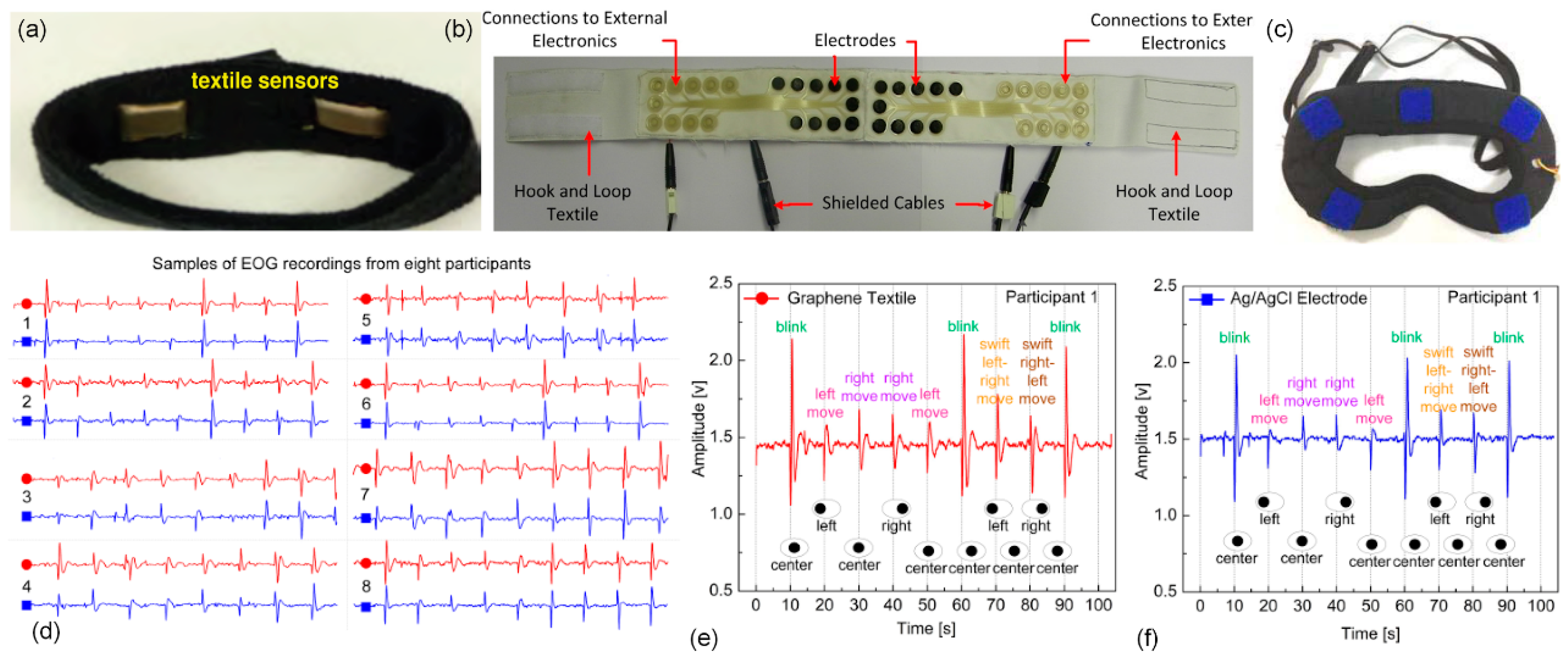
It has been shown that a wearable monitoring system with textile electrodes designed for babies can increase the comfort of both the baby and the mother (Figure 4a,b) [108,109,132]. Moreover, textile electrodes are implemented in different forms such as belts (Figure 4c) [59], armbands (Figure 4d) [69], and t-shirts (Figure 4e–g) [110,133,134].

Figure 4.
Wearable electrocardiography (ECG) systems: (a) jacket for baby [108]; (b) textile electrodes embedded into a baby suit [109]; (c) belt with embroidered electrodes [59]; (d) armband with embedded textile electrode [69]; (e) Bluetooth-enabled mobile ECG monitoring system integrated on a t-shirt [133]; (f) t-shirt embedded with textile electrodes and a local portable device [110]; (g) t-shirt with embroidered electrodes [134].
4.2. Electroencephalography (EEG)
EEG is one of the few non-invasive methods to check brain activity in real-time and is the cheapest technique due to low-cost hardware [135]. It measures pyramidal neuron postsynaptic potential activities and picks up biopotential signals through surface electrodes placed on the scalp [136]. In spite of more powerful examination techniques, EEG is well integrated into clinical diagnostic tests and still widely used in a large number of applications from the detection of tumors to the confirmation of brain death, the monitoring of brain status while a patient is fully anesthetized, and the diagnosis of neuropsychological disorders, as well as BCI [135,137]. Especially for the diagnosis of epilepsy and seizure monitoring, extended EEG recordings over a number of days are needed. Long EEG recordings can be performed either in a clinical setting (inpatient) with bulky EEG acquisition systems, or at home (outpatient), otherwise known as ambulatory EEG, with portable devices that do not disrupt a patient’s daily routine.
To advance EEG technology for use in clinical environments as well as outside of lab settings [138], further developments to realize mobile, low-cost, and wearable EEG monitoring devices that offer minimal discomfort to the user will be necessary. Such devices will have a significant impact on many of EEG’s current applications, especially seizure prediction devices [139], event-related potential-based applications like P300 writing systems [140], and image reconstruction using EEG mind-reading algorithms [141]. Besides these, wearable EEG instruments are also anticipated to empower new applications in the future, potentially in the areas of augmented reality [142] and robotics [143].
