The Impact of Enterprise Resource Planning on Business Performance: With the Discussion on Its Relationship with Open Innovation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. ERP Revolution
2.2. ERP System Usage
2.3. Factors Affecting ERP System Usage
2.4. ERP and Business Performance
3. Theoretical Framework
3.1. Contingency Theory
3.2. Contingency Factors
3.3. The Exploratory Study
3.3.1. Knowledge Sharing
3.3.2. Vendor Support
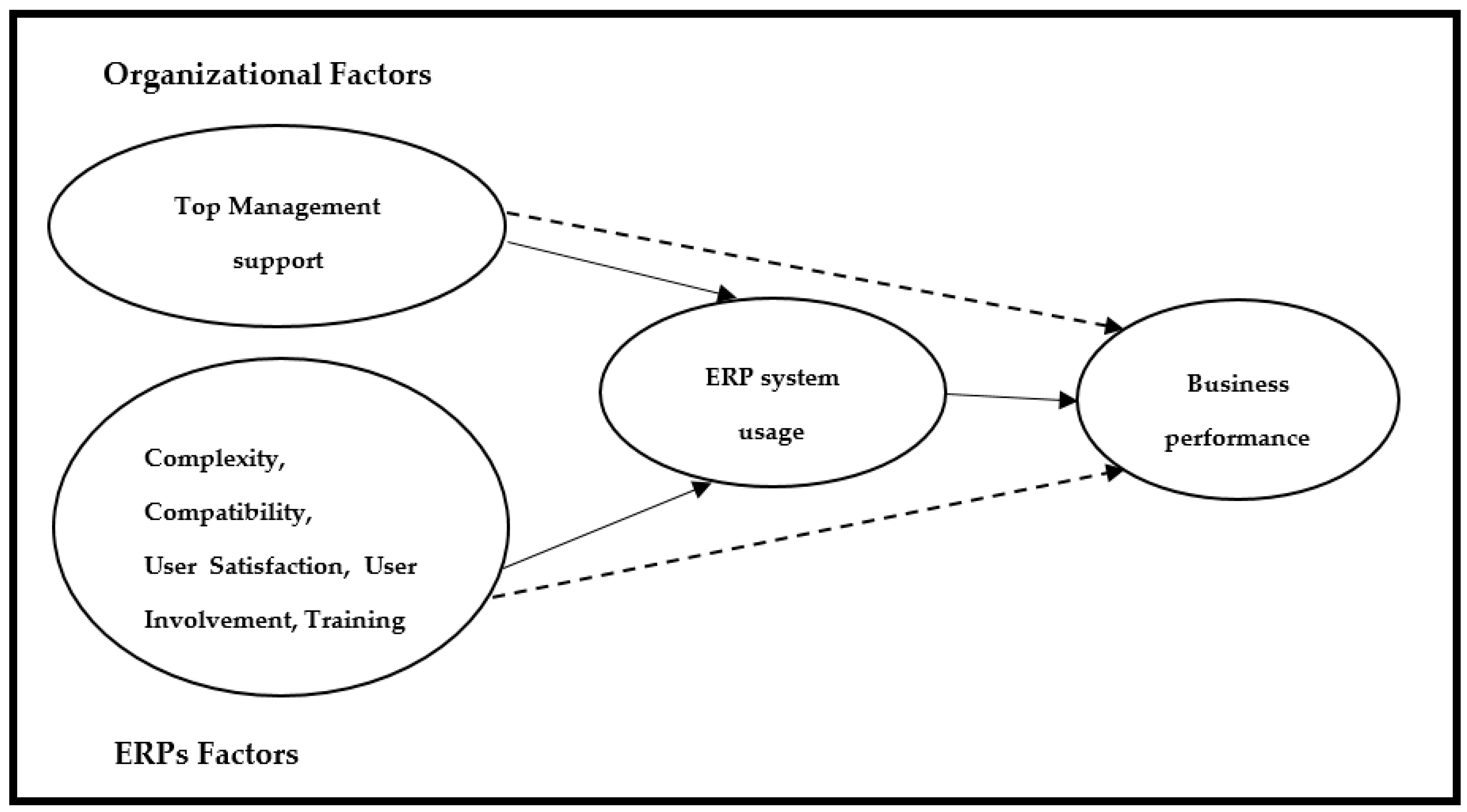
3.4. Research Framework and Hypotheses
3.4.1. Organizational Factors and ERPs Usage
3.4.2. ERPs Factors and ERPs Usage
3.4.3. ERPs Usage and Business Performance
4. Methodology
4.1. Research Design and Data Collection Procedures
4.1.1. The Exploratory Study
4.1.2. Hypotheses Testing (Questionnaire)
4.2. The Measures
5. Analysis
5.1. The Exploratory Study’s Results
5.2. The Quantitative Study Finding
5.2.1. The Measurement Model
5.2.2. The Structure Model
6. Discussion
6.1. The Relation between ERP and Business Performance
6.2. The Relation between ERP and Open Innovation
7. Implication and limitations of the Study
7.1. Implication
7.2. Limitations of the Study and Future Research
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liem, N.T.; Khuong, N.V.; Khanh, T.H.T.; Liem, T.; Khuong, V.; Khanh, T. Firm Constraints on the Link between Proactive Innovation, Open Innovation and Firm Performance. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2019, 5, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, Y.; Gunasekaran, A.; Abthorpe, M.S. Enterprise information systems project implementation. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2004, 87, 251–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E Hunton, J.; Lippincott, B.; Reck, J.L. Enterprise resource planning systems: Comparing firm performance of adopters and nonadopters. Int. J. Account. Inf. Syst. 2003, 4, 165–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melville, N.; Gurbaxani, K.K.V. Review: Technology Information An Performance: Organizational Integrative Model of IT Business Value. MIS Q. 2004, 28, 283–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.J.; Ferreira, E.; Bento, F.; Aparicio, M. Enterprise resource planning adoption and satisfaction determinants. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2016, 63, 659–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallunki, J.-P.; Laitinen, E.K.; Silvola, H. Impact of enterprise resource planning systems on management control systems and firm performance. Int. J. Account. Inf. Syst. 2011, 12, 20–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wieder, B.; Booth, P.; Matolcsy, Z.P.; Ossimitz, M.-L. The impact of ERP systems on firm and business process performance. J. Enterp. Inf. Manag. 2006, 19, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deep, A.; Guttridge, P.; Dani, S.; Burns, N. Investigating factors affecting ERP selection in made-to-order SME sector. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2008, 19, 430–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, A.; Almaleh, A.I.; Alshahri, S.; Alqahtani, S.S.; Alqahtani, N.D. Role of Information Systems in KSA Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs). Int. J. Adv. Res. Comput. Commun. Eng. 2015, 4, 6–11. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Mashari, M.; Al-Mudimigh, A.; Zairi, M. Enterprise resource planning: A taxonomy of critical factors. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2003, 146, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umble, E.J.; Haft, R.R.; Umble, M. Enterprise resource planning: Implementation procedures and critical success factors. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2003, 146, 241–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngai, E.W.; Law, C.; Wat, F. Examining the critical success factors in the adoption of enterprise resource planning. Comput. Ind. 2008, 59, 548–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, M.; Cuenca, R.P. Critical success factors for ERP implementation in SMEs. Robot. Comput. Manuf. 2013, 29, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ağaoğlu, M.; Yurtkoru, E.S.; Ekmekçi, A.K. The Effect of ERP Implementation CSFs on Business Performance: An Empirical Study on Users’ Perception. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015, 210, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, M.I.M.; Abbas, H.I. User adaptation and ERP benefits: Moderation analysis of user experience with ERP. Kybernetes 2017, 46, 530–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gable, G.G.; Sedera, D.; Chan, T. Enterprise System Success: A Measurement Model. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Fourth International Conference on Information Systems, Seattle, DC, USA, 14–17 December 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ifinedo, P. Extending the Gable et al. enterprise systems success measurement model: A preliminary study. J. Inf. Technol. Manag. 2006, 17, 14–33. [Google Scholar]
