Abstract
We report triple differential cross-sections (TDCSs) for the electron impact single ionization of tungsten atoms for the ionization taking place from the outer sub shells of tungsten atoms, viz. W (6s), W (5d), W (5p) and W (4f). The study of the electron-induced processes such as ionization, excitation, autoionization from tungsten and its charged states is strongly required to diagnose and model the fusion plasma in magnetic devices such as Tokamaks. Particularly, the cross-section data are important to understand the electron spectroscopy involved in the fusion plasma. In the present study, we report TDCS results for the ionization of W atoms at 200, 500 and 1000 eV projectile energy at different values of scattered electron angles. It was observed that the trends of TDCSs for W (5d) are significantly different from the trends of TDCSs for W (6s), W (5p) and W (4f). It was further observed that the TDCS for W atoms has sensitive dependence on value of momentum transfer and projectile energy.
1. Introduction
The study of the charged particle impact ionization of atomic, ionic and molecular targets has been of importance for a long time, having several potential applications, a few of which are semiconductor physics, the diagnostics and modeling of fusion plasmas, physics and chemistry of atmosphere, effect of ionizing radiation on biological tissues, etc. In the pioneering work, Ehrhardt et al. [1] obtained triple differential cross-sections (TDCS) by studying the electron impact collision process through the coincidence technique. The TDCS obtained by this kind of study provides complete information about the collision dynamics involved. Following this, significant progress has been made in the study of the electron impact single ionization of various atomic, ionic and molecular targets and reasonable agreement has been obtained between the experimental and theoretical results [2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13]. As already mentioned, the electron-induced ionization of atomic as well as ionic targets is of prime importance for the diagnostics and modeling of fusion plasma. In particular, the electron-induced ionization of tungsten atoms (W) and its charged states are of recent interest as tungsten has very good refractory properties which makes it a good candidate to be used inside the fusion devices such as ITER (international thermonuclear experimental reactor), DEMO (Demonstration power plant), JET (Joint European Torus) and ASDEX Upgrade (axially symmetric divertor experiment) [14,15,16]. W is proposed to be used as plasma facing tungsten-coated divertors and the material of the wall due to its low rate of sputtering and good resistivity to chemical erosion. As tungsten is released by sputtering from walls and plasma-facing divertors, a lot of spectroscopy is involved [17]. Knowledge of atomic processes such as electron impact excitation and ionization and electron ion recombination is essential to understand the possible impact of tungsten on fusion plasma in the form of an impurity [18,19] and the cross-section data of these processes are required for modeling and diagnostics of the plasma.
To date, it has not been possible to perform measurements on tungsten atoms, so the theoretical efforts to study the electron-induced processes on W atoms are of vital importance and various theoretical approaches have a crucial role in providing information required for plasma modeling. At the same time, it is worth mentioning that the theoretical treatment is complex and challenging for the electron- and photon-induced processes on high Z atoms such as W due to many electron effects in such targets [19], and there exist certain phenomena in these high Z systems, which are very different from lighter targets. Few attempts have been made to study electron impact total ionization cross-sections for the direct ionization of tungsten atoms and its various charged states (W ions). A semi-relativistic distorted wave approach has been used to calculate direct ionization cross-sections of the outer sub-shells of W atoms [20]; however, Deutsch Märk (DM) formalism has been used by Deutsch and coworkers for obtaining ionization cross-sections of tungsten atoms [21]. In further efforts, binary encounter Bethe (BEB) and plane wave Born (PWB) approaches have been used to obtain ionization cross-section of W atoms [22]. Electron impact ionization cross-sections of W were calculated using a Coulomb Born approach [23] and semi-empirical complex scattering potential [24].
Recently, electron-induced cross-sections of tungsten atoms have been reported for ionization [25] and ionization as well as excitation [26]. Very recently, electron-induced direct ionization cross-sections have been calculated for W atoms in variants of distorted wave [27,28] and modified BEB approaches [28] and differential cross-sections have been reported for the electron impact ionization of W atoms at 100 eV projectile energy [29]. The differential cross-section obtained for the energy and angle resolved conditions may be of further importance to understand the electron spectroscopy involved in fusion plasma [29,30]. The kinetic modeling of discharges which have non-Maxwellian velocity distributions for electrons may be executed efficiently using differential cross-section data [31].
Earlier studies to calculate TDCS of W atoms [27,29] have been carried out at projectile energy 100 eV for various scattering angles and ejected electron energies. In this communication, we report the TDCS results obtained for the electron impact single ionization of W atoms at various projectile energies, i.e., 200, 500 and 1000 eV for ejected electron energy 2 eV and 10 eV for different scattering angles. The present investigation is helpful to understand the effect of projectile energy on the collision dynamics of the W atoms. The TDCSs have been calculated in distorted wave Born approximation (DWBA) formalism for various momentum transfer conditions and ionization taking place from W(6s), W(5d), W(5p) and W(4f) sub-shells. Atomic units () have been used for the calculations in the present paper. The theoretical approach used for the calculation of TDCS is described in the next section.
2. Theory
The electron impact ionization process on tungsten W (5p64f145d46s2) atoms is given by the reaction:
The incident electron is specified by energy and momentum E0 and k1, respectively. The two outgoing electrons (scattered and ejected) are described by the energy ad momentum (k1, E1) and (k2, E2), respectively. The scattered electron is specified by subscript ‘1’ and the ejected (ionized) electron is specified by subscript ‘2’. The ionization reaction (Equation (1)) is governed by the energy conservation principle:
where BE is the ionization potential or binding energy of the bound electron.
Triple differential cross-sections (TDCSs) for the ionization taking place from nl orbital are given as:
here
are the direct and exchange amplitudes respectively for ionization taking place from the (n,l) shell of the target atom and is the corresponding target orbital from which the ionization is taking place. The interaction potential between the incident and target electrons, which is responsible for the ionization, is . is the distorted wavefunction for the projectile electron and and are the distorted wavefunctions for the scattered and ejected electrons, respectively; each is orthogonalized with respect to .We have used Hartree–Fock orbitals of McLEAN and McLEAN [32] for obtaining the target orbitals .The spin-averaged static-exchange potential of Furness and McCarthy [33] as modified by Riley and Truhlar [34] has been used to calculate the distorted wavefunction, which is given as:
where is the electron density.
