Verifying the Effectiveness of New Face Spoofing DB with Capture Angle and Distance
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. PR-FSAD
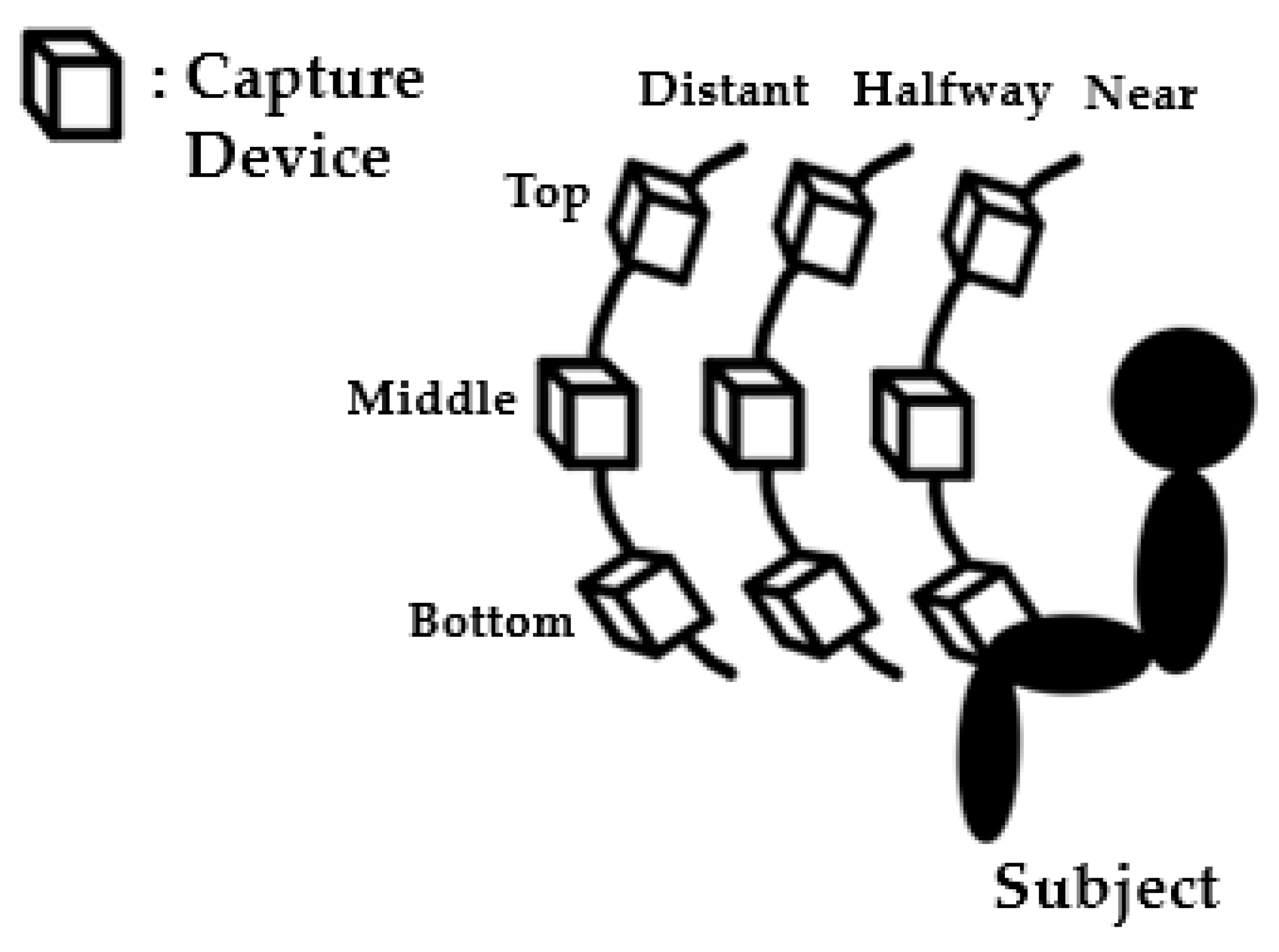
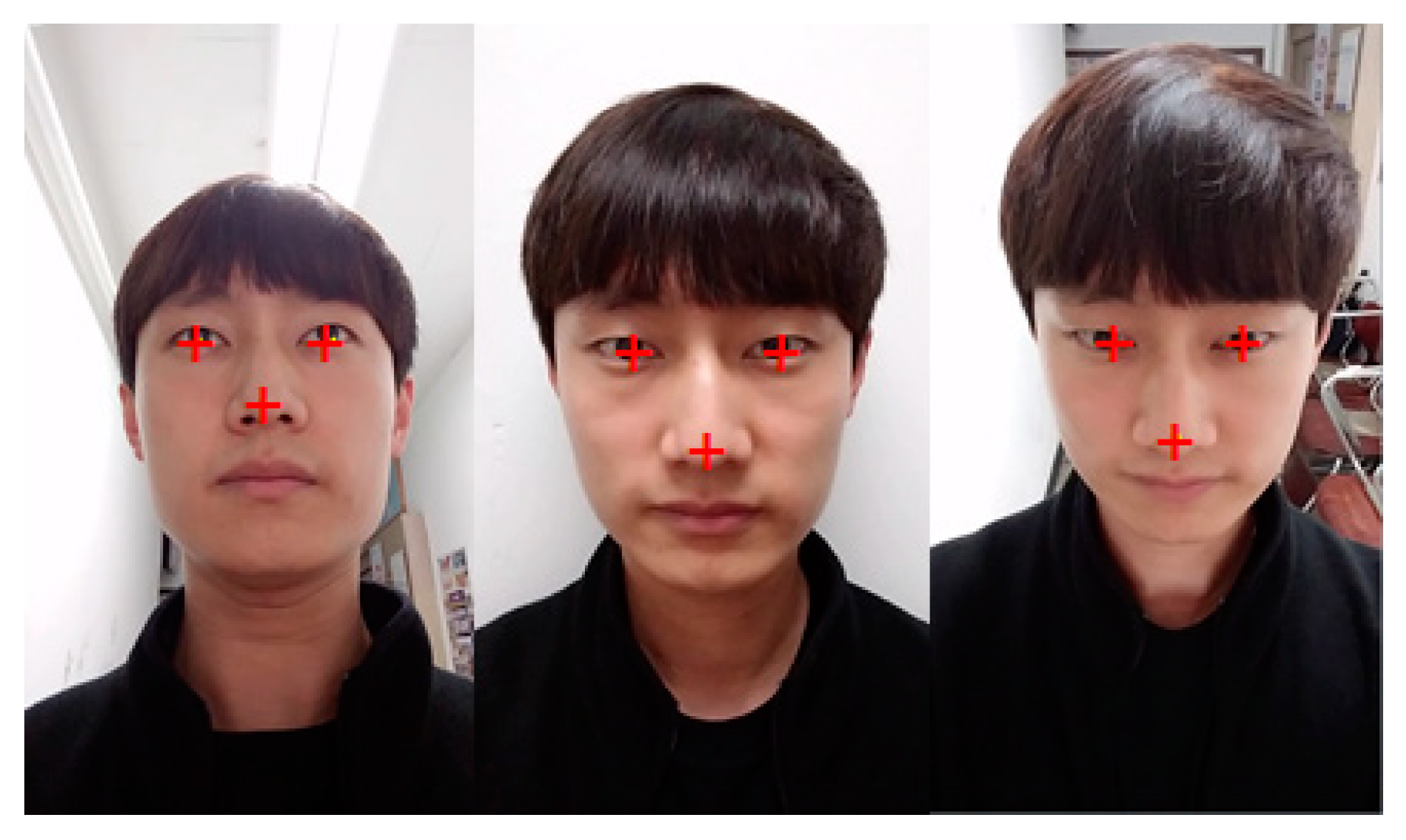
2.1.1. Camera System