- Costa, C.J.; Aparicio, M.; Raposo, J. Determinants of the management learning performance in ERP context. Heliyon 2020, 6, e03689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selchert, M. Enhanced Project Success through SAP Best Practices—International Benchmark. Study; SAP Press: Bonn, Germany, 2004; ISBN 13-9781592290314. [Google Scholar]
- Muscatello, J.R.; Small, M.H.; Chen, I.J. Implementing enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems in small and midsize manufacturing firms. Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2003, 23, 850–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Muharfi, A. Forms of Organizational Changes and Accountant Participation in the SAP Implemenation Process: A Case Study from Saudi Arabia. Inf. Technol. J. 2010, 9, 632–642. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, S.; Park, J.; Yang, H. ERP Alignment for Positive Business Performance: Evidence from Korea’ s ERP Market. J. Comput. Inf. Syst. 2008, 48, 25–38. [Google Scholar]
- Veljanoska, F.; Axhiu, M. Information Systems as Support to Corporate Management. Manag. Inf. Syst. 2013, 8, 3–9. [Google Scholar]
- Calisir, F.; Calisir, F. The relation of interface usability characteristics, perceived usefulness, and perceived ease of use to end-user satisfaction with enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2004, 20, 505–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, H.-W.; Chang, H.-H.; Lin, Y.-H.; Chou, S.-B. Drivers and effects of post-implementation learning on ERP usage. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2014, 35, 267–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, T.H. Putting the enterprise into the enterprise system. Harv. Bus. Rev. 1998, 76, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Al-Turki, U.M. An exploratory study of ERP implementation in Saudi Arabia. Prod. Plan. Control. 2011, 22, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olhager, J.; Selldin, E. Enterprise resource planning survey of Swedish manufacturing firms. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2003, 146, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdinnour-Helm, S.; Lengnick-Hall, M.L.; Lengnick-Hall, C.A. Pre-implementation attitudes and organizational readiness for implementing an Enterprise Resource Planning system. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2003, 146, 258–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, M.R.J.; Abdulkhalaq, A.M. Increasing ERP Implementation Success Ratio by Focusing on Data Quality & User Participation. Int. J. Inf. Eng. Electron. Bus. 2015, 7, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Equey, C.; Fragniere, E. Elements of Perception Regarding the Implementation of ERP Systems in Swiss SMEs. Int. J. Enterp. Inf. Syst. 2008, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Dwivedi, Y.K.; Papazafeiropoulo, A.; Esteves, J. A benefits realistaion road-map framework for ERP usage in small and medium-sized enterprises. J. Enterp. Inf. Manag. 2009, 22, 25–35. [Google Scholar]
- Doom, C.; Milis, K.; Poelmans, S.; Bloemen, E. Critical success factors for ERP implementations in Belgian SMEs. J. Enterp. Inf. Manag. 2010, 23, 378–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ian, O.; Lee, G.L. The ‘pros’ and ‘cons’ of total quality management for smaller firms in manufaturing: Some experiences down the supply chain. Total Qual. Manag. 1995, 6, 413–426. [Google Scholar]
- Mabert, V.A.; Soni, A.; Venkataramanan, M. The impact of organization size on enterprise resource planning (ERP) implementations in the US manufacturing sector. Omega 2003, 31, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christofi, M.; Nunes, M.; Peng, G.C.; Lin, A. Towards ERP success in SMEs through business process review prior to implementation. J. Syst. Inf. Technol. 2013, 15, 304–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekaran, A.; Okko, P.; Martikainen, T.; Yli-Olli, P. Improving Productivity and Quality in SMEs: Cases and Analysis. Int. Small Bus. J. 1996, 15, 59–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinni, B.T. Process improvement, Part 2. Ind. Week 1995, 244, 45–50. [Google Scholar]
- Federici, T. Factors influencing ERP outcomes in SMEs: A post-introduction assessment. J. Enterp. Inf. Manag. 2009, 22, 81–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iris, C.; Cebeci, U. Analyzing relationship between ERP utilization and lean manufacturing maturity of Turkish SMEs. J. Enterp. Inf. Manag. 2014, 27, 261–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruivo, P.; Oliveira, T.; Neto, M.D.C. ERP use and value: Portuguese and Spanish SMEs. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2012, 112, 1008–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V.; Morris, M.G.; Davis, G.B.; Davis, F.D. User Acceptance of Information Technology: Toward a Unified View. MIS Q. 2003, 27, 425–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delone, W.H.; McLean, E.R. The DeLone and McLean Model of Information Systems Success: A Ten-Year Update. J. Manag. Inf. Syst. 2003, 19, 9–30. [Google Scholar]
