Agent-Based In-Vehicle Infotainment Services in Internet-of-Things Environments
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Works
2.1. IVI Systems/Services by Industry
2.2. Centralized IVI System (C-IVI)
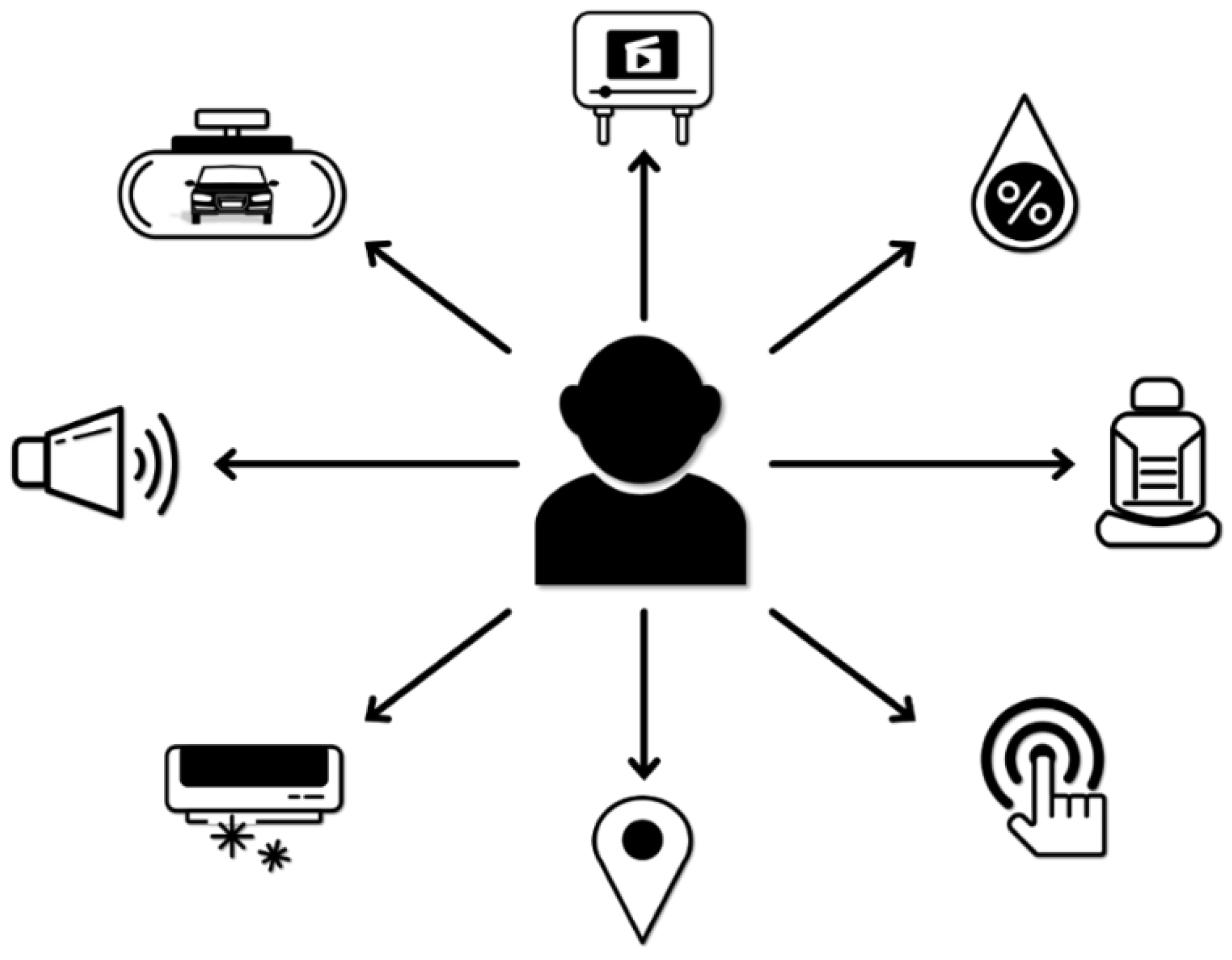
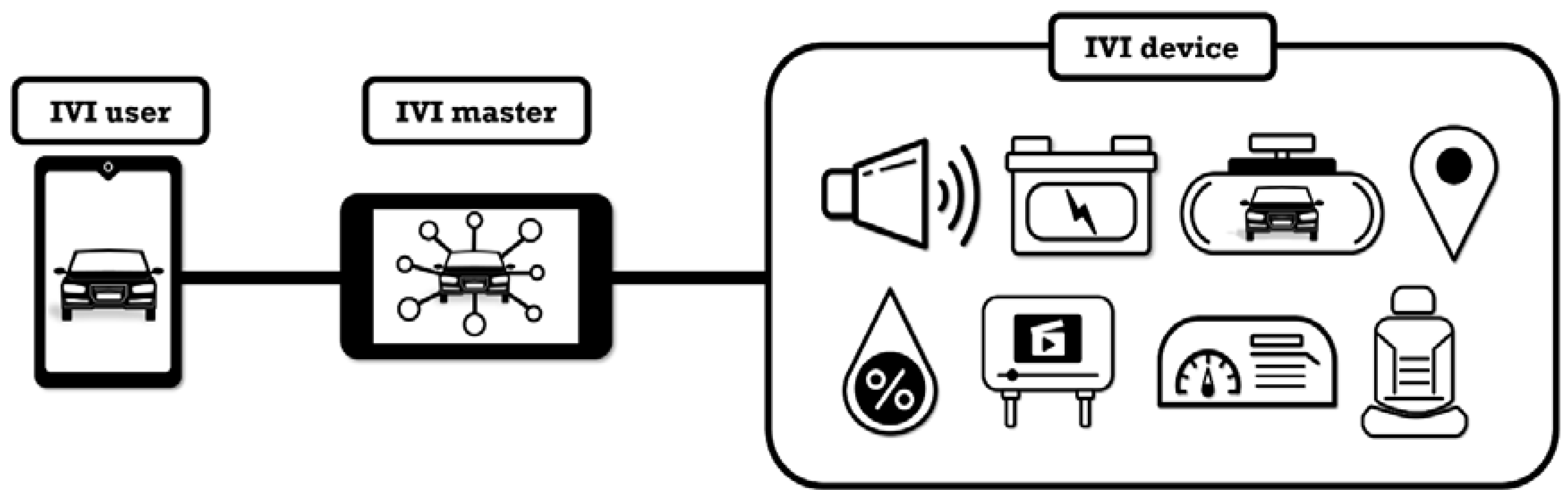
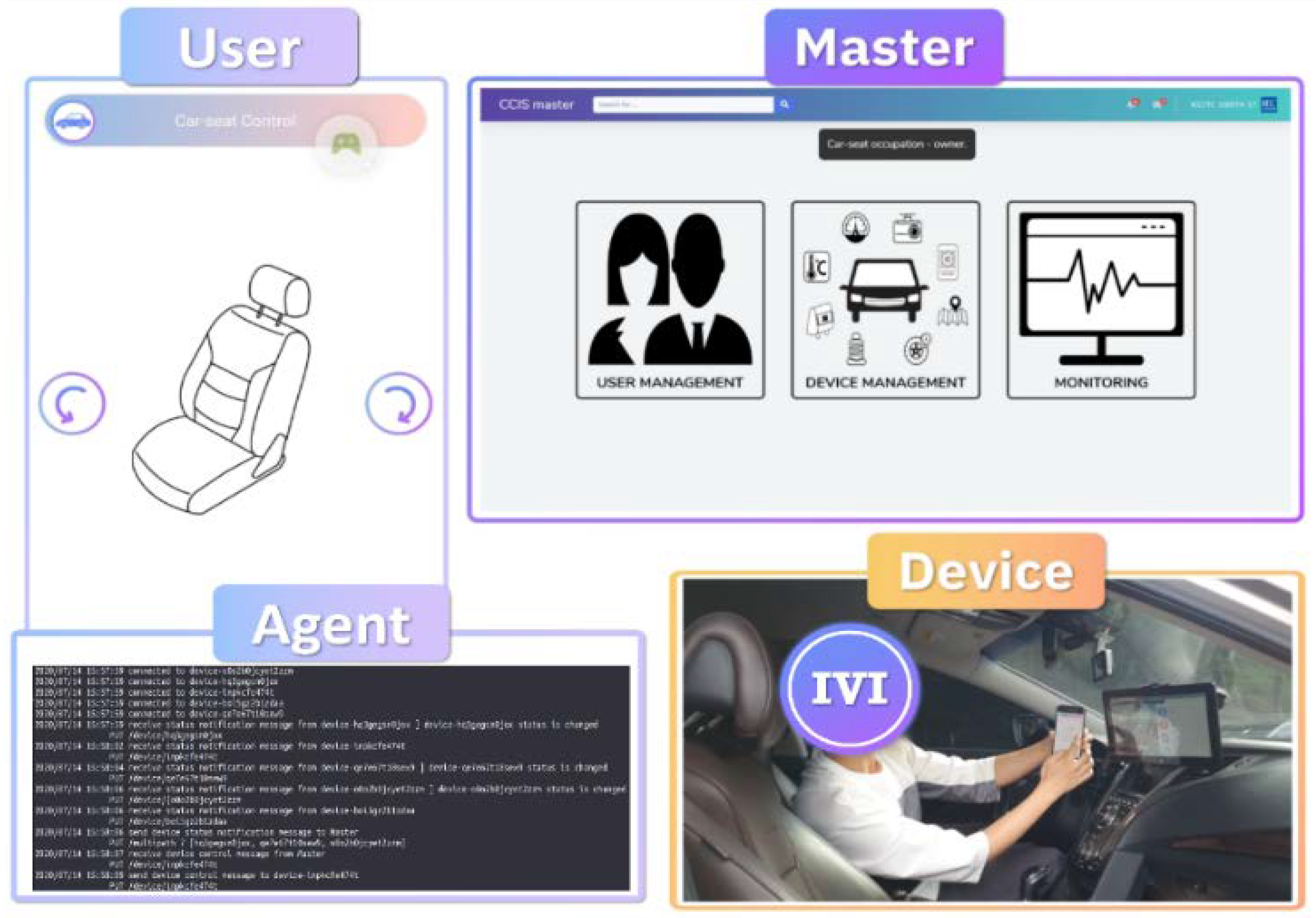
3. Proposed Agent-Based IVI (A-IVI) System
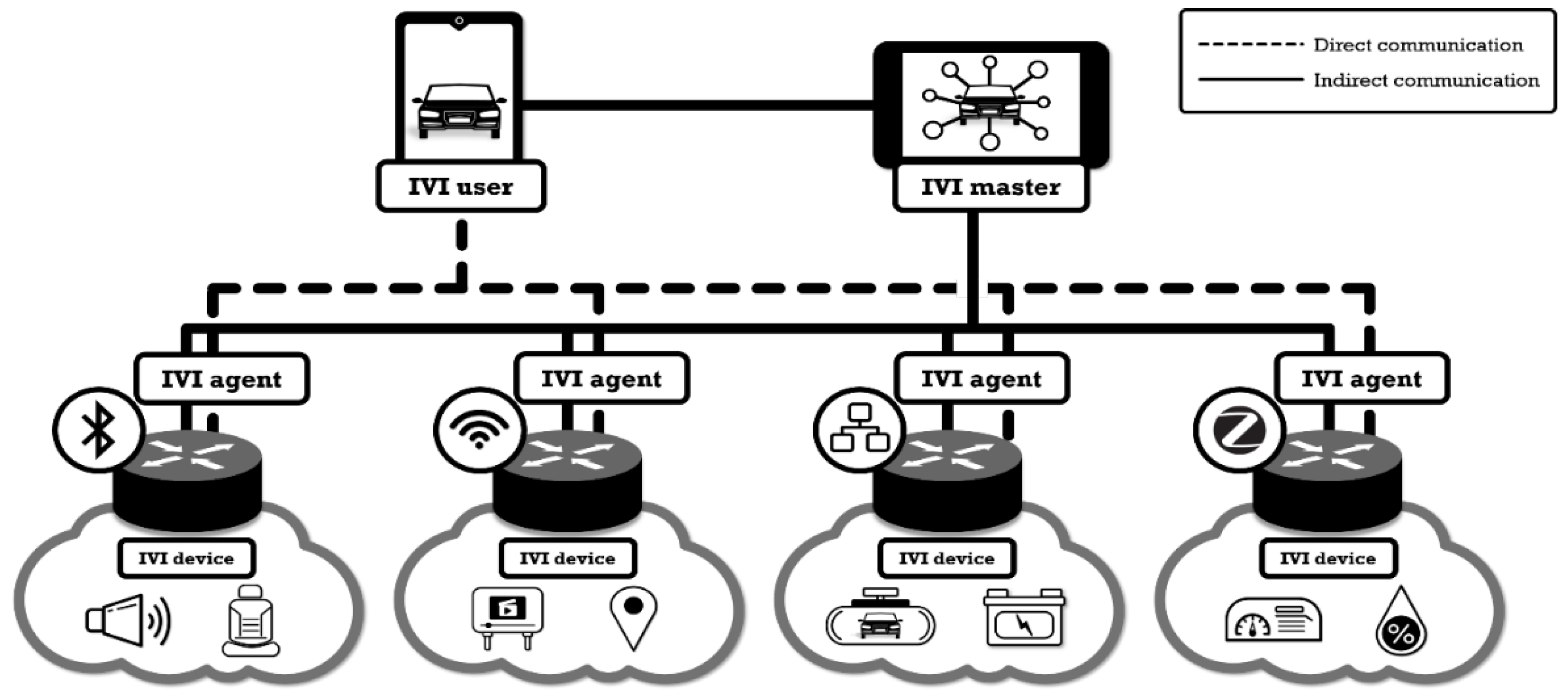
3.1. System Architecture for A-IVI
3.2. A-IVI Functions
3.2.1. Registration
3.2.2. Authentication Management
3.2.3. Device Control
3.2.4. Device Monitoring
3.2.5. Profile Management
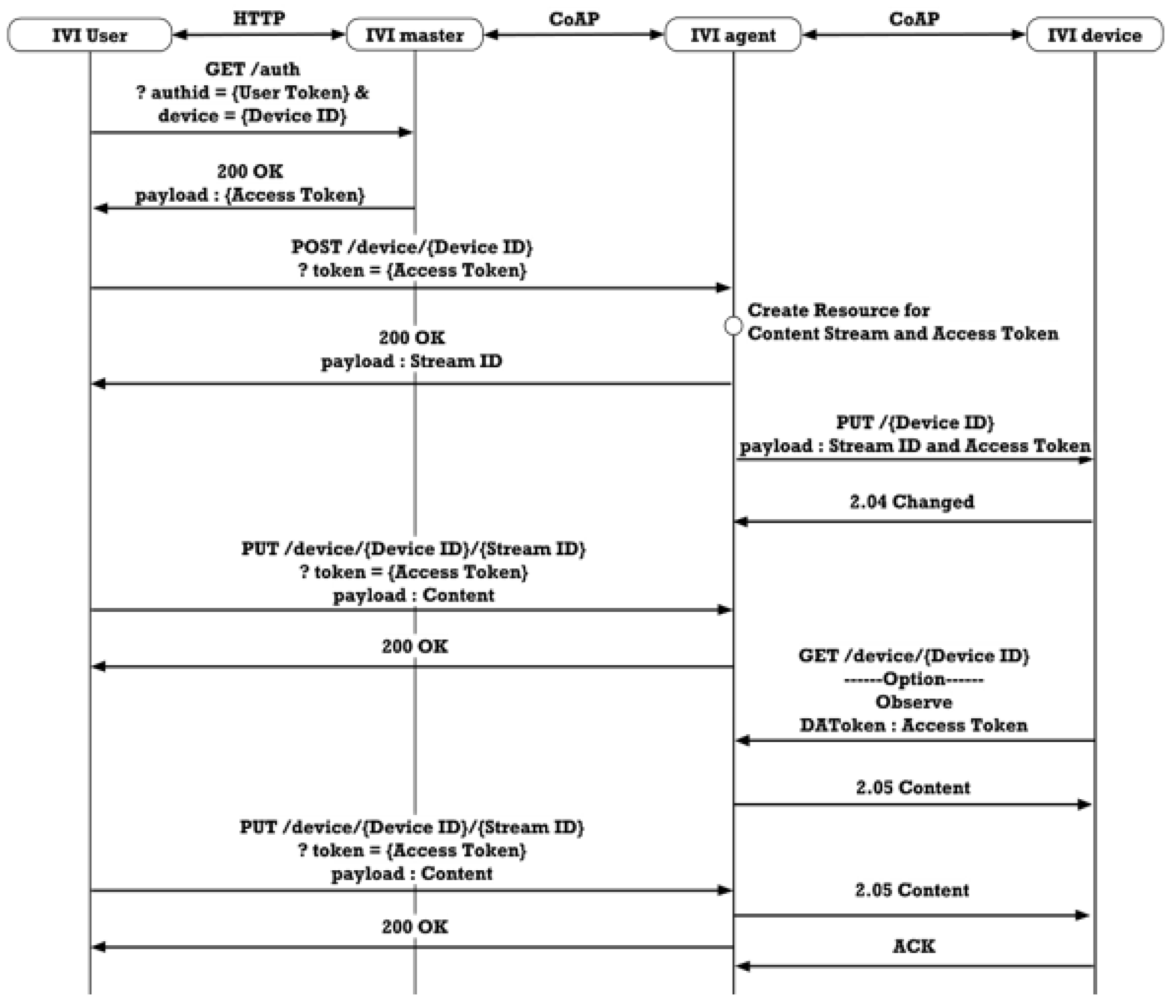
3.2.6. Content Delivery
3.3. A-IVI Communication Mechanisms
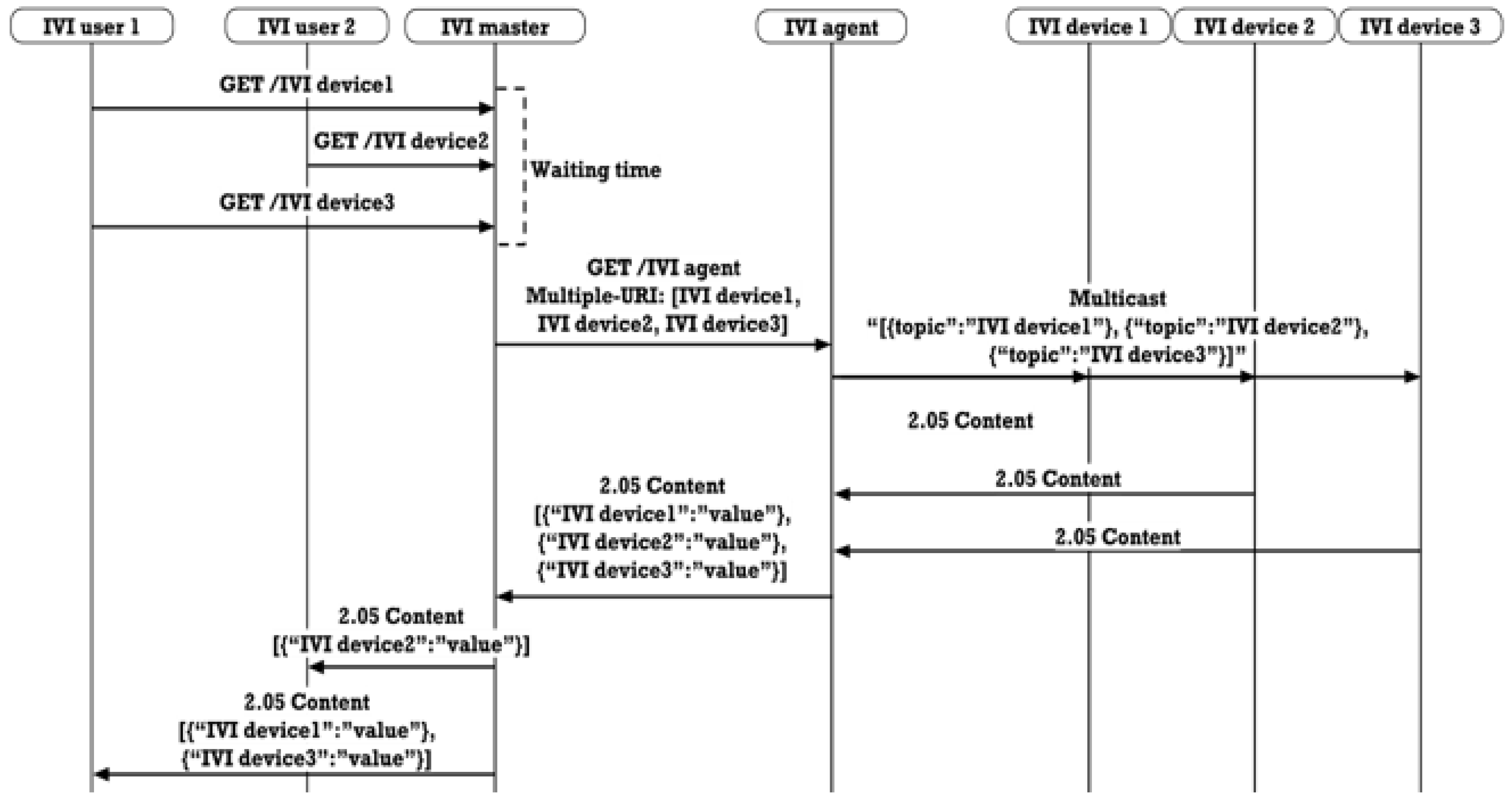
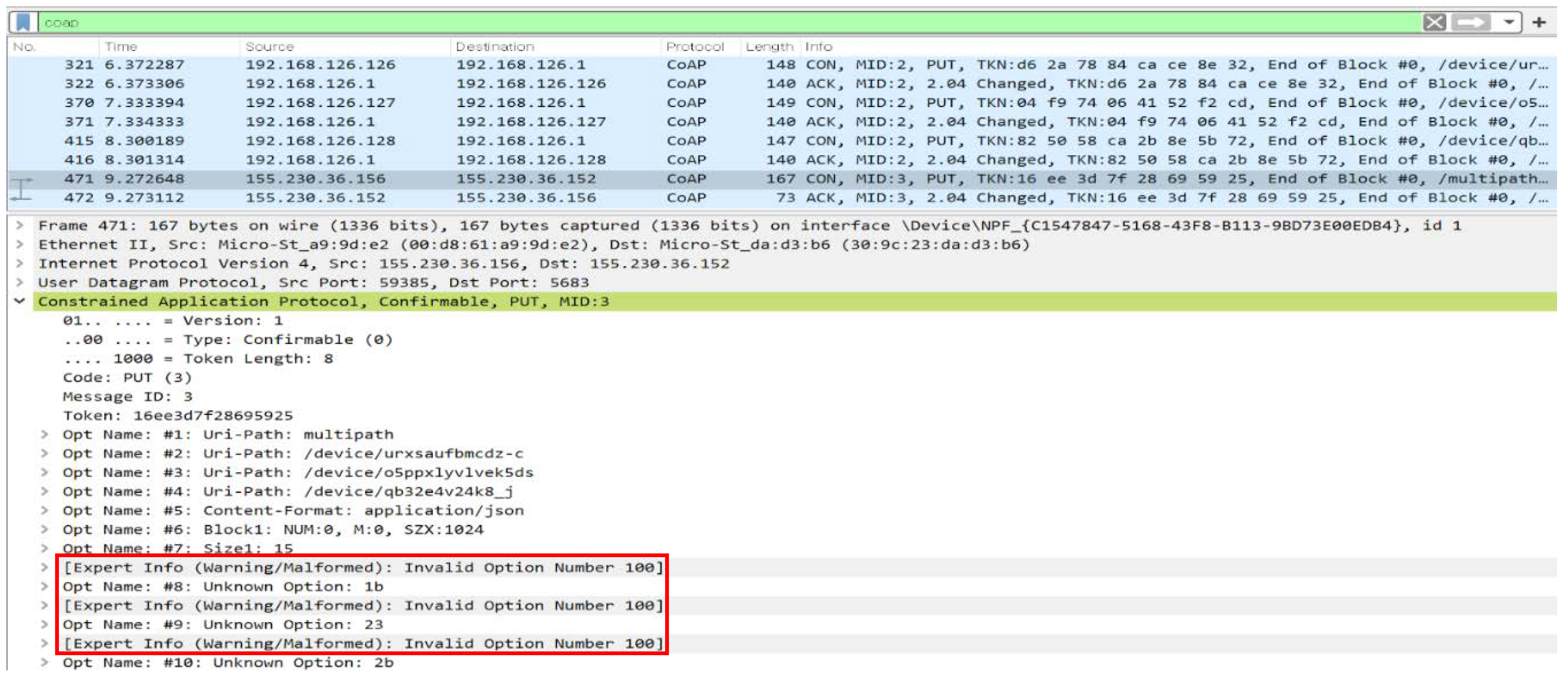
3.3.1. Multiple URI Communication
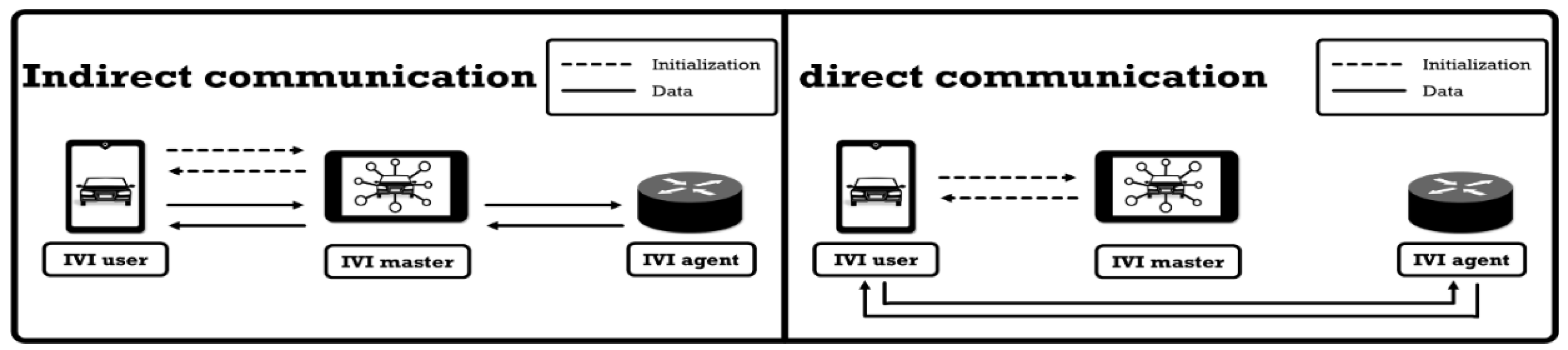
3.3.2. Indirect and Direct Communications
3.4. Operations for Registration and Data Communication
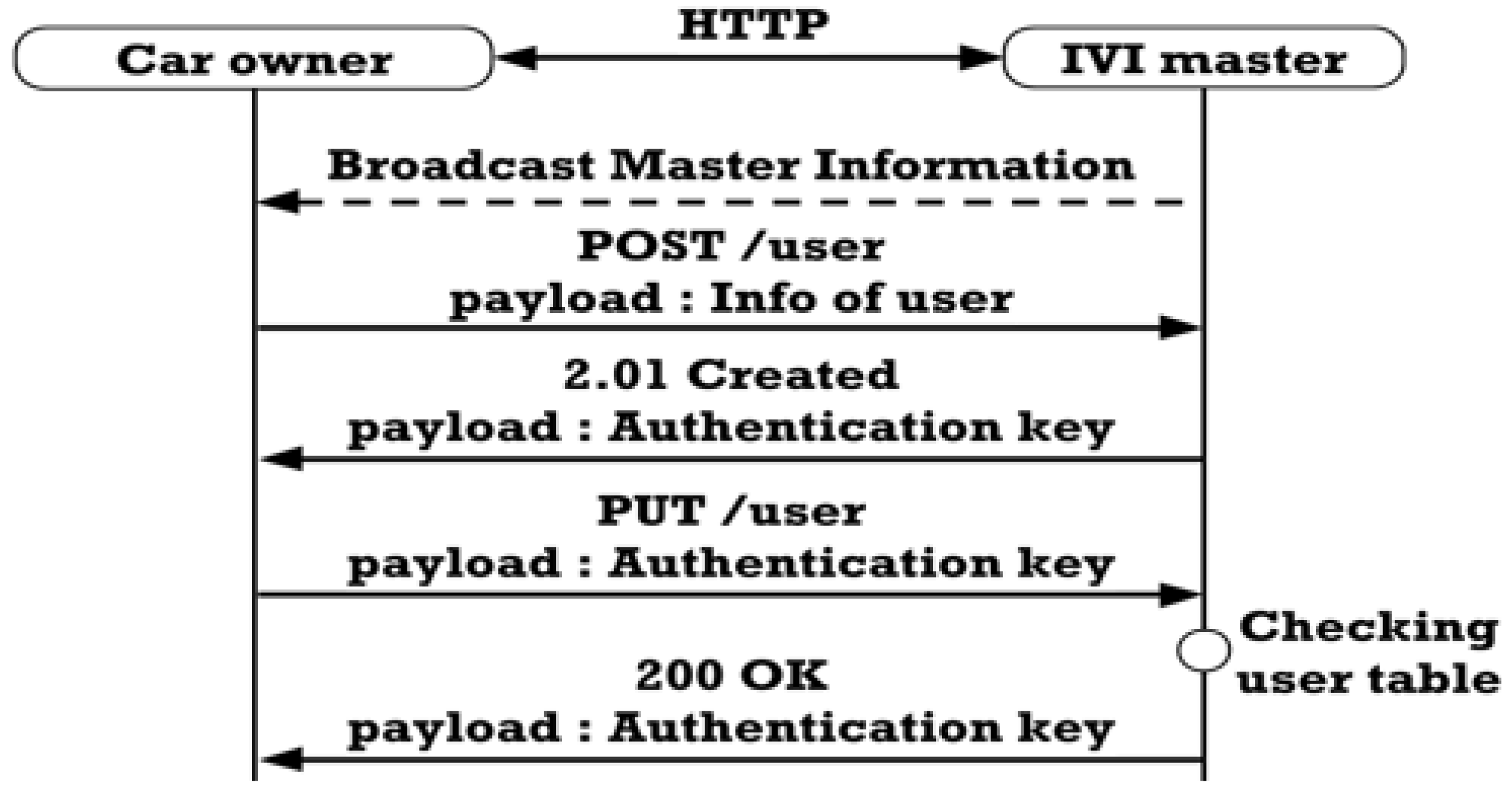
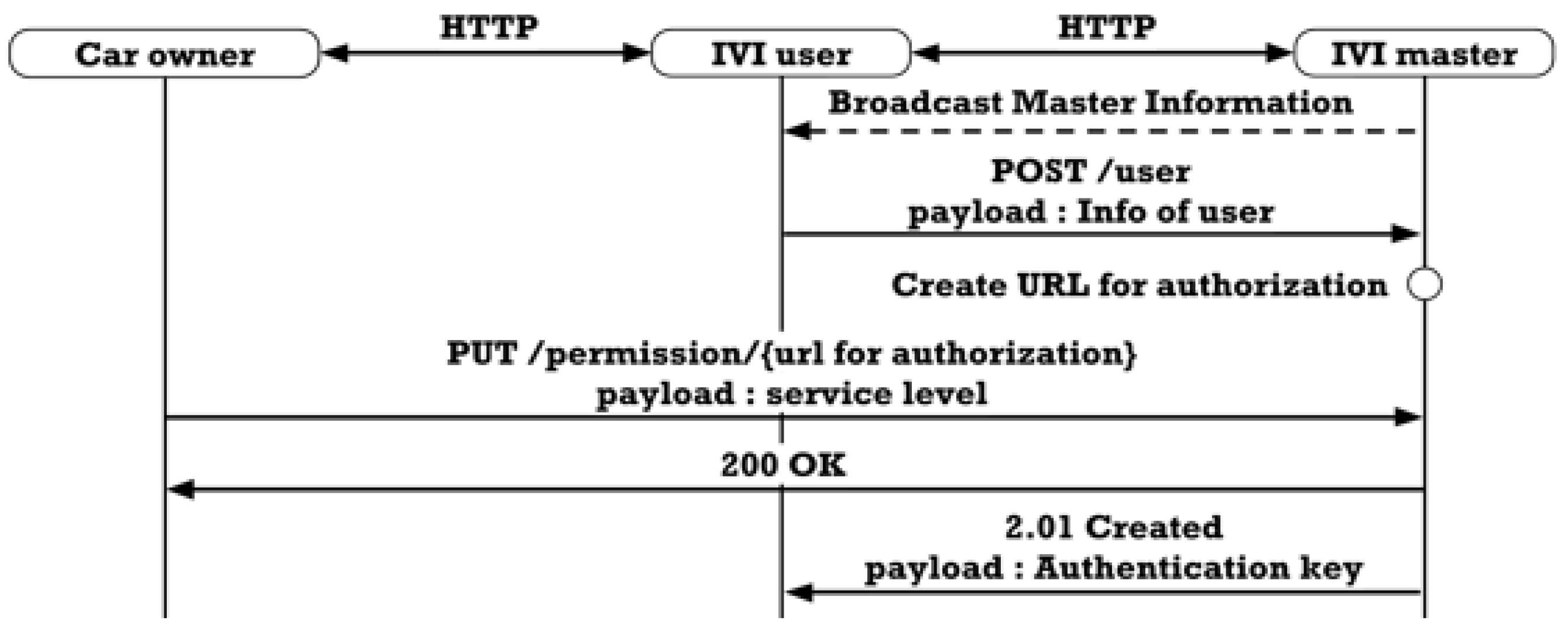
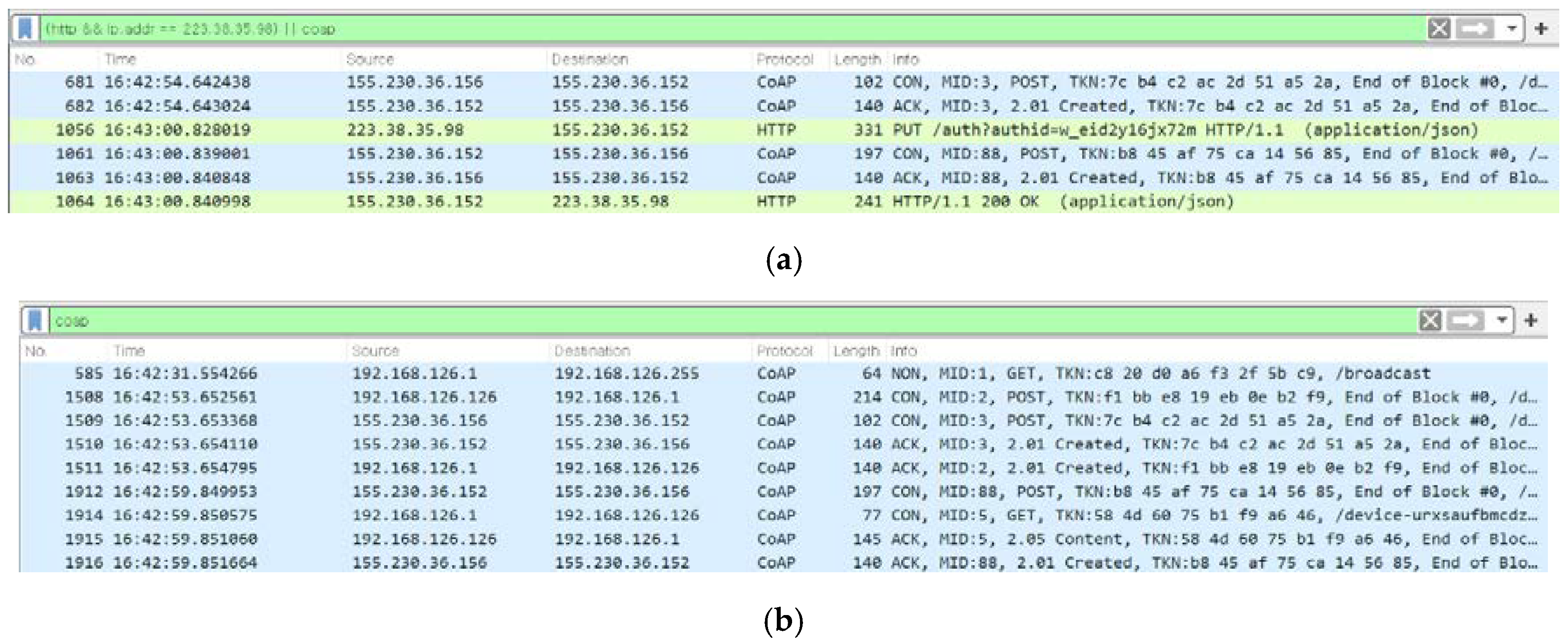
