A Sub-Threshold Differential CMOS Schmitt Trigger with Adjustable Hysteresis Based on Body Bias Technique
Abstract
:1. Introduction
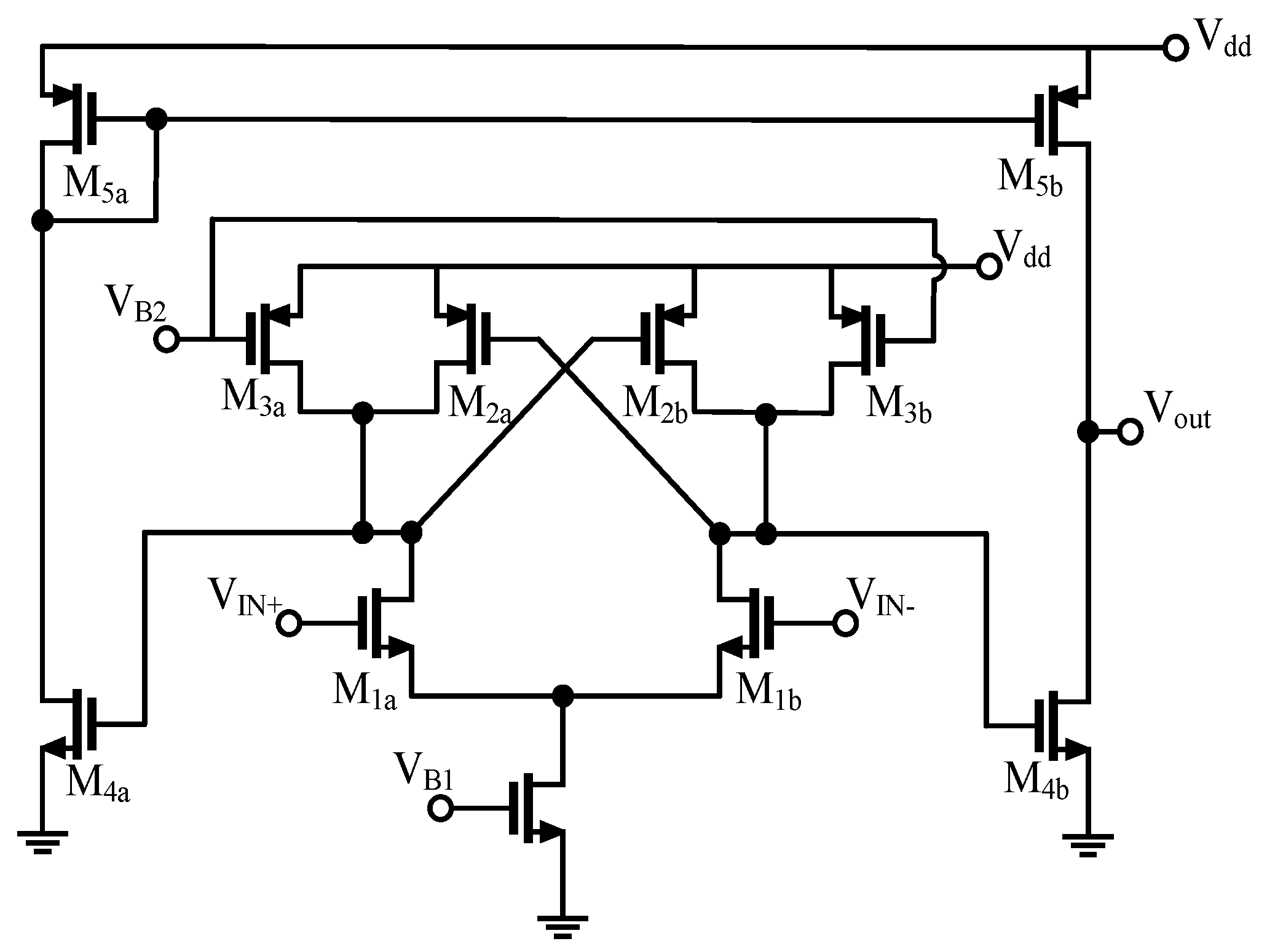
2. Proposed Schmitt Trigger Circuit Description
2.1. Differential Pair of the Circuit
2.2. Two-Stage Schmitt Trigger Circuit
2.3. Proposed Structure of the Two-Stage Schmitt Trigger with Adjustable Hysteresis
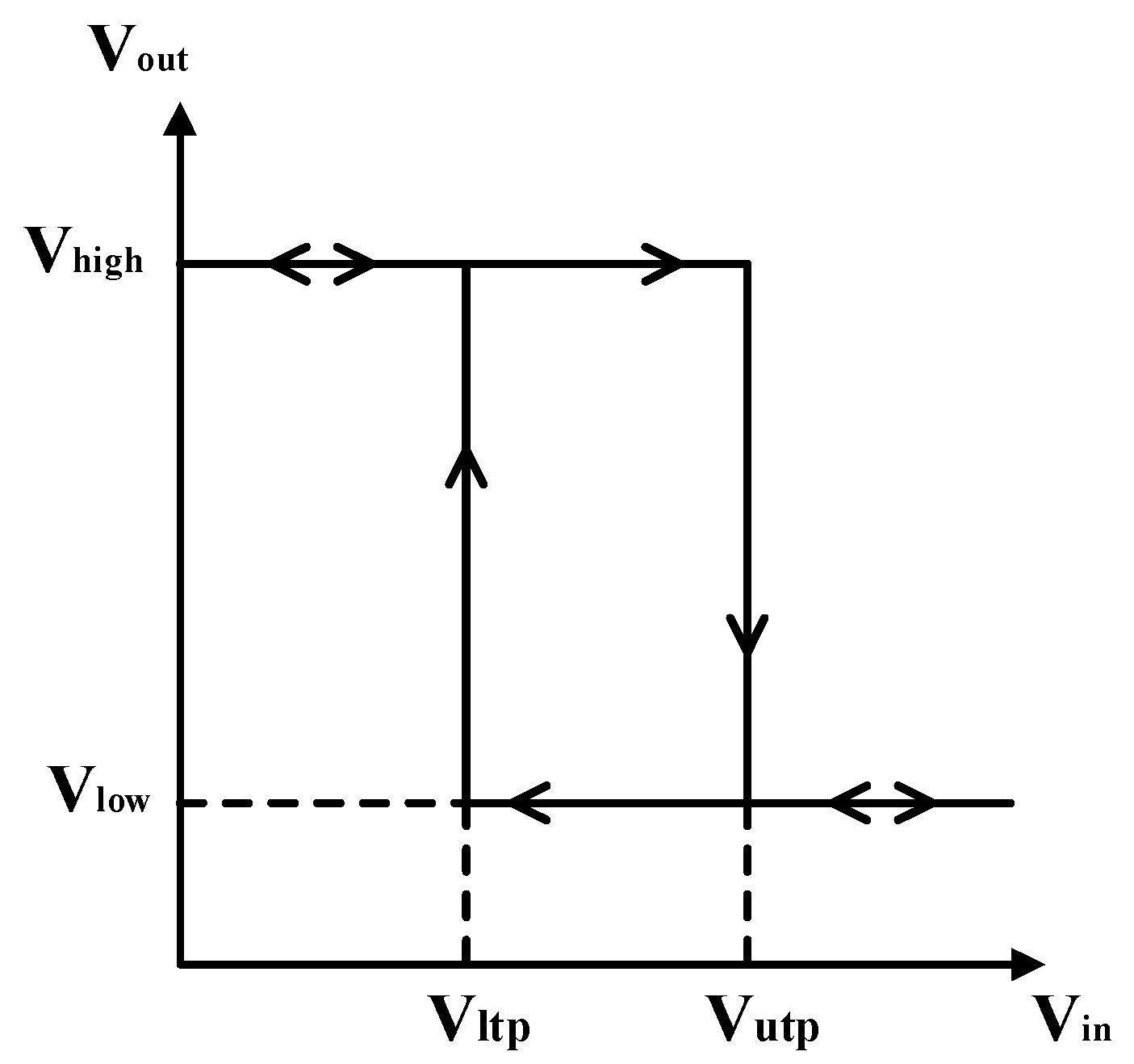
3. Post-Layout Simulation Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sansen, W. Analog Design Essentials; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Rajput, S.; Jamuar, S. Low Voltage Analog Circuit Design Techniques. IEEE Circuits Syst. Mag. 2002, 2, 24–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calhoun, B.; Chandrakasan, A. A 256-Kb 65-Nm Sub-Threshold SRAM Design for Ultra-Low-Voltage Operation. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2007, 42, 680–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Mohammadi, S. A 3GHz Subthreshold CMOS Low Noise Amplifier. In Proceedings of the IEEE Radio Frequency Integrated Circuits (RFIC) Symposium, San Francisco, CA, USA, 10–13 June 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kulkarni, J.; Roy, K. Ultralow-Voltage Process-Variation-Tolerant Schmitt-Trigger-Based SRAM Design. IEEE Trans. on Very Large Scale Integr. (VLSI) Syst. 2012, 20, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotze, N.; Manoli, Y. A 62 mV 0.13 µm CMOS Standard-Cell-Based Design Technique Using Schmitt-Trigger Logic. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2012, 47, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tache, M.; Ibrahim, W.; Kharbash, F.; Beiu, V. Reliability and Performance of Optimised Schmitt Trigger Gates. J. Eng. 2018, 2018, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F. Differential CMOS Schmitt Trigger with Tunable Hysteresis. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 2009, 62, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagiwara, T.; Yamaguchi, K.; Shojiro, A. Threshold voltage deviation in very small MOS transistors due to local impurity fluctuations. In Proceedings of the 1982 Symposium on VLSI Technology. Digest of Technical Papers, Oiso, Japan, 1–3 September 1982; pp. 46–47. [Google Scholar]
