Deceptive Targets Generation Simulation Against Multichannel SAR
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- Point out that to generate false targets and scenes against multichannel SAR, the number of transponders must be more than that of SAR receiving channels.
- Propose a new jamming method for jointly employing three transponders against three-channel SAR-GMTI.
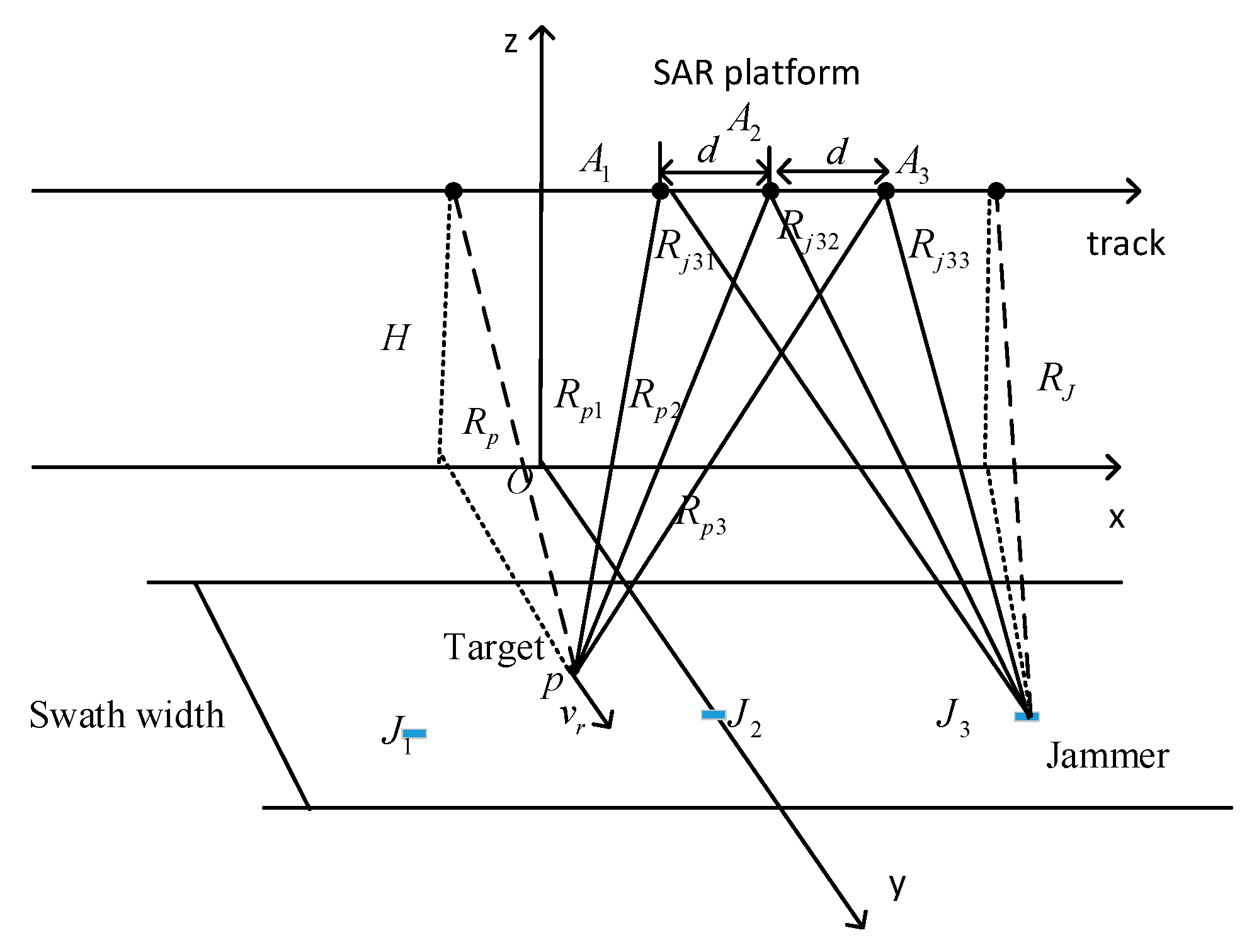
- Give a general scheme of multiple transponders interfering multichannel SAR, which is applicable to multichannel InSAR and SAR-GMTI systems.
