Purification of Andrographolide Methanolic Extract Using Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Prepared by Precipitation Polymerization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.1.1. Synthesis of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer (MIP)
2.1.2. Surface Morphology Characterization with Scanning Electron Microscopes (SEM)
2.1.3. Determination of Particle Size and Polydispersity Index (PI)
2.1.4. Characterization of MIP and NIP by Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR)
2.1.5. Isotherm Adsorption Evaluation
2.1.6. MIP and NIP Performance Evaluation
2.1.7. Reuse Ability Test
2.1.8. Purification of Andrographolide Methanolic Extract
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis of MIP and NIP
3.2. Characterization of MIP and NIP by SEM
3.3. Determination of Particle Size and Polydispersity Index
3.4. Characterization MIP and NIP by FTIR
3.5. Isotherm Adsorption Evaluation
3.6. Imprinting Factor (IF) and Selectivity Factor (α) Determination
3.7. Reuse Ability Test
3.8. Application of MIP for Andrographolide Purification
3.9. Characterization of Andrographolide Isolate
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benoy, G.K.; Animesh, D.K.; Aninda, M.; Priyanka, D.K.; Sandip, H. An overview on andrographis paniculata (burm. F.) Nees. Int. J. Ayurveda Res. 2012, 3, 752–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wencheng, Z.; Haitao, Z.; Ruixia, W.; Renjuan, Z. Method for Separating and Purifying Deoxyandrographolide. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/CN101671320B/en?oq=CN101671320B (accessed on 14 September 2019).
- Zhaokai, L.; Dongyang, X.; Depin, Z.; Huaxiang, L.; Shi, Y. Method for Extracting Andrographolidume from Andrographis Paniculata (Burm. F.) Nees. Available online: https://patents.google.com/patent/CN105294618A/en?oq=CN105294618A (accessed on 10 January 2020).
- Pundarikakshudu, K. A Simple and Facile Method for the Isolation of Andrographolide from Andrographis Paniculata Nees. Am. J. PharmTech Res. 2016, 6, 266–275. [Google Scholar]
- Turiel, E.; Esteban, A.M. Molecularly imprinted polymers. In Solid-Phase Extraction; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 215–233. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L.J.; Qu, J.R.; Miao, S.S.; Geng, H.R.; Yang, H. Development of a molecularly imprinted polymer for prometryne clean-up in the environment. J. Sep. Sci. 2013, 36, 3911–3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karnka, R.; Chaiyasat, P.; Chaiyasat, A. Synthesis of Uniform and Stable Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Particles by Precipitation Polymerization. Orient. J. Chem. 2017, 33, 2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.Y.; Cao, X.J. Preparation of molecularly imprinted polymers for artemisinin based on the surfaces of silica gel. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 53, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Deng, Q.; Tao, D.; Yang, K.; Zhang, L.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, Y. Preparation of protein imprinted materials by hierarchical imprinting techniques and application in selective depletion of albumin from human serum. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Li, L.; Zuo, P.; Zhao, F.; Liu, M.; Ye, B.C.; Li, Y. Pneumocandin B 0 -imprinted polymer using surface-imprinting technique for efficient purification of crude product. Anal. Sci. 2016, 32, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bakhtiar, S.; Bhawani, S.A.; Shafqat, S.R. Synthesis and characterization of molecular imprinting polymer for the removal of 2-phenylphenol from spiked blood serum and river water. Chem. Biol. Technol. Agric. 2019, 6, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joke Chow, A.L.; Bhawani, S.A. Synthesis and characterization of molecular imprinting polymer microspheres of cinnamic acid: Extraction of cinnamic acid from spiked blood plasma. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2016, 2016, 2418915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauziah, S.; Gafur, A.M.M.; Soekamto, N.H.; Taba, P.; Sapar, A. Synthesis and characterization of molecularly imprinted polymers of di-(2-Ethylhexyl) phthalate using the precipitation polymerization method. Egypt. J. Chem. 2021, 64, 2385–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasapollo, G.; Sole, R.; Del Mergola, L.; Lazzoi, M.R.; Scardino, A.; Scorrano, S.; Mele, G. Molecularly imprinted polymers: Present and future prospective. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 5908–5945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Lu, W.; Wu, X.; Li, J. Molecular imprinting: Perspectives and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 2137–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belbruno, J.J. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 94–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güney, O.; Serin, E. Stimuli-responsive molecularly imprinted hybrid polymer gel as a potential system for controlled release. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2016, 133, 42913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lulinski, P. Molecularly imprinted polymers as the future drug delivery devices. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2013, 70, 601–609. [Google Scholar]
