The Potent G-Quadruplex-Binding Compound QN-302 Downregulates S100P Gene Expression in Cells and in an In Vivo Model of Pancreatic Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. RNA-seq Analysis of RNA from Cell-Based Studies
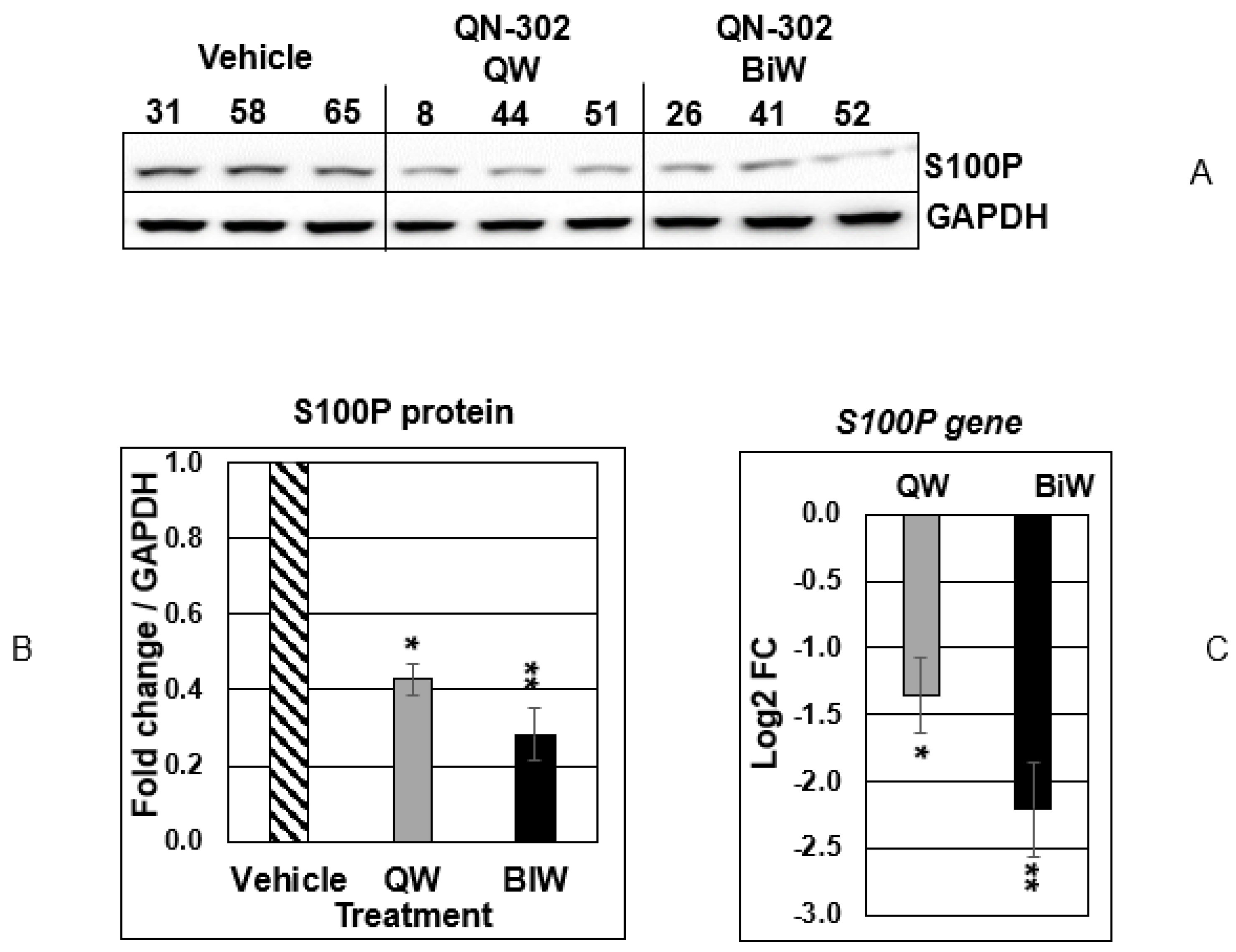
2.2. QN-302 Downregulates S100P Expression in an In Vivo Xenograft Model
2.3. RNA-seq Analysis of Human PDAC Tumor Tissues
2.4. Bioinformatics Analyses
2.5. Biophysical Studies
2.6. Molecular Modeling
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. RNA-seq Analysis of RNA from Cell-Based Studies
4.2. RNA-seq Analysis of Tumor Material from Xenograft Studies
| Target | Supplier | Catalogue Number | Dilution | Incubation Details |
| S100P | Cell Signaling Technology | 7677 | 1:1000 | Overnight @4 °C |
| GAPDH | Cell Signaling Technology | 5174 | 1:1000 | Overnight @4 °C |
| Anti-Rabbit IgG | Cell Signaling Technology | 7074 | 1:3000 | RT for 1 h |
| Target Gene | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
| S100P | CTCAAGGTGCTGATGGAGAAGG | GAACTCACTGAAGTCCACCTGG |
| HPRT1 | CATTATGCTGAGGATTTGGAAAGG | CTTGAGCACACAGAGGGCTACA |
4.3. RNA-seq Analysis of Human PDAC Tumor Tissues
4.4. Bioinformatics Analyses
4.5. Biophysical Studies
4.6. Molecular Modeling
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kamisawa, T.; Wood, L.D.; Itoi, T.; Takaori, K. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet 2016, 388, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Fagman, J.B.; Ma, Y.; Liu, J.; Vihav, C.; Engstrom, C.; Liu, D.; Chen, C. A comprehensive review of pancreatic cancer and its therapeutic challenges. Aging 2022, 14, 7635–7649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, W.; Chawla, A.; O’Reilly, E.M. Pancreatic cancer: A review. JAMA 2021, 326, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, K.H.; Theocharides, V.A.; Lei, Y.; Rana, S.K.; Rana, R.K.; Mansour, M.H.; Ganjam, M.K.; Ahmed, J. Pancreatic Cancer: Review of the current and investigational drug landscape. J. Hematol. Oncol. Pharm. 2022, 12, 323–333. [Google Scholar]
- Von Hoff, D.D.; Ervin, T.; Arena, F.P.; Chiorean, E.G.; Infante, J.; Moore, M.; Seay, T.; Tjulandin, S.A.; Ma, W.W.; Saleh, M.N.; et al. Increased survival in pancreatic cancer with nab-paclitaxel plus gemcitabine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 1691–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conroy, T.; Desseigne, F.; Ychou, M.; Bouché, O.; Guimbaud, R.; Bécouarn, Y.; Adenis, A.; Raoul, J.-L.; Gourgou-Bourgade, S.; De La Fouchardière, C.; et al. FOLFIRINOX versus gemcitabine for metastatic pancreatic cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 1817–1825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carmichael, J.; Fink, U.; Russell, R.C.; Spittle, M.F.; Harris, A.; Spiessi, G.; Blatter, J. Phase II study of gemcitabine in patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. Br. J. Cancer 1996, 73, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beutel, A.K.; Halbrook, C.J. Barriers and Opportunities for gemcitabine in pancreatic cancer therapy. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2022, 324, C540–C552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, V.; Fabozzi, T.; Bareschino, M.A.; Barletta, E.; Germano, D.; Paciolla, I.; Tinessa, V.; Grimaldi, A.M. Pancreatic cancer: Beyond Brca mutations. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, B.M.; Ellis, H.; Jordan, A.C.; Freed-Pastor, W.A.; Perez, K.; Rubinson, D.A.; Sethi, N.; Singh, H.; Surana, R.; Wolpin, B.M.; et al. Emerging role of targeted therapy in metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 6223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Iovanna, J.; Santofimia-Castaño, P. Stroma-targeting strategies in pancreatic cancer: A double-edged sword. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 79, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowzer, D.; Zameer, M.; Conroy, M.; Kolch, W.; Duffy, A.G. Targeting KRAS in pancreatic cancer. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rémond, M.S.; Pellat, A.; Brezault, C.; Dhooge, M.; Coriat, R. Are targeted therapies or immunotherapies effective in metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma? ESMO Open 2022, 7, 100638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, P.J.; Yachida, S.; Mudie, L.J.; Stephens, P.J.; Pleasance, E.D.; Stebbings, L.A.; Morsberger, L.A.; Latimer, C.; McLaren, S.; Lin, M.-L.; et al. The patterns and dynamics of genomic instability in metastatic pancreatic cancer. Nature 2010, 467, 1109–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waddell, N.; Pajic, M.; Patch, A.M.; Chang, D.K.; Kassahn, K.S.; Bailey, P.; Johns, A.L.; Miller, D.; Nones, K.; Quek, K.; et al. Whole genomes redefine the mutational landscape of pancreatic cancer. Nature 2015, 518, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Makohon-Moore, A.P.; Zhang, M.; Reiter, J.G.; Bozic, I.; Allen, B.; Kundu, D.; Chatterjee, K.; Wong, F.; Jiao, Y.; Kohutek, Z.A.; et al. Limited heterogeneity of known driver gene mutations among the metastases of individual patients with pancreatic cancer. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jones, S.; Zhang, X.; Parsons, D.W.; Lin, J.C.; Leary, R.J.; Angenendt, P.; Mankoo, P.; Carter, H.; Kamiyama, H.; Jimeno, A.; et al. Core signaling pathways in human pancreatic cancers revealed by global genomic analyses. Science 2008, 321, 1801–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sardar, M.; Recio-Boiles, A.; Mody, K.; Karime, C.; Chandana, S.R.; Mahadevan, D.; Starr, J.; Jones, J.; Borad, M.; Babiker, H. Pharmacotherapeutic options for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2022, 23, 2079–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Kane, G.M.; Lowery, M.A. Moving the needle on precision medicine in pancreatic cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 2693–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herreros-Villanueva, M.; Bujanda, L. Non-invasive biomarkers in pancreatic cancer diagnosis: What we need versus what we have. Ann. Transl. Med. 2016, 4, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ahmed, A.A.; Angell, R.; Oxenford, S.; Worthington, J.; Williams, N.; Barton, N.; Fowler, T.G.; O’Flynn, D.E.; Sunose, M.; McConville, M.; et al. Asymmetrically substituted quadruplex-binding naphthalene diimide showing potent activity in pancreatic cancer models. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 1634–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vo, T.; Oxenford, S.; Angell, R.; Marchetti, C.; Ohnmacht, S.A.; Wilson, W.D.; Neidle, S. Substituted naphthalenediimide compounds bind selectively to two human quadruplex structures with parallel topology. ACS. Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burge, S.; Parkinson, G.N.; Hazel, P.; Todd, A.K.; Neidle, S. Quadruplex DNA: Sequence, topology and structure. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 5402–5415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bochman, M.L.; Paeschke, K.; Zakian, V.A. DNA secondary structures: Stability and function of G-quadruplex structures. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 770–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spiegel, J.; Adhikari, S.; Balasubramanian, S. The structure and function of DNA G-quadruplexes. Trends Chem. 2019, 2, 123–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huppert, J.L.; Balasubramanian, S. G-quadruplexes in promoters throughout the human genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balasubramanian, S.; Hurley, L.H.; Neidle, S. Targeting G-quadruplexes in gene promoters: A novel anticancer strategy? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 261–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rigo, R.; Palumbo, M.; Sissi, C. G-quadruplexes in human promoters: A challenge for therapeutic applications. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2017, 1861, 1399–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lago, S.; Nadai, M.; Cernilogar, F.M.; Kazerani, M.; Domíniguez Moreno, H.; Schotta, G.; Richter, S.N. Promoter G-quadruplexes and transcription factors cooperate to shape the cell type-specific transcriptome. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Varshney, D.; Simeone, A.; Zhang, X.; Adhikari, S.; Tannahill, D.; Balasubramanian, S. Promoter G-quadruplex folding precedes transcription and is controlled by chromatin. Genome Biol. 2021, 22, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchetti, C.; Zyner, K.G.; Ohnmacht, S.A.; Robson, M.; Haider, S.M.; Morton, J.P.; Marsico, G.; Vo, T.; Laughlin-Toth, S.; Ahmed, A.A.; et al. Targeting multiple effector pathways in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma with a G-quadruplex-binding small molecule. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 2500–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.A.; Marchetti, C.; Ohnmacht, S.A.; Neidle, S. A G-quadruplex-binding compound shows potent activity in human gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Guo, F.; Chen, M.; Tao, X.; Dong, D. S100 proteins in pancreatic cancer: Current knowledge and future perspectives. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 711180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prica, F.; Radon, T.; Cheng, Y.; Crnogorac-Jurcevic, T. The life and works of S100P—From conception to cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2016, 6, 562–576. [Google Scholar]
- Data was taken from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) Project of Genomic Data Commons. Available online: https://www.proteinatlas.org/ENSG00000163993-S100P/pathology/pancreatic+cancer (accessed on 12 June 2022).