- Shaikh, A.A.; Karjaluoto, H. Making the most of information technology & systems usage: A literature review, framework and future research agenda. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2015, 49, 541–566. [Google Scholar]
- Jasperson, J.; Carter, P.E.; Zmud, R.W. A Comprehensive Conceptualization of Post-Adoptive Behaviors Associated with Information Technology Enabled Work Systems. MIS Q. Manag. Inf. Syst. 2005, 29, 525–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nah, F.F.-H.; Tan, X.; Teh, S.H. An Empirical Investigation on End-Users’ Acceptance of Enterprise Systems. Inf. Resour. Manag. J. 2004, 17, 32–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwahk, K.-Y.; Lee, J.-N. The role of readiness for change in ERP implementation: Theoretical bases and empirical validation. Inf. Manag. 2008, 45, 474–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudreau, M.C. Learning to use ERP technology: A causal model. In Proceedings of the 36th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Big Island, HI, USA, 6–9 January 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Garson, D.G. Human factors in information systems. In Handbook of Organizational Behavior; Golembiewski, R.T., Ed.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1993; pp. 100–138. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Gathani, S.S. Computer technology adoption in Saudi Arabia: Correlates of perceived innovation attributes. Inf. Technol. Dev. 2003, 10, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basahel, A.; Yamin, M.; Drijan, A. Barriers to Cloud Computing Adoption for SMEs in Saudi Arabia. Int. J. Inf. Technol. 2016, 48, 159–175. [Google Scholar]
- Bokhari, R.H. The relationship between system usage and user satisfaction: A meta-analysis. J. Enterp. Inf. Manag. 2005, 18, 211–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, M.; Cheung, W.; Cheng, C.; Yeung, J.H.Y. Understanding ERP system adoption from the user’s perspective. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2008, 113, 928–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-F. An investigation into the effects of IS quality and top management support on ERP system usage. Total Qual. Manag. Bus. Excel. 2010, 21, 335–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruivo, P.; Johansson, B.; Oliveira, T.; Neto, M.D.C. Determinants that Influence ERP Use and Value: Cross-Country Evidence on Scandinavian and Iberian SMEs. Procedia Technol. 2012, 5, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nwankpa, J.; Roumani, Y. Understanding the link between organizational learning capability and ERP system usage: An empirical examination. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2014, 33, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baroudi, J.J.; Olson, M.H.; Ives, B. Impact of User Involvement on Information Satisfaction.pdf. Manag. Comput. 1986, 29, 232–238. [Google Scholar]
- Uddin, A.; Alam, M.S.; Al Mamun, A.; Khan, T.-U.-Z.; Akter, A. A Study of the Adoption and Implementation of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): Identification of Moderators and Mediator. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2019, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. ERP adoption in Chinese small enterprise: An exploratory case study. J. Manuf. Technol. Manag. 2011, 22, 489–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hailu, T. The Impact of Information System (IS) on Organziational Performace: With Special Refernce to Ethio-Telecom Southern Region, Hawassa. Eur. J. Bus. Manag. 2014, 6, 331–339. [Google Scholar]
- Chien, S.-W.; Tsaur, S.-M. Investigating the success of ERP systems: Case studies in three Taiwanese high-tech industries. Comput. Ind. 2007, 58, 783–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velcu, O. Exploring the effects of ERP systems on organizational performance. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2007, 107, 1316–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poston, R.; Grabski, S. Financial impacts of enterprise resource planning implementations. Int. J. Account. Inf. Syst. 2001, 2, 271–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, P.R.; Lorsch, J.W. Organization and Environment; Division of Research, Graduate School of Business Administration, Harvard University: Boston, MA, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Tait, P.; Vessey, I. The Effect of User Involvement on System Success: A Contingency Approach. MIS Q. 1988, 12, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ifinedo, P.; Nahar, N. Interactions between contingency, organizational IT factors, and ERP success. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2009, 109, 118–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksoud, A.A.; Dugdale, D.; Luther, R. Non-financial performance measurement in manufacturing companies. Br. Account. Rev. 2005, 37, 261–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otley, D.T. The contingency theory of management accounting: Achievement and prognosis. Account. Organ. Soc. 1980, 5, 413–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ittner, C.D.; Larcker, D.F. Are Nonfinancial Measures Leading Indicators of Financial Performance? An Analysis of Customer Satisfaction. J. Account. Res. 1998, 36, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiedler, F. A Contingency Model of Leadership Effectiveness. Adv. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 1964, 1, 149–190. [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson, L. The Contingency Theory of Organizations; Sage Publications: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.-L.; Chen, C.-T. How consumers become loyal fans on Facebook. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2018, 82, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.-F. Knowledge sharing and firm innovation capability: An empirical study. Int. J. Manpow. 2007, 28, 315–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soh, C.; Kien, S.S.; Tay-Yap, J. Enterprise resource planning: Cultural fits and misfits: Is ERP a universal solution? Commun. ACM 2000, 43, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krumbholz, M.; Maiden, N. The implementation of enterprise resource planning packages in different organisational and national cultures. Inf. Syst. 2001, 26, 185–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.G.; Lee, H.; Lee, J. Applying social exchange theory in IT service relationships: Exploring roles of exchange characteristics in knowledge sharing. Inf. Technol. Manag. 2015, 16, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dell, C.; Grayson, C.J. If Only We Knew What We Know: Identification and Transfer of Internal Best Practices. Calif. Manag. Rev. 1998, 40, 154–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cummings, J.N. Work Groups, Structural Diversity, and Knowledge Sharing in a Global Organization. Manag. Sci. 2004, 50, 352–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, C.J.; Smith, K.G. Knowledge Exchange and Combination: The Role of Human Resource Practices in the Performance of High-Technology Firms. Acad. Manag. J. 2006, 49, 544–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Z.; Lee, J. An ERP implementation case study from a knowledge transfer perspective. J. Inf. Technol. 2000, 15, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Z.; Feng, Y.; Liu, L. The mediating effect of organizational culture and knowledge sharing on transformational leadership and Enterprise Resource Planning systems success: An empirical study in China. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2012, 28, 2400–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-H.; Suh, H.-J.; Yang, H.-D. Perceived absorptive capacity of individual users in performance of Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) usage: The case for Korean firms. Inf. Manag. 2007, 44, 300–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lee, M.K.; Huang, P.; Zhang, L.; Huang, X. A framework of ERP systems implementation success in China: An empirical study. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2005, 98, 56–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.-H.; Lee, P.-L.; Shen, Y.-S.; Lin, H.-L. A comprehensive study of the relationship between enterprise resource planning selection criteria and enterprise resource planning system success. Inf. Manag. 2012, 49, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.-H.; Wang, Y.-M. Measuring ERP success: The key-users’ viewpoint of the ERP to produce a viable IS in the organization. Comput. Hum. Behav. 2007, 23, 1582–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SDezdar, S.; Sulaiman, A. Successful enterprise resource planning implementation: Taxonomy of critical factors. Ind. Manag. Data Syst. 2009, 109, 1037–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thong, J.Y.L.; Yap, C.S.; Raman, K.S. Consultant and vendor for information systems in small business: To combine or to separate? In Proceedings of the Twenty-sixth Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Wailea, HI, USA, 8 January 1993; Volume 4, pp. 509–517. [Google Scholar]
- Collis, J.; Hussey, R. Business Research, a Practional Guide for Undergraduate & Postgraduate Students; Palgrave Macmillan: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Saunders, M.; Lewis, P.; Thornhill, A. Research Methods for Business Students Essex; Pearson Education Limited: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ittner, C.D.; Larcker, D.F. Assessing empirical research in managerial accounting: A value-based management perspective. J. Account. Econ. 2001, 32, 349–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zikmund, W.G. Business Research Methods USA; The Dryden Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Sekaran, U. Research Methods for Business: A Skill-Building Approach, 4th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Shaiti, H.; Abdel-Kader, Y.D.M. Investigating the Relationship between Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) System and Internal Control: Exploratory Study. In Athens: ATINER’S Conference Paper Series, No: BUS2013-0626. 2013, pp. 1–18. Available online: https://www.atiner.gr/papers/BUS2013-0626.pdf (accessed on 14 September 2020).