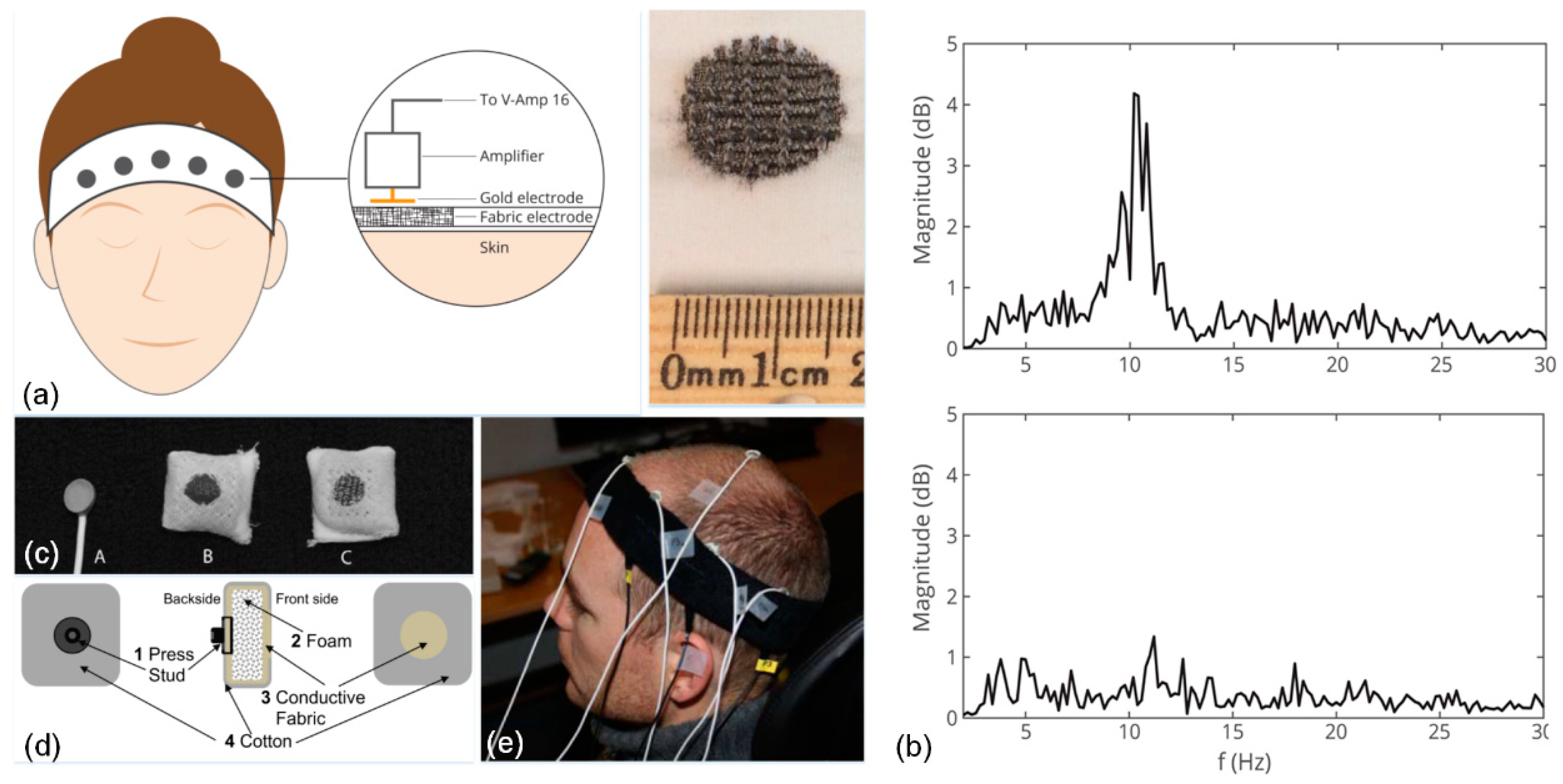
A fundamental challenge in recording EEG waves with textile electrodes is the likely presence of hair on the scalp [144]. Hence, textile electrodes for EEG recording are usually placed on the forehead where there is no hair, and signals from the frontal lobe (e.g., alpha and beta waves) are measured. Alpha waves increase and decrease by the opening and closing of the eyes, respectively; beta waves occur when the subject is actively thinking or performing reasoning tasks like solving mental math questions. Therefore, the monitoring of alpha and beta waves would be useful for a variety of applications including cognitive neuroscience and perception. For instance, a headband with conductive fabrics and a custom-designed EEG amplifier was developed that detects drowsiness by measuring both alpha and beta waves [145]. Similarly, as illustrated in Figure 5a, Ag/AgCl-coated threads were integrated into a nylon headband through a seamless knitting technique, and its functionality was tested by monitoring alpha and beta waves; Figure 5b illustrates the associated power spectra plots [111]. In a different electrode placement where electrodes were placed on approximate locations of F3, C3, and P3 according to the international 10–20 system, conductive fabric-based textile electrodes were padded in a tight-fitting headband and used for EEG measuring of five participants who had thin hair. Two different composites of conductive fabric were reported; Figure 5c (inset A) illustrates a standard electrode; Figure 5c (inset B) shows the type I electrode composed of 78% polyamide and 22% elastomer, which was plated with 99% pure silver. The type II electrode (Figure 5c, inset C) was composed of 15% nylon, 30% silver-plated conductive fibers, 20% spandex, and 35% polypropylene. Feasibility of the design was further investigated for applications in neonatal EEG monitoring (Figure 5e) [146]. Furthermore, a headband with integrated active electrodes, which were realized by screen printing using composite materials, was developed and the system powered by a flexible solar panel. It achieved a correlation reaching 70% in comparison to commercial passive electrodes [112]. In addition, a novel electrically conductive polymer fabric, which has 0.07 Ω/square of conductivity, was coated on a 0.2 mm thick taffeta material and benchmarked against standard electrodes, showing a high correlation of ~96% and ~90% from the forehead and hairy sites on the head, respectively [147]. Most recently, textile electrodes fabricated by jet-printing using Ag-powder/fluoropolymer-based nanocomposite ink with two-layer e-textiles were developed, and their functionality was demonstrated in EEG monitoring experiments including activities of closing and opening the eyes for a duration up to 15 minutes, with the electrodes mounted behind the ears on hairless regions [113].
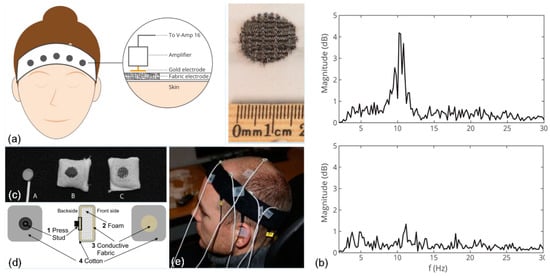
Figure 5.
(a) Seamless knitted Ag/AgCl electrodes in a nylon headband along with electrode configuration on forehead; (b) associated power spectra for the relaxation and mental math conditions [111]; (c) standard electrode (A), textile electrode type I (B), and type II (C); (d) schematic structure of type I and II textile electrodes; (e) an experimental setup where the white leads are connected to standard electrodes, whereas the black leads are connected to the textile electrodes [146].
4.3. Electromyography (EMG)
Surface electrodes can be employed to measure the myoelectric potentials of skeletal muscles throughout a recording technique called EMG [148]. Its applications include prosthetic devices, neuromuscular diagnostic tests, rehabilitation, ergonomics, and sports science [149,150,151,152]. Unlike ECG biopotentials, myoelectric signals are quite localized on the skin surface over the muscle of interest. This makes recordings more prone to motion artifacts due to muscle movements beneath the electrodes, which places a larger burden on the constraints of the electrode area to avoid possible crosstalk from neighboring muscles [153]. Typically, EMG electrodes are smaller in size, which results in higher skin–electrode impedance, and the signal quality of textile electrodes suffers even more since they do not incorporate electrolyte gel and adhesives. One strategy has been to implement active electrodes or use electrode support structures to acquire EMG signals with the desired fidelity [154,155]. As a different performance metric than other biosignals, pattern recognition/classification accuracies are also important to evaluate and characterize the performance of textile electrodes used specifically in EMG acquisition for prosthetics applications [114].
