Sialyltransferases and Neuraminidases: Potential Targets for Cancer Treatment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
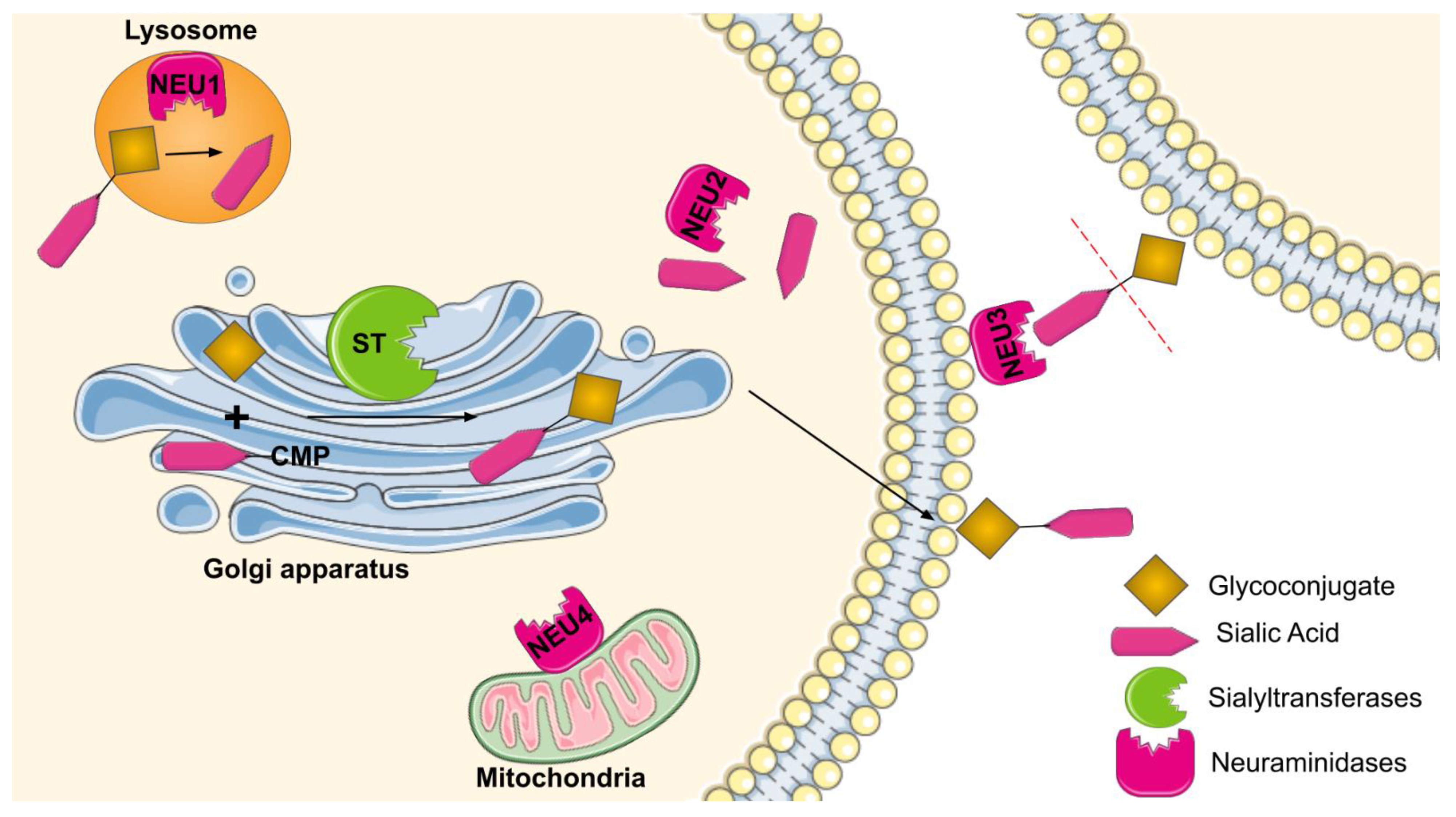
2. Sialyltransferases and Neuraminidases: Types and Functions
2.1. Types of Sialyltransferases
2.2. Types of Neuraminidases
3. Role of Sialyltransferases and Neuraminidases in Tumor Growth and Metastasis
3.1. Maintaining Tumor Growth and Proliferation
3.2. EMT Inducing Events, Invasion, and Metastasis Activating Events
3.3. Immunological Evasion
3.4. Evading Cell Death and Apoptosis
4. Role of Sialyltransferases and Neuraminidases in Various Cancers
4.1. Breast Cancer
4.2. Pancreatic Cancer
4.3. Ovarian Cancer
4.4. Other Cancers
5. Resistance against Traditional Cancer Treatments
5.1. Chemoresistance
5.2. Radiotherapy
6. Sialyltransferase Inhibitors
7. Neuraminidase Inhibitors
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Weir, H.K.; Thompson, T.D.; Stewart, S.L.; White, M.C. Cancer Incidence Projections in the United States between 2015 and 2050. Prev. Chronic Dis. 2021, 18, E59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, S.J.L.P.; Fu, C.-W.; Li, W.-S. Sialyltransferase Inhibitors for the Treatment of Cancer Metastasis: Current Challenges and Future Perspectives. Molecules 2021, 26, 5673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobie, C.; Skropeta, D. Insights into the role of sialylation in cancer progression and metastasis. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 124, 76–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reily, C.; Stewart, T.J.; Renfrow, M.B.; Novak, J. Glycosylation in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2019, 15, 346–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Ding, J. Sialylation is involved in cell fate decision during development, reprogramming and cancer progression. Protein Cell 2019, 10, 550–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietrobono, S.; Stecca, B. Aberrant Sialylation in Cancer: Biomarker and Potential Target for Therapeutic Intervention? Cancers 2021, 13, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, P.C.; Lötscher, M.; Streiff, M.; Kleene, R.; Kaissling, B.; Berger, E.G. Immunocytochemical Localization of α2,3(N)-sialyltransferase (ST3Gal III) in Cell Lines and Rat Kidney Tissue Sections: Evidence for Golgi and Post-Golgi Localization. 1998. Available online: https://academic.oup.com/glycob/article-abstract/8/3/245/560307 (accessed on 28 August 2022).