- Saxena, A.; Akashe, S. Comparative Analysis of Schmitt Trigger with AVL (AVLG and AVLS) Technique Using Nanoscale CMOS Technology. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Advanced Computing and Communication Technologies (ACCT), Rohtak, India, 6–7 April 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Nandhasri, K.; Ngarmnil, J. Hysteresis tunable FGMOS comparator. In Proceedings of the ICSE 2000, 2000 IEEE International Conference on Semiconductor Electronics. Proceedings (Cat. No.00EX425), Guoman Port Dickson Resort, Malaysia, 13–15 November 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Ekekwe, N.; Etienne-Cummings, R. Adaptive Hysteretic Comparator with Op-amp Threshold Level Setting. In Proceedings of the 51st Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Knoxville, TN, USA, 10–13 August 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Goll, B.; Zimmermann, H. Comparators in Nanometer CMOS Technology; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Amiri, P.; Nabavi, A.; Mortazavi, S. Low Distortion CMOS Class-D Amplifier with Double-Band Hysteresis. IEICE Electron. Express 2010, 7, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, F. A High-Speed Differential CMOS Schmitt Trigger with Regenerative Current Feedback and Adjustable Hysteresis. Analog Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 2009, 63, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allstot, D. A Precision Variable-Supply CMOS Comparator. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 1982, 17, 1080–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minaei, S.; Yuce, E. A Simple Schmitt Trigger Circuit with Grounded Passive Elements and Its Application to Square/Triangular Wave Generator. Circuits Syst. Signal Process. 2011, 31, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Chaturvedi, B. Single Active Element-Based Tunable Square/Triangular Wave Generator with Grounded Passive Components. Circuitssyst. Signal Process. 2017, 36, 3875–3900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, W.; Kim, H.; Cha, H.; Kim, H. Triangular/Square-Wave Generator with Independently Controllable Frequency and Amplitude. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2005, 54, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onomi, T. Experimental Demonstration and Performance Estimation of a New Relaxation Oscillator Using a Superconducting Schmitt Trigger Inverter. Phys. Procedia 2016, 81, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, D.; Khatri, R. Function Generator Using Current Conveyor (CCII). Int. J. Comput. Appl. 2016, 147, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chien, H.