- Introduce a numerical optimization algorithm utilizing the minimum condition number to deploy multiple transponders excellently.
- Carry out comparative experiments on the jamming performance against three-channel SAR-GMTI between using three transponders and using a single transponder or two transponders.
2. Analysis of a Single Transponder Against Dual-Channel SAR-GMTI Processing
2.1. A Real Moving Target
2.2. A False Target Generated by a Single Transponder
3. Synergetic Jamming with Two Transponders
3.1. The Effectiveness of two Transponders Against Dual-Channel SAR-GMTI
3.2. The Limitaion of Two Transponders Against Three-Channel SAR-GMTI
4. Synergetic Jamming with Three Transponders
4.1. The Effectiveness of Three Transponders Against Three-Channel SAR-GMTI
4.2. Layout optimization of Multiple Transponders
5. Multiple Transponders Against Multi-Channel SAR
6. Simulations Results
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cumming, I.G.; Wong, F.H. Digital Processing of Synthetic Aperture Radar Data: Algorithm and Implementation; Artech House: Boston, MA, USA, 2004; pp. 323–362. [Google Scholar]
- Richards, J.A. Remote Sensing with Imaging Radar; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Romeiser, R.; Suchandt, S.; Runge, H.; Steinbrecher, U.; Grunler, S. First analysis of TerraSAR-X along-track InSAR-derived current fields. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens. 2009, 48, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerutti-Maori, D.; Sikaneta, I. A generalization of DPCA processing for multichannel SAR/GMTI radars. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2012, 51, 560–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudczyk, J.; Kawalec, A. Optimizing the minimum cost flow algorithm for the phase unwrapping process in SAR radar. Bulletin. Pol. Aca. Sci. Tech. Sci. 2014, 62, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rosenberg, L.; Gray, D. Anti-jamming techniques for multichannel SAR imaging. IEE Radar Sonar Navig. 2006, 153, 782–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sjögren, T.K.; Vu, V.T.; Pettersson, M.I.; Wang, F.; Murdin, D.J.G.; Gustavsson, A.; Ulander, L.M. Suppression of clutter in multichannel SAR GMTI. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens. 2013, 52, 4005–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matuszewski, J. Evaluation of jamming efficiency for the protection of a single ground object. Proc. SPIE 2018, 10715, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Matuszewski, J. Jamming Efficiency of Land-Based Radars by the Airborne Jammers. In Proceedings of the MIKON 2018—22nd International Microwave and Radar Conference, Poznan, Poland, 14–17 May 2018; pp. 324–327. [Google Scholar]
- Ferraioli, G. Multichannel InSAR building edge detection. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens. 2009, 48, 1224–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroer, R. Electronic warfare. IEEE Aerosp. Electron. Syst. Mag. 2003, 18, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Neng-Jing, L.; Yi-Ting, Z. A survey of radar ECM and ECCM. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 1995, 31, 1110–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harness, R.S.; Budge, M.C. A study on SAR noise jamming and false target insertion. In Proceedings of the IEEE SoutheastCon, Lexington, KY, USA, 13–16 March 2014; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Pace, P.E.; Fouts, D.J.; Ekestorm, S.; Karow, C. Digital false-target image synthesiser for countering ISAR. IEE Radar Sonar Navig. 2002, 149, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, D.H.; Wu, X.F.; Wang, X.S.; Xiao, S.P. SAR active-decoys jamming based on DRFM. In Proceedings of the 2007 IET International Conference on Radar Systems 2007, Edinburgh, UK, 15–18 October 2007; pp. 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, L.; Dong, C.; Shen, Z.; Zhao, G. The influence of rebound jamming on SAR GMTI. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2014, 12, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Chang, X. A novel scattered wave deception jamming against three channel SAR GMTI. IEEE Access. 2018, 6, 53882–53889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Pan, X.; Dai, D.; Feng, D. A frequency-domain three-stage algorithm for active deception jamming against synthetic aperture radar. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2014, 8, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Zhao, B.; Tao, M.; Bai, X.; Chen, B.; Sun, G. A large scene deceptive jamming method for space-borne SAR. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2013, 51, 4486–4495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Wu, Z.; Liu, W.; Li, J.; Feng, Q. Analysis of the effect of interference on InSAR. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 5659–5668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chunxi, D.; Guoqing, Z. Investigation on countermeasure against InSAR dual-channel cancellation technique with multi-antenna transponder. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2015, 37, 913–918. [Google Scholar]
- Gan, R.B.; Wang, J.G.; He, C.; Xu, M.L. An improved rebound jamming to SAR. J. Electron. Inf. Technol. 2005, 27, 256–258. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, B.; Guo, K.; Wang, J. The 3D Active Deception Jamming of SAR. Acta Electron. Sin. 2007, 35, 1203–1206. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Dai, D.; Qi, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Xiao, S. Analysis of deceptive moving target generated by single transponder in multichannel SAR-GMTI. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Applied Computational Electromagnetics Society Symposium (ACES), Suzhou, China, 1–4 August 2017; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, X.; Dong, C. A Barrage Noise Jamming Method Based on Two Transponders Against Three Channel SAR GMTI. IEEE Access. 2019, 7, 18755–18763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xing, S.; Dai, D.; Li, Y.; Xiao, S. Three-dimensional deceptive scene generation against single-pass InSAR based on coherent transponders. IET Radar Sonar Navig. 2016, 10, 477–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.-F.; Xu, H.-P.; Li, J.-W.; Liu, W. Research of 3-D deceptive interfering method for single-pass spaceborne InSAR. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2015, 51, 2834–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Qi, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, L. Deceptive jamming against multi-channel SAR-GMTI. J. Eng. 2019, 20, 7105–7109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Shu, T.; Yu, K.-B.; Yu, W. A Novel Deceptive Jamming Method against Two-Channel SAR-GMTI Based on Two Transponders. IEEE Sens. J. 2019, 19, 5600–5610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deming, R.; Best, M.; Farrell, S. Simultaneous SAR and GMTI using ATI/DPCA. In Algorithms for Synthetic Aperture Radar Imagery XXI, Proceedings of the SPIE, Baltimore, MD, USA, 5–9 May 2014; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2014; Volume 9093, p. 19. [Google Scholar]