The direct distorting potential for the incident electron is obtained from the target radial orbital [35] as:
where is greater of and r′. The equivalent local ground state potential U, which is the sum of exchange and direct potentials, is given as:
For the work reported here, we have made a careful check to ensure that the cross-sections converge satisfactorily. The TDCS results for the electron impact single ionization of W (6s), W (5d), W (5p) and W (4f) at incident electron energies 200, 500 and 1000 eV are presented in the next section.
3. Results and Discussion
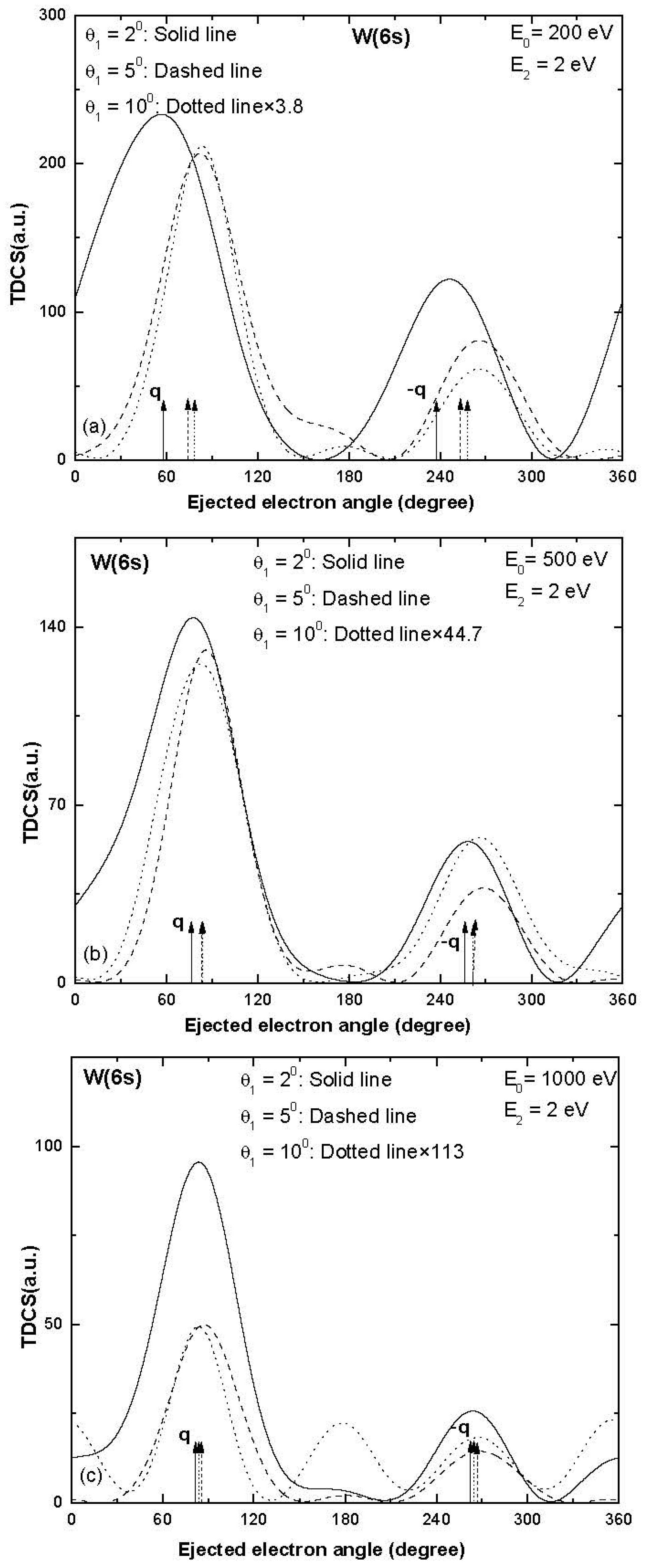
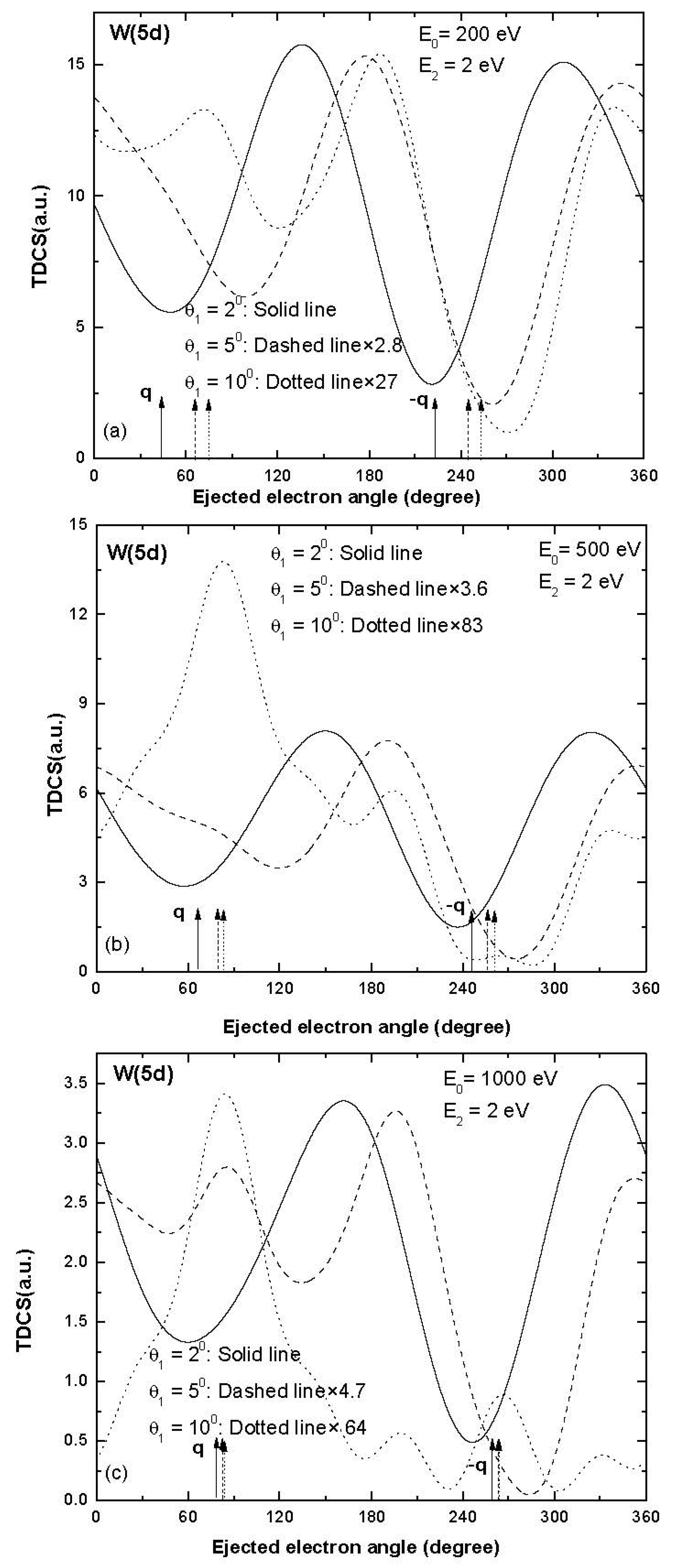
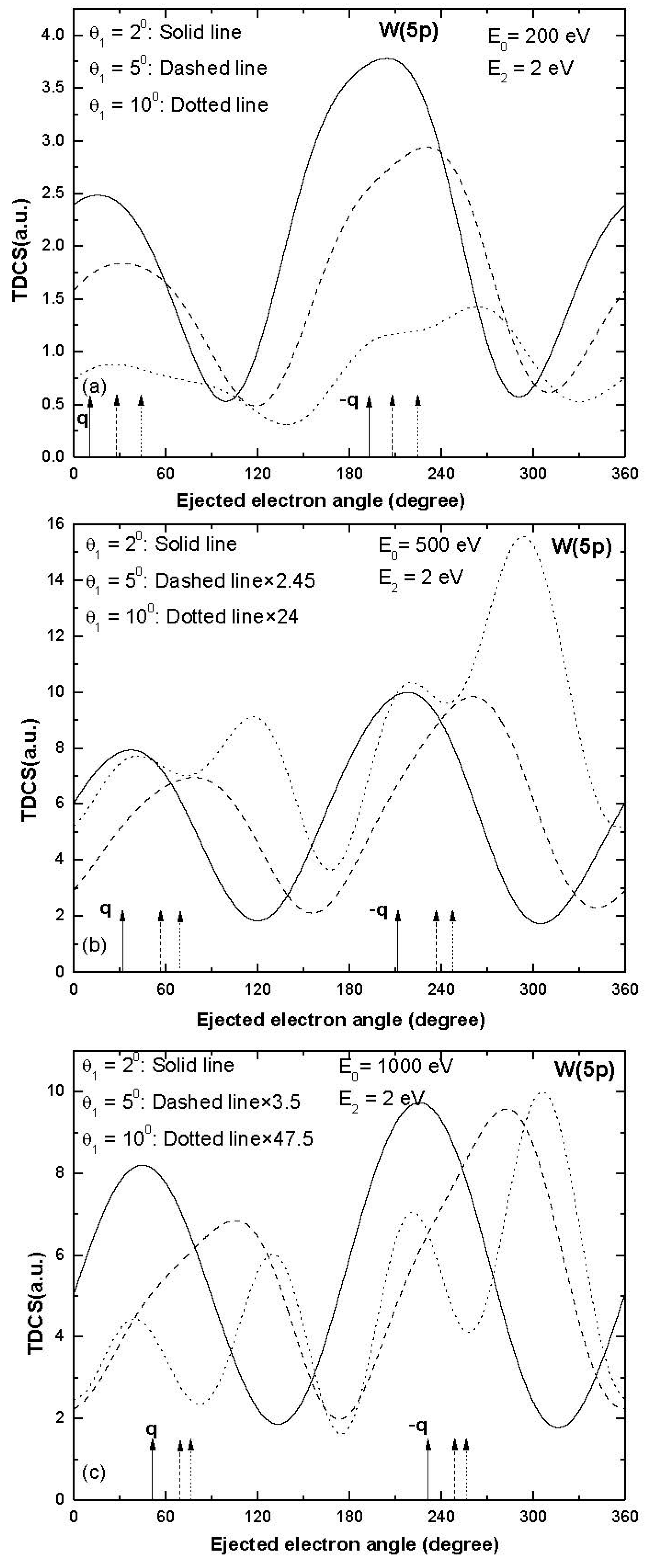
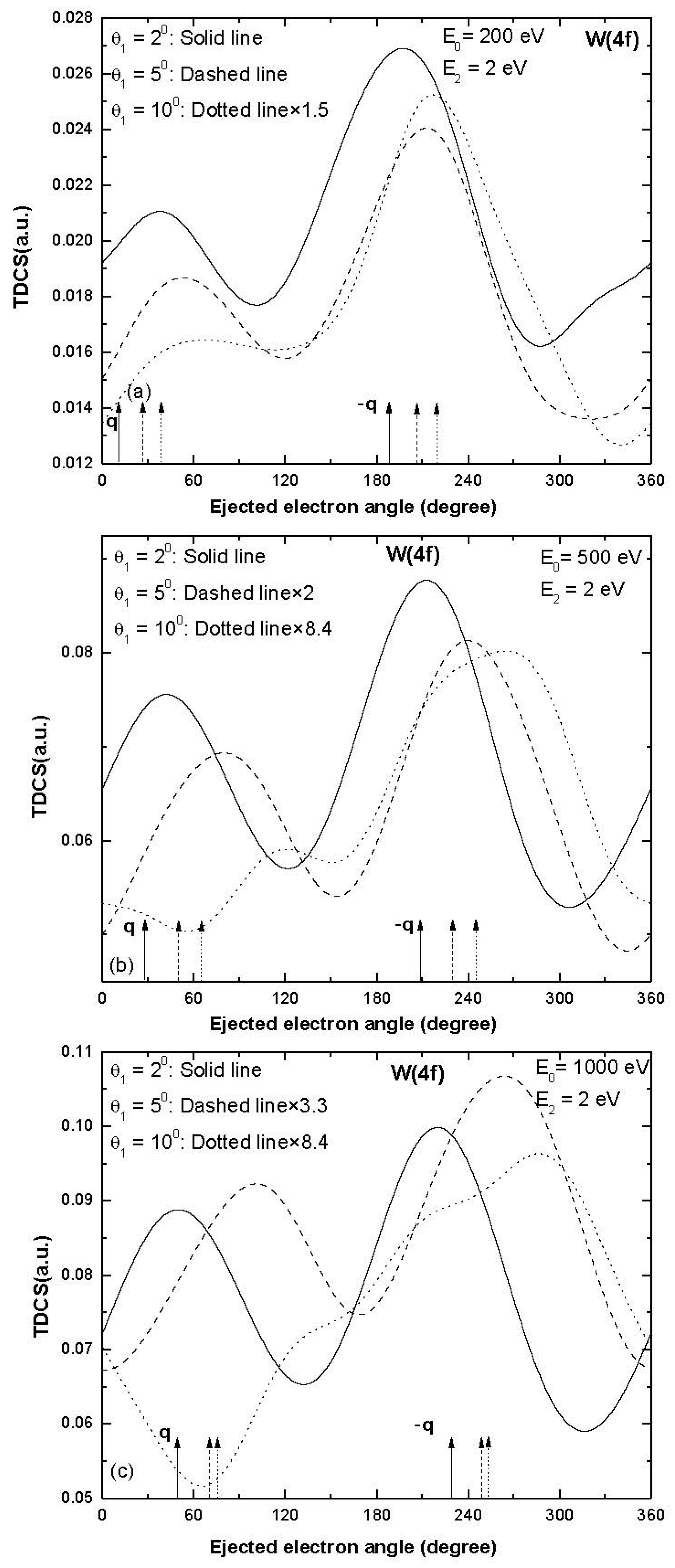
We report electron impact single ionization TDCS results for the ionization taking place from a few outer sub-shells of tungsten (W) atoms, i.e., W (6s), W (5d), W (5p) and W (4f), as shown in Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4. The electron-induced single ionization TDCSs of W atoms have been calculated for 200, 500 and 1000 eV incident energies at ejected electron energy 2 eV and scattering angles 2°, 5° and 10°.