2.1.2. Environmental Conditions
2.1.3. Consideration of PR-FSAD
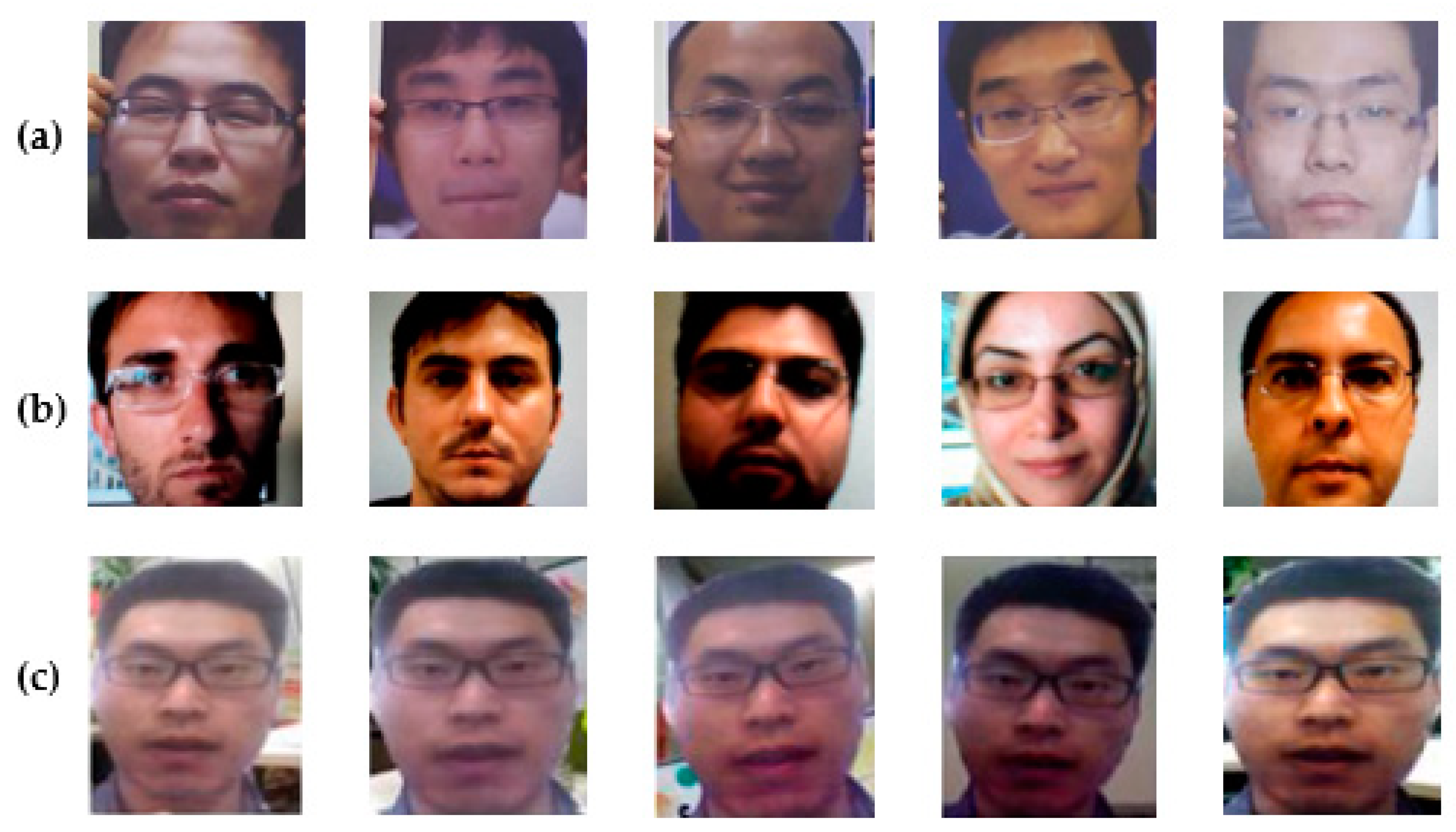
2.1.4. Real Face Database
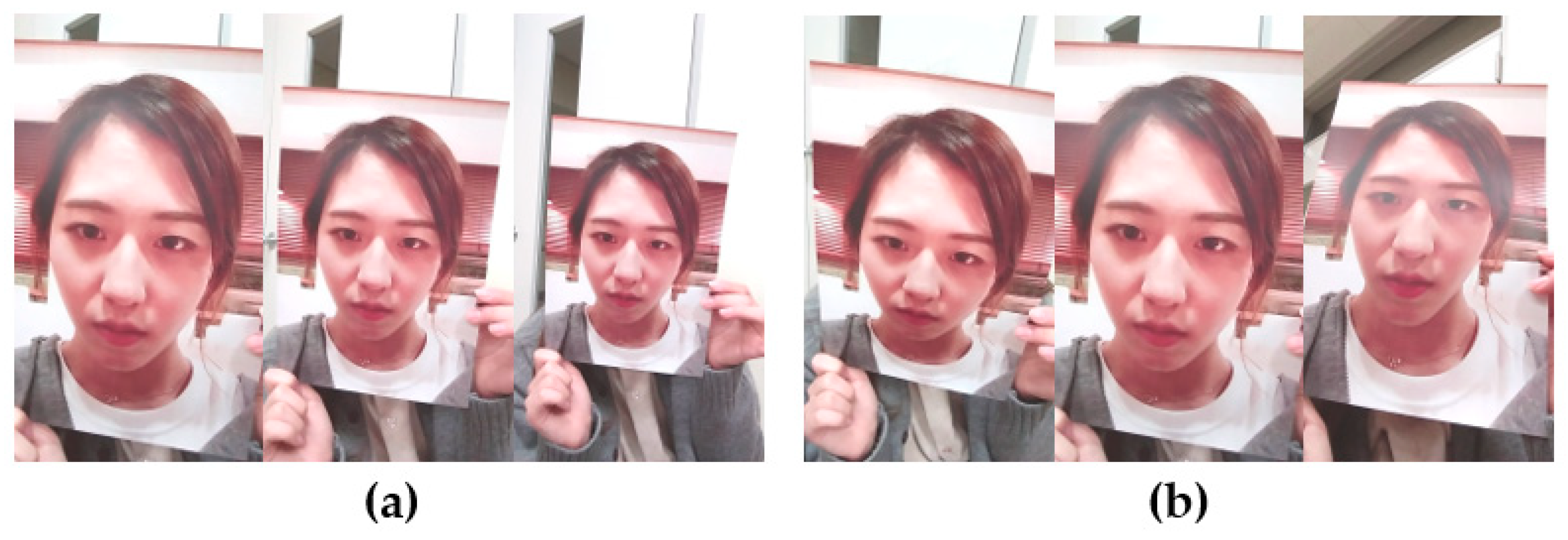
2.1.5. Fake Face Database
2.2. Evaluation Protocols
- Angle test: At each of the three different angles, real and fake data for all the three distances are used:
- Top-angle protocol: use {TN1-3, TH1-3, TD1-3};
- Middle-angle protocol: use {MN1-3, MH1-3, MD1-3};
- Bottom-angle protocol: use {BN1-3, BH1-3, BD1-3}.