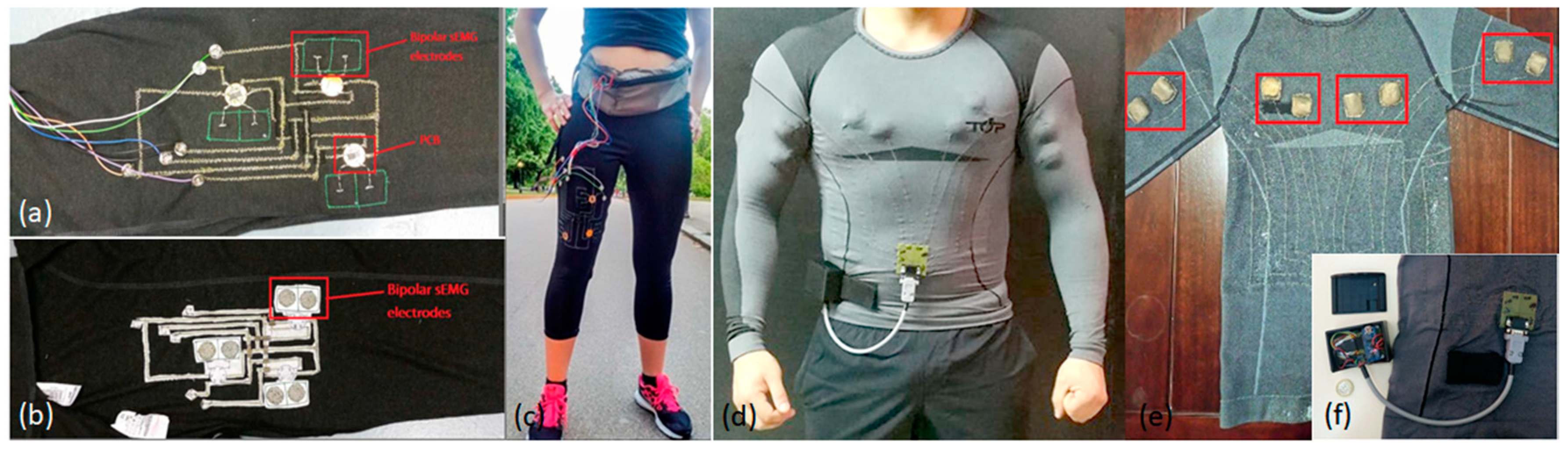
EMG could benefit from the advantages of textile platforms since they enable data acquisition in more realistic, casual, and out-of-lab settings. Research on EMG recording with textile electrodes either focuses on showing the feasibility of new electrode designs for the desired application or studies the proof-of-concept of an embedded textile electrode in wearable smart garments. Some of the popular application areas enabled by the acquisition of EMG with textile electrodes include muscle status monitoring [115,156,157], prosthetics [116,158], and rehabilitation [117]. Other possible uses of wearable EMG platforms with integrated textile electrodes have also been demonstrated, including running leggings for muscle fatigue detection (Figure 6a–c) [153]; shorts for energy expenditure analysis [159] and ventilatory threshold estimation [160]; eyeglasses for the analysis of chewing cycle [118]; and a shirt for athlete training (Figure 6d–f) [115].

Figure 6.
Wearable electromyography (EMG) acquisition garments: running leggings and a sports shirt. Electrode placement in the (a) exterior; and (b) interior of leggings; (c) actual view of leggings when worn by a subject [153]; (d) shirt as worn by a subject; (e) location of electrodes on the shirt; (f) close-up view of the acquisition unit attached to the shirt [115].
The concept of a compression garment with integrated EMG textile electrodes was recently commercialized by two companies: Athos (Mad Apparel Inc., CA, US) and Myontec (Myontec Ltd., Kuopio, Finland). Both are mainly focused on athlete training, with Myontec also advertising their products for rehabilitation and ergonomic studies. We anticipate that, with the advances in wearable computing, similar products will emerge at a competitive price in the near future and possibly offering additional capabilities.
4.4. Electrooculography (EOG)
EOG is a well-known ocular activity monitoring technique that measures the electric potential differences between the cornea and retina by placing electrodes around the eyes [161]. Essential EOG signal attributes (i.e., blinking and saccadic movements) have many potential applications in somnolence studies, activity monitoring, assistive technology, and HCI/HMI, as well as cognitive neuroscience and mental disorder diagnosis [162]. Despite the growth of EOG-based eye tracking systems, their full potential is yet to be recognized and there is still space for improvement both in the existing devices and in the rise of new applications combining EOG and e-textile technologies.
EOG signals are highly sensitive to electrode placement, and different electrode placements and configurations have been investigated. Despite the existence of various wearable accessories and electrode configuration approaches (e.g., vertical and horizontal EOG acquisition with glasses [163]), considering overall comfort and operability by everybody (i.e., including bespectacled individuals), placing the electrodes on the forehead, known as “forehead EOG” is preferred. This can be achieved by embedding electrodes on a wearable elastic headband [164]. For instance, using screen and stencil printing processes, an electrode network was fabricated and embedded on a headband and used for horizontal EOG acquisition (Figure 7a) [119]. Similarly, conductive fabrics used in a headband to measure EOG have been capitalized on in a drowsiness detection application [145]. Additionally, a silver-coated nylon textile was integrated into a headband and adapted for gesture recognition (Figure 7b) [80]. Silver/polyamide compound textiles have also been employed to develop a wearable eye mask for sleep monitoring and automatic sleep staging (Figure 7c) [120]. Moreover, graphene-based textile electrodes were fabricated through a simple dip-dry-reduce cycle and used in EOG recordings. Their performance was benchmarked against clinical electrodes in a set of experiments with multiple participants that revealed ~80% correlation over durations exceeding ~90 s (Figure 7d–f) [121]. Furthermore, novel self-wetting electrodes composed of PEDOT:PSS fibers were integrated into a thin layer of a membrane by dip-coating and then tested in a short (~8 s) EOG experiment where results showed 93% correlation with those of wet electrodes [165]. Finally, a novel conductive polymer foam with a conductivity of about 0.07 Ω/square was fabricated and tested in forehead EOG and displayed ~84% correlation against standard electrodes [147].
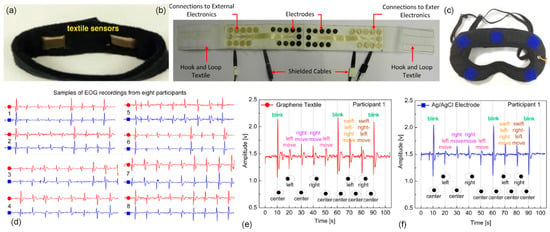
Figure 7.
Wearable elastic garments; (a) headband developed for gesture recognition [119]; (b) headband used for horizontal electrooculography (EOG) acquisition [80]; (c) eye mask developed for sleep monitoring [120]; (d) subset of electrooculography recordings obtained using graphene textile and Ag/AgCl electrodes that displayed the highest correlation of 87% for a 95 s recording in 2 trials on 8 different participants. Zoom-in view of EOG signals showing the unique eye movement patterns acquired from participant 1 using (e) graphene textile electrodes; and (f) Ag/AgCl electrodes [121].
Compared to other biopotentials, EOG signals are less complex to process and easy to detect due to their high amplitude and linearity in certain eye movement ranges [166]. This property could be harnessed to further advance wearable EOG devices based on textile electrodes.