- Li, Y.; Chen, X. Sialic acid metabolism and sialyltransferases: Natural functions and applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 94, 887–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Louten, J. Influenza Viruses. In Essential Human Virology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; pp. 171–191. Available online: https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/B9780128009475000107 (accessed on 13 August 2022). [CrossRef]
- Miyagi, T.; Tsuiki, S. Rat-liver lysosomal sialidase. Solubilization, substrate specificity and comparison with the cytosolic sialidase. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 1984, 141, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyagi, T.; Tsuiki, S. Purification and Characterization of Cytosolic Sialidase from Rat Liver. J. Biol. Chem. 1985, 260, 6710–6716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büll, C.; Stoel, M.A.; Brok, M.H.D.; Adema, G.J. Sialic Acids Sweeten a Tumor’s Life. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 3199–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Picco, G.; Julien, S.; Brockhausen, I.; Beatson, R.; Antonopoulos, A.; Haslam, S.; Mandel, U.; Dell, A.; Pinder, S.; Taylor-Papadimitriou, J.; et al. Over-expression of ST3Gal-I promotes mammary tumorigenesis. Glycobiology 2010, 20, 1241–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, J.; Wang, R.; Zhong, G.; Chen, X.; Cheng, Y.; Li, W.; Yang, Y. ST6GAL2 Downregulation Inhibits Cell Adhesion and Invasion and is Associated with Improved Patient Survival in Breast Cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 903–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, X.; Wu, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Meng, Q.; Wang, S. Silencing of ST6GalNAc I suppresses the proliferation, migration and invasion of hepatocarcinoma cells through PI3K/AKT/NF-κB pathway. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 12213–12221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Dong, W.; Su, Z.; Zhao, L.; Miao, Y.; Li, N.; Zhou, H.; Jia, L. Functional roles of sialylation in breast cancer progression through miR-26a/26b targeting ST8SIA4. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroes, R.A.; He, H.; Emmett, M.R.; Nilsson, C.L.; Leach, F.E.; Amster, I.J.; Marshall, A.G.; Moskal, J.R. Overexpression of ST6GalNAcV, a ganglioside-specific α2,6-sialyltransferase, inhibits glioma growth in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 12646–12651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schnaar, R.L.; Gerardy-Schahn, R.; Hildebrandt, H. Sialic acids in the brain: Gangliosides and polysialic acid in nervous system development, stability, disease, and regeneration. Physiol. Rev. 2014, 94, 461–518. Available online: www.prv.org (accessed on 13 August 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Welch, D.R.; Hurst, D.R. Defining the Hallmarks of Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 3011–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongre, A.; Weinberg, R.A. New insights into the mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and implications for cancer. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Shi, X.-L.; Zhang, H.-J.; Hu, W.-D.; Mei, G.-L.; Chen, X.; Song, Q.-J.; Mao, Q.-S.; Chen, Z.; Yang, X.-B. Overexpression of ST3Gal-I promotes migration and invasion of HCCLM3 in vitro and poor prognosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma. OncoTargets Ther. 2016, 9, 2227–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, K.-C.; Sung, P.-L.; Hsieh, S.-L.; Chou, Y.-T.; Lee, O.K.-S.; Wu, C.-W.; Wang, P.-H. α2,3-sialyltransferase type I regulates migration and peritoneal dissemination of ovarian cancer cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 29013–29027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhao, J.; Ruan, Y.; Sun, L.; Xu, C.; Jiang, H. Sialyltransferase ST3GAL1 promotes cell migration, invasion, and TGF-β1-induced EMT and confers paclitaxel resistance in ovarian cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cui, H.-X.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Song, J.; Tian, H.; Xia, C.; Shen, Y. ST3Gal III modulates breast cancer cell adhesion and invasion by altering the expression of invasion-related molecules. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 3317–3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pérez-Garay, M.; Arteta, B.; Pagès, L.; de Llorens, R.; de Bolòs, C.; Vidal-Vanaclocha, F.; Peracaula, R. α2,3-Sialyltransferase ST3Gal III Modulates Pancreatic Cancer Cell Motility and Adhesion In Vitro and Enhances Its Metastatic Potential In Vivo. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guerrero, P.E.; Miró, L.; Wong, B.S.; Massaguer, A.; Martínez-Bosch, N.; De Llorens, R.; Navarro, P.; Konstantopoulos, K.; Llop, E.; Peracaula, R. Knockdown of α2,3-Sialyltransferases Impairs Pancreatic Cancer Cell Migration, Invasion and E-selectin-Dependent Adhesion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, E.; Schetters, S.T.T.; Van Kooyk, Y. The tumour glyco-code as a novel immune checkpoint for immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Büll, C.; Boltje, T.J.; Balneger, N.; Weischer, S.M.; Wassink, M.; van Gemst, J.J.; Bloemendal, V.R.; Boon, L.; van der Vlag, J.; Heise, T.; et al. Sialic Acid Blockade Suppresses Tumor Growth by Enhancing T-cell–Mediated Tumor Immunity. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 3574–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perdicchio, M.; Cornelissen, L.A.M.; Streng-Ouwehand, I.; Engels, S.; Verstege, M.I.; Boon, L.; Geerts, D.; van Kooyk, Y.; Unger, W.W.J. Tumor sialylation impedes T cell mediated anti-tumor responses while promoting tumor associated-regulatory T cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 8771–8782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, L.; Li, S.; Yu, X.; Han, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, S.; Chen, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, S. α2,6-Sialylation promotes immune escape in hepatocarcinoma cells by regulating T cell functions and CD147/MMP signaling. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 75, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locksley, R.M.; Killeen, N.; Lenardo, M.J. The TNF and TNF Receptor Review Superfamilies: Integrating Mammalian Biology. Cell 2001, 104, 487–501. Available online: http://www.gene (accessed on 13 August 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swindall, A.F.; Bellis, S.L. Sialylation of the Fas Death Receptor by ST6Gal-I Provides Protection against Fas-mediated Apoptosis in Colon Carcinoma Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 22982–22990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holdbrooks, A.T.; Britain, C.M.; Bellis, S.L. ST6Gal-I sialyltransferase promotes tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-mediated cancer cell survival via sialylation of the TNF receptor 1 (TNFR1) death receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 1610–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jiang, Y.; Wen, T.; Yan, R.; Kim, S.; Stowell, S.R.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; An, G.; Cummings, R.D.; Ju, T. O-glycans on death receptors in cells modulate their sensitivity to TRAIL-induced apoptosis through affecting on their stability and oligomerization. FASEB J. 2020, 34, 11786–11801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Recchi, M.A.; Hebbar, M.; Hornez, L.; Harduin-Lepers, A.; Peyrat, J.P.; Delannoy, P. Multiplex reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction assessment of sialyltransferase expression in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 4066–4070. [Google Scholar]
