Supply-Scalable High-Speed I/O Interfaces
Abstract
:1. Introduction
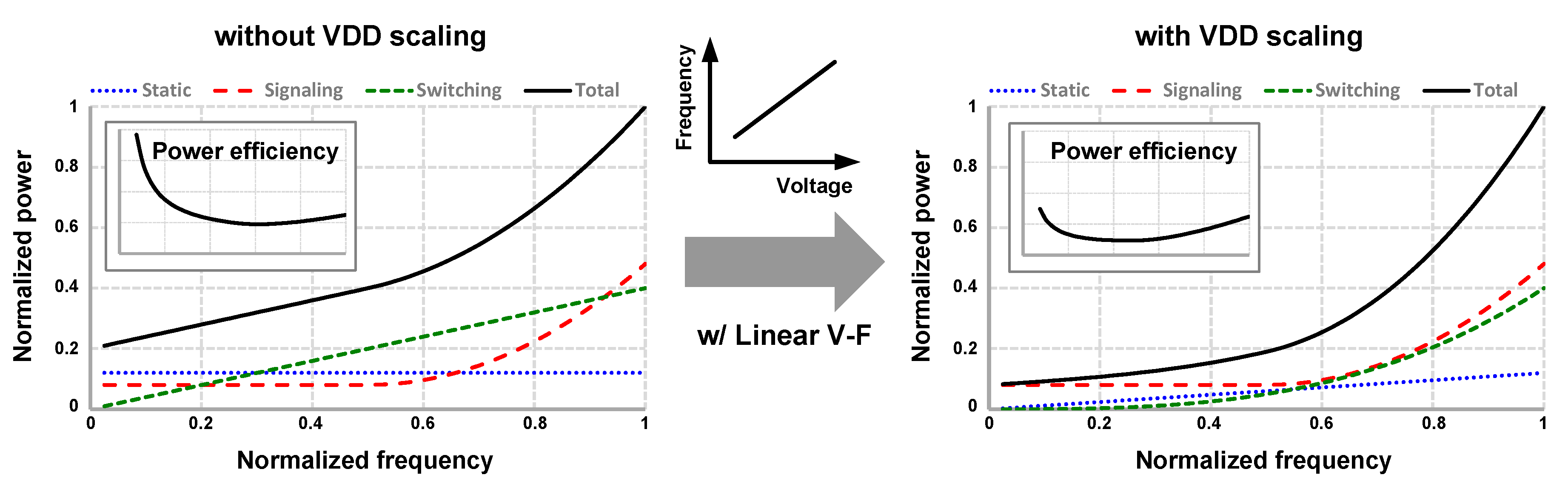
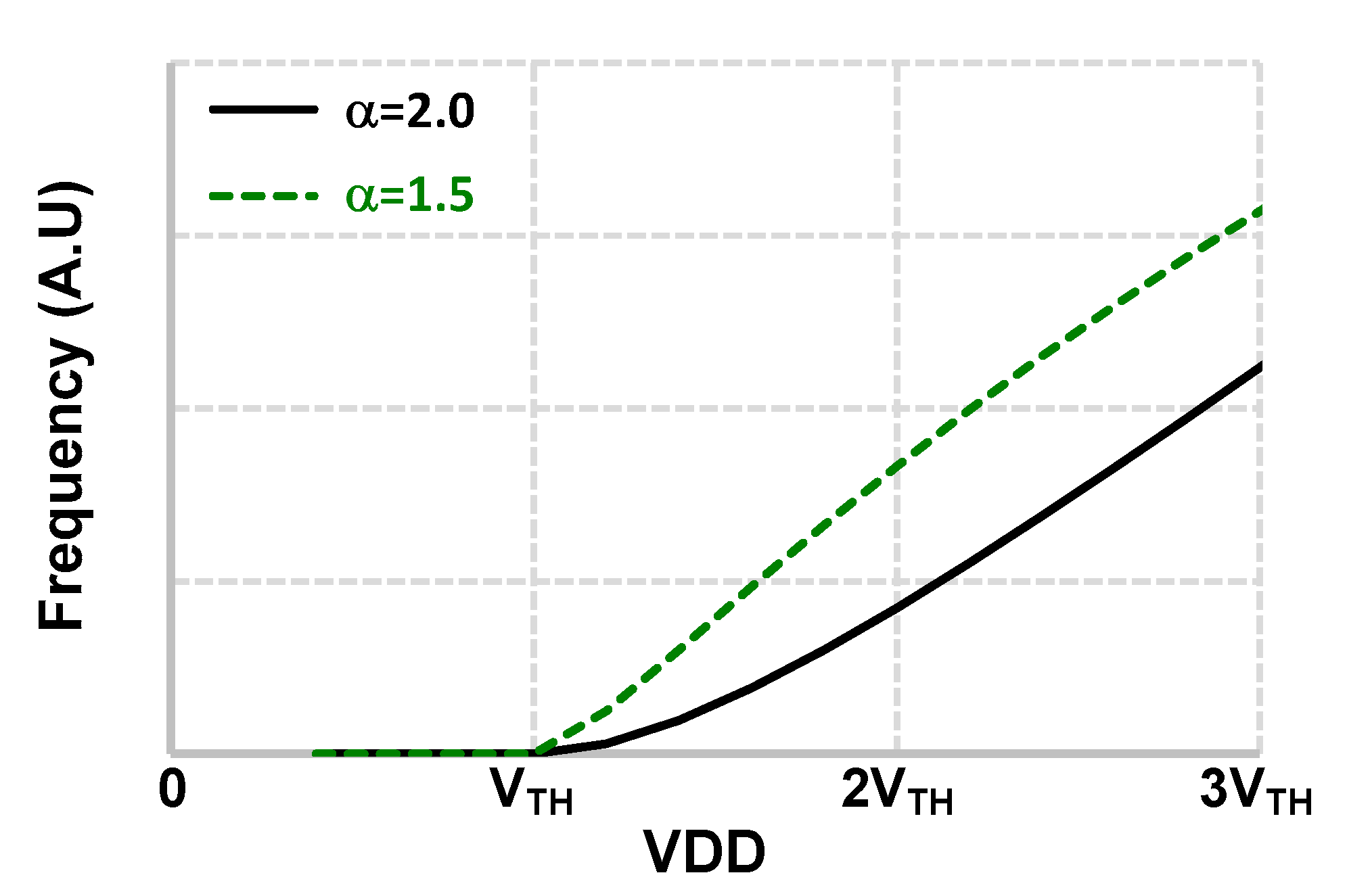
2. Basic Concept of Supply-Scalable I/O
3. Design Considerations of Supply-Scalable I/O
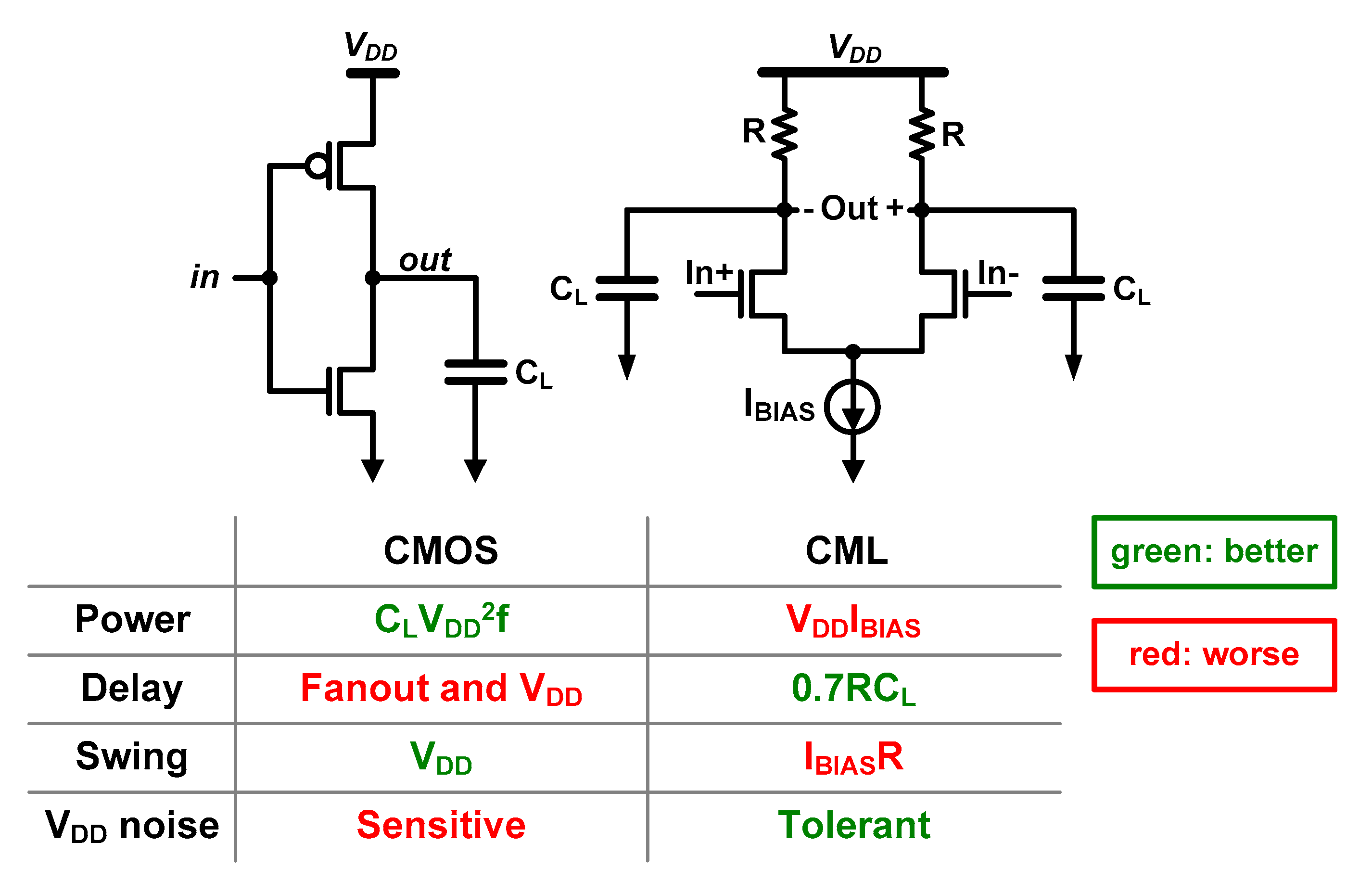
3.1. Base Circuit Topology