- Ringle, C.M.; Wende, S.; Will, A. Smartpls, Hamburg, Germany. 2005. Available online: https://www.smartpls.com/smartpls2 (accessed on 14 September 2020).
- Doll, W.J.; Torkzadeh, G. The Measurement of End-User Computing Satisfaction. MIS Q. 1988, 12, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Premkumar, G.; Ramamurthy, K. The Role of Interorganizational and Organizational Factors on the Decision Mode for Adoption of Interorganizational Systems. Decis. Sci. 1995, 26, 303–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, V.; Davis, F.D. A Model of the Antecedents of Perceived Ease of Use: Development and Test. Decis. Sci. 1996, 27, 451–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barki, H.; Hartwick, J. Measuring User Participation, User Involvement, and User Attitude. MIS Q. Manag. Inf. Syst. 1994, 18, 59–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoako-Gyampah, K.; Salam, A.F. An extension of the technology acceptance model in an ERP implementation environment. Inf. Manag. 2004, 41, 731–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, R.L.; Higgins, C.A.; Howell, J.M. Personal Computing: Toward a Conceptual Model of Utilization. MIS Q. Manag. Inf. Syst. 1991, 15, 125–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, S.H.; Gao, S. Attitude towards knowledge sharing behavior. J. Comput. Inf. Syst. 2005, 46, 45–51. [Google Scholar]
- Robert, S.K.; Norton, D.P. The Balanced Scorecard—Measures That Drive. Harvard Bus. Rev. 1992, 70, 71. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, R.S.; Norton, D.P. strategic learning & the balanced scorecard. Strat. Leadersh. 1996, 24, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Chin, W.W. The partial least squares approach to structural equation modeling. In Modern Methods for Business Research; Marcoulides, G.A., Ed.; Lawrence Erlbaum Associatesz: Mahwah, NJ, USA, 1998; pp. 295–336. [Google Scholar]
- Vinzi, V.E.; Chin, W.W.; Henseler, J.; Wang, H. (Eds.) Handbook of Partial Least Squares Concepts, Methods and Application; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Fornell, C.; Larcker, D.F. Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. J. Mark. Res. 1981, 18, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulland, J. Use of Partial Least Squares (Pls) in Strategic Management Research: A Review of Four Recent. Strateg. Manag. J. 1999, 20, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hair, J.F.; Anderson, R.; Black, B.; Babin, B.; CBlack, W. Multivariate Data Analysis; Pearson: London, UK; Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Croteau, A.-M.; Bergeron, F. An information technology trilogy: Business strategy, technological deployment and organizational performance. J. Strat. Inf. Syst. 2001, 10, 77–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiaroni, D.; Chiesa, V.; Frattini, F. The Open Innovation Journey: How firms dynamically implement the emerging innovation management paradigm. Technovation 2011, 31, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chesbrough, H.W. Open Innovation; Harvard Business School Publishing Corp.: Brighton, MA, USA, 2003; pp. 61–63. [Google Scholar]
- Kautz, K.; Bunker, D.; Rab, S.M.; Sinnet, M. Investigating Open Innovation and Interorganizational Networks in the IT Industry: The Case of Standard Software Customization. Integr. Intern. Control Inf. Syst. 2011, 356, 231–246. [Google Scholar]