- Burchell, J.; Poulsom, R.; Hanby, A.; Whitehouse, C.; Cooper, L.; Clausen, H.; Miles, D.; Taylor-Papadimitriou, J. An 2,3 sialyltransferase (ST3Gal I) is elevated in primary breast carcinomas. Glycobiology 1999, 9, 1307–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hait, N.C.; Maiti, A.; Wu, R.; Andersen, V.L.; Hsu, C.-C.; Wu, Y.; Chapla, D.G.; Takabe, K.; Rusiniak, M.E.; Bshara, W.; et al. Extracellular sialyltransferase st6gal1 in breast tumor cell growth and invasiveness. Cancer Gene Ther. 2022, 29, 1662–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sewell, R.; Bäckström, M.; Dalziel, M.; Gschmeissner, S.; Karlsson, H.; Noll, T.; Gätgens, J.; Clausen, H.; Hansson, G.C.; Burchell, J.; et al. The ST6GalNAc-I Sialyltransferase Localizes throughout the Golgi and Is Responsible for the Synthesis of the Tumor-associated Sialyl-Tn O-Glycan in Human Breast Cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 3586–3594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murugaesu, N.; Iravani, M.; van Weverwijk, A.; Ivetic, A.; Johnson, D.A.; Antonopoulos, A.; Fearns, A.; Jamal-Hanjani, M.; Sims, D.; Fenwick, K.; et al. An In Vivo Functional Screen Identifies ST6GalNAc2 Sialyltransferase as a Breast Cancer Metastasis Suppressor. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 304–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Drolez, A.; Vandenhaute, E.; Delannoy, C.P.; Dewald, J.H.; Gosselet, F.; Cecchelli, R.; Julien, S.; Dehouck, M.-P.; Delannoy, P.; Mysiorek, C. ST6GALNAC5 Expression Decreases the Interactions between Breast Cancer Cells and the Human Blood-Brain Barrier. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kan, J.-Y.; Moi, S.-H.; Hung, W.-C.; Hou, M.-F.; Chen, F.-M.; Shih, S.-L.; Shiau, J.-P.; Li, C.-L.; Chiang, C.-P. Comprehensive Transcriptomic Analysis Identifies ST8SIA1 as a Survival-Related Sialyltransferase Gene in Breast Cancer. Genes 2020, 11, 1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruckhäberle, E.; Karn, T.; Rody, A.; Hanker, L.; Gätje, R.; Metzler, D.; Holtrich, U.; Kaufmann, M. Gene expression of ceramide kinase, galactosyl ceramide synthase and ganglioside GD3 synthase is associated with prognosis in breast cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 135, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battula, V.L.; Shi, Y.; Evans, K.W.; Wang, R.-Y.; Spaeth, E.; Jacamo, R.O.; Guerra, R.; Sahin, A.A.; Marini, F.C.; Hortobagyi, G.; et al. Ganglioside GD2 identifies breast cancer stem cells and promotes tumorigenesis. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 2066–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thulasiraman, P.; Kerr, K.; McAlister, K.; Hardisty, S.; Wistner, A.; McCullough, I. Neuraminidase 1 regulates proliferation, apoptosis and the expression of Cadherins in mammary carcinoma cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 462, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyagi, T. Aberrant expression of sialidase and cancer progression. Reviews 2008, 84, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chakraborty, A.; Dorsett, K.A.; Trummell, H.Q.; Yang, E.S.; Oliver, P.G.; Bonner, J.A.; Buchsbaum, D.J.; Bellis, S.L. ST6Gal-I sialyltransferase promotes chemoresistance in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by abrogating gemcitabine-mediated DNA damage. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 984–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Yuan, S.; Wu, Q.; Zhu, X.; Niang, B.; Wang, S.; Zhang, J. ST6Gal-I modulates docetaxel sensitivity in human hepatocarcinoma cells via the p38 MAPK/caspase pathway. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 51955–51964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Britain, C.M.; Dorsett, K.A.; Bellis, S.L. The Glycosyltransferase ST6Gal-I Protects Tumor Cells against Serum Growth Factor Withdrawal by Enhancing Survival Signaling and Proliferative Potential. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 4663–4673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, R.B.; Dorsett, K.A.; Hjelmeland, A.B.; Bellis, S.L. The ST6Gal-I sialyltransferase protects tumor cells against hypoxia by enhancing HIF-1α signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 5659–5667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schultz, M.J.; Holdbrooks, A.T.; Chakraborty, A.; Grizzle, W.E.; Landen, C.N.; Buchsbaum, D.J.; Conner, M.G.; Arend, R.C.; Yoon, K.J.; Klug, C.A.; et al. The Tumor-Associated Glycosyltransferase ST6Gal-I Regulates Stem Cell Transcription Factors and Confers a Cancer Stem Cell Phenotype. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 3978–3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swindall, A.F.; Londoño-Joshi, A.I.; Schultz, M.J.; Fineberg, N.; Buchsbaum, D.J.; Bellis, S.L. ST6Gal-I Protein Expression Is Upregulated in Human Epithelial Tumors and Correlates with Stem Cell Markers in Normal Tissues and Colon Cancer Cell Lines. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 2368–2378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, C.-C.; Shyr, Y.-M.; Liao, W.-Y.; Chen, T.-H.; Wang, S.-E.; Lu, P.-C.; Lin, P.-Y.; Chen, Y.-B.; Mao, W.-Y.; Han, H.-Y.; et al. Elevation of β-galactoside α2,6-sialyltransferase 1 in a fructose-responsive manner promotes pancreatic cancer metastasis. Oncotarget 2016, 8, 7691–7709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Britain, C.M.; Holdbrooks, A.T.; Anderson, J.C.; Willey, C.D.; Bellis, S.L. Sialylation of EGFR by the ST6Gal-I sialyltransferase promotes EGFR activation and resistance to gefitinib-mediated cell death. J. Ovarian Res. 2018, 11, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moore, M.J.; Goldstein, D.; Hamm, J.; Figer, A.; Hecht, J.R.; Gallinger, S.; Au, H.J.; Murawa, P.; Walde, D.; Wolff, R.A.; et al. Erlotinib Plus Gemcitabine Compared With Gemcitabine Alone in Patients With Advanced Pancreatic Cancer: A Phase III Trial of the National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 1960–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Y.; Srivatana, U.; Ullah, A.; Gagneja, H.; Berenson, C.S.; Lance, P. Suppression of a sialyltransferase by antisense DNA reduces invasiveness of human colon cancer cells in vitro. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2001, 1536, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ulloa, F.; Real, F.X. Differential Distribution of Sialic Acid in α2,3 and α2,6 Linkages in the Apical Membrane of Cultured Epithelial Cells and Tissues. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2001, 49, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mandal, C.; Tringali, C.; Mondal, S.; Anastasia, L.; Chandra, S.; Venerando, B.; Mandal, C. Down regulation of membrane-bound Neu3 constitutes a new potential marker for childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia and induces apoptosis suppression of neoplastic cells. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 126, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, S.; Mandal, C.; Chatterjee, U.; Mandal, C. Association of cytosolic sialidase Neu2 with plasma membrane enhances Fas-mediated apoptosis by impairing PI3K-Akt/mTOR-mediated pathway in pancreatic cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pérez-Garay, M.; Arteta, B.; Llop, E.; Cobler, L.; Pagès, L.; Ortiz, R.; Ferri, M.J.; de Bolós, C.; Figueras, J.; de Llorens, R.; et al. α2,3-Sialyltransferase ST3Gal IV promotes migration and metastasis in pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells and tends to be highly expressed in pancreatic adenocarcinoma tissues. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 1748–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Momenimovahed, Z.; Tiznobaik, A.; Taheri, S.; Salehiniya, H. Ovarian cancer in the world: Epidemiology and risk factors. Int. J. Women’s Health 2019, 11, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sung, P.-L.; Wen, K.-C.; Horng, H.-C.; Chang, C.-M.; Chen, Y.-J.; Lee, W.-L.; Wang, P.-H. The role of α2,3-linked sialylation on clear cell type epithelial ovarian cancer. Taiwan. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 57, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wichert, B.; Milde-Langosch, K.; Galatenko, V.; Schmalfeldt, B.; Oliveira-Ferrer, L. Prognostic role of the sialyltransferase ST6GAL1 in ovarian cancer. Glycobiology 2018, 28, 898–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dorsett, K.A.; Jones, R.B.; Ankenbauer, K.E.; Hjelmeland, A.B.; Bellis, S.L. Sox2 promotes expression of the ST6Gal-I glycosyltransferase in ovarian cancer cells. J. Ovarian Res. 2019, 12, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, X.; Chen, M.; Zheng, S.; Li, J.; Lin, S.; Wang, X. ST3Gal3 confers paclitaxel-mediated chemoresistance in ovarian cancer cells by attenuating caspase-8/3 signaling. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 4499–4506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ren, L.-R.; Zhang, L.-P.; Huang, S.-Y.; Zhu, Y.-F.; Li, W.-J.; Fang, S.-Y.; Shen, L.; Gao, Y.-L. Effects of sialidase NEU1 siRNA on proliferation, apoptosis, and invasion in human ovarian cancer. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 411, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kvorjak, M.; Ahmed, Y.; Miller, M.L.; Sriram, R.; Coronnello, C.; Hashash, J.G.; Hartman, D.J.; Telmer, C.A.; Miskov-Zivanov, N.; Finn, O.J.; et al. Cross-talk between Colon Cells and Macrophages Increases ST6GALNAC1 and MUC1-sTn Expression in Ulcerative Colitis and Colitis-Associated Colon Cancer. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2020, 8, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyazaki, K.; Ohmori, K.; Izawa, M.; Koike, T.; Kumamoto, K.; Furukawa, K.; Ando, T.; Kiso, M.; Yamaji, T.; Hashimoto, Y.; et al. Loss of Disialyl Lewis a, the Ligand for Lymphocyte Inhibitory Receptor Sialic Acid-Binding Immunoglobulin-Like Lectin-7 (Siglec-7) Associated with Increased Sialyl Lewis a Expression on Human Colon Cancers. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 4498–4505. Available online: http://aacrjournals.org/cancerres/article-pdf/64/13/4498/2516047/zch01304004498.pdf (accessed on 25 August 2022). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Penrose, H.; Cable, C.; Heller, S.; Ungerleider, N.; Nakhoul, H.; Baddoo, M.; Hartono, A.B.; Lee, S.; Burow, M.E.; Flemington, E.F.; et al. Loss of Forkhead Box O3 Facilitates Inflammatory Colon Cancer: Transcriptome Profiling of the Immune Landscape and Novel Targets. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 7, 391–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wei, A.; Fan, B.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Yu, X.; Yuan, Q.; Yang, D.; Wang, S. ST6Gal-I overexpression facilitates prostate cancer progression via the PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling pathway. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 65374–65388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Munkley, J.; Oltean, S.; Vodák, D.; Wilson, B.T.; Livermore, K.E.; Zhou, Y.; Star, E.; Floros, V.I.; Johannessen, B.; Knight, B.; et al. The androgen receptor controls expression of the cancer-associated sTn antigen and cell adhesion through induction of ST6GalNAc1 in prostate cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 34358. Available online: www.impactjournals.com/oncotarget/ (accessed on 24 August 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haldrup, C.; Pedersen, A.L.; Øgaard, N.; Strand, S.H.; Høyer, S.; Borre, M.; Ørntoft, T.F.; Sørensen, K.D. Biomarker potential of ST6GALNAC3 and ZNF660 promoter hypermethylation in prostate cancer tissue and liquid biopsies. Mol. Oncol. 2018, 12, 545–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, F.; Sato, Y.; Hirakawa, M.; Yoshida, M.; Ono, M.; Osuga, T.; Okagawa, Y.; Uemura, N.; Arihara, Y.; Murase, K.; et al. RNAi-mediated gene silencing of ST6GalNAc I suppresses the metastatic potential in gastric cancer cells. Gastric Cancer 2016, 19, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Özlem Elpek, G.; Gelen, T.; Karpuzoǧlu, G.; Karpuzoǧlu, T.; Keles, N. Clinicopathologic evaluation of CDw75 antigen expression in patients with gastric carcinoma. J. Pathol. A J. Pathol. Soc. Great Br. Irel. 2001, 193, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gretschel, S.; Haensch, W.; Schlag, P.M.; Kemmner, W. Clinical Relevance of Sialyltransferases ST6GAL-I and ST3GAL-III in Gastric Cancer. Oncology 2003, 65, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, Y.; Ito, A.; Kakoi, N.; Shimada, S.; Itoh, J.; Mitsuzuka, K.; Arai, Y. Ganglioside, Disialosyl Globopentaosylceramide (DSGb5), Enhances the Migration of Renal Cell Carcinoma Cells. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2015, 236, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y. Epidemiology of esophageal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 5598–5606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaya, T.; Sawada, G.; Amano, S.; Kume, K.; Ito, C.; Endo, F.; Konosu, M.; Shioi, Y.; Akiyama, Y.; Takahara, T.; et al. Downregulation of ST6GALNAC1 is associated with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma development. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 50, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, X.; Teng, Y.; Jiang, X.; Yuan, H.; Jiang, W. Genome-Wide DNA Methylation Pattern of Cancer Stem Cells in Esophageal Cancer. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 19, 1533033820983793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mimori, K.; Ishii, H.; Inoue, H.; Barnard, G.F.; Mori, M. Identification of the expression profile of apoptotic esophageal cancer cells by adenoviral-fragile histidine triad treatment. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 23, S205–S209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, K.A.; Patel, K.A.; Pandya, S.J.; Patel, P.S. Aberrant sialylation plays a significant role in oral squamous cell carcinoma progression. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2020, 49, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiga, K.; Takahashi, K.; Sato, I.; Kato, K.; Saijo, S.; Moriya, S.; Hosono, M.; Miyagi, T. Upregulation of sialidaseNEU3 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma associated with lymph node metastasis. Cancer Sci. 2015, 106, 1544–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, O.; Abe, M.; Hashimoto, Y. Sialylation by β-galactoside α-2,6-sialyltransferase and N-glycans regulate cell adhesion and invasion in human anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 46, 973–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shah, I.; Chou, T.; Tapazoglou, E.; Kessel, D. Role of sialyltransferase in hypercupraemia of non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Scand. J. Haematol. 1984, 32, 332–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pietrobono, S.; Anichini, G.; Sala, C.; Manetti, F.; Almada, L.L.; Pepe, S.; Carr, R.M.; Paradise, B.D.; Sarkaria, J.N.; Davila, J.I.; et al. ST3GAL1 is a target of the SOX2-GLI1 transcriptional complex and promotes melanoma metastasis through AXL. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 5865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, S.; Vasconcelos, J.; Silva, R.; Cavalcanti, C.; Bezerra, C.; Rêgo, M.; Beltrão, E. Expression patterns of α2,3-Sialyltransferase I and α2,6-Sialyltransferase I in human cutaneous epithelial lesions. Eur. J. Histochem. 2013, 57, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yu, S.; Wang, S.; Sun, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, J.; Yang, D.; Jiang, Y. ST8SIA1 inhibits the proliferation, migration and invasion of bladder cancer cells by blocking the JAK/STAT signaling pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 22, 736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torre, L.A.; Bray, F.; Siegel, R.L.; Ferlay, J.; Lortet-Tieulent, J.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2015, 65, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walboomers, J.M.; Jacobs, M.V.; Manos, M.M.; Bosch, F.X.; Kummer, J.A.; Shah, K.V.; Snijders, P.J.; Peto, J.; Meijer, C.J.; Muñoz, N. Human papillomavirus is a necessary cause of invasive cervical cancer worldwide. J. Pathol. 1999, 189, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, X.; Dong, W.; Xu, Z.; Jian, Y.; Xu, C.; Zhang, L.; Wei, A.; Yu, X.; Wang, S.; et al. ST3Gal IV Mediates the Growth and Proliferation of Cervical Cancer Cells In Vitro and In Vivo Via the Notch/p21/CDKs Pathway. Front. Oncol. 2021, 10, 540332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Dong, W.; Zhou, H.; Li, H.; Wang, N.; Miao, X.; Jia, L. α-2,8-sialyltransferase is involved in the development of multidrug resistance via PI3K/Akt pathway in human chronic myeloid leukemia. IUBMB Life 2015, 67, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Li, Y.; Liu, B.; Shan, Y.; Zhao, L.; Su, Z.; Jia, L. Downregulation of miR-224 and let-7i contribute to cell survival and chemoresistance in chronic myeloid leukemia cells by regulating ST3GAL IV expression. Gene 2017, 626, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Chen, X.; Han, Y.; Lei, T.; Wu, Q.; Yu, X.; Wang, L.; Fan, Z.; Wang, S. Modification of α2,6-sialylation mediates the invasiveness and tumorigenicity of non-small cell lung cancer cellsin vitro and in vivo via Notch1/Hes1/MMPs pathway. Int. J. Cancer 2018, 143, 2319–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Park, J.-J.; Yi, J.Y.; Jin, Y.B.; Lee, Y.-J.; Lee, J.-S.; Lee, Y.-S.; Ko, Y.-G.; Lee, M. Sialylation of epidermal growth factor receptor regulates receptor activity and chemosensitivity to gefitinib in colon cancer cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 83, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz, M.J.; Swindall, A.F.; Wright, J.W.; Sztul, E.S.; Landen, C.N.; Bellis, S.L. ST6Gal-I sialyltransferase confers cisplatin resistance in ovarian tumor cells. J. Ovarian Res. 2013, 6, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Smithson, M.; Irwin, R.; Williams, G.; Alexander, K.L.; Smythies, L.E.; Nearing, M.; McLeod, M.C.; Al Diffalha, S.; Bellis, S.L.; Hardiman, K.M. Sialyltransferase ST6GAL-1 mediates resistance to chemoradiation in rectal cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 101594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balmaña, M.; Diniz, F.; Feijão, T.; Barrias, C.C.; Mereiter, S.; Reis, C.A. Analysis of the Effect of Increased α2,3-Sialylation on RTK Activation in MKN45 Gastric Cancer Spheroids Treated with Crizotinib. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, H.; Zhou, H.; Song, X.; Shi, S.; Zhang, J.; Jia, L. Modification of sialylation is associated with multidrug resistance in human acute myeloid leukemia. Oncogene 2015, 34, 726–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wan, H.; Li, Z.; Cai, F.; Wang, L. ST8SIA1 inhibition sensitizes triple negative breast cancer to chemotherapy via suppressing Wnt/β-catenin and FAK/Akt/mTOR. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 23, 902–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, S.N.; Junqueira, M.S.; Francisco, G.; Vilanova, M.; Magalhães, A.; Dias Baruffi, M.; Chammas, R.; Harris, A.L.; Reis, C.A.; Bernardes, E.S. O-glycan sialylation alters galectin-3 subcellular localization and decreases chemotherapy sensitivity in gastric cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 83570. Available online: www.impactjournals.com/oncotarget/ (accessed on 24 August 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Pan, Y.; Shan, Y.; Li, Y.; Jia, L. Upregulation of microRNA-135b and microRNA-182 promotes chemoresistance of colorectal cancer by targeting ST6GALNAC2 via PI3K/AKT pathway. Mol. Carcinog. 2017, 56, 2669–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, L.; Luo, S.; Ren, X.; Li, Y.; Hu, J.; Liu, B.; Zhao, L.; Shan, Y.; Zhou, H. miR-182 and miR-135b Mediate the Tumorigenesis and Invasiveness of Colorectal Cancer Cells via Targeting ST6GALNAC2 and PI3K/AKT Pathway. Am. J. Dig. Dis. 2017, 62, 3447–3459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, S.; Aoki, H.; Ito, A.; Ueno, S.; Wada, T.; Mitsuzuka, K.; Satoh, M.; Arai, Y.; Miyagi, T. Human α2,3-Sialyltransferase (ST3Gal II) Is a Stage-specific Embryonic Antigen-4 Synthase. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 26474–26479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aloia, A.; Petrova, E.; Tomiuk, S.; Bissels, U.; Déas, O.; Saini, M.; Zickgraf, F.M.; Wagner, S.; Spaich, S.; Sütterlin, M.; et al. The sialyl-glycolipid stage-specific embryonic antigen 4 marks a subpopulation of chemotherapy-resistant breast cancer cells with mesenchymal features. Breast Cancer Res. 2015, 17, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, H.; Liu, Y.; Tan, Y.; Lin, J.; Gao, F.; Lin, S. Alpha2,3-sialyltransferase III knockdown sensitized ovarian cancer cells to cisplatin-induced apoptosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 482, 758–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lillehoj, E.P.; Hyun, S.W.; Feng, C.; Zhang, L.; Liu, A.; Guang, W.; Nguyen, C.; Luzina, I.G.; Atamas, S.P.; Passaniti, A.; et al. NEU1 Sialidase Expressed in Human Airway Epithelia Regulates Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) and MUC1 Protein Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 8214–8231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nath, S.; Daneshvar, K.; Roy, L.D.; Grover, P.; Kidiyoor, A.; Mosley, L.; Sahraei, M.; Mukherjee, P. MUC1 induces drug resistance in pancreatic cancer cells via upregulation of multidrug resistance genes. Oncogenesis 2013, 2, e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, M.; Lee, H.-J.; Bae, S.; Lee, Y.