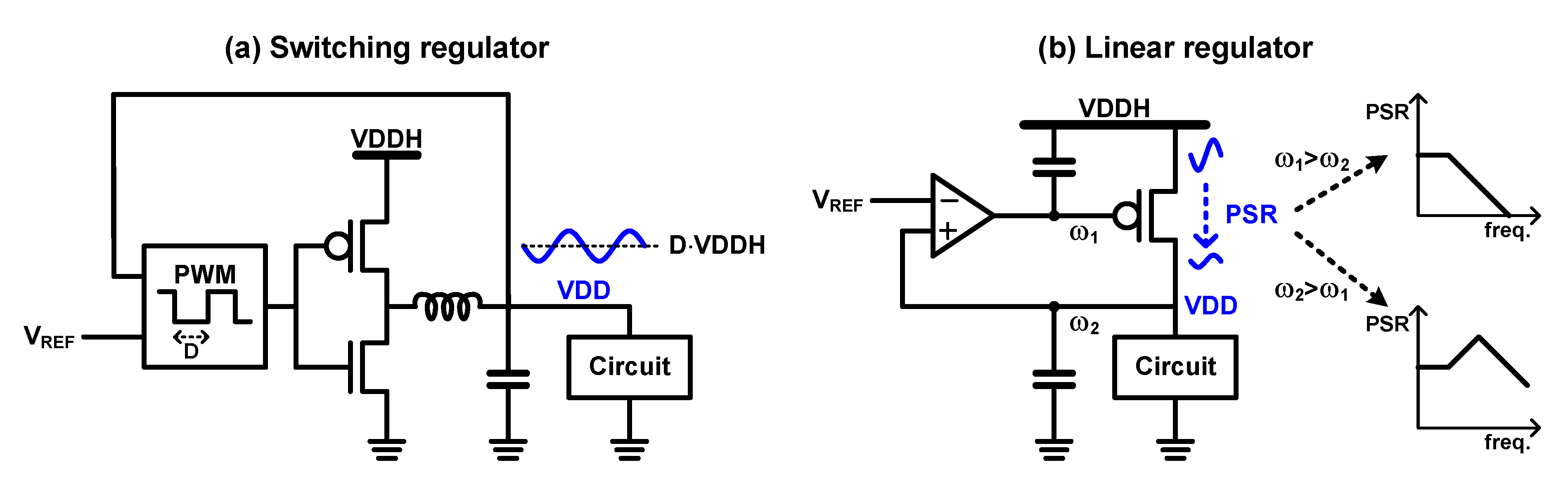
3.2. On-Chip Supply Control
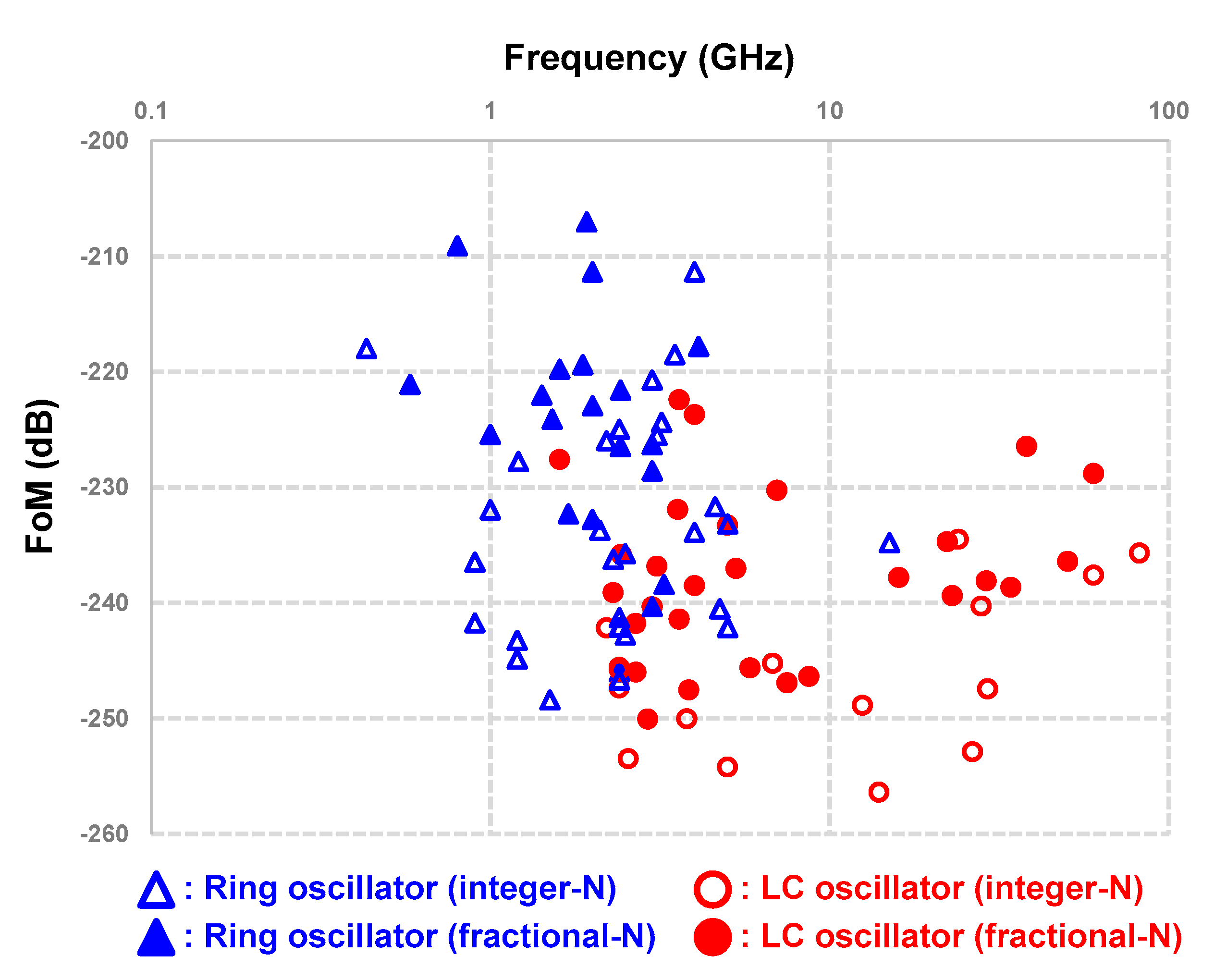
3.3. Clock Generation
3.4. TX Driver Topology
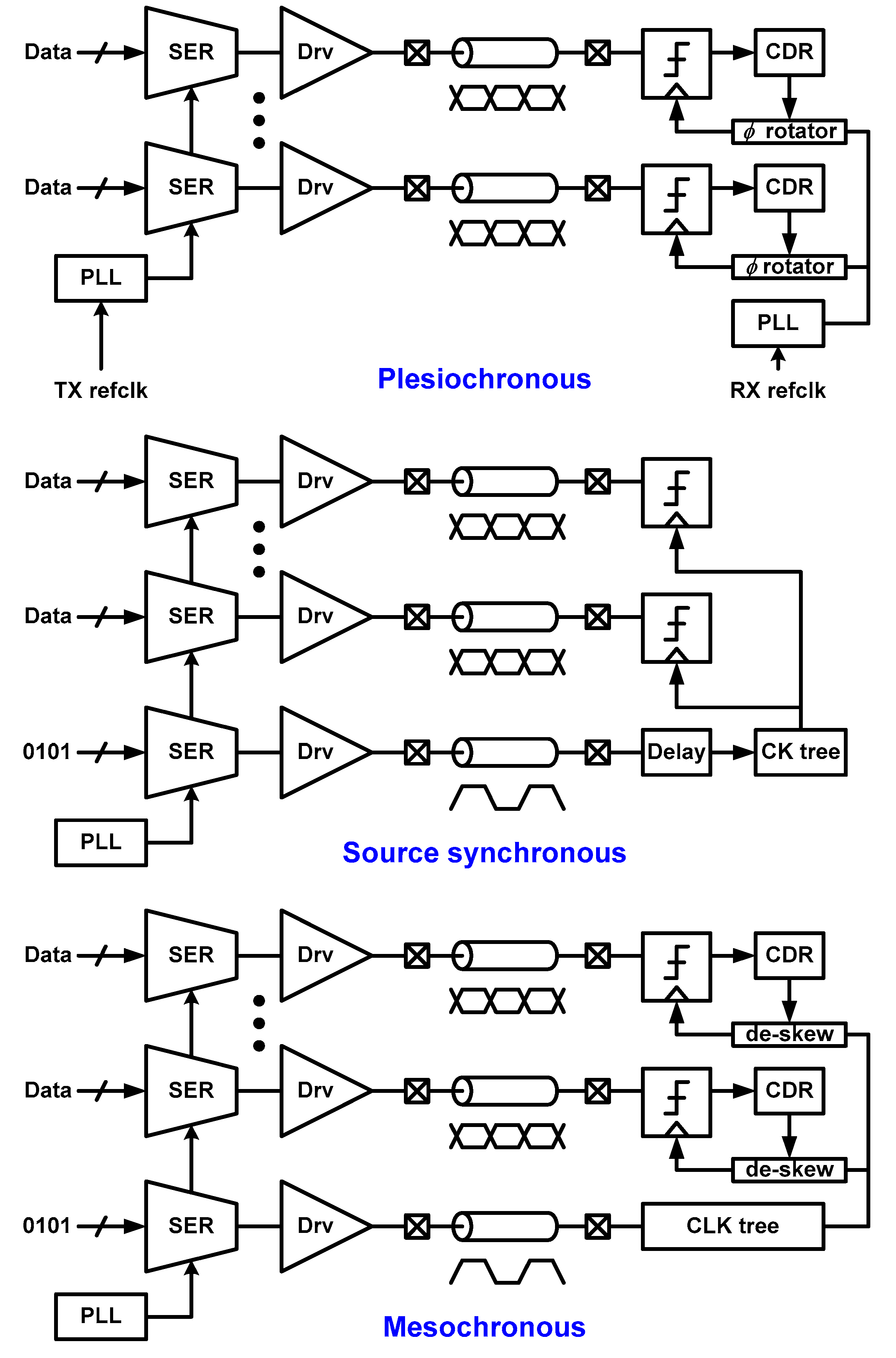
3.5. Clocking Architecture
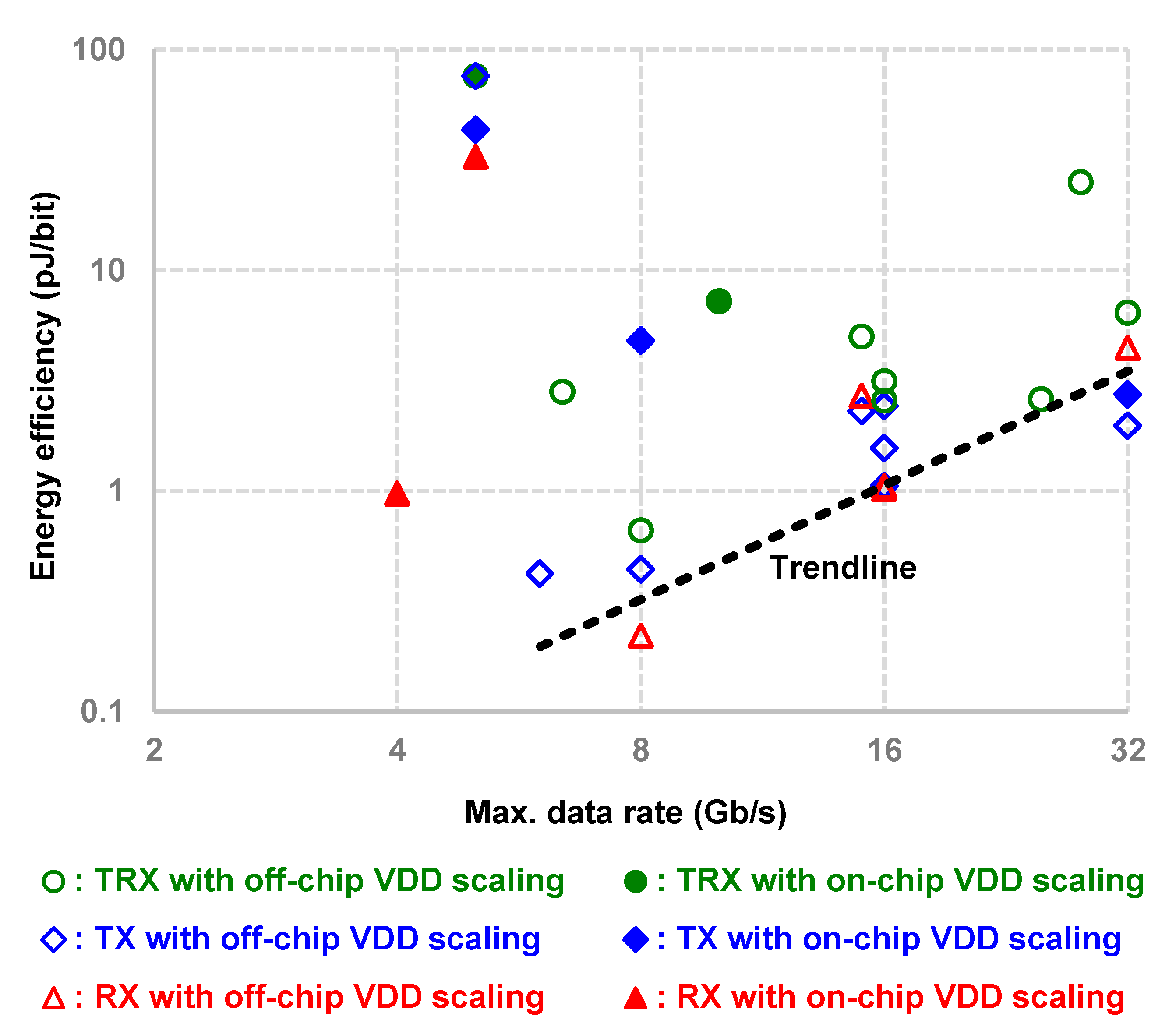
4. Survey on State-Of-The-Art Supply-Scalable I/O
5. Summary and Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, K. Silicon Technologies and Solutions for the Data-Driven World. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference-(ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 22–26 February 2015; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Cisco Annual Internet Report (2018–2023) White Paper. CISCO. Available online: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/solutions/collateral/executive-perspectives/annual-internet-report/white-paper-c11-741490.pdf (accessed on 8 July 2020).
