Chaotic Pattern Array for Single-Pixel Imaging
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Simple Modeling of the SPI Architecture
- Modulation: how to design or select the predefined SLM patterns ?
- Reconstruction: With known and , how is the image of the scene reconstructed?
2.2. Basics of CS Theory
3. Single-Pixel Imaging with the Chaotic Pattern Array
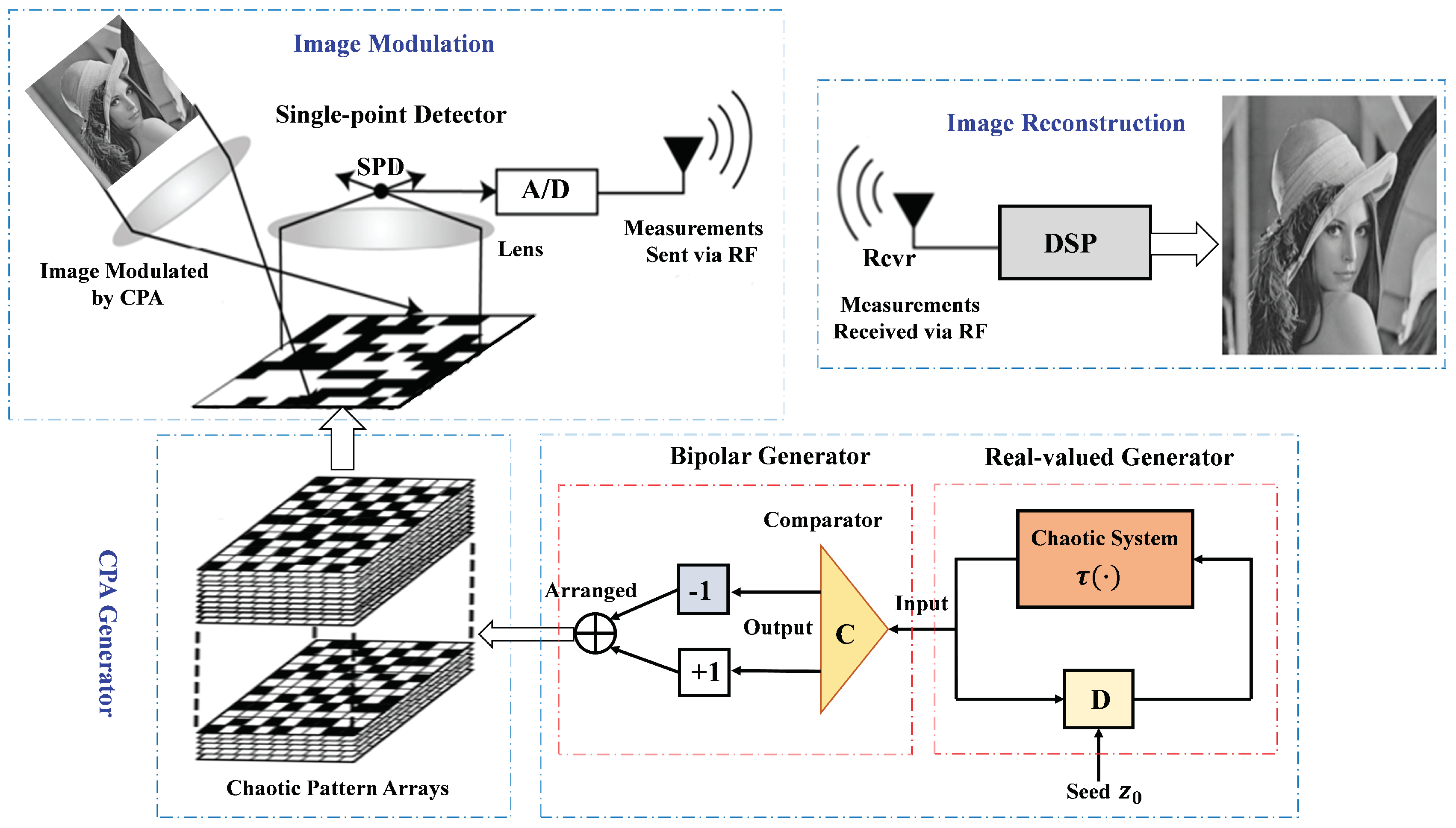
3.1. Overall Framework
3.2. Construction of the Chaotic Pattern Array
3.2.1. Reviews for the Chaotic Bipolar Sequence
3.2.2. Construction and Performance Analysis
3.3. Mechanism of the Chaotic Pattern Array
4. Numerical Experiments
4.1. CPA with Different Recovery Algorithms
4.2. CPA vs. Different Modulation Patterns
4.3. Encryption Property of CPA
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. Lemma 3
Appendix B. Proof of Lemma 2
References
- Candès, E.J.; Romberg, J.; Tao, T. Robust uncertainty principles: Exact signal reconstruction from highly incomplete frequency information. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2006, 52, 489–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Tian, Y.; Kurths, J.; Li, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, D. Secure and energy-efficient data transmission system based on chaotic compressive sensing in body-to-body networks. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Circuits Syst. 2017, 11, 558–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Deng, W.; Yang, Q.; Migliore, M. A hybrid non-convex compressed sensing approach for array diagnosis using sparse promoting norm with perturbation technique. Electronics 2018, 7, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.T.; Kong, X.J.; Xia, F. Joint range-doppler-angle estimation for intelligent tracking of moving aerial targets. IEEE Internet Things J. 2018, 5, 1625–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, H.; Xiao, S.; Zhao, Y. A large class of chaotic sensing matrices for compressed sensing. Signal Process. 2018, 149, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Cao, Z.; Chen, Z.; Liu, L.; Feng, M. Compressed sensing-based DOA estimation with unknown mutual coupling effect. Electronics 2018, 7, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, X.; Chen, P. Compressed sensing-based DOA estimation with antenna phase errors. Electronics 2019, 8, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, M.F.; Davenport, M.A.; Takhar, D.; Laska, J.N.; Sun, T.; Kelly, K.F.; Baraniuk, R.G. Single-pixel imaging via compressive sampling. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2008, 25, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rousset, F. Single-Pixel Imaging: Development and Applications of Adaptive Methods. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Lyon, Politecnico di Milano, Lyon, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hadfield, R.H. Single-photon detectors for optical quantum information applications. Nat. Photonics 2009, 3, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, W. Fluorescence lifetime imaging-techniques and applications. J. Microsc. 2012, 247, 119–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.; Bosworth, B.T.; Foster, M.A. Single-pixel imaging using compressed sensing and wavelength-dependent scattering. Opt. Lett. 2016, 41, 886–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador-Balaguer, E.; Clemente, P.; Tajahuerce, E.; Pla, F.; Lancis, J. Full-color stereoscopic imaging with a single-pixel photodetector. J. Disp. Technol. 