Three-Phase PWM Voltage-Source-Inverter Weight Optimization for Aircraft Application Using Deterministic Algorithm
Abstract
:1. Introduction
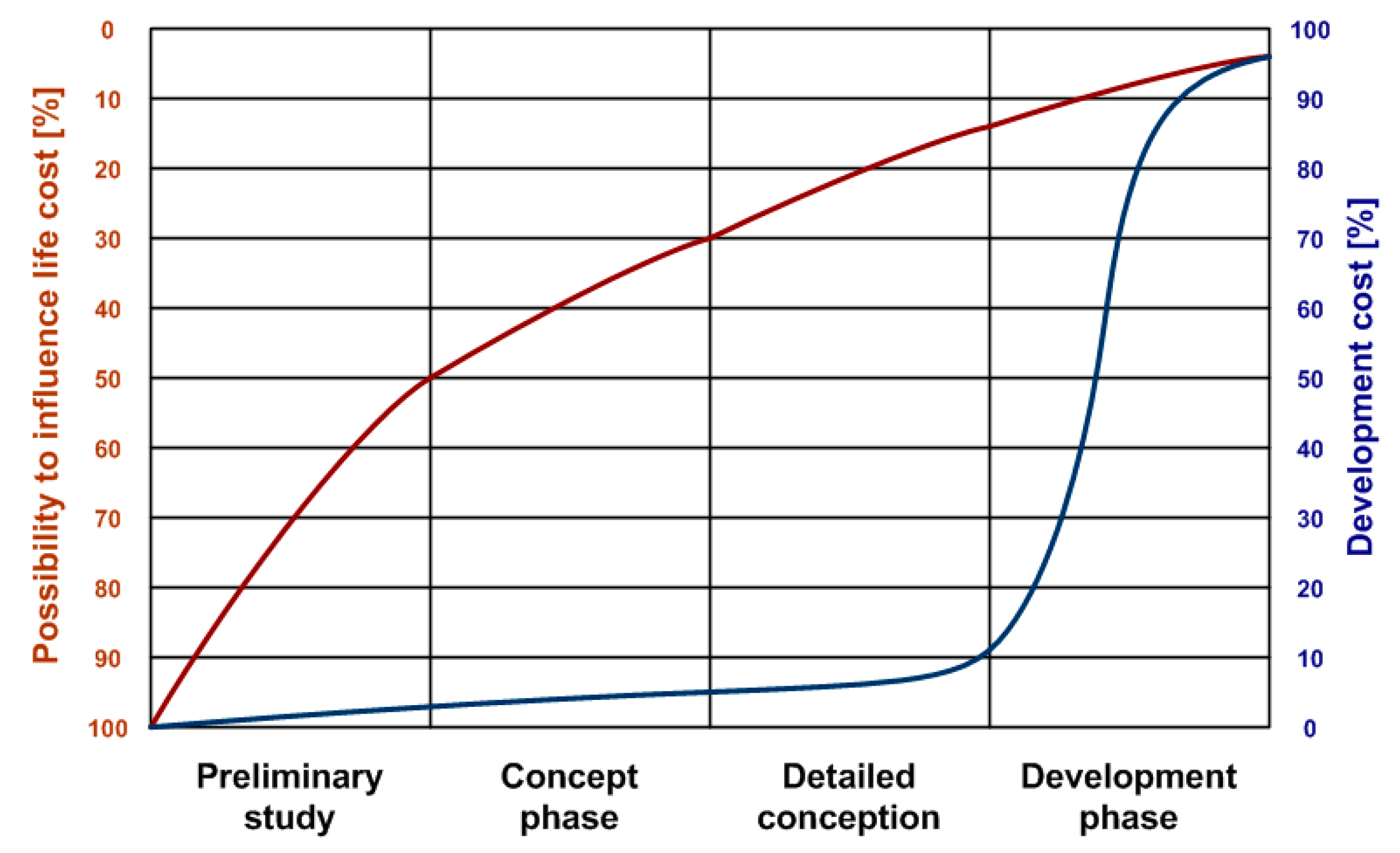
2. Analytical Models Suitable for Deterministic Optimization
2.1. Topology and Specifications
- Maximum junction temperature for semiconductor devices, maximum RMS current in capacitors, maximum loss density in inductors;
- Power quality requirements (total harmonic distortion on AC side; voltage and current ripple on DC side);