- Bae, W.; Yoon, K.J. Comprehensive Read Margin and BER Analysis of One Selector-One Memristor Crossbar Array Considering Thermal Noise of Memristor with Noise-Aware Device Model. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2020, 19, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frans, Y.; Carey, D.; Erett, M.; Amir-Aslanzadeh, H.; Fang, W.Y.; Turker, D.; Jose, A.P.; Bekele, A.; Im, J.; Upadhyaya, P.; et al. A 0.5–16.3 Gb/s Fully Adaptive Flexible-Reach Transceiver for FPGA in 20 nm CMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2015, 50, 1932–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, M.S.; Taghavi, M.H.; Melaren, A.; Pham, J.; Farzan, K.; DiClemente, D.; Van Ierssel, M.; Song, W.; Asgaran, S.; Holdenried, C.; et al. A 4-Lane 1.25-to-28.05Gb/s Multi-Standard 6pJ/b 40dB Transceiver in 14nm FinFET with Independent TX/RX Rate Support. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference-(ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 11–15 February 2018; pp. 106–107. [Google Scholar]
- Upadhyaya, P.; Bekele, A.; Melek, D.T.; Zhao, H.; Im, J.; Cho, J.; Tan, K.H.; McLeod, S.; Chen, S.; Zhang, W.; et al. A Fully-Adaptive Wideband 0.5-32.75Gb/s FPGA Transceiver in 16nm FinFET CMOS Technology. In Proceedings of the Symposium on VLSI Circuits, Honolulu, HI, USA, 13–16 June 2016; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Khanoyan, K.; Hatamkhani, H.; Tong, H.; Hu, K.; Fallahi, S.; Abdul-Latif, M.; Vakilian, K.; Fujimori, I.; Brewster, A. A 28 Gb/s Multistandard Serial Link Transceiver for Backplane Applications in 28 nm CMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2015, 50, 3089–3100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyaya, P.; Savoj, J.; An, F.-T.; Bekele, A.; Jose, A.; Xu, B.; Wu, D.; Turker, D.; Aslanzadeh, H.; Hedayati, H.; et al. A 0.5-to-32.75Gb/s Flexible-Reach Wireline Transceiver in 20nm CMOS. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference-(ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 22–26 February 2015; pp. 56–57. [Google Scholar]
- Nishi, Y.; Abe, K.; Ribo, J.; Roederer, B.; Gopalan, A.; Benmansour, M.; Ho, A.; Bhoi, A.; Konishi, M.; Moriizumi, R.; et al. An ASIC-Ready 1.25-6.25Gb/s SerDes in 90nm CMOS with Multi-Standard Compatibility. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE Asian Solid-State Circuits Conference-(A-SSCC), Fukuoka, Japan, 3–5 November 2008; pp. 37–40. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, H.; Aziz, P.M.; Jing, T.; Sinha, A.; Kotagiri, S.P.; Narayan, R.; Gao, H.; Jing, P.; Hom, G.; Liang, A.; et al. A 28 Gb/s 560 mW Multi-Standard SerDes with Single-Stage Analog Front-End and 14-Tap Decision Feedback Equalizer in 28 nm CMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2014, 49, 3091–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamoto, T.; Norimatsu, T.; Kogo, K.; Yuki, F.; Nakajima, N.; Tsuge, M.; Usugi, T.; Hokari, T.; Koba, H.; Komori, T.; et al. Multi-Standard 185fsrms 0.3-to-28Gb/s 40dB Backplane Signal Conditioner with Adaptive Pattern-Match 36-Tap DFE and Data-Rate-Adjustment PLL in 28nm CMOS. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference-(ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 22–26 February 2015; pp. 54–55. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, W.; Ju, H.; Park, K.; Han, J.; Jeong, D.-K. A supply-scalable-serializing transmitter with controllable output swing and equalization for next-generation standards. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 5979–5989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Spagna, F.; Chen, J.; Wang, X.; Tong, L.; Gowder, S.; Jia, W.; Nicholson, R.; Iyer, S.; Song, R.; et al. A Power and Area Efficient 2.5-16 Gbps Gen4 PCIe PHY in 10nm FinFET CMOS. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Asian Solid-State Circuits Conference-(A-SSCC), Tainan, Taiwan, 5–7 November 2018; pp. 5–8. [Google Scholar]
- Alon, E. Mixed-Signal Electrical Interfaces. In Proceedings of the IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference, Austin, TX, USA, 14–17 April 2019; pp. 1–57. [Google Scholar]
- Mansuri, M.; Jaussi, J.E.; Kennedy, J.T.; Hsueh, T.-C.; Shekhar, S.; Balamurugan, G.; O’Mahony, F.; Roberts, C.; Mooney, R.; Casper, B. A Scalable 0.128–1 Tb/s, 0.8–2.6 pJ/bit, 64-Lane Parallel I/O in 32-nm CMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2013, 48, 3229–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musah, T.; Jaussi, J.E.; Balamurugan, G.; Hyvonen, S.; Hsueh, T.C.; Keskin, G.; Shekhar, S.; Kennedy, J.; Sen, S.; Inti, R.; et al. A 4–32 Gb/s Bidirectional Link with 3-Tap FFE/6-Tap DFE and Collaborative CDR in 22 nm CMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2014, 49, 3079–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, T.O.; Liu, Y.; Rylov, S.V.; Agrawal, A.; Kim, S.; Hsieh, P.H.; Bulzacchelli, J.F.; Ferriss, M.; Ainspan, H.A.; Rylyakov, A.; et al. A 1.4 pJ/bit, Power-Scalable 16×12 Gb/s Source-Synchronous I/O with DFE Receiver in 32 nm SOI CMOS Technology. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2015, 50, 1917–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casper, B.; O’Mahony, F. Clocking Analysis, Implementation and Measurement Techniques for High-Speed Data Links—A Tutorial. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2009, 56, 17–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, W.; Jeong, D.-K. Analysis and Design of CMOS Clocking Circuit for Low Phase Noise; Institute of Engineering and Technology: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sidiropoulos, S.; Horowitz, M. A semidigital dual delay-locked loop. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 1997, 32, 1683–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.J.; Dally, W.J.; Chiang, P. Low-power area-efficient high-speed I/O circuit techniques. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2000, 35, 1591–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Horowitz, M. Adaptive Supply Serial Links with Sub-1-V Operation and Per-Pin Clock Recovery. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2002, 37, 1403–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, W.; Ju, H.; Park, K.; Cho, S.-Y.; Jeong, D.-K. A 7.6 mW, 414 fs RMS-Jitter 10 GHz Phase-Locked Loop for a 40 Gb/s Serial Link Transmitter Based on a Two-Stage Ring Oscillator in 65 nm CMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2016, 51, 2357–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.-Y.; Kim, J.; Liu, D.; Sidiropoulos, S.; Horowitz, M. A Variable-Frequency Parallel I/O Interface with Adaptive Power-Supply Regulation. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2000, 35, 1600–1610. [Google Scholar]