5. Conclusions
Wearable textile electronics and their application to biopotential signal acquisition is an emerging trend in the broader field of wearable or ubiquitous computing, which aims to develop and improve personalized routine health monitoring, rehabilitation devices, brain–computer interfaces (BCIs), human–computer/machine interfaces (HCI/HMIs), prosthetics, and possibly many other applications that exploit biopotential feedback or control. The development of textile electrodes as a valid alternative to standard clinical electrodes is therefore critical due to their potential for seamless integration into daily clothing, the possibility of long-term functionality, breathability, stretchability, and for achieving “truly wearable” soft electronics. Further developments from fundamental materials and system-level integration, including embedding of electronics, to strategies for compensating signal artifacts in dynamic operation and novel algorithms for a target application will determine the success and widespread use of wearable e-textile-based devices in the years to follow.
Author Contributions
G.A. and O.O. contributed equally to this work. All authors contributed to the writing, editing, and revision of the paper. M.K.Y. conceptualized the manuscript, prepared draft, supervised the research, and administered the project.
Funding
This work was supported by Sabanci University.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| Ag/AgCl | Silver/silver chloride |
| BCI | Brain computer interface |
| CNT | Carbon nanotube |
| CVD | Chemical vapor deposition |
| DSP | Digital signal processing |
| ECG | Electrocardiography |
| ECP | Extrinsically conductive polymers |
| EEG | Electroencephalography |
| EMG | Electromyography |
| EOG | Electrooculography |
| e-textile | Electronic textile |
| GO | Graphene oxide |
| HCI | Human–computer interaction |
| HMI | Human–machine interface |
| ICP | Intrinsically conductive polymers |
| ISO | International Organization of Standardization |
| mHealth | Mobile health |
| MWNT | Multi-walled carbon nanotubes |
| PANI | Polyaniline |
| PEDOT | Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) |
| PEDOT:PSS | Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) polystyrene sulfonate |
| PET | Polyethyleneterephthalate |
| PPy | Polypyrrole |
| PU | Polyurethane |
| PVD | Physical vapor deposition |
| R&D | Research and development |
| R2R | Roll-to-roll |
| SWNT | Single-walled carbon nanotubes |
References
- Tao, X. Wearable Electronics and Photonics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Wearable Electronics and Technology Market by Applications. Available online: http://www.marketsandmarkets.com/Market-Reports/wearable-electronics-market-983.html (accessed on 27 April 2019).
- Lee, S.; Lee, Y.; Park, J.; Choi, D. Stitchable organic photovoltaic cells with textile electrodes. Nano Energy 2014, 9, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Hussain, M.; Nur, O.; Willander, M. Fabrication of zinc oxide nanoneedles on conductive textile for harvesting piezoelectric potential. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2014, 612, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvado, R.; Loss, C.; Gonçalves, R.; Pinho, P. Textile Materials for the Design of Wearable Antennas: A Survey. Sensors 2012, 12, 15841–15857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, E.; Kaynak, A.; Li, Y. Development of a cooling fabric from conducting polymer coated fibres: Proof of concept. Synth. Met. 2005, 150, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostmann, A.; Vieroth, R.; Seckel, M.; Löher, T.; Reichl, H. Stretchable circuit board technology in textile applications. In Proceedings of the 2009 4th International Microsystems, Packaging, Assembly and Circuits Technology Conference, Taipei, Taiwan, 21–23 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Morris, D.; Coyle, S.; Wu, Y.; Lau, K.; Wallace, G.; Diamond, D. Bio-sensing textile based patch with integrated optical detection system for sweat monitoring. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2009, 139, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanatà, A.; Valenza, G.; Scilingo, E. A novel EDA glove based on textile-integrated electrodes for affective computing. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2012, 50, 1163–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Cho, G. Thermal Storage/Release, Durability, and Temperature Sensing Properties of Thermostatic Fabrics Treated with Octadecane-Containing Microcapsules. Text. Res. J. 2002, 72, 1093–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, S.D.; Yun, Y.; Shin, H. Simplified Structural Textile Respiration Sensor Based on Capacitive Pressure Sensing Method. IEEE Sens. J. 2014, 14, 3245–3251. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, J.; Arnrich, B.; Schumm, J.; Troster, G. Design and Modeling of a Textile Pressure Sensor for Sitting Posture Classification. IEEE Sens. J. 2010, 10, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgutsa, S.; Bélanger-Garnier, V.; Ung, B.; Viens, J.; Gosselin, B.; LaRochelle, S.; Messaddeq, Y. Novel Wireless-Communicating Textiles Made from Multi-Material and Minimally-Invasive Fibers. Sensors 2014, 14, 19260–19274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.-D.; Chung, W.-Y. Wireless sensor network based wearable smart shirt for ubiquitous health and activity monitoring. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2009, 140, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.; Moon, J.; Jeong, K.; Cho, G.J. Application of PU-sealing into Cu/Ni electroless plated polyester fabrics for e-textiles. Fibers Polym. 2007, 8, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, J.J.; Brown, J.M. Introduction to Biomedical Equipment Technology; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Huigen, E. Noise Characteristics of Surface Electrodes. Master’s Thesis, Section Medical Physics, University of Amsterdam, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, Y.; Jung, T.; Cauwenberghs, G. Dry-Contact and Noncontact Biopotential Electrodes: Methodological Review. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 3, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golparvar, A.J.; Yapici, M.K. Wearable graphene textile-enabled EOG sensing. In Proceedings of the IEEE SENSORS, Glasgow, UK, 29 October–1 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Stoppa, M.; Chiolerio, A. Wearable Electronics and Smart Textiles: A Critical Review. Sensors 2014, 14, 11957–11992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Jung, S.M.; Lee, C.K.; Jeong, K.S.; Cho, G.; Yoo, S.K. Wearable ECG monitoring system using conductive fabrics and active electrodes. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 15–20 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, H.; Li, J.; He, B.; Sun, J.; Li, L.; Qian, L. Novel Wearable Electrodes Based on Conductive Chitosan Fabrics and Their Application in Smart Garments. Materials 2018, 11, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alzaidi, A.; Zhang, L.; Bajwa, H. Smart textiles based wireless ECG system. In Proceedings of the Systems, Applications and Technology Conference (LISAT), Farmingdale, NY, USA, 4 May 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, G.; Jeong, K.; Paik, M.J.; Kwun, Y.; Sung, M. Performance evaluation of textile-based electrodes and motion sensors for smart clothing. IEEE Sens. J. 2011, 11, 3183–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Ding, X.; Zhang, J.; Duan, Y.; Hu, J.; Yang, X.J. Fabrication of conductive fabric as textile electrode for ECG monitoring. Fibers Polym. 2014, 15, 2260–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yapici, M.K.; Alkhidir, T.; Samad, Y.A.; Liao, K. Graphene-clad textile electrodes for Enabled electrocardiogram monitoring. Sens. Actuator B Chem. 2015, 221, 1469–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamatsu, S.; Lonjaret, T.; Crisp, D.; Badier, J.-M.; Malliaras, G.G.; Ismailova, E. Direct patterning of organic conductors on knitted textiles for long-term electrocardiography. Nature 2015, 5, 15003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pola, T.; Vanhala, J. Textile electrodes in ECG measurement. In Proceedings of the 2007 3rd International Conference on Intelligent Sensors, Sensor Networks and Information, Melbourne, QLD, Australia, 3–6 December 2007; pp. 635–639. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, S.; Cho, J.; Jeong, K.; Cho, G. Exploring possibilities of ECG electrodes for bio-monitoring smartwear with Cu sputtered fabrics. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction, Bijing, China, 22–27 July 2017; pp. 1130–1137. [Google Scholar]