- User requests (efficiency, cost, etc.).
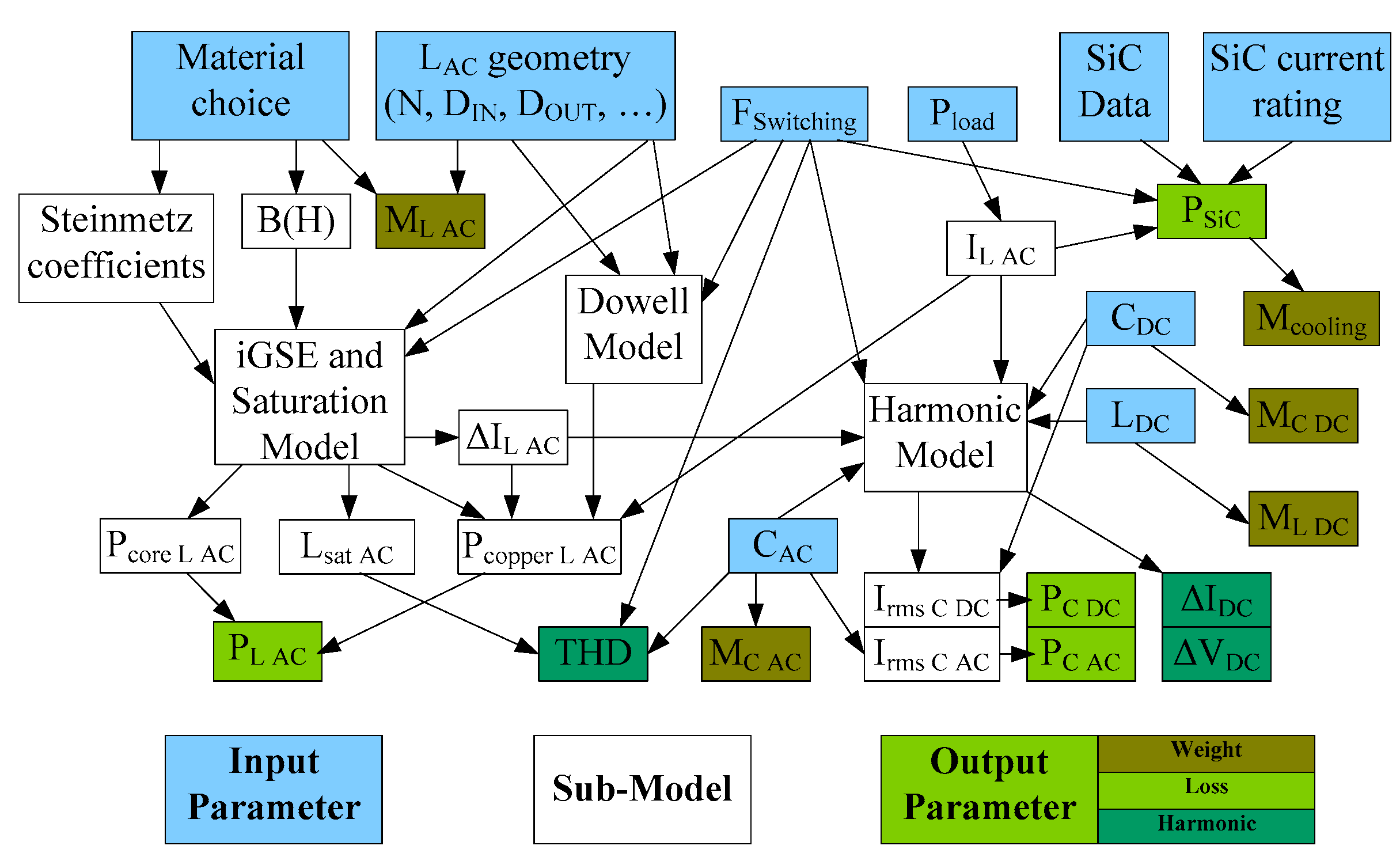
2.2. Semi-Conductor Losses
2.3. Harmonic Calculation
2.4. Inductor Models
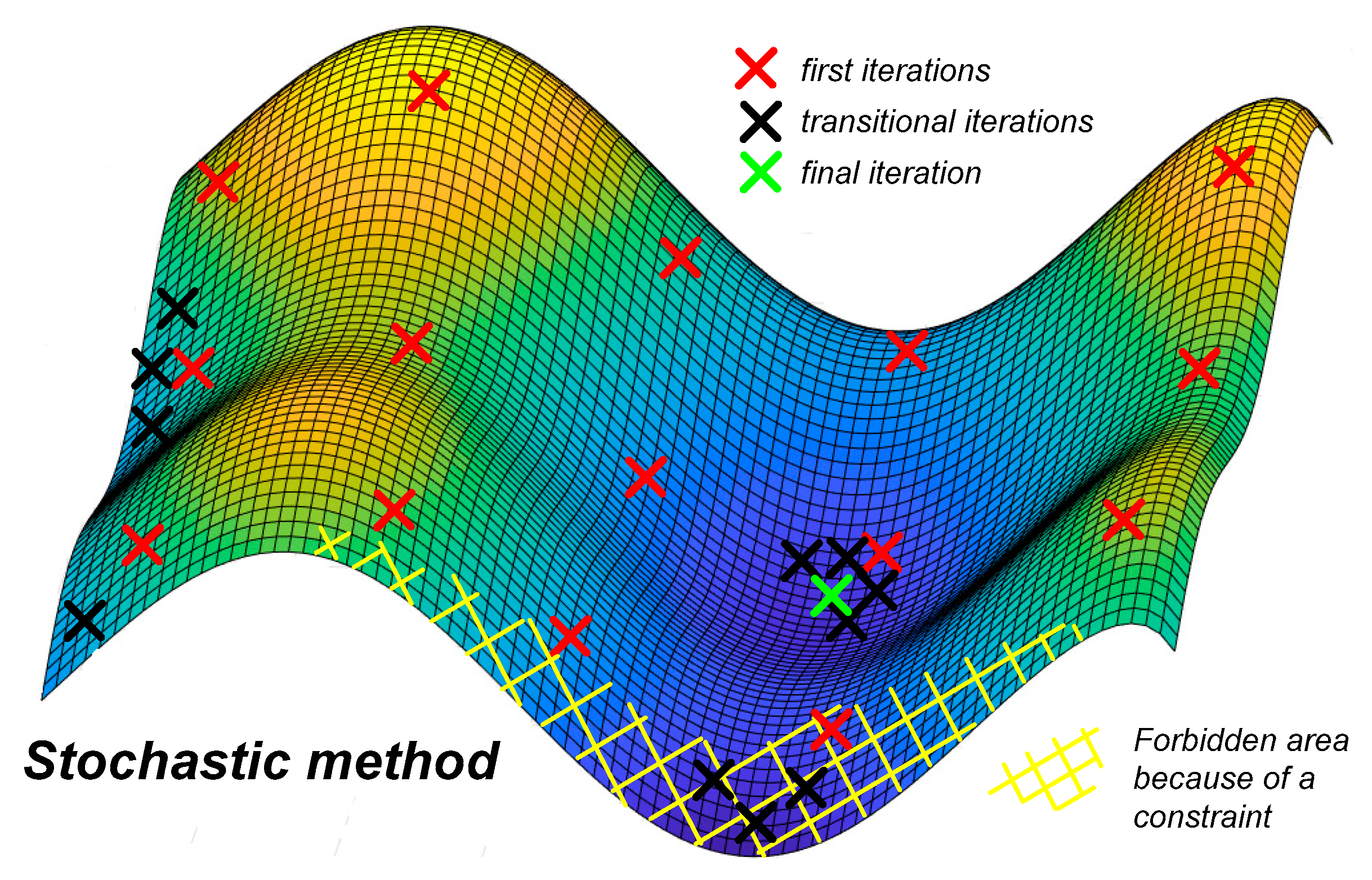
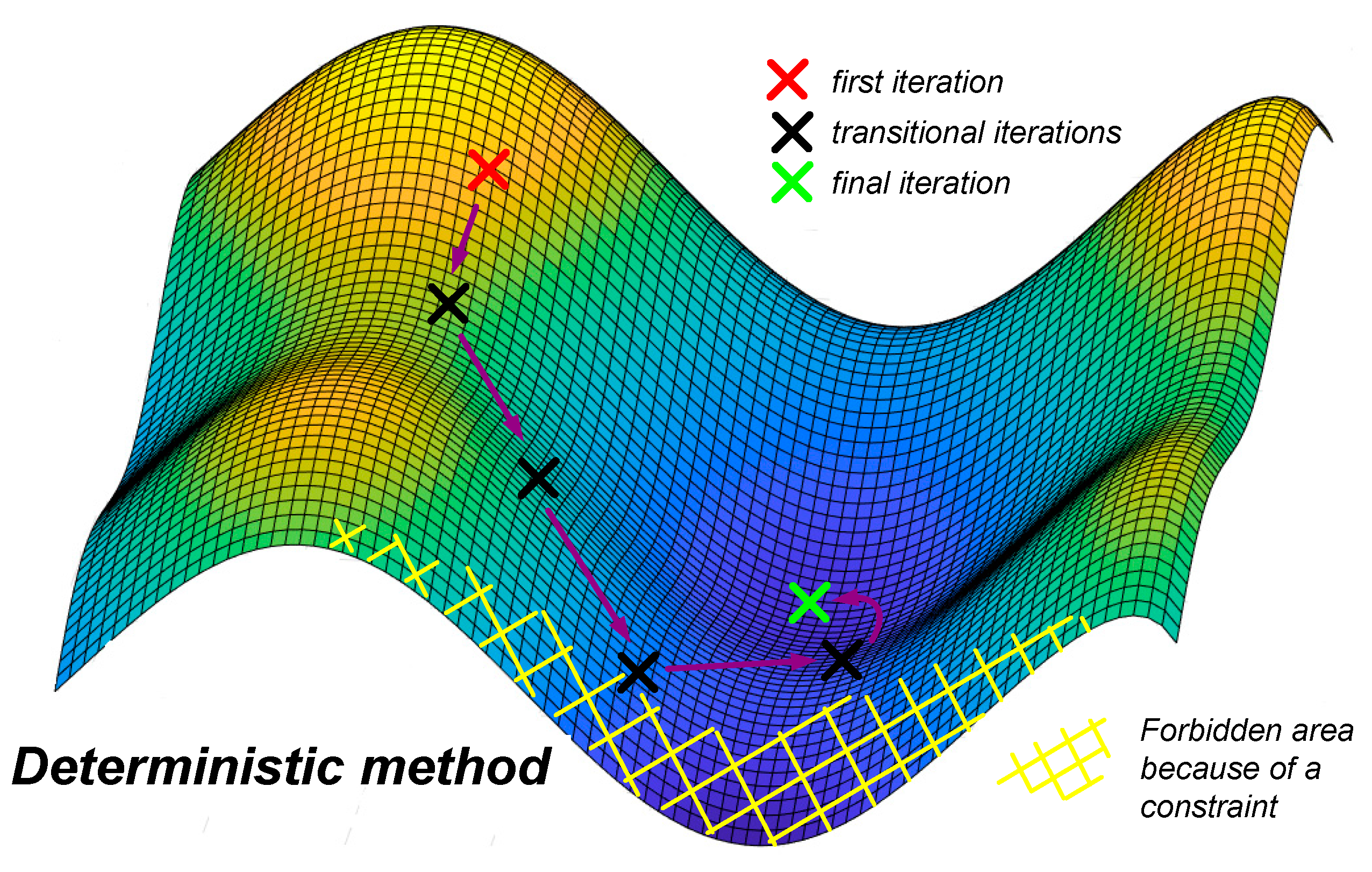
3. Optimization Result
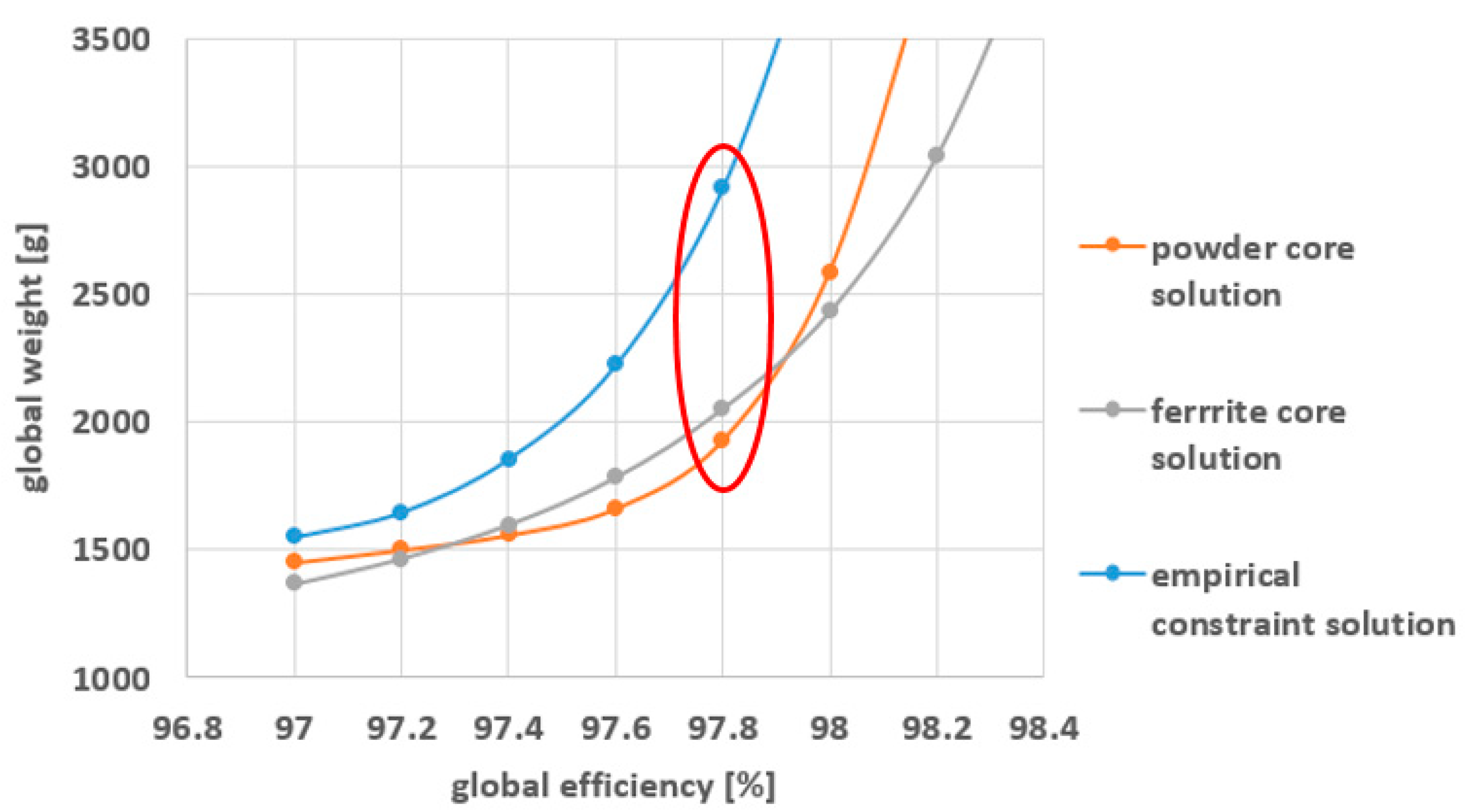
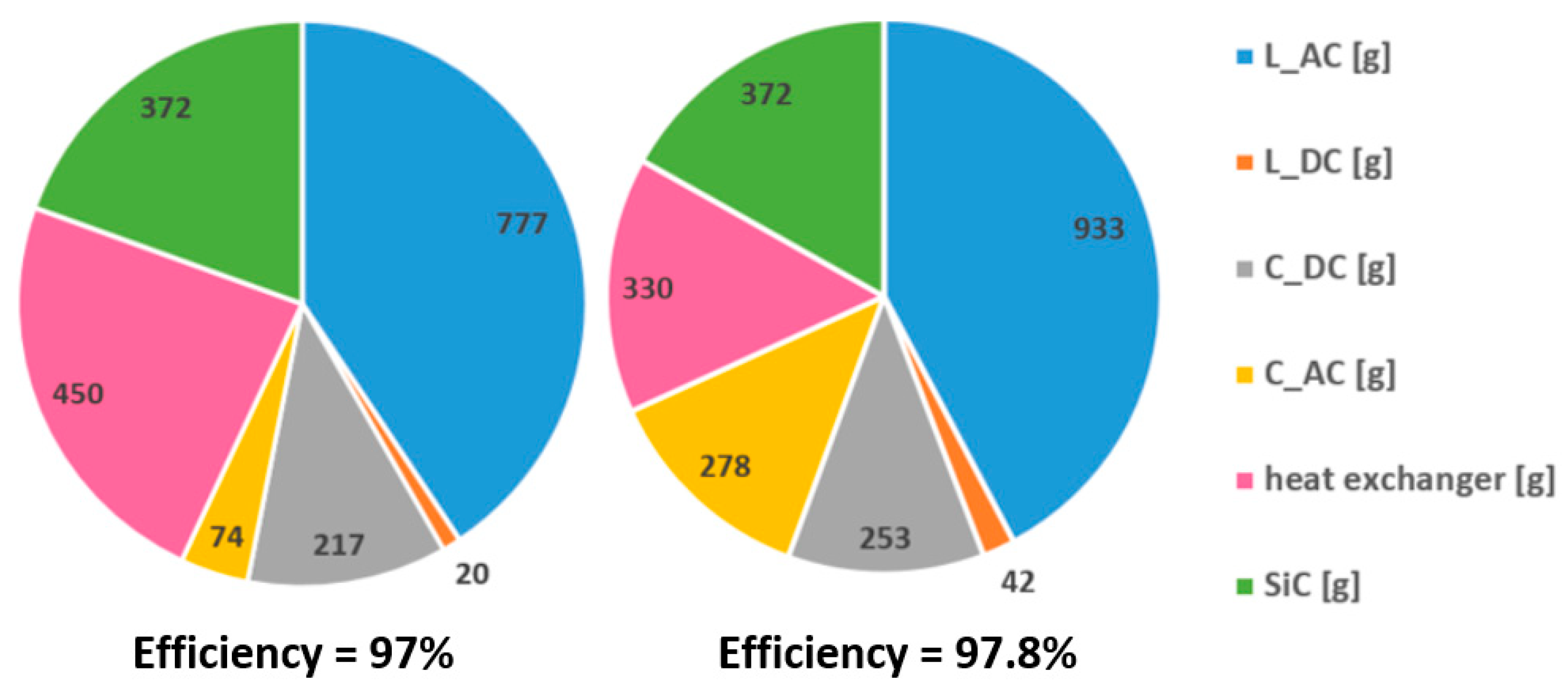
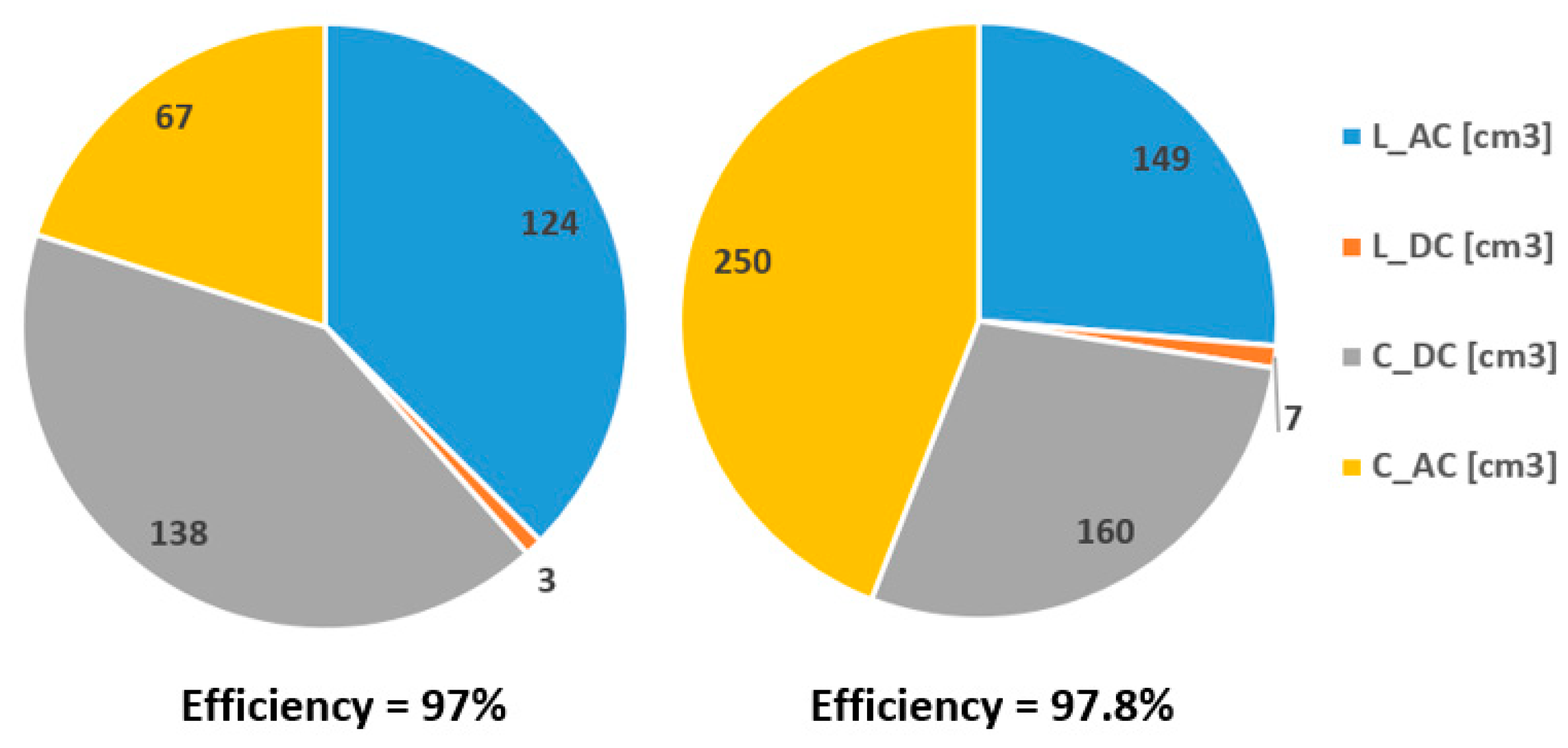
3.1. Comparison of Different Solutions
- When high efficiency is required, the AC current ripple should decrease to get lower losses. This is achieved by increasing the AC inductor value and, consequently, its weight.
- For lower frequencies, filter cut-off frequencies should increase to respect ripples standards. The AC inductor value and weight increase.
- Therefore, the lightest inductor is not necessarily the best choice for obtaining the lightest inverter, which justifies the use of a global methodology.
