Data-Driven Inverse Kinematics Approximation of a Delta Robot with Stepper Motors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Dynamic Model of the Delta Robot
Inverse Kinematics
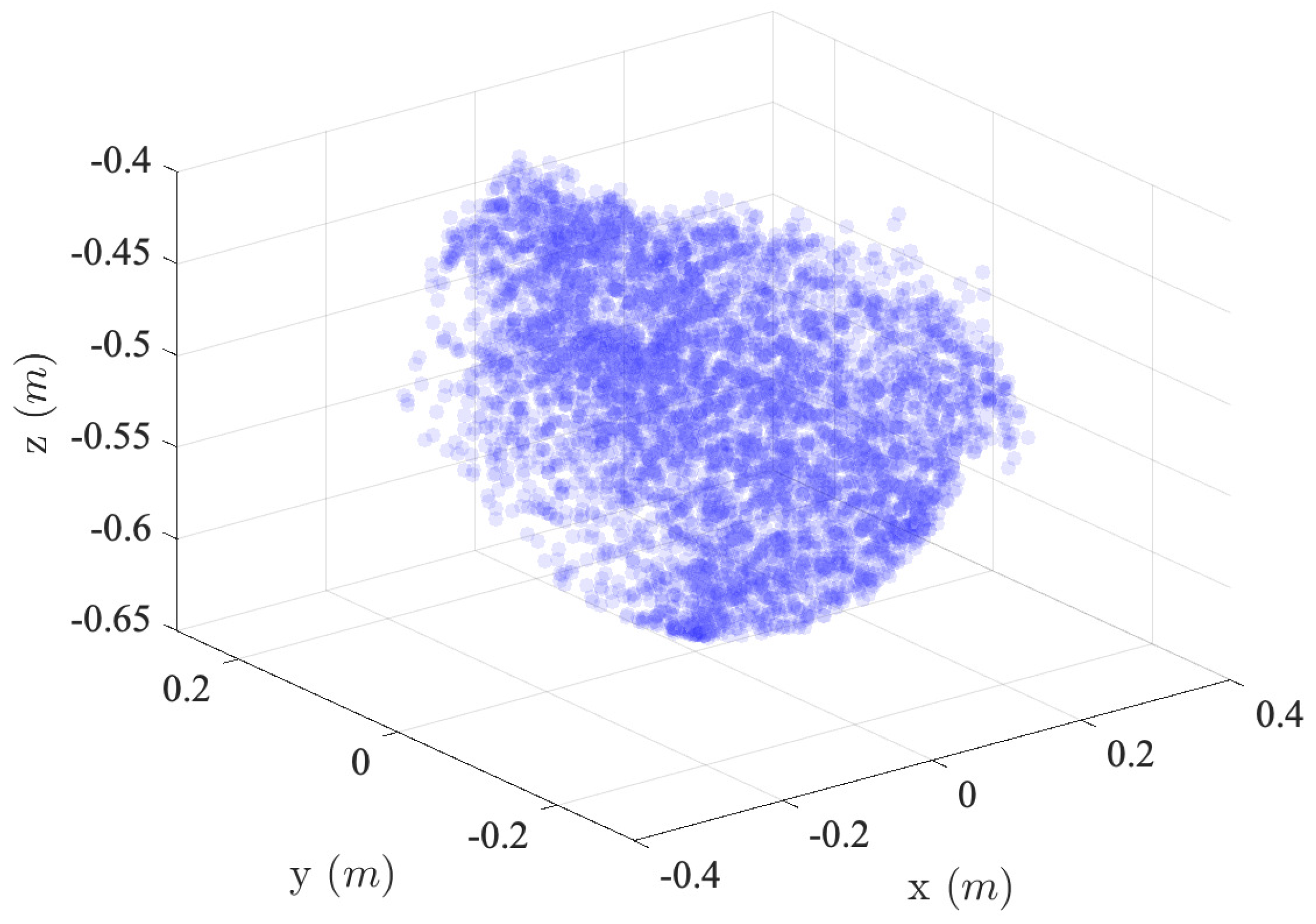
3. Neural Network Model
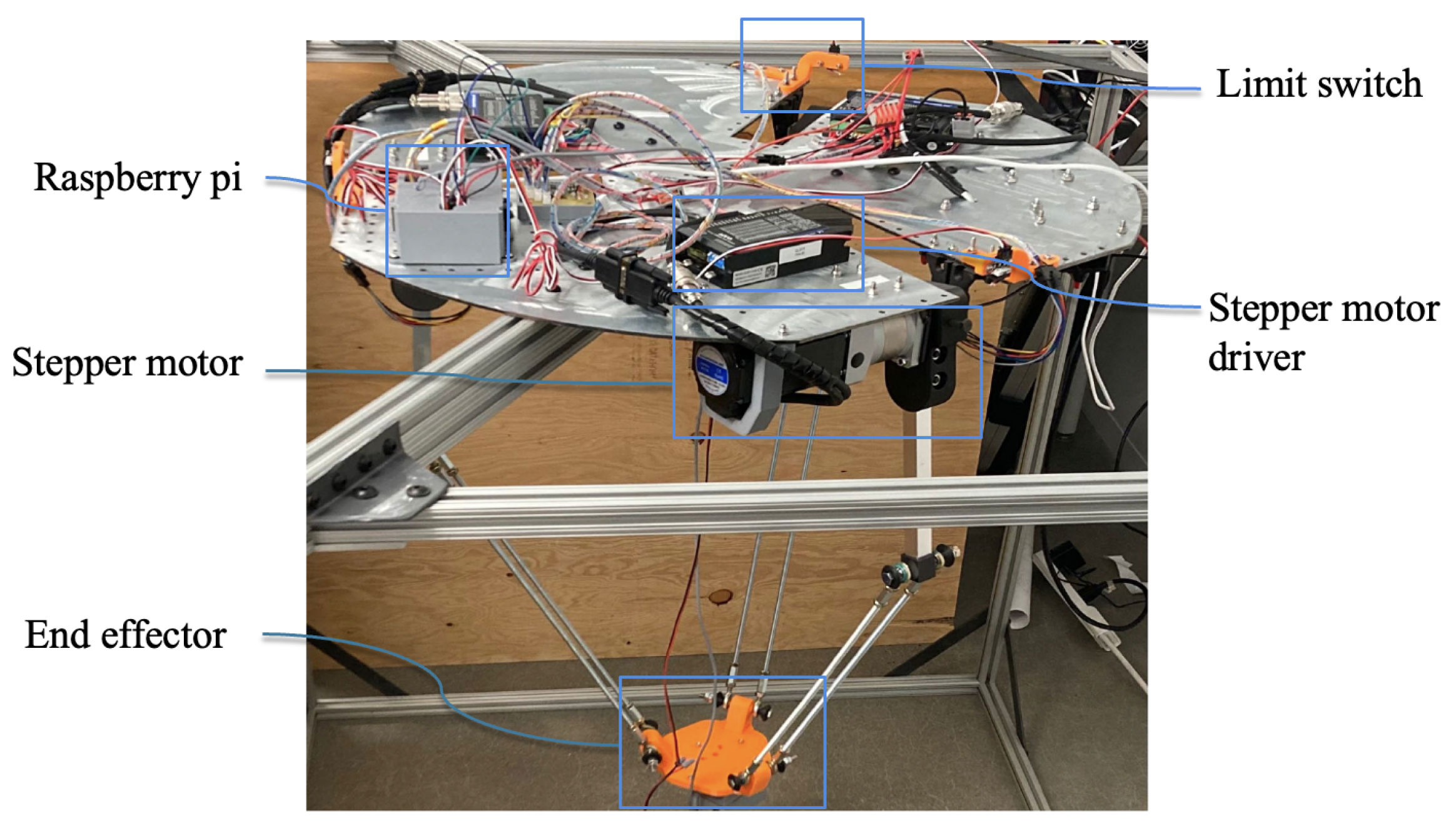
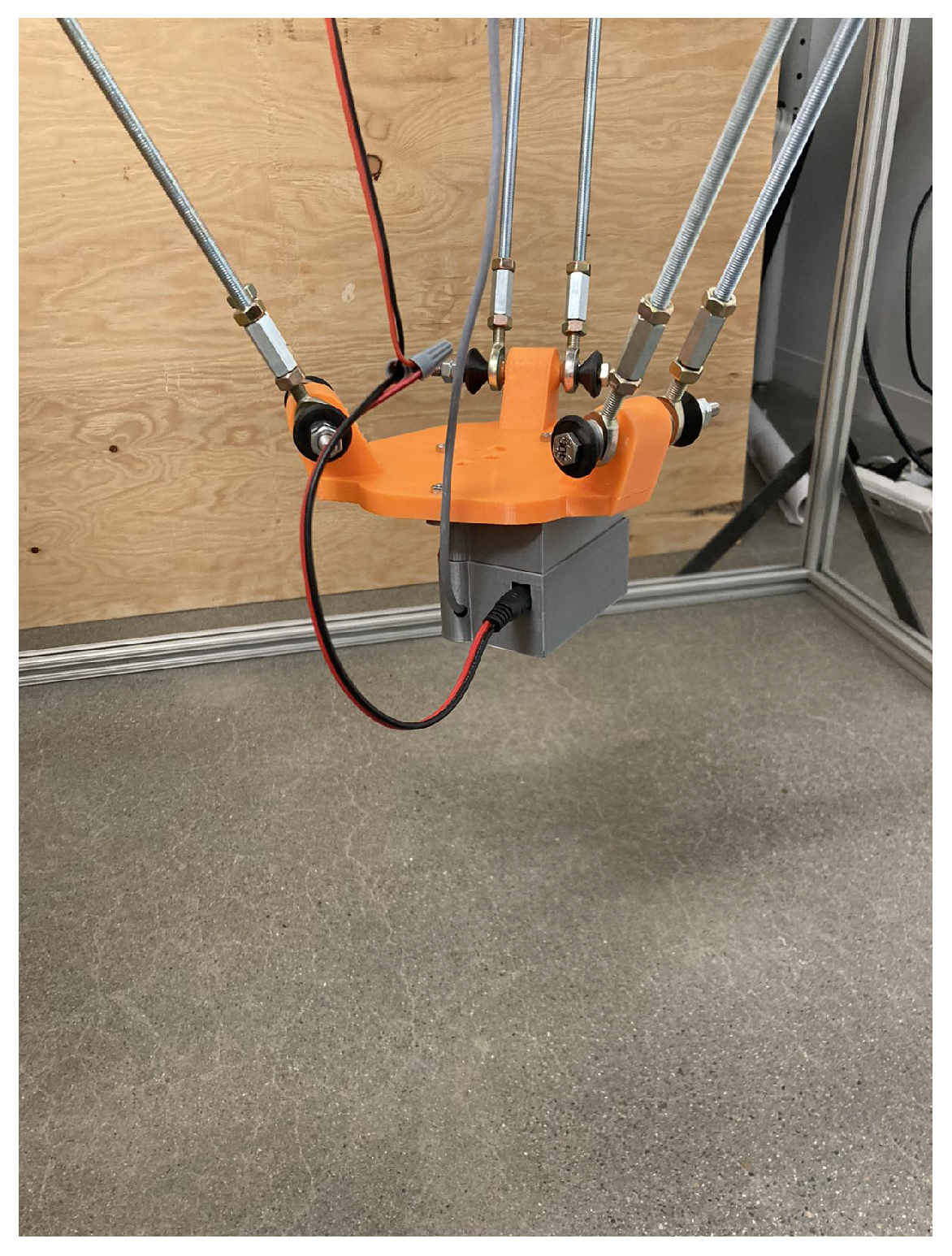
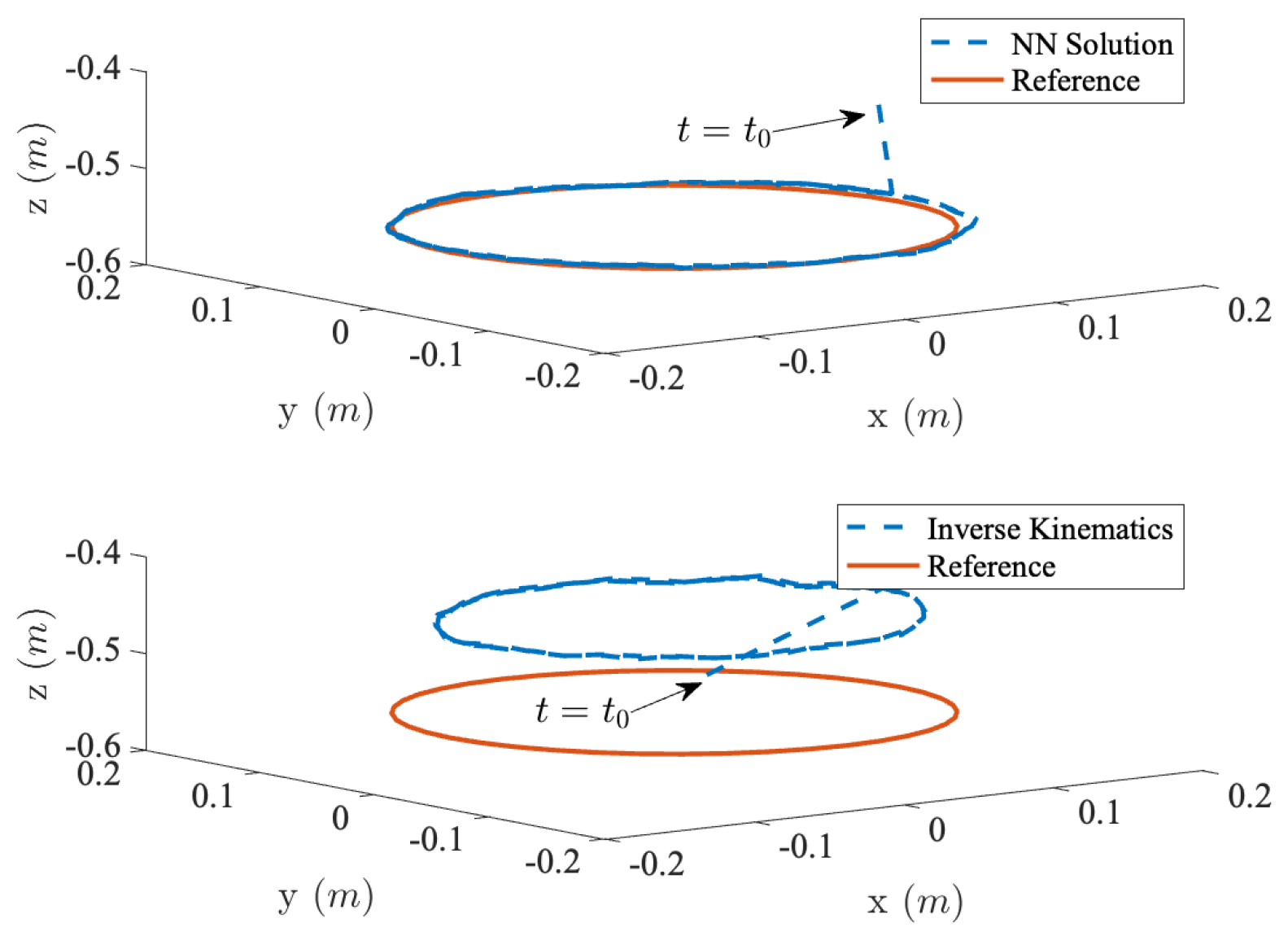
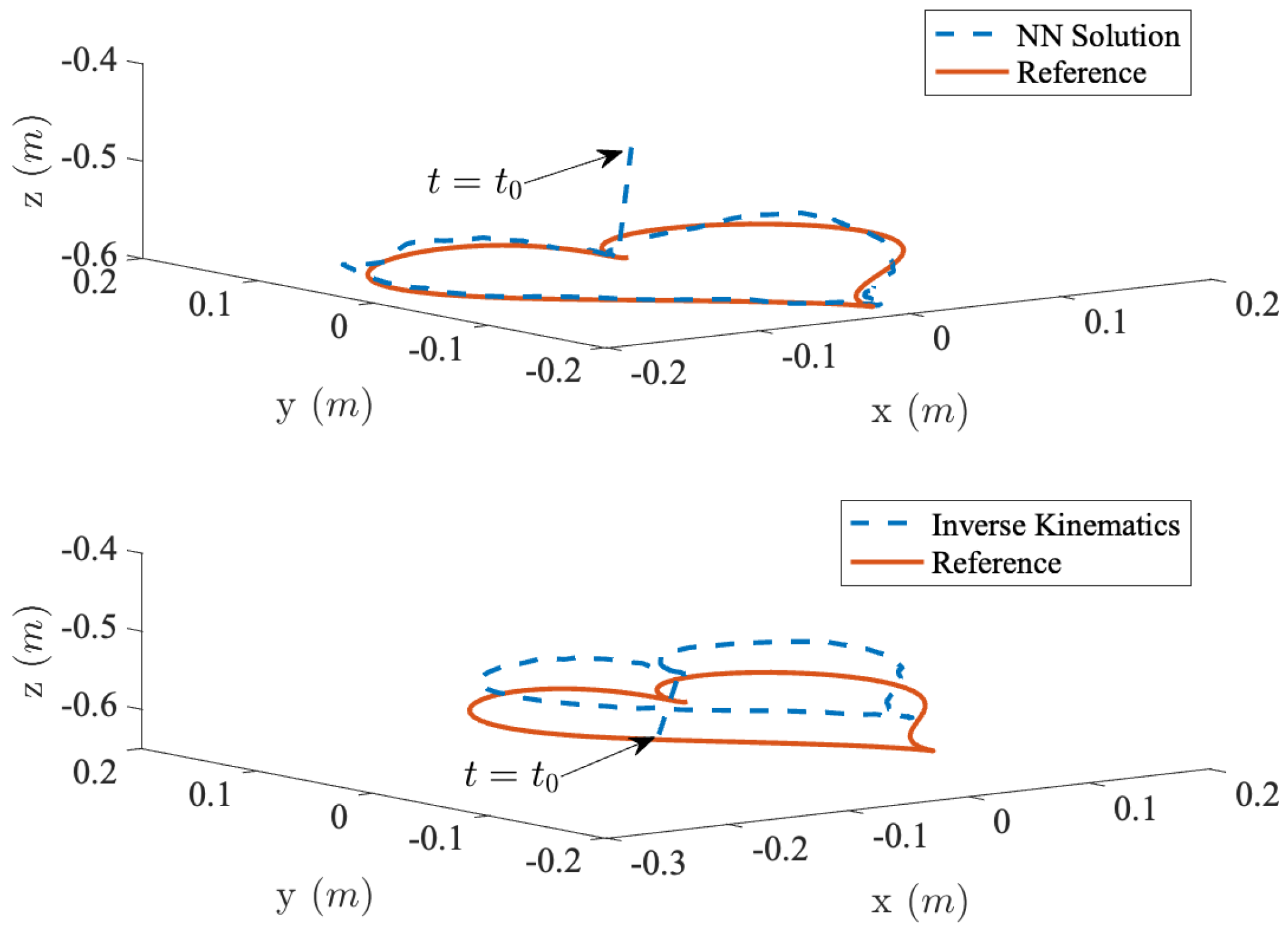
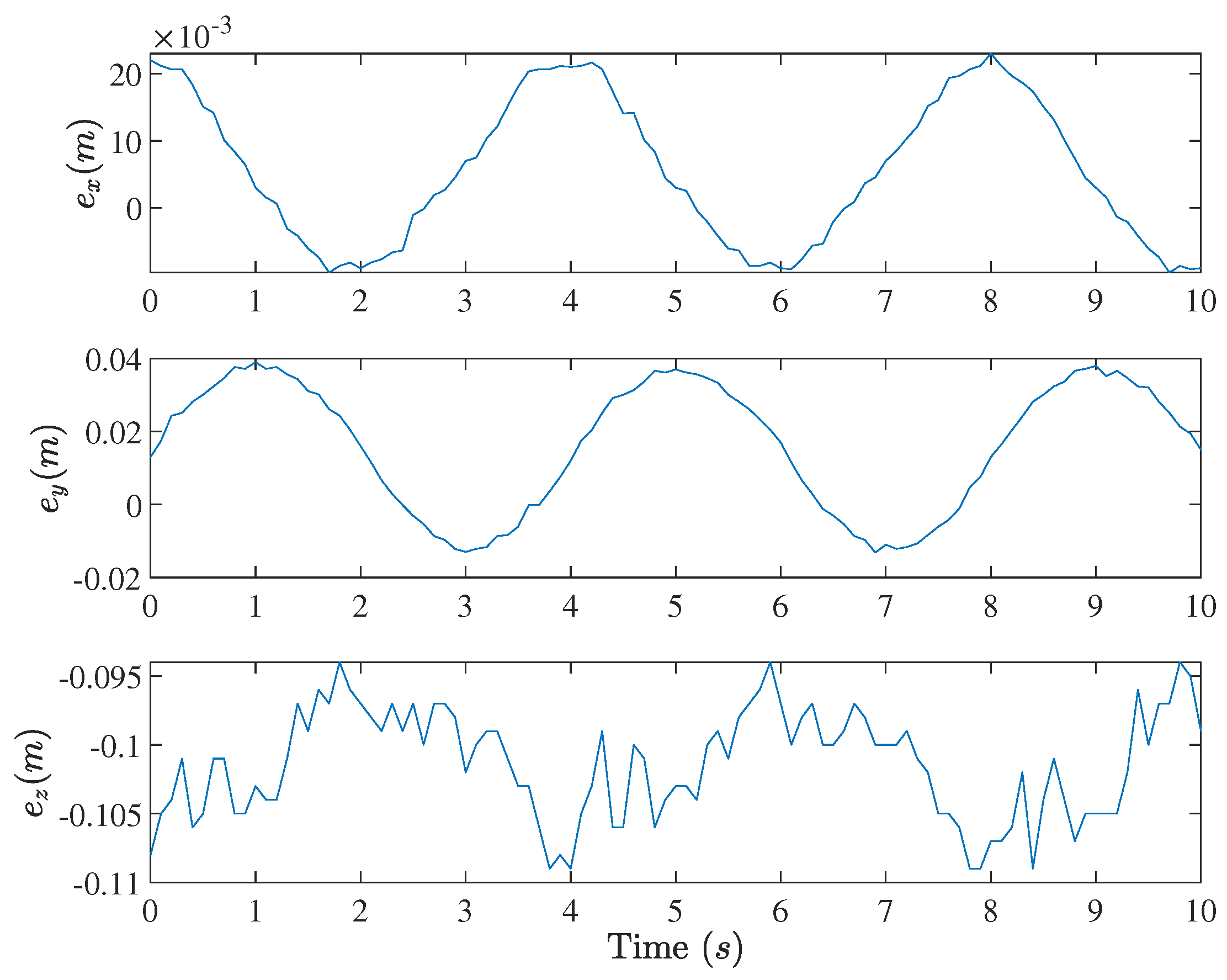
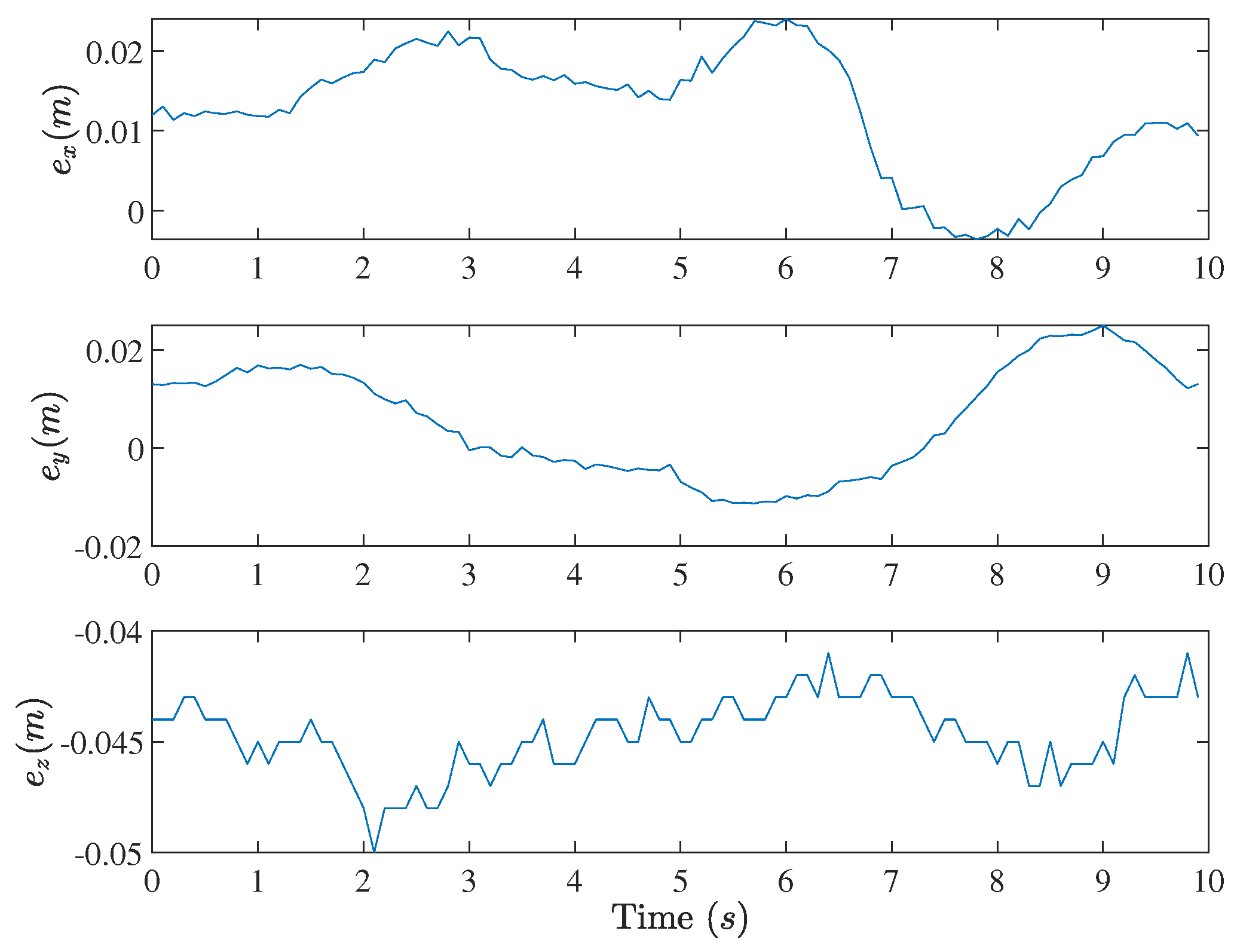
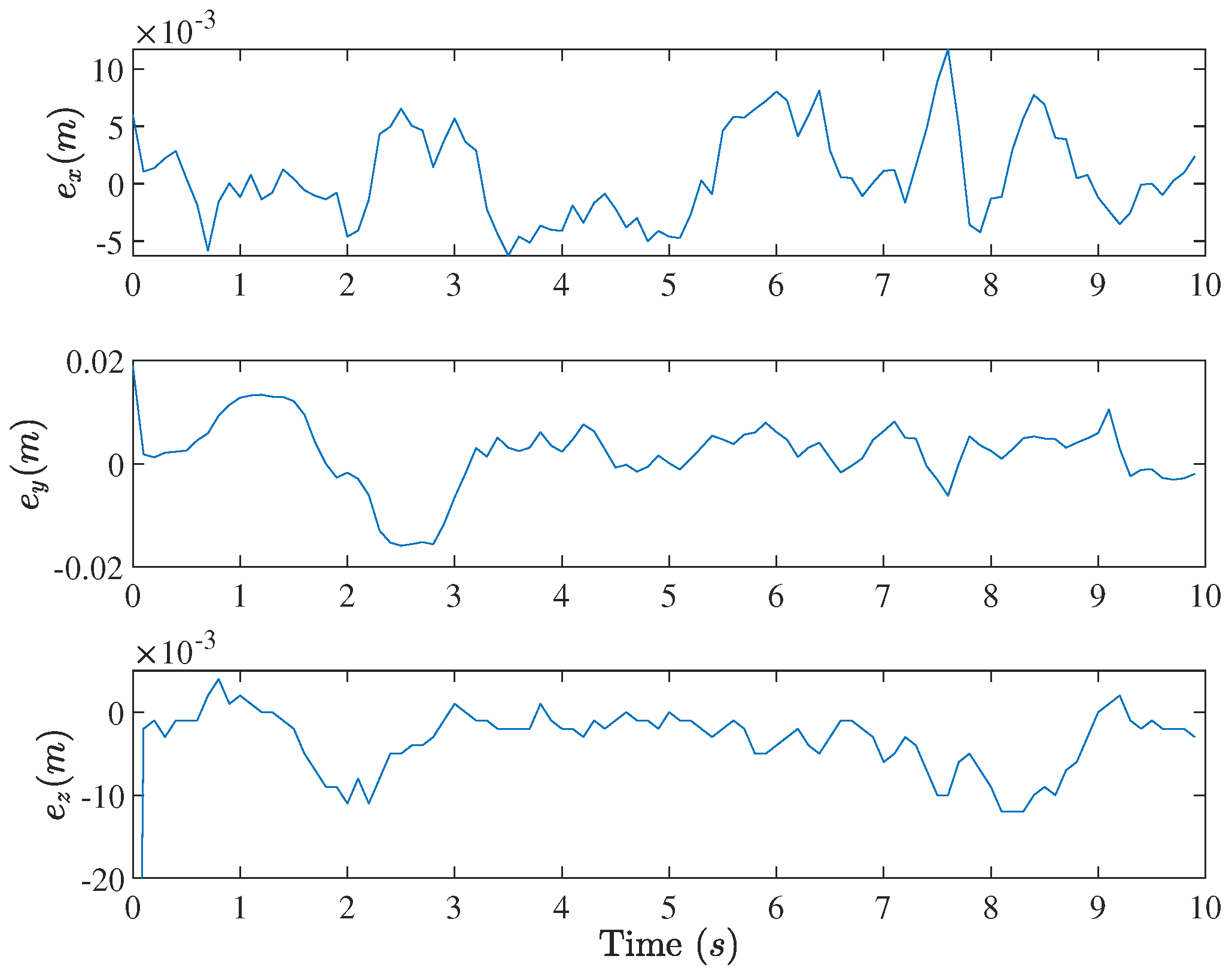
4. Experimental Validations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Castañeda, L.A.; Luviano-Juárez, A.; Chairez, I. Robust trajectory tracking of a Delta robot through adaptive active disturbance rejection control. IEEE Trans. Control Syst. Technol. 2014, 23, 1387–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angel, L.; Viola, J. Fractional order PID for tracking control of a parallel robotic manipulator type delta. ISA Trans. 