Antiphase Method of the CMOS Power Amplifier Using PMOS Driver Stage to Enhance Linearity
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Antiphase Technique
2.1. IMD3 in the Middle-Power Region
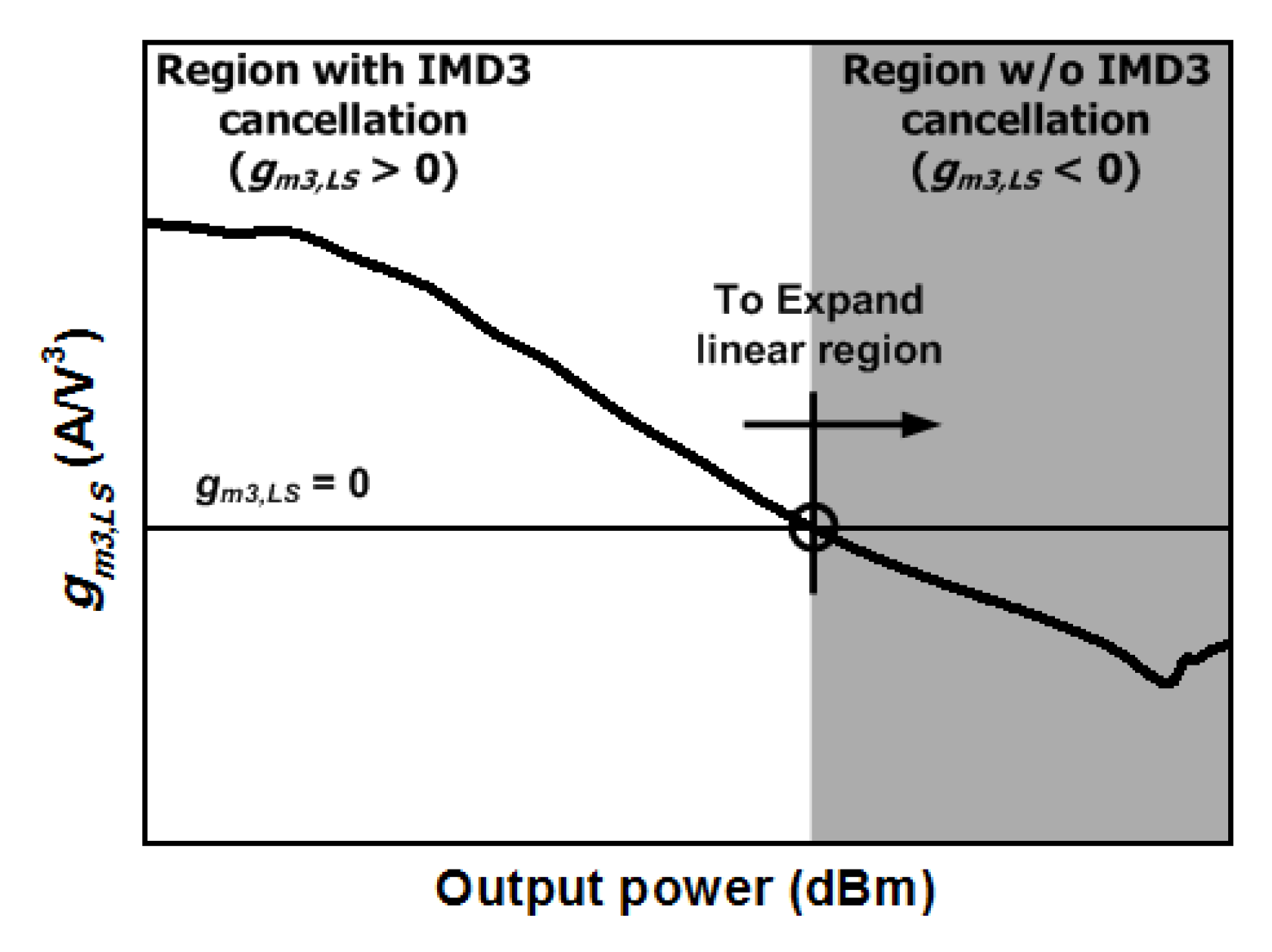
2.2. Expansion of Linear Region
2.3. AM-AM Distortion
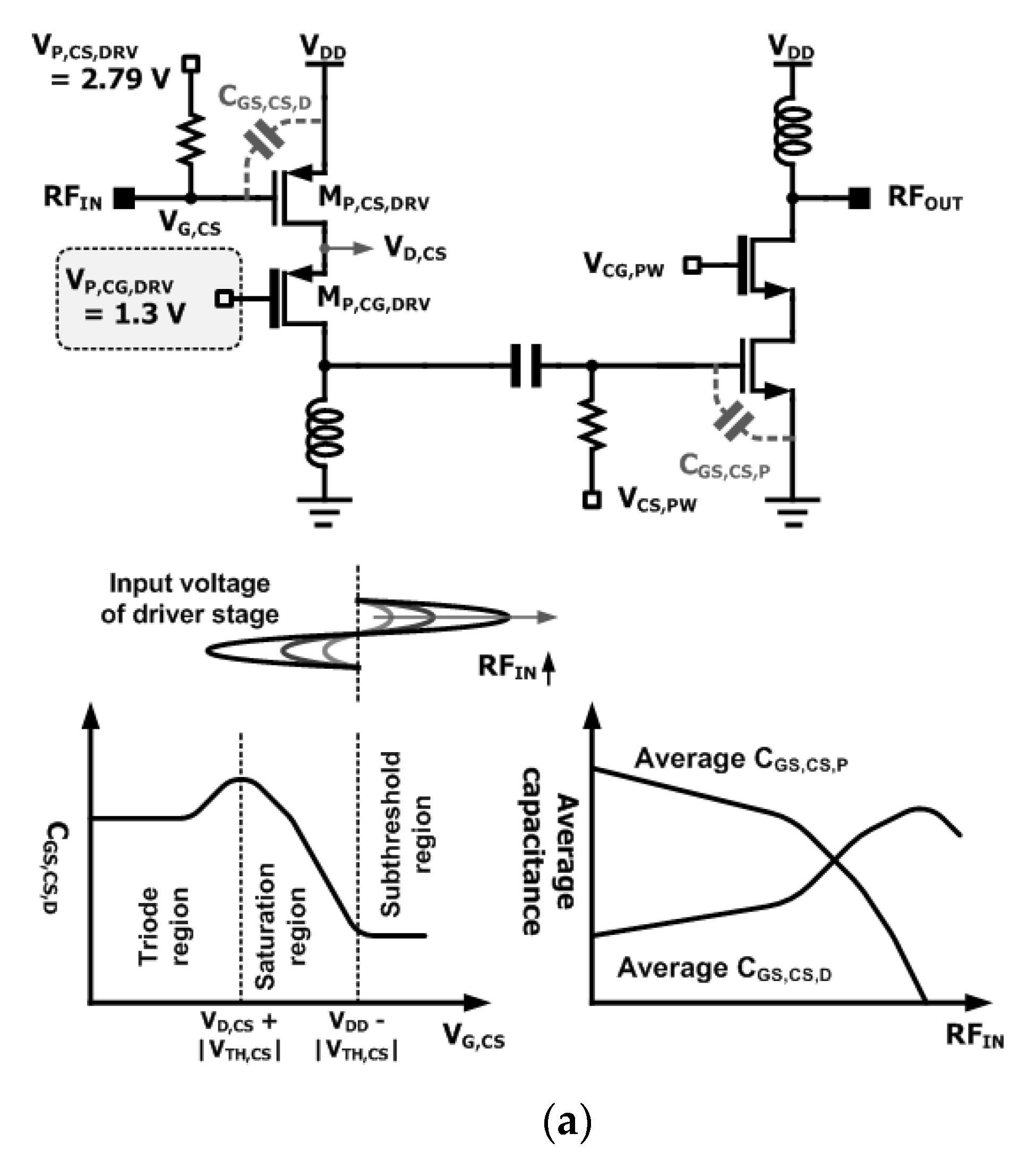
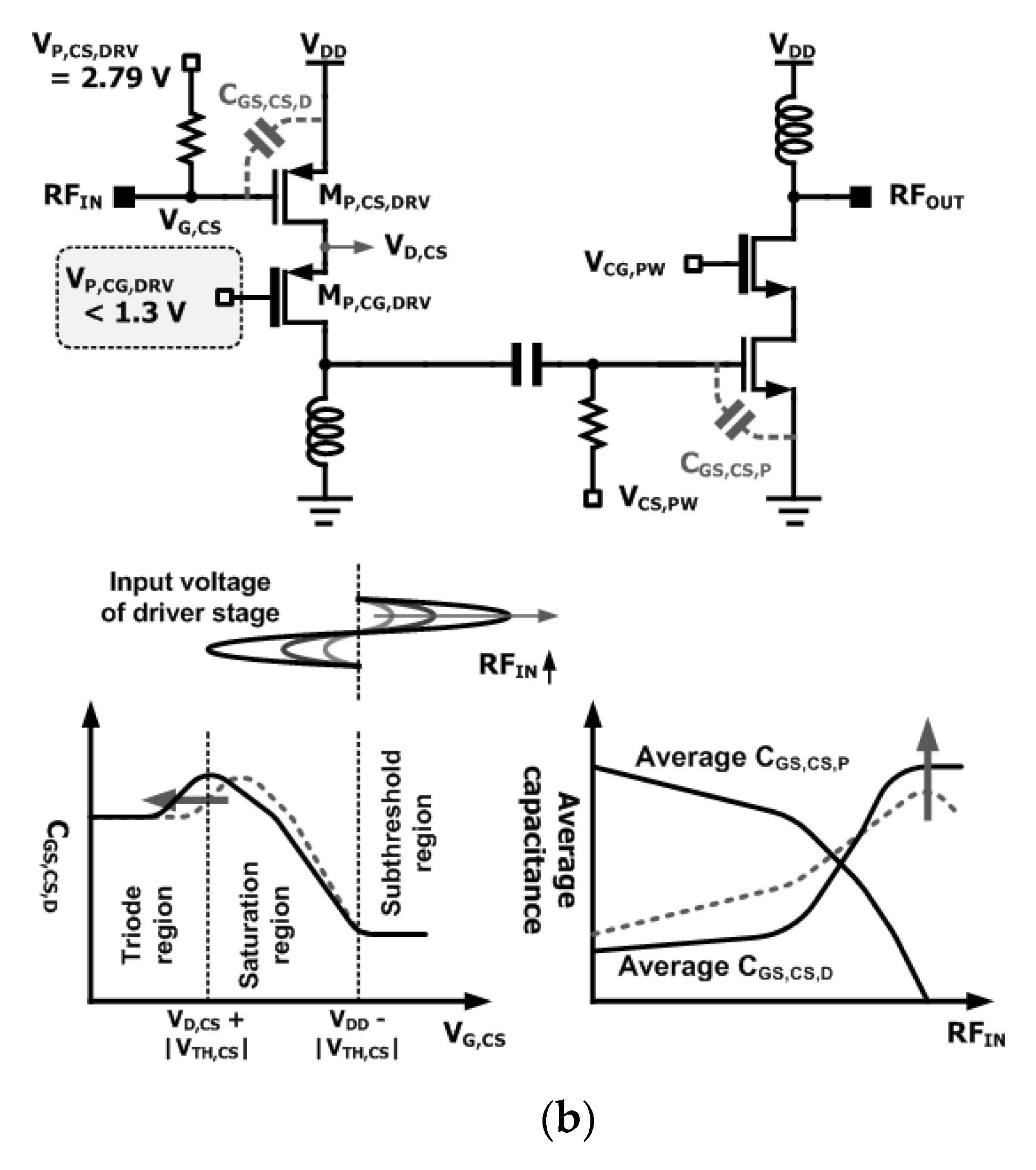
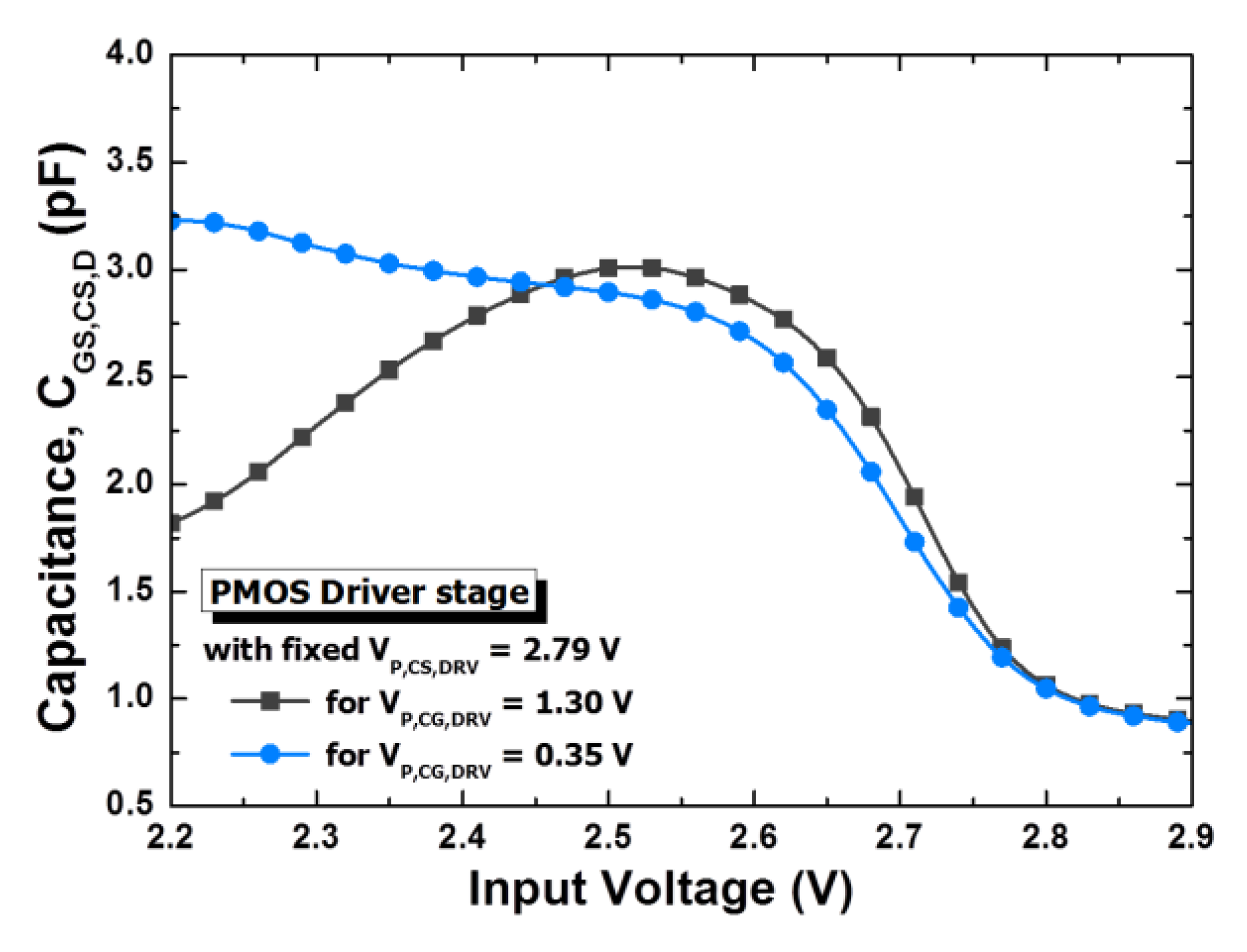
3. Antiphase Technique Using PMOS Driver Stage
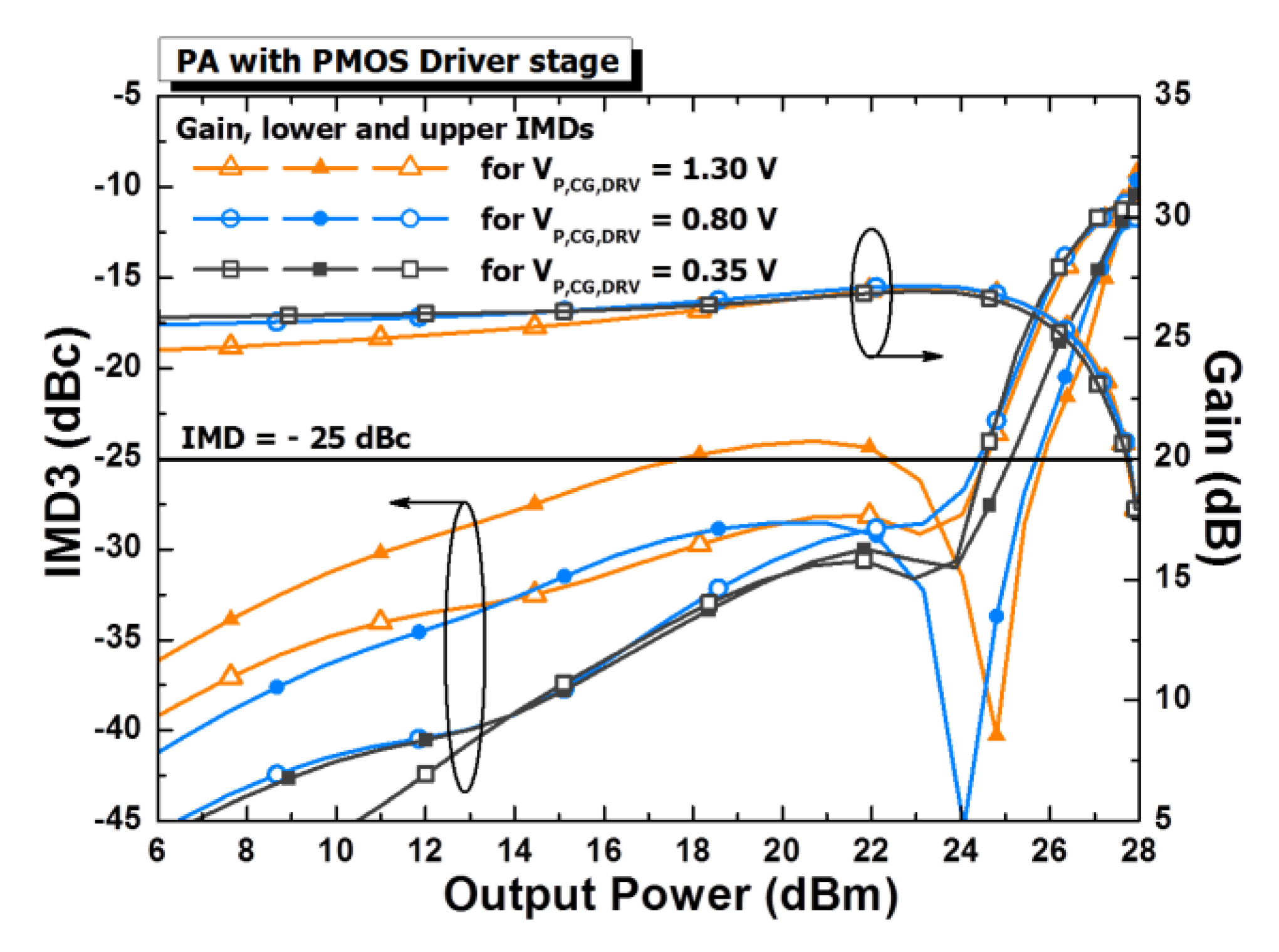
3.1. IMD3 in the Middle-Power Region
3.2. Expansion of Linear Region
3.3. AM-AM Distortion
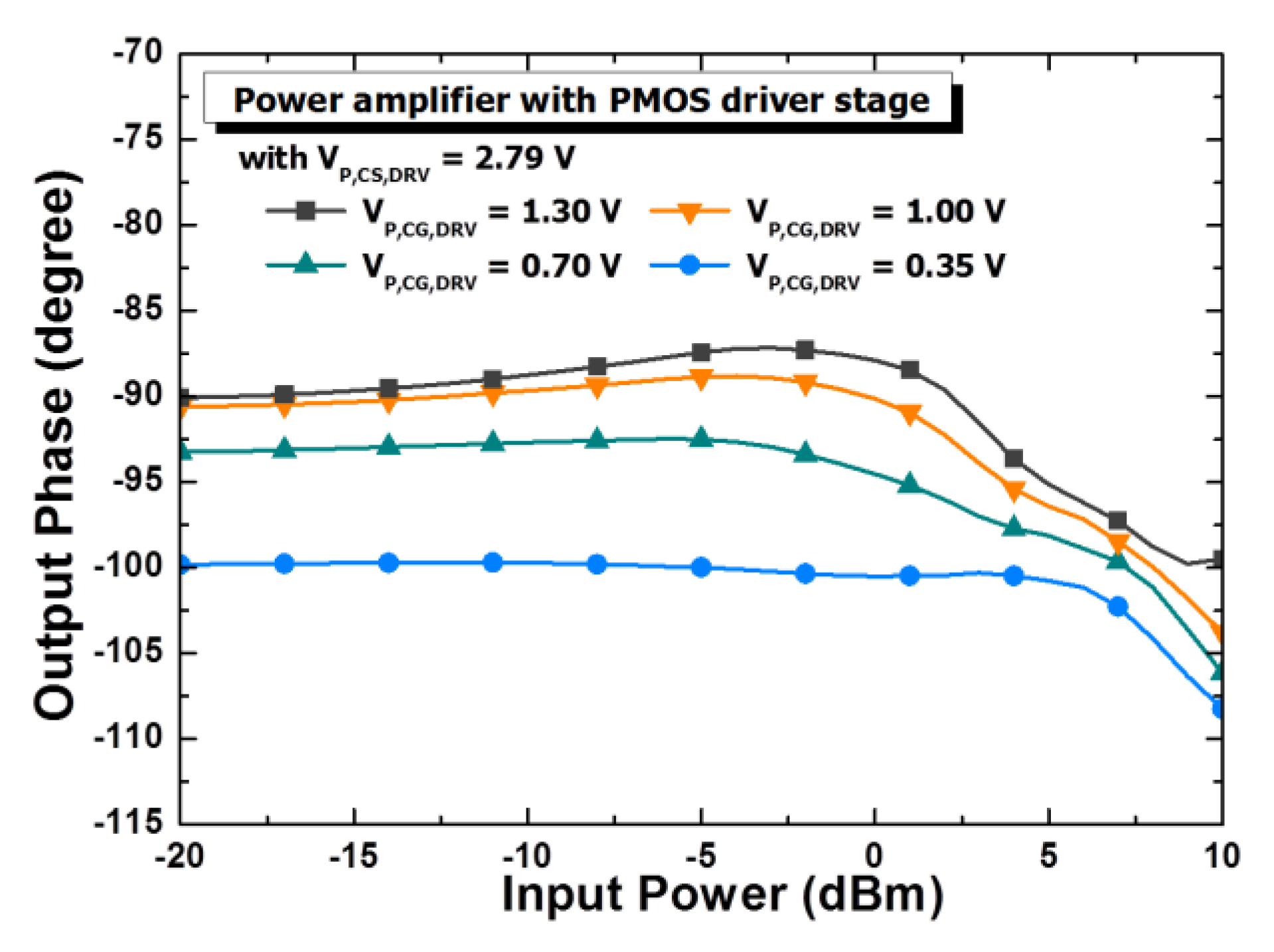
4. Technique of Suppression of AM-PM Distortion
5. Implementation and Measured Results
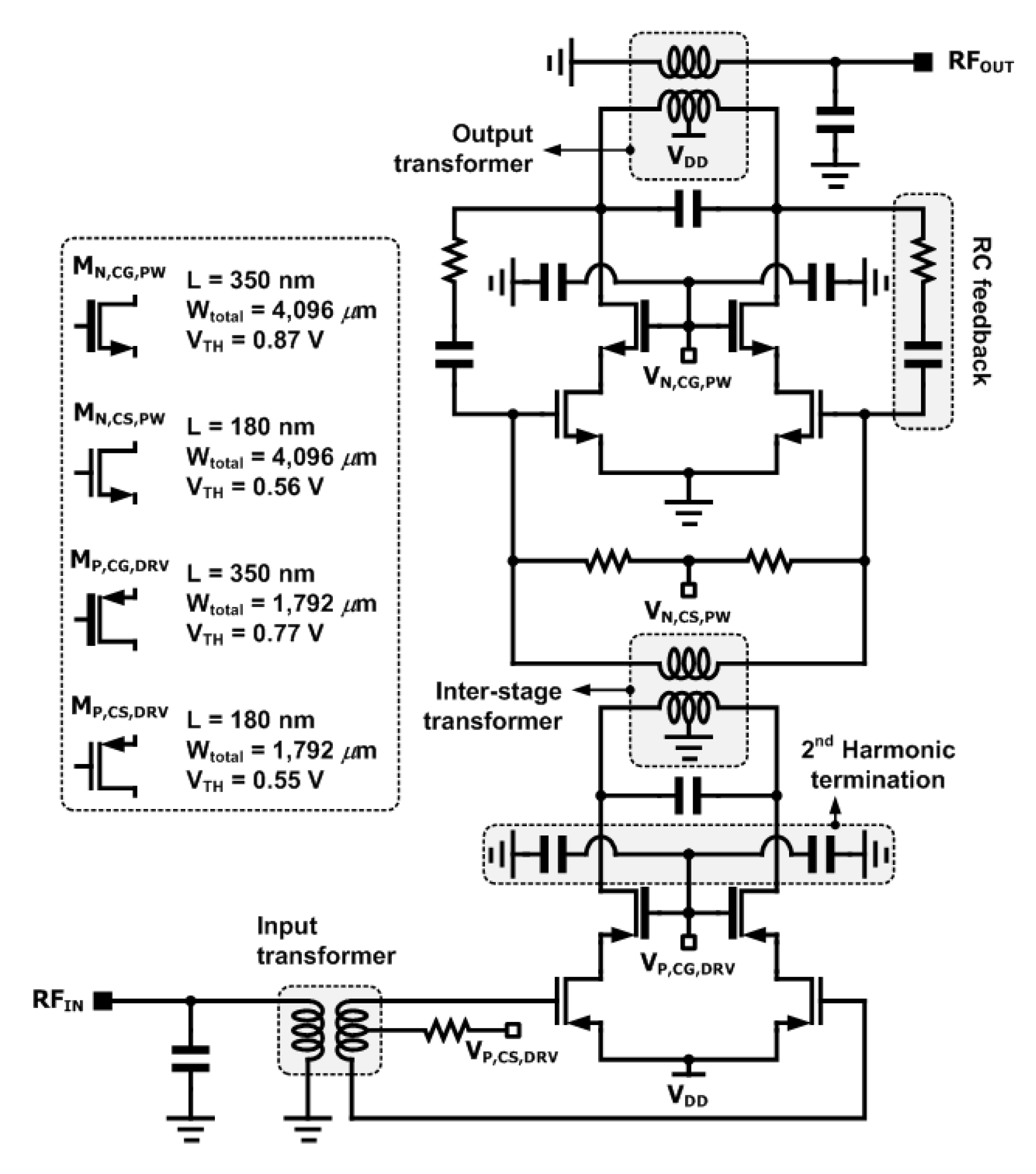
5.1. Implementation
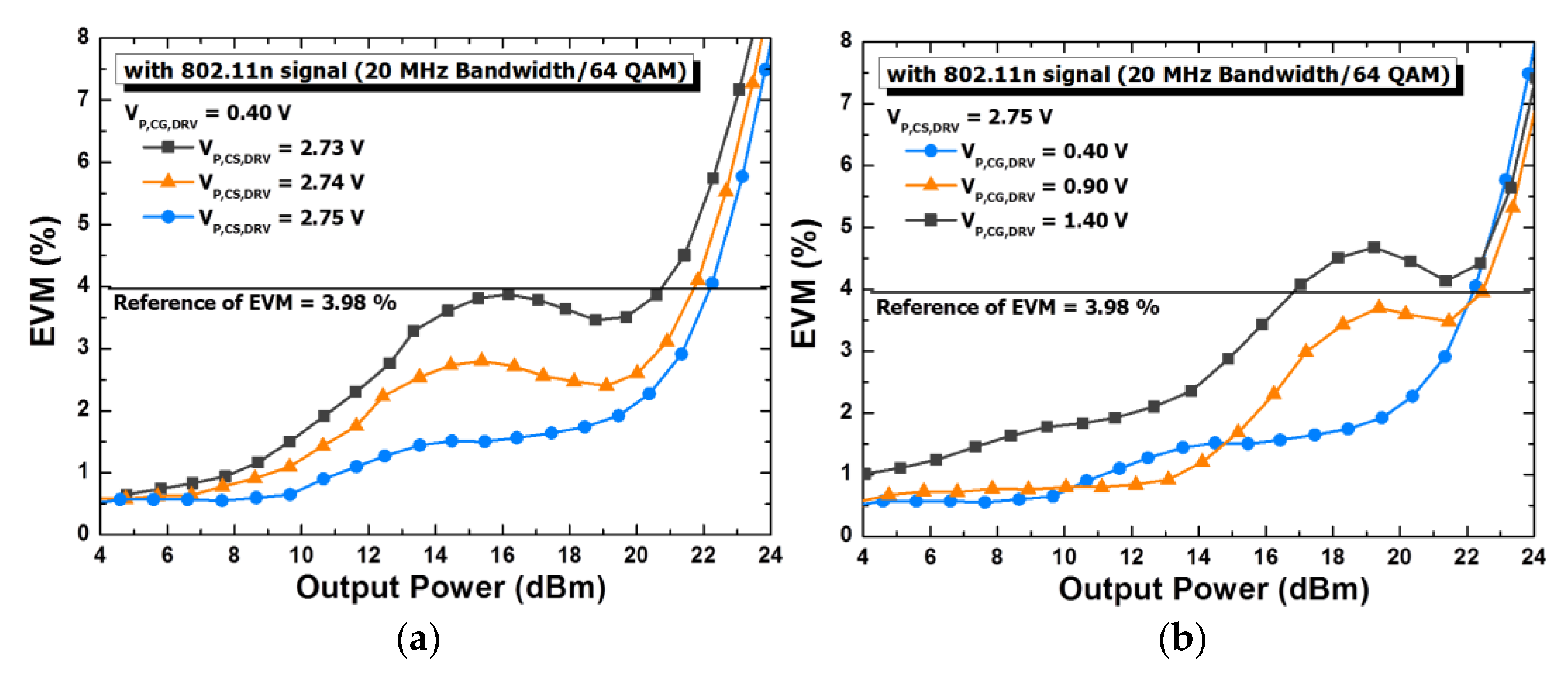
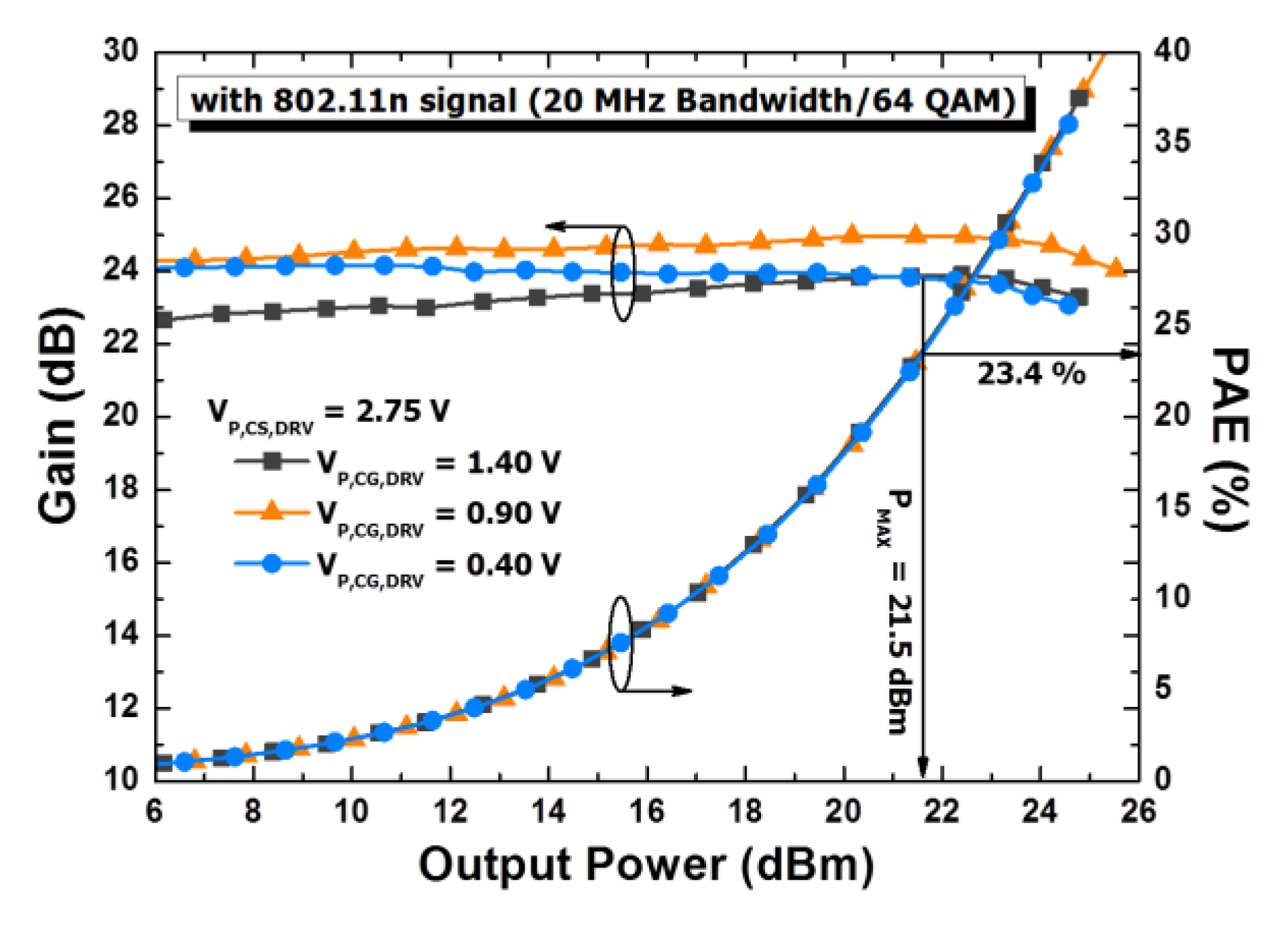
5.2. Measured Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| gm,LS | |
| Large signal gm | |
| gm3,LS | Large signal gm3 |
| gm,LS,DRV | gm,LS of two-tone input signal of driver stage |
| gm3,LS,DRV | gm3,LS of two-tone input signal of driver stage |
| gm,LS,PW | gm,LS of power stage |
| gm3,LS,PW | gm3,LS of power stage |
| A | Amplitude of two-tone input signal of driver stage |