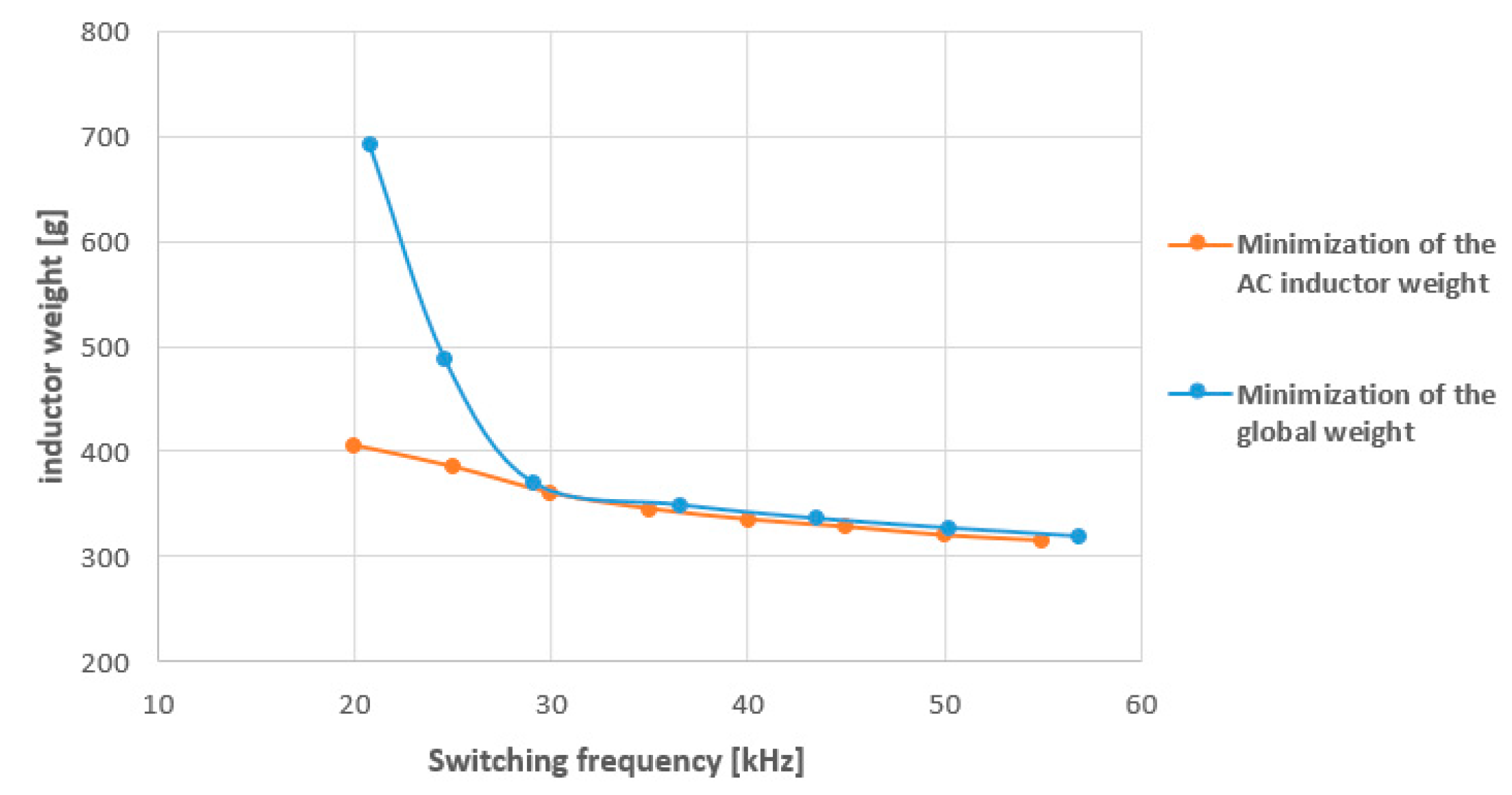
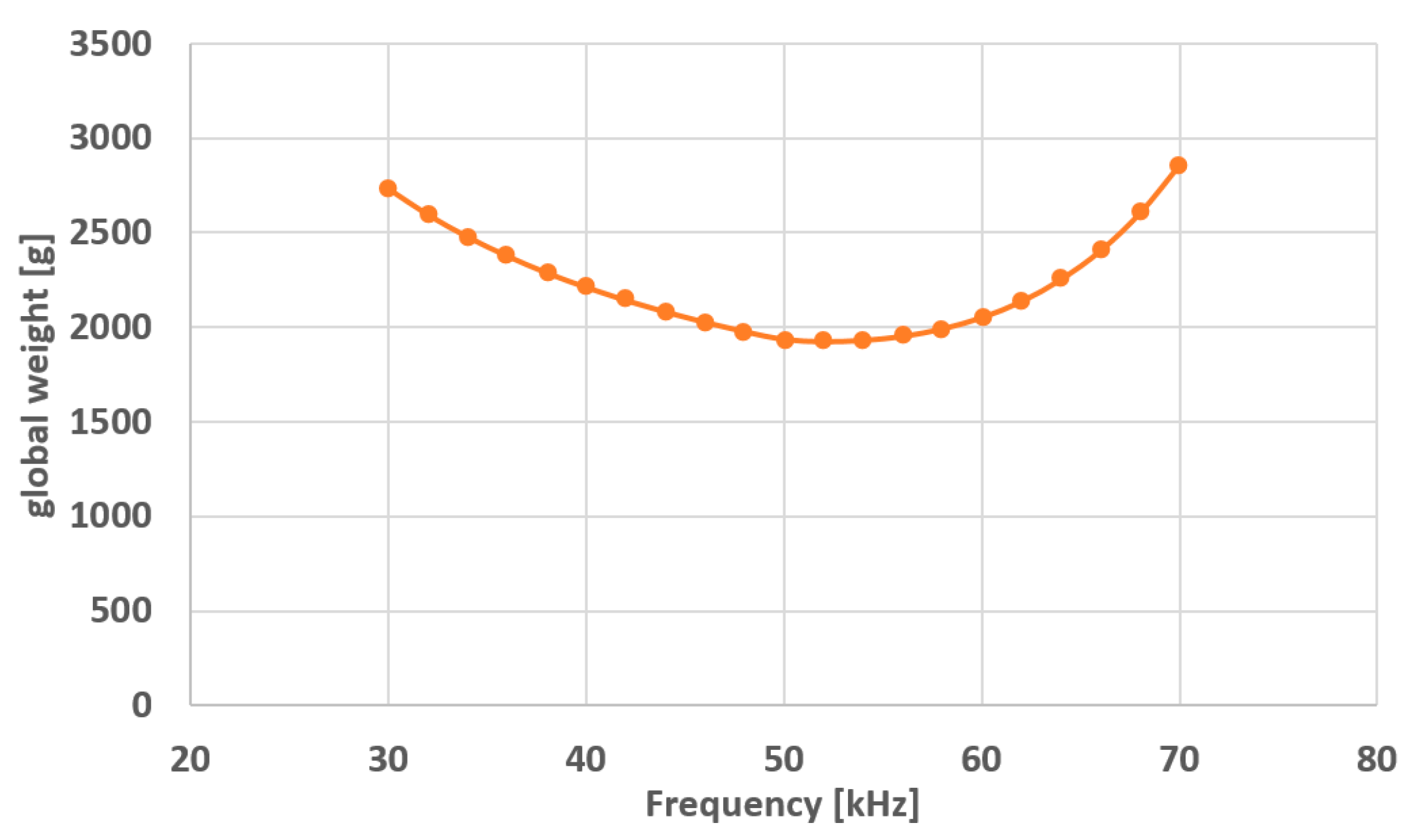
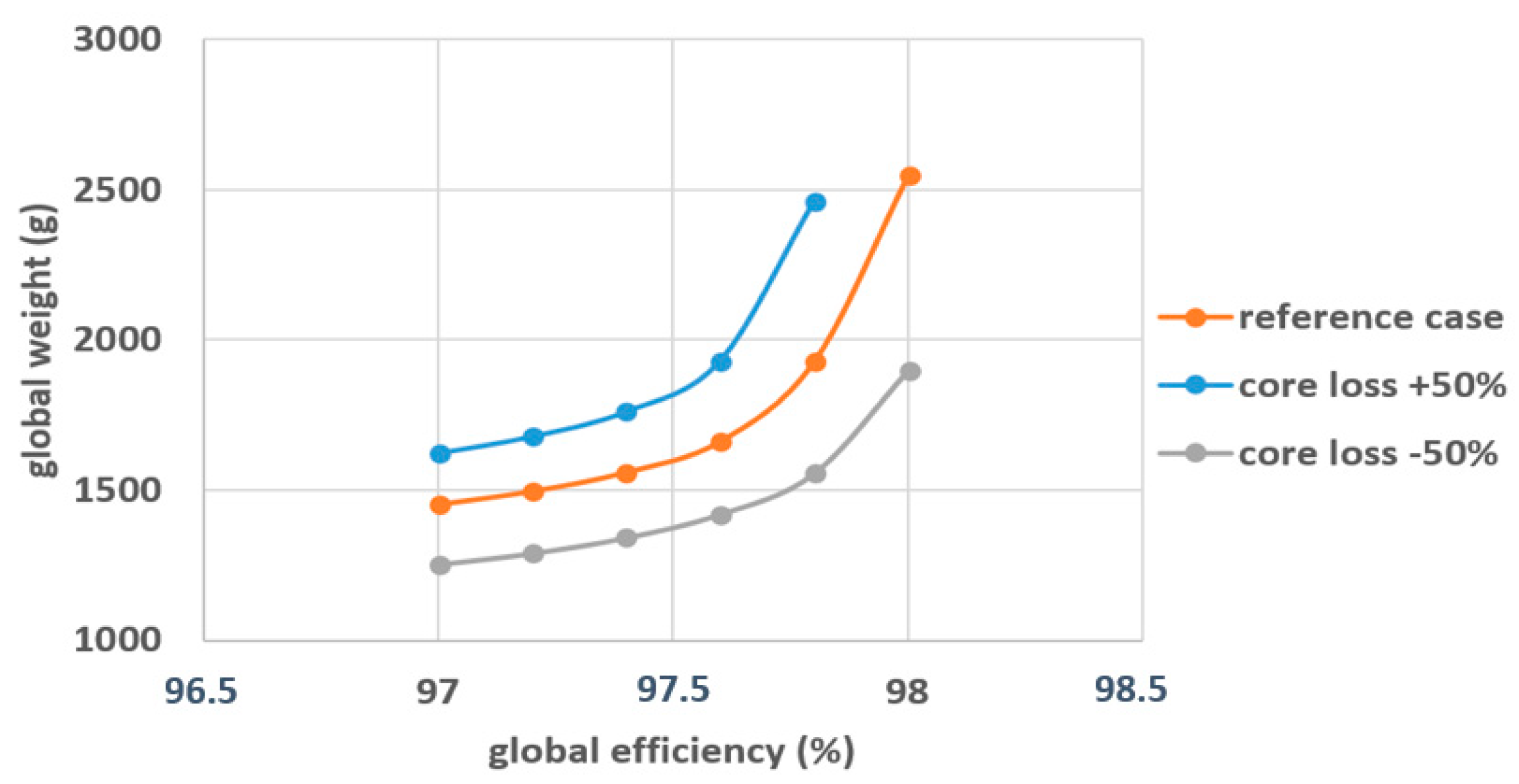
3.2. Sensitivity Analysis and Optimality Demonstration
- The optimal converter, with a switching frequency of 52 kHz;
- The same converter, with a switching frequency of 42 kHz (−10 kHz);
- The same converter, with a switching frequency of 62 kHz (+10 kHz).
