Parkinson’s Disease Detection from Drawing Movements Using Convolutional Neural Networks
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset
2.2. Signal Preprocessing
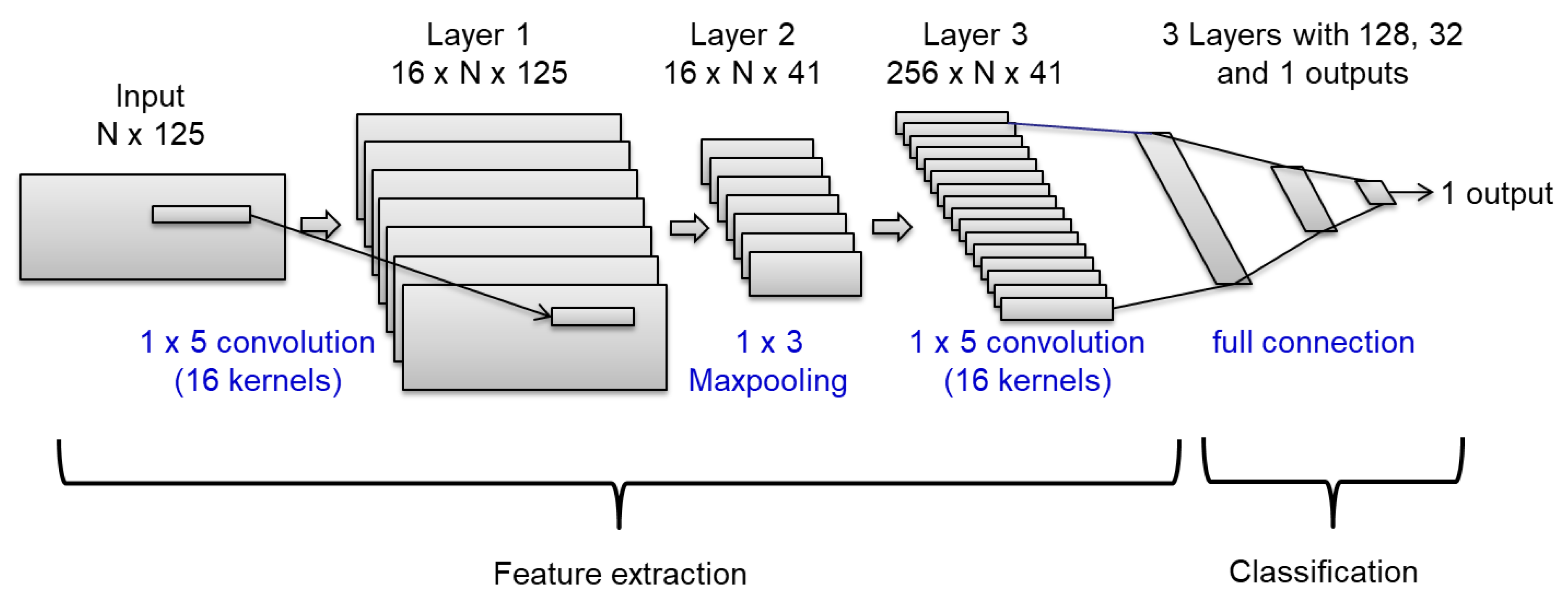
2.3. Convolutional Neural Networks
2.4. Subject-Wise Cross-Validation
3. Experiments and Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O’Neil King, R. Biometrics in Healthcare; Biometrics Research Group, Inc.: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2017; Available online: https://www.biometricupdate.com/wp-content/uploads/2017/04/special-report-global-biometric-healthcare.pdf (accessed on 11 August 2019).
