Internet of Things Applications as Energy Internet in Smart Grids and Smart Environments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- We provide a comprehensive discussion for IoT applications in smart grids and give a comparison for ICTs utilized in these applications.
- We investigate IoT applications for smart cities, several challenges, and their potential solutions.
- We discuss smart home applications based on IoT technologies and highlight communication structure and security background.
- We provide a detailed discussion for smart metering and energy management applications in IoT systems.
- We also provide a detailed discussion for open research topics of future IoT systems.
2. IoT-Based Applications for Smart Grids
3. IoT Applications in Smart Cities
4. IoT-Enabled Applications for Smart Homes
5. Smart Energy Metering and Management Applications Based on IoT
6. Open Research Topics for Future IoT
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Central Intelligence Agency (CIA). The World Fact Book. 2019. Available online: https://goo.gl/b8fbrk (accessed on 25 June 2019).
- Grant, L. The End of Fossil Fuels. 2004. Available online: https://goo.gl/n8zEmQ (accessed on 25 June 2019).
- Kabalci, E. A smart monitoring infrastructure design for distributed renewable energy systems. Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 90, 336–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, R. Some Aspects of Stability in Microgrids. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2013, 28, 3243–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, J.M.; Franquelo, L.G.; Bialasiewicz, J.T.; Galvan, E.; PortilloGuisado, R.C.; Prats, M.A.M.; Leon, J.I.; Moreno-Alfonso, N. Power-Electronic Systems for the Grid Integration of Renewable Energy Sources: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2006, 53, 1002–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaabjerg, F.; Teodorescu, R.; Liserre, M.; Timbus, A.V. Overview of Control and Grid Synchronization for Distributed Power Generation Systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2006, 53, 1398–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olivares, D.E.; Mehrizi-Sani, A.; Etemadi, A.H.; Canizares, C.A.; Iravani, R.; Kazerani, M.; Hajimiragha, A.H.; Gomis-Bellmunt, O.; Saeedifard, M.; Palma-Behnke, R.; et al. Trends in Microgrid Control. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2014, 5, 1905–1919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Zhang, Y.; He, H.; Ma, D.; Zhang, H. A Novel Energy Function-Based Stability Evaluation and Nonlinear Control Approach for Energy Internet. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2017, 8, 1195–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Li, H.; Feng, Y.; Tian, G. Big Data Analytics for System Stability Evaluation Strategy in the Energy Internet. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2017, 13, 1969–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Hu, X.; Li, H.; Li, P.; Zeng, D.; Guo, S. A Survey on Energy Internet Communications for Sustainability. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Comput. 2017, 2, 231–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A. FREEDM system - A vision for the future grid. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Power and Energy Society General Meeting, Providence, RI, USA, 25–29 July 2010; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Appelrath, H.J.; Kagermann, H.; Mayer, C. Future Energy Grid. Migration to the Internet of Energy. 2012. Available online: https://www.google.com.hk/url?sa=t&rct=j&q=&esrc=s&source=web&cd=8&cad=rja&uact=8&ved=2ahUKEwj06pnNoKXkAhWaMN4KHQOWBKwQFjAHegQIABAC&url=https%3A%2F%2Feitdigital.eu%2Ffileadmin%2Fstudies%2FJoint_EIT-ICT-Labs_acatech_Study_Future-Energy-Grid.pdf&usg=AOvVaw1pvdtWl64N-oUtEaiLt7Sz (accessed on 25 June 2019).