- Balamurugan, G.; Kennedy, J.; Banerjee, G.; Jaussi, J.E.; Mansuri, M.; O’Mahony, F.; Casper, B.; Mooney, R. A Scalable 5–15 Gbps, 14–75 mW Low-Power I/O Transceiver in 65 nm CMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2008, 43, 1010–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balamurugan, G.; O’Mahony, F.; Mansuri, M.; E Jaussi, J.; Kennedy, J.T.; Casper, B. A 5-to-25Gb/s 1.6-to-3.8mW/(Gb/s) Reconfigurable Transceiver in 45nm CMOS. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference-(ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 8 February 2010; pp. 372–373. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.-H.; Bai, R.; Hu, K.; Yang, H.-W.; Chiang, P.Y.; Palermo, S. A 0.47–0.66 pJ/bit, 4.8–8 Gb/s I/O Transceiver in 65 nm CMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2013, 48, 1276–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.-H.; Yang, H.-W.; Li, H.; Chiang, P.Y.; Palermo, S. An 8–16 Gb/s, 0.65–1.05 pJ/b, Voltage-Mode Transmitter with Analog Impedance Modulation Equalization and Sub-3 ns Power-State Transitioning. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2014, 49, 2631–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inti, R.; Shekhar, S.; Balamurugan, G.; Jaussi, J.; Roberts, C.; Hsueh, T.-C.; Casper, B.; Rajesh, I. A 0.5-to-0.75V, 3-to-8 Gbps/lane, 385-to-790 fJ/b, Bi-Directional, Quad-Lane Forwarded-Clock Transceiver in 22 nm CMOS. In Proceedings of the Symposium on VLSI Circuits, Kyoto, Japan, 16–19 June 2015; pp. C346–C347. [Google Scholar]
- Shekhar, S.; Inti, R.; Jaussi, J.; Hsueh, T.-C.; Casper, B. A 1.2–5Gb/s 1.4–2pJ/b serial link in 22 nm CMOS with a direct data-sequencing blind oversampling CDR. In Proceedings of the Symposium on VLSI Circuits, Kyoto, Japan, 16–19 June 2015; pp. C350–C351. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, G.; Hanumolu, P.K.; Choi, W.-S.; Saxena, S.; Kim, S.-J.; Talegaonkar, M.; Nandwana, R.; Elkholy, A.; Wei, D.; Nandi, T. A 16Mb/s-to-8Gb/s 14.1-to-5.9pJ/b Source Synchronous Transceiver Using DVFS and Rapid On/Off in 65nm CMOS. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference-(ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 31 January–4 February 2016; pp. 398–399. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, W.; Ju, H.; Park, K.; Jeong, D.-K. A 6-to-32 Gb/s Voltage-Mode Transmitter with Scalable Supply, Voltage Swing, and Pre-Emphasis in 65-nm CMOS. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Asian Solid-State Circuits Conference-(A-SSCC), Toyama, Japan, 7–9 November 2016; pp. 241–244. [Google Scholar]
- Byun, S. 0.97 mW/Gb/s, 4 Gb/s CMOS clock and data recovery IC with dynamic voltage scaling. IET Circuits Devices Syst. 2016, 10, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, A.; Anand, T. A 0.5-to-0.9V, 3-to-16Gb/s, 1.6-to-3.1pJ/b Wireline Transceiver Equalizing 27dB Loss at 10Gb/s with Clock-Domain Encoding Using Integrated Pulse-Width Modulation (iPWM) in 65nm CMOS. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference-(ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 11–15 February 2018; pp. 268–269. [Google Scholar]
- Shekhar, S.; Inti, R.; Jaussi, J.; Hsueh, T.-C.; Casper, B. A Low-Power Bidirectional Link with a Direct Data-Sequencing Blind Oversampling CDR. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2019, 54, 1669–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello, O.; Crovetti, P.; Alioto, M. Standard cell-based ultra-compact DACs in 40-nm CMOS. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 126479–126488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.; Peh, L.-S.; Jha, N.K. Dynamic Voltage Scaling with Links for Power Optimization of Interconnection Networks. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on High-Performance Computer Architecture (HPCA), Anaheim, CA, USA, 8–12 February 2003; pp. 91–102. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, D.; Kim, J. Power-Aware Communication Optimization for Networks-on-Chips with Voltage Scalable Links. In Proceedings of the IEEE/ACM/IFIP International Conference on Hardware/Software Codesign and System Synthesis, Stockholm, Sweden, 8–10 September 2004; pp. 170–175. [Google Scholar]
- Barroso, L.A.; Hölzle, U. The Case for Energy-Proportional Computing. Computer 2007, 40, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abts, D.; Marty, M.R.; Wells, P.M.; Klausler, P.; Liu, H. Energy Proportional Datacenter Networks. In Proceedings of the International Symposium on Computer Architecture (ISCA), Saint-Malo, France, 19–23 June 2010; pp. 338–347. [Google Scholar]
- Bohr, M.T.; Young, I.A. CMOS Scaling Trends and Beyond. IEEE Mirco 2017, 37, 20–29. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Wei, G.; Peh, L.-S. Design of Low-Power Short-Distance Opto-Electronic Transceiver Front-Ends with Scalable Supply Voltages and Frequencies. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Symposium on Low Power Electronics & Design, Bangalore, India, 11–13 August 2008; pp. 277–282. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, K.; Wei, J.; Huang, C.; Li, S.; Donnelly, K.; Horowitz, M.; Li, Y.; Sidiropoulos, S. A 0.4–4-Gb/s CMOS Quad Transceiver Cell Using On-Chip Regulated Dual-Loop PLLs. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2003, 38, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eble, J.C.; Best, S.; Leibowitz, B.; Luo, L.; Palmer, R.; Wilson, J.; Zerbe, J.; Amirkhany, A.; Nguyen, N. Power-Efficient I/O Design Considerations for High-Bandwidth Applications. In Proceedings of the IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference, San Jose, CA, USA, 17–20 September 2011; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Hatamkhani, H.; Yang, C.