-C.; Lo, Y.-K. Design and Implementation of Monostable Multivibrators Employing Differential Voltage Current Conveyors. Microelectron. J. 2011, 42, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B. Phase-Shift PWM Converter with Wide Voltage Operation Capability. Electronics 2019, 9, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Newsom, R.; Dillard, W.; Nelms, R. Digital Power-Factor Correction for a Capacitor-Charging Power Supply. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2002, 49, 1146–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejati, A.; Bastan, Y.; Amiri, P.; Maghami, M. A Low-Voltage Bulk-Driven Differential CMOS Schmitt Trigger with Tunable Hysteresis. J. Circuitssystems Comput. 2019, 28, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kim, K.; Huynh, H.A.; Joo, S.; Kim, S. EM Noise Immunity Enhancement Using Schmitt Trigger Logic Gates in CMOS Process. In Proceedings of the URSI Asia-Pacific Radio Science Conference (URSI AP-RASC), Seoul, Korea, 21–25 August 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Nejati, A.; Bastan, Y.; Amiri, P. 0.4 V Ultra-Low Voltage Differential CMOS Schmitt Trigger. In Proceedings of the Iranian Conference on Electrical Engineering (ICEE), Tehran, Iran, 2–4 May 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Melek, L.A.P.; Silva, A.L.D.; Schneider, M.C.; Galup-Montoro, C. Analysis and Design of the Classical CMOS Schmitt Trigger in Subthreshold Operation. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2017, 64, 869–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, S. A High-Speed Low Voltage CMOS Schmitt Trigger with Adjustable Hysteresis. In Proceedings of the IEEE/ACIS 16th International Conference on Computer and Information Science (ICIS), Wuhan, China, 24–26 May 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bastan, Y.; Nejati, A.; Radfar, S.; Amiri, P.; Nasrollahpour, M.; Hamedi-Hagh, S. An Ultra-Low-Voltage Sub-Threshold Pseudo-Differential CMOS Schmitt Trigger. In Proceedings of the 31st IEEE International System-on-Chip Conference (SOCC), Arlington, VA, USA, 4–7 September 2018. [Google Scholar]















| Transistor | W/L |
|---|---|
| M1a,b | 0.44 µm/0.18 µm |
| M2a,b | 0.88 µm/0.18 µm |
| M3a,b | 0.44 µm/0.18 µm |
| M4a,b | 0.44 µm/0.18 µm |
| M5a,b | 0.88 µm/0.18 µm |
| Mt | 0.44 µm/0.18 µm |