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, W.; Juneja, A.; Bhattacharya, S. Energy router: Architectures and functionalities toward Energy Internet. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Smart Grid Communications (SmartGridComm), Brussels, Belgium, 17–20 October 2011; pp. 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Geidl, M.; Koeppel, G.; Favre-Perrod, P.; Klockl, B.; Andersson, G.; Frohlich, K. Energy hubs for the future. IEEE Power Energy Mag. 2007, 5, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Wang, F.; Luo, J.; Zhang, L. Review of energy routers applied for the energy internet integrating renewable energy. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE 8th International Power Electronics and Motion Control Conference (IPEMC-ECCE Asia), Hefei, China, 22–26 May 2016; pp. 1997–2003. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, W.; Yu, R.; Xie, S.; Zhang, Y.; Tsang, D.H.K. Software Defined Networking for Flexible and Green Energy Internet. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2016, 54, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, P.; Zhu, T.; Jiang, B.; Jin, R.; Wang, B. Deploying Energy Routers in an Energy Internet Based on Electric Vehicles. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2016, 65, 4714–4725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.D.; He, W.; Li, S. Internet of Things in Industries: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2014, 10, 2233–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alrawais, A.; Alhothaily, A.; Hu, C.; Cheng, X. Fog Computing for the Internet of Things: Security and Privacy Issues. IEEE Internet Comput. 2017, 21, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, P.P. A Survey on Internet of Things Architectures. J. King Saud Univ. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2018, 30, 291–319. [Google Scholar]
- Zanella, A.; Bui, N.; Castellani, A.; Vangelista, L.; Zorzi, M. Internet of Things for Smart Cities. IEEE Internet Things J. 2014, 1, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, M.M.; Li, L. Microgrid state estimation and control for smart grid and Internet of Things communication network. Electron. Lett. 2015, 51, 149–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafidh, B.; Al Osman, H.; Arteaga-Falconi, J.S.; Dong, H.; El Saddik, A. SITE: The Simple Internet of Things Enabler for Smart Homes. IEEE Access 2017, 5, 2034–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez López, T.; Ranasinghe, D.C.; Harrison, M.; McFarlane, D. Adding sense to the Internet of Things: An architecture framework for Smart Object systems. Pers. Ubiquitous Comput. 2012, 16, 291–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minoli, D.; Sohraby, K.; Occhiogrosso, B. IoT Considerations, Requirements, and Architectures for Smart Buildings – Energy Optimization and Next Generation Building Management Systems. IEEE Internet Things J. 2017, 4, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, M.; Rana, M.M. Architecture of the Internet of Energy Network: An Application to Smart Grid Communications. IEEE Access. 2017, 5, 4704–4710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, R.; Xiong, X.; Zheng, K.; Wang, X. Design and prototyping of low-power wide area networks for critical infrastructure monitoring. IET Commun. 2017, 11, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palattella, M.R.; Dohler, M.; Grieco, A.; Rizzo, G.; Torsner, J.; Engel, T.; Ladid, L. Internet of Things in the 5G Era: Enablers, Architecture, and Business Models. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2016, 34, 510–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, W.; Wang, M.; Zhang, J.; Zou, J.; Hua, M.; Xia, T.; You, X. Narrowband Wireless Access for Low-Power Massive Internet of Things: A Bandwidth Perspective. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2017, 24, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyene, Y.D.; Jantti, R.; Tirkkonen, O.; Ruttik, K.; Iraji, S.; Larmo, A.; Tirronen, T.; Torsner, J. NB-IoT Technology Overview and Experience from Cloud-RAN Implementation. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2017, 24, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carvalho Silva, J.; Rodrigues, J.J.; Alberti, A.M.; Solic, P.; Aquino, A.L. LoRaWAN—A low power WAN protocol for Internet of Things: A review and opportunities. In Proceedings of the 2017 2nd International Multidisciplinary Conference on Computer and Energy Science (SpliTech), Split, Croatia, 12–14 July 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Georgiou, O.; Raza, U. Low Power Wide Area Network Analysis: Can LoRa Scale? IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2017, 6, 162–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, X.; Adhikary, A.; Eric Wang, Y.-P. Random Access Preamble Design and Detection for 3GPP Narrowband IoT Systems. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2016, 5, 640–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.-P.E.; Lin, X.; Adhikary, A.; Grovlen, A.; Sui, Y.; Blankenship, Y.; Bergman, J.; Razaghi, H.S. A Primer on 3GPP Narrowband Internet of Things. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2017, 55, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, N.; Castellani, A.P.; Casari, P.; Zorzi, M. The internet of energy: a web-enabled smart grid system. IEEE Netw. 2012, 26, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcadius Tokognon, C.; Gao, B.; Tian, G.Y.; Yan, Y. Structural Health Monitoring Framework Based on Internet of Things: A Survey. IEEE Internet Things J. 2017, 4, 619–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzaque, M.A.; Milojevic-Jevric, M.; Palade, A.; Clarke, S. Middleware for Internet of Things: A Survey. IEEE Internet Things J. 2016, 3, 70–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shifeng Fang; Li Da Xu; Yunqiang Zhu; Jiaerheng Ahati; Huan Pei; Jianwu Yan; Zhihui Liu An Integrated System for Regional Environmental Monitoring and Management Based on Internet of Things. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2014, 10, 1596–1605. [CrossRef]
- Kelly, S.D.T.; Suryadevara, N.K.; Mukhopadhyay, S.C. Towards the Implementation of IoT for Environmental Condition Monitoring in Homes. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 13, 3846–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynggaard, P.; Skouby, K. Complex IoT Systems as Enablers for Smart Homes in a Smart City Vision. Sensors 2016, 16, 1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, C.-S.; Chou, J.-J.; Reijers, N.; Kuo, T.-W. Designing CPS/IoT applications for smart buildings and cities. IET Cyber-Phys. Syst. Theory Appl. 2016, 1, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvillo, C.F.; Sánchez-Miralles, A.; Villar, J. Energy management and planning in smart cities. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 55, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brundu, F.G.; Patti, E.; Osello, A.; Giudice, M.D.; Rapetti, N.; Krylovskiy, A.; Jahn, M.; Verda, V.; Guelpa, E.; Rietto, L.; et al. IoT Software Infrastructure for Energy Management and Simulation in Smart Cities. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2017, 13, 832–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, S.; Villa, N.; Stewart-Weeks, M.; Lange, A. The Internet of Everything for Cities; Cisco: San Jose, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Haider, H.T.; See, O.H.; Elmenreich, W. A review of residential demand response of smart grid. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 59, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y. Residential Appliances Direct Load Control in Real-Time Using Cooperative Game. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 2016, 31, 226–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finster, S.; Baumgart, I. Privacy-Aware Smart Metering: A Survey. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2015, 17, 1088–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inga, E.; Cespedes, S.; Hincapie, R.; Cardenas, C.A. Scalable Route Map for Advanced Metering Infrastructure Based on Optimal Routing of Wireless Heterogeneous Networks. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2017, 24, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safdarian, A.; Fotuhi-Firuzabad, M.; Lehtonen, M. Optimal Residential Load Management in Smart Grids: A Decentralized Framework. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2016, 7, 1836–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anvari-Moghaddam, A.; Monsef, H.; Rahimi-Kian, A. Optimal Smart Home Energy Management Considering Energy Saving and a Comfortable Lifestyle. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2015, 6, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melhem, F.Y.; Grunder, O.; Hammoudan, Z.; Moubayed, N. Optimization and Energy Management in Smart Home Considering Photovoltaic, Wind, and Battery Storage System With Integration of Electric Vehicles. Can. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2017, 40, 128–138. [Google Scholar]
- Erol-Kantarci, M.; Mouftah, H.T. Energy-Efficient Information and Communication Infrastructures in the Smart Grid: A Survey on Interactions and Open Issues. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2015, 17, 179–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celik, B.; Roche, R.; Suryanarayanan, S.; Bouquain, D.; Miraoui, A. Electric energy management in residential areas through coordination of multiple smart homes. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 80, 260–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viswanath, S.K.; Yuen, C.; Tushar, W.; Li, W.-T.; Wen, C.-K.; Hu, K.; Chen, C.; Liu, X. System design of the internet of things for residential smart grid. IEEE Wirel. Commun. 2016, 23, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komninos, N.; Philippou, E.; Pitsillides, A. Survey in Smart Grid and Smart Home Security: Issues, Challenges and Countermeasures. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2014, 16, 1933–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, S.-C.; Kim, N.-W.; Lee, B.-T.; Cho, C.H.; Chong, J.W. A time synchronization technique for coap-based home automation systems. IEEE Trans. Consum. Electron. 2016, 62, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collier, S.E. The Emerging Enernet: Convergence of the Smart Grid with the Internet of Things. IEEE Ind. Appl. Mag. 2017, 23, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spano, E.; Niccolini, L.; Pascoli, S.D.; Iannaccone, G. Last-Meter Smart Grid Embedded in an Internet-of-Things Platform. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2015, 6, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.M.E.A.; Saputro, N.; Akula, P.K.; Akkaya, K. Privacy-Preserving Power Injection Over a Hybrid AMI/LTE Smart Grid Network. IEEE Internet Things J. 2017, 4, 870–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keyhani, A.; Chatterjee, A. Automatic generation control structure for smart power grids. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2012, 3, 1310–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Song, Z.; Xu, J. Data-Driven Wind Turbine Power Generation Performance Monitoring. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2015, 62, 6627–6635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Zhan, L.; Liu, Y.; Gao, W. A Microgrid Monitoring System Over Mobile Platforms. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2016, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, P.; Arboleya, P.; Mohamed, B.; Vega, A.A.C. Implementation of a Hybrid Distributed/Centralized Real-Time Monitoring System for a DC/AC Microgrid With Energy Storage Capabilities. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2016, 12, 1900–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kong, P.-Y.; Liu, C.-W.; Jiang, J.-A. Cost-Efficient Placement of Communication Connections for Transmission Line Monitoring. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2017, 64, 4058–4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarafi, A.M.; Voulkidis, A.C.; Cottis, P.G. Optimal TDMA Scheduling in Tree-Based Power-Line Communication Networks. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. 2014, 29, 2189–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabalci, E.; Kabalci, Y. A Measurement and Power Line Communication System Design for Renewable Smart Grids. Meas. Sci. Rev. 2013, 13, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moness, M.; Moustafa, A.M. A Survey of Cyber-Physical Advances and Challenges of Wind Energy Conversion Systems: Prospects for Internet of Energy. IEEE Internet Things J. 2016, 3, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciavarella, S.; Joo, J.-Y.; Silvestri, S. Managing Contingencies in Smart Grids via the Internet of Things. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 2016, 7, 2134–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, T.-C.; Shih, Y.-Y.; Pang, A.-C.; Pai, C.-W. Optimized Day-Ahead Pricing With Renewable Energy Demand-Side Management for Smart Grids. IEEE Internet Things J. 2017, 4, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Yu, W.; Griffith, D.; Golmie, N.; Moulema, P. Towards Integrating Distributed Energy Resources and Storage Devices in Smart Grid. IEEE Internet Things J. 2017, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rana, M.M.; Li, L. Kalman Filter Based Microgrid State Estimation Using the Internet of Things Communication Network. In Proceedings of the 2015 12th International Conference on Information Technology - New Generations, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 13–15 April 2015; pp. 501–505. [Google Scholar]
- Saputro, N.; Akkaya, K. Investigation of Smart Meter Data Reporting Strategies for Optimized Performance in Smart Grid AMI Networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2017, 4, 894–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, A.F.A.; Khalid, S.N.; Mustafa, M.W.; Shareef, H.; Aliyu, G. Artificial Intelligent Meter development based on Advanced Metering Infrastructure technology. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 27, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, H.R.; Tsang, K.F.; Chui, K.T.; Chung, H.S.-H.; Ling, B.W.K.; Lai, L.L. Interference-Mitigated ZigBee-Based Advanced Metering Infrastructure. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2016, 12, 672–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Li, H.; Ma, Z.; Wang, C.; Campillo, J.; Zhang, Q.; Wallin, F.; Guo, J. A Comprehensive Review of Smart Energy Meters in Intelligent Energy Networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2016, 3, 464–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabalcı, Y.; Kabalcı, E. Design and Implementation of Wireless Energy Monitoring System for Smart Grids. Gazi Univ. J. Sci. Part C 2017, 5, 137–145. [Google Scholar]
- Kabalci, E.; Kabalci, Y. From Smart Grid to Internet of Energy; Academic Press: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Munshi, A.A.; Mohamed, Y.A.-R.I. Big data framework for analytics in smart grids. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2017, 151, 369–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuelke-Leech, B.-A.; Barry, B.; Muratori, M.; Yurkovich, B. Big Data issues and opportunities for electric utilities. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 52, 937–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oussous, A.; Benjelloun, F.-Z.; Ait Lahcen, A.; Belfkih, S. Big Data technologies: A survey. J. King Saud Univ. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2018, 30, 431–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabalci, Y.; Ali, M. Emerging LPWAN Technologies for Smart Environments: An Outlook. In Proceedings of the 2019 1st Global Power, Energy and Communication Conference (GPECOM), Nevsehir, Turkey, 12–15 June 2019; pp. 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
