Encapsulation in Amylose Inclusion Complex Enhances the Stability and Release of Vitamin D
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Inclusion Complexes
2.3. Determination of Loading Capacity
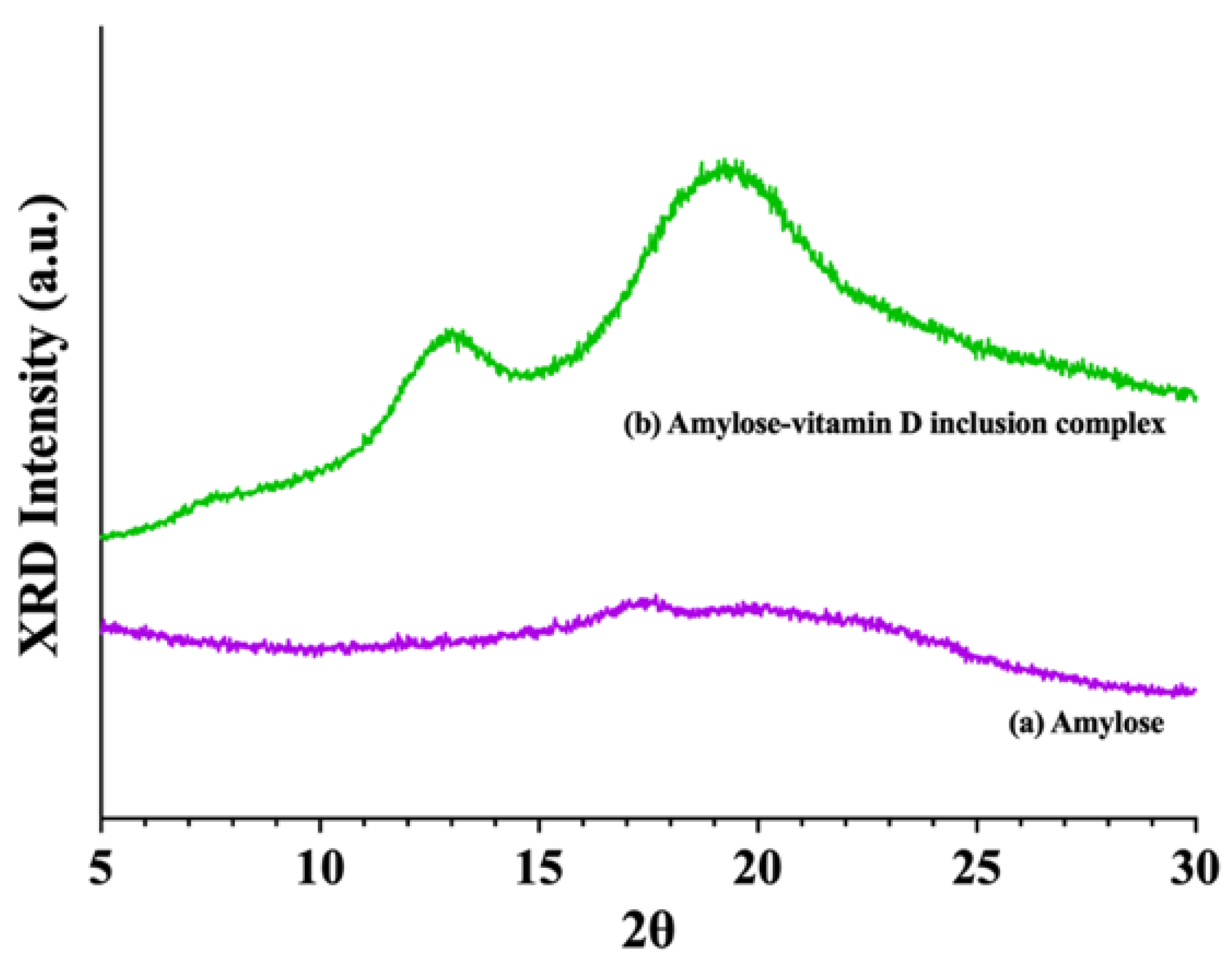
2.4. X−ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
2.5. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) Analysis
2.6. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR) Analysis
2.7. Stability Tests
2.7.1. Photostability
2.7.2. Thermal Stability
2.8. In Vitro Release of Vitamin D
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the Inclusion Complex (IC)
3.1.1. Loading Capacity
3.1.2. X−ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
3.1.3. Thermal Analysis
3.1.4. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Investigation
3.2. Stability Studies
3.2.1. Photostability
3.2.2. Thermal Stability
3.3. In Vitro Release Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bikle, D.D. Vitamin D Metabolism, Mechanism of Action, and Clinical Applications. Chem. Biol. 2014, 21, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Autier, P.; Boniol, M.; Pizot, C.; Mullie, P. Vitamin D status and ill health: A systematic review. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014, 2, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilz, S.; März, W.; Cashman, K.D.; Kiely, M.E.; Whiting, S.J.; Holick, M.F.; Grant, W.B.; Pludowski, P.; Hiligsmann, M.; Trummer, C.; et al. Rationale and Plan for Vitamin D Food Fortification: A Review and Guidance Paper. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, J.W. Vitamin D and Cardiovascular Disease. Annu. Rev. Med. 2016, 67, 261–272. [Google Scholar]
- Holick, M.F. Vitamin D deficiency−reply. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 266–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heaney, R.P. Functional indices of vitamin D status and ramifications of vitamin D deficiency. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2004, 80, 1706S–1709S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galior, K.; Grebe, S.; Singh, R. Development of Vitamin D Toxicity from Overcorrection of Vitamin D Deficiency: A Review of Case Reports. Nutrients 2018, 10, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holick, M.F. The vitamin D deficiency pandemic: Approaches for diagnosis, treatment and prevention. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2017, 18, 153–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuoka, L.Y.; Ide, L.; Wortsman, J.; MacLaughlin, J.A.; Holick, M.F. Sunscreens suppress cutaneous vitamin D3 synthesis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1987, 64, 1165–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gessner, B.D.; Plotnik, J.; Muth, P.T. 25−Hydroxyvitamin D levels among healthy children in Alaska. J. Pediatr. 2003, 143, 434–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laird, E.; O’Halloran, A.M.; Carey, D.; Healy, M.; O’Connor, D.; Moore, P.; Shannon, T.; Molloy, A.M.; Kenny, R.A. The prevalence of vitamin D deficiency and the determinants of 25(OH)D concentration in older Irish adults: Data from The Irish Longitudinal Study on Ageing (TILDA). J. Gerontol. Ser. A−Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2017, 73, 519–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hasanvand, E.; Fathi, M.; Bassiri, A.; Javanmard, M.; Abbaszadeh, R. Novel starch based nanocarrier for vitamin D fortification of milk: Production and characterization. Food Bioprod. Process. 