- Trindade, I.G.; Martins, F.; Baptista, P. High electrical conductance poly (3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene) coatings on textile for electrocardiogram monitoring. Synth. Met. 2015, 210, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, X.; Stylios, G. A Hybrid Textile Electrode for Electrocardiogram (ECG) Measurement and Motion Tracking. Materials 2018, 11, 1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mestrovic, M.A.; Helmer, R.J.; Kyratzis, L.; Kumar, D. Preliminary study of dry knitted fabric electrodes for physiological monitoring. In Proceedings of the Intelligent Sensors, Sensor Networks and Information, Melbourne, QLD, Australia, 3–6 December 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, P.; Zhang, H.; Tao, X. Textile-structured electrodes for electrocardiogram. Text. Prog. 2008, 40, 183–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Yang, G.; Xu, L.; Seoane, F.; Chen, Q.; Zheng, L. Characterization of dry biopotential electrodes. In Proceedings of the 2013 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, EMBC 2013, Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; pp. 1478–1481. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Li, W.; Tao, X.; Xu, P.; Liu, H. Textile-structured human body surface biopotential signal acquisition electrode. In Proceedings of the 2011 4th International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, Shanghai, China, 15–17 October 2011; pp. 2792–2797. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, R.H.; Wright, R.M. Fancy Yarns: Their Manufacture and Application; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Apiwattanadej, T.; Zhang, L.; Li, H. Electrospun polyurethane microfiber membrane on conductive textile for water-supported textile electrode in continuous ECG monitoring application. In Proceedings of the 2018 Symposium on Design, Test, Integration & Packaging of MEMS and MOEMS (DTIP), Roma, Italy, 22–25 May 2018; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Poggio, C.; Trovati, F.; Ceci, M.; Chiesa, M.; Colombo, M.; Pietrocola, G. Biological and antibacterial properties of a new silver fiber post: In vitro evaluation. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2017, 9, e387–e393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marquez, J.C.; Seoane, F.; Välimäki, E.; Lindecrantz, K. Comparison of dry-textile electrodes for electrical bioimpedance spectroscopy measurements. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2010, 224, 012140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishijima, M.J.M.; Engineering, B. Cardiopulmonary monitoring by textile electrodes without subject-awareness of being monitored. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 1997, 35, 685–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puurtinen, M.M.; Komulainen, S.M.; Kauppinen, P.K.; Malmivuo, J.A.V.; Hyttinen, J.A.K. Measurement of noise and impedance of dry and wet textile electrodes, and textile electrodes with hydrogel. In Proceedings of the 2006 International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, New York, NY, USA, 30 August–3 September 2006; pp. 6012–6015. [Google Scholar]
- Catrysse, M.; Puers, R.; Hertleer, C.; Van Langenhove, L.; Van Egmond, H.; Matthys, D. Towards the integration of textile sensors in a wireless monitoring suit. Sens. Actuator A Phys. 2004, 114, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Nguyen, N.H.; Baheti, V.; Ashraf, M.; Militky, J.; Mansoor, T.; Noman, M.T.; Ahmad, S. Electrical conductivity and physiological comfort of silver coated cotton fabrics. J. Text. Inst. 2018, 109, 620–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grancarić, A.M.; Jerković, I.; Koncar, V.; Cochrane, C.; Kelly, F.M.; Soulat, D.; Legrand, X.J. Conductive polymer for smart textile applications. J. Ind. Text. 2018, 48, 612–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jianming, J.; Wei, P.; Shenglin, Y.; Guang, L. Electrically conductive PANI-DBSA/Co-PAN composite fibers prepared by wet spinning. Synth. Met. 2005, 149, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroughi, J.; Spinks, G.M.; Wallace, G.G.; Whitten, P.G. Production of polypyrrole fibres by wet spinning. Synth. Met. 2008, 158, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuzaki, H.; Harashina, Y.; Yan, H.J. Highly conductive PEDOT/PSS microfibers fabricated by wet-spinning and dip-treatment in ethylene glycol. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 45, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshari, M. Electrospun Nanofibers, 1st ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Duxford, UK, 2017; pp. 467–519. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Z.-M.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. A review on polymer nanofibers by electrospinning and their applications in nanocomposites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 2223–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, N.; Kundu, S.C. Electrospinning: A fascinating fiber fabrication technique. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 325–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Xu, W.; Wang, W.; Fong, H.; Zhu, Z. Scalable and Facile Preparation of Highly Stretchable Electrospun PEDOT: PSS@PU Fibrous Nonwovens toward Wearable Conductive Textile Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 30014–30023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallory, G.O.; Hajdu, J.B. Electroless Plating: Fundamentals and Applications; William Andrew: Norwich, NY, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, J.; Moon, J.; Jeong, K.; Cho, G. An exploration of electrolessly Cu/Ni plated polyester fabrics as E-textiles. In Proceedings of the Ninth IEEE International Symposium on Wearable Computers (ISWC’05), Osaka, Japan, 18–21 October 2005; pp. 206–207. [Google Scholar]