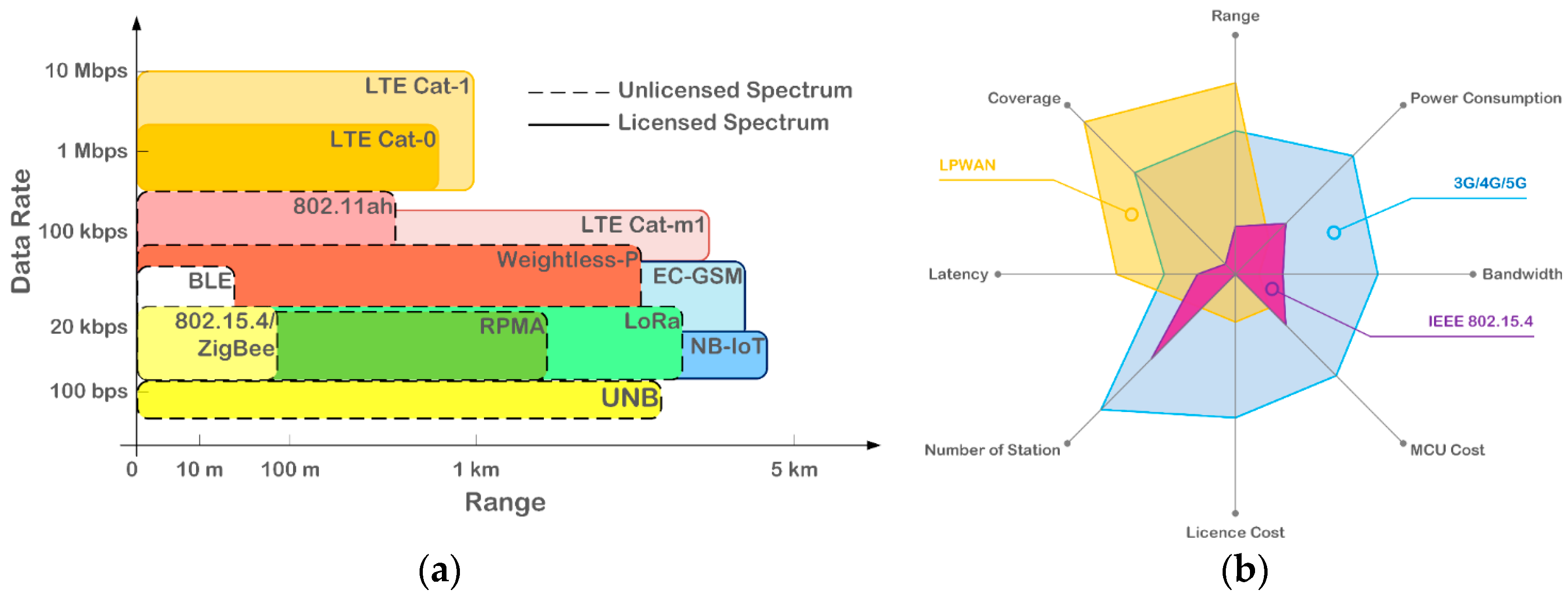



| Technology | LTE-M | NB-IoT | LoRa | Sigfox UNB |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard | LTE (R12) | LTE (R13) | LoRaWAN | N/A |
| Modulation method | BPSK, QPSK, OFDMA | π/2 BPSK, π/4 QPSK | GFSK, SS Chirp | D-BPSK |
| Data rate | 0.2–1 Mbps | Up to 100 kbps | 0.3–38.4 kbps | 100 bps |
| Frequency band | Licensed Cellular | Licensed Cellular | Sub-GHz | Sub-GHz (868 MHz, 902 MHz) |
| Minimum transmission bandwidth | 180 kHz | 3.75 kHz | 125 kHz | 100 Hz, 600 Hz |
| Range | 35 km-GSM 200 km-UMTS, LTE | 2.5–15 km urban, up to 50 km rural | 2.5–15 km urban, up to 50 km rural | 3–10 km urban, 30–50 km rural |
| Bidirectional | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Interference immunity | Medium | Low | Very high | Low |
| Security | 32-bit | N/A | 32-bit | 16-bit |
| Max coupling loss | 155 dB | 160 dB | 157 dB | 162 dB |
| Receiver sensitivity | −132 dBm | −137 dBm | −137 dBm | −147 dBm |
| Power efficiency | Medium | Very high | Very high | Very high |
| Transmitter power | 23 dBm | 23 dBm | 20 dBm | 15 dBm |
| Battery lifetime | 7–8 years | 1–2 years | 8–10 years | 7–8 years |
| Required Improvements on | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SG Stage | Application Type | Communication | Security | Big Data |
| Generation | Real Time Monitoring | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Power Plant Control | ✓ | ✓ | — | |
| Distributed Generation | ✓ | ✓ | — | |
| Renewable Sources | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Transmission | Substation Monitoring | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Line Fault Monitoring | ✓ | ✓ | — | |
| Line Measurements | ✓ | ✓ | — | |
| Power Quality Analysis | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Distribution | Direct Load Control | ✓ | ✓ | — |
| Smart Transformer Control | ✓ | ✓ | — | |
| AMI and DSM | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Substation Automation | ✓ | ✓ | — | |
| Consumption | Home Energy Management System | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Microgrid Management | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Electric Vehicle Control | ✓ | ✓ | — | |
| Appliance Control | ✓ | ✓ | — | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kabalci, Y.; Kabalci, E.; Padmanaban, S.; Holm-Nielsen, J.B.; Blaabjerg, F. Internet of Things Applications as Energy Internet in Smart Grids and Smart Environments. Electronics 2019, 8, 972. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8090972
Kabalci Y, Kabalci E, Padmanaban S, Holm-Nielsen JB, Blaabjerg F. Internet of Things Applications as Energy Internet in Smart Grids and Smart Environments. Electronics. 2019; 8(9):972. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8090972
Chicago/Turabian StyleKabalci, Yasin, Ersan Kabalci, Sanjeevikumar Padmanaban, Jens Bo Holm-Nielsen, and Frede Blaabjerg. 2019. "Internet of Things Applications as Energy Internet in Smart Grids and Smart Environments" Electronics 8, no. 9: 972. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8090972
APA StyleKabalci, Y., Kabalci, E., Padmanaban, S., Holm-Nielsen, J. B., & Blaabjerg, F. (2019). Internet of Things Applications as Energy Internet in Smart Grids and Smart Environments. Electronics, 8(9), 972. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics8090972