- Distance test: To clarify the difference in the distances, the three angles of real and fake data are used for two of the distances, where the halfway distance is excluded:
- Near distance protocol: use {TN1-3, MN1-3, BN1-3};
- Distant distance protocol: use {TD1-3, MD1-3, BD1-3}.
- Counterfeit face test: For all the angles and distances, two types of counterfeit face tests are used:
- Printed photo attack protocol: this uses real and printed photo attack data at all the angles and distances (or uses 1 and 2 at all the angles and distances);
- Replay video attack protocol: this uses real and replay video attack data at all the angles and distances (or uses 1 and 3 at all the angles and distances).
- Overall test: The evaluation test is conducted using all the angles and distances of PR-FSAD:
- Entire data protocol: all the real and fake face data are used.
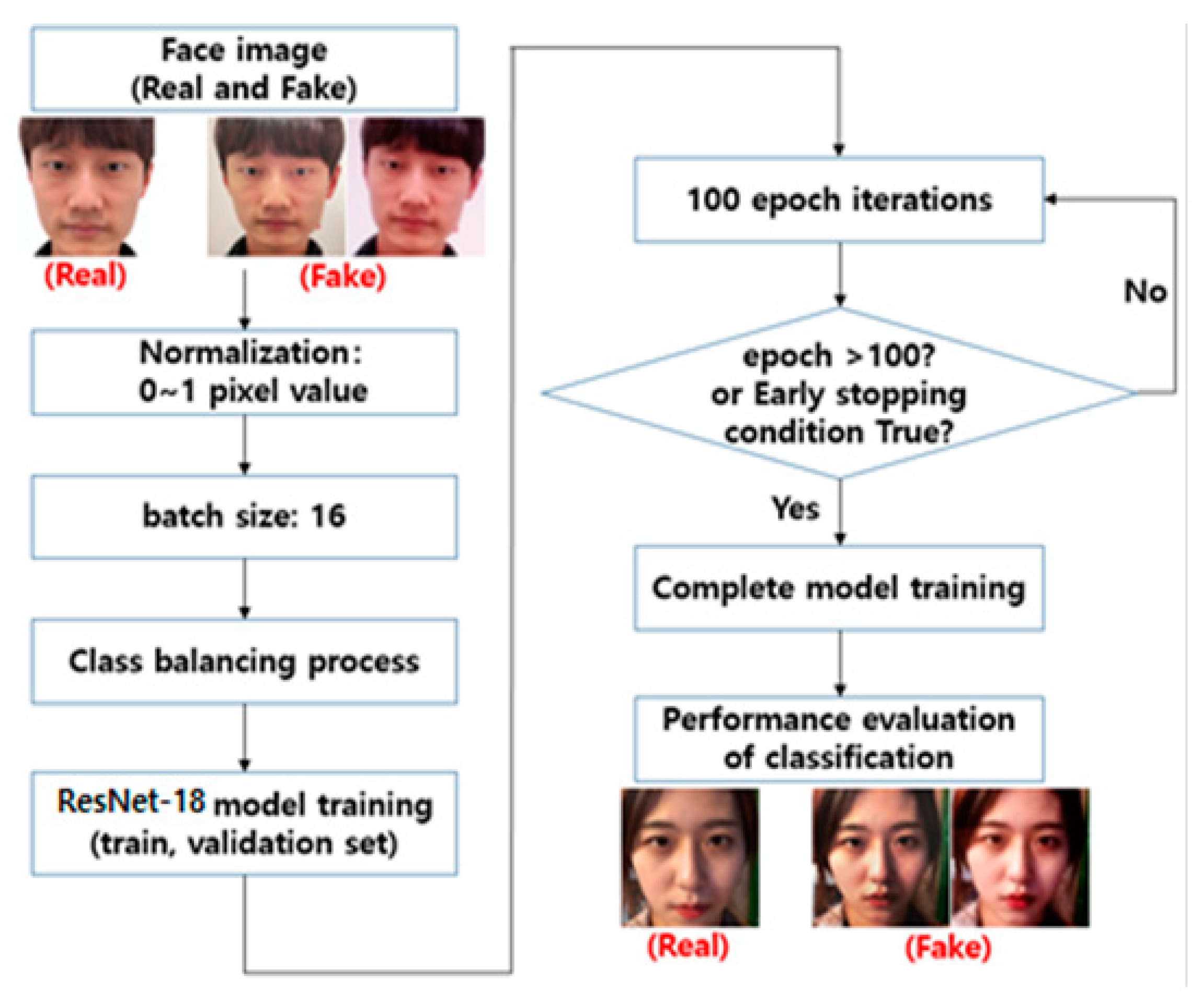
2.3. Face Spoofing Detection Method
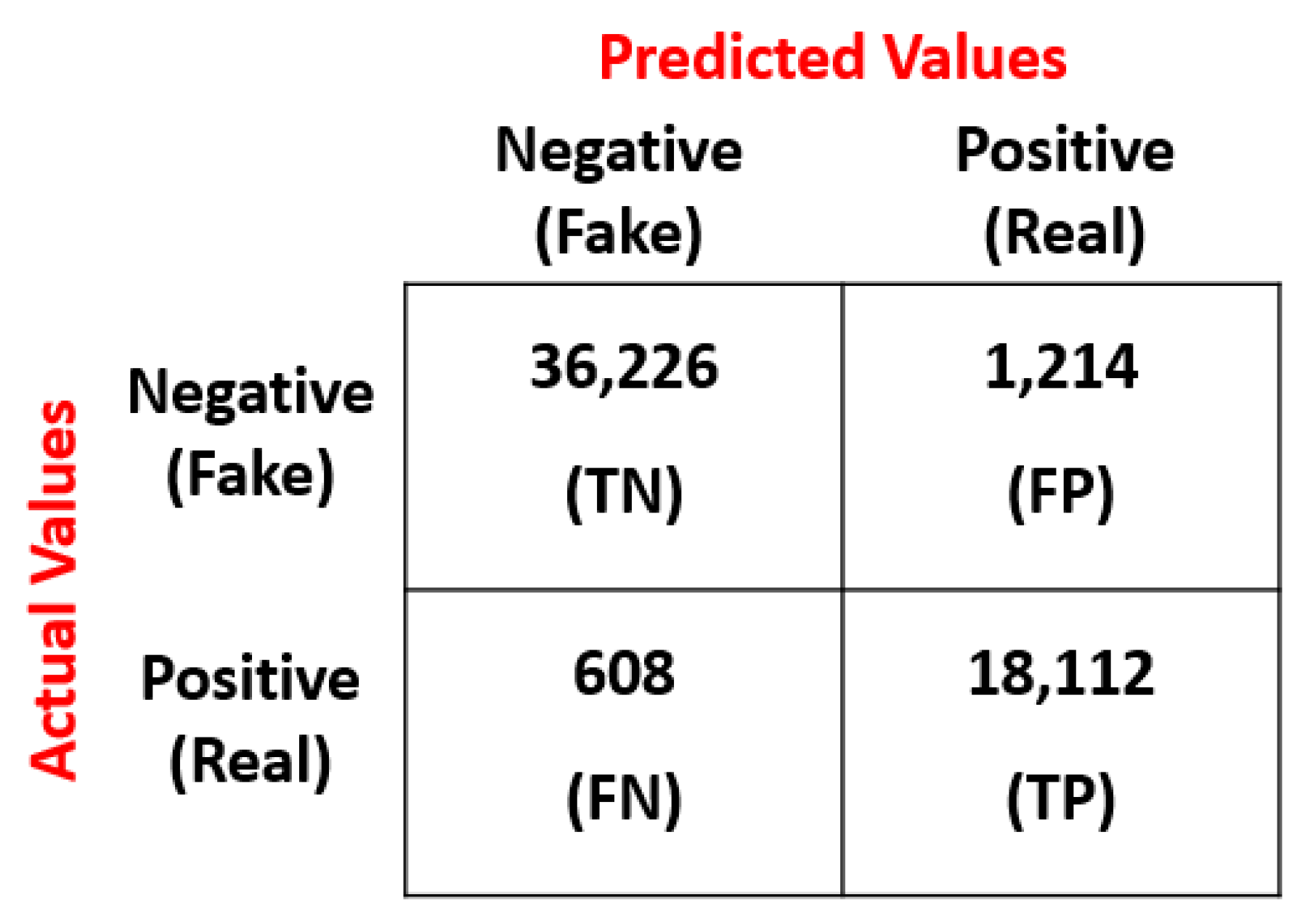
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jain, A.K.; Ross, A.; Pankanti, S. Biometrics: A tool for information security. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2006, 1, 125–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ross, A.; Jain, A. Information fusion in biometrics. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2003, 24, 2115–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.F.; Liao, H.Y.M.; Ko, M.T.; Lin, J.C.; Yu, G.J. A new LDA-based face recognition system which can solve the small sample size problem. Pattern Recognit. 2000, 33, 1713–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeng, S.H.; Liao, H.Y.M.; Han, C.C.; Chern, M.Y.; Liu, Y.T. Facial feature detection using geometrical face model: An efficient approach. Pattern Recognit. 1998, 31, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.C.; Liao, H.Y.M.; Yu, G.J.; Chen, L.H. Fast face detection via morphology-based pre-processing. Pattern Recognit. 2000, 33, 1701–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Chellappa, R.; Phillips, P.J.; Rosenfeld, A. Face recognition: A literature survey. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2003, 35, 399–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahonen, T.; Hadid, A.; Pietikainen, M. Face description with local binary patterns: Application to face recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2006, 28, 2037–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkhi, O.M.; Vedaldi, A.; Zisserman, A. Deep face recognition. BMVC 2015, 1, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gunlu, G.; Bilge, H.S. Face Recognition by Using 3D Discrete Cosine Transform. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE 15th Signal Processing and Communications Applications, Eskisehir, Turkey, 11–13 June 2007; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Yan, S.; Hu, Y.; Niyogi, P.; Zhang, H.J. Face recognition using laplacianfaces. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2005, 27, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Heisele, B.; Blanz, V. Component-based face recognition with 3D morphable models. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Audio-and Video-Based Biometric Person Authentication, Guildford, UK, 9–11 June 2003; pp. 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biggio, B.; Akhtar, Z.; Fumera, G.; Marcialis, G.L.; Roli, F. Security evaluation of biometric authentication systems under real spoofing attacks. IET Biom. 2012, 1, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hadid, A. Face biometrics under spoofing attacks: Vulnerabilities, countermeasures, open issues, and research directions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdogmus, N.; Marcel, S. Spoofing face recognition with 3D masks. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2014, 9, 1084–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Jiang, L. Face liveness detection from a single image with sparse low rank bilinear discriminative model. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Heraklion, Greece, 5–11 September 2010; pp. 504–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georghiades, A.S.; Belhumeur, P.N.; Kriegman, D.J. From few to many: Illumination cone models for face recognition under variable lighting and pose. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2001, 23, 643–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pinto, A.; Schwartz, W.R.; Pedrini, H.; de Rezende Rocha, A. Using visual rhythms for detecting video-based facial spoof attacks. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2015, 10, 1025–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yan, J.; Liu, S.; Lei, Z.; Yi, D.; Li, S.Z. A face antispoofing database with diverse attacks. In Proceedings of the 2012 5th IAPR International Conference on BIOMETRICS (ICB), New Delhi, India, 29 March–1 April 2012; pp. 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chingovska, I.; Anjos, A.; Marcel, S. On the effectiveness of local binary patterns in face anti-spoofing. In Proceedings of the 2012 BIOSIG International Conference of Biometrics Special Interest Group (BIOSIG), Darmstadt, Germany, 6–7 September 2012; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, D.; Han, H.; Jain, A.K. Face spoof detection with image distortion analysis. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2015, 10, 746–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.; Han, H.; Jain, A.K. Secure face unlock: Spoof detection on smartphones. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2016, 11, 2268–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa-Pazo, A.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Vazquez-Fernandez, E.; Marcel, S. The replay-mobile face presentation-attack database. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference of the Biometrics Special Interest Group (BIOSIG), Darmstadt, Germany, 21–23 September 2016; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boulkenafet, Z.; Komulainen, J.; Li, L.; Feng, X.; Hadid, A. OULU-NPU: A mobile face presentation attack database with real-world variations. In Proceedings of the 2017 12th IEEE International Conference on Automatic Face & Gesture Recognition (FG 2017), Washington, DC, USA, 30 May–3 June 2017; pp. 612–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Li, W.; Cao, H.; Wang, S.; Huang, F.; Kot, A.C. Unsupervised domain adaptation for face anti-spoofing. IEEE Trans. Inf. Forensics Secur. 2018, 13, 1794–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: http://pr.smu.ac.kr/patent (accessed on 17 April 2020).