- Hegemann, D.; Amberg, M.; Ritter, A.; Heuberger, M. Recent developments in Ag metallised textiles using plasma sputtering. Adv. Perform. Mater. 2009, 24, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.-H.; Yeom, S.-W.; Oh, I.-K.J. Fabrication and actuation of ionic polymer metal composites patterned by combining electroplating with electroless plating. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2008, 39, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattox, D.M. Handbook of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) Processing; William Andrew: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Pawlak, R.; Korzeniewska, E.; Koneczny, C.; Hałgas, B. Properties of thin metal layers deposited on textile composites by using the PVD method for textronic applications. Autex Res. J. 2017, 17, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacerda Silva, N.; Goncalves, L.M.; Carvalho, H. Deposition of conductive materials on textile and polymeric flexible substrates. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2012, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weder, M.; Hegemann, D.; Amberg, M.; Hess, M.; Boesel, L.; Abächerli, R.; Meyer, V.; Rossi, R. Embroidered Electrode with Silver/Titanium Coating for Long-Term ECG Monitoring. Sensors 2015, 15, 1750–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, M.; Ritter, A.; Reimann, P.; Thommen, V.; Fischer, A.; Hegemann, D. Comparative study of plasma-induced and wet-chemical cleaning of synthetic fibers. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 200, 1045–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, S.; Zeng, W. Conductive nanofibres and nanocoatings for smart textiles. In Multidisciplinary Know-How for Smart-Textiles Developers; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2013; pp. 92–128. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.; Yan, X.J. Dip-coating for fibrous materials: Mechanism, methods and applications. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2017, 81, 378–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ankhili, A.; Tao, X.; Cochrane, C.; Coulon, D.; Koncar, V. Washable and Reliable Textile Electrodes Embedded into Underwear Fabric for Electrocardiography (ECG) Monitoring. Materials 2018, 11, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Cao, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhan, Z.; Li, X.; Li, W.J. Single-Wall Carbon Nanotube-Coated Cotton Yarn for Electrocardiography Transmission. Micromachines 2018, 9, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sen, A. Coated Textiles; CRC Press c/o Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Breijo, E.; Prats-Boluda, G.; Lidon-Roger, J.V.; Ye-Lin, Y.; Garcia-Casado, J. A comparative analysis of printing techniques by using an active concentric ring electrode for bioelectrical recording. Microelectron. Int. 2015, 32, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoselov, K.S.; Fal, V.; Colombo, L.; Gellert, P.; Schwab, M.; Kim, K. A roadmap for graphene. Nature 2012, 490, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina, J. Graphene-based fabrics and their applications: A review. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 68261–68291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acar, G.; Ozturk, O.; Yapici, M.K. Wearable Graphene Nanotextile Embedded Smart Armband for Cardiac Monitoring. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE SENSORS, New Delhi, India, 28–31 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.-Z.; Sun, J.-X.; Li, L.-F.; Ding, Y.-S.; Xu, H.-A. Performance evaluation of a novel cloth electrode. In Proceedings of the Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering (iCBBE), Chengdu, China, 18–20 June 2010; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Lam, C.L.; Rajdi, N.N.Z.M.; Wicaksono, D.H. MWCNT/Cotton-based flexible electrode for electrocardiography. In Proceedings of the IEEE SENSORS, Baltimore, MD, USA, 3–6 November 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madani, S.Y.; Mandel, A.; Seifalian, A.M. A concise review of carbon nanotube’s toxicology. Nano Rev. 2013, 4, 21521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelin, M.; Fusco, L.; León, V.; Martín, C.; Criado, A.; Sosa, S.; Vázquez, E.; Tubaro, A.; Prato, M. Differential cytotoxic effects of graphene and graphene oxide on skin keratinocytes. Nature 2017, 7, 40572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yapici, M.K.; Alkhidir, T.E. Intelligent medical garments with graphene-functionalized smart-cloth ECG sensors. Sensors 2017, 17, 875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ujiie, H. Digital Printing of Textiles; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Hart, J.P.; Wring, S.A. Screen-printed voltammetric and amperometric electrochemical sensors for decentralized testing. Electroanalysis 1994, 6, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Otley, M.T.; Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Sinha, S.K.; Treich, G.M.; Sotzing, G.A. PEDOT: PSS “wires” printed on textile for wearable electronics. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 26998–27005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Li, D.; Ala, O.; Manandhar, P.; Fan, Q.; Kasilingam, D.; Calvert, P.D.J.A.F.M. Textile-Based Flexible Electroluminescent Devices. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaguzel, B.; Merritt, C.; Kang, T.; Wilson, J.; Nagle, H.; Grant, E.; Pourdeyhimi, B. Utility of nonwovens in the production of integrated electrical circuits via printing conductive inks. J. Text. I 2008, 99, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, G.; Torah, R.; Beeby, S.; Tudor, J. The development of screen printed conductive networks on textiles for biopotential monitoring applications. Sens. Actuator A Phys. 2014, 206, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamyshny, A.; Steinke, J.; Magdassi, S. Metal-based inkjet inks for printed electronics. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 4, 19–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-P.; Chiu, H.-L.; Wang, P.-H.; Liao, Y.-C. Inkjet printed conductive tracks for printed electronics. ECS J. Solid State Sci. Technol. 2015, 4, P3026–P3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bihar, E.; Roberts, T.; Ismailova, E.; Saadaoui, M.; Isik, M.; Sanchez-Sanchez, A.; Mecerreyes, D.; Hervé, T.; De Graaf, J.B.; Malliaras, G.G. Fully printed electrodes on stretchable textiles for long-term electrophysiology. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2017, 2, 160025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrzetuska, E.; Puchalski, M.; Krucińska, I. Chemically driven printed textile sensors based on graphene and carbon nanotubes. Sensors 2014, 14, 16816–16828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, N.; Afroj, S.; Malandraki, A.; Butterworth, S.; Beach, C.; Rigout, M.; Novoselov, K.S.; Casson, A.J.; Yeates, S.G. All inkjet-printed graphene-based conductive patterns for wearable e-textile applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2017, 5, 11640–11648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, L.; Hoxie, S.; Andrew, T.L. Towards seamlessly-integrated textile electronics: Methods to coat fabrics and fibers with conducting polymers for electronic applications. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 7182–7193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Kim, H.; Byun, S.; Jeong, S.; Hong, Y.; Joo, J.; Song, K.; Kim, J.; Lee, C.; Lee, J. PET fabric/polypyrrole composite with high electrical conductivity for EMI shielding. Synth. Met. 2002, 126, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taji, B.; Shirmohammadi, S.; Groza, V.; Batkin, I. Impact of Skin–Electrode Interface on Electrocardiogram Measurements Using Conductive Textile Electrodes. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2014, 63, 1412–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, J.G. Medical Instrumentation Application and Design; John Wiley & Sons: Temple Terrace, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Beckmann, L.; Neuhaus, C.; Medrano, G.; Jungbecker, N.; Walter, M.; Gries, T.; Leonhardt, S. Characterization of textile electrodes and conductors using standardized measurement setups. Physiol. Meas. 2010, 31, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, A.; Burke, M.; Mastorakis, N. Electrical characterization of dry electrodes for ecg recording. In Proceedings of the 12th WSEAS International Conference, Heraklion, Greece, 22–24 July 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Scilingo, E.; Gemignani, A.; Paradiso, R.; Taccini, N.; Ghelarducci, B.; DeRossi, D. Performance Evaluation of Sensing Fabrics for Monitoring Physiological and Biomechanical Variables. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2005, 9, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Pirbhulal, S.; Sangaiah, A.K.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C.; Li, G. Optimization of signal quality over comfortability of textile electrodes for ECG monitoring in fog computing based medical applications. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2018, 86, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simakov, A.; Webster, J. Motion artifact from electrodes and cables. Iran. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2010, 9, 139–143. [Google Scholar]