2018, 79, 172–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, Y.L.; Huang, P.Y. Experimental and simulation studies of motion control of a Delta robot using a model-based approach. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2017, 14, 1729881417738738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, M.; Castillo, E.; García, G.; Bashir, A. Delta robot: Inverse, direct, and intermediate Jacobians. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2006, 220, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zsombor-Murray, P. Descriptive Geometric Kinematic Analysis of Clavel’s “Delta” Robot; Centre of Intelligent Machines, McGill University: Montreal, QC, Canada, 2004; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Abed Azad, F.; Ansari Rad, S.; Hairi Yazdi, M.R.; Tale Masouleh, M.; Kalhor, A. Dynamics analysis, offline–online tuning and identification of base inertia parameters for the 3-DOF Delta parallel robot under insufficient excitations. Meccanica 2022, 57, 473–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzunovic, T.; Golubovic, E.; Baran, E.A.; Sabanovic, A. Configuration space control of a parallel Delta robot with a neural network based inverse kinematics. In Proceedings of the 2013 8th International Conference on Electrical and Electronics Engineering (ELECO), Bursa, Turkey, 28–30 November 2013; pp. 497–501. [Google Scholar]
- Almusawi, A.R.; Dülger, L.C.; Kapucu, S. A new artificial neural network approach in solving inverse kinematics of robotic arm. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2016, 2016, 5720163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zubizarreta, A.; Larrea, M.; Irigoyen, E.; Cabanes, I.; Portillo, E. Real time direct kinematic problem computation of the 3PRS robot using neural networks. Neurocomputing 2018, 271, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tejomurtula, S.; Kak, S. Inverse kinematics in robotics using neural networks. Inf. Sci. 1999, 116, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Peng, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H. A new solution for inverse kinematics of 7-DOF manipulator based on neural network. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Conference on Automation and Logistics, Jinan, China, 18–21 August 2007; pp. 1958–1962. [Google Scholar]