-S. Protein Sialylation by Sialyltransferase Involves Radiation Resistance. Mol. Cancer Res. 2008, 6, 1316–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, M.; Lee, H.-J.; Seo, W.D.; Park, K.H.; Lee, Y.-S. Sialylation of Integrin β1 is Involved in Radiation-Induced Adhesion and Migration in Human Colon Cancer Cells. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2010, 76, 1528–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, M.; Liu, D.; Duan, H.; Shen, B.; Guo, N. Metastasis-related miRNAs, active players in breast cancer invasion, and metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2010, 29, 785–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okazaki, K.; Nishigaki, S.; Ishizuka, F.; Kajihara, Y.; Ogawa, S. Potent and specific sialyltransferase inhibitors: Imino-linked 5a′-carbadisaccharides. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2003, 1, 2229–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaub, C.; Muller, B.; Schmidt, R.R. New sialyltransferase inhibitors based on CMP-quinic acid: Development of a new sialyltransferase assay. Glycoconj. J. 1998, 15, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Saraireh, Y.M.J.; Sutherland, M.; Springett, B.R.; Freiberger, F.; Morais, G.R.; Loadman, P.M.; Errington, R.J.; Smith, P.J.; Fukuda, M.; Gerardy-Schahn, R.; et al. Pharmacological Inhibition of polysialyltransferase ST8SiaII Modulates Tumour Cell Migration. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miyazaki, T.; Angata, K.; Seeberger, P.H.; Hindsgaul, O.; Fukuda, M. CMP substitutions preferentially inhibit polysialic acid synthesis. Glycobiology 2008, 18, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hinou, H.; Sun, X.-L.; Ito, Y. Bisubstrate-type inhibitor of sialyltransferases. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 9147–9150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosoguchi, K.; Maeda, T.; Furukawa, J.-I.; Shinohara, Y.; Hinou, H.; Sekiguchi, M.; Togame, H.; Takemoto, H.; Kondo, H.; Nishimura, S.-I. An Efficient Approach to the Discovery of Potent Inhibitors against Glycosyltransferases. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 5607–5619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wuab, C.Y.; Hsua, C.C.; Chenb, S.T.; Tsai, Y.-C. Soyasaponin I, a Potent and Specific Sialyltransferase Inhibitor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 284, 466–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.-W.; Yu, C.-Y.; Lin, T.-W.; Wang, P.-H.; Tsai, Y.-C. Soyasaponin I decreases the expression of α2,3-linked sialic acid on the cell surface and suppresses the metastatic potential of B16F10 melanoma cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 341, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.-C.; Lin, T.-W.; Chang, W.-W.; Wu, C.-Y.; Lo, W.-H.; Wang, P.-H.; Tsai, Y.-C. Soyasaponin-I-modified invasive behavior of cancer by changing cell surface sialic acids. Gynecol. Oncol. 2005, 96, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwashina, T. Flavonoid Function and Activity to Plants and Other Organisms. Biol. Sci. Space 2003, 17, 24–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonfili, L.; Cecarini, V.; Amici, M.; Cuccioloni, M.; Angeletti, M.; Keller, J.N.; Eleuteri, A.M. Natural polyphenols as proteasome modulators and their role as anti-cancer compounds. FEBS J. 2008, 275, 5512–5526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, A.; Fernandes, E.; Lima, J.; Mira, L.; Corvo, M. Molecular Mechanisms of Anti-Inflammatory Activity Mediated by Flavonoids. Curr. Med. Chem. 2008, 15, 1586–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, M. Overview of antibacterial, antitoxin, antiviral, and antifungal activities of tea flavonoids and teas. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2007, 51, 116–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice-Evans, C.A.; Miller, N.J. Biochemical Society Transactions Antioxidant activities of flavonoids as bioactive components of food. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1996, 24, 790–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidari, K.I.; Oyama, K.-I.; Ito, G.; Nakayama, M.; Inai, M.; Goto, S.; Kanai, Y.; Watanabe, K.-I.; Yoshida, K.; Furuta, T.; et al. Identification and characterization of flavonoids as sialyltransferase inhibitors. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 382, 609–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Luo, S.; Dong, W.; Song, X.; Zhou, H.; Zhao, L.; Jia, L. Alpha-2, 3-sialyltransferases regulate the multidrug resistance of chronic myeloid leukemia through miR-4701-5p targeting ST3GAL1. Lab. Investig. 2016, 96, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Severino, P.F.; Silva, M.; Carrascal, M.; Malagolini, N.; Chiricolo, M.; Venturi, G.; Forleo, R.B.; Astolfi, A.; Catera, M.; Videira, P.A.; et al. Oxidative damage and response to Bacillus Calmette-Guérin in bladder cancer cells expressing sialyltransferase ST3GAL1. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gong, A.; Zhao, X.; Pan, Y.; Qi, Y.; Li, S.; Huang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Qi, X.; Zheng, W.; Jia, L. LncRNA MEG3 mediates renal cell cancer progression by regulating ST3Gal1 transcription and EGFR sialylation. J. Cell Sci. 2020, 133, jcs244020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-Y.; Kim, H.G.; Hwang, M.R.; Chae, J.I.; Yang, J.M.; Lee, Y.C.; Choo, Y.K.; Lee, S.-S.; Do, S.-I. The Hexapeptide Inhibitor of Galβ1,3GalNAc-specific α2,3-Sialyltransferase as a Generic Inhibitor of Sialyltransferases. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 49341–49351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, T.-W.; Chang, W.-W.; Chen, C.-C.; Tsai, Y.-C. Stachybotrydial, a potent inhibitor of fucosyltransferase and sialyltransferase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 331, 953–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-Y.; Tang, Y.-A.; Huang, S.-M.; Juan, H.-F.; Wu, L.-W.; Sun, Y.-C.; Wang, S.-C.; Wu, K.-W.; Balraj, G.; Chang, T.-T.; et al. A Novel Sialyltransferase Inhibitor Suppresses FAK/Paxillin Signaling and Cancer Angiogenesis and Metastasis Pathways. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 473–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, C.-W.; Tsai, H.-E.; Chen, W.-S.; Chang, T.-T.; Chen, C.-L.; Hsiao, P.-W.; Li, W.-S. Sialyltransferase Inhibitors Suppress Breast Cancer Metastasis. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 64, 527–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roa-de La Cruz, L.; Martínez-Morales, P.; Morán-Cruz, I.; Milflores-Flores, L.; Rosas-Murrieta, N.; González-Ramírez, C.; Ortiz-Mateos, C.; Monterrosas-Santamaría, R.; González-Frías, C.; Rodea-Ávila, C.; et al. Expression analysis of ST3GAL4 transcripts in cervical cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 617–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dalangood, S.; Zhu, Z.; Ma, Z.; Li, J.; Zeng, Q.; Yan, Y.; Shen, B.; Yan, J.; Huang, R. Identification of glycogene-type and validation of ST3GAL6 as a biomarker predicts clinical outcome and cancer cell invasion in urinary bladder cancer. Theranostics 2020, 10, 10078–10091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, H.-J.; Krasnova, L.; Dey, S.; Cheng, T.; Liu, H.; Tsai, T.-I.; Wu, K.B.; Wu, C.-Y.; Wong, C.-H. Synthesis of Sialidase-Resistant Oligosaccharide and Antibody Glycoform Containing α2,6-Linked 3Fax-Neu5Ac. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 6484–6488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturi, G.; Ferreira, I.G.; Pucci, M.; Ferracin, M.; Malagolini, N.; Chiricolo, M.; Dall’Olio, F. Impact of sialyltransferase ST6GAL1 overexpression on different colon cancer cell types. Glycobiology 2019, 29, 684–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, H.O.; Rodrigues, J.G.; Gomes, C.; Hensbergen, P.J.; Ederveen, A.L.H.; de Ru, A.H.; Mereiter, S.; Polónia, A.; Fernandes, E.; Ferreira, J.A.; et al. ST6Gal1 targets the ectodomain of ErbB2 in a site-specific manner and regulates gastric cancer cell sensitivity to trastuzumab. Oncogene 2021, 40, 3719–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Britain, C.M.; Bhalerao, N.; Silva, A.D.; Chakraborty, A.; Buchsbaum, D.J.; Crowley, M.R.; Crossman, D.K.; Edwards, Y.J.; Bellis, S.L. Glycosyltransferase ST6Gal-I promotes the epithelial to mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Pan, C.; Zhou, L.; Cai, Z.; Zhao, S.; Yu, D. Knockdown of ST6Gal-I increases cisplatin sensitivity in cervical cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Minami, A.; Shimono, Y.; Mizutani, K.; Nobutani, K.; Momose, K.; Azuma, T.; Takai, Y. Reduction of the ST6 β-Galactosamide α-2,6-Sialyltransferase 1 (ST6GAL1)-catalyzed Sialylation of Nectin-like Molecule 2/Cell Adhesion Molecule 1 and Enhancement of ErbB2/ErbB3 Signaling by MicroRNA-199a. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 11845–11853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ozaki, H.; Matsuzaki, H.; Ando, H.; Kaji, H.; Nakanishi, H.; Ikehara, Y.; Narimatsu, H. Enhancement of metastatic ability by ectopic expression of ST6GalNAcI on a gastric cancer cell line in a mouse model. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2012, 29, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferrer, C.M.; Reginato, M.J. Sticking to Sugars at the Metastatic Site: Sialyltransferase ST6GalNAc2 Acts as a Breast Cancer Metastasis Suppressor. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 275–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.; He, S.; Qiu, G.; Lu, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Fan, L.; Zhao, W.; Che, X. MicroRNA-125b promotes invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer by targeting STARD13 and NEU1. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 12141–12151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qorri, B.; Harless, W.; Szewczuk, M.R. Novel Molecular Mechanism of Aspirin and Celecoxib Targeting Mammalian Neuraminidase-1 Impedes Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Signaling Axis and Induces Apoptosis in Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2020, 14, 4149–4167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhai, Y.; Liu, C.; Yang, G.; Guo, J.; Li, G.; Sun, C.; Qi, X.; Li, X.; Guan, F. Sialidase NEU1 suppresses progression of human bladder cancer cells by inhibiting fibronectin-integrin α5β1 interaction and Akt signaling pathway. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 18, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tringali, C.; Lupo, B.; Silvestri, I.; Papini, N.; Anastasia, L.; Tettamanti, G.; Venerando, B. The Plasma Membrane Sialidase NEU3 Regulates the Malignancy of Renal Carcinoma Cells by Controlling β1 Integrin Internalization and Recycling. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 42835–42845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forcella, M.; Oldani, M.; Epistolio, S.; Freguia, S.; Monti, E.; Fusi, P.; Frattini, M. Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), EGFR downstream pathway activation and TKI targeted therapies sensitivity: Effect of the plasma membrane-associated NEU3. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, T.; Lv, H.; Fei, J.; Xie, Y.; Lian, D.; Hu, J.; Tang, L.; Shi, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; et al. p53-R273H promotes cancer cell migration via upregulation of neuraminidase-1. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 6874–6882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.; Woods, E.C.; Vukojicic, P.; Bertozzi, C.R. Precision glycocalyx editing as a strategy for cancer immunotherapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 10304–10309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Che, J.; Xu, L.; Gatlin, W.; LeBlanc, R.; Cao, L.; Broderick, J.; Peng, L. Abstract LB221: Development of PD-L1-targeted sialidase as a novel cancer immunotherapeutic approach. Cancer Res. 2022, 82 (Suppl. 12), LB221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Che, J.; Chesney, A.; Dixit, R.; Zheng, N.; Zane, N.; Broderick, J.; Peng, L. Abstract LB203: Assessment of the safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of a first-in-class cancer drug candidate E-602, a sialoglycan degrader, in non-human primates. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, LB203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, J.T.; Santos, A.L.; Gomes, C.; Barros, R.; Ribeiro, C.; Mendes, N.; de Matos, A.J.; Vasconcelos, M.H.; Oliveira, M.J.; Reis, C.A.; et al. Anti-Influenza Neuraminidase Inhibitor Oseltamivir Phosphate Induces Canine Mammary Cancer Cell Aggressiveness. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.; Cao, L.; Nerle, S.; LeBlanc, R.; Das, A.; Shelke, S.; Turner, A.; Che, J.; Siddiquee, Z.; Xu, H.; et al. 843 Development and engineering of human sialidase for degradation of immunosuppressive sialoglycans to treat cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9 (Suppl. 2), A884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palleon Pharmaceuticals-Press Releases. Palleon Pharmaceuticals and Henlius Enter into Strategic Collaboration to Develop Bifunctional Sialidase Therapies; Palleon Pharmaceuticals-Press Releases: Waltham, MA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, T.; Dätwyler, P.; Demina, E.; Richards, M.R.; Ge, P.; Zou, C.; Zheng, R.B.; Fougerat, A.; Pshezhetsky, A.V.; Ernst, B.; et al. Selective Inhibitors of Human Neuraminidase 3. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 1990–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Varki, A. Advances in the Biology and Chemistry of Sialic Acids. ACS Chem. Biol. 2009, 5, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varki, A. Sialic acids in human health and disease. Trends Mol. Med. 2008, 14, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Magesh, S.; Savita, V.; Moriya, S.; Suzuki, T.; Miyagi, T.; Ishida, H.; Kiso, M. Human sialidase inhibitors: Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of 4-acetamido-5-acylamido-2-fluoro benzoic acids. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 4595–4603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairo, C.W. Inhibitors of the human neuraminidase enzymes. MedChemComm 2014, 5, 1067–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haxho, F.; Neufeld, R.J.; Szewczuk, M.R. Neuraminidase-1: A novel therapeutic target in multistage tumorigenesis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 40860–40881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Glycan Mediated Immune Regulation with a Bi-Sialidase Fusion Protein (GLIMMER-01) (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT05259696). 2022. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05259696 (accessed on 6 November 2022).