- Priniotakis, G.; Westbroek, P.; Van Langenhove, L.; Hertleer, C. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy as an objective method for characterization of textile electrodes. Trans. Inst. Meas. Control 2007, 29, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, J.G. Reducing motion artifacts and interference in biopotential recording. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1984, 823–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cömert, A.; Hyttinen, J. Investigating the possible effect of electrode support structure on motion artifact in wearable bioelectric signal monitoring. Biomed. Eng. Online 2015, 14, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratz, A.G. Triboelectric noise (Triboelectric noise in mechanically flexed low level signal cables for piezoelectric transducers with high gain amplifiers). ISA Trans. 1969, 9, 154–158. [Google Scholar]
- Meziane, N.; Yang, S.; Shokoueinejad, M.; Webster, J.; Attari, M.; Eren, H. Simultaneous comparison of 1 gel with 4 dry electrode types for electrocardiography. Physiol. Meas. 2015, 36, 513–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taji, B.; Shirmohammadi, S.; Groza, V. Measuring skin-electrode impedance variation of conductive textile electrodes under pressure. In Proceedings of the Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (I2MTC), Montevideo, Uruguay, 12–15 May 2014; pp. 1083–1088. [Google Scholar]
- ISO. 6330: 2012 Textiles—Domestic Washing and Drying Procedures for Textile Testing; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kazani, I.; Hertleer, C.; De Mey, G.; Schwarz, A.; Guxho, G.; Van Langenhove, L. Electrical conductive textiles obtained by screen printing. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2012, 20, 57–63. [Google Scholar]
- Merritt, C.R.; Nagle, H.T.; Grant, E. Fabric-based active electrode design and fabrication for health monitoring clothing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2009, 13, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, J.; Lung, C.-H.; Ocneanu, A.; Thakral, A.; Jones, C.; Adler, A. Internet of things: Remote patient monitoring using web services and cloud computing. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Internet of Things (iThings), and IEEE Green Computing and Communications (GreenCom) and IEEE Cyber Physical and Social Computing (CPSCom), Taipei, Taiwan, 1–3 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Boehm, A.; Yu, X.; Neu, W.; Leonhardt, S.; Teichmann, D. A novel 12-lead ECG T-shirt with active electrodes. mdpi electronics. Electronics 2016, 5, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H.-J.; Yoo, J.; Yan, L. Wireless fabric patch sensors for wearable healthcare. In Proceedings of the 2010 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 31 August–4 September 2010; pp. 5254–5257. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, M.; Catarino, A.; Carvalho, H.; Rocha, A.; Monteiro, J.; Montagna, G. Study of vital sign monitoring with textile sensors in swimming pool environment. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual Conference of IEEE Industrial Electronics, Porto, Portugal, 3–5 November 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouwstra, S.; Chen, W.; Feijs, L.; Oetomo, S.B. Smart jacket design for neonatal monitoring with wearable sensors. In Proceedings of the Sixth International Workshop on Wearable and Implantable Body Sensor Networks, Berkeley, CA, USA, 3–5 June 2009; pp. 162–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coosemans, J.; Hermans, B.; Puers, R.J.S.; Physical, A.A. Integrating wireless ECG monitoring in textiles. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2006, 130, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, T.; Zhang, Y. A wearable mobihealth care system supporting real-time diagnosis and alarm. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2007, 45, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleury, A.; Alizadeh, M.; Stefan, G.; Chau, T. Toward fabric-based EEG access technologies: Seamless knit electrodes for a portable brain-computer interface. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Life Sciences Conference (LSC), Sydney, NSW, Australia, 13–15 December 2017; pp. 35–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matiko, J.W.; Wei, Y.; Torah, R.; Grabham, N.; Paul, G.; Beeby, S.; Tudor, J. Wearable EEG headband using printed electrodes and powered by energy harvesting for emotion monitoring in ambient assisted living. Smart Mater. Struct. 2015, 24, 125028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La, T.G.; Qiu, S.; Scott, D.K.; Bakhtiari, R.; Kuziek, J.W.; Mathewson, K.E.; Rieger, J.; Chung, H.J. Two-Layered and Stretchable e-Textile Patches for Wearable Healthcare Electronics. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 1801033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, M.-O.; Kang, T.; Park, J.; Choi, Y. Knit Band Sensor for Myoelectric Control of Surface EMG-based Prosthetic Hand. IEEE Sens. J. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pino, E.J.; Arias, Y.; Aqueveque, P. Wearable EMG Shirt for Upper Limb Training. In Proceedings of the 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 18–21 July 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, D.; Lorrain, T.; Negro, F.; Jiang, N. High-density EMG E-Textile systems for the control of active prostheses. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology, Buenos Aires, Argentina, 31 August–4 September 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Yu, S.; Li, Y.; Huang, T.-H.; Wang, J.; Lynn, B.; Fidock, J.; Shen, C.-L.; Edwards, D.; Su, H. A soft robotic exo-sheath using fabric EMG sensing for hand rehabilitation and assistance. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Soft Robotics (RoboSoft), Livorno, Italy, 24–28 April 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Bernhart, S.; Amft, O. Diet eyeglasses: Recognising food chewing using EMG and smart eyeglasses. In Proceedings of the IEEE 13th International Conference on Wearable and Implantable Body Sensor Networks (BSN), San Francisco, CA, USA, 14–17 June 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, A.; Schmandt, J.; Shyamkumar, P.; Wilkins, W.; Lachut, D.; Banerjee, N.; Rollins, S.; Parkerson, J.; Varadan, V. Wearable multi-sensor gesture recognition for paralysis patients. In Proceedings of the IEEE SENSORS, Baltimore, MD, USA, 3–6 November 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, S.-F.; Kuo, C.-E.; Lee, Y.-C.; Lin, W.-C.; Liu, Y.-C.; Chen, P.-Y.; Cherng, F.-Y.; Shaw, F.-Z. Development of an EOG-based automatic sleep-monitoring eye mask. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2015, 64, 2977–2985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golparvar, A.J.; Yapici, M.K. Electrooculography by Wearable Graphene Textiles. IEEE Sens. J. 2018, 18, 8971–8978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardiovascular Diseases (CVDs). Available online: https://www.who.int/cardiovascular_diseases/en/ (accessed on 25 November 2018).