3.3. From the Imaginary World to the Real World
4. Test Benches
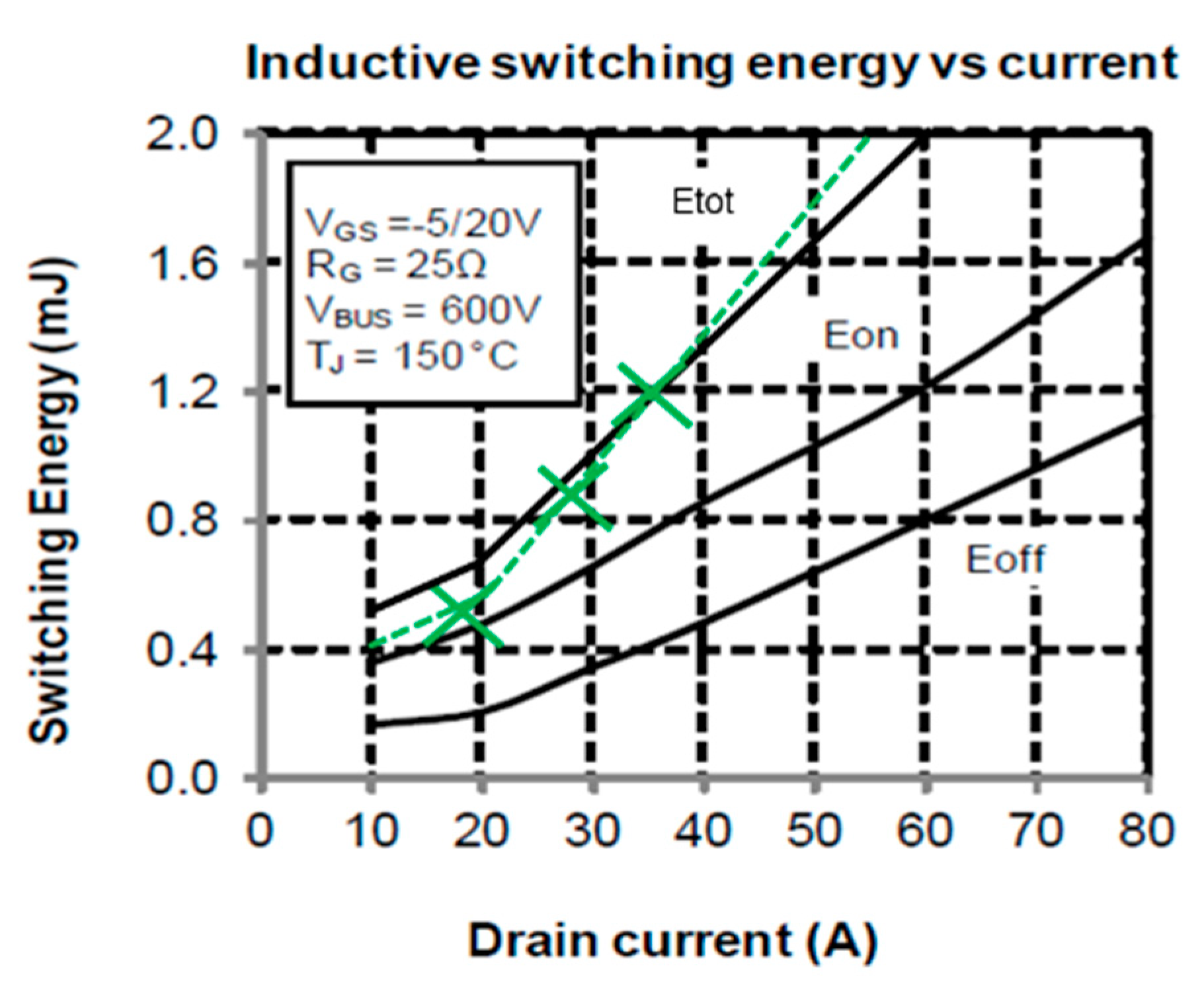
4.1. Semi-Conductor Loss Measurement
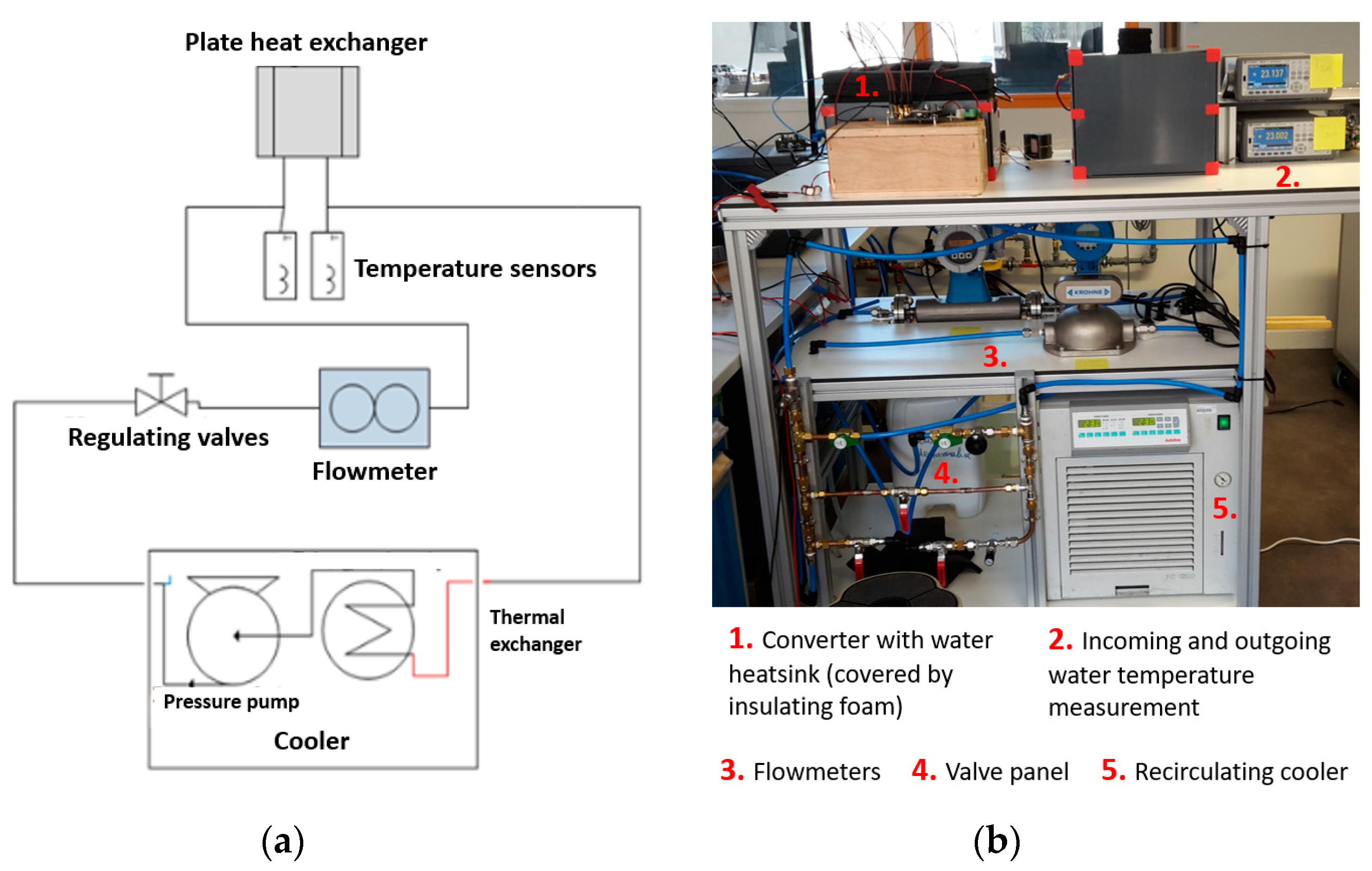
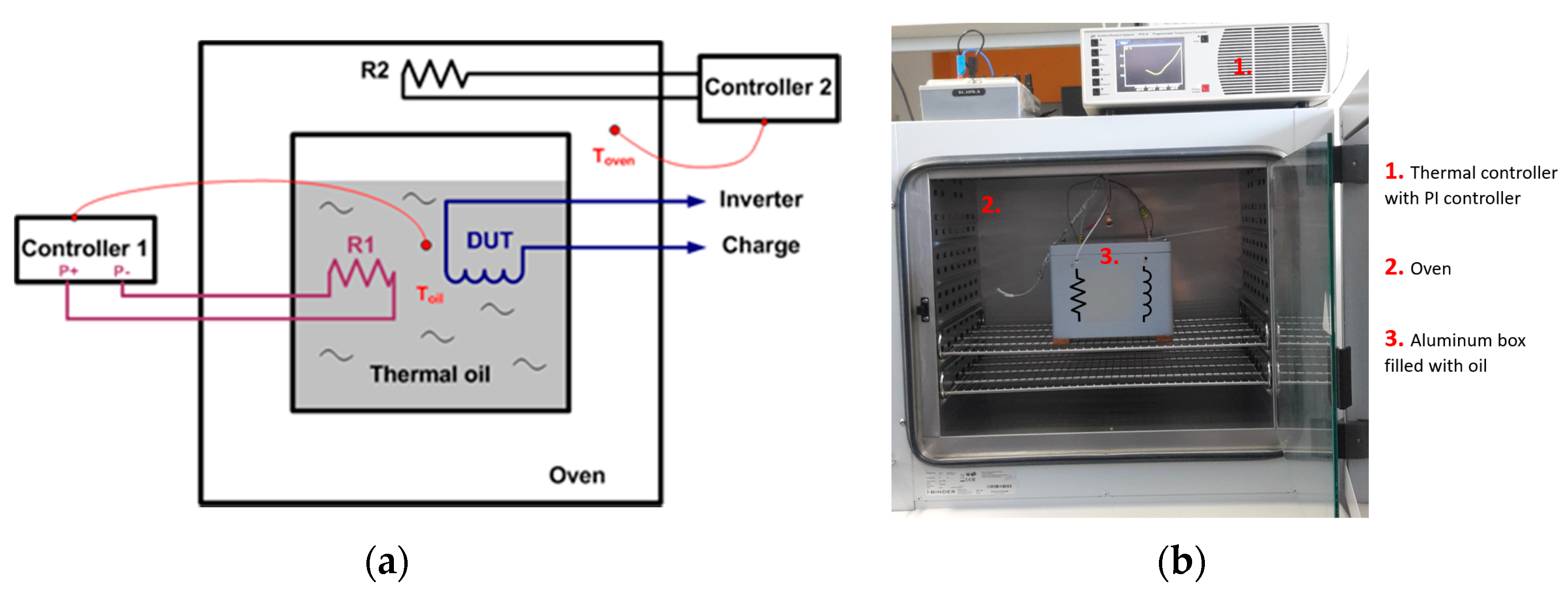
4.2. Inductor Loss Measurement
5. Experimental Validation of Optimization Results
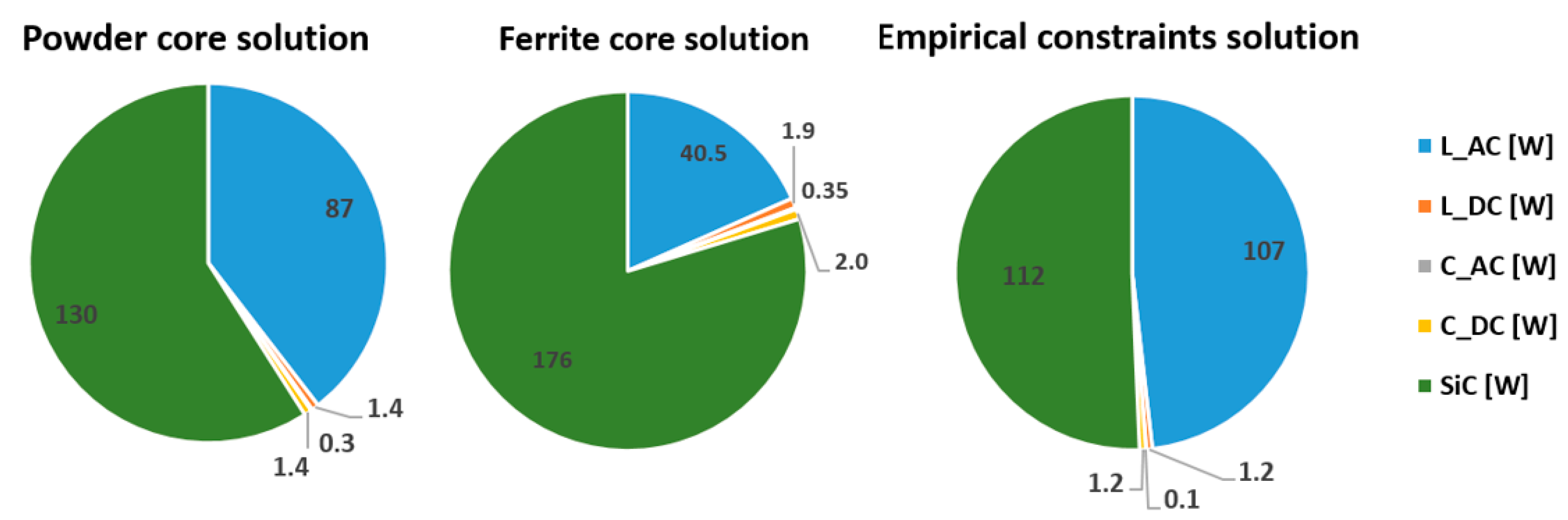
5.1. Powder Core Solution
5.2. Ferrite Core Solution
5.3. Empirical Constraint Solution
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kolar, J.W.; Biela, J.; Waffler, S.; Friedli, T.; Badstuebner, U. Performance trends and limitations of power electronic systems. In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Integrated Power Electronics Systems, Nuremberg, Germany, 16–18 March 2010; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Song, S.; Wang, H.; Blaabjerg, F. Cost-Volume-Reliability Pareto Optimization of a Photovoltaic Microinverter. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), Anaheim, CA, USA, 17–21 March 2019; pp. 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjafari, M.; Harb, S.; Balog, R.S. Multiobjective Optimization and Topology Selection for a Module-Integrated Inverter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 4219–4231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, K.; Pratap, A.; Agarwal, S.; Meyarivan, T. A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2002, 6, 182–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boillat, D.O.; Krismer, F.; Kolar, J.W. Design Space Analysis andρ–ηPareto Optimization of LC Output Filters for Switch-Mode AC Power Sources. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 30, 6906–6923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.-B.; Kieferndorf, F.; Drofenik, U.; Pettersson, S.; Canales, F. Weight Minimization of LCL Filters for High Power Converters: Impact of PWM Method on Power Loss and Power Density. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laird, I.; Yuan, X.; Scoltock, J.; Forsyth, A.J. A Design Optimization Tool for Maximizing the Power Density of 3-Phase DC–AC Converters Using Silicon Carbide (SiC) Devices. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2018, 33, 2913–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giglia, G.; Ala, G.; Di Piazza, M.C.; Giaconia, G.C.; Luna, M.; Vitale, G.; Zanchetta, P. Automatic EMI Filter Design for Power Electronic Converters Oriented to High Power Density. Electronics 2018, 7, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zimmer, L.; Zablit, P. ‘Global aircraft’ pre-design based on constraint propagation and interval analysis. In Proceedings of the CEAS Conference on Multidisciplinary Aircraft Design and Optimization, Koln, Germany, 25–26 June 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Enciu, P.; Gerbaud, L.; Wurtz, F. Automatic Differentiation for Sensitivity Calculation in Electromagnetism: Application for Optimization of a Linear Actuator. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2011, 47, 1238–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delhommais, M.; Schanen, J.; Wurtz, F.; Rigaud, C.; Chardon, S. First order design by optimization method: Application to an interleaved buck converter and validation. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), San Antonio, TX, USA, 4–8 March 2018; pp. 