A Helical Microrobot with an Optimized Propeller-Shape for Propulsion in Viscoelastic Biological Media
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
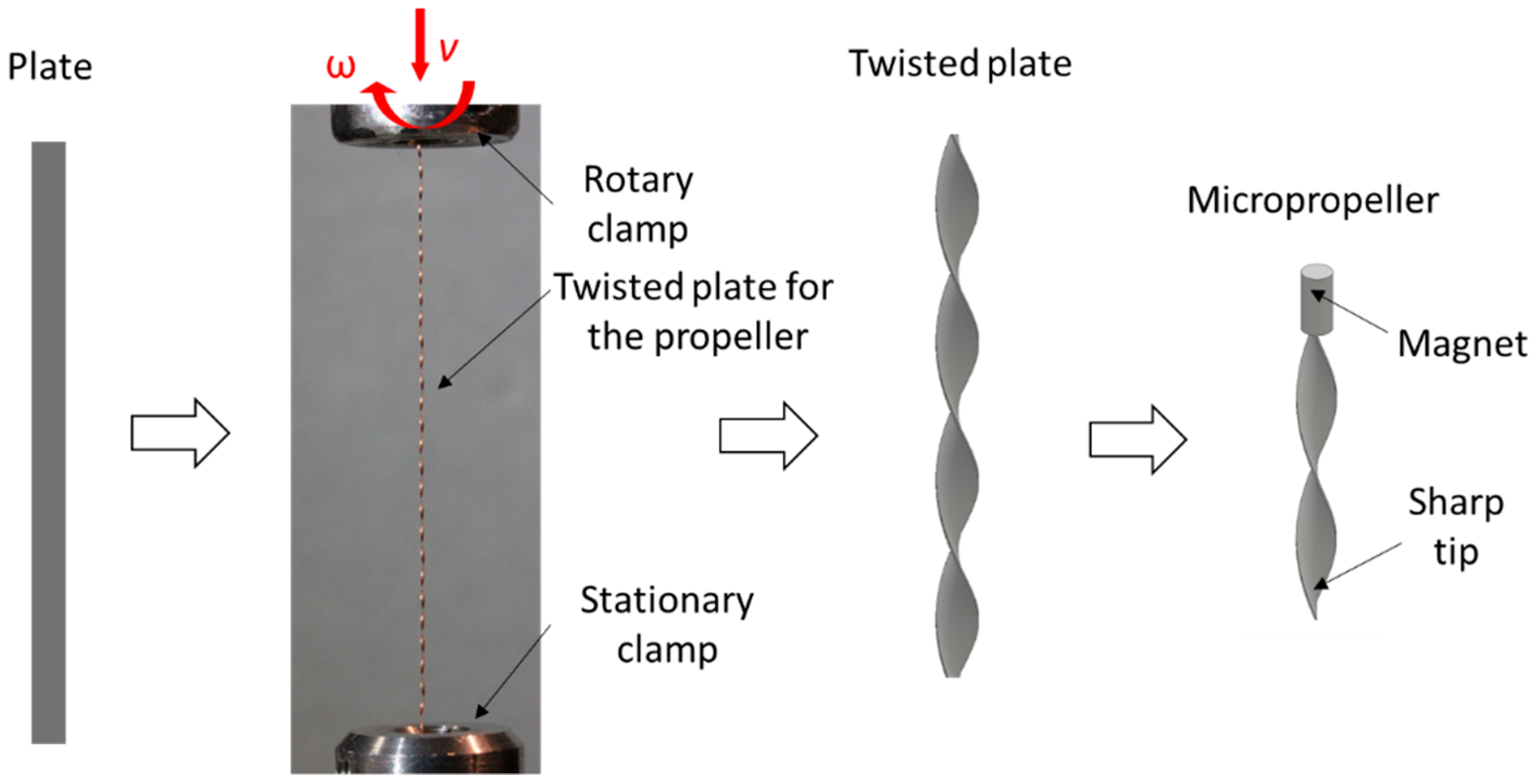
2.1. Fabrication of the Micropropellers
2.2. Etching of the Sharp Tips
2.3. Magnetic Actuation Set-up
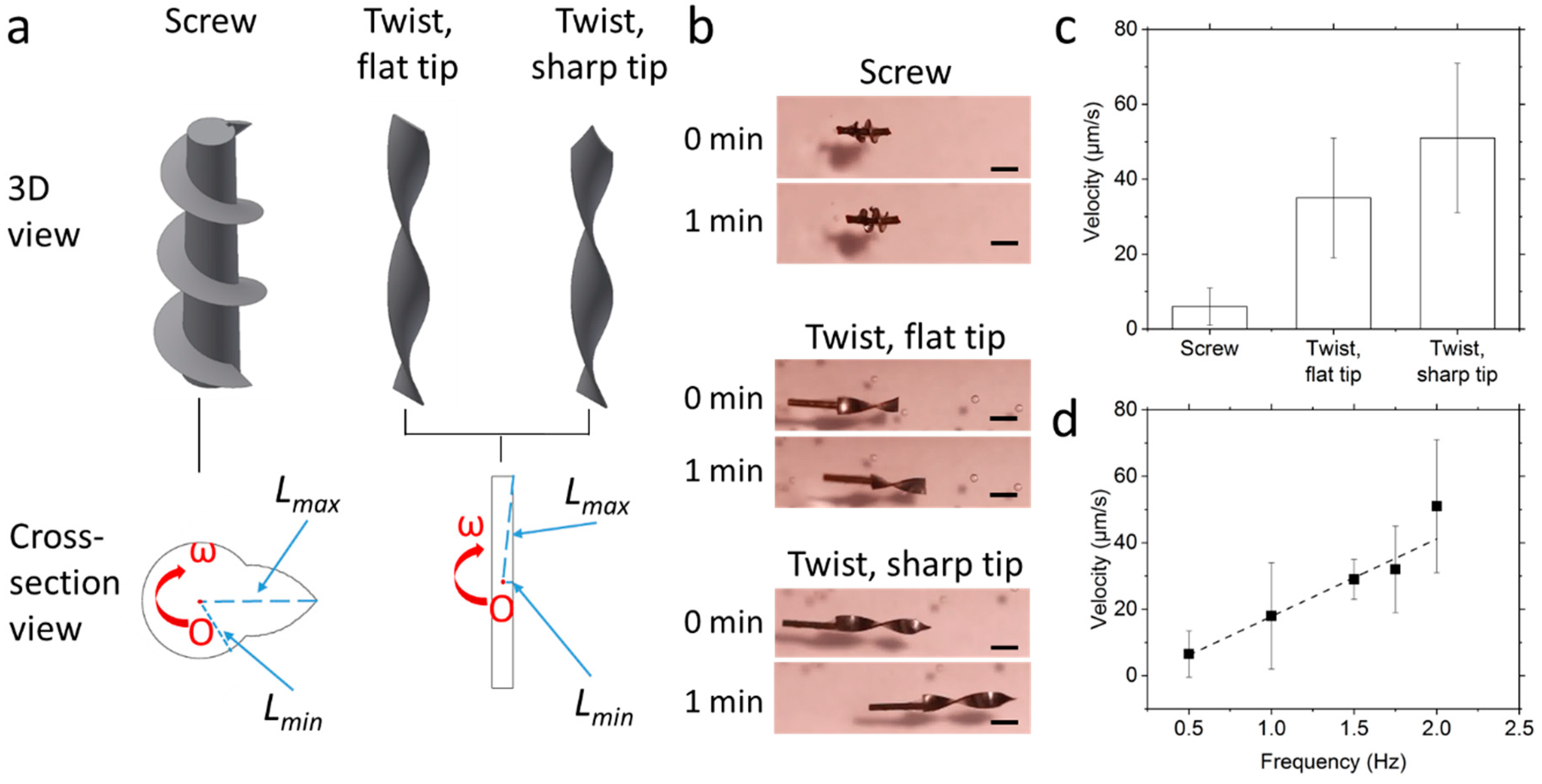
2.4. Propulsion Tests
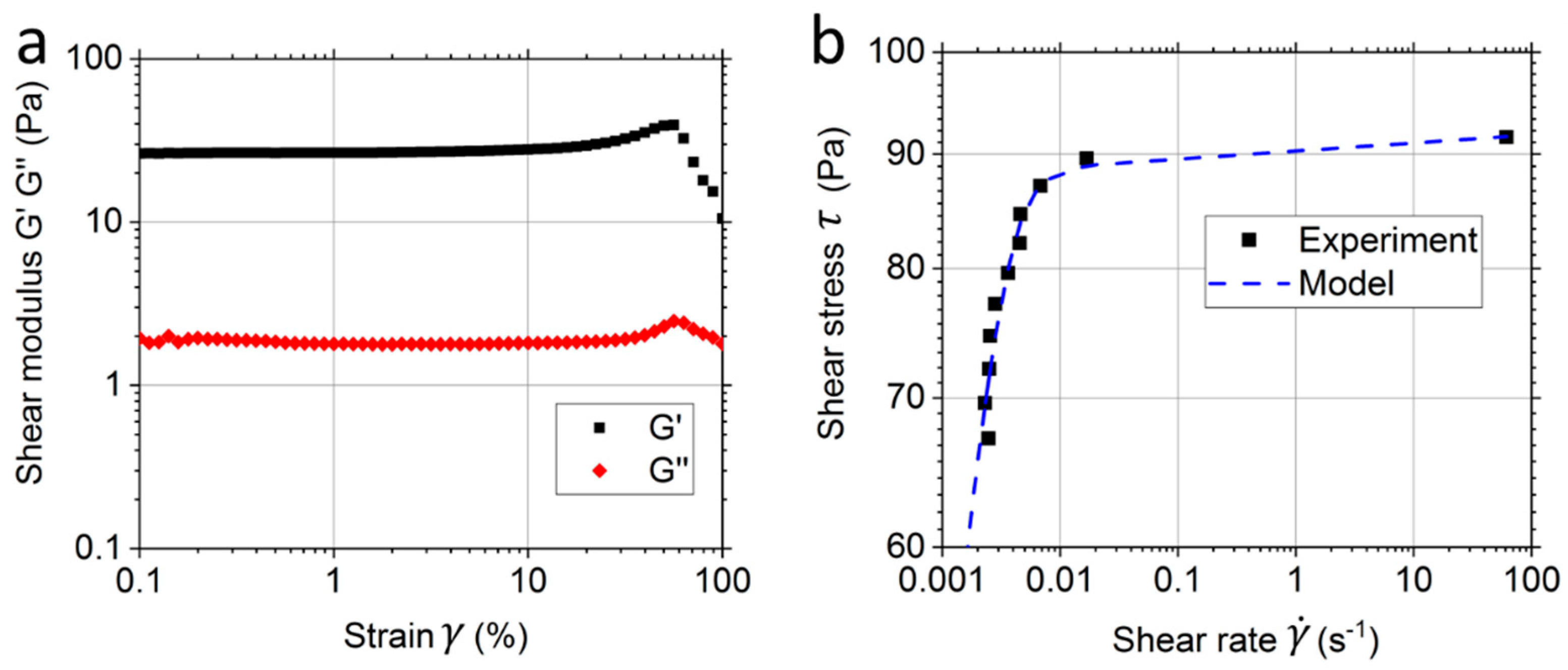
2.5. Rheology Measurement
3. Results
3.1. Fabrication of the Micropropellers
3.2. Rheological Results and Modelling of the Matrigel
3.3. Propulsion in the Matrigel
3.4. Propulsion in the Mouse Liver
4. Discussion
5. Patent
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, J.X.; de Avila, B.E.F.; Gao, W.; Zhang, L.F.; Wang, J. Micro/nanorobots for biomedicine: Delivery, surgery, sensing, and detoxification. Sci. Robot. 2017, 2, eaam6431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fung, Y.C. Biomechanics; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Esteban-Fernandez de Avila, B.; Angsantikul, P.; Li, J.X.; Lopez-Ramirez, M.A.; Ramirez-Herrera, D.E.; Thamphiwatana, S.; Chen, C.R.; Delezuk, J.; Samakapiruk, R.; Ramez, V.; et al. Micromotor-enabled active drug delivery for in vivo treatment of stomach infection. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.G.; Li, L.; Yang, Y.R.; Hu, P.; Li, Y.; Yang, S.Y.O.; Wang, L.V.; Gao, W. A microrobotic system guided by photoacoustic computed tomography for targeted navigation in intestines in vivo. Sci. Robot. 2019, 4, eaax0613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Servant, A.; Qiu, F.; Mazza, M.; Kostarelos, K.; Nelson, B.J. Controlled In Vivo Swimming of a Swarm of Bacteria-Like Microrobotic Flagella. Adv. Mater. 2015, 27, 2981–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, T.; Lee, T.C.; Mark, A.G.; Morozov, K.I.; Munster, R.; Mierka, O.; Turek, S.; Leshansky, A.M.; Fischer, P. Swimming by reciprocal motion at low Reynolds number. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, Z.G.; Troll, J.; Jeong, H.H.; Wei, Q.; Stang, M.; Ziemssen, F.; Wang, Z.G.; Dong, M.D.; Schnichels, S.; Qiu, T.; et al. A swarm of slippery micropropellers penetrates the vitreous body of the eye. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaat4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Peyer, K.E.; Tottori, S.; Qiu, F.M.; Zhang, L.; Nelson, B.J. Magnetic Helical Micromachines. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishiyama, K.; Sendoh, M.; Yamazaki, A.; Arai, K.I. Swimming micro-machine driven by magnetic torque. Sens. Actuat. A Phys. 2001, 91, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmer, J.; Stehning, C.; Gleich, B. Remote magnetic actuation using a clinical scale system. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, S.; Choi, H.; Cha, K.; Li, J.; Park, J.O.; Park, S. Enhanced locomotive and drilling microrobot using precessional and gradient magnetic field. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2011, 171, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.T.; Yu, J.F.; Yan, X.H.; Choi, H.; Zhang, L. Magnetic Actuation Based Motion Control for Microrobots: An Overview. Micromachines 2015, 6, 1346–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibe, J.P.; Bey, P.P.; Brandow, S.L.; Brizzolara, R.A.; Burnham, N.A.; Dilella, D.P.; Lee, K.P.; Marrian, C.R.K.; Colton, R.J. On the Electrochemical Etching of Tips for Scanning Tunneling Microscopy. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 1990, 8, 3570–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, T.; Palagi, S.; Sachs, J.; Fischer, P. Soft Miniaturized Linear Actuators Wirelessly Powered by Rotating Permanent Magnets. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), Brisbane, Australia, 21–25 May 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Jeong, M.; Choi, E.; Li, D.; Palagi, S.; Fischer, P.; Qiu, T. A Magnetic Actuation System for the Active Microrheology in Soft Biomaterials. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Manipulation Automation and Robotics at Small Scales (MARSS), Helsinki, Finland, 13–17 July 2019; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Mezger, T.G. The Rheology Handbook, 3rd ed.; Vincentz Network: Hanover, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mitsoulis, E. Flows of Viscoplastic Materials: Models and Computations. Rheol. Rev. 2007, 2007, 135–178. [Google Scholar]
- Zuidema, J.M.; Rivet, C.J.; Gilbert, R.J.; Morrison, F.A. A protocol for rheological characterization of hydrogels for tissue engineering strategies. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B 2014, 102, 1063–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, S.L.; Lyshchik, A.; Washington, M.K.; Gore, J.C.; Miga, M.I. Development of a mechanical testing assay for fibrotic murine liver. Med. Phys. 2007, 34, 4439–4450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Abbott, J.J.; Dong, L.X.; Kratochvil, B.E.; Bell, D.; Nelson, B.J. Artificial bacterial flagella: Fabrication and magnetic control. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 064107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schamel, D.; Mark, A.G.; Gibbs, J.G.; Miksch, C.; Morozov, K.I.; Leshansky, A.M.; Fischer, P. Nanopropellers and Their Actuation in Complex Viscoelastic Media. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 8794–8801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tottori, S.; Zhang, L.; Qiu, F.M.; Krawczyk, K.K.; Franco-Obregon, A.; Nelson, B.J. Magnetic Helical Micromachines: Fabrication, Controlled Swimming, and Cargo Transport. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 811–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, K.; Ikuta, K. 3D Magnetic Microactuator Made of Newly Developed Magnetically Modified Photocurable Polymer and Application to Swimming Micromachine and Microscrewpump. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE 22nd International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems, Sorrento, Italy, 25–29 January 2009; pp. 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Fischbach, C.; Chen, R.; Matsumoto, T.; Schmelzle, T.; Brugge, J.S.; Polverini, P.J.; Mooney, D.J. Engineering tumors with 3D scaffolds. Nat. Methods 2007, 4, 855–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langhans, S.A. Three-Dimensional in Vitro Cell Culture Models in Drug Discovery and Drug Repositioning. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, D.; Jeong, M.; Oren, E.; Yu, T.; Qiu, T. A Helical Microrobot with an Optimized Propeller-Shape for Propulsion in Viscoelastic Biological Media. Robotics 2019, 8, 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics8040087
Li D, Jeong M, Oren E, Yu T, Qiu T. A Helical Microrobot with an Optimized Propeller-Shape for Propulsion in Viscoelastic Biological Media. Robotics. 2019; 8(4):87. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics8040087
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Dandan, Moonkwang Jeong, Eran Oren, Tingting Yu, and Tian Qiu. 2019. "A Helical Microrobot with an Optimized Propeller-Shape for Propulsion in Viscoelastic Biological Media" Robotics 8, no. 4: 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics8040087
APA StyleLi, D., Jeong, M., Oren, E., Yu, T., & Qiu, T. (2019). A Helical Microrobot with an Optimized Propeller-Shape for Propulsion in Viscoelastic Biological Media. Robotics, 8(4), 87. https://doi.org/10.3390/robotics8040087