- Miranda, M.Q.; Farias, J.S.; Schwartz, C.D.A.; De Almeida, J.P.L. Technology Adoption in Diffusion OF innovations perspective: Introduction of an ERP system in a non-profit organization. Rev. Adm. Innov. RAI 2016, 13, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, T.H.; Cantrell, J.G.H.S. Enterprise systems and ongoing process change. Bus. Process Manag. J. 2004, 10, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, R.; Allen, T. Investigating the Not Invented Here (NIH) Syndrome: A Look at the Performance, Tenure Communication Patterns of 50 R&D Project Groups: R&D Management. J. Sci. Policy Res. Manag. 1982, 2, 519–520. [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen, S.; Pedersen, L.J.T. Sustainable Business Model Innovation; Palgrave Macmillan: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
| Company. I | Company. A | Company. S | Company. N | Company. J | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERP Brand | SAP | SAP | Oracle | SAP | SAP |
| Sector | Services | Manufacturing | Manufacturing | Manufacturing | Manufacturing |
| Company Size | Medium | Medium | Small | Medium | Medium |
| Respondent Position | Director of administration &personnel affairs | ERP section Head | IT Manager | Director of Accounting Department | SAP Technical Consultant |
| Impl. period | 5–6 years | 6 months | 2 years | 9 months | 6–9 months |
| Characteristic | N | N% | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Participant Position | General Manager | 15 | 12.5% |
| Accounting manager | 13 | 10.8% | |
| CIO | 7 | 5% | |
| IT manager | 53 | 44% | |
| HR manager | 9 | 7.5% | |
| Financial manager | 10 | 8% | |
| Other | 14 | 11.6% | |
| Size | 6 to 49 | 42 | 35% |
| 50 to 249 | 78 | 65% | |
| More than 250 | 0 | 0.0% | |
| Implementation duration | Less than 1 year | 16 | 13.3% |
| 1–2 years | 52 | 43.3% | |
| 3–4 years | 18 | 15.0% | |
| 5 years and above | 34 | 28.3% | |
| ERP Brand | Oracle | 34 | 28.3% |
| SAP | 26 | 21.7% | |
| Delta | 9 | 7.5% | |
| Microsoft Dynamic AX | 9 | 7.5% | |
| Inbuilt ERP application | 8 | 6.7% | |
| PeopleSoft | 5 | 4.2% | |
| Other ERP brand | 20 | 16% |
| Construct | Number of Measures | Source |
|---|---|---|
| 1.User satisfaction | 4 items | [95] |
| 2. Top Management Support | 4 items | [96] |
| 3. Training | 4 items | [97] |
| 4. Vendor support | 4 items | [17] |
| 5. User involvement | 4 items | [98,99] |
| 6. Complexity | 4 items | [100] |
| 7. Knowledge sharing | 4 items | [101] |
| 8. ERPs usage Success | 6 items | [43] |
| 9.Business Performance | 9 items | [102,103] |
| Constructs | Items | Lading | AVE | CA | CR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Management support | - The top management is highly interested in using ERP | 0.904 | 0.797 | 0.915 | 0.940 |
| - The top management believes the cost of ERP is a long-term investment. | 0.909 | ||||
| - The top management is aware of the benefits ERP for the future success of a firm | 0.888 | ||||
| - The top management has allocated adequate financial and other resources for the development and operation of ERP. | 0.868 | ||||
| Knowledge Sharing | - Our approaches to sharing knowledge are very flexible in time and place | 0.864 | 0.776 | 0.904 | 0.933 |
| - Overall, we can conduct knowledge sharing conveniently | 0.919 | ||||
| - I think that knowledge sharing is beneficial to my study | 0.885 | ||||
| - My feeling toward knowledge sharing is favorable. | 0.856 | ||||
| User Satisfaction | - The ERP system provides the precise information needed for my job | 0.870 | 0.825 | 0.893 | 0.934 |
| - The ERP system provides sufficient information. | 0.958 | ||||
| - The ERP system provides reports that exactly match my needs | 0.894 | ||||
| Complexity | - Working with the ERP system is complicated; it is difficult to understand what is going on. | 0.894 | 0.728 | 0.878 | 0.914 |