- Jankovic, J. Parkinson’s disease: Clinical features and diagnosis. J Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2008, 79, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contreras-Vidal, J.L.; Stelmach, G.E. Effects of parkinsonism on motor control. Life Sci. 1995, 58, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tysnes, O.B.; Storstein, A. Epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease. J. Neural Transm. 2017, 124, 901–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, G.; Copetti, M.; Arcuti, S.; Martino, D.; Fontana, A.; Logroscino, G. Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of Parkinson disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurology 2016, 86, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammenwerth, E.; Nykanen, P.; Rigby, M.; de Keizer, N. Clinical decision support systems: Need for evidence, need for evaluation. Artif. Intell. Med. 2013, 59, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dreiseitl, S.; Binder, M. Do physicians value decision support? A look at the effect of decision support systems on physician opinion. Artif. Intell. Med. 2005, 33, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattison, H.A.; Stewart, T.; Zhang, J. Applying bioinformatics to proteomics: Is machine learning the answer to biomarker discovery for PD and MSA? Mov. Disord. 2012, 27, 1595–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahmiri, S.; Shmuel, A. Detection of Parkinson’s disease based on voice patterns ranking and optimized support vector machine. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2018, 49, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-García, J.A.; Moro-Velázquez, L.; Godino-Llorente, J.I. On the design of automatic voice condition analysis systems. Part I: Review of concepts and an insight to the state of the art. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2019, 51, 181–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gómez-García, J.A.; Moro-Velázquez, L.; Godino-Llorente, J.I. On the design of automatic voice condition analysis systems. Part II: Review of speaker recognition techniques and study on the effects of different variability factors. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2019, 48, 128–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viteckova, S.; Kutilek, P.; Svoboda, Z.; Krupicka, R.; Kauler, J.; Szabo, Z. Gait symmetry measures: A review of current and prospective methods. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2018, 42, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San-Segundo, R.; Navarro-Hellín, H.; Torres-Sánchez, R.; Hodgins, J.; De la Torre, F. Increasing Robustness in the Detection of Freezing of Gait in Parkinson’s Disease. Electronics 2019, 8, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLennan, J.E.; Nakano, K.; Tyler, H.R.; Schwab, R.S. Micrographia in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol. Sci. 1972, 15, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zham, P.; Arjunan, S.P.; Raghav, S.; Kumar, D.K. Efficacy of Guided Spiral Drawing in the Classification of Parkinson’s Disease. IEEE J. Biomed. Health Inform. 2018, 22, 1648–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potgieser, A.R.; Roosma, E.; Beudel, M.; de Jong, B.M. The effect of visual feedback on writing size in parkinson’s disease. Parkinsons Dis. 2015, 2015, 857041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drotár, P.; Mekyska, J.; Rektorová, I.; Masarová, L.; Smékal, Z.; Faundez-Zanuy, M. Evaluation of handwriting kinematics and pressure for differential diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease. Artif. Intell. Med. 2016, 67, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letanneux, A.; Danna, J.; Velay, J.L.; Viallet, F.; Pinto, S. From micrographia to Parkinson’s disease dysgraphia. Mov. Disord. 2014, 29, 1467–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.; Lenka, A.; Kumar Pal, P. Handwriting Analysis in Parkinson’s Disease: Current Status and Future Directions. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2017, 4, 806–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenblum, S.; Samuel, M.; Zlotnik, S.; Erikh, I.; Schlesinger, I. Handwriting as an objective tool for Parkinson’s disease diagnosis. J. Neurol. 2013, 260, 2357–2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Impedovo, D.; Pirlo, G. Dynamic Handwriting Analysis for the Assessment of Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Pattern Recognition Perspective. IEEE Rev. Biomed. 2019, 12, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Impedovo, D.; Pirlo, G. Chapter 7: Online Handwriting Analysis for the Assessment of Alzheimer’s Disease and Parkinson’s Disease: Overview and Experimental Investigation. In Series on Language Processing, Pattern Recognition, and Intelligent Systems. Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence; World Scientific Publishing: Singapore, 2019; pp. 113–128. [Google Scholar]