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjafari, M.; Balog, R.S. Survey of modelling techniques used in optimisation of power electronic components. IET Power Electron. 2014, 7, 1192–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touré, B.; Schanen, J.-L.; Gerbaud, L.; Meynard, T.; Roudet, J.; Ruelland, R. EMC Modeling of Drives for Aircraft Applications: Modeling Process, EMI Filter Optimization, and Technological Choice. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 28, 1145–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acquaviva, A.; Thiringer, T. Energy efficiency of a SiC MOSFET propulsion inverter accounting for the MOSFET’s reverse conduction and the blanking time. In Proceedings of the 19th European Conference on Power Electronics and Applications (EPE’17 ECCE Europe), Warsaw, Poland, 11–14 September 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cougo, B.; Morais, L.M.F.; Segond, G.; Riva, R.; Duc, H.T. Influence of PWM Methods on Semiconductor Losses and Thermal Cycling of 15-kVA Three-Phase SiC Inverter for Aircraft Applications. Electronics 2020, 9, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Delhommais, M. Preliminary Design Method in Power Electronics. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Grenoble Alpes, Saint-Martin-d’Hères, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gammeter, C.; Krismer, F.; Kolar, J.W. Weight Optimization of a Cooling System Composed of Fan and Extruded-Fin Heat Sink. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2014, 51, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, D.G.; Lipo, T.A. Modulation of ThreePhase Voltage Source Inverters, in Pulse Width Modulation for Power Converters: Principles and Practice; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2003; pp. 215–258. [Google Scholar]
- Voldoire, A.; Schanen, J.; Ferrieux, J.P.; Gautier, C.; Saber, C. Analytical Calculation of DC-Link Current for N-Interleaved 3-Phase PWM Inverters Considering AC Current Ripple. In Proceedings of the 20th International Scientific Conference on Electric Power Engineering (EPE), Kouty nad Desnou, Czech Republic, 15–17 May 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Dowell, P. Effects of eddy currents in transformer windings. Proc. Inst. Electr. Eng. 1966, 113, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.A. Improved analytical modeling of conductive losses in magnetic components. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 1994, 9, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefevre, G.; Chazal, H.; Ferrieux, J.P.; Roudet, J. Application of Dovvell method for nanocrystalline toroid high frequency transformers. In Proceedings of the IEEE 35th Annual Power Electronics Specialists Conference (IEEE Cat. No.04CH37551), Aachen, Germany, 20–25 June 2004; Volume 2, pp. 899–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voldoire, A.; Schanen, J.; Ferrieux, J.; Gautier, C.; Saber, C. Optimal Design of an AC Filtering Inductor for a 3-Phase PWM Inverter Including Saturation Effect. In Proceedings of the 10th International Power Electronics, Drive Systems and Technologies Conference (PEDSTC), Shiraz, Iran, 12–14 February 2019; pp. 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatachalam, K.; Sullivan, C.R.; Abdallah, T.; Tacca, H. Accurate prediction of ferrite core loss with nonsinusoidal waveforms using only Steinmetz parameters. In Proceedings of the IEEE Workshop on Computers in Power Electronics, Mayaguez, Puerto Rico, 3–4 June 2002; pp. 