| ZL,DRV | Load impedance of two-tone input signal of driver stage |
| ZL,PW | Load impedance of power stage |
| vSig,DRV | Desired signal voltage |
| v3rd,DRV | Third-order distortion voltage |
| v3rd,PA | Overall third-order distortion voltage of power amplifier |
| IDS,SUB | Drain current of driver stage in the subthreshold region |
| VP-P | Peak-to-Peak voltage of the input voltage of driver stage |
| VDD | |
| Supply voltage | |
| VN,CS,DRV | Common-source gate bias of NMOS driver stage |
| VP,CS,DRV | Common-source gate bias of PMOS driver stage |
| VN,CG,DRV | Common-gate gate bias of NMOS driver stage |
| VP,CG,DRV | Common-gate gate bias of PMOS driver stage |
| MN,CS,DRV | Common-source transistor of NMOS driver stage |
| MN,CG,DRV | Common-gate transistor of NMOS driver stage |
| MP,CS,DRV | Common-source transistor of PMOS driver stage |
| MP,CG,DRV | Common-gate transistor of PMOS driver stage |
| MN,CS,PW | Common-source transistor of NMOS power stage |
| MN,CG,PW | Common-gate transistor of NMOS power stage |
| CGS,CS,P | CGS of common-source transistor of power stage |
| CGS,CS,D | CGS of common-source transistor of driver stage |
References