- van Drempt, N.; McCluskey, A.; Lannin, N.A. A review of factors that influence adult handwriting performance. Aust. Occup. Ther. J. 2011, 58, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsavasiloglou, C.; Kostikis, N.; Hristu-Varsakelis, D.; Arnaoutoglou, M. Machine learning-based classification of simple drawing movements in Parkinson’s disease. Biomed. Signal Process. Control 2017, 31, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallicchio, C.; Micheli, A.; Pedrelli, L. Deep Echo State Networks for Diagnosis of Parkinson’s Disease. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1802.06708. [Google Scholar]
- Khatamino, P.; Cantürk, İ.; Özyılmaz, L. A Deep Learning-CNN Based System for Medical Diagnosis: An Application on Parkinson’s Disease Handwriting Drawings. In Proceedings of the 2018 6th International Conference Control Engineering Information Technology, Istanbul, Turkey, 25–27 October 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isenkul, M.E.; Sakar, B.E.; Kursun, O. Improved spiral test using digitized graphics tablet for monitoring Parkinson’s disease. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on e-Health and Telemedicine (ICEHTM-2014), Istanbul, Turkey, 22–24 May 2014; pp. 171–175. Available online: https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/Parkinson+Disease+Spiral+Drawings+Using+Digitized+Graphics+Tablet (accessed on 11 August 2019). [CrossRef]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sustskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahne, U.; Schild, J.; Elstner, S.; Alexa, M. Multi-touch focus+ context sketch-based interaction. In Proceedings of the 6th Eurographics Symposium on Sketch-Based Interfaces and Modeling, New Orleans, LA, USA, 1–2 August 2009; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 77–83. [Google Scholar]
- Saunders-Pullman, R.; Derby, C.; Stanley, K.; Floyd, A.; Bressman, S.; Lipton, R.B.; Deligtisch, A.; Severt, L.; Yu, Q.; Kurtis, M.; et al. Validity of spiral analysis in early Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2008, 23, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chui, K.T.; Lytras, M.D. A Novel MOGA-SVM Multinomial Classification for Organ Inflammation Detection. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deuschl, G.; Fietzek, U.; Klebe, S.; Volkmann, J. Chapter 24 clinical neurophysiology and pathophysiology of Parkinsonian tremor. In Handbook of Clinical Neurophysiology; Hallett, M., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; Volume 1, pp. 377–396. [Google Scholar]
- Hanley, J.A.; McNeil, B.J. The meaning and use of the area under a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Radiology 1982, 143, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shargel, L.; Mutnick, A.H.; Souney, P.F.; Swanson, L.N. Comprehensive Pharmacy Review; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Goetz, C.G.; Tilley, B.C.; Shaftman, S.R.; Stebbins, G.T.; Fahn, S.; Martinez Martin, P.; Poewe, W.; Sampaio, C.; Stern, M.B.; Dodel, R.; et al. Movement disorder society-sponsored revision of the unified Parkinson’s disease rating scale (mds-updrs): Scale presentation and clinimetric testing results. Mov. Disord. 2008, 23, 2129–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Reference | Participants | Tasks | Methodology | Performance | Granularity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kotsavasiloglou et al. [24] | 24 PD 20 Control | Line drawing | Naïve Bayes with Handcrafted features | ACC = 88.6% | Line drawing (2 s. aprox.) |
| Zham et al. [15] | 31 PD 31 Control | Archimedean guided spiral | Naïve Bayes with Handcrafted features | AUC = 93.3% | Segments between pen-down and pen-up (2 s. aprox.) |
| Gallicchio et al. [25] | 62 PD 15 Control | Spirals and stability movement | Deep Echo State Networks (DeepESNs) | ACC = 89.3% | Drawing (> 10 s.) |
| Khatamino et al. [26] | 62 PD 15 Control | Spirals and stability movement | Convolution Neural Network from raw data | ACC = 72.5% | Drawing (> 10 s.) |
| This work | 62 PD 15 Control | Spirals and stability movement | Convolution Neural Network from spectrum | ACC = 96.5% AUC = 99.2% | Fraction of drawing (3 s.) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gil-Martín, M.; Montero, J.M.; San-Segundo, R. Parkinson’s Disease Detection from Drawing Movements Using Convolutional Neural Networks. Electronics 2019, 8, 907. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8080907
Gil-Martín M, Montero JM, San-Segundo R. Parkinson’s Disease Detection from Drawing Movements Using Convolutional Neural Networks. Electronics. 2019; 8(8):907. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8080907
Chicago/Turabian StyleGil-Martín, Manuel, Juan Manuel Montero, and Rubén San-Segundo. 2019. "Parkinson’s Disease Detection from Drawing Movements Using Convolutional Neural Networks" Electronics 8, no. 8: 907. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8080907
APA StyleGil-Martín, M., Montero, J. M., & San-Segundo, R. (2019). Parkinson’s Disease Detection from Drawing Movements Using Convolutional Neural Networks. Electronics, 8(8), 907. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8080907