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, Z.; Wang, H.; Shen, Y.; Qin, Z.; Blaabjerg, F. An Improved Stray Capacitance Model for Inductors. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 11153–11170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fefermann, Y.; Maury, C.; Isikveren, A.T. Hybrid-Electric Motive Power Systems for Commuter Transport Applications. In Proceedings of the 30th Congress of the International Council of the Aeronautical Sciences, Daejeon, Korea, 25–30 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Boggs, P.T.; Tolle, J.W. Sequential Quadratic Programming. Acta Numer. 1995, 4, 1–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schanen, J.-L.; Avenas, Y. Teaching how to characterize and implement high speed power devices for tomorrow’s engineers. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition (ECCE), Baltimore, MD, USA, 29 September–3 October 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kyaw, P.A.; Delhommais, M.; Qiu, J.; Sullivan, C.R.; Schanen, J.-L.; Rigaud, C. Thermal Modeling of Inductor and Transformer Windings Including Litz Wire. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 35, 867–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, S.-H.; Kim, J.-M. Dead Time Compensation Method for Voltage-Fed PWM Inverter. IEEE Trans. Energy Convers. 2009, 25, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herran, M.A.; Fischer, J.R.; González, S.A.; Judewicz, M.G.; Carrica, D.O. Adaptive Dead-Time Compensation for Grid-Connected PWM Inverters of Single-Stage PV Systems. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2012, 28, 2816–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



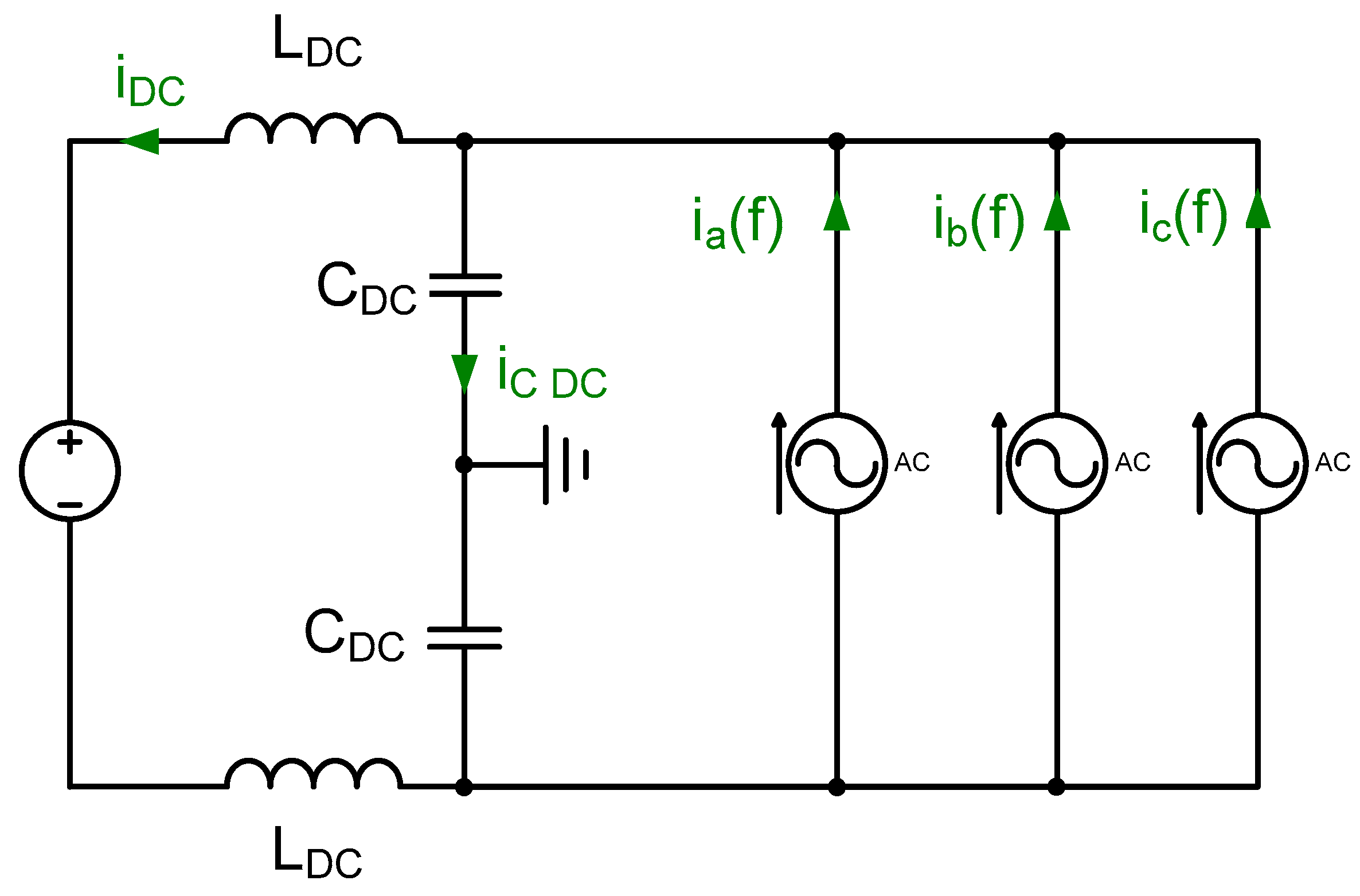



| Symbol | Quantity | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pload | Power | W | 10,000 |
| PF | Load power factor | - | 1 |
| VIN | DC voltage | V | 540 |
| VOUT | RMS * AC voltage | V | 115 |
| FGRID | Grid frequency | Hz | 400 |
| FSW | Switching frequency | Hz | Variable |
| Symbol | Quantity | Unit | Limit Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| TJ MOSFET | MOSFET junction temperature | °C | <150 |
| TJ diode | Diode junction temperature | °C | <150 |
| THD | AC voltage THD * | % | <3 |
| hmax AC | Maximum value of individual voltage harmonic | % | <2 |
| ΔVDC | DC bus voltage ripple | % | <1 |
| ΔIDC | DC source current ripple | % | <5 |
| PTOT VOL DC | Volumetric loss of DC inductor | mW/cm3 | <500 |
| PTOT VOL AC | Volumetric loss of AC inductor | mW/cm3 | <500 |
| IRMS C DC | DC capacitor RMS current | % | <100 |
| IRMS C AC | AC capacitor RMS current | % | <100 |
| η | Global efficiency | % | Variable |
| Symbol | Limit Value | Unit | Optimal Point | −10 kHz | +10 kHz |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| THD | 3 | % | 2.1 | 3.2 | 1.5 |
| hmax AC | 2 | % | 2.0 | 3.1 | 1.4 |
| ΔVDC | 1 | % | 1 | 1.2 | 0.8 |
| ΔIDC | 5 | % | 5 | 8 | 3.6 |
| PTOT VOL AC | 500 | mW/cm3 | 484 | 516 | 462 |
| PTOT VOL DC | 500 | mW/cm3 | 500 | 507 | 486 |
| IRMS C DC | 100 | % | 84 | 86 | 83 |
| IRMS C AC | 100 | % | 29 | 34 | 25 |
| η | 97.8 | % | 97.8 | 97.86 | 97.71 |
| Quantity | Unit | Design | Experiment | Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
