PDMS Micropatterns Coated with PDA and RGD Induce a Regulatory Macrophage-like Phenotype
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
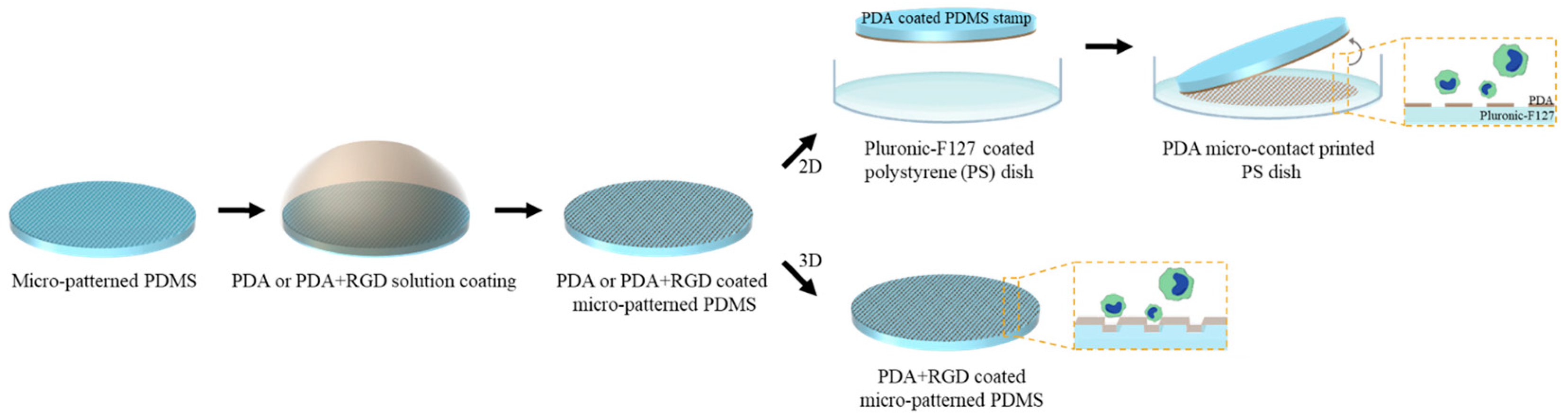
2.2. Fabrication of 2D Micropattern
2.3. Fabrication of 3D Micropattern
2.4. X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)
2.5. Cell Culture and Treatment
2.6. Flow Cytometry
2.7. Immunofluorescence
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. XPS Analysis
3.2. PDA-Microcontact Printed Micropatterns Induce Cell Elongation
3.3. PDA+RGD-20/20 3D Micropatterns Strongly Enhance Expression of Mreg Markers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lavin, Y.; Winter, D.; Blecher-Gonen, R.; David, E.; Keren-Shaul, H.; Merad, M.; Jung, S.; Amit, I. Tissue-Resident Macrophage Enhancer Landscapes Are Shaped by the Local Microenvironment. Cell 2014, 159, 1312–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gosselin, D.; Link, V.M.; Romanoski, C.E.; Fonseca, G.J.; Eichenfield, D.Z.; Spann, N.J.; Stender, J.D.; Chun, H.B.; Garner, H.; Geissmann, F.; et al. Environment Drives Selection and Function of Enhancers Controlling Tissue-Specific Macrophage Identities. Cell 2014, 159, 1327–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mass, E.; Ballesteros, I.; Farlik, M.; Halbritter, F.; Günther, P.; Crozet, L.; Jacome-Galarza, C.E.; Händler, K.; Klughammer, J.; Kobayashi, Y.; et al. Specification of Tissue-Resident Macrophages during Organogenesis. Science 2016, 353, aaf4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mosser, D.M. The Many Faces of Macrophage Activation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2003, 73, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mosser, D.M.; Edwards, J.P. Exploring the Full Spectrum of Macrophage Activation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 958–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, J.P.; Zhang, X.; Frauwirth, K.A.; Mosser, D.M. Biochemical and Functional Characterization of Three Activated Macrophage Populations. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2006, 80, 1298–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chandrasekaran, P.; Izadjoo, S.; Stimely, J.; Palaniyandi, S.; Zhu, X.; Tafuri, W.; Mosser, D.M. Regulatory Macrophages Inhibit Alternative Macrophage Activation and Attenuate Pathology Associated with Fibrosis. The J. Immunol. 2019, 203, 2130–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Zhang, J.; Cao, P.; Sun, Z.; Wang, W. The Characteristics of Regulatory Macrophages and Their Roles in Transplantation. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 91, 107322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Goethem, E.; Poincloux, R.; Gauffre, F.; Maridonneau-Parini, I.; le Cabec, V. Matrix Architecture Dictates Three-Dimensional Migration Modes of Human Macrophages: Differential Involvement of Proteases and Podosome-Like Structures. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 1049–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jacob, S.S.; Sudhakaran, P.R. Molecular Mechanism Involved in Matrix Dependent Upregulation of Matrix Metalloproteinases in Monocyte/Macrophage. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Biophys. 2002, 6, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McWhorter, F.Y.; Wang, T.; Nguyen, P.; Chung, T.; Liu, W.F. Modulation of Macrophage Phenotype by Cell Shape. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 17253–17258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.; Jones, J.A.; Xu, Y.; Low, H.Y.; Anderson, J.M.; Leong, K.W. Characterization of Topographical Effects on Macrophage Behavior in a Foreign Body Response Model. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 3479–3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barth, K.A.; Waterfield, J.D.; Brunette, D.M. The Effect of Surface Roughness on RAW 264.7 Macrophage Phenotype. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2013, 101, 2679–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luu, T.U.; Gott, S.C.; Woo, B.W.K.; Rao, M.P.; Liu, W.F. Micro- and Nanopatterned Topographical Cues for Regulating Macrophage Cell Shape and Phenotype. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 28665–28672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adlerz, K.M.; Aranda-Espinoza, H.; Hayenga, H.N. Substrate Elasticity Regulates the Behavior of Human Monocyte-Derived Macrophages. Eur. Biophys. J. 2016, 45, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, N.; Vogel, V. Spatial Confinement Downsizes the Inflammatory Response of Macrophages. Nat. Mater. 2018, 17, 1134–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mata, A.; Fleischman, A.J.; Roy, S. Characterization of Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) Properties for Biomedical Micro/Nanosystems. Biomed. Microdevices 2005, 7, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halldorsson, S.; Lucumi, E.; Gómez-Sjöberg, R.; Fleming, R.M.T. Advantages and Challenges of Microfluidic Cell Culture in Polydimethylsiloxane Devices. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 63, 218–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perikamana, S.K.M.; Shin, Y.M.; Lee, J.K.; Lee, Y.B.; Heo, Y.; Ahmad, T.; Park, S.Y.; Shin, J.; Park, K.M.; Jung, H.S.; et al. Graded Functionalization of Biomaterial Surfaces Using Mussel-Inspired Adhesive Coating of Polydopamine. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 159, 546–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.H.; Jung, S.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, N.Y. Fabrication of a Cell-Friendly Poly(Dimethylsiloxane) Culture Surface via Polydopamine Coating. Micromachines 2022, 13, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabaghi, M.; Shahriari, S.; Saraei, N.; Da, K.; Chandiramohan, A.; Selvaganapathy, P.R.; Hirota, J.A. Article Surface Modification of Pdms-Based Microfluidic Devices with Collagen Using Polydopamine as a Spacer to Enhance Primary Human Bronchial Epithelial Cell Adhesion. Micromachines 2021, 12, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sainio, A.; Järveläinen, H. Extracellular Matrix-Cell Interactions: Focus on Therapeutic Applications. Cell Signal. 2020, 66, 109487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tjong, W.Y.; Lin, H.H. The RGD Motif Is Involved in CD97/ADGRE5-Promoted Cell Adhesion and Viability of HT1080 Cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clark, A.Y.; Martin, K.E.; García, J.R.; Johnson, C.T.; Theriault, H.S.; Han, W.M.; Zhou, D.W.; Botchwey, E.A.; García, A.J. Integrin-Specific Hydrogels Modulate Transplanted Human Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Survival, Engraftment, and Reparative Activities. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zaveri, T.D.; Lewis, J.S.; Dolgova, N.V.; Clare-Salzler, M.J.; Keselowsky, B.G. Integrin-Directed Modulation of Macrophage Responses to Biomaterials. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 3504–3515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, Z.; Wang, W.; Xu, X.; Nie, Y.; Liu, Y.; Gould, O.E.C.; Ma, N.; Lendlein, A. Biofunction of Polydopamine Coating in Stem Cell Culture. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 10748–10759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, A.J. Get a Grip: Integrins in Cell-Biomaterial Interactions. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 7525–7529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; So, E.C.; Strome, S.E.; Zhang, X. Impact of Detachment Methods on M2 Macrophage Phenotype and Function. J. Immunol. Methods 2015, 426, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Min, J.; Lee, E.C.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, N.Y. Targeted Cell Adhesion on Selectively Micropatterned Polymer Arrays on a Poly(Dimethylsiloxane) Surface. Biomed. Microdevices 2010, 12, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerasubramanian, P.K.; Joe, V.C.; Liu, W.F.; Downing, T.L. Characterization of Macrophage and Cytokine Interactions with Biomaterials Used in Negative-Pressure Wound Therapy. Bioengineering 2022, 9, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riquelme, P.; Haarer, J.; Kammler, A.; Walter, L.; Tomiuk, S.; Ahrens, N.; Wege, A.K.; Goecze, I.; Zecher, D.; Banas, B.; et al. TIGIT+ ITregs Elicited by Human Regulatory Macrophages Control T Cell Immunity. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakamura, K.; Smyth, M.J. TREM2 Marks Tumor-Associated Macrophages. Signal. Transduct. Target. Ther 2020, 5, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riquelme, P.; Amodio, G.; Macedo, C.; Moreau, A.; Obermajer, N.; Brochhausen, C.; Ahrens, N.; Kekarainen, T.; Fändrich, F.; Cuturi, C.; et al. DHRS9 Is a Stable Marker of Human Regulatory Macrophages. Transplantation 2017, 101, 2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoang, T.X.; Kim, J.Y.; Pham, H.L.; Nguyen, N.L.; Jeong, J.; Kim, Y.J.; Tran, T.M.; Kim, M.H.; Lee, M.K. Generation and Characterization of Regulatory Macrophages for Xenotransplantation. Korean J. Transplant. 2022, 36, S334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, C.T.; Cheng, H.W.; Huang, C.M.; Li, H.R.; Ou, M.H.; Huang, J.R.; Khoo, K.H.; Yu, H.W.; Chen, Y.Q.; Wang, Y.K.; et al. Fibronectin in Cell Adhesion and Migration via N-Glycosylation. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 70653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mosesson, M.W. The Role of Fibronectin in Monocyte/Macrophage Function. Prog. Clin. Biol. Res. 1984, 154, 155–175. [Google Scholar]
- Sikkema, A.H.; Stoffels, J.M.J.; Wang, P.; Basedow, F.J.; Bulsink, R.; Bajramovic, J.J.; Baron, W. Fibronectin Aggregates Promote Features of a Classically and Alternatively Activated Phenotype in Macrophages. J. Neuroinflammation 2018, 15, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plow, E.F.; Haas, T.A.; Zhang, L.; Loftus, J.; Smith, J.W. Ligand Binding to Integrins. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 21785–21788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Yan, C.; Ye, K.; He, Y.; Li, Z.; Ding, J. Effect of RGD Nanospacing on Differentiation of Stem Cells. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 2865–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batalov, I.; Stevens, K.R.; DeForest, C.A. Photopatterned Biomolecule Immobilization to Guide Three-Dimensional Cell Fate in Natural Protein-Based Hydrogels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2014194118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilian, K.A.; Bugarija, B.; Lahn, B.T.; Mrksich, M. Geometric Cues for Directing the Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 4872–4877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, L.; McBeath, R.; Chen, C.S. Stem Cell Shape Regulates a Chondrogenic versus Myogenic Fate through Rac1 and N-Cadherin. Stem Cells 2010, 28, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kshitiz; Park, J.; Kim, P.; Helen, W.; Engler, A.J.; Levchenko, A.; Kim, D.H. Control of Stem Cell Fate and Function by Engineering Physical Microenvironments. Integr. Biol. 2012, 4, 1008–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.S.; Alonso, J.L.; Ostuni, E.; Whitesides, G.M.; Ingber, D.E. Cell Shape Provides Global Control of Focal Adhesion Assembly. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 307, 2262–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBeath, R.; Pirone, D.M.; Nelson, C.M.; Bhadriraju, K.; Chen, C.S. Cell Shape, Cytoskeletal Tension, and RhoA Regulate Stem Cell Lineage Commitment. Dev. Cell 2004, 6, 483–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, G.; Tison, C.K.; Chatterjee, K.; Pine, P.S.; McDaniel, J.H.; Salit, M.L.; Young, M.F.; Simon, C.G. The Determination of Stem Cell Fate by 3D Scaffold Structures through the Control of Cell Shape. Biomaterials 2011, 32, R713–R715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Isali, I.; McClellan, P.; Shankar, E.; Gupta, S.; Jain, M.; Anderson, J.M.; Hijaz, A.; Akkus, O. Genipin Guides and Sustains the Polarization of Macrophages to the Pro-Regenerative M2 Subtype via Activation of the PSTAT6-PPAR-Gamma Pathway. Acta Biomater. 2021, 131, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lendeckel, U.; Venz, S.; Wolke, C. Macrophages: Shapes and Functions. ChemTexts 2022, 8, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, J.A.; Riquelme, P.; Sawitzki, B.; Tomiuk, S.; Miqueu, P.; Zuhayra, M.; Oberg, H.H.; Pascher, A.; Lützen, U.; Janßen, U.; et al. Cutting Edge: Immunological Consequences and Trafficking of Human Regulatory Macrophages Administered to Renal Transplant Recipients. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 2072–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Conde, P.; Rodriguez, M.; van der Touw, W.; Jimenez, A.; Burns, M.; Miller, J.; Brahmachary, M.; Chen, H.-M.; Boros, P.; Rausell-Palamos, F.; et al. DC-SIGN+ Macrophages Control the Induction of Transplantation Tolerance. Immunity 2015, 42, 1143–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sawitzki, B.; Harden, P.N.; Reinke, P.; Moreau, A.; Hutchinson, J.A.; Game, D.S.; Tang, Q.; Guinan, E.C.; Battaglia, M.; Burlingham, W.J.; et al. Regulatory Cell Therapy in Kidney Transplantation (The One Study): A Harmonised Design and Analysis of Seven Non-Randomised, Single-Arm, Phase 1/2A Trials. Lancet 2020, 395, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pham, H.L.; Yang, D.H.; Chae, W.R.; Jung, J.H.; Hoang, T.X.; Lee, N.Y.; Kim, J.Y. PDMS Micropatterns Coated with PDA and RGD Induce a Regulatory Macrophage-like Phenotype. Micromachines 2023, 14, 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14030673
Pham HL, Yang DH, Chae WR, Jung JH, Hoang TX, Lee NY, Kim JY. PDMS Micropatterns Coated with PDA and RGD Induce a Regulatory Macrophage-like Phenotype. Micromachines. 2023; 14(3):673. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14030673
Chicago/Turabian StylePham, Hoang Lan, Da Hyun Yang, Woo Ri Chae, Jong Hyeok Jung, Thi Xoan Hoang, Nae Yoon Lee, and Jae Young Kim. 2023. "PDMS Micropatterns Coated with PDA and RGD Induce a Regulatory Macrophage-like Phenotype" Micromachines 14, no. 3: 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14030673
APA StylePham, H. L., Yang, D. H., Chae, W. R., Jung, J. H., Hoang, T. X., Lee, N. Y., & Kim, J. Y. (2023). PDMS Micropatterns Coated with PDA and RGD Induce a Regulatory Macrophage-like Phenotype. Micromachines, 14(3), 673. https://doi.org/10.3390/mi14030673






