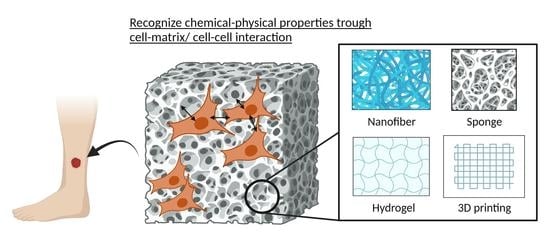
Recent Tissue Engineering Approaches to Mimicking the Extracellular Matrix Structure for Skin Regeneration
Abstract
Share and Cite
Hama, R.; Reinhardt, J.W.; Ulziibayar, A.; Watanabe, T.; Kelly, J.; Shinoka, T. Recent Tissue Engineering Approaches to Mimicking the Extracellular Matrix Structure for Skin Regeneration. Biomimetics 2023, 8, 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8010130
Hama R, Reinhardt JW, Ulziibayar A, Watanabe T, Kelly J, Shinoka T. Recent Tissue Engineering Approaches to Mimicking the Extracellular Matrix Structure for Skin Regeneration. Biomimetics. 2023; 8(1):130. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8010130
Chicago/Turabian StyleHama, Rikako, James W. Reinhardt, Anudari Ulziibayar, Tatsuya Watanabe, John Kelly, and Toshiharu Shinoka. 2023. "Recent Tissue Engineering Approaches to Mimicking the Extracellular Matrix Structure for Skin Regeneration" Biomimetics 8, no. 1: 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8010130
APA StyleHama, R., Reinhardt, J. W., Ulziibayar, A., Watanabe, T., Kelly, J., & Shinoka, T. (2023). Recent Tissue Engineering Approaches to Mimicking the Extracellular Matrix Structure for Skin Regeneration. Biomimetics, 8(1), 130. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomimetics8010130