Figure 1.
Electron-induced TDCSs plotted against the angle of the ejected electron for the single ionization of W (6s) at projectile energy (a) 200 eV (b) 500 eV and (c) 1000 eV at ejected electron energy E2 = 2 eV for scattering angles; θ1 = 2°: solid curve, θ1 = 5°: dashed curve and θ1 = 10°: dotted curve. q and −q represent the direction of momentum transfer and its opposite.
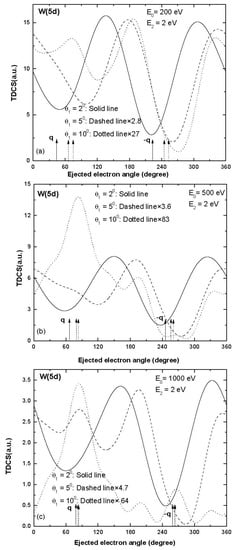
Figure 2.
Same as Figure 1 but for ionization of W (5d).
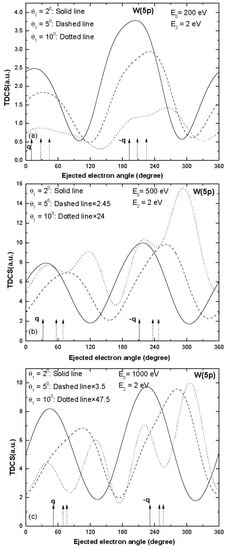
Figure 3.
Same as Figure 1 but for ionization of W (5p).
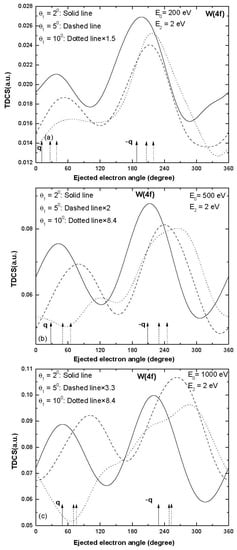
Figure 4.
Same as Figure 1 but for ionization of W (4f).
The TDCSs obtained for the ionization taking place from the W (6s) sub-shell are displayed in Figure 1. A two-peak structure, which is a signature of the coplanar symmetric emission of electrons, is observed in the TDCS at 200 and 500 eV incident energy for the scattering angle 2° (Figure 1a,b). As the value of momentum transfer increases (i.e., increase of scattering angle), apart from the two peaks, a small peak appears around the ejected electron angle (dashed and dotted curves in Figure 1).The two peaks observed in the TDCS for the coplanar asymmetric emission of electrons are termed as binary and recoil peaks. The binary peak expected to be present in the direction of momentum transfer from incident electron to target is obtained due to direct binary collision and the recoil peak is observed in the opposite direction of momentum transfer due to recoil of remainder ion core. The momentum transfer (q) from the projectile to the target is given by the relation .The directions of momentum transfer are shown by arrows in the figures, and we have also listed the expected values of momentum transfer and the directions in Table 1 for all the kinematical conditions used in the present work. It is interesting to observe that for projectile energy 1000 eV at scattering angle 10°, the third peak observed around becomes very significant and it becomes larger than the recoil peak (dotted curve in Figure 1c).

