Magnetic Angle Changer for Studies of Electronically Excited Long-Living Atomic States
Abstract
:1. Introduction
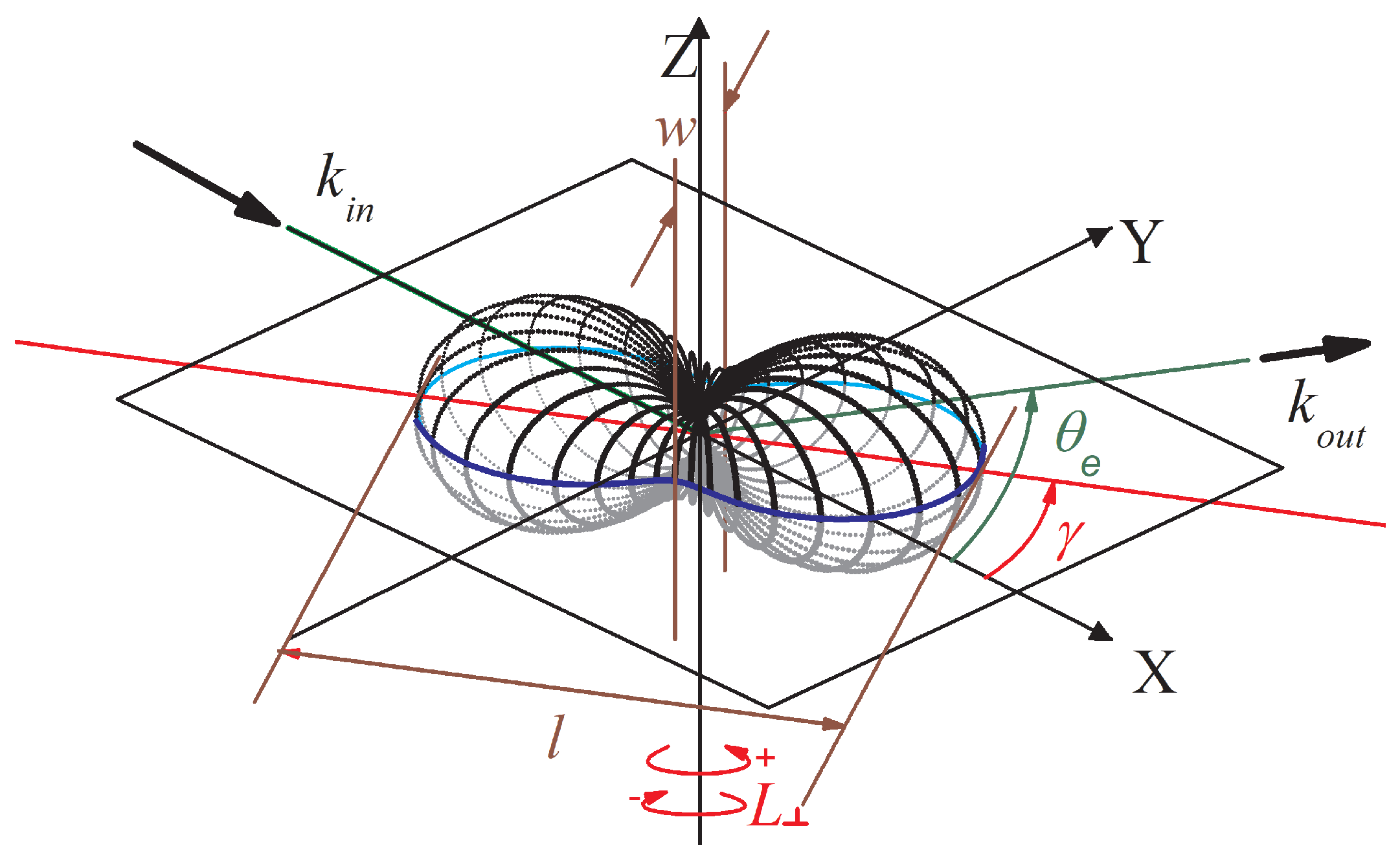
2. New Magnetic Angle Changer Geometry
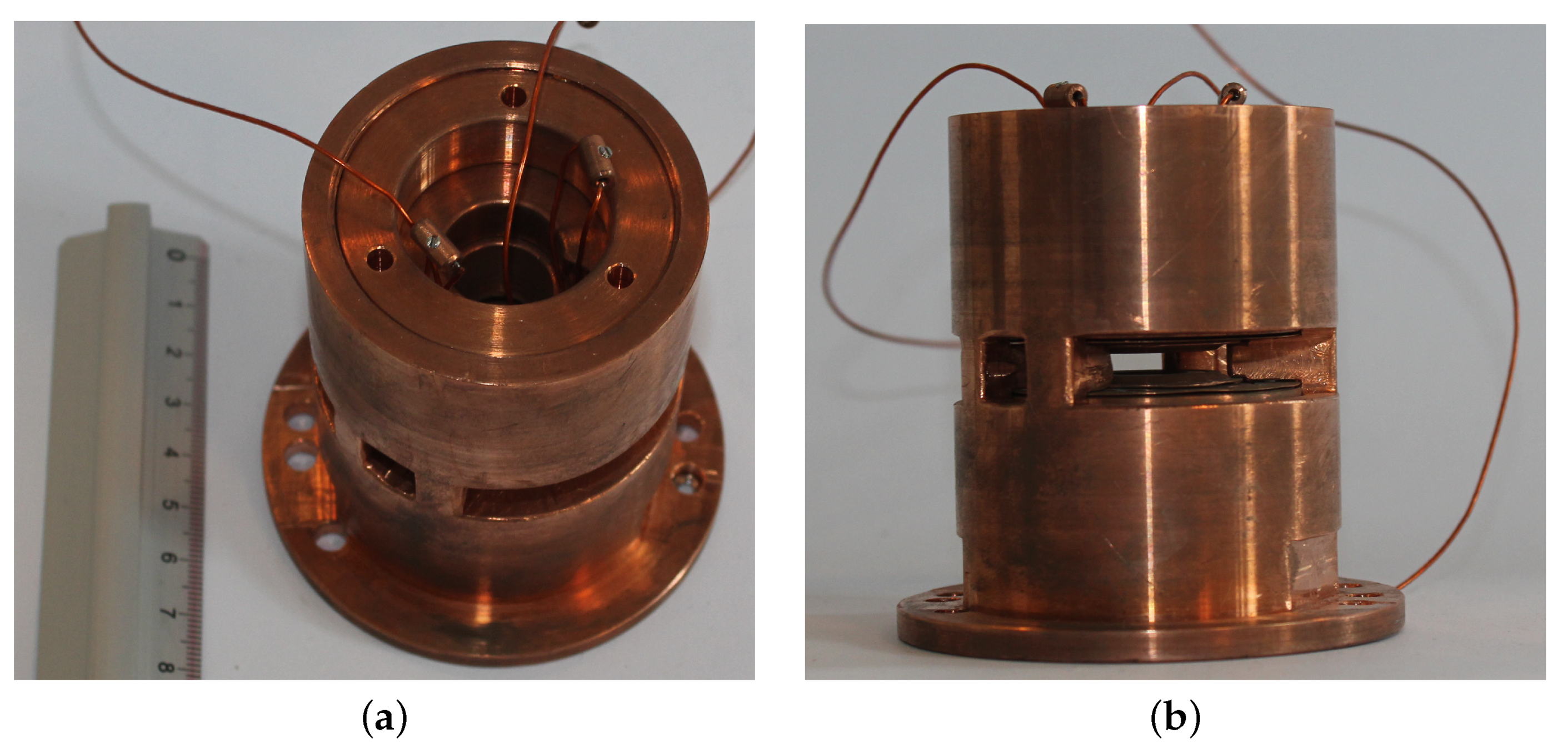
2.1. The Device Used in the Experiment
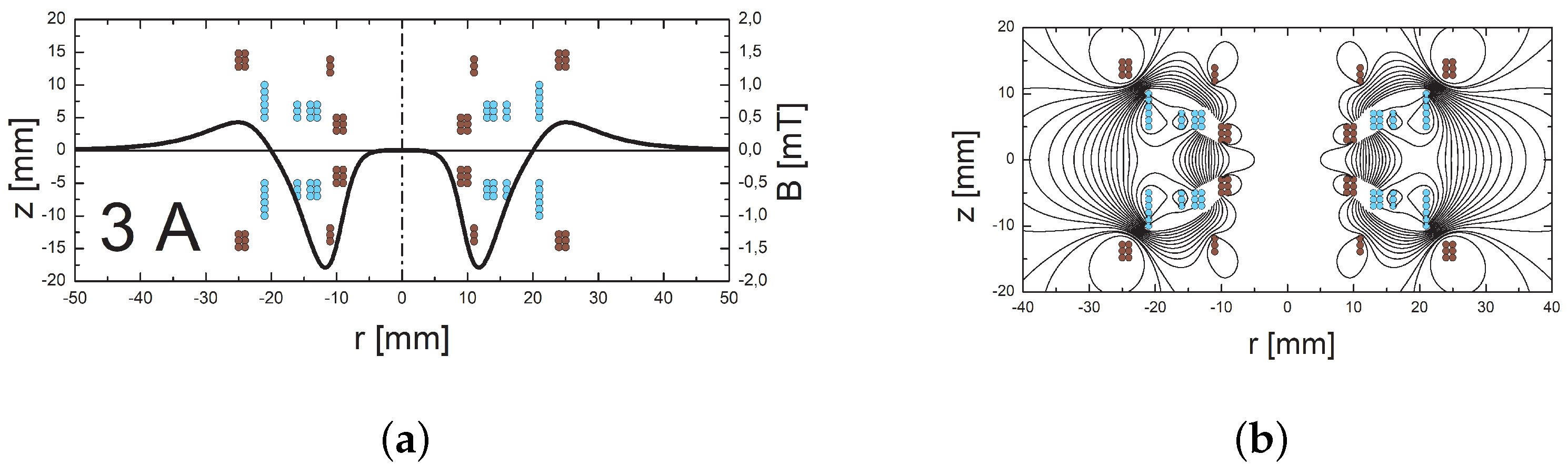
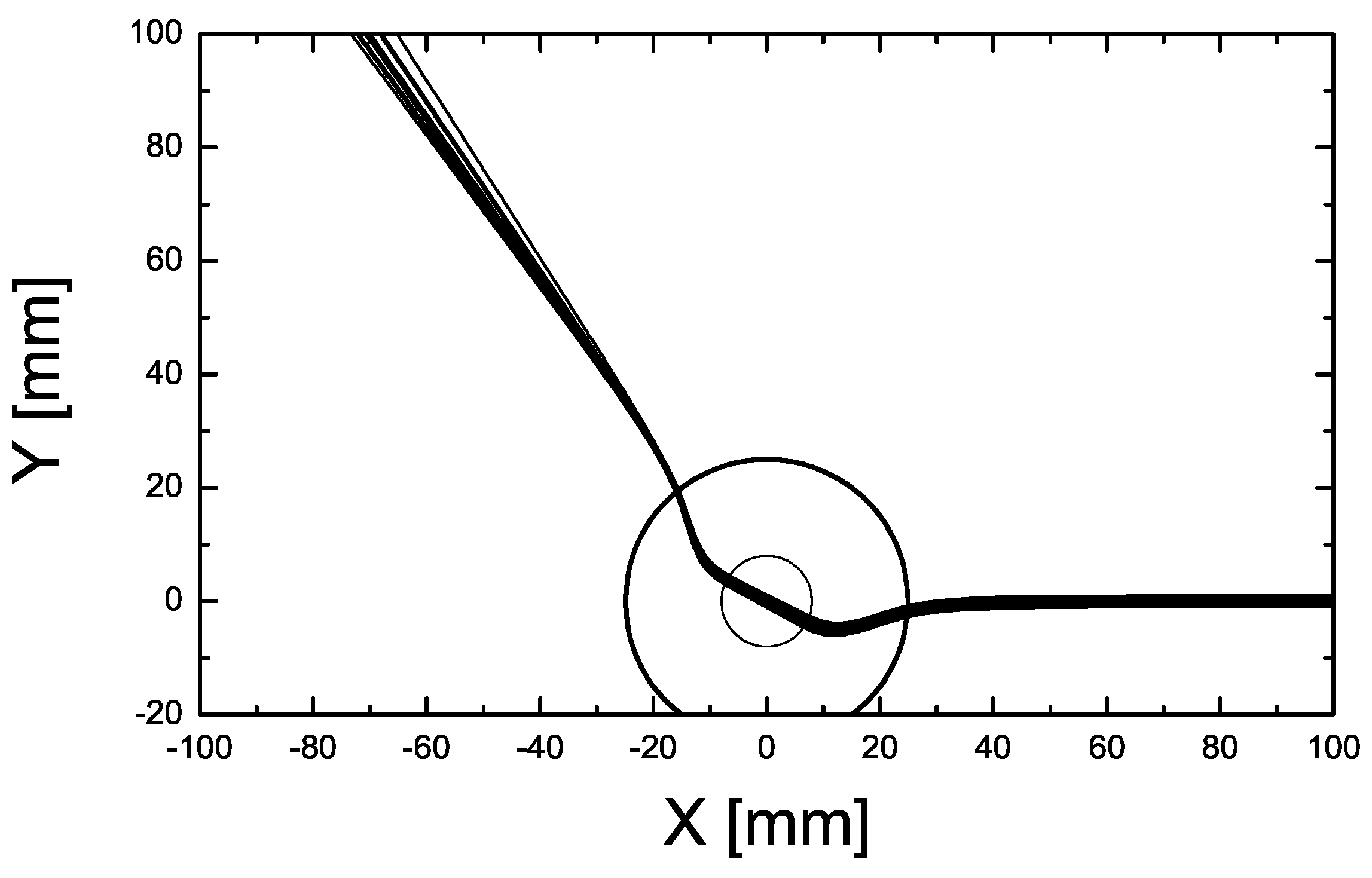
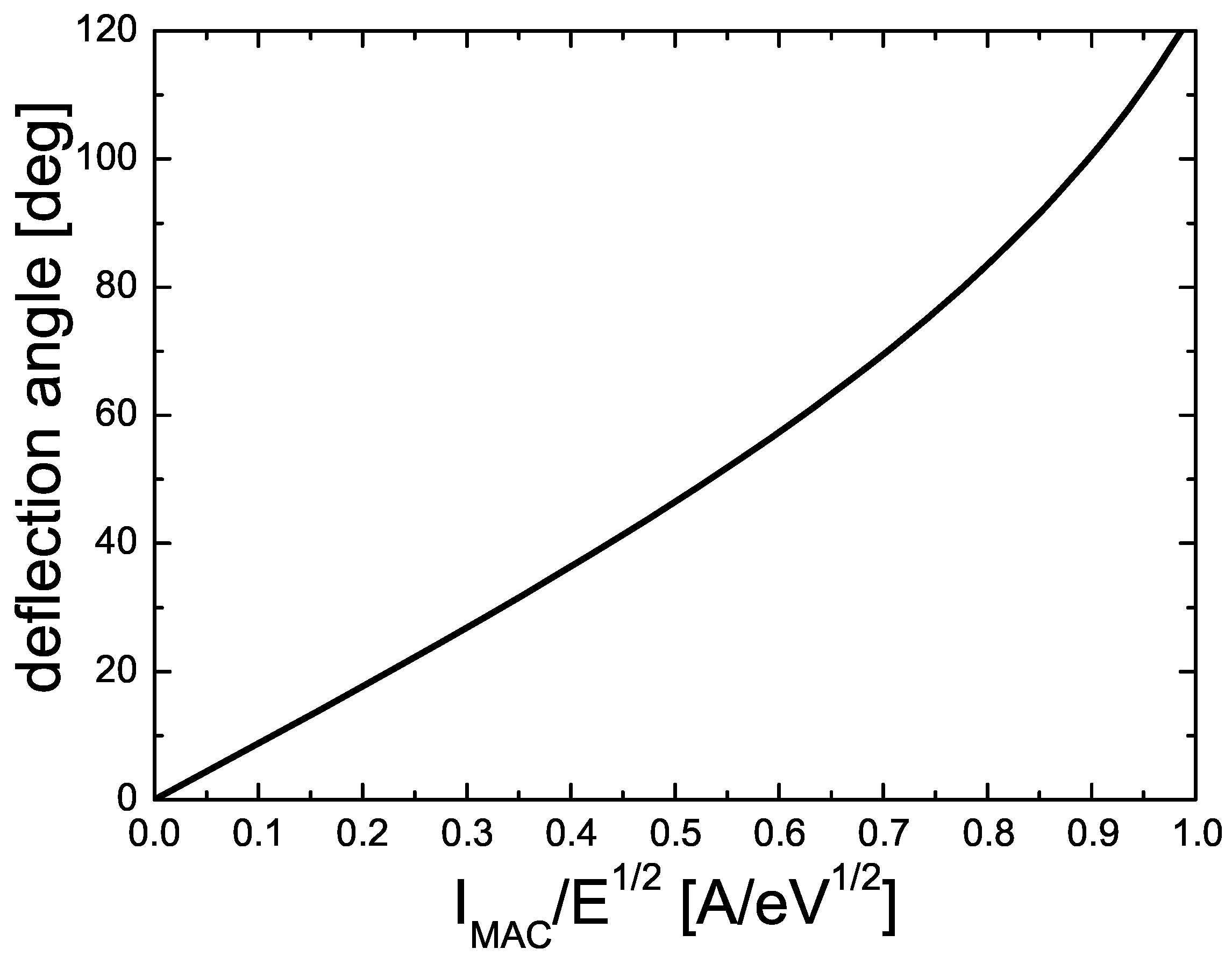
2.2. Numerical Analysis of the MAC’s Performance
3. Summary
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Read, F.H.; Channing, J.M. Production and optical properties of an unscreened but localized magnetic field. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1996, 67, 2372–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubek, M.; Gulley, N.; King, G.C.; Read, F.H. Measurements of elastic electron scattering in the backward hemisphere. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 1996, 29, L239–L244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, G.C. Chapter 1-the use of the magnetic angle changer in atomic and molecular physics. In Advances in Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics; Arimondo, E., Berman, P.R., Lin, C.C., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011; Volume 60, pp. 1–64. [Google Scholar]
- Allan, M. Excitation of the 23S state of helium by electron impact from threshold to 24 eV: measurements with the ‘magnetic angle changer’. J. Phys. At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2000, 33, L215–L220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielewska, B.; Linert, I.; King, G.C.; Zubek, M. Differential cross sections for elastic electron scattering in argon over the angular range 130∘–180∘. Phys. Rev. A 2004, 69, 062716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linert, I.; King, G.C.; Zubek, M. A study of electron impact excitation of molecular oxygen at a scattering angle of 180∘. J. Electron Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 2004, 134, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, N.; Gallagher, J.W.; Hertel, I.V. Collisional alignment and orientation of atomic outer shells I. Direct excitation by electron and atom impact. Phys. Rep. 1988, 165, 1–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, N.; Hertel, I.V.; Kleinpoppen, H. Shape and dynamics of states excited in electron-atom collisions: A comment on orientation and alignment parameters by consideration of attractive and repulsive forces. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Phys. 1984, 17, L901–L908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanle, W. Zuschriften und vorläufige Mitteilungen. Naturwissenschaften 1923, 11, 690–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kłosowski, Ł.; Piwiński, M.; Dziczek, D.; Wiśniewska, K.; Chwirot, S. Magnetic angle changer—New device allowing extension of electron–photon coincidence measurements to arbitrarily large electron scattering angles. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2007, 18, 3801–3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, A.J.; MacGillivray, W.; Hussey, M. Theoretical modeling of resonant laser excitation of atoms in a magnetic field. Phys. Rev. A 2008, 77, 013409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wood, R.W.; Ellett, A. On the influence of magnetic fields on the polarisation of resonance radiation. Proc. R. Soc. London. Ser. Contain. Pap. Math. Phys. Character 1923, 103, 396–403. [Google Scholar]
- Moruzzi, G.; Strumia, F. (Eds.) The Hanle Effect and Level-Crossing Spectroscopy; Atomic, Molecular, Optical and Plasma Physics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Presura, R. Hanle effect as candidate for measuring magnetic fields in laboratory plasmas. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2012, 83, 10D528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raouafi, N.E.; Riley, P.; Gibson, S.; Fineschi, S.; Solanki, S.K. Diagnostics of coronal magnetic fields through the hanle effect in uv and ir lines. Front. Astron. Space Sci. 2016, 3, L215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bederson, B. The “perfect” scattering experiment. II. Comments At. Mol. Phys. 1969, 1, 65–69. [Google Scholar]
- Macek, J.; Jaecks, D.H. Theory of atomic photon–particle coincidence measurements. Phys. Rev. A 1971, 4, 2288–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussey, M.; Murray, A.; MacGillivray, W.; King, G.C. Low energy super-elastic scattering studies of calcium over the complete angular range using a magnetic angle changing device. J. Phys. B At. Mol. Opt. Phys. 2008, 41, 055202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://physics.nist.gov/PhysRefData/Handbook/Tables/calciumtable3.htm (accessed on 15 August 2021).