- Zou, W.; Li, L.; Wang, Z.; Jiang, N.; Wang, F.; Hu, M.; Liu, R. Up-regulation of S100P predicts the poor long-term survival and construction of prognostic signature for survival and immunotherapy in patients with pancreatic cancer. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 9006–9020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ideno, N.; Mori, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Ohtsuka, T. Early detection of pancreatic cancer: Role of biomarkers in pancreatic fluid samples. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Fang, Y.; Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Feng, X.; Zhan, Y.; Xie, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, G.; et al. S100P contributes to promoter demethylation and transcriptional activation of SLC2A5 to promote metastasis in colorectal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 125, 734–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, T.; Ohtsuka, T.; Asano, K.; Kimura, H.; Ohuchida, K.; Kitada, H.; Ideno, N.; Mori, Y.; Tokunaga, S.; Oda, Y.; et al. S100P in duodenal fluid is a useful diagnostic marker for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Pancreas 2017, 46, 1288–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer Genetics Web. Pancreatic cancer. Available online: http://www.cancerindex.org/geneweb/X0603.htm (accessed on 12 June 2022).
- Mergny, J.L.; Li, J.; Lacroix, L.; Amrane, S.; Chaires, J.B. Thermal difference spectra: A specific signature for nucleic acid structures. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, e138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kypr, J.; Kejnovská, I.; Renciuk, D.; Vorlícková, M. Circular dichroism and conformational polymorphism of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 1713–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kikin, O.; D’Antonio, L.; Bagga, P.S. QGRS Mapper: A web-based server for predicting G-quadruplexes in nucleotide sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, W676–W682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locker, G.; Hamilton, S.; Harris, J.; Jessup, J.; Kemeny, N.; Macdonald, J.; Somerfield, M.; Hayes, D.; Bast, R. ASCO 2006 update of recommendations for the use of tumor markers in gastrointestinal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 5313–5327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane, L.E.; Mellotte, G.S.; Mylod, E.; O’Brien, R.M.; O’Connell, F.; Buckley, C.E.; Arlow, J.; Nguyen, K.; Mockler, D.; Meade, A.D.; et al. Diagnostic accuracy of blood-based biomarkers for pancreatic cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Res. Commun. 2022, 2, 1229–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibadulinova, A.; Oveckova, I.; Parkkila, S.; Pastorekova, S.; Pastorek, J. Key promoter elements involved in transcriptional activation of the cancer-related gene coding for S100P calcium-binding protein. Oncol. Rep. 2008, 20, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Collie, G.W.; Promontorio, R.; Hampel, S.M.; Micco, M.; Neidle, S.; Parkinson, G.N. Structural basis for telomeric G-quadruplex targeting by naphthalene diimide ligands. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 2723–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micco, M.; Collie, G.W.; Dale, A.G.; Ohnmacht, S.A.; Pazitna, I.; Gunaratnam, M.; Reszka, A.P.; Neidle, S. Structure-based design and evaluation of naphthalene diimide G-quadruplex ligands as telomere targeting agents in pancreatic cancer cells. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 2959–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo Krauss, I.; Ramaswamy, S.; Neidle, S.; Haider, S.; Parkinson, G.N. Structural insights into the quadruplex-duplex 3′ interface formed from a telomeric repeat: A potential molecular target. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 1226–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vianney, Y.M.; Weisz, K. Solution structure of Phen-DC3 intercalating into a quadruplex-duplex hybrid. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, 11948–11964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, A.K.; Johnston, M.; Neidle, S. Highly prevalent putative quadruplex sequence motifs in human DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005, 33, 2901–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siddiqui-Jain, A.; Grand, C.L.; Bearss, D.J.; Hurley, L.H. Direct evidence for a G-quadruplex in a promoter region and its targeting with a small molecule to repress c-MYC transcription. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11593–11598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Calabrese, D.R.; Chen, X.; Leon, E.C.; Gaikwad, S.M.; Phyo, Z.; Hewitt, W.M.; Alden, S.; Hilimire, T.A.; He, F.; Michalowski, A.M.; et al. Chemical and structural studies provide a mechanistic basis for recognition of the MYC G-quadruplex. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monsen, R.C.; Maguire, J.M.; DeLeeuw, L.W.; Chaires, J.B.; Trent, J.O. Drug discovery of small molecules targeting the higher-order hTERT promoter G-quadruplex. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0270165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.H.; Kang, H.J.; Luevano, L.A.; Gokhale, V.; Wu, K.; Pandey, R.; Sherry Chow, H.H.; Hurley, L.H.; Kraft, A.S. Small-molecule-targeting hairpin loop of hTERT promoter G-quadruplex induces cancer cell death. Cell Chem. Biol. 2019, 26, 1110–1121.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, R.; Dutta, D.; Das, T.; Debnath, M.; Dash, J. G4 sensing pyridyl-thiazole polyamide represses c-KIT expression in leukemia cells. Chemistry 2021, 27, 8590–8599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunaratnam, M.; Swank, S.; Haider, S.M.; Galesa, K.; Reszka, A.P.; Beltran, M.; Cuenca, F.; Fletcher, J.A.; Neidle, S. Targeting human gastrointestinal stromal tumor cells with a quadruplex-binding small molecule. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 3774–3783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spiegel, J.; Cuesta, S.M.; Adhikari, S.; Hänsel-Hertsch, R.; Tannahill, D.; Balasubramanian, S. G-quadruplexes are transcription factor binding hubs in human chromatin. Genome Biol. 2021, 22, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camara, R.; Ogbeni, D.; Gerstmann, L.; Ostovar, M.; Hurer, E.; Scott, M.; Mahmoud, N.G.; Radon, T.; Crnogorac-Jurcevic, T.; Patel, P.; et al. Discovery of novel small molecule inhibitors of S100P with in vitro anti-metastatic effects on pancreatic cancer cells. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 203, 112621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakhel, S.; Padilla, L.; Adan, J.; Masa, M.; Martinez, J.M.; Roque, L.; Coll, T.; Hervas, R.; Calvis, C.; Messeguer, R.; et al. S100P antibody-mediated therapy as a new promising strategy for the treatment of pancreatic cancer. Oncogenesis 2014, 3, e92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, D.; Han, M.; Zhou, M.; Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Xu, B.; Zhang, A. Down-regulation of S100P induces apoptosis in endometrial epithelial cell during GnRH antagonist protocol. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2021, 19, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marco, C.; Laudanna, C.; Rinaldo, N.; Oliveira, D.M.; Ravo, M.; Weisz, A.; Ceccarelli, M.; Caira, E.; Rizzuto, A.; Zoppoli, P.; et al. Specific gene expression signatures induced by the multiple oncogenic alterations that occur within the PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway in lung cancer. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, T.; Du, G.; Wang, D. The S100 protein family in lung cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta 2021, 520, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathai, A.M.; Alexander, J.; Huang, H.Y.; Li, C.F.; Jeng, Y.M.; Fung, K.M.; Harris, W.P.; Swanson, P.E.; Truong, C.; Yeh, M.M. S100P as a marker for poor survival and advanced stage in gallbladder carcinoma. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2021, 52, 151736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Luo, L.; Fang, D.; Tang, T.; Ni, W.; Dai, B.; Sun, H.; Jiang, L. A novel DNA aptamer targeting s100p induces antitumor effects in colorectal cancer cells. Nucleic Acid Ther. 2020, 30, 402–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 21120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Girardot, C.; Scholtalbers, J.; Sauer, S.; Su, S.Y.; Furlong, E.E. Je, a versatile suite to handle multiplexed NGS libraries with unique molecular identifiers. BMC Bioinform. 2016, 17, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. FeatureCounts: An efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varet, H.; Brillet-Guéguen, L.; Coppée, J.-Y.; Dillies, M.A. SARTools: A DESeq2- and EdgeR-based r pipeline for comprehensive differential analysis of RNA-seq data. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, D.W.; Sherman, B.T.; Lempicki, R.A. Bioinformatics enrichment tools: Paths toward the comprehensive functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Parkinson, G.N.; Lee, M.P.; Neidle, S. Crystal structure of parallel quadruplexes from human telomeric DNA. Nature 2002, 417, 876–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
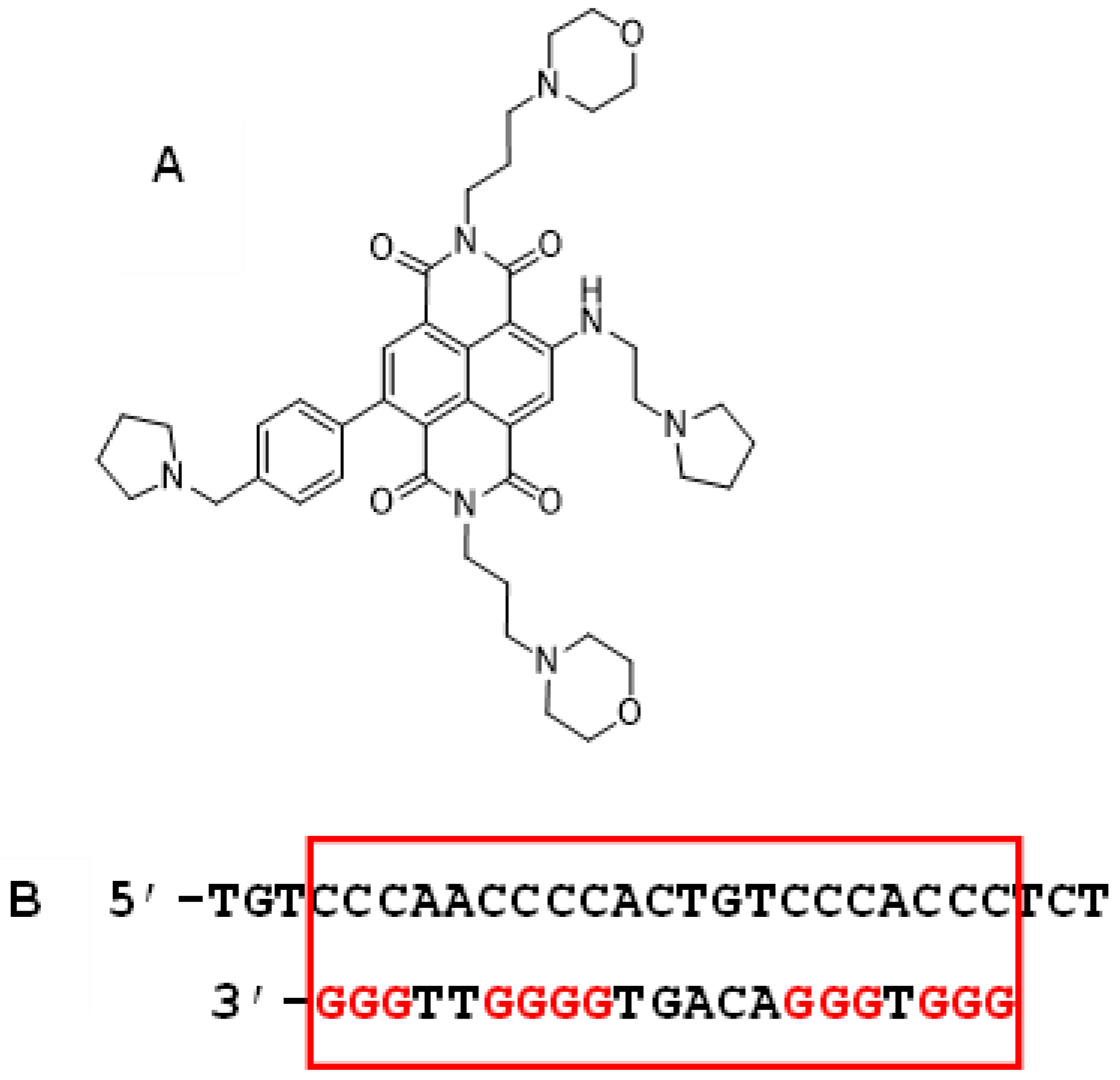




| Gene | QN-302, 24 h in MIA PaCa-2 Cells | p Value | PDAC P-D Minus Normal | p Value | No of PGQs | Gene Function | PDAC Occurrence and Function |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPARC | −2.252 | 0.61 | 2.685 | 0.071 | 10 | Secreted protein acidic and cysteine rich | Promotes pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and migration |
| S100P | −3.230 | 0.08 | 45.27 | 0.054 | 60 | Calcium binding protein involved in multiple signal transduction pathways | Sensitive and specific marker for the detection of PDAC, promotes PDAC growth and survival |