- Yang, G.-Z.; Yang, G. Body Sensor Networks; Springer: London, UK, 2006; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Sornmo, P.; Laguna, L. The Electrocardiogram-a Brief Background. In Bioelectrical Signal Processing in Cardiac and Neurological Applications; Elsevier Academic Press: Burlington, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, D.T.H.; Palaniswami, M.; Begg, R. Healthcare Sensor Networks: Challenges toward Practical Implementation; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- López, G.; Custodio, V.; Moreno, J. LOBIN: E-textile and wireless-sensor-network-based platform for healthcare monitoring in future hospital environments. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2010, 14, 1446–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darling, C.E.; Dovancescu, S.; Saczynski, J.S.; Riistama, J.; Kuniyoshi, F.S.; Rock, J.; Meyer, T.E.; McManus, D.D. Bioimpedance-Based Heart Failure Deterioration Prediction Using a Prototype Fluid Accumulation Vest-Mobile Phone Dyad: An Observational Study. JMIR Cardio 2017, 1, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttussi, F.; Chittaro, L. MOPET: A context-aware and user-adaptive wearable system for fitness training. Artif. Intell. Med. 2008, 42, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coyle, S.; Lau, K.-T.; Moyna, N.; O’Gorman, D.; Diamond, D.; Di Francesco, F.; Costanzo, D.; Salvo, P.; Trivella, M.G.; De Rossi, D.E. BIOTEX—Biosensing textiles for personalized healthcare management. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. 2010, 14, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandian, P.; Mohanavelu, K.; Safeer, K.; Kotresh, T.; Shakunthala, D.; Gopal, P.; Padaki, V. Smart Vest: Wearable multi-parameter remote physiological monitoring system. Med. Eng. Phys. 2008, 30, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Rienzo, M.; Vaini, E.; Lombardi, P.J.S.; Physical, A.A. Development of a smart garment for the assessment of cardiac mechanical performance and other vital signs during sleep in microgravity. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2018, 274, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linti, C.; Horter, H.; Osterreicher, P.; Planck, H. Sensory baby vest for the monitoring of infants. In Proceedings of the Wearable and Implantable Body Sensor Networks. International Workshop on Wearable and Implantable Body Sensor Networks (BSN’06), Cambridge, MA, USA, 3–5 April 2006; pp. 3–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottenbacher, J.; Romer, S.; Kunze, C.; Großmann, U.; Stork, W. Integration of a bluetooth based ECG system into clothing. In Proceedings of the Eighth International Symposium on Wearable Computers, Arlington, VA, USA, 31 October–3 November 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linz, T.; Kallmayer, C.; Aschenbrenner, R.; Reichl, H. Fully untegrated EKG shirt based on embroidered electrical interconnections with conductive yarn and miniaturized flexible electronics. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Wearable and Implantable Body Sensor Networks (BSN’06), Cambridge, MA, USA, 3–5 April 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teplan, M. Fundamentals of EEG measurement. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2002, 2, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Kirschstein, T.; Köhling, R. What is the Source of the EEG? Sage Open 2009, 40, 146–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guger, C.; Edlinger, G.; Harkam, W.; Niedermayer, I.; Pfurtscheller, G. How many people are able to operate an EEG-based brain-computer interface (BCI)? IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 2003, 11, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casson, A.J.; Smith, S.; Duncan, J.S.; Rodriguez-Villegas, E. Wearable EEG: What is it, why is it needed and what does it entail? In Proceedings of the 2008 30th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–25 August 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhlmann, L.; Lehnertz, K.; Richardson, M.P.; Schelter, B.; Zaveri, H.P. Seizure prediction ready for a new era. Nat. Rev. Neurol 2018, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guy, V.; Soriani, M.-H.; Bruno, M.; Papadopoulo, T.; Desnuelle, C.; Clerc, M. Brain computer interface with the P300 speller: Usability for disabled people with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2018, 61, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, M.K.; Stahlhut, C.; Stopczynski, A.; Larsen, J.E.; Hansen, L.K. Smartphones get emotional: Mind reading images and reconstructing the neural sources. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Affective Computing and Intelligent Interaction, Memphis, TN, USA, 9–12 October 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesárošová, A.; Hernández, M.F.; Mesároš, P.; Behún, M. Mixing augmented reality and EEG technology to create an unique learning tool for construction process. In Proceedings of the 2017 15th International Conference on Emerging eLearning Technologies and Applications (ICETA), Stary Smokovec, Slovakia, 26–27 October 2017; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simic, M.; Tariq, M.; Trivailo, P.M. EEG-Based BCI Control Schemes for Lower-Limb Assistive-Robots. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.-L.; Kuo, P.-C.; Cheng, C.-Y.; Chen, Y. Challenges and Future Perspectives on Electroencephalogram-Based Biometrics in Person Recognition. Front. Neuroinform. 2018, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnin, J.; Anopas, D.; Horapong, M.; Triponyuwasi, P.; Yamsa-ard, T.; Iampetch, S.; Wongsawat, Y. Wireless-based portable EEG-EOG monitoring for real time drowsiness detection. In Proceedings of the 2013 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013; pp. 4977–4980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löfhede, J.; Seoane, F.; Thordstein, M.J.S. Textile electrodes for EEG recording—A pilot study. Sensors 2012, 12, 16907–16919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-T.; Liao, L.-D.; Liu, Y.-H.; Wang, I.-J.; Lin, B.-S.; Chang, J.-Y. Novel dry polymer foam electrodes for long-term EEG measurement. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 2011, 58, 1200–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, M.C.; Vieira, T.M.M. Surface electromyography: Why, when and how to use it. Rev. Andal. Med. Deport. 2011, 4, 17–28. [Google Scholar]
- Mathiassen, S.; Winkel, J.; Hägg, G. Normalization of surface EMG amplitude from the upper trapezius muscle in ergonomic studies—A review. J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol. 1995, 5, 197–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellini, C.; Smagt, P.V.D. Surface EMG in advanced hand prosthetics. Biol. Cybern. 2008, 100, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turker, H.; Soze, H. Surface Electromyography in Sports and Exercise. In Electrodiagnosis in New Frontiers of Clinical Research; InTech: London, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mulla, M.R.; Sepulveda, F.; Colley, M. A Review of Non-Invasive Techniques to Detect and Predict Localised Muscle Fatigue. Sensors 2011, 11, 3545–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafti, A.; Manero, R.B.R.; Borg, A.M.; Althoefer, K.; Howard, M.J. Embroidered Electromyography: A Systematic Design Guide. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 2017, 25, 1472–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, S.; Tomita, Y.; Horiuchi, T. Clinical application of an active electrode using an operational amplifier. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag. 1992, 39, 1096–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cömert, A.; Honkala, M.; Hyttinen, J. Effect of pressure and padding on motion artifact of textile electrodes. Biomed. Eng. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, B.; Mancuso, C.; Paradiso, R. Performances evaluation of textile electrodes for EMG remote measurements. In Proceedings of the 35th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Osaka, Japan, 3–7 July 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niijima, A.; Isezaki, T.; Aoki, R.; Watanabe, T.; Yamada, T. hitoeCap: Wearable EMG sensor for monitoring masticatory muscles with PEDOT-PSS textile electrodes. In Proceedings of the 2017 ACM International Symposium on Wearable Computers—ISWC 17, Maui, Hawaii, 11–15 September 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Geng, Y.; Tao, D.; Zhou, P. Performance of electromyography recorded using textile electrodes in classifying arm movements. In Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Boston, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikkanen, O.; Kärkkäinen, S.; Haakana, P.; Kallinen, M.; Pullinen, T.; Finni, T. EMG, Heart Rate, and Accelerometer as Estimators of Energy Expenditure in Locomotion. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2014, 46, 1831–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikkanen, O.; Hu, M.; Vilavuo, T.; Tolvanen, P.; Cheng, S.; Finni, T. Ventilatory threshold during incremental running can be estimated using EMG shorts. Physiol. Meas. 2012, 33, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino, M.; Gómez, I.M.; Molina, A. Envelope filter sequence to delete blinks and overshoots. BioMed. Eng. OnLine. 2015, 14, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Golparvar, A.J.; Yapici, M.K. Graphene-coated wearable textiles for EOG-based human-computer interaction. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 15th International Conference on Wearable and Implantable Body Sensor Networks (BSN), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 4–7 March 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Bulling, A.; Roggen, D.; Tröster, G. It’s in your eyes: Towards context-awareness and mobile HCI using wearable EOG goggles. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Ubiquitous Computing, Seoul, Korea, 21–24 September 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, J.; Yoon, H.; Park, K.S.J.S. A novel wearable forehead eog measurement system for human computer interfaces. Sensors 2017, 17, 1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Pei, W.; Wang, Y.; Gong, Q.; Zhang, H.; Xing, X.; Xie, Y.; Gui, Q.; Chen, H. A Self-Wetting Paper Electrode for Ubiquitous Bio-Potential Monitoring. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 2654–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameri, S.K.; Kim, M.; Kuang, I.A.; Perera, W.K.; Alshiekh, M.; Jeong, H.; Topcu, U.; Akinwande, D.; Lu, N. Imperceptible electrooculography graphene sensor system for human–robot interface. Nature 2018, 2, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).