2016, 12, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, C.M.; Shrekenhamer, D.; Montoya, J.; Lipworth, G.; Hunt, J.; Sleasman, T.; Krishna, S.; Smith, D.R.; Padilla, W.J. Terahertz compressive imaging with metamaterial spatial light modulators. Nat. Photonics 2014, 8, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, G.M.; Sun, B.; Edgar, M.P.; Phillips, D.B.; Hempler, N.; Maker, G.T.; Malcolm, G.P.; Padgett, M.J. Real-time imaging of methane gas leaks using a single-pixel camera. Opt. Express 2017, 25, 2998–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starling, D.J.; Storer, I.; Howland, G.A. Compressive sensing spectroscopy with a single pixel camera. Appl. Opt. 2016, 55, 5198–5202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraniuk, R.G.; Goldstein, T.; Sankaranarayanan, A.C.; Studer, C.; Veeraraghavan, A.; Wakin, M.B. Compressive video sensing: Algorithms, architectures, and applications. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2017, 34, 52–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhong, J. Three-dimensional single-pixel imaging with far fewer measurements than effective image pixels. Opt. Lett. 2016, 41, 2497–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radwell, N.; Mitchell, K.J.; Gibson, G.M.; Edgar, M.P.; Bowman, R.; Padgett, M.J. Single-pixel infrared and visible microscope. Optica 2014, 1, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lochocki, B.; Gambín, A.; Manzanera, S.; Irles, E.; Tajahuerce, E.; Lancis, J.; Artal, P. Single pixel camera ophthalmoscope. Optica 2016, 3, 1056–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousset, F.; Ducros, N.; Farina, A.; Valentini, G.; D’Andrea, C.; Peyrin, F. Adaptive basis scan by wavelet prediction for single-pixel imaging. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 2017, 3, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Jiang, H.; Matthews, K.; Wilford, P. Lensless imaging by compressive sensing. In Proceedings of the 2013 20th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), Melbourne, VIC, Australia, 15–18 September 2013; pp. 2101–2105. [Google Scholar]
- Clemente, P.; Durán, V.; Tajahuerce, E.; Andrés, P.; Climent, V.; Lancis, J. Compressive holography with a single-pixel detector. Opt. Lett. 2013, 38, 2524–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rousset, F.; Peyrin, F.; Ducros, N. A semi nonnegative matrix factorization technique for pattern generalization in single-pixel imaging. IEEE Trans. Comput. Imaging 2018, 4, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Zhao, H.; Jia, M.; Wang, G.; Shen, J. An improved Hadamard measurement matrix based on Walsh code for compressive sensing. In Proceedings of the 2013 9th International Conference on Information, Communications Signal Processing, Tainan, Taiwan, 10–13 December 2013; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Pastuszczak, A.; Szczygieł, B.; Mikołajczyk, M.; Kotyński, R. Efficient adaptation of complex-valued noiselet sensing matrices for compressed single-pixel imaging. Appl. Opt. 2016, 55, 5141–5148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.S.; Choi, G.S. Programmable compressed sensing using simple deterministic sensing matrices. In Optoelectronic Imaging and Multimedia Technology V; International Society for Optics and Photonics: San Diego, CA, USA, 2018; Volume 10817, p. 108170C. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, T.; Chen, D.; Wang, J.; Xu, D. Single-pixel color imaging method with a compressive sensing measurement matrix. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donoho, D.L.; Huo, X. Uncertainty principles and ideal atomic decomposition. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2001, 47, 2845–2862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donoho, D.L. Compressed sensing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2006, 52, 1289–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strohmer, T.; Heath, R.W., Jr. Grassmannian frames with applications to coding and communication. Appl. Comput. Harmon. Anal. 2003, 14, 257–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boufounos, P.; Kutyniok, G.; Rauhut, H. Sparse recovery from combined fusion frame measurements. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2011, 57, 3864–3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geršgorin, S. Über die abgrenzung der eigenwerte einer matrix. Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR Ser. Mat. 1931, 1, 749–755. [Google Scholar]
- Duarte, M.F.; Eldar, Y.C. Structured compressed sensing: From theory to applications. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 2011, 59, 4053–4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baraniuk, R.; Davenport, M.; De Vore, R.; Wakin, M. A simple proof of the restricted isometry property for random matrices. Constr. Approx. 2008, 28, 253–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C. An Efficient Algorithm for Total Variation Regularization with Applications to the Single Pixel Camera and Compressive Sensing. Ph.D. Thesis, Rice University, Houston, TX, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Takhar, D.; Laska, J.N.; Wakin, M.B.; Duarte, M.F.; Baron, D.; Sarvotham, S.; Kelly, K.F.; Baraniuk, R.G. A new compressive imaging camera architecture using optical-domain compression. In Computational Imaging IV; International Society for Optics and Photonics: San Diego, CA, USA, 2006; Volume 6065, p. 606509. [Google Scholar]
- Kohda, T.; Tsuneda, A. Statistics of chaotic binary sequences. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 1997, 43, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohda, T. Stream cipher systems using a chaotic sequence of i.i.d. random variables. Regul. Pept. 2001, 1240, 74–87. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, H.; Xiao, S.; Zhao, Y.; Xue, X. Construction of efficient and structural chaotic sensing matrix for compressive sensing. Signal Process. Image Commun. 2018, 68, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, H.; Xiao, S.; Zhang, T.; Liu, F. Bipolar measurement matrix using chaotic sequence. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2019, 72, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achlioptas, D. Database-friendly random projections. In Proceedings of the ACM Twentieth ACM Sigmod-Sigact-Sigart Symposium on Principles of Database Systems, Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 21–24 May 2001; pp. 274–281. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Li, C.; Wong, K.; Shu, S.; Chen, G. Cryptanalyzing a chaos-based image encryption algorithm using alternate structure. J. Syst. Softw. 2012, 85, 2077–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wong, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J. Bi-level protected compressive sampling. IEEE Trans. Multimed. 2016, 18, 1720–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, D.; Peng, H.; Li, L.; Yang, Y. An efficient privacy-preserving scheme for secure network coding based on compressed sensing. AEU-Int. J. Electron. Commun. 2017, 79, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xiang, Y.; Zhang, L. Concluding remarks and future research. In Secure Compressive Sensing in Multimedia Data, Cloud Computing and IoT; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 113–115. [Google Scholar]
- Mohimani, G.H.; Babaie-Zadeh, M.; Jutten, C. Fast sparse representation based on smoothed l0 norm. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Independent Component Analysis and Signal Separation, London, UK, 9–12 September 2007; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007; pp. 389–396. [Google Scholar]
- Tropp, J.A.; Gilbert, A.C. Signal recovery from random measurements via orthogonal matching pursuit. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2007, 53, 4655–4666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Milenkovic, O. Subspace pursuit for compressive sensing signal reconstruction. IEEE Trans. Inf. Theory 2009, 55, 2230–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, M.A.; Nowak, R.D.; Wright, S.J. Gradient projection for sparse reconstruction: Application to compressed sensing and other inverse problems. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Signal Process. 2007, 1, 586–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Approach | Sampling Patterns | Image Reconstruction | Required Measurements |
|---|---|---|---|
| Compressive sampling | Sensing matrix | / norm minimization | Few |
| Basis scan | Basis | Inverse transform | Large |
| Adaptive basis scan | Basis | Inverse transform | Few |
| Sampling Rate ♮ | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | |
| MSE | 0.923 | 0.689 | 0.215 | 0.054 | 0.038 | 0.027 | 0.020 | 0.014 |
| PSNR (dB) | 4.852 | 6.762 | 17.89 | 27.99 | 31.32 | 34.20 | 36.92 | 39.82 |
| RecTime (s) | 0.077 | 0.196 | 0.215 | 0.276 | 0.287 | 0.323 | 0.350 | 0.412 |
| Modulation Pattern | Sampling Rate | Index | Image | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| “House” | “Camera” | “Baboon” | “Mena” | “Starfish” | “Straw” | |||
| CPA | 0.2 | MSE | 0.689 | 0.643 | 0.714 | 0.514 | 0.554 | 0.731 |
| PSNR (dB) | 6.762 | 8.261 | 7.272 | 10.51 | 9.354 | 5.083 | ||
| RecTime (s) | 0.196 | 0.278 | 0.190 | 0.207 | 0.228 | 0.237 | ||
| 0.4 | MSE | 0.054 | 0.083 | 0.104 | 0.066 | 0.110 | 0.126 | |
| PSNR (dB) | 27.99 | 24.78 | 23.29 | 27.79 | 22.98 | 19.89 | ||
| RecTime (s) | 0.251 | 0.329 | 0.287 | 0.354 | 0.282 | 0.362 | ||
| 0.6 | MSE | 0.027 | 0.049 | 0.075 | 0.039 | 0.063 | 0.087 | |
| PSNR (dB) | 34.20 | 29.41 | 26.01 | 32.40 | 27.81 | 23.08 | ||
| RecTime (s) | 0.323 | 0.417 | 0.378 | 0.384 | 0.391 | 0.415 | ||
| 0.8 | MSE | 0.014 | 0.024 | 0.047 | 0.019 | 0.030 | 0.051 | |
| PSNR (dB) | 39.82 | 35.77 | 29.94 | 38.29 | 34.00 | 27.64 | ||
