Entire Magnetic Integration Method of Multi-Transformers and Resonant Inductors for CLTLC Resonant Converter
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Investigation of Magnetic Integration Solution
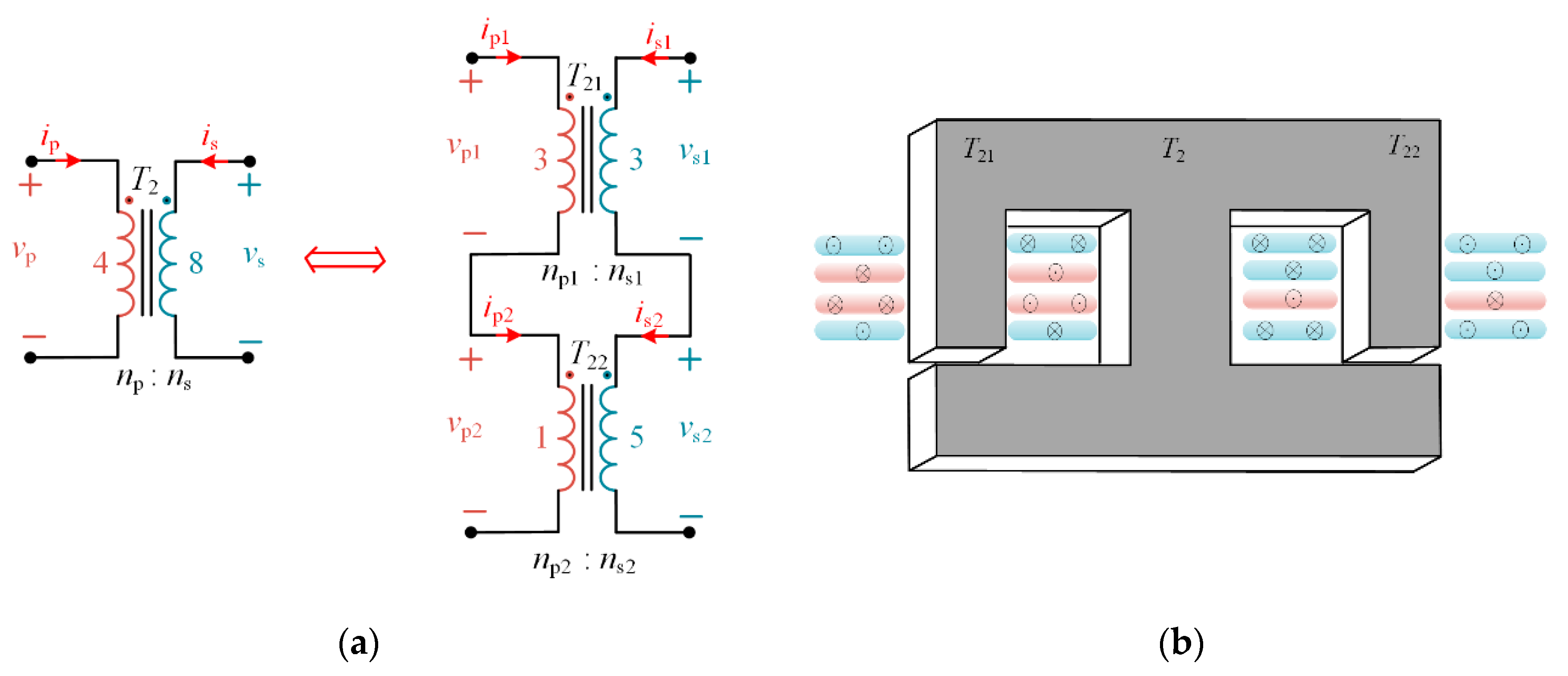
2.1. Investigation of Matrix Transformer
2.2. Investigation of Uneven Distribution Windings
- (1)
- The permeability of the magnetic core is much greater than that of the air, so the core reluctance is negligible compared to the air reluctance.
- (2)
- Flux leakage in the air is very small and can be ignored as well.
- (3)
- Under the magnetic circuit analysis, the influence of the fringing flux of magnetic fields is not considered.