- Gao, W.; Cao, B.; Shan, S.; Chen, X.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, D. The CAS-PEAL large-scale Chinese face database and baseline evaluations. IEEE Trans. Syst. Manand Cybern. Part A Syst. Hum. 2007, 38, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, Z.; Li, Z.; Qiao, Y. Joint face detection and alignment using multitask cascaded convolutional networks. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2016, 23, 1499–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, S.; Zhong, S.; Liu, Y. Deep residual learning for image steganalysis. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2018, 77, 10437–10453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Shichen, L.; Laurens, M.; Kilian, Q.W. CondenseNet: An efficient DenseNet using learned group convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 2752–2761. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, L.; Xiaoyi, F.; Zhaoqiang, X.; Xiaoyue, J.; Abdenour, H. Face spoofing detection with local binary pattern network. J. Vis. Commun. Image Represent. 2018, 54, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, D.M. Evaluation: From precision, recall and F-measure to ROC, informedness, markedness and correlation. J. Mach. Learn Technol. 2011, 2, 37–63. [Google Scholar]







| Year | Database | # of Subjects | # of Samples (Real/Fake) | Attack Type (Medium) | Consideration of Positional Variation between Camera and Face |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | NUAA-PI [15] | 15 | 5105/7509 | printed photo | angle (yaw) |
| 2011 | Yale-Recaptured [16] | 10 | 640/1920 | displayed photo | angle (yaw) |
| 2012 | CASIA-FASD [18] | 50 | 150/450 | printed photo, replayed video | distance |
| 2012 | REPLAY-ATTACK [19] | 50 | 200/1000 | displayed photo, replayed video, printed photo | distance |
| 2014 | MSU-MFSD [20] | 35 | 70/210 | printed photo, replayed video | distance |
| 2015 | UVAD [17] | 404 | 808/16,268 | replayed video | - |
| 2016 | MSU-USSA [21] | 1000 | 1000/8000 | printed photo, displayed photo | - |
| 2016 | REPLAY-MOBILE [22] | 40 | 390/640 | displayed photo, replayed video, printed photo | - |
| 2017 | OULU-NPU [23] | 55 | 990/3960 | printed photo, replayed video | - |
| 2018 | ROSE-Youtu [24] | 20 | 899/2598 | replayed video, printed photo | angle (yaw and pitch) |
| 2019 | Our DB (PR-FSAD) | 30 | 42,480/84,960 | printed photo, replayed video | angle (yaw and pitch), distance |
| Device | Category | Display Size | Pixel/Inch | Spatial Resolution | fps |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Galaxy Tab 3 | Tablet | 7.0 Inch | 170 ppi | 1920 × 1080 | 30 |
| iPad 6 | Tablet | 9.7 Inch | 264 ppi | 1280 × 720 | 30 |
| iPhone X | Smartphone | 5.8 Inch | 463 ppi | 1920 × 1080 | 30 |
| Nexus 5X | Smartphone | 5.2 Inch | 424 ppi | 1920 × 1080 | 30 |
| Protocols 1–4 | Number of Images | Total Processing Time (s) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training (32.2%) | Validation (23.7%) | Test (44.1%) | Training | Test | ||