Table 1.
Momentum transfer values and directions for the ionization taking place from various sub-shells of W atoms.
We observe that the magnitude of the TDCS decreases as the value of scattering angle increases (i.e., momentum transfer values increase). For the smaller values of scattering angle, 2° (solid curves in Figure 1), the binary and recoil peaks are observed nearly in the expected direction of momentum transfer; however, both the peaks are shifted towards higher values of ejected electron angles for the higher values of scattering angles. As the value of momentum transfer increases, the recoil to the binary peak ratio decreases and a slight shoulder is developed in the TDCS around , which becomes a significant peak at 1000 eV projectile energy for the scattering angle 10° (Figure 1c).The possible reason for the three-peak structure obtained at the higher momentum transfer condition is still unknown; however, it may be due to possible relativistic effects in the high Z many-electron target W. We would also like to mention that in the present investigation, we have considered ionization from the outer sub-shells of tungsten at intermediate projectile energy, so the relativistic effects may not be so significant.
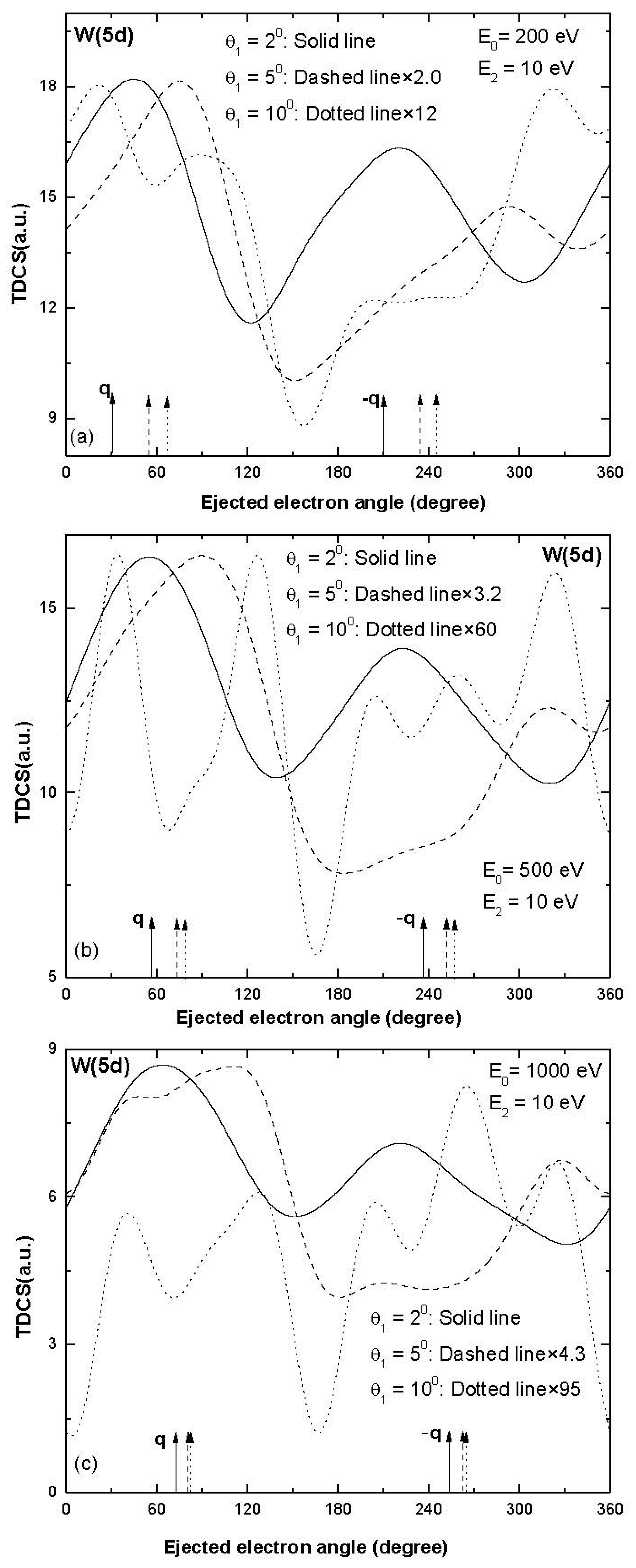
The TDCS results for the ionization from W (5d) are displayed in Figure 2. At smaller values of scattering angles, the two peaks are shifted by large values towards higher ejected electron directions. For the higher momentum transfer conditions (scattering angle 10°), three or more peaks were observed (see dotted curves in Figure 2) and the binary and recoil peaks were observed nearly in the expected direction of momentum transfer for the projectile energy 1000 eV (dotted curve in Figure 2c). Thus, the trends of TDCS observed for W (5d) are significantly different from the trends of TDCS observed for ionization from W (6s) for the coplanar symmetric emission of electrons. Another point to be noted is that the magnitude of TDCS decreases greatly with an increase in scattering angle. The open d shell present in W (5d) may be responsible for these significantly different features of TDCS.
A two-peak structure was obtained in the TDCS for the ionization from the W (5p) sub-shell and the binary and recoil peaks were in the expected direction of momentum transfer (Figure 3) at smaller values of scattering angles 2° and 5°.Some signature of binary as well as recoil peak splitting was observed at higher scattering angle 10° (dotted curve in Figure 3c) and the splitting of peaks became significant as the projectile energy increased (dotted curves in Figure 3b,c).There was a asymmetric splitting of binary and recoil peaks and the minima were observed in the expected direction of momentum transfer and its opposite direction (dotted curve in Figure 3c).Finally, the TDCS results obtained for the ionization from the W (4f) sub-shell are presented in Figure 4.The binary and recoil peaks were observed at scattering angles 2° and 5° and the peak directions were shifted towards higher values of ejected electron angles (solid and dashed curves in Figure 4a,b).For the larger values of momentum transfer (i.e., scattering angle 10°), the trend of TDCS had some signature of splitting of peaks (dotted curves in Figure 4).