- Singla, A.; Narayan, J.; Arora, H. Investigating the potential of redundant manipulators in narrow channels. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 2021, 235, 3723–3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Luo, M.; Pang, F. An algorithm for solving robot inverse kinematics based on FOA optimized BP neural network. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 7129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šegota, S.B.; Anđelić, N.; Mrzljak, V.; Lorencin, I.; Kuric, I.; Car, Z. Utilization of multilayer perceptron for determining the inverse kinematics of an industrial robotic manipulator. Int. J. Adv. Robot. Syst. 2021, 18, 1729881420925283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamseldin, M. Real-time inverse dynamic deep neural network tracking control for Delta robot based on a COVID-19 optimization. J. Robot. Control 2023, 4, 643–649. [Google Scholar]
- Boanta, C.; Brişan, C. Estimation of the kinematics and workspace of a robot Using artificial neural networks. Sensors 2022, 22, 8356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iklima, Z.; Muthahhar, M.I.; Khan, A.; Zody, A. Self-learning of Delta robot using inverse kinematics and artificial neural networks. Sinergi 2021, 25, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, A.; Homayouni, T.; Ehsani, R.; Sun, J.Q. Inverse kinematic control of a Delta robot using neural networks in real-time. Robotics 2021, 10, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, A.; Sun, J.Q.; Ehsani, R. Neural networks based optimal tracking control of a Delta robot with unknown dynamics. Int. J. Control Autom. Syst. 2023, 21, 3382–3390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- Abadi, M.; Agarwal, A.; Barham, P.; Brevdo, E.; Chen, Z.; Citro, C.; Corrado, G.S.; Davis, A.; Dean, J.; Devin, M.; et al. TensorFlow: Large-Scale Machine Learning on Heterogeneous Systems. arXiv 2016, arXiv:1603.04467. [Google Scholar]