| ID2 | −1.215 | 0.0001 | 0.398 | 0.014 | 3 | DNA-binding pro-proliferative gene | Over-expressed in PDAC |
| CLDN7 | −2.39 | 0.429 | 1.213 | 0.643 | 4 | Involved in junction formation | Over-expressed in PDAC and other cancers |
| CX3CL1 | −2.912 | 0.040 | 2.87 | 0.017 | 5 | Chemokine | Modulates the development of PDAC via JAK/STAT signalling pathway; upregulated in PDAC |
| Sample ID | Age | Gender | Diagnosis/Tissue Composition |
|---|---|---|---|
| R2971 | 65 | Male | Poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma with invasion (PanIN) |
| R2944 | 65 | Male | Poorly differentiated ductal adenocarcinoma with necrosis (PanIN) |
| R2824 | 71 | Male | Moderately differentiated ductal adenocarcinoma of the head of pancreas with invasion (ductal epithelial changes in high grade PanIN) |
| R2700 | 70 | Male | Moderately differentiated ductal adenocarcinoma with invasion and necrosis (PanIN) |
| CR560569 | 53 | Male | Normal pancreatic tissue comprised of 75% Exocrine epithelium, 10% Endocrine epithelium, 15% Ducts |
| CR562915 | 66 | Male | Normal pancreatic tissue comprised of 90% Acini, 5% Ducts, 5% Islet cells |
| CR561640 | 69 | Male | Normal pancreatic tissue comprised of 90% acini, 0% islets, 5% ducts, 5% fibrofatty stroma |
| Position in Seq | 5′-Sequence | G4 Score | Strand | Gene Region |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2251 | GGGAACTTGGGCTTGGGGCTCGGGG | 41 | Coding | Intron |
| 2524 | GGGCAGGGCTGGGCTGGG | 42 | Coding | Intron |
| 548 | GGGTGGGACAGTGGGGTTGGG | 38 | Template | Promoter |
| 1239 | GGGAGCAGGGAAAGCGGGCAAGTGGG | 41 | Template | Intron |
| 1487 | GGGGTCAAAGGGAAGGGGAAATGGAGAGGG | 36 | Template | Intron |
| 2467 | GGGAGGGCTGAGAAGGGCACCCAGGG | 36 | Template | Intron |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahmed, A.A.; Greenhalf, W.; Palmer, D.H.; Williams, N.; Worthington, J.; Arshad, T.; Haider, S.; Alexandrou, E.; Guneri, D.; Waller, Z.A.E.; et al. The Potent G-Quadruplex-Binding Compound QN-302 Downregulates S100P Gene Expression in Cells and in an In Vivo Model of Pancreatic Cancer. Molecules 2023, 28, 2452. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062452
Ahmed AA, Greenhalf W, Palmer DH, Williams N, Worthington J, Arshad T, Haider S, Alexandrou E, Guneri D, Waller ZAE, et al. The Potent G-Quadruplex-Binding Compound QN-302 Downregulates S100P Gene Expression in Cells and in an In Vivo Model of Pancreatic Cancer. Molecules. 2023; 28(6):2452. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062452
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhmed, Ahmed A., William Greenhalf, Daniel H. Palmer, Nicole Williams, Jenny Worthington, Tariq Arshad, Shozeb Haider, Effrosyni Alexandrou, Dilek Guneri, Zoe A. E. Waller, and et al. 2023. "The Potent G-Quadruplex-Binding Compound QN-302 Downregulates S100P Gene Expression in Cells and in an In Vivo Model of Pancreatic Cancer" Molecules 28, no. 6: 2452. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062452
APA StyleAhmed, A. A., Greenhalf, W., Palmer, D. H., Williams, N., Worthington, J., Arshad, T., Haider, S., Alexandrou, E., Guneri, D., Waller, Z. A. E., & Neidle, S. (2023). The Potent G-Quadruplex-Binding Compound QN-302 Downregulates S100P Gene Expression in Cells and in an In Vivo Model of Pancreatic Cancer. Molecules, 28(6), 2452. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules28062452