It has been observed that the trends of TDCS for the ionization of W (5d) are significantly different from the trends of TDCS observed for the ionization taking place from other sub-shells. To further investigate the collision dynamics of W (5d), we present TDCS of W (5d) for ejected electron energy 10 eV in Figure 5. A two peak structure was observed at scattering angle 2° at all the projectile energies (see solid line in Figure 5). The directions of binary and recoil peaks were nearly in the expected direction of momentum transfer at 200 and 500 eV (solid line in Figure 5a,b); however, the direction of binary and recoil peaks were shifted toward a lower value of ejected electron angle at 1000 eV projectile energy. As the scattering angle increased to 5°, the binary and recoil peaks shifted towards a higher ejected electron angle at 200 and 500 eV projectile energies (see dashed curves in Figure 5a,b). For the further higher value of momentum transfer (i.e., scattering angle 10°), splitting of binary and recoil peaks was observed. Comparing with the trends of TDCS for the W (5d) at ejected electron energy 10 eV, we observed that at scattering angles 2° and 5°, the trends of TDCS were nearly the same as observed for ionization from other sub-shells; however, the trends of TDCS at ejected electron energy 2 eV are significantly different.
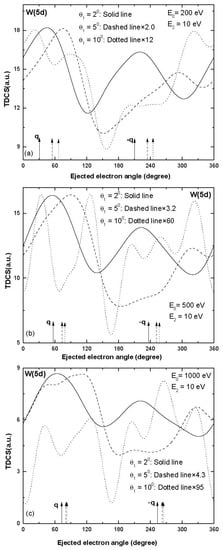
Figure 5.
Electron-induced TDCSs plotted against the angle of the ejected electron for the single ionization of W (5d) at projectile energy (a) 200 eV (b) 500 eV and (c) 1000 eV at ejected electron energy E2 = 10 eV for scattering angles; θ1 = 2°: solid curve, θ1 = 5°: dashed curve and θ1 = 10°: dotted curve. q and −q represent the direction of momentum transfer and its opposite.
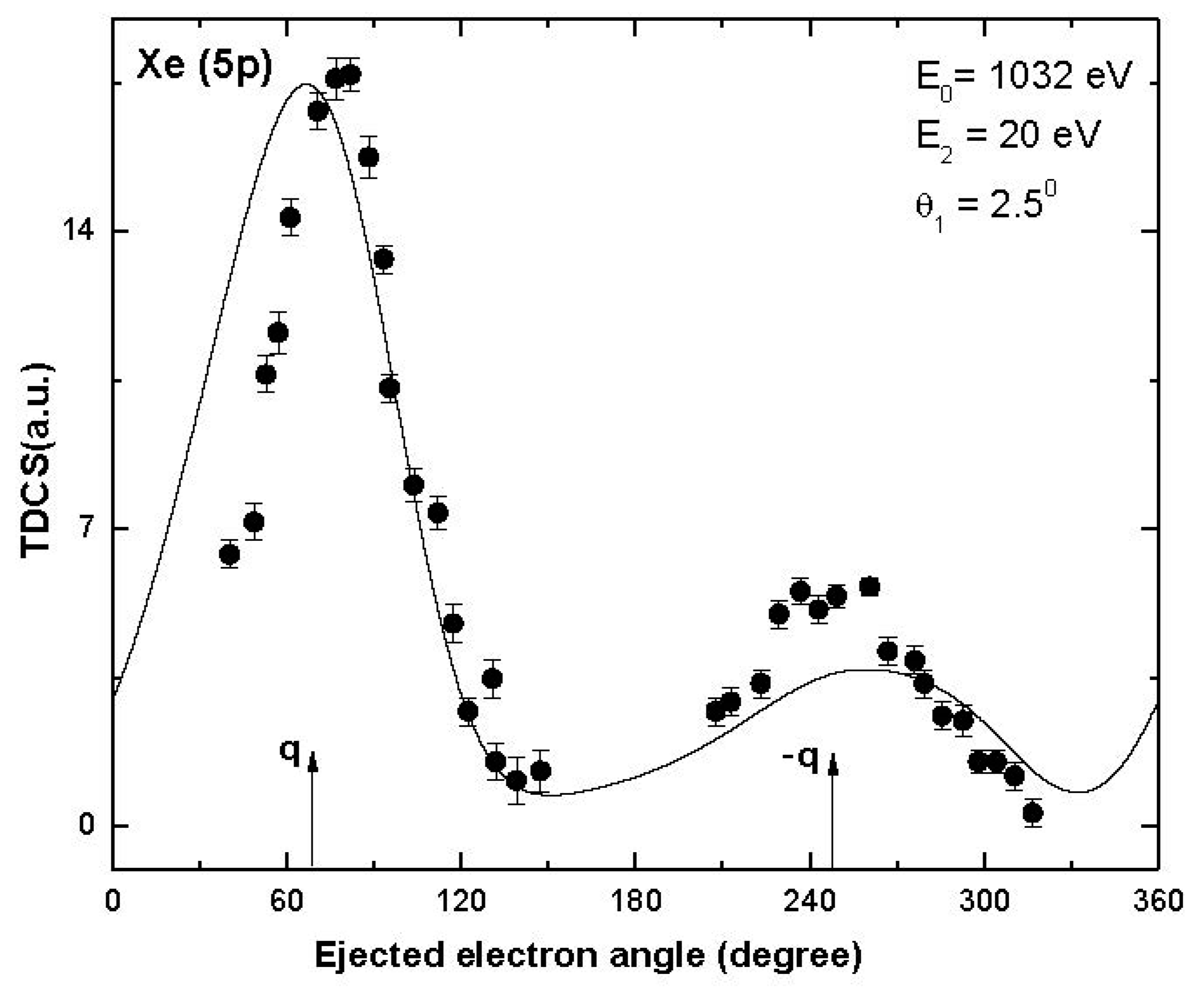
In the present study, we calculated TDCS at small values of ejected electron energy and scattering angles since the ionized electron moving with small energies (near or below threshold energy) with small momentum transfer provides a stringent test of the theoretical models. Effects such as electron correlation, exchange and distortion play an important role and we receive better insight into the collision dynamics. We used the standard DWBA approach for the calculation of TDCS in the present investigation, which is suitable for the kinematics used in the present work as ionization was taking place in the intermediate energy range up to 1 keV. We recently reported that distorted wave approximation (DWA) is able to give reasonable agreement with the other theoretical results available for the W atoms [28] in case of total ionization cross-sections. As mentioned in the theory section, we have ensured that convergence is obtained in the calculated cross-sections. There are no experimental data available for the W atoms to compare with, but we compare the DWBA TDCS results obtained by us for the ionization of Xe (5p) at 1032 eV with the measurements [36] (Figure 6), which justifies the use of the DWBA approach for the present calculations. A good agreement was obtained with the measurements in case of Xe (5p) in present study (Figure 6), which was also the case for our earlier reported DWBA results for Xe (5p) [37], Ar (3s) [38], He (2s) [11], etc.