3.4.1. IVI User Registration
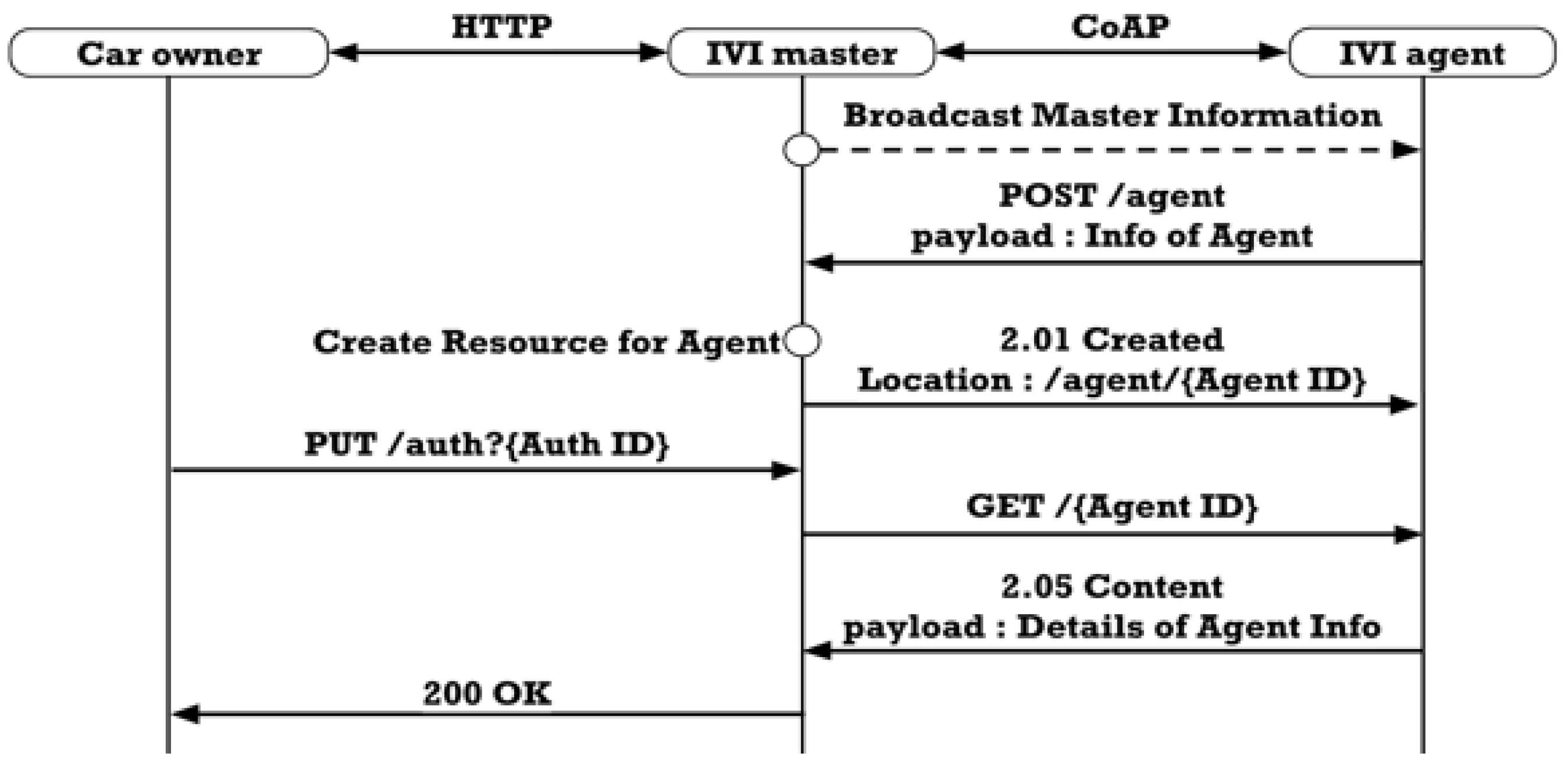
3.4.2. IVI Resource Registration
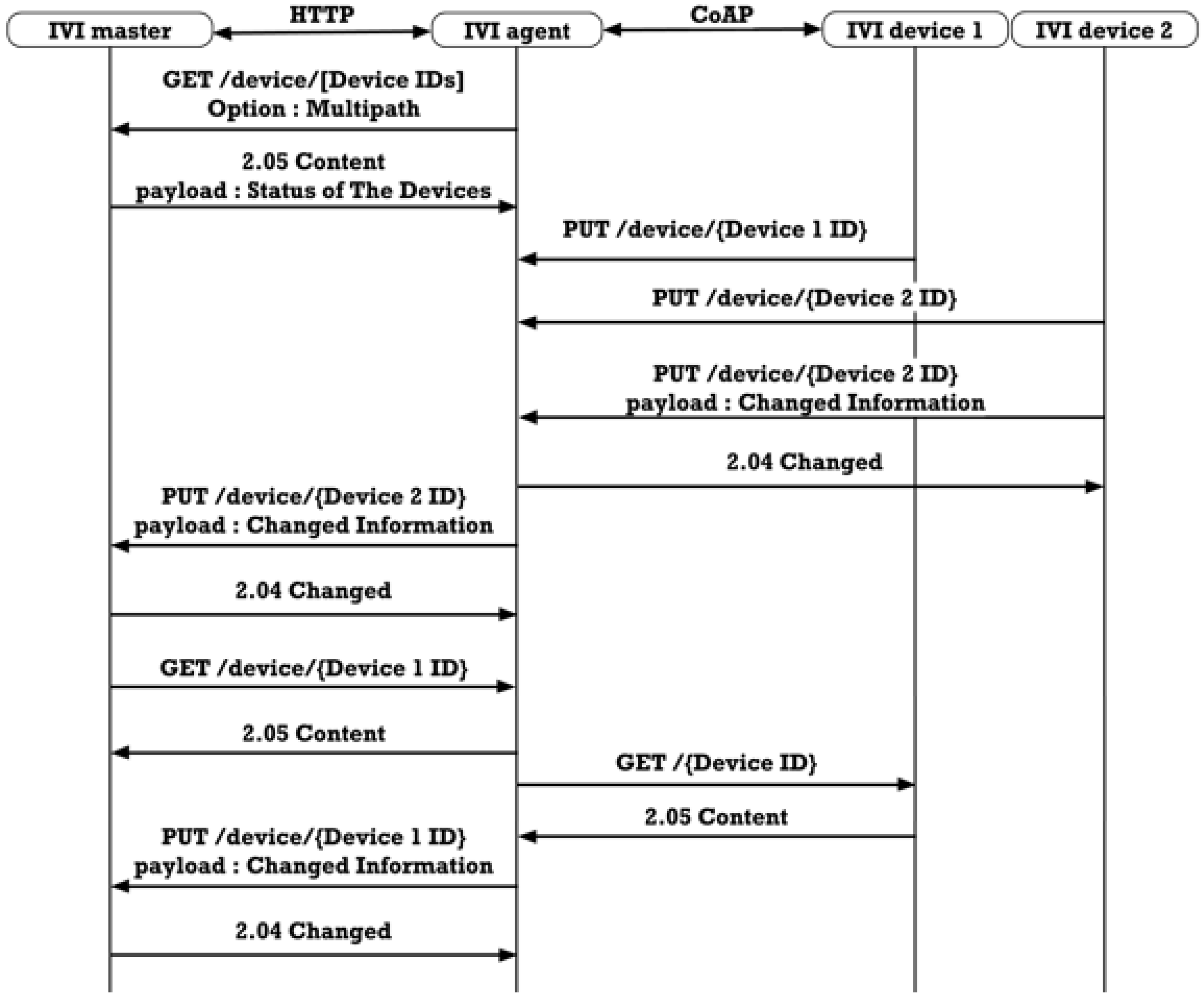
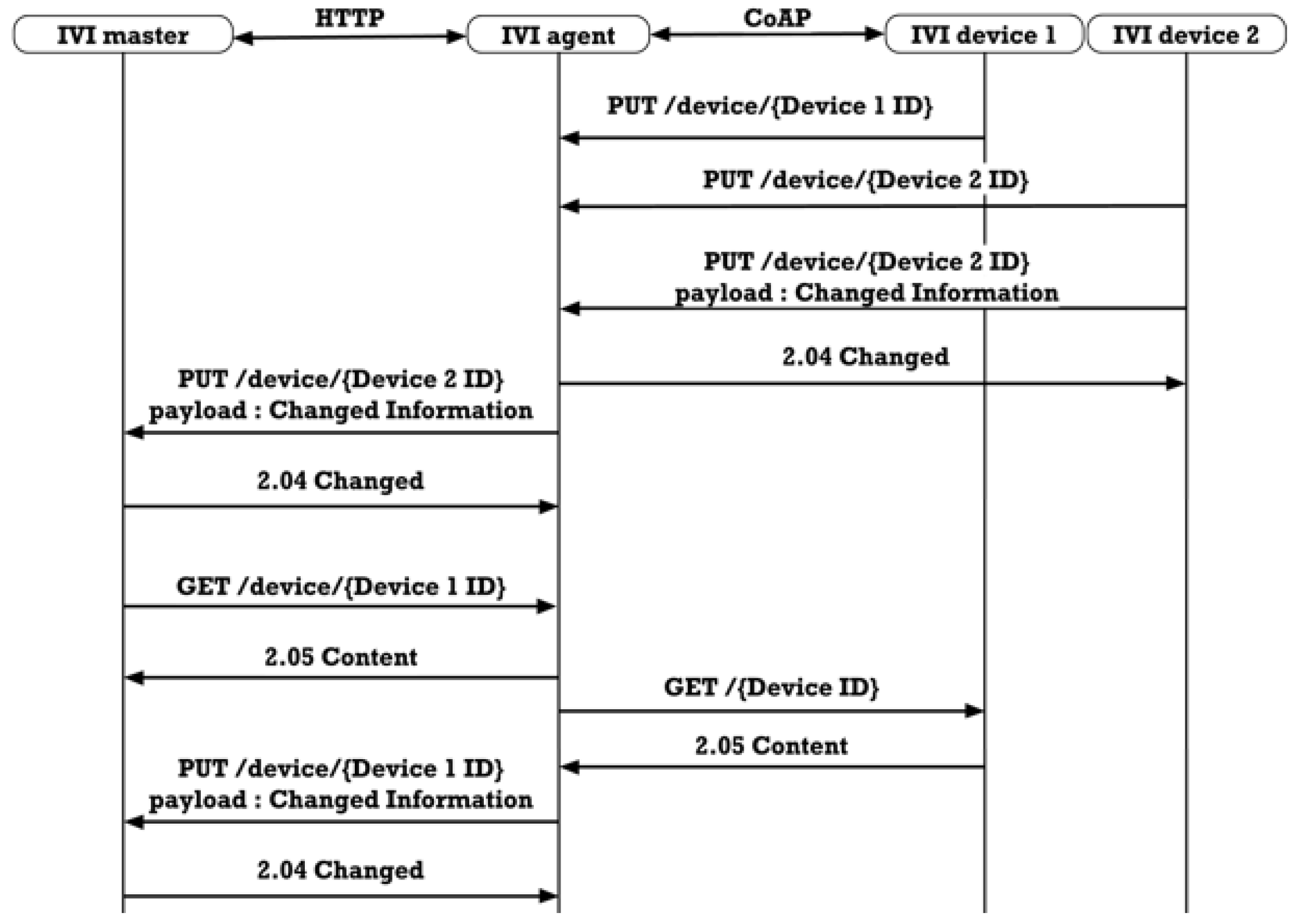
3.4.3. IVI Device Monitoring
3.4.4. Indirect Data Communication
3.4.5. Direct Data Communication
4. Implementations
4.1. Testbed Configuration
4.2. IVI Agent Registration
4.3. IVI Device Registration
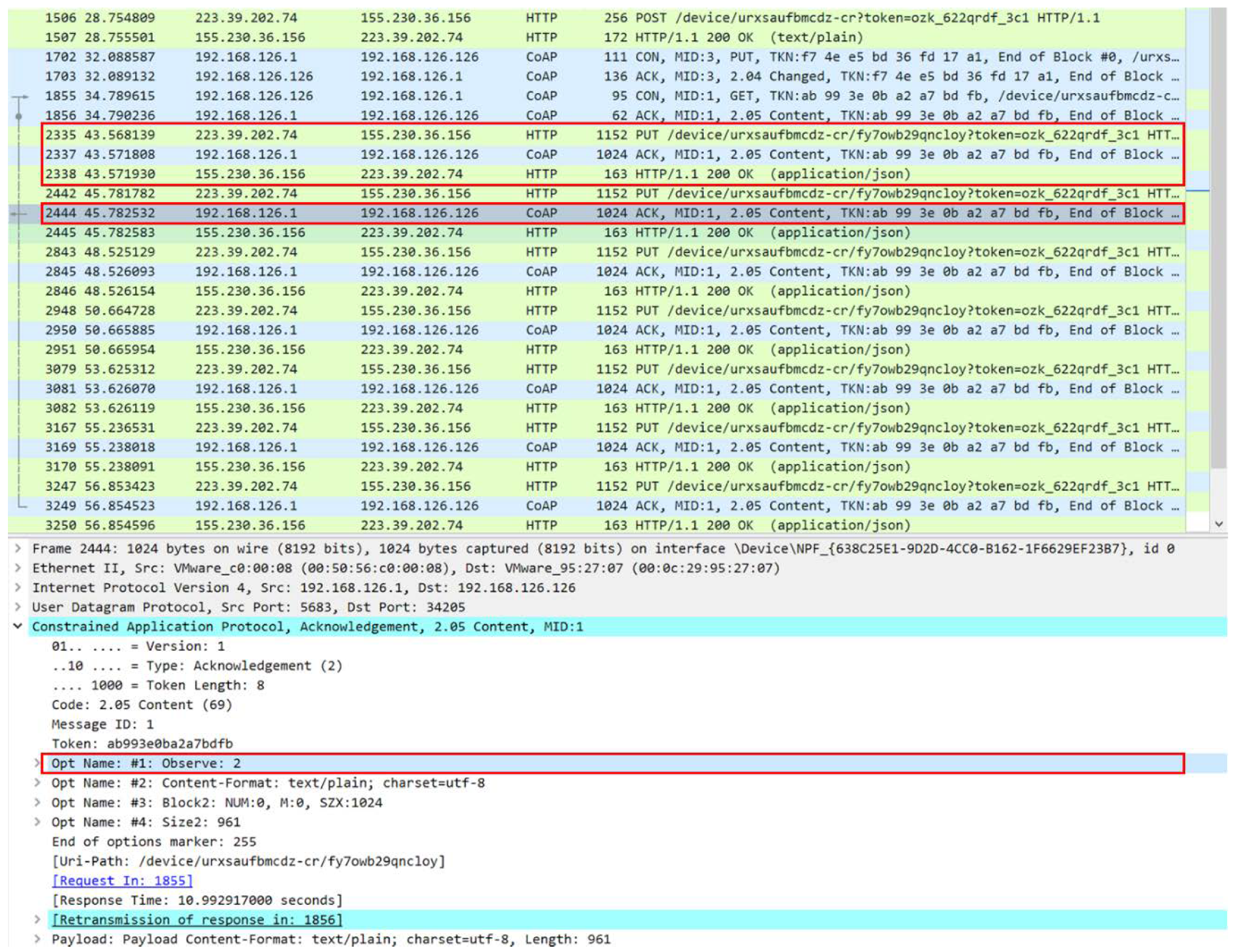
4.4. Indirect and Direct Data Communications
4.5. Multiple URI Communication
5. Performance Analysis by Experimentation
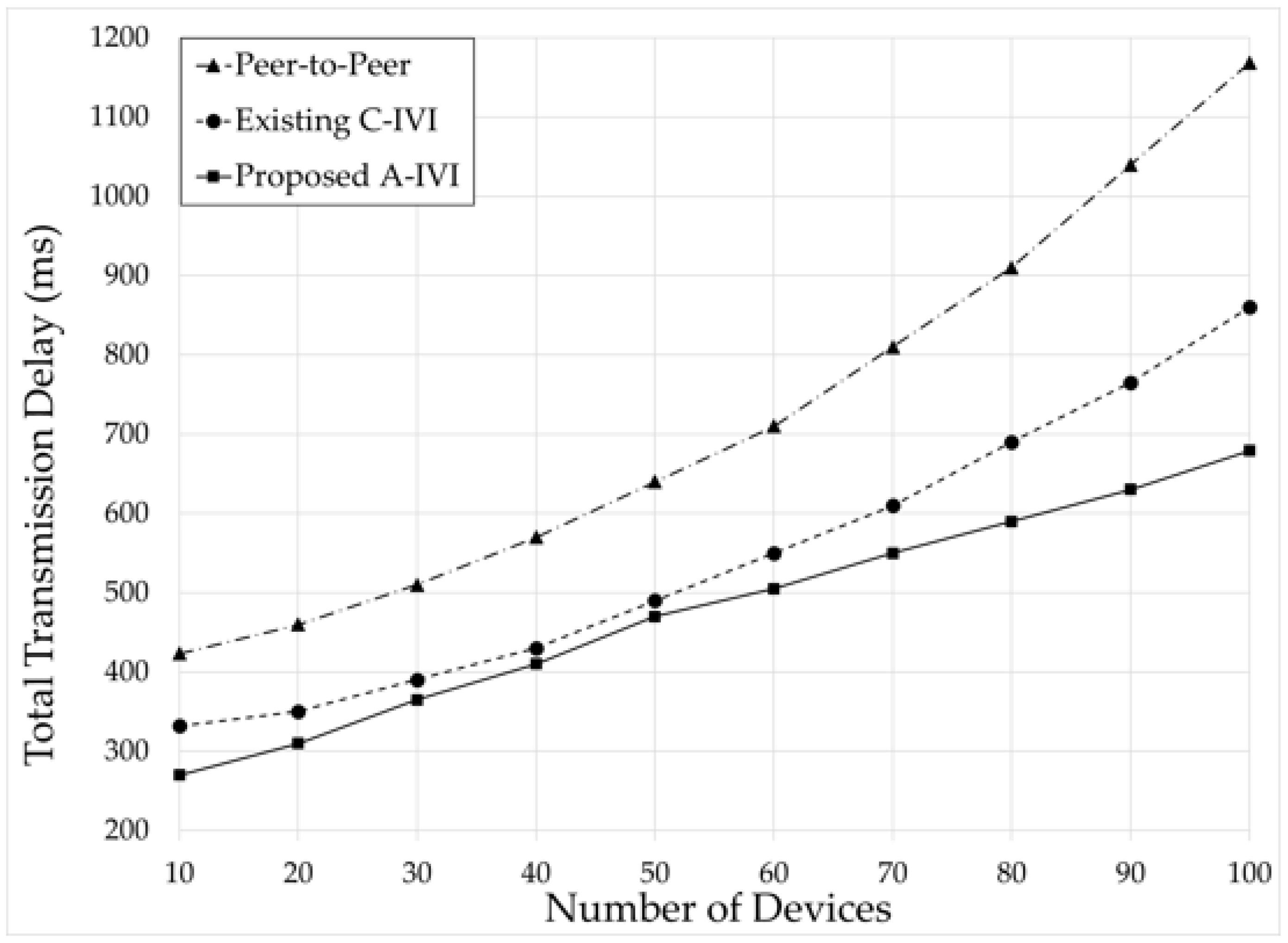
5.1. Total Transmission Delay (TTD)
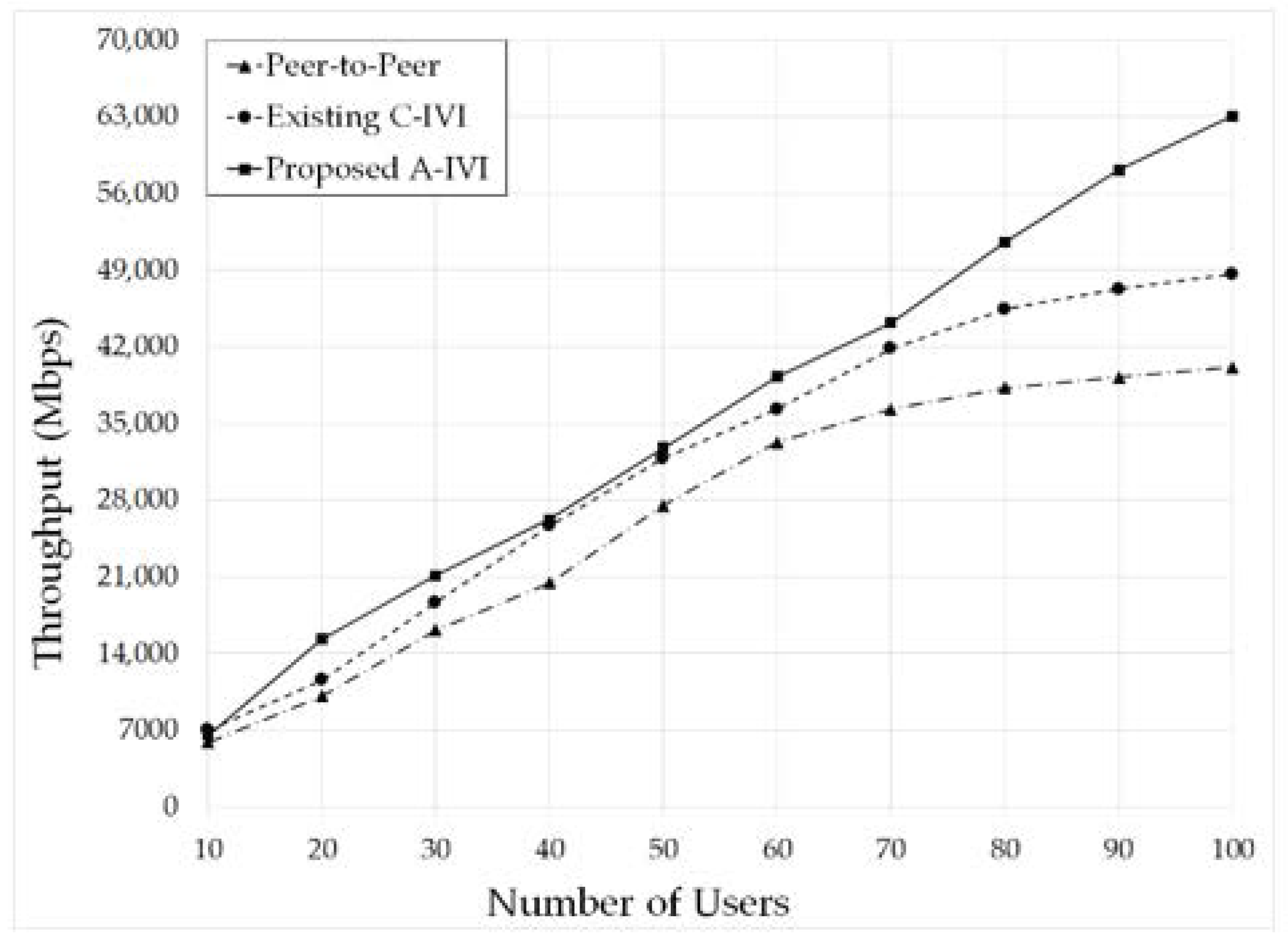
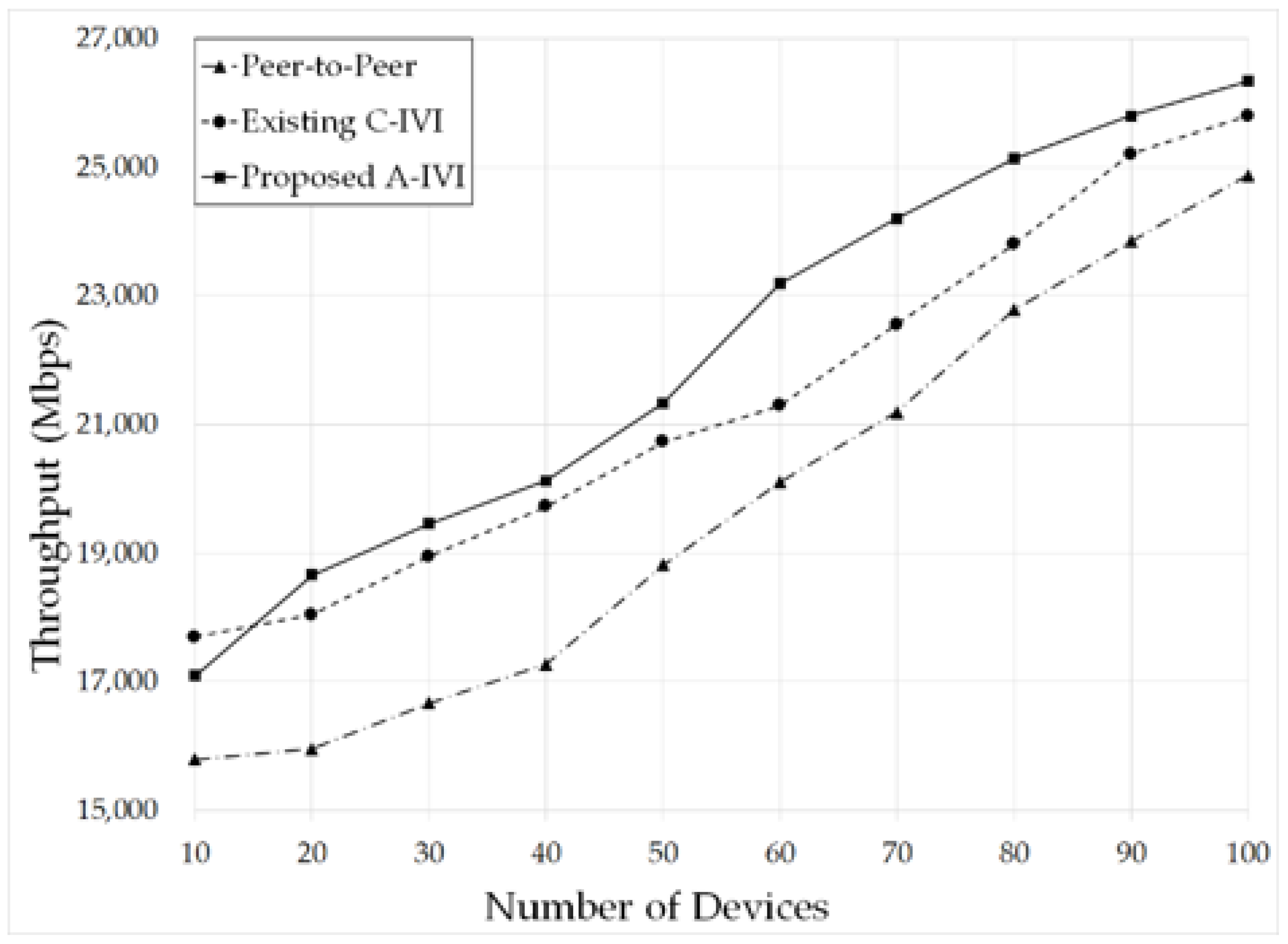
5.2. Throughput
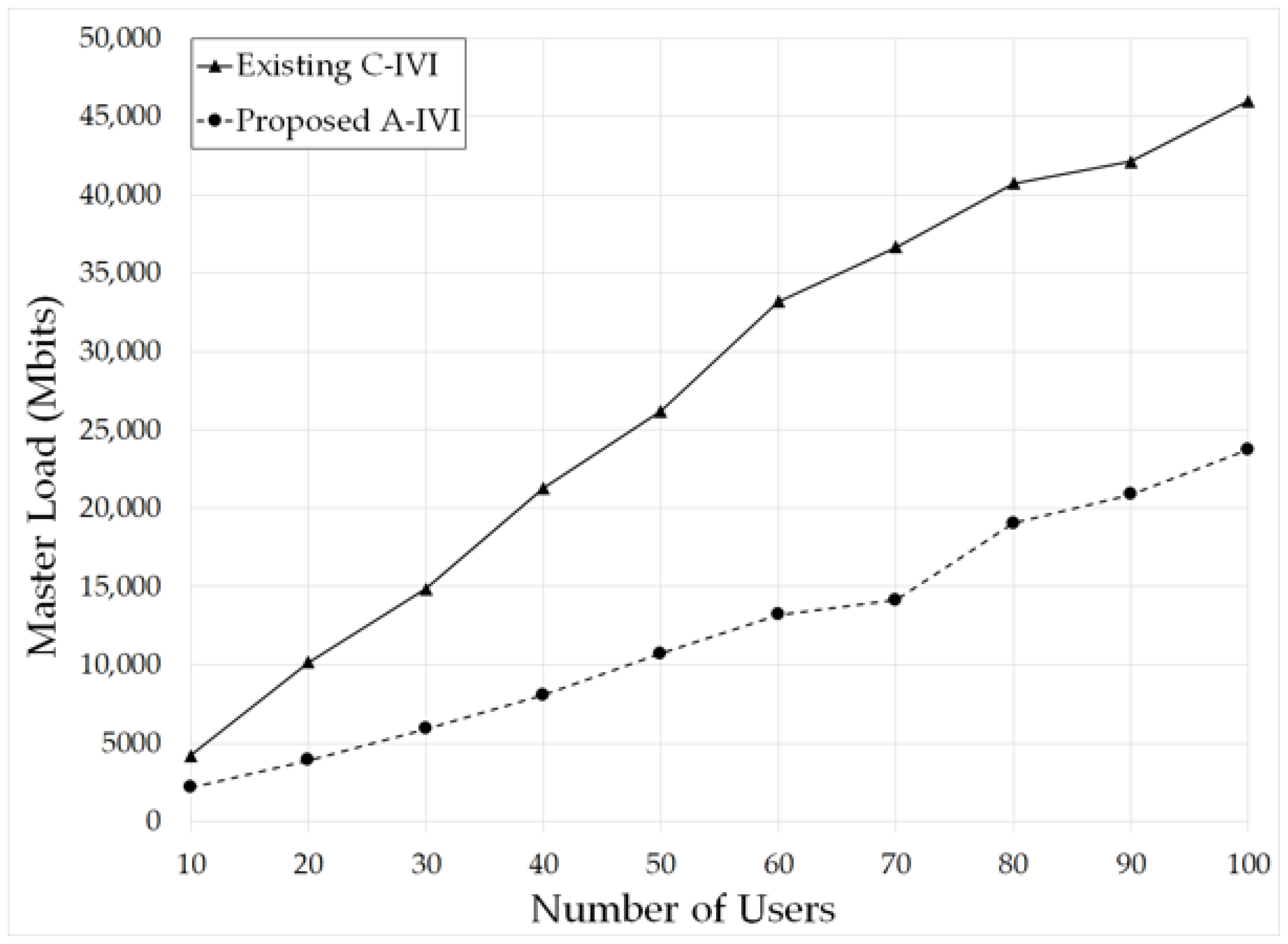
5.3. Master Load
6. Conclusions and Future Works
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Coppoal, R.; Morisio, M. Connected Car: Technologies, Issues, Future Trends. ACM Comput. Surv. 2016, 49, 1–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swan, M. Connected Car: Quantified Self becomes Quantified Car. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2015, 4, 2–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, C.P. Network Selector in a Vehicle Infotainment System. U.S. Patent Application No 20130219039A1, 22 August 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, S.A.; Marko, P.; Patsiokas, S. Remote Vehicle Infotainment Apparatus and Interface. U.S. Patent Application No. 20090075624A1, 19 March 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Macario, G.; Torchiano, M.; Violante, M. An In-Vehicle Infotainment Software Architecture Based on Google Android. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Embedded Systems, Lausanne, Switzerland, 8–10 July 2009; pp. 257–260. [Google Scholar]
- Rao, Q.; Grunler, C.; Hammori, M.; Chakraborty, S. Design methods for augmented reality in-vehicle infotainment system. In Proceedings of the 51st ACM/EDAC/IEEE Design Automation Conference (DAC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 1–5 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hassija, V.; Chamola, V.; Saxena, V.; Jain, D.; Goyal, P.; Sikdar, B. A survey on IoT security: Application areas, security threats, and solution architectures. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 82721–82743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodirguez-Rodriguez, I.; Rodriguez, J.V.; Zamora-Izquierdo, M.A. Variables to be monitored via biomedical sensors for complete type 1 diabetes mellitus management: An extension of the “on-board” concept. J. Diabetes Res. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, D.K.; Jung, J.H.; Kim, J.I.; Gohar, M.; Koh, S.J. IoT-based Resource Control for In-Vehicle Infotainment Services: Design and Experimentation. Sensors 2019, 19, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Choi, D.K.; Jung, J.H.; Koh, S.J. Enhanced Cluster-Based CoAP in Internet-of-Things Networks. In Proceedings of the ICOIN, Chiang Mai, Thailand, 10–12 January 2018; pp. 652–656. [Google Scholar]
- MBUX. Available online: https://www.mercedes-benz.com/en/innovation/connected/mbux-mercedes-benz-user-experience-revolution-in-the-cockpit/ (accessed on 5 June 2020).