| -. It takes too long to learn how to use the ERP system | 0.866 | ||||
| - Using the ERP system involves much time doing mechanical operations (e.g., data input) | 0.757 | ||||
| - In general, the ERP system is very complex to use | 0.889 | ||||
| User Involvement | - I had different responsibilities during different stages of ERP implementation | 0.825 | 0.751 | 0.837 | 0.901 |
| - I was informed of problems occurring during different stages of ERP implementation. | 0.904 | ||||
| - The organization involves employees when it develops or introduces new systems. | 0.870 | ||||
| Vender Support | - Our ERP vendor/consultant has good relationships with my organization | 0.937 | 0.814 | 0.778 | 0.897 |
| - Our ERP vendor/consultant is experienced and provides quality training and support services | 0.870 | ||||
| Training | - My level of understanding was substantially improved after going through the training program | 0.921 | 0.837 | 0.903 | 0.939 |
| - The training gave me confidence in using ERP. | 0.922 | ||||
| - Training programs precede effectively IS usage. | 0.902 | ||||
| ERPs usage | - Our ERP improves individual productivity | 0.821 | 0.673 | 0.838 | 0.892 |
| - Our ERP system is beneficial for me for performing all the tasks assigned to me in a timely fashion | 0.842 | ||||
| - Our ERP reduces organizational costs | 0.762 | ||||
| - Our ERP system improved overall productivity | 0.854 | ||||
| Business Performance | - The reputation of our company in the eyes of the customers has improved | 0.718 | 0.591 | 0.826 | 0.878 |
| - We consider our relations with suppliers to be excellent because we maintain genuine partnerships with them | 0.719 | ||||
| - We retain existing clients and manage to attract new ones. | 0.732 | ||||
| - Quality of our products is well above the industry average | 0.865 | ||||
| - The profitability of the firm increases faster compared to the industry average | 0.800 |
| BP | ERPs Usage | Training | Complex. | KS | MS | User Inv. | User Sati. | VS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BP | 0.769 | ||||||||
| ERPs usage | 0.631 | 0.820 | |||||||
| Training | 0.444 | 0.503 | 0.915 | ||||||
| Complex. | −0.119 | −0.207 | −0.194 | 0.854 | |||||
| KS | 0.586 | 0.418 | 0.493 | −0.166 | 0.881 | ||||
| MS | 0.484 | 0.536 | 0.405 | −0.177 | 0.545 | 0.893 | |||
| User Inv. | 0.276 | 0.372 | 0.339 | −0.006 | 0.496 | 0.415 | 0.867 | ||
| User Sati. | 0.608 | 0.548 | 0.391 | −0.236 | 0.517 | 0.531 | 0.316 | 0.908 | |
| VS | 0.298 | 0.294 | 0.242 | −0.045 | 0.287 | 0.327 | 0.435 | 0.375 | 0.902 |
| BP | ERPs Usage | Training | Complex. | KS | MS | User inv. | User sati. | VS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Complex.1 | −0.153 | −0.173 | −0.162 | 0.894 | −0.12 | −0.119 | −0.02 | −0.15 | −0.03 |
| Complex.2 | −0.073 | −0.184 | −0.090 | 0.866 | −0.07 | −0.138 | 0.05 | −0.18 | −0.00 |
| Complex.3 | 0.006 | −0.097 | −0.148 | 0.757 | −0.16 | −0.138 | −0.02 | −0.15 | −0.03 |
| Complex.4 | −0.137 | −0.218 | −0.246 | 0.889 | −0.20 | −0.201 | −0.02 | −0.28 | −0.07 |
| ERPs usage 1 | 0.718 | 0.426 | 0.295 | −0.062 | 0.46 | 0.367 | 0.23 | 0.42 | 0.26 |
| ERPs usage 2 | 0.719 | 0.408 | 0.372 | −0.084 | 0.47 | 0.328 | 0.21 | 0.50 | 0.21 |
| ERPs usage 3 | 0.504 | 0.821 | 0.382 | −0.191 | 0.37 | 0.360 | 0.37 | 0.42 | 0.17 |
| ERPs usage 4 | 0.440 | 0.842 | 0.411 | −0.148 | 0.31 | 0.482 | 0.34 | 0.47 | 0.28 |
| KS1 | 0.506 | 0.313 | 0.341 | −0.123 | 0.86 | 0.371 | 0.43 | 0.41 | 0.27 |
| KS 2 | 0.563 | 0.425 | 0.496 | −0.213 | 0.91 | 0.469 | 0.45 | 0.52 | 0.27 |
| KS 3 | 0.534 | 0.387 | 0.448 | −0.152 | 0.88 | 0.546 | 0.41 | 0.43 | 0.25 |