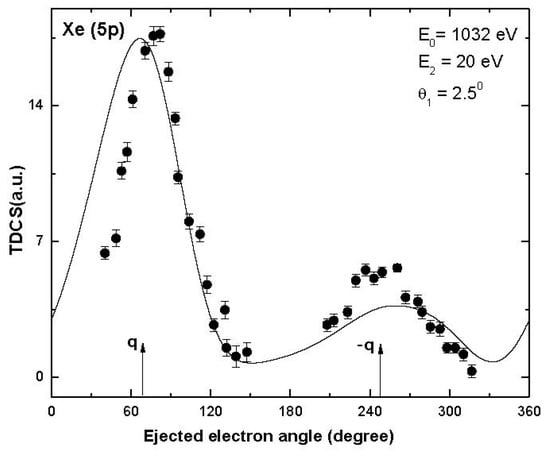
Figure 6.
Electron-induced TDCS plotted against the angle of the ejected electron for the single ionization of Xe (5p) at projectile energy 1032 eV, ejected electron energy 20 eV and scattering angle 2.5°. Solid curve: present DWBA results; solid circles: measurements [36]. The experiment is relative, and it has been normalized to the present DWBA results to give the best visual fit.
It is also worth mentioning that the energy range considered in the present investigation is suitable for plasma applications as the electron temperatures vary from a few hundred eV at the outside of the separatrix (scrape-off layer) down to a few eV in the vicinity of the divertor surfaces [19,29]. The separatrix is a boundary between confined plasma and external plasma. Apart from the total ionization cross-sections [28], the present energy and angle resolved cross-section data will be of further importance for the plasma modelers and discharge-related studies as it gives kinematically complete cross-section data.
4. Conclusions
We have reported the results of TDCS for the electron-induced single ionization of W (6s), W (5d), W (5p) and W (4f) at projectile energies 200, 500 and 1000 eV for different momentum transfer conditions. We observed that the trends of TDCS obtained for the W (6s) ionization are similar to the trends of TDCS obtained for the ionization of lighter targets for coplanar asymmetric emission of electrons. However, the TDCS trends have sensitive dependence on the scattering angle and projectile energy and a three-peak TDCS structure was obtained for higher values of scattering angle and projectile energy for the ionization of W (6s). The binary and recoil peaks were observed in the expected direction of momentum transfer for W (6s), W (4f) and W (5p) at smaller values of scattering angle and projectile energy. The trends of TDCS observed for ionization taking place from W (5d) are significantly different from the other orbital investigated with large shift in the peak positions and complex structure of TDCS at large values on momentum transfer. The open d shell present in W (5d) along with possible many electron effects due to high Z target may be responsible for the observed differences. Our present effort is vital to understand the collision dynamics of W atoms, which is very important from the application point, as very few theoretical studies are available for the differential cross-sections of W and no experimental studies are available for the electron-induced ionization processes on W atoms, even for total ionization.
Funding
This research was funded by SERB, New Delhi, Grant No. CRG/2019/001059.
Acknowledgments
We thank Daiji Kato and Izumi Murakami, NIFS, Japan for useful discussion regarding this work. GP acknowledges the grant received from Science and Engineering Research Board (SERB), New Delhi in the form of SERB CRG project (File No. CRG/2019/001059).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ehrhardt, H.; Hesselbacher, K.H.; Jung, K.; Willmann, K. Collisional Ionization of Helium by Slow Electrons. J. Phys. B 1972, 5, 1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madison, D.H. Full Second-Order Distorted Wave Calculation Without Approximations for Atomic Excitation by Electron Impact. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1984, 53, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahmam-Bennani, A. Recent developments and New Trends in (e, 2e) and (e, 3e) Studies. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 1991, 24, 2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rescigno, T.N.; Baertschy, M.W.; Isaacs, A.; McCurdy, C.W. Collisional Breakup in a Quantum System of Three Charged Particles. Science 1999, 286, 2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakel, W.; Whelan, C.T. Relativistic (e, 2e) Processes. Phys. Rep. 1999, 315, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, I.; Fursa, D.V.; Kheifets, A.S.; Stelbovics, A.T. Electtrons and Photons Colliding With Atoms: Development and Application of the Convergent Close-Coupling Method. J. Phys. B 2002, 35, R117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartschat, K.; Vorov, O. Channel-coupling, Target-structure and Second-order Effects in Electron-impact Ionization of Ar (3p) and Ar (3s). Phys. Rev. A 2005, 72, 022728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, G.; Patidar, V.; Sud, K.K. Triple Differential Cross Section of Potassium for Doubly Symmetric Ionization. Phys. Lett. A. 2010, 374, 2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, G.; Singh, P.; Patidar, V.; Azuma, Y.; Sud, K.K. Effect of Target Polarization and Post Collision Interaction on the Electron Impact Single Ionization of Ne (2p), Ar (3p) and Na (3s) atoms. Phys. Rev. A. 2012, 85, 022714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madison, D.H.; Al-Hagan, O. The Distorted-Wave Born Approach for Calculating Electron-Impact Ionization of Molecules. J. At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2010, 2010, 367180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, G.; Kato, D. Calculation for Electron Impact Ionization of Be atoms and its charged states Be+ and Be+2. J. Phys. B At. Mol.Opt. Phys. 2018, 51, 135201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, G.; Kato, D. Projectile Charge Effects on the Differential Cross Sections for the Ionization of Molecular Nitrogen by Positrons and Electrons. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2018, 51, 135202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Mars, C.M.; Ward, S.J.; Colgan, J.; Amami, S.; Madison, D.H. Deep Minima in the Triply Differential Cross Section for Ionization of Atomic Hydrogen by Electron and Positron Impact. Atoms 2020, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitts, R.A.; Carpentier, S.; Escourbiac, F.; Hirai, T.; Komarov, V.; Kukushkin, A.S.; Lisgo, S.; Loarte, A.; Merola, M.; Mitteau, R.; et al. Physics Basis and Design of the ITER Plasma-Facing Components. J. Nucl. Mater. 2011, 415, 5957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federici, G. Plasma Wall Interactions in ITER. Phys. Scr. 2006, T124, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neu, R.; Bobkov, V.; Dux, R.; Kallenbach, A.; Pütterich, T.; Greuner, H.; Gruber, O.; Herrmann, A.; Hopf, C.; Krieger, K.; et al. Final Steps to an All Tungsten Divertor Tokamak. J. Nucl. Mater. 2007, 52, 363–365. [Google Scholar]