2015, 96, 264–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballard, J.M.; Zhu, L.M.; Nelson, E.D.; Seburg, R.A. Degradation of vitamin D3 in a stressed formulation: The identification of esters of vitamin D3 formed by a transesterification with triglycerides. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2007, 43, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, S.Y.; Lin, H.Y.; Hong, W.P.; Lin, C.P. Evaluation of preliminary causes for vitamin D series degradation via DSC and HPLC analyses. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2017, 130, 1357–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zareie, M.; Abbasi, A.; Faghih, S. Thermal Stability and Kinetic Study on Thermal Degradation of Vitamin D3 in Fortified Canola Oil. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 2475–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, H.; Hayakawa, S.; Wada, S.; Okazaki, E.; Yamazawa, M. Effect of solar drying on vitamin D3 and provitamin D3 contents in fish meat. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1988, 36, 803–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diarrassouba, F.; Garrait, G.; Remondetto, G.; Alvarez, P.; Beyssac, E.; Subirade, M. Food protein−based microspheres for increased uptake of vitamin D3. Food Chem. 2015, 173, 1066–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, S.; Livney, Y.D. Potato protein based nanovehicles for health promoting hydrophobic bioactives in clear beverages. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 57, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jannasari, N.; Fathi, M.; Moshtaghian, S.J.; Abbaspourrad, A. Microencapsulation of vitamin D using gelatin and cress seed mucilage: Production, characterization and in vivo study. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 129, 972–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Q.; Kong, L.Y.; Zhao, Y.; Tan, L.B.; Zhang, J.; Du, Z.Y.; Zhang, H. Lipophilization and molecular encapsulation of p−coumaric acid by amylose inclusion complex. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 93, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Z.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Guan, L.; Wang, S.Q.; Zhang, J.; Tan, L.B.; Kong, L.Y.; Zhang, H. Lipophilization and amylose inclusion complexation enhance the stability and release of catechin. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 269, 118251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, S.R.; Marathe, S.J.; Singhal, R.S. Co−encapsulation of vitamins B12 and D3 using spray drying: Wall material optimization, product characterization, and release kinetics. Food Chem. 2021, 335, 127642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Y.C.; Teng, Z.; Wang, Q. Development of zein nanoparticles coated with carboxymethyl chitosan for encapsulation and controlled release of vitamin D3. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 836–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, M.B.; Carvalho, M.G.; Garcia−Rojas, E.E. Carboxymethyl tara gum−lactoferrin complex coacervates as carriers for vitamin D3: Encapsulation and controlled release. Food Hydrocoll. 2021, 112, 106347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, A.C.; Taylor, C.L.; Yaktine, A.L.; Valle, H.B.D. Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium and Vitamin D; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2010; p. 999. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Gladden, I.; Guo, J.Y.; Tan, L.B.; Kong, L.Y. Enzymatic digestion of amylose and high amylose maize starch inclusion complexes with alkyl gallates. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 108, 106009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.Y.; Kong, L.Y. Enhancement of enzymatic resistance in V−type starch inclusion complexes by hydrothermal treatments. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 127, 107533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.Y.; Ziegler, G.R.; Kong, L.Y. Polymorphic transitions of V−type amylose upon hydration and dehydration. Food Hydrocoll. 2022, 125, 107372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.Y.; Shi, L.F.; Kong, L.Y. Structure−digestibility relationship of starch inclusion complex with salicylic acid. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 299, 120147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamin, C. CHOLECALCIFEROL|Properties and Determination. In Encyclopedia of Food Sciences and Nutrition, 2nd ed.; Woollard, D.C., Indyk, H.E., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2003; pp. 1205–1213. [Google Scholar]
- Nordmark, T.S.; Ziegler, G.R. Spherulitic crystallization of gelatinized maize starch and its fractions. Carbohydr. Polym. 2002, 49, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simi, C.K.; Abraham, T.E. Hydrophobic grafted and cross−linked starch nanoparticles for drug delivery. Bioprocess. Biosyst. Eng. 2007, 30, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, A.M.; Wang, L.J.; Li, D.; Adhikari, B. The effect of annealing and cryoprotectants on the properties of vacuum−freeze dried starch nanoparticles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 88, 1334–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, X.; Liu, S.W. Encapsulation of tangeretin into debranched−starch inclusion complexes: Structure, properties and stability. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 100, 105409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, V.S.S.; Poejo, J.; Matias, A.A.; Rodríguez−Rojo, S.; Cocero, M.J.; Duarte, C.M.M. Using different natural origin carriers for development of epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) solid formulations with improved antioxidant activity by PGSS−drying. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 67599–67609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Kong, L.; Huang, T.; Wei, X.; Tan, L.; Luo, H.; Zhang, H. Encapsulation in Amylose Inclusion Complex Enhances the Stability and Release of Vitamin D. Nutrients 2023, 15, 1111. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15051111
Liu S, Kong L, Huang T, Wei X, Tan L, Luo H, Zhang H. Encapsulation in Amylose Inclusion Complex Enhances the Stability and Release of Vitamin D. Nutrients. 2023; 15(5):1111. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15051111
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Simiao, Lingyan Kong, Tianzhuo Huang, Xiaohui Wei, Libo Tan, Hailing Luo, and Hao Zhang. 2023. "Encapsulation in Amylose Inclusion Complex Enhances the Stability and Release of Vitamin D" Nutrients 15, no. 5: 1111. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15051111
APA StyleLiu, S., Kong, L., Huang, T., Wei, X., Tan, L., Luo, H., & Zhang, H. (2023). Encapsulation in Amylose Inclusion Complex Enhances the Stability and Release of Vitamin D. Nutrients, 15(5), 1111. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu15051111