-K. A Study of the Optimal Data Rate for Minimum Power of I/Os. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2006, 53, 1230–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B. Multi-Gbps Serial Backplane Transceiver: From Dilemma to Solution. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Asian Solid-State Circuits Conference-(A-SSCC), Xiamen, China, 9–11 November 2015; pp. 1–87. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, L.; Zhuang, I.; Im, J.; Melek, D.; Namkoong, J.; Raj, M.; Shin, J.; Frans, Y.; Chang, K. A 4-to-16GHz Inverter-Based Injection-Locked Quadrature Clock Generator with Phase Interpolators for Multi-Standard I/Os in 7nm FinFET. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference-(ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 11–15 February 2018; pp. 390–391. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, W. CMOS Inverter as Analog Circuit: An overview. J. Low Power Electron. Appl. 2019, 9, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frans, Y.; McLeod, S.; Hedayati, H.; Elzeftawi, M.; Namkoong, J.; Lin, W.; Im, J.; Upadhyaya, P.; Chang, K. A 40-to-64 Gb/s NRZ Transmitter with Supply-Regulated Front-End in 16 nm FinFET. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2016, 51, 3167–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansuri, M.; Yang, C.-K. A low-power adaptive bandwidth PLL and clock buffer with supply-noise compensation. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2003, 38, 1804–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.; Kim, Y.-H.; Lee, D.; Kim, L.-S. A 0.65-V, 11.2-Gb/s Power Noise Tolerant Source-Synchronous Injection-Locked Receiver with Direct DTLB DFE. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2018, 65, 1564–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alon, E.; Kim, J.; Pamarti, S.; Chang, K.; Horowitz, M. Replica Compensated Linear Regulators for Supply-Regulated Phase-Locked Loops. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2006, 41, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savoj, J.; Hsieh, K.C.-H.; An, F.-T.; Gong, J.; Im, J.; Jiang, X.; Jose, A.P.; Kireev, V.; Lim, S.-W.; Roldan, A.; et al. A Low-Power 0.5–6.6 Gb/s Wireline Transceiver Embedded in Low-Cost 28 nm FPGAs. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2013, 48, 2582–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Klumperink, E.A.; Geraedts, P.F.; Nauta, B. Jitter analysis and a benchmarking figure-of-merit for phase-locked loops. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2009, 56, 117–121. [Google Scholar]
- Hossain, M.; El-Halwagy, W.; Hossain, A.D. Fractional-N DPLL-Based Low-Power Clocking Architecture for 1–14 Gb/s Multi-Standard Transmitter. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2017, 52, 2647–2662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Balankutty, A.; Elshazly, A.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Song, H.; Yu, K.; O’Mahony, F. A 16-to-40Gb/s Quarter-Rate NRZ/PAM4 Dual-Mode Transmitter in 14nm CMOS. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference-(ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 22–26 February 2015; pp. 60–61. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, W.-S.; Shu, G.; Talegaonkar, M.; Liu, Y.; Wei, D.; Benini, L.; Hanumolu, P.K. A 0.45–0.7 V 1–6 Gb/s 0.29–0.58 pJ/b Source-Synchronous Transceiver Using Near-Threshold Operation. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2018, 53, 884–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.; Kaviani, K.; Daly, B.; Shirasgaonkar, M.; Dettloff, W.; Stone, T.; Prabhu, K.; Tsang, B.; Eble, J.; Zerbe, J. A 6.4/3.2/1.6 Gb/s Low Power Interface with All Digital Clock Multiplier for On-the-Fly Rate Switching. In Proceedings of the IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference, San Jose, CA, USA, 9–12 September 2012; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Leibowitz, B.; Palmer, R.; Poulton, J.; Frans, Y.; Li, S.; Wilson, J.; Bucher, M.; Fuller, A.M.; Eyles, J.; Aleksic, M.; et al. A 4.3 GB/s Mobile Memory Interface with Power-Efficient Bandwidth Scaling. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2010, 45, 889–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menolfi, C.; Toifl, T.; Buchmann, P.; Kossel, M.; Morf, T.; Weiss, J.; Schmatz, M. A 16Gb/s source-series terminated transmitter in 65nm CMOS SOI. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, Digest of Technical Papers, San Francisco, CA, USA, 11–15 February 2007; pp. 446–614. [Google Scholar]
- Inti, R.; Elshazly, A.; Young, B.; Yin, W.; Kossel, M.; Toifl, T.; Hanumolu, P.K. A Highly Digital 0.5-to-4Gb/s 1.9mW/Gb/s Serial Link Transceiver Using Current-Recycling in 90nm CMOS. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference-(ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 20–24 February 2011; pp. 152–153. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.-H.; Palermo, S. A 6-Gbit/s Hybrid Voltage-Mode Transmitter with Current-Mode Equalization in 90-nm CMOS. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2012, 59, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.L.; Tan, K.H.; Frans, Y.; Im, J.; Upadhyaya, P.; Lim, S.W.; Chiang, P.C. A 32.75-Gb/s voltage-mode transmitter with three-tap FFE in 16-nm CMOS. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2017, 52, 2663–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Kim, S.; Shin, Y.; Jeong, D.-K.; Lim, G.; Kim, B.; Da Costa, V.; Lee, D. A Jitter-Tolerant 4.5Gb/s CMOS Interconnect for Digital Display. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference-(ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 5 February 1998; pp. 310–311. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, K.; Bai, R.; Jiang, T.; Ma, C.; Ragab, A.; Palermo, S.; Chiang, P.Y. 0.16-0.25 pJ/bit, 8 Gb/s Near-Threshold Serial Link Receiver with Super-Harmonic Injection-Locking. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2012, 47, 1842–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bae, W.; Jeong, G.