| 1 | Top | 13,680 | 10,080 | 18,720 | 1898 | 374 (20.0 ms/image) |
| Middle | 13,680 | 10,080 | 18,720 | 1920 | 376 (20.1 ms/image) | |
| Bottom | 13,680 | 10,080 | 18,720 | 1886 | 374 (20.0 ms/image) | |
| 2 | Near | 13,680 | 10,080 | 18,720 | 1869 | 372 (19.9 ms/image) |
| Distant | 13,680 | 10,080 | 18,720 | 1906 | 375 (20.0 ms/image) | |
| 3 | 27,360 | 20,160 | 37,440 | 3895 | 751 (20.1 ms/image) | |
| Replay | 27,360 | 20,160 | 37,440 | 3912 | 755 (20.2 ms/image) | |
| 4 | Total | 41,040 | 30,240 | 56,160 | 5985 | 1132 (20.2 ms/image) |
| Protocol 1–4 | HTER (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Top | 2.34 |
| Middle | 4.96 | |
| Bottom | 2.84 | |
| 2 | Near | 1.41 |
| Distant | 4.24 | |
| 3 | 5.36 | |
| Replay | 3.60 | |
| 4 | Total | 3.25 |
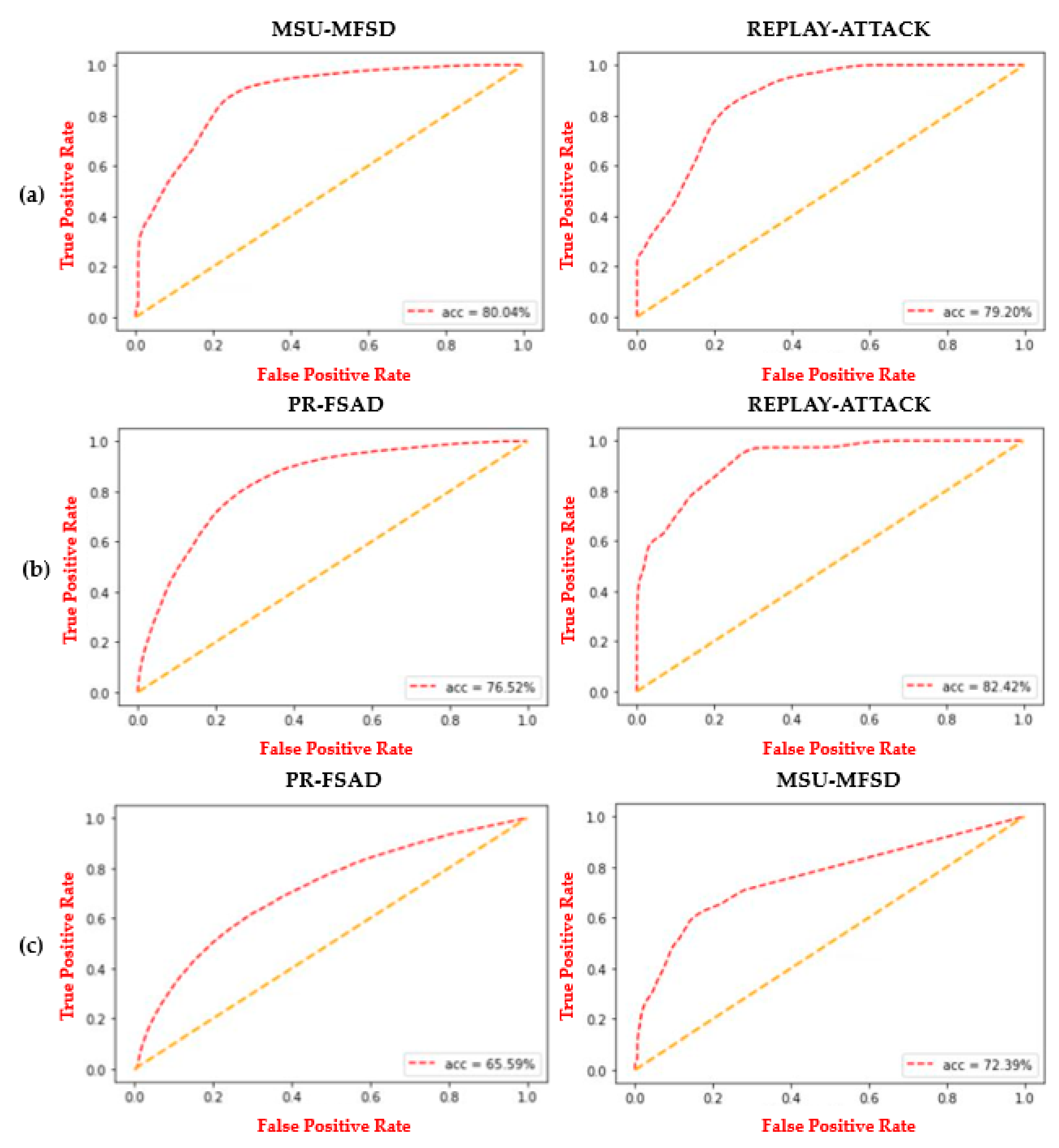
| Cross-Database Scenarios | HTER (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ResNet-18 | DenseNet | LBP | ||
| PR-FSAD | MSU-MFSD | 19.96 | 18.52 | 23.10 |
| REPLAY-ATTACK | 20.80 | 19.67 | 25.12 | |
| MSU-MFSD | PR-FSAD | 23.48 | 25.21 | 28.36 |
| REPLAY-ATTACK | 17.58 | 18.36 | 21.53 | |
| REPLAY-ATTACK | PR-FSAD | 34.41 | 32.23 | 35.36 |
| MSU-MFSD | 28.44 | 30.81 | 33.29 | |
| Cross-Database Scenarios | HTER (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ResNet-18 | DenseNet | LBP | ||
| PR-FSAD | MSU-MFSD | 13.45% | 14.28% | 21.15% |
| REPLAY-ATTACK | 14.93 | 16.50% | 23.96% | |
| MSU-MFSD | PR-FSAD | 16.36% | 17.13% | 23.83% |
| REPLAY-ATTACK | 17.58% | 18.36% | 21.53% | |
| REPLAY-ATTACK | PR-FSAD | 18.76% | 18.37% | 30.21% |
| MSU-MFSD | 28.44% | 30.81% | 33.29% | |
| Training with only Front Face Image | Training with Total Image | |
|---|---|---|
| Processing time (ms) | 320/20 | 321/20 |
| Accuracy (HTER (%)) | 5.12 | 3.25 |
| Test | Galaxy Tab 3 | iPad 6 | iPhone X | Nexus 5X | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training | |||||
| Galaxy Tab 3 | 3.32 | 3.30 | 3.29 | 3.25 | |
| iPad 6 | 3.18 | 3.17 | 3.20 | 3.21 | |
| iPhone X | 3.18 | 3.25 | 3.23 | 3.19 | |
| Nexus 5X | 3.32 | 3.28 | 3.26 | 3.28 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bok, J.Y.; Suh, K.H.; Lee, E.C. Verifying the Effectiveness of New Face Spoofing DB with Capture Angle and Distance. Electronics 2020, 9, 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9040661
Bok JY, Suh KH, Lee EC. Verifying the Effectiveness of New Face Spoofing DB with Capture Angle and Distance. Electronics. 2020; 9(4):661. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9040661
Chicago/Turabian StyleBok, Jin Yeong, Kun Ha Suh, and Eui Chul Lee. 2020. "Verifying the Effectiveness of New Face Spoofing DB with Capture Angle and Distance" Electronics 9, no. 4: 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9040661
APA StyleBok, J. Y., Suh, K. H., & Lee, E. C. (2020). Verifying the Effectiveness of New Face Spoofing DB with Capture Angle and Distance. Electronics, 9(4), 661. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9040661