| Description | Notation | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Radius of the fixed platform | R | 0.325 m |
| Radius of the moving platform | r | 0.075 m |
| Length of the active arm | 0.5 m | |
| Length of the passive arm | 0.25 m | |
| Mass of the active arm | 0.205 kg | |
| Mass of the passive arm | 0.153 kg | |
| Mass of the end effector | 0.653 kg |
| Product | Model | Specification |
|---|---|---|
| Stepper Motor (Stepperonline, New York, NY, USA) | 23HS30-5004D-E1000 | Motor type: Bipolar |
| Holding torque: 2.00 N·m | ||
| Step accuracy: | ||
| Resistance: 0.42 | ||
| Inductance: 1.72 | ||
| Micro-steppping: 1600 pulses/rev | ||
| Stepper Motor Driver (Stepperonline) | CL57T | Weight: 290 g |
| Input voltage: 24–48 VDC | ||
| Pulse input frequency: 0–500 kHz | ||
| Min. Pulse width: 1 µS | ||
| Planetary Gearbox (Stepperonline) | PLE23-G10-D8 | Gear ratio: 10 |
| Efficiency: 94.00% | ||
| Max. Permissible Torque: 10 N·m | ||
| Moment permissible torque: 20 N·m | ||
| Backlash (arcmin): ≤15 | ||
| Noise ≤ 60 dB | ||