- iDrive. Available online: https://www.bmwusa.com/explore/connecteddrive.html (accessed on 5 June 2020).
- Audi Connect. Available online: https://www.audi.com/en/experience-audi/models-and-technology/digital-services/audi-connect.html (accessed on 5 June 2020).
- Hyundai BlueLink. Available online: https://www.hyundaiusa.com/us/en/blue-link (accessed on 5 June 2020).
- Google Android Auto. Available online: https://www.android.com/auto/ (accessed on 5 June 2020).
- Apple Car Play. Available online: https://www.apple.com/ios/carplay/ (accessed on 5 June 2020).
- Microsoft Windows in the Car. Available online: https://www.theverge.com/2014/4/5/5585148/microsoft-windows-in-the-car-concept (accessed on 15 June 2020).
- Samsung Digital Cockpit. Available online: https://news.samsung.com/global/samsung-pioneers-5g-based-mobility-with-launch-of-digital-cockpit-2020 (accessed on 15 June 2020).
- Naver AWAY. Available online: https://away.naverlabs.com/ (accessed on 15 June 2020).
- Rao, S.; Chendanda, D.; Deshpande, C.; Lakkundi, V. Implementing LWM2M in Constrained IoT Devices. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Wireless Sensors (ICWiSe), Melaka, Malaysia, 24–26 August 2015; pp. 52–57. [Google Scholar]
- Shelby, Z.; Hartke, K.; Bormann, C. The Constrained Application Protocol (CoAP). 2014. Available online: https://iottestware.readthedocs.io/en/master/coap_rfc.html (accessed on 15 June 2020).
- Raspberry Pi. Available online: https://www.raspberrypi.org/ (accessed on 12 May 2020).
- Iris. Available online: https://github.com/kataras/iris/ (accessed on 1 June 2020).
- Go-Coap. Available online: https://github.com/go-ocf/go-coap/ (accessed on 1 June 2020).









| Company | IVI System | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Mercedes-Benz | MBUX [11] | AI assistant |
| Predictive user experience based | ||
| Touch screen/pad | ||
| BMW | iDrive [12] | Status monitoring |
| Driver assistance and Emergency service | ||
| Remote diagnosis service | ||
| Audi | Audi Connect [13] | 4G/LTE wireless communication |
| Google earth | ||
| User pattern deep learning | ||
| Hyundai | BlueLink [14] | Remote control and Safe security |