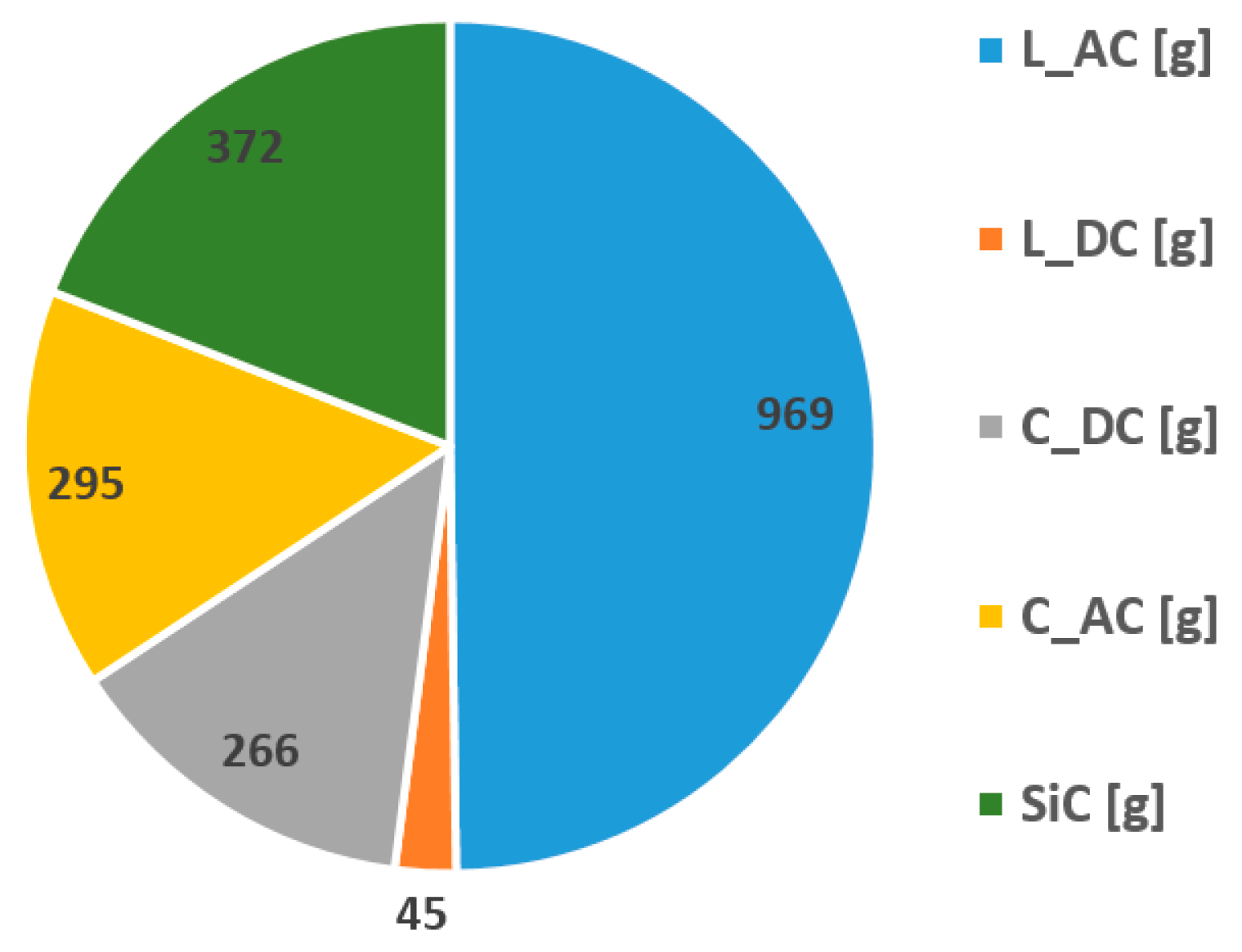
| AC inductor losses (×3) | W | 87 | 84 | 3.4 |
| DC inductor losses (×2) | W | 1.44 | 1.2 | 16 |
| AC capacitor losses (×3) | W | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0 |
| DC capacitor losses (×2) | W | 1.44 | 1.46 | 1.4 |
| Semi-conductor losses | W | 130 | 123 | 5.4 |
| Global efficiency | % | 97.8 | 97.88 | 0.08 |
| RMS AC capacitor current | A | 5.6 | 5.4 | 3.5 |
| RMS DC capacitor current | A | 21.9 | 22 | 0.5 |
| Peak-peak DC source current ripple | A | 0.9 | 0.6 | 33 |
| Peak-peak DC bus voltage ripple | V | 5.0 | 4.0 | 20 |
| AC THD on voltage | % | 2.1 | 1.8 | 14 |
| AC max voltage harmonics | % | 2.0 | 1.7 | 15 |
| Quantity | Unit | Design | Experiment | Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AC inductor losses (×3) | W | 40.5 | 47.7 | 18 |
| DC inductor losses (×2) | W | 1.9 | 2.1 | 10 |
| AC capacitor losses (×3) | W | 1.05 | 0.72 | 31 |
| DC capacitor losses (×2) | W | 1.98 | 2.14 | 8 |
| Semi-conductor losses | W | 175 | 155 | 11 |
| Global efficiency | % | 97.8 | 97.96 | 0.16 |
| RMS AC capacitor current | A | 10.8 | 9 | 17 |
| RMS DC capacitor current | A | 23.4 | 24.4 | 4.2 |
| Peak-peak DC source current ripple | A | 0.9 | 0.4 | 55 |
| Peak-peak DC bus voltage ripple | V | 4.1 | 3 | 27 |
| AC THD on voltage | % | 2.0 | 1.7 | 15 |
| AC max voltage harmonics | % | 2.0 | 1.6 | 20 |
| Quantity | Unit | Design | Experiment | Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AC inductor losses (×3) | W | 108 | 95 | 12 |
| DC inductor losses (×2) | W | 1.2 | 1.1 | 8.3 |
| AC capacitor losses (×3) | W | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0 |
| DC capacitor losses (×2) | W | 1.2 | 1.4 | 8 |
| Semi-conductor losses | W | 113 | 107 | 5.3 |
| Global efficiency | % | 97.8 | 97.97 | 0.17 |
| RMS AC capacitor current | A | 5.6 | 5.8 | 3.6 |
| RMS DC capacitor current | A | 21.9 | 21.8 | 0.5 |
| Peak-peak DC source current ripple | A | 0.9 | 0.5 | 44 |
| Peak-peak DC bus voltage ripple | V | 5.2 | 4 | 23 |
| AC THD on voltage | % | 2.1 | 1.8 | 14 |
| AC max voltage harmonics | % | 2.0 | 1.7 | 15 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Voldoire, A.; Schanen, J.-L.; Ferrieux, J.-P.; Derbey, A.; Gautier, C. Three-Phase PWM Voltage-Source-Inverter Weight Optimization for Aircraft Application Using Deterministic Algorithm. Electronics 2020, 9, 1393. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9091393
Voldoire A, Schanen J-L, Ferrieux J-P, Derbey A, Gautier C. Three-Phase PWM Voltage-Source-Inverter Weight Optimization for Aircraft Application Using Deterministic Algorithm. Electronics. 2020; 9(9):1393. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9091393
Chicago/Turabian StyleVoldoire, Adrien, Jean-Luc Schanen, Jean-Paul Ferrieux, Alexis Derbey, and Cyrille Gautier. 2020. "Three-Phase PWM Voltage-Source-Inverter Weight Optimization for Aircraft Application Using Deterministic Algorithm" Electronics 9, no. 9: 1393. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9091393
APA StyleVoldoire, A., Schanen, J.-L., Ferrieux, J.-P., Derbey, A., & Gautier, C. (2020). Three-Phase PWM Voltage-Source-Inverter Weight Optimization for Aircraft Application Using Deterministic Algorithm. Electronics, 9(9), 1393. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics9091393