| Laser Sensor | VL53L1X | 50 Hz ranging frequency |
| Field-of-View: | ||
| Ranging error (mm): | ||
| IC interface | ||
| Raspberry Pi 4 | Model B | 64-bit Cortex-A72 processor |
| 4 GB LPDDR4 RAM |
| Algorithm | Curve | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Circle | Neural networks | 0.002 | 0.0038 | 0.0056 | 0.0112 |
| 0.006 | 0.0045 | 0.0057 | 0.0112 | ||
| 0.01 | 0.0059 | 0.0064 | 0.0111 | ||
| 0.02 | 0.0041 | 0.0047 | 0.0115 | ||
| Inverse Kinematics | 0.006 | 0.0122 | 0.0238 | 0.1015 | |
| Heart Curve | Neural networks | 0.002 | 0.004 | 0.0067 | 0.0128 |
| 0.006 | 0.004 | 0.0069 | 0.0128 | ||
| 0.01 | 0.004 | 0.0068 | 0.0126 | ||
| 0.02 | 0.0072 | 0.0081 | 0.0132 | ||
| Inverse Kinematics | 0.006 | 0.0148 | 0.0125 | 0.0447 | |
| Logarithmic Spiral | Neural networks | 0.002 | 0.0086 | 0.0041 | 0.0124 |
| 0.006 | 0.0097 | 0.0068 | 0.0068 | ||
| 0.01 | 0.0183 | 0.0101 | 0.0069 | ||
| 0.02 | 0.0125 | 0.0079 | 0.0100 | ||
| Inverse Kinematics | 0.006 | 0.0149 | 0.0087 | 0.0271 |
| (s) | mm/s |
|---|---|
| 0.002 | 46.5250 |
| 0.006 | 15.5083 |
| 0.01 | 9.3050 |
| 0.02 | 4.66525 |
| 0.006 | 0.0122 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, A.; Toudeshki, A.; Ehsani, R.; Sun, J.-Q. Data-Driven Inverse Kinematics Approximation of a Delta Robot with Stepper Motors. Robotics 2023, 12, 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics12050135
Zhao A, Toudeshki A, Ehsani R, Sun J-Q. Data-Driven Inverse Kinematics Approximation of a Delta Robot with Stepper Motors. Robotics. 2023; 12(5):135. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics12050135
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Anni, Arash Toudeshki, Reza Ehsani, and Jian-Qiao Sun. 2023. "Data-Driven Inverse Kinematics Approximation of a Delta Robot with Stepper Motors" Robotics 12, no. 5: 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics12050135
APA StyleZhao, A., Toudeshki, A., Ehsani, R., & Sun, J.-Q. (2023). Data-Driven Inverse Kinematics Approximation of a Delta Robot with Stepper Motors. Robotics, 12(5), 135. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics12050135