- Livingstone, C.; Sikaneta, I.; Gierull, C.H.; Chiu, S.; Beaudoin, A.; Campbell, J.; Beaudoin, J.; Gong, S.; Knight, T.A. An airborne synthetic aperture radar (SAR) experiment to support RADARSAT-2 ground moving target indication (GMTI). Can. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 28, 794–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Tian, T.; Zhao, B.; Bai, X.; Fan, W. Deception Against Near-Field Synthetic Aperture Radar Using Networked Jammers. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2019, 55, 3365–3377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Huang, L.; Zhou, F.; Zhang, J. Performance improvement of deception jamming against SAR based on minimum condition number. IEEE J. Sel. Top Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2016, 10, 1039–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamy, D.L. Digital RF Memories. In EW 104: EW against a New Generation of Threats; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Schleher, D.C. Introduction to Electronic Warfare; IEEE Press: Dedham, MA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]





| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Carrier frequency | 10 GHz |
| Bandwidth | 70 MHz |
| Beam width | 0.5o |
| Platform velocity | 250 m/s |
| Numbers of channel | 3 |
| PRF | 1000 Hz |
| Center range | 10,000 m |
| Baseline length | 4 m |
| Targets | ||||||
| Coordinates | ||||||
| −0.5 | 0.7 | 0 | 0.4 | −0.6 | 0 |
| Index | Radial Velocity | Azimuth Position | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Estimation (m/s) | Error (m/s) | Estimation (m) | Displacement (m) | Relocation (m) | Error (m) | ||
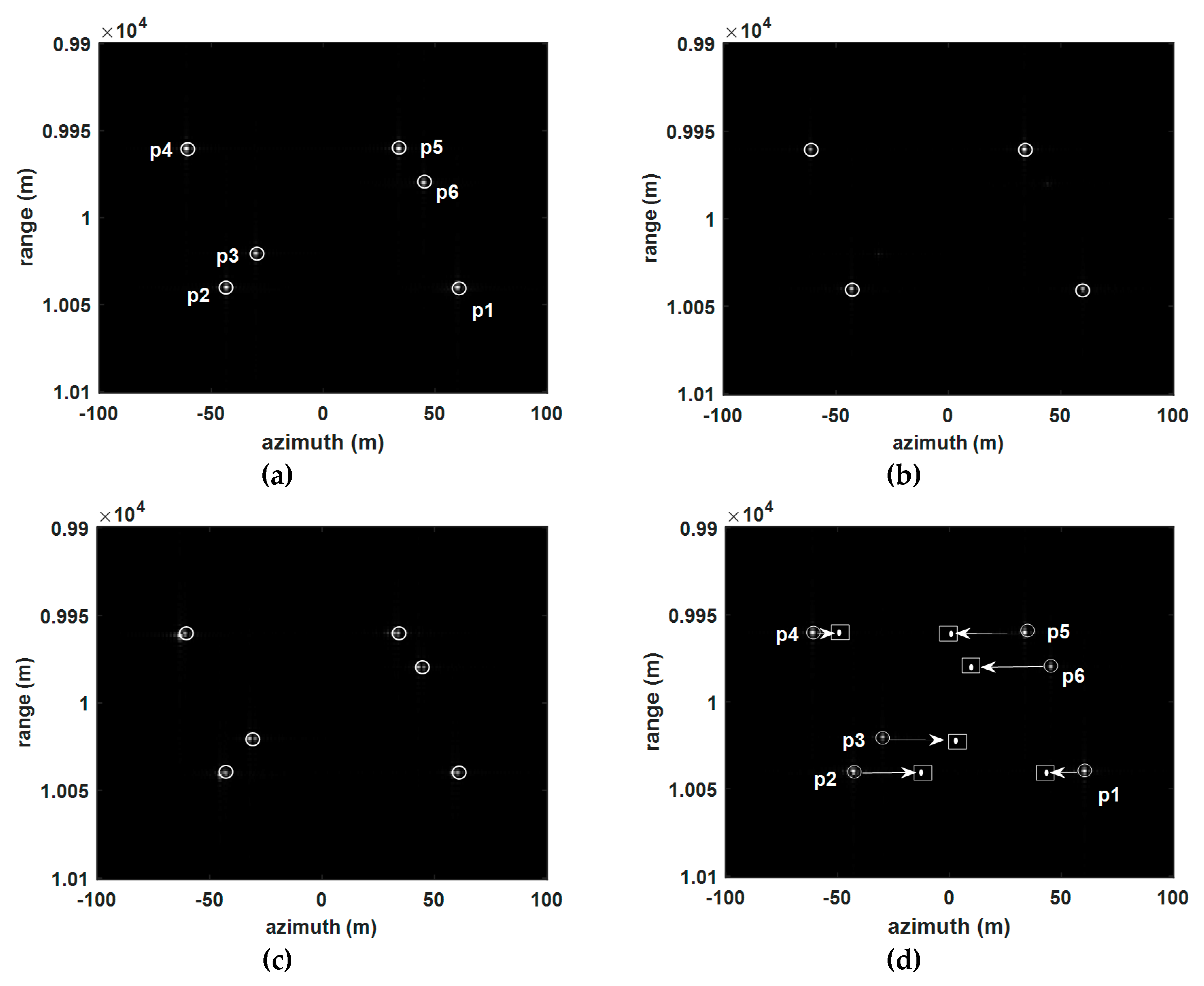
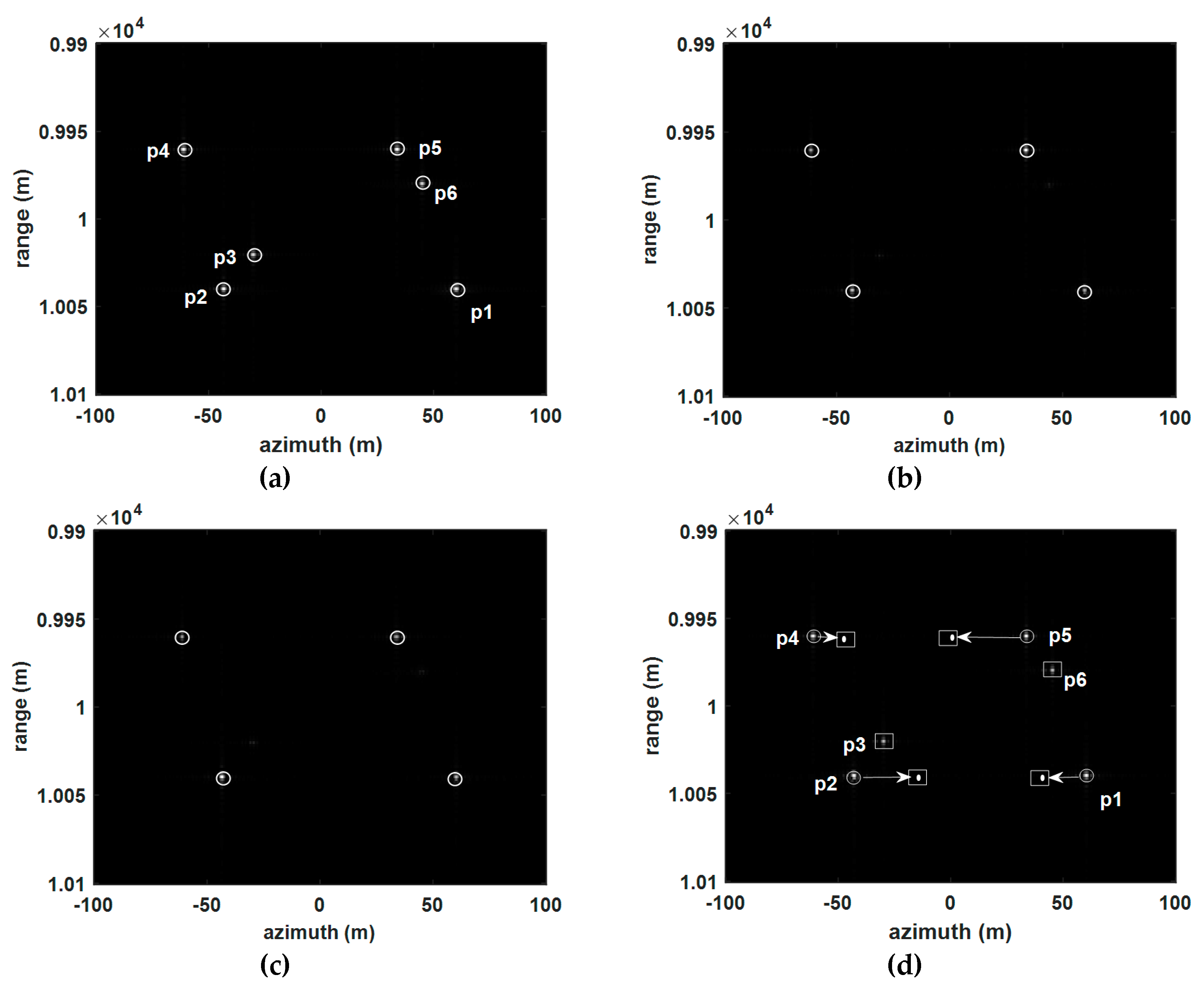
| A single transponder | P1 | −1.5 | −1 | 60.2 | 60 | 0.2 | 39.8 |
| P2 | 1.075 | 0.375 | −43 | −43 | 0 | −15 | |
| P3 | 0.75 | 0.75 | −29.9 | −30 | 0.1 | −30.1 | |
| P4 | 1.525 | 1.125 | −60.8 | −61 | 0.2 | −45.2 | |
| P5 | −0.85 | −0.25 | 34 | 34 | 0 | 10 | |
| P6 | −1.125 | −1.125 | 45.2 | 45 | 0.2 | 44.8 | |