| KS 4 | 0.450 | 0.328 | 0.433 | −0.078 | 0.85 | 0.528 | 0.44 | 0.44 | 0.19 |
| BP2 | 0.732 | 0.510 | 0.338 | −0.111 | 0.38 | 0.317 | 0.21 | 0.54 | 0.31 |
| BP 3 | 0.865 | 0.547 | 0.358 | −0.083 | 0.51 | 0.429 | 0.22 | 0.44 | 0.14 |
| BP 4 | 0.800 | 0.513 | 0.349 | −0.114 | 0.43 | 0.413 | 0.18 | 0.42 | 0.22 |
| BP5 | 0.550 | 0.762 | 0.417 | −0.198 | 0.35 | 0.415 | 0.25 | 0.39 | 0.21 |
| BP6 | 0.568 | 0.854 | 0.436 | −0.147 | 0.32 | 0.495 | 0.26 | 0.50 | 0.28 |
| MS1 | 0.481 | 0.516 | 0.414 | −0.194 | 0.50 | 0.904 | 0.43 | 0.51 | 0.29 |
| MS2 | 0.370 | 0.537 | 0.361 | −0.212 | 0.51 | 0.909 | 0.38 | 0.45 | 0.26 |
| MS 3 | 0.441 | 0.443 | 0.279 | −0.055 | 0.41 | 0.888 | 0.33 | 0.41 | 0.26 |
| MS4 | 0.446 | 0.395 | 0.389 | −0.157 | 0.50 | 0.868 | 0.31 | 0.51 | 0.34 |
| Training1 | 0.375 | 0.478 | 0.921 | −0.234 | 0.39 | 0.341 | 0.29 | 0.36 | 0.20 |
| Training2 | 0.410 | 0.433 | 0.922 | −0.201 | 0.51 | 0.439 | 0.32 | 0.37 | 0.23 |
| Training3 | 0.435 | 0.467 | 0.902 | −0.097 | 0.45 | 0.337 | 0.31 | 0.33 | 0.22 |
| UserInv.1 | 0.128 | 0.276 | 0.210 | −0.022 | 0.31 | 0.314 | 0.82 | 0.22 | 0.36 |
| UserInvo.2 | 0.225 | 0.290 | 0.274 | −0.029 | 0.43 | 0.338 | 0.90 | 0.29 | 0.36 |
| UserInvo.4 | 0.331 | 0.381 | 0.369 | 0.025 | 0.51 | 0.409 | 0.87 | 0.29 | 0.40 |
| UserSati.1 | 0.631 | 0.451 | 0.435 | −0.197 | 0.53 | 0.488 | 0.31 | 0.87 | 0.35 |
| UserSati.3 | 0.553 | 0.556 | 0.341 | −0.204 | 0.43 | 0.478 | 0.29 | 0.95 | 0.31 |
| UserSati.4 | 0.481 | 0.480 | 0.299 | −0.243 | 0.45 | 0.487 | 0.25 | 0.89 | 0.36 |
| VS3 | 0.291 | 0.304 | 0.191 | −0.026 | 0.25 | 0.323 | 0.37 | 0.38 | 0.93 |
| VS4 | 0.240 | 0.213 | 0.261 | −0.062 | 0.26 | 0.261 | 0.42 | 0.28 | 0.86 |
| Hypotheses | Beta | T Value | Decision | f Square |
|---|---|---|---|---|
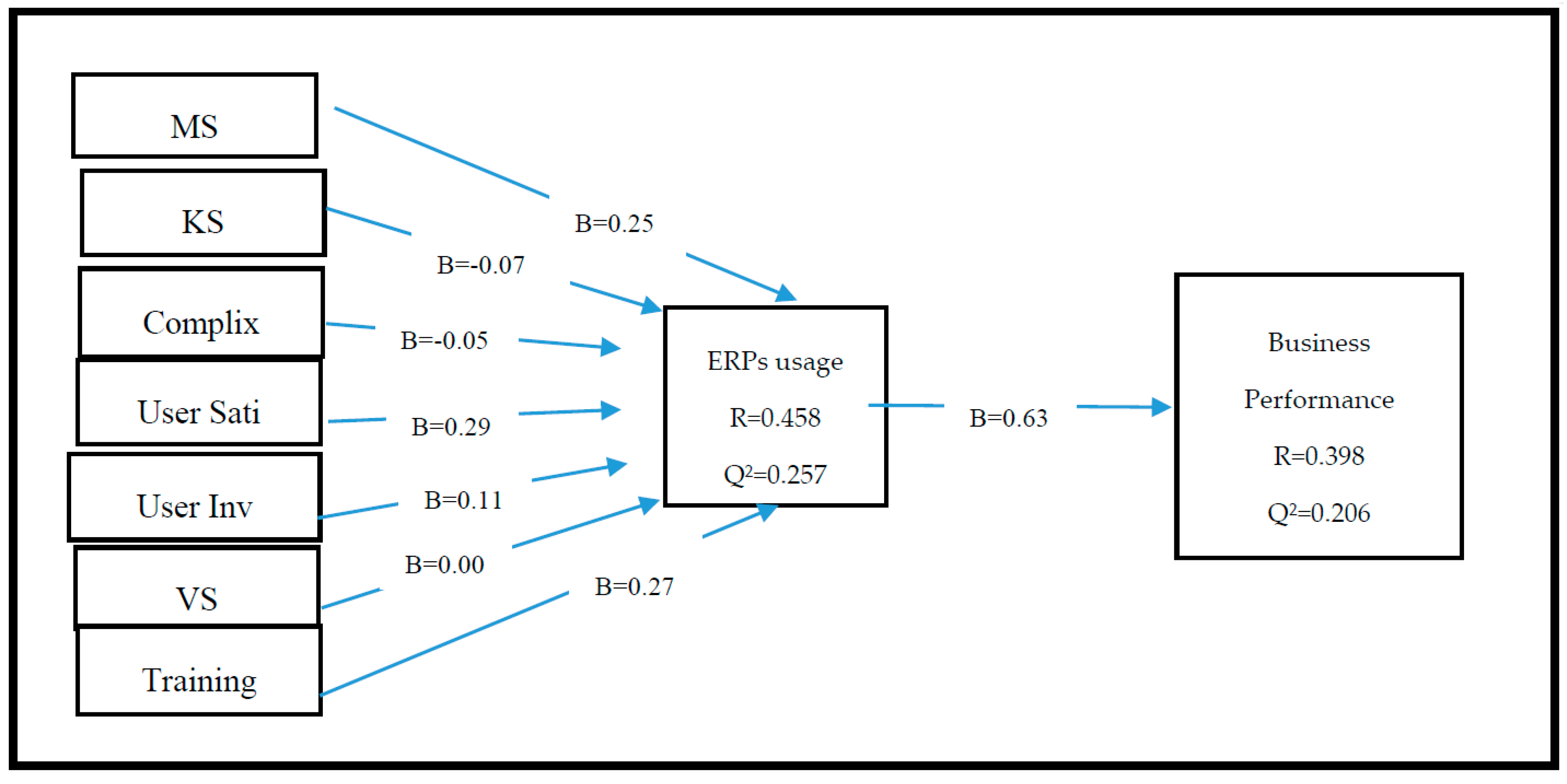
| H1. Management support--→ ERPs usage | 0.25 * | 2.31 | Sig. | 0.067 |
| H2. Knowledge Sharing--→ ERPs usage | −0.07 | 0.726 | Non-Sig. | 0.005 |
| H3. User satisfaction--→ ERPs usage | 0.297 * | 2.43 | Sig | 0.096 |
| H4. User Involvement → ERPs usage | 0.118 | 1.525 | Non-Sig | 0.016 |
| H5 Complexity → ERPs usage | −0.05 | 0.630 | Non-Sig | 0.005 |
| H6. Training → ERPs usage | 0.271 ** | 3.17 | Sig | 0.661 |
| H7. Vender support → ERPs usage | 0.002 | 0.02 | Non-Sig | 0.000 |
| H8. ERPs usage → Business Performance | 0.631 ** | 6.85 | Sig. | 0.661 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
AlMuhayfith, S.; Shaiti, H. The Impact of Enterprise Resource Planning on Business Performance: With the Discussion on Its Relationship with Open Innovation. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2020, 6, 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/joitmc6030087
AlMuhayfith S, Shaiti H. The Impact of Enterprise Resource Planning on Business Performance: With the Discussion on Its Relationship with Open Innovation. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity. 2020; 6(3):87. https://doi.org/10.3390/joitmc6030087
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlMuhayfith, Sara, and Hani Shaiti. 2020. "The Impact of Enterprise Resource Planning on Business Performance: With the Discussion on Its Relationship with Open Innovation" Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity 6, no. 3: 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/joitmc6030087
APA StyleAlMuhayfith, S., & Shaiti, H. (2020). The Impact of Enterprise Resource Planning on Business Performance: With the Discussion on Its Relationship with Open Innovation. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 6(3), 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/joitmc6030087