| This Work | [15] | [25] | [26] | [27] | [28] | [29] | [30] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technology | 0.18 µm CMOS | 0.18 µm CMOS | 0.18 µm CMOS | 0.18 µm CMOS | 0.18 µm CMOS | 0.18 µm CMOS | 40 nm CMOS | 0.18 µm CMOS |
| Power Supply | 0.6 V | 1.8 V | 0.8 V | 0.6 V | 0.4 V | 0.15 V | 1 V | 0.4 V |
| Single/Differential Input | Diff. | Diff. | Diff. | Single | Diff. | Single | Single | Pseudo Diff. |
| V/I Mode | Current Mode (I) | Current Mode (I) | Current Mode (I) | Voltage Mode (V) | Current Mode (I) | Current Mode (I) | Voltage Mode (V) | Current Mode (I) |
| Variable/Fixed Hysteresis | Variable | Variable | Variable | Fixed | Fixed | Fixed | Variable | Fixed |
| 19.4% | 6.66% | 12.5% | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.8% | 0 | |
| Power Consumption | 1.38 µW | - | 0.48–1.12 mW | 2.64 mW | - | - | - | 150 nW |
| Chip Area | (10.52 × 7.91) μm2 | - | (39 × 17.5) µm2 | - | - | (20.37 × 10.41) µm2 | - | (14.8 × 7) µm2 |
| No. of Transistors | 11 + bias | 13 | 16 + bias | 9 | 14 + bias | 6 | 6 | 10 + bias |
| Simulation/Measurement | Post-layout Sim. | Sim. | Post-layout Sim. | Meas. | Sim. | Meas. | Sim. | Post-layout Sim. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Radfar, S.; Nejati, A.; Bastan, Y.; Amiri, P.; Maghami, M.H.; Nasrollahpour, M.; Hamedi-Hagh, S. A Sub-Threshold Differential CMOS Schmitt Trigger with Adjustable Hysteresis Based on Body Bias Technique. Electronics 2020, 9, 806. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9050806
Radfar S, Nejati A, Bastan Y, Amiri P, Maghami MH, Nasrollahpour M, Hamedi-Hagh S. A Sub-Threshold Differential CMOS Schmitt Trigger with Adjustable Hysteresis Based on Body Bias Technique. Electronics. 2020; 9(5):806. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9050806
Chicago/Turabian StyleRadfar, Sara, Ali Nejati, Yasin Bastan, Parviz Amiri, Mohammad Hossein Maghami, Mehdi Nasrollahpour, and Sotoudeh Hamedi-Hagh. 2020. "A Sub-Threshold Differential CMOS Schmitt Trigger with Adjustable Hysteresis Based on Body Bias Technique" Electronics 9, no. 5: 806. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9050806
APA StyleRadfar, S., Nejati, A., Bastan, Y., Amiri, P., Maghami, M. H., Nasrollahpour, M., & Hamedi-Hagh, S. (2020). A Sub-Threshold Differential CMOS Schmitt Trigger with Adjustable Hysteresis Based on Body Bias Technique. Electronics, 9(5), 806. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9050806