| Two transponders | P1 | −0.3060 | −0.1940 | 60.4 | 12 | 48.4 | −8.4 |
| P2 | 0.7770 | 0.0770 | −43 | −31.08 | −11.92 | −3.08 | |
| P3 | 0.8144 | 0.8144 | −29.4 | −32.38 | 2.98 | −32.98 | |
| P4 | 0.2591 | 0.1409 | −61.3 | 10.36 | −50.94 | 5.94 | |
| P5 | −0.8160 | −0.2160 | 33.7 | 32.64 | 1.06 | 8.94 | |
| P6 | −0.8132 | −0.8132 | 45.6 | 32.53 | 13.17 | 31.83 | |
| Three transponders | P1 | −0.538 | 0.038 | 60.2 | 21.52 | 38.68 | 1.32 |
| P2 | 0.7088 | 0.0088 | −42.8 | −28.35 | −14.45 | −0.55 | |
| P3 | 0.0135 | 0.0135 | −29.9 | −0.54 | −29.36 | −0.64 | |
| P4 | 0.3862 | 0.0138 | −60.8 | −15.45 | −45.35 | 0.35 | |
| P5 | −0.6314 | −0.0314 | 33.7 | 25.26 | 8.44 | 1.56 | |
| P6 | −0.0281 | −0.0281 | 45.2 | 1.12 | 44.08 | 0.92 | |
| Targets | P1 | P2 | P3 |
| 0.0709 − 0.6750i | 0.9291 − 0.6750i | 0.2652 − 0.8161i | |
| 0.9291 + 0.6750i | 0.0709 + 0.6750i | 0.7348 + 0.8161i | |
| Targets | P4 | P5 | P6 |
| −0.0742 − 0.2283i | 0.6200 + 0.2761i | 0.1606 + 0.1784i | |
| 1.0742 + 0.2283i | 0.3800 − 0.2761i | 0.8394 − 0.1784i |
| Targets | P1 | P2 | P3 |
| −0.3188 + 0.0000i | 0.5393 + 0.0000i | −0.2060 − 0.0000i | |
| 0.5393 + 0.0000i | −0.3188 + 0.0000i | 0.2636 + 0.0000i | |
| 0.7794 − 0.0000i | 0.7794 − 0.0000i | 0.9424 + 0.0000i | |
| Targets | P4 | P5 | P6 |
| −0.2060 − 0.0000i | 0.7794 − 0.0000i | 0.2636 + 0.0000i | |
| 0.9424 + 0.0000i | 0.5393 − 0.0000i | 0.9424 − 0.0000i | |
| 0.2636 − 0.0000i | −0.3188 + 0.0000i | −0.2060 − 0.0000i |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, P.; Xing, S.; Dai, D.; Pang, B. Deceptive Targets Generation Simulation Against Multichannel SAR. Electronics 2020, 9, 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9040597
Ji P, Xing S, Dai D, Pang B. Deceptive Targets Generation Simulation Against Multichannel SAR. Electronics. 2020; 9(4):597. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9040597
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Penghui, Shiqi Xing, Dahai Dai, and Bo Pang. 2020. "Deceptive Targets Generation Simulation Against Multichannel SAR" Electronics 9, no. 4: 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9040597
APA StyleJi, P., Xing, S., Dai, D., & Pang, B. (2020). Deceptive Targets Generation Simulation Against Multichannel SAR. Electronics, 9(4), 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9040597