- Kang, D.; Park, B.; Kim, D.; Kim, J.; Cho, Y.; Kim, B. Envelope-tracking CMOS power amplifier module for LTE applications. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2013, 61, 3763–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Woo, J.-L.; Kwon, Y. Broadband CMOS stacked RF power amplifier using reconfigurable interstage network for wideband envelope tracking. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2015, 63, 1174–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Yoon, Y.; Kim, H.; An, K.H.; Kim, W.; Kim, H.-W.; Lee, C.-H.; Kornegay, K.T. A linear multi-mode CMOS power amplifier with discrete resizing and concurrent power combining structure. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2011, 46, 1034–1048. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, M.; Larson, L.E.; Leung, V.W.; Kimball, D.F.; Asbeck, P.M. A wideband CMOS/GaAs HBT envelope tracking power amplifier for 4G LTE mobile terminal applications. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2012, 60, 1321–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, M.; Yoo, J.; Kang, I.; Lee, C.; Kim, J.; Park, H.J.; Park, Y.-B.; Park, C. RF CMOS power amplifier using a split inter-stage inductor for IEEE 802.11n applications. Int. J. Microw. Wirel. Technol. 2017, 9, 719–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, Y.; Park, J.; Yoo, J.; Lee, C.; Park, C. A CMOS power amplifier using an active balun as a driver stage to enhance its gain. Microelectron. J. 2017, 63, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, H.; Lee, C.; Park, J.; Park, C. A current-shared cascade structure with an auxiliary power regulator for switching mode RF power amplifiers. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2014, 62, 2711–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Yoon, S.; Park, C. A differentially coupled series inductor for differential RFICs. Microw. Opt. Technol. Lett. 2015, 57, 2223–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golara, S.; Moloudi, S.; Abidi, A.A. Process of AM-PM distortion in large signal single-FET amplifiers. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2017, 64, 245–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, T.; Koo, B.; Hong, S. A WLAN RF CMOS PA with large signal MGTR method. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2013, 61, 1272–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onizuka, K.; Ishihara, H.; Hosoya, M.; Saigusa, S.; Watanabe, O.; Otaka, S. A 1.9 GHz CMOS power amplifier with embedded linearizer to compensate AM-PM distortion. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2012, 47, 1820–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, B.; Na, Y.; Hong, S. Integrated bias circuits of RF CMOS cascode power amplifier for linearity enhancement. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2012, 60, 340–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Vaidyanathan, M.; Larson, L.E. A capacitance compensation technique for improved linearity in CMOS class-AB power amplifiers. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2004, 39, 1927–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, S.; Reynaert, P. A 60-GHz power amplifier with AM-PM distortion cancellation in 40-nm CMOS. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2016, 64, 2284–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigilante, M.; Reynaert, P. A wideband class-AB power amplifier with 29-57-GHz AM-PM compensation in 0.9-V 28-nm Bulk CMOS. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2018, 53, 1288–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lee, C.; Park, C. A quad-band CMOS linear power amplifier for EDGE applications using an anti-phase method to enhance its linearity. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2016, 64, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lee, C.; Park, C. A CMOS antiphase power amplifier with an MGTR technique for mobile applications. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2017, 65, 4545–4656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.; Kim, M.; Kim, H.; Jung, S.; Cho, J.; Yoo, S.; Kim, Y.H.; Yoo, H.; Yang, Y. A highly linear two-stage amplifier integrated circuit using InGaP/GaAs HBT. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2010, 45, 2038–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Yoon, J.; Min, K.; Yu, D.; Nam, D.; Yang, Y.; Kim, B. A highly linear and efficient differential CMOS power amplifier with harmonic control. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2006, 41, 1314–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Nam, S. A CMOS outphasing power amplifier with integrated single-ended chireix combiner. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2010, 45, 411–415. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, S.; Park, B.; Moon, K.; Kwon, M.; Kim, B. Linearization of CMOS cascade power amplifiers through adaptive bias control. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2013, 61, 4534–4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Kwon, M.; Moon, K.; Park, B.; Kim, B. Control of IMD asymmetry of CMOS power amplifier for broadband operation using wideband signal. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2013, 61, 3753–3762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaymaksut, E.; Reynaert, P. Transformer based uneven Doherty power amplifier in 90 nm CMOS for WLAN applications. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2012, 47, 1659–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Yu, X.; Wang, Z.; Chi, B. An efficiency-enhanced stacked 2.4-GHz CMOS power amplifier with mode switching scheme for WLAN applications. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2015, 63, 672–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, G.; Kang, S.; Joo, T.; Hong, S. An integrated dual-mode CMOS power amplifier with linearizing body network. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2017, 64, 1037–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Reference | Tech./VDD | WLAN Signal | Pout | PAE | Gain | EVM | Freq. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (V) | (dBm) | (%) | (dB) | (%) | (GHz) | ||
| [10] 2013 T-MTT | 130 nm/3.3 | 802.11 g (64-QAM, 20 MHz) | 18.2 | 21.3 | 21 | 3.98 | 2.412 |
| [23] 2012 JSSC | 90 nm/2.0 | 802.11 g (64-QAM, 20 MHz) | 19.3 | 22.9 | 17.5 | 5.62 | 2.45 |
| [24] 2015 T-MTT | 180 nm/5.6 | 802.11 g (64-QAM, 20 MHz) | 23 | 21.3 | 22.5 | 4.51 | 2.4 |
| [25] 2017 T-CAS II | 55 nm/3.3 | 802.11 g (64-QAM, 20 MHz) | 16 | 5.8 | 26.5 | 4.47 | 2.45 |
| This works | 180 nm/3.3 | 802.11 n (64-QAM, 20 MHz) | 21.5 | 23.4 | 23.8 | 3.14 | 2.42 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, J.; Lee, C.; Yoo, J.; Park, C. Antiphase Method of the CMOS Power Amplifier Using PMOS Driver Stage to Enhance Linearity. Electronics 2020, 9, 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9010103
Kim J, Lee C, Yoo J, Park C. Antiphase Method of the CMOS Power Amplifier Using PMOS Driver Stage to Enhance Linearity. Electronics. 2020; 9(1):103. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9010103
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Jiwon, Changhyun Lee, Jinho Yoo, and Changkun Park. 2020. "Antiphase Method of the CMOS Power Amplifier Using PMOS Driver Stage to Enhance Linearity" Electronics 9, no. 1: 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9010103
APA StyleKim, J., Lee, C., Yoo, J., & Park, C. (2020). Antiphase Method of the CMOS Power Amplifier Using PMOS Driver Stage to Enhance Linearity. Electronics, 9(1), 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9010103