| Enzymes | Other Names | Substrate Carrier | Structure Formed |
|---|---|---|---|
| ST3Gal1 | SIAT4A, ST3O, ST3GalA.1 | O-GP > GL | Neu5Acα2-3Galβ1-3GalNAc- |
| ST3Gal2 | SIAT4B, ST3GalA.2, SAT4 | GL > O-GP | Neu5Acα2-3Galβ1-3GalNAc- |
| ST3Gal3 | SIAT6 | GP | Neu5Acα2-3Galβ1-3/4GlcNAcβ- |
| ST3Gal4 | SIAT4, STZ, SAT3, SIAT4C | GP > GL | Neu5Acα2-3Galβ1-3GalNAc- Neu5Acα2-3Galβ1-4GlcNAc- |
| ST3Gal5 | SIAT9, SIATGM3S | GL | Neu5Acα2-3Galβ1-4Glc-Cer |
| ST3Gal6 | SIAT10 | GP, GL | Neu5Acα2-3Galβ1-4GlcNAcβ- |
| ST6Gal1 | SIAT1 | N-GP, OL, GL | Neu5Acα2-6Galβ1-4GlcNAcβ- |
| ST6Gal2 | SIAT2 | N-GP, OL | - |
| ST6GalNAc1 | SIAT7A | O-GP | (Neu5Acα2-3)0-1(Galβ1-3)0-1GalNAc-Ser/Neu5Acα2-6 |
| ST6GalNAc2 | SIAT7, SIAT7B, SIATL1 | O-GP | (Neu5Acα2-3)0-1Galβ1-3GalNAc-Ser/Neu5Acα2-6 |
| ST6GalNAc3 | SIAT7C | O-GP, GL | Neu5Acα2-3Galβ1-3GalNAc-R/Neu5Acα2-6 |
| ST6GalNAc4 | SIAT3C, SIAT7D | O-GP, OL > GL | Neu5Acα2-3Galβ1-3GalNAc-R/Neu5Acα2-6 |
| ST6GalNAc5 | SIAT7E | GL | GD1α |
| ST6GalNAc6 | SIAT7F | GL > GP | GD1α, (GT1α) |
| ST8Sia1 | SIAT8, SIAT8A | GL | Neu5Acα2-8Neu5Acα2-3Galβ1-4Glc-Cer |
| ST8Sia2 | SIAT8B, ST8SIA-II, STX | GP | Neu5Acα2-8Neu5Acα2-3Galβ1-4GlcNAc |
| ST8Sia3 | SIAT8C | GP, GL | Neu5Acα2-8Neu5Acα2-3Gal1-4GlcNAc |
| ST8Sia4 | SIAT8D | GP | Neu5Acα2-8(Neu5Acα2-8) nNeu5Acα2-3Galβ1-R |
| ST85Sia5 | SIAT8E | GL | GD1c, GT1a, GQ1b, GT3 |
| ST8Sia6 | SIAT8F | O-GP, OL | - |
| Enzymes | Other Names | Substrate Carrier | Tissue Expression | Intracellular Localization | Glycosidic Linkage Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NEU1 | Lysosomal sialidase, SIAL1 | OL, glycopeptides | Kidney, pancreas, skeletal muscle, liver, lungs, placenta, and brain | Lysosomal and plasma membranes | α2-3 faster than α2-6 and α2-8 [10] |
| NEU2 | Cytosolic sialidase, SIAL2 | OL, GP, GL | Skin | Cytosol | α2-3 faster than α2-6 and α2-8 [10] |
| NEU3 | Membrane sialidase, SIAL3 | GL, Grb2 | Adrenal gland, skeletal muscle, heart, testis, and thymus | Caveolae microdomains of plasma, endosomal and lysosomal membranes | α2-3 and α2-8 almost equally and faster than α2-6 [11] |
| NEU4 | Sialidase | OL, GP, GL, phospholipid scramblase 1 | Brain, skeletal muscle, heart, placenta, and liver | ER membrane, mitochondria, and lysosomes | - |
| Enzyme | Type of Cancer in Which the Enzyme is Involved | Treatment/Drug |
|---|---|---|
| ST3GAL1 | Breast Cancer [37], Leukemia [126], Bladder cancer [127], RCC [128], Melanoma [85], Ovarian cancer [23] | Hexapeptide NH2GNWWWW [129], Stachybotrydial [130], Lith-O-Asp (Pan ST) [131], Soyasaponin-I [117,118] |
| ST3GAL3 | Breast Cancer [24] | Lith-O-Asp analogues FCW34 and FCW66 [132] |
| ST3GAL4 | Pancreatic cancer [60], Cervical cancer [133], Leukemia [92] | Soyasaponin-I [119] |
| ST3GAL6 | Bladder cancer [134] | 3Fax-Neu5Ac [135] |
| ST6GAL1 | Colon cancer [136], Rectal cancer [96], Prostate cancer [70], Breast cancer [38], Gastric cancer [137], Pancreatic cancer [138], Cervical cancer [139], RCC [140], Ovarian cancer [63] | - |
| ST6GALNAC1 | Gastric cancer [141], ESCC [78] | - |
| ST6GALNAC2 | Breast [142] | - |
| ST8SIA Family | Breast cancer [42], Bladder cancer [87] | 2′-O-methyl CMP [114] |
| NEU Family | Gastric cancer [143], Pancreatic cancer [59,144] Bladder cancer [145], Ovarian cancer [66], HNSCC [82], RCC [146], Lung cancer [147,148] | Sialidase conjugation to trastuzumab (Precision glycocalyx editing) [149], Engineered PD-L1-targeted sialidase [150], Bi-Sialidase E602-GLIMMER-01 (Glycan-Mediated Immune Regulation) study [151], Oseltamivir [152], Zanamivir [153], Bifunctional HER2-Sialidase [154], DANA Analogues [155] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nag, S.; Mandal, A.; Joshi, A.; Jain, N.; Srivastava, R.S.; Singh, S.; Khattri, A. Sialyltransferases and Neuraminidases: Potential Targets for Cancer Treatment. Diseases 2022, 10, 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases10040114
Nag S, Mandal A, Joshi A, Jain N, Srivastava RS, Singh S, Khattri A. Sialyltransferases and Neuraminidases: Potential Targets for Cancer Treatment. Diseases. 2022; 10(4):114. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases10040114
Chicago/Turabian StyleNag, Sagorika, Abhimanyu Mandal, Aryaman Joshi, Neeraj Jain, Ravi Shanker Srivastava, Sanjay Singh, and Arun Khattri. 2022. "Sialyltransferases and Neuraminidases: Potential Targets for Cancer Treatment" Diseases 10, no. 4: 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases10040114
APA StyleNag, S., Mandal, A., Joshi, A., Jain, N., Srivastava, R. S., Singh, S., & Khattri, A. (2022). Sialyltransferases and Neuraminidases: Potential Targets for Cancer Treatment. Diseases, 10(4), 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/diseases10040114