- Kłosowski, Ł.; Piwiński, M.; Dziczek, D.; Wiśniewska, K.; Zubek, M.; Chwirot, S. Coincidence investigation of inelastic electron-atom collisions with magnetic selection of scattering angle—Feasibility study. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. 2007, 144, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kłosowski, Ł.; Piwiński, M.; Dziczek, D.; Pleskacz, K.; Chwirot, S. Coincidence measurements of electron-impact coherence parameters for e-he scattering in the full range of scattering angles. Phys. Rev. A 2009, 80, 062709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://physics.nist.gov/PhysRefData/Handbook/Tables/heliumtable3.htm (accessed on 15 August 2021).
- Humphrey, I.; Williams, J.F.; Heck, E.L. A feasibility study of the measurement of the stokes parameters of the 33p, 31d and 33d states of helium. J. Phys. At. Mol. Phys. 1987, 20, 367–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fon, W.C.; Berrington, K.A.; Burke, P.G.; Kingston, A.E. The 11s to 23s and 11s to 23p excitation of helium by electron impact. J. Phys. At. Mol. Phys. 1979, 12, 1861–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartwright, D.C.; Csanak, G. Electron-photon coincidence parameters for the excitation of the n3P (n = 2–8) states of helium. J. Phys. B 1986, 19, L485–L491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| i | [mm] | [mm] | Current Direction |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 9 | 3 | + |
| 2 | 9 | 4 | + |
| 3 | 9 | 5 | + |
| 4 | 10 | 3 | + |
| 5 | 10 | 4 | + |
| 6 | 10 | 5 | + |
| 7 | 11 | 11.9 | + |
| 8 | 11 | 12.9 | + |
| 9 | 11 | 13.9 | + |
| 10 | 13 | 5 | − |
| 11 | 13 | 6 | − |
| 12 | 13 | 7 | − |
| 13 | 14 | 5 | − |
| 14 | 14 | 6 | − |
| 15 | 14 | 7 | − |
| 16 | 16 | 5 | − |
| 17 | 16 | 6 | − |
| 18 | 16 | 7 | − |
| 19 | 21 | 5 | − |
| 20 | 21 | 6 | − |
| 21 | 21 | 7 | − |
| 22 | 21 | 8 | − |
| 23 | 21 | 9 | − |
| 24 | 21 | 10 | − |
| 25 | 24 | 12.8 | + |
| 26 | 24 | 13.8 | + |
| 27 | 24 | 14.8 | + |
| 28 | 25 | 12.8 | + |
| 29 | 25 | 13.8 | + |
| 30 | 25 | 14.8 | + |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kłosowski, Ł.; Piwiński, M. Magnetic Angle Changer for Studies of Electronically Excited Long-Living Atomic States. Atoms 2021, 9, 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms9040071
Kłosowski Ł, Piwiński M. Magnetic Angle Changer for Studies of Electronically Excited Long-Living Atomic States. Atoms. 2021; 9(4):71. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms9040071
Chicago/Turabian StyleKłosowski, Łukasz, and Mariusz Piwiński. 2021. "Magnetic Angle Changer for Studies of Electronically Excited Long-Living Atomic States" Atoms 9, no. 4: 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms9040071
APA StyleKłosowski, Ł., & Piwiński, M. (2021). Magnetic Angle Changer for Studies of Electronically Excited Long-Living Atomic States. Atoms, 9(4), 71. https://doi.org/10.3390/atoms9040071