| RecTime (s) | 0.412 | 0.465 | 0.407 | 0.540 | 0.431 | 0.526 | ||
| RGP | 0.2 | MSE | 0.769 | 0.611 | 0.532 | 0.689 | 0.643 | 0.808 |
| PSNR (dB) | 6.101 | 8.729 | 9.462 | 7.519 | 8.282 | 4.162 | ||
| RecTime (s) | 0.214 | 0.252 | 0.224 | 0.213 | 0.225 | 0.257 | ||
| 0.4 | MSE | 0.078 | 0.107 | 0.106 | 0.067 | 0.114 | 0.128 | |
| PSNR (dB) | 25.49 | 23.03 | 23.10 | 27.56 | 22.71 | 19.79 | ||
| RecTime (s) | 0.286 | 0.342 | 0.311 | 0.296 | 0.326 | 0.373 | ||
| 0.6 | MSE | 0.028 | 0.049 | 0.075 | 0.038 | 0.064 | 0.091 | |
| PSNR (dB) | 34.09 | 29.13 | 26.01 | 32.54 | 27.58 | 22.85 | ||
| RecTime (s) | 0.360 | 0.397 | 0.381 | 0.362 | 0.396 | 0.446 | ||
| 0.8 | MSE | 0.014 | 0.023 | 0.046 | 0.019 | 0.031 | 0.052 | |
| PSNR (dB) | 39.63 | 35.85 | 30.14 | 38.12 | 33.93 | 27.16 | ||
| RecTime (s) | 0.432 | 0.469 | 0.403 | 0.396 | 0.461 | 0.513 | ||
| RBP | 0.2 | MSE | 0.759 | 0.476 | 0.795 | 0.739 | 0.705 | 0.761 |
| PSNR (dB) | 5.771 | 10.63 | 6.302 | 7.304 | 7.292 | 4.995 | ||
| RecTime (s) | 0.285 | 0.252 | 0.235 | 0.247 | 0.248 | 0.278 | ||
| 0.4 | MSE | 0.057 | 0.084 | 0.107 | 0.063 | 0.112 | 0.128 | |
| PSNR (dB) | 27.45 | 24.64 | 23.07 | 27.99 | 22.80 | 19.78 | ||
| RecTime (s) | 0.304 | 0.334 | 0.302 | 0.284 | 0.320 | 0.364 | ||
| 0.6 | MSE | 0.027 | 0.047 | 0.075 | 0.039 | 0.064 | 0.089 | |
| PSNR (dB) | 34.26 | 29.80 | 26.07 | 32.33 | 27.65 | 22.86 | ||
| RecTime (s) | 0.346 | 0.413 | 0.371 | 0.356 | 0.373 | 0.449 | ||
| 0.8 | MSE | 0.013 | 0.023 | 0.047 | 0.019 | 0.030 | 0.050 | |
| PSNR (dB) | 40.09 | 35.97 | 29.85 | 38.23 | 34.03 | 27.84 | ||
| RecTime (s) | 0.416 | 0.490 | 0.430 | 0.439 | 0.483 | 0.505 | ||
| HMP | 0.2 | MSE | 0.484 | 0.434 | 0.878 | 1.120 | 0.849 | 0.558 |
| PSNR (dB) | 8.964 | 10.90 | 4.953 | 3.090 | 5.230 | 7.046 | ||
| RecTime (s) | 0.264 | 0.320 | 0.357 | 0.374 | 0.341 | 0.402 | ||
| 0.4 | MSE | 0.054 | 0.084 | 0.105 | 0.066 | 0.109 | 0.126 | |
| PSNR (dB) | 28.00 | 24.29 | 23.15 | 27.50 | 22.90 | 19.86 | ||
| RecTime (s) | 0.363 | 0.405 | 0.457 | 0.360 | 0.356 | 0.424 | ||
| 0.6 | MSE | 0.027 | 0.047 | 0.075 | 0.039 | 0.064 | 0.088 | |
| PSNR (dB) | 34.25 | 29.80 | 25.97 | 32.45 | 27.38 | 22.99 | ||
| RecTime (s) | 0.453 | 0.413 | 0.462 | 0.419 | 0.462 | 0.542 | ||
| 0.8 | MSE | 0.014 | 0.023 | 0.047 | 0.019 | 0.031 | 0.050 | |
| PSNR (dB) | 38.80 | 35.60 | 29.77 | 38.17 | 33.77 | 27.58 | ||
| RecTime (s) | 0.585 | 0.524 | 0.623 | 0.439 | 0.534 | 0.559 | ||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gan, H.; Xiao, S.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Li, J.; Gao, Y. Chaotic Pattern Array for Single-Pixel Imaging. Electronics 2019, 8, 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8050536
Gan H, Xiao S, Zhang T, Zhang Z, Li J, Gao Y. Chaotic Pattern Array for Single-Pixel Imaging. Electronics. 2019; 8(5):536. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8050536
Chicago/Turabian StyleGan, Hongping, Song Xiao, Tao Zhang, Zhimin Zhang, Jie Li, and Yang Gao. 2019. "Chaotic Pattern Array for Single-Pixel Imaging" Electronics 8, no. 5: 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8050536
APA StyleGan, H., Xiao, S., Zhang, T., Zhang, Z., Li, J., & Gao, Y. (2019). Chaotic Pattern Array for Single-Pixel Imaging. Electronics, 8(5), 536. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8050536