-S.; Park, K.; Cho, S.-Y.; Kim, Y.; Jeong, D.-K. A 0.36 pJ/bit, 0.025 mm2, 12.5 Gb/s Forwarded-Clock Receiver with a Stuck-Free Delay-Locked Loop and a Half-Bit Delay Line in 65-nm CMOS Technology. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2016, 63, 1393–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baronti, F.; Lunardini, D.; Roncella, R.; Saletti, R. A self-calibrating delay-locked delay line with shunt-capacitor circuit scheme. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2004, 39, 384–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Ko, H.-G.; Cho, S.-Y.; Lee, J.; Shin, S.; Choo, M.-S.; Chi, H.; Jeong, D.-K. 29.7 A 2.5GHz injection-locked ADPLL with 197fsrms integrated jitter and −65dBc reference spur using time-division dual calibration. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference-(ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 5–9 February 2017; pp. 494–495. [Google Scholar]
- Daly, D.C.; Fujino, L.C.; Smith, K.C. Through the looking glass-the 2018 edition: Trends in solid-state circuits from the 65th ISSCC. IEEE Solid-State Circuits Mag. 2018, 10, 30–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Process (nm) | Min. Rate (Gb/s) | Max. Rate (Gb/s) | Signaling Mode | Equalizer | Clocking | # of PLLs | Supply Scaling | Min. Supply (V) | Max. Supply (V) | TX Swing (Vppd) | Area (mm2) | FoM (pJ/b) @Min Rate | FoM (pJ/bit) @Max Rate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [24] | 350 | 0.2 | 0.8 | Open drain | None | Half rate | External | DC–DC | 1.3 | 3.2 | 0.1–0.15 | N/A | N/A | 26.875 |
| [22] | 250 | 0.65 | 5 | Current | None | 1/5 rate | 1 | DC–DC | 0.9 | 2.5 | 0.1–0.3 | N/A | 8.5 | 43.3 |
| [25] | 65 | 5 | 15 | Current | 3-tap FFE | Half rate | External | External source | 0.68 | 1.05 | 0.1–0.72 | 0.033 | 1.5 | 2.3 |
| [26] | 45 | 5 | 25 | Voltage | None | Half rate | External | External source | 0.75 | 1.1 | 0.082–0.36 | 0.077 | N/A | N/A |
| [15] | 32 | 2 | 16 | Voltage/ current | 3-tap FFE | Quarter rate | External | External source | 0.6 | 1.08 | 0.36–0.5 | 0.014 | 0.47 | 1.56 |
| [27] | 65 | 4.8 | 8 | Voltage | None | Quarter rate | External | External source | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.1–0.2 | 0.027 | 0.34 | 0.44 |
| [16] | 22 | 8 | 32 | Voltage | 3-tap FFE | Quarter rate | 1 | External source | 0.72 | 1.07 | 0.1–0.6 | N/A | 2.19 | 1.97 |
| [31] | 65 | 3 | 10 | Current | 3-tap FFE | Half rate | 1 | DC–DC + LDO | 0.7 | 1.4 | N/A | N/A | 2.7 | 4.8 |
| [12] | 65 | 5 | 32 | Voltage | 2-tap FFE | Quarter rate | 1 | LDO | 0.85 | 1.3 | 0.4–1.3 | 0.17 | 3.45 | 2.74 |
| [34] | 65 | 3 | 16 | Voltage | PWM | Quarter rate | External | External source | 0.5 | 0.9 | N/A | N/A | 1.04 | 2.42 |
| Process (nm) | Min. Rate (Gb/s) | Max. Rate (Gb/s) | Equalizer | Clocking | CDR/Deskew Loop | Eye Opening (UI) | Supply Scaling | Min. Supply (V) | Max. Supply (V) | Area (mm2) | FoM (pJ/b) @Min Rate | Fom (Pj/Bit) @Max Rate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [24] | 350 | 0.2 | 0.8 | None | Half rate | Mesochronous DLL + PI | N/A | DC–DC | 1.3 | 3.2 | N/A | N/A | 38.75 |
| [22] | 250 | 0.65 | 5 | None | 1/5 rate | Plesiochronous PLL | N/A | DC–DC | 0.9 | 2.5 | N/A | 6.5 | 32.7 |
| [25] | 65 | 5 | 15 | CTLE | Half rate | Mesochronous External CDR | N/A | External source | 0.68 | 1.05 | 0.055 | 1.2 | 2.7 |
| [26] | 40 | 1.6 | 6.4 | None | Half rate | Mesochronous DLL + PI | N/A | External source | 0.75 | 1.1 | 0.133 | N/A | N/A |
| [15] | 32 | 2 | 16 | CTLE | Quarter rate | Mesochronous External CDR | 0.5 | External source | 0.6 | 1.08 | 0.02 | 0.52 | 1.02 |
| [27] | 65 | 4.8 | 8 | CTLE | Quarter rate | Mesochronous External CDR | 0.05 | External source | 0.6 | 0.75 | 0.032 | 0.17 | 0.22 |
| [16] | 22 | 8 | 32 | CTLE + 6-tap DFE | Quarter rate | Plesiochronous DLL + PI | 0.5 | External source | 0.72 | 1.07 | N/A | 1.06 | 4.45 |
| [33] | 110 | 0.5 | 4 | None | Half rate | Plesiochronous PLL | N/A | DC–DC | 0.685 | 0.784 | 0.56 | 5.36 | 0.97 |
| Process (nm) | Min. Rate (Gb/s) | Max. Rate (Gb/s) | Clocking | Clock Rate | # of PLLs | Channel Loss (dB) | Equalizer | Supply Scaling | Min. Supply (V) | Max. Supply (V) | Area (mm2) | FoM (pJ/b) @Min Rate | FoM (pJ/b) @Max Rate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [24] | 350 | 0.2 | 0.8 | Mesochronous | Half rate | External | N/A | None | DC–DC | 1.3 | 3.2 | 1.625 | N/A | 65.625 |
| [22] | 250 | 0.65 | 5 | Plesiochronous | 1/5 rate | 1 | N/A | None | DC–DC | 0.9 | 2.5 | 0.63 | 15 | 76 |
| [25] | 65 | 5 | 15 | Mesochronous | Half rate | External | 10 | TX FFE + CTLE | External source | 0.68 | 1.05 | 0.088 | 2.7 | 5 |
| [26] | 45 | 5 | 25 | Mesochronous | Half rate | External | N/A | TX FFE + DFE | External source | 0.75 | 1.1 | 0.21 | 1.6 | 2.6 |
| [15] | 32 | 2 | 16 | Mesochronous | Quarter rate | External | 11 | TX FFE + CTLE | External source | 0.6 | 1.08 | 0.039 | 0.99 | 2.56 |
| [27] | 65 | 4.8 | 8 | Mesochronous | Quarter rate | External | 8.4 | CTLE | External source | 0.6 | 0.8 | 0.057 | 0.51 | 0.66 |
| [16] | 22 | 8 | 32 | Plesiochronous | Quarter rate | 1 | 16 | TX FFE + CTLE + DFE | External source | 0.72 | 1.07 | 0.079 | 3.25 | 6.41 |
| [31] | 65 | 3 | 10 | Source synchronous | Half rate | 1 | N/A | TX FFE | DC-DC + LDO | 0.9 | 1.3 | 2.37 | 3.6 | 7.24 |
| [34] | 65 | 3 | 16 | N/A (no CDR) | Quarter rate | External | 24 | TX PWM + RX passive | External source | 0.5 | 0.9 | 0.13 | 1.65 | 3.14 |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bae, W. Supply-Scalable High-Speed I/O Interfaces. Electronics 2020, 9, 1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9081315
Bae W. Supply-Scalable High-Speed I/O Interfaces. Electronics. 2020; 9(8):1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9081315
Chicago/Turabian StyleBae, Woorham. 2020. "Supply-Scalable High-Speed I/O Interfaces" Electronics 9, no. 8: 1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9081315
APA StyleBae, W. (2020). Supply-Scalable High-Speed I/O Interfaces. Electronics, 9(8), 1315. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9081315