- Luliński, P. Molecularly imprinted polymers based drug delivery devices: A way to application in modern pharmacotherapy. A review. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 76, 1344–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suksuwan, A.; Lomlim, L.; Rungrotmongkol, T.; Nakpheng, T.; Dickert, F.L.; Suedee, R. The composite nanomaterials containing (R)-thalidomide-molecularly imprinted polymers as a recognition system for enantioselective-controlled release and targeted drug delivery. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anene, A.; Hosni, K.; Chevalier, Y.; Kalfat, R.; Hbaieb, S. Molecularly imprinted polymer for extraction of patulin in apple juice samples. Food Control 2016, 70, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anirudhan, T.S.; Christa, J.; Deepa, J.R. Extraction of melamine from milk using a magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer. Food Chem. 2017, 227, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Qin, C.; Li, D.; Hou, Y.; Li, S.; Sun, J. Molecularly imprinted polymer for specific extraction of hypericin from Hypericum perforatum L. herbal extract. J. Pharm. Biomed. 2014, 98, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, Z.K.; Sardari, S. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer (MIP) Applications in Natural Product Studies Based on Medicinal Plant and Secondary Metabolite Analysis. Iran. Biomed. J. 2021, 25, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Row, K.H. Molecularly Imprinted Solid-Phase Extractionof Caffeine from Green Tea. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2006, 12, 494–499. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Lin, H.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, X.; Han, J.; She, Y.; Rabah, T. Preparation and characterization of dummy molecularly imprinted polymers for separation and determination of farrerol from Rhododendron aganniphum using HPLC. Green Chem. Lett. Rev. 2018, 11, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theodoridis, G.; Lasáková, M.; Škeříková, V.; Tegou, A.; Giantsiou, N.; Jandera, P. Molecular imprinting of natural flavonoid antioxidants: Application in solid-phase extraction for the sample pretreatment of natural products prior to HPLC analysis. J. Sep. Sci. 2006, 29, 2310–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, H.; Islam, A.K.M.S.; Hamzah, Z.; Nadaraja, P.; Ahmad, M.N. A Novel Molecular Imprint Polymer Synthesis for Solid Phase Extraction of Andrographolide. Indones. J. Chem. 2019, 19, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Qi, Y.; Sun, Z.; Gong, B. Preparation of thiamphenicol magnetic surface molecularly imprinted polymers for its selective recognition of thiamphenicol in milk samples. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2018, 41, 868–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.X.; Gan, Q.; Feng, C.G. An Ion-imprinted Silica Gel Polymer Prepared by Surface Imprinting Technique Combined with Aqueous Solution Polymerization for Selective Adsorption of Ni(II) from Aqueous Solution. Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 2018, 36, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Guo, J.; Liu, Y. Silica-based surface molecular imprinting for recognition and separation of lysozymes. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 8584–8591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slomkowski, S.; Alemán, J.V.; Gilbert, R.G.; Hess, M.; Horie, K.; Jones, R.G.; Kubisa, P.; Meisel, I.; Mormann, W.; Penczek, S. Terminology of polymers and polymerization processes in dispersed systems (IUPAC Recommendations 2011). Pure Appl. Chem. 2011, 83, 2229–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamayo, F.G.; Casillas, J.L.; Martin-Esteban, A. Evaluation of new selective molecularly imprinted polymers prepared by precipitation polymerisation for the extraction of phenylurea herbicides. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1069, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roland, R.M.; Bhawani, S.A. Synthesis and Characterization of Molecular Imprinting Polymer Microspheres of Piperine: Extraction of Piperine from Spiked Urine. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2016, 2016, 5671507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasanah, A.N.; Dwi Utari, T.N.; Pratiwi, R. Synthesis of Atenolol-Imprinted Polymers with Methyl Methacrylate as Functional Monomer in Propanol Using Bulk and Precipitation Polymerization Method. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2019, 2019, 9853620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimatsu, K.; Reimhult, K.; Krozer, A.; Mosbach, K.; Sode, K.; Ye, L. Uniform molecularly imprinted microspheres and nanoparticles prepared by precipitation polymerization: The control of particle size suitable for different analytical applications. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2007, 584, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orowitz, T.E.; Ana Sombo, P.P.; Rahayu, D.; Hasanah, A.N. Microsphere polymers in molecular imprinting: Current and future perspectives. Molecules 2020, 25, 3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhi, K.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Yasin, A. Influence of size and shape of silica supports on the sol–gel surface molecularly imprinted polymers for selective adsorption of gossypol. Materials 2018, 11, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Edet, U.A.; Ifelebuegu, A.O. Kinetics, isotherms, and thermodynamic modeling of the adsorption of phosphates from model wastewater using recycled brick waste. Processes 2020, 8, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boroumand Jazi, M.; Arshadi, M.; Amiri, M.J.; Gil, A. Kinetic and thermodynamic investigations of Pb(II) and Cd(II) adsorption on nanoscale organo-functionalized SiO2Al2O3. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 422, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Purohit, A.K.; Chinthakindi, S.; Goud, R.D.; Tak, V.; Pardasani, D.; Shrivastava, A.R.; Dubey, D.K. Analysis of chemical warfare agents in organic liquid samples with magnetic dispersive solid phase extraction and gas chromatography mass spectrometry for verification of the chemical weapons convention. J. Chromatogr. A 2016, 1448, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indrati, O.; Martien, R.; Rohman, A.; Nugroho, A.K. Employment of ATR-FTIR and HPLC-UV method for detection and quantification of andrographolide. Int. J. Appl. Pharm. 2018, 10, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




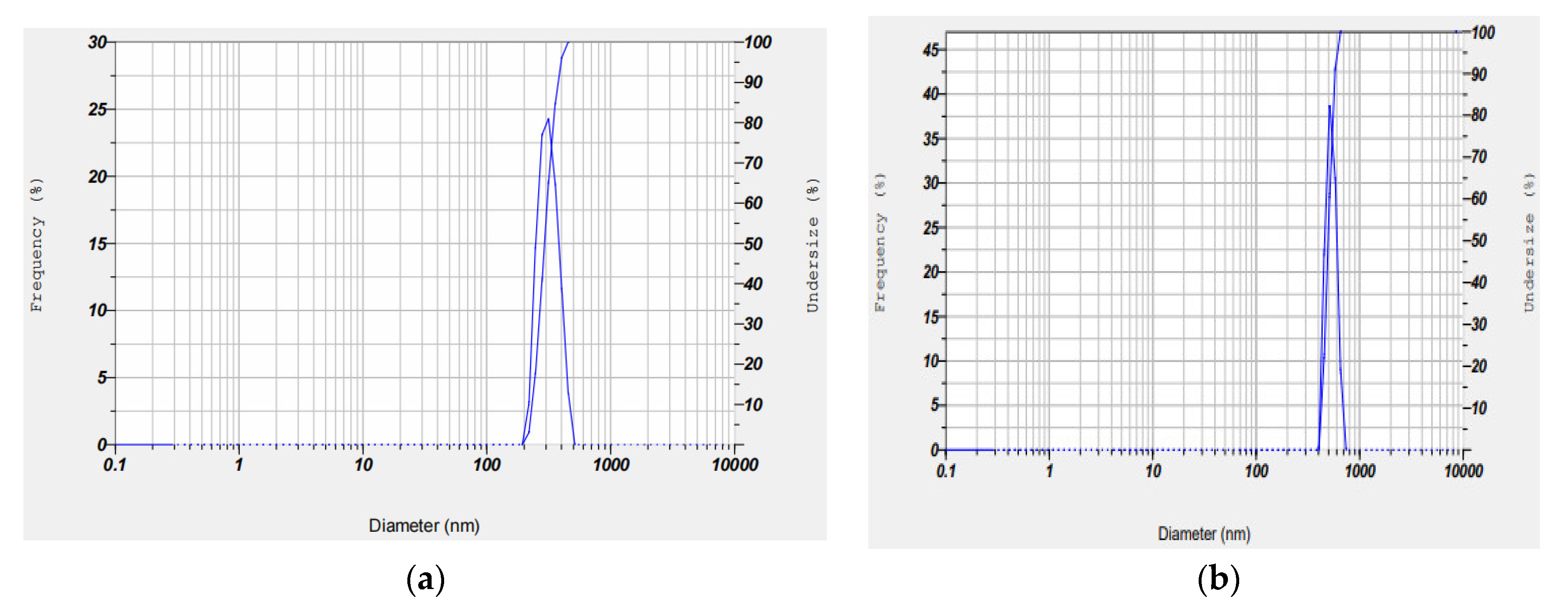

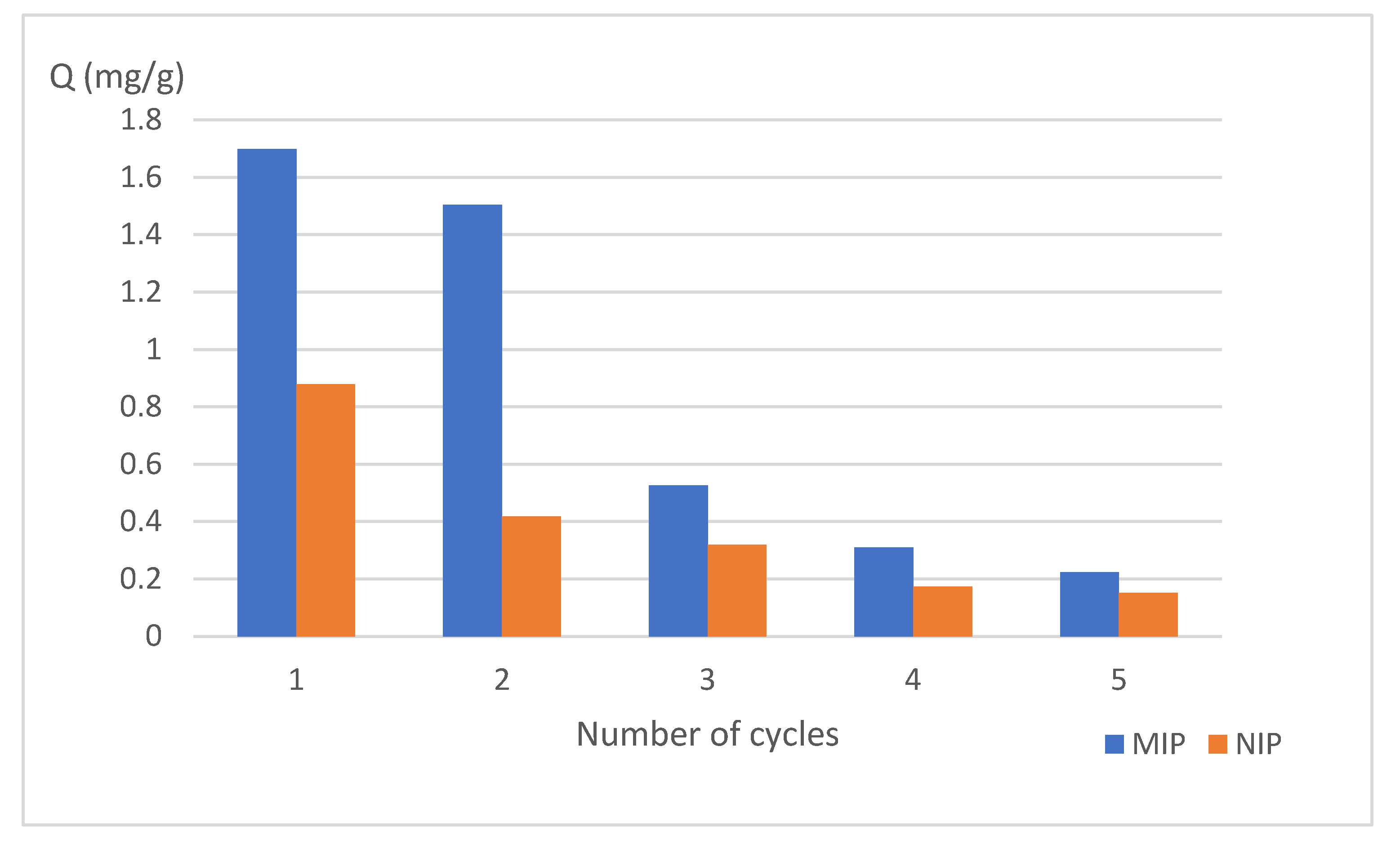





| Sample | Particle Size (nm) | Polydispersity Index |
|---|---|---|
| MIP | 295.5 | 0.064 |
| NIP | 450.4 | 0.222 |
| Isotherm Adsorption Model | Parameters | Polymer | |
|---|---|---|---|
| MIP | NIP | ||
| Langmuir | Qm (mg/g) | 1.2486 | 0.1681 |
| KL (L/mg) | 4.1462 | 8.4509 | |
| RL | 0.8599 | 0.7534 | |
| R2 | 0.9939 | 0.9929 | |
| Freundlich | Kf (mg/g) | 1.6982 | 0.8784 |
| 1/n | 0.5843 | 0.8235 | |
| n | 1.7114 | 1.2143 | |
| R2 | 0.9981 | 0.9902 | |
| Temkin | Aϒ (L/mg) | 0.623 | 0.2027 |
| b | 2.2188 | 0.3376 | |
| B (J/mol) | 3.747 | 5.149 | |
| R2 | 0.9766 | 0.9382 | |
| Henry | KHE | 0.3678 | 0.4922 |
| R2 | 0.9929 | 0.9912 | |
| Polymer | KDandro | KDquer | IFandro | IFquer | α |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIP | 0.659 | 0.0102 | 1.148 | 0.0928 | 12.37 |
| NIP | 0.574 | 0.1094 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Winingsih, W.; Ibrahim, S.; Damayanti, S. Purification of Andrographolide Methanolic Extract Using Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Prepared by Precipitation Polymerization. Sci. Pharm. 2022, 90, 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm90020027
Winingsih W, Ibrahim S, Damayanti S. Purification of Andrographolide Methanolic Extract Using Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Prepared by Precipitation Polymerization. Scientia Pharmaceutica. 2022; 90(2):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm90020027
Chicago/Turabian StyleWiningsih, Wiwin, Slamet Ibrahim, and Sophi Damayanti. 2022. "Purification of Andrographolide Methanolic Extract Using Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Prepared by Precipitation Polymerization" Scientia Pharmaceutica 90, no. 2: 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm90020027
APA StyleWiningsih, W., Ibrahim, S., & Damayanti, S. (2022). Purification of Andrographolide Methanolic Extract Using Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Prepared by Precipitation Polymerization. Scientia Pharmaceutica, 90(2), 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/scipharm90020027