- Balance, C.P.; Loch, S.D.; Pinzola, M.S.; Griffin, D.C. Electron Impact Excitation and Ionization of W3+ for the determination of tungsten influx in a fusion plasma. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2013, 46, 055202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spruck, K.; Becker, A.; Borovik, A., Jr.; Gharaibeh, M.F.; Rausch, J.; Schippers, S.; Muller, A. Electron-Impact Ionization of Multiply Charged Tungsten Ions. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2014, 488, 062026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, A. Fusion-Related Ionization and Recombination Data for Tungsten Ions in Low to Moderately High Charge States. Atoms 2015, 3, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pindzola, M.S.; Griffin, D.C. Electron-Impact Ionization of the Tungsten Atoms. Phys. Rev. A 1992, 46, 2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutsch, H.; Hilpert, K.; Becker, K.; Probst, M.; Märk, T.D. Calculated Absolute Electron-Impact Ionization Cross Sections for AlO, Al2O, and WOx (x = 1-3). J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 89, 1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kwon, D.H.; Rhee, Y.J.; Kim, Y.K. Ionization of W and W+ by Electron Impact. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 252, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vainshtein, L.; Beigman, I.; Mertens, P.; Brezinse, S.; Pospieszczykand, A.; Borodin, D. Ionization of W atoms and W+ ions by Electrons. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2011, 44, 125201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, B.; Naghma, R.; Antony, B. Calculation of Electron Impact Total Ionization Cross sections for tungsten, uranium and their oxide radicals. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2014, 372, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pindzola, M.S.; Loch and, S.D.; Foster, A.R. Electron Impact Single and Double Ionization of W. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2017, 50, 095201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, F.; Ferreira da Silva, F.; Limão-Vieiraand, P.; García, G. Electron Scattering Cross Section Data for Tungsten and Beryllium atoms from 0.1 to 5000 eV. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 2017, 26, 085004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, G.; Kato, D.; Murakami, I. Electron Impact Ionization Cross Sections of Tungsten Atoms and Tungsten Ions. Plasma Fusion Res. 2018, 13, 3401026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, G.; Kato, D.; Murakami, I.; Gupta, S.; Sinha, P. Calculation of Electron Induced Ionization Cross Sections of Fusion Plasma Relevant Material: W atoms. Eur. Phys. J. D. 2021, 75, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, G. Electron Impact Single Ionization Differential Cross Sections of W(6s), W(5d), W(5p) and W(4f). J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2021, 54, 065203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, G.; Kato, D. Dependence of Electron Impact Differential Cross Sections on the Ionic Charge to Mass Ratio for the A/3+(2p) and Be2+(1s) ions. J. Chem. Phys. 2018, 148, 084307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahedi, V.; Surendra, M. A Monte Carlo Collision Model for the Particle-in-Cell Method: Applications to Argon and Oxygen Discharges. Comput. Phys. Commun. 1995, 87, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mclean, A.D.; Mclean, R.S. Roothaan-Hartree-Fock Atomic Wave Functions Slater Basis-Set Expansions for Z = 55-92. At. Data Nucl. Data Tab. 1981, 26, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furness, J.B.; McCarthy, I.E. Semiphenomenological Optical Model for Electron Scattering on Atoms. J. Phys. B. 1973, 6, 2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, M.E.; Truhlar, D.G. Approximations for the Exchange Potential in Electron Scattering. J. Chem. Phys. 1975, 63, 2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, I.E. Distorted-Wave Born and Impulse Approximations for Electron-Atom Ionisation. Aust. J. Phys. 1995, 48, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasch, J.; Zitnik, M.; Avaldi, L.; Colm, T.; Whelan, G.; Stefani, R.; Camilloni, R.; Allan, J.; Walters, H.R.J. Theoretical and Experimental Investigation of the Triple-Differential Cross Sections for Electron-Impact Ionization of Kr(4p) and Xe(5p) at 1-keV Impact Energy. Phys. Rev. A. 1997, 56, 4644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, G.; Singh, P.; Patidar, V. Fully Differential Cross Sections for Low to Intermediate Energy Perpendicular Plane Ionization of Xenon Atoms. J. Elec. Spec. Rel. Phenom. 2014, 197, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purohit, G.; Patidar, V.; Sud, K.K. Importance of Polarization Effects in Electron Impact Single Ionization of Argon Atom. J. Elec. Spec. Rel. Phenom. 2009, 175, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).