2.3. Reluctance Model
3. Winding Arrangement and Integrated Core Structure
4. Experimental Result
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PCB | printed circuit board |
| CLTLC | capacitor-inductor-transformer-inductor-capacitor |
| UI | U-type and I-type |
| EI | E-type and I-type |
| EIE | E-type and I-type and E-type |
References
- Yi, K. Capacitive Coupling Wireless Power Transfer with Quai-LLC Resonant Converter Using Electric Vehicle’s Windows. Electronics 2020, 9, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, P.; Yuan, Y. Analysis and Implementation of LC Series Resonant Converter with Secondary Side Clamp Diodes under DCM Operation for High Step-Up Applications. J. Power Electron. 2019, 19, 363–379. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Wang, H.; Shen, Z.; Yang, Y.; Blaabjerg, F. A 1-MHz Series Resonant DC-DC Converter with a Dual-Mode Rectifier for PV Microinverters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 34, 6544–6564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yi, K. Output Voltage Analysis of Inductive Wireless Power Transfer with Series LC and LLC Resonance Operations Depending on Coupling Condition. Electronics 2020, 9, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Hu, Z.; Liu, Y.-F.; Liu, X.; Afsharian, J.; Yang, Z. LCLC Converter With Optimal Capacitor Utilization for Hold-Up Mode Operation. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 34, 2385–2396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Jin, X.; Hu, H.; Xing, Y. Multielement Resonant Converters with a Notch Filter on Secondary Side. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 31, 3999–4004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, D.G.; Wang, W. A 1 MHz Half-Bridge Resonant DC/DC Converter Based on GaN FETs and Planar Magnetics. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 2876–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-F.; Han, F.; Yang, L.; Wang, C.; Chen, B.; Xu, R. A Novel D-CLT Multi-Resonant DC-DC Converter with Reduced Voltage Stresses for Wide Frequency Variation Applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 34, 4509–4523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Z.; Andersen, M.A.E. Overview of Planar Magnetic Technology—Fundamental Properties. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2013, 29, 4888–4900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Z.; Thomsen, O.C.; Andersen, M.A.E. Optimal Design and Tradeoff Analysis of Planar Transformer in High-Power DC-DC Converters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2010, 59, 2800–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, M.; Lee, F.C. Design and Optimization of a 380–12V High-Frequency, High-Current LLC Converter with GaN Devices and Planar Matrix Transformers. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2016, 4, 854–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buccella, C.; Cecati, C.; De Monte, F. A Coupled Electrothermal Model for Planar Transformer Temperature Distribution Computation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 3583–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, R.; Oliver, J.A.; Cobos, J.A.; Christini, M. Magnetic Component Model for Planar Structures Based on Transmission Lines. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 57, 1663–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quirke, M.T.; Barrett, J.J.; Hayes, M. Planar magnetic component technology—A review. IEEE Trans. Compon. Hybrids Manuf. Technol. 1992, 15, 884–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauwers, J.-P.; Nunes, C.; Velaerts, B.; Robert, F.; Mathys, P. Planar transformer technology applied to AC/DC conversion. In Proceedings of the 21st International Telecommunications Energy Conference, INTELEC’99 (Cat. No.99CH37007), Copenhagen, Denmark, 9 June 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Quinn, C.; Rinne, K.; O’Donnell, T.; Duffy, M.; Mathuna, C.O. A Review of Planar Magnetic Techniques and Technologies. In Proceedings of the 16th Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition, APEC 2001 (Cat. No. 01CH37181), Anaheim, CA, USA, 4–8 March 2001; pp. 1175–1183. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Lee, F.C.; Zhou, X.; Xu, P. Integrated planar inductor scheme for multi-module interleaved quasi-square-wave (QSW) DC/DC converter. In Proceedings of the 30th Annual IEEE Power Electronics Specialists Conference, Record (Cat. No.99CH36321), Charleston, SC, USA, 1 July 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, Z.; Sen, G.; Thomsen, O.C.; Andersen, M.A. Analysis and Design of Fully Integrated Planar Magnetics for Primary–Parallel Isolated Boost Converter. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2012, 60, 494–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biela, J.; Kolar, J.W. Electromagnetic integration of high power resonant circuits comprising high leakage inductance transformers. In Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE 35th Annual Power Electronics Specialists Conference (IEEE Cat. No.04CH37551), Aachen, Germany, 20–25 June 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Ouyang, Z.; Duffy, M.C.; Andersen, M.A.E.; Hurley, W.G. Leakage Inductance Calculation for Planar Transformers With a Magnetic Shunt. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2014, 50, 4107–4112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, D.; Ji, S.; Lee, F.C. LLC Resonant Converter with Matrix Transformer. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2014, 29, 4339–4347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, R.W.; Maksimovic, D. Fundamentals of Power Electronics, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Imran, M.; Iqbal, S. A Wide Ouput Range HB-2LLC Resonant Converter with Hybrid Rectifier for PEV Battery Charging. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 3, 520–531. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Li, Z. A PWM LLC Type Resonant Converter Adapted to Wide Output Range in PEV Charging Applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 3791–3801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Li, Y.; Xing, Y. LLC Resonant Converter with Semi-active Variable Structure Rectifier. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 31, 3389–3394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Ouyang, Z.; Andersen, M.A.E. High-Frequency LLC Resonant Converter with Magnetic Shunt Integrated Planar Transformer. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 34, 2405–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Li, Q.; Lee, F.C.; Yang, Y. A symmetrical resonant converter and PCB transformer structure for common mode noise reduction. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Cincinnati, OH, USA, 1–5 October 2017; pp. 5362–5368. [Google Scholar]












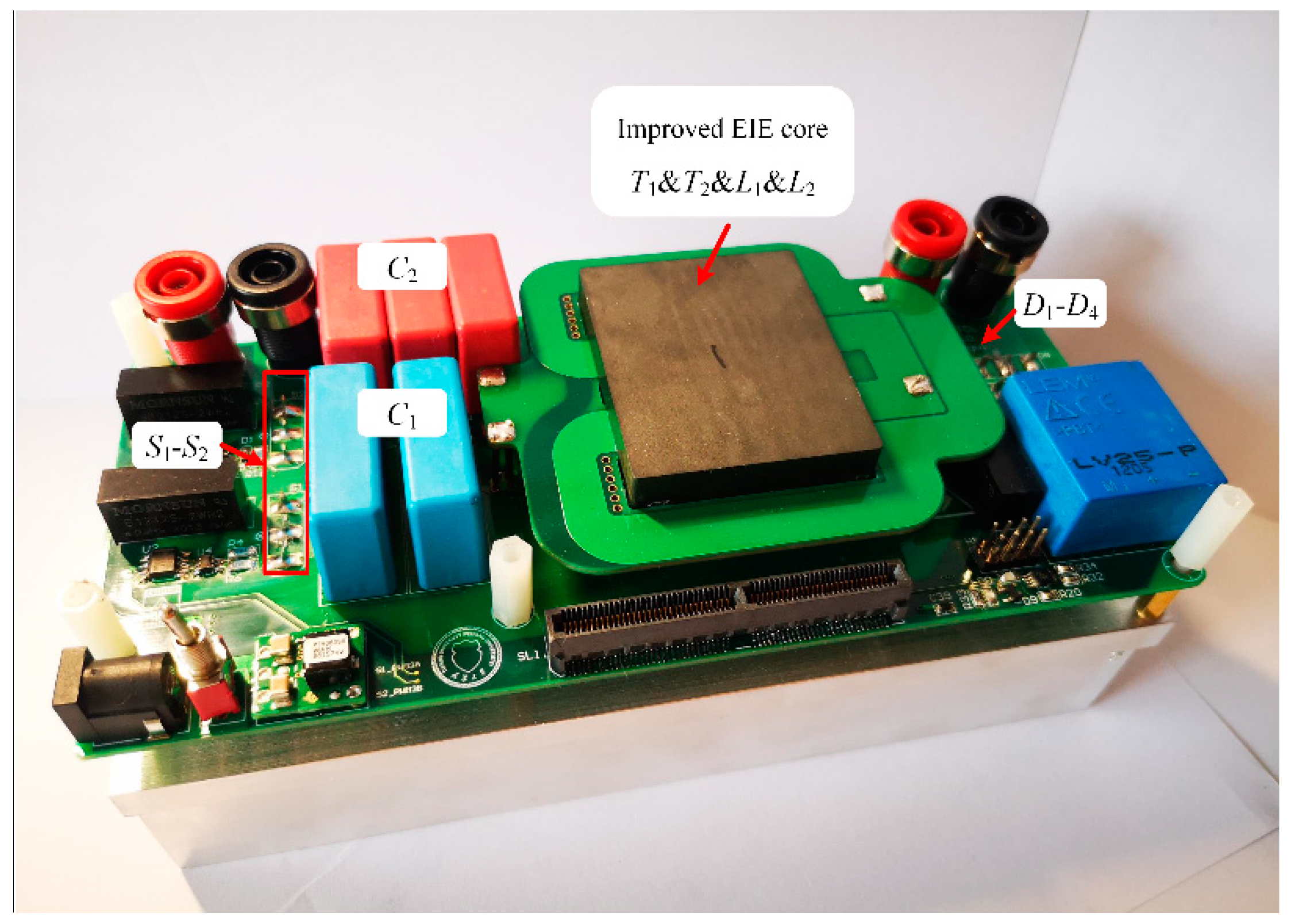





| Parameter | Improved EIE Core Structure (PCB Magnetics) | Discrete Magnetics (Litz Wire) |
|---|---|---|
| Inductor L1 | Integrated | PQ2620 |
| Inductor L2 | Integrated | PQ2620 |
| Transformer T1 | Improved EI core structure | PQ4040 |
| Transformer T2 | Improved EI core structure | PQ3535 |
| Total volume (mm3) | 52,920 | 95,760 |
| Footprint (mm2) | 1960 | 3053.6 |
| Total losses (W) | 15.1 | 22.7 |
| Parameter | Values |
|---|---|
| Rated power P | 1 kW |
| Rated load R | 0.9 Ω |
| Rated switching frequency fs | 300 kHz |
| Input voltage Vin | 400 V |
| Output voltage Vo | 30 V |
| Inductor L1 | 25 μH |
| Inductor L2 | 24 μH |
| Turns ratio np′:ns′ | 6:1 |
| Turns ratio np:ns | 0.5:1 |
| Capacitor C1 | 5 nF |
| Capacitor C2 | 3 nF |
| Topology Descriptions | Input Voltage Vin | Rated Power P | Rated Operating Frequency fs | Peak Efficiency | Magnetic Integration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HB-2LLC [23] | 400 V | 1.5 kW | 170 kHz | 95.21% | No |
| PWM LLC [24] | 390 V | 1 kW | 100 kHz | 96.7% | No |
| SA-VSR [25] | 400 V | 1.5 kW | 100 kHz | Above 95% | No |
| LLC [26] | 380 V | 100 W | 1 MHz | Above 95% | Yes |
| CLLC [27] | 350 V | 6.6 kW | 500 kHz | 97.8% | Yes |
| CLTLC | 400 V | 1 kW | 300 kHz | 96.6% | Yes |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, R.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Han, F.; Meng, Z. Entire Magnetic Integration Method of Multi-Transformers and Resonant Inductors for CLTLC Resonant Converter. Electronics 2020, 9, 1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9091386
Liu R, Wang Y, Chen Q, Han F, Meng Z. Entire Magnetic Integration Method of Multi-Transformers and Resonant Inductors for CLTLC Resonant Converter. Electronics. 2020; 9(9):1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9091386
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Ruixin, Yifeng Wang, Qing Chen, Fuqiang Han, and Zhun Meng. 2020. "Entire Magnetic Integration Method of Multi-Transformers and Resonant Inductors for CLTLC Resonant Converter" Electronics 9, no. 9: 1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9091386
APA StyleLiu, R., Wang, Y., Chen, Q., Han, F., & Meng, Z. (2020). Entire Magnetic Integration Method of Multi-Transformers and Resonant Inductors for CLTLC Resonant Converter. Electronics, 9(9), 1386. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9091386