| Car management | ||
| Navigation | ||
| Android Auto [15] | AI assistant (Google NOW) | |
| Navigation with learning features | ||
| Automotive entertainment app | ||
| Apple | Car Play [16] | AI assistant (Siri) |
| Voice message | ||
| Dial control support | ||
| Microsoft | Windows in the Car [17] | AI assistant (Cortana) |
| MirrorLink | ||
| Samsung | Digital Cockpit [18] | AI assistant (Bixby) |
| Smart things | ||
| Digital cluster and Circular UX | ||
| Naver | AWAY [19] | AI assistant (Clova) |
| Driver friendly UX | ||
| Streaming media service |
| Classification | Long-Term Use | Short-Term Use |
|---|---|---|
| Owner (Authentication not required) | Car Owner | Temporary Owner |
| Client (Authentication required) | Private Client | Public Client |
| IVI Services | Level High | Level Medium | Level Low |
|---|---|---|---|
| System settings | V | ||
| Device registration and deregistration | V | ||
| Authority check | V | ||
| Client registration and deregistration | V | ||
| Usage of shared service | V | ||
| Usage of high-level personal service | V | ||
| Usage of medium-level personal service | V | ||
| Usage of low-level personal service | V |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, D.-K.; Jung, J.-H.; Nam, H.-B.; Koh, S.-J. Agent-Based In-Vehicle Infotainment Services in Internet-of-Things Environments. Electronics 2020, 9, 1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9081288
Choi D-K, Jung J-H, Nam H-B, Koh S-J. Agent-Based In-Vehicle Infotainment Services in Internet-of-Things Environments. Electronics. 2020; 9(8):1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9081288
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Dong-Kyu, Joong-Hwa Jung, Hye-Been Nam, and Seok-Joo Koh. 2020. "Agent-Based In-Vehicle Infotainment Services in Internet-of-Things Environments" Electronics 9, no. 8: 1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9081288
APA StyleChoi, D.-K., Jung, J.-H., Nam, H.-B., & Koh, S.-J. (2020). Agent-Based In-Vehicle Infotainment Services in Internet-of-Things Environments. Electronics, 9(8), 1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9081288






