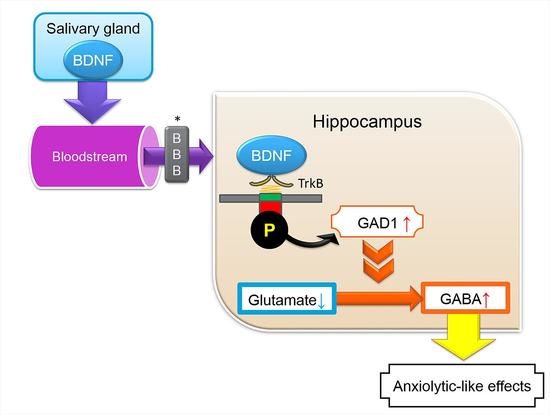
Salivary Gland Derived BDNF Overexpression in Mice Exerts an Anxiolytic Effect
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Expression of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor-Hemagglutinin (Bdnf-HA) Transgene
2.2. Analysis of BDNF-HA Protein
2.3. Analysis of Endogenous or Total BDNF and Phospho-TrkB
2.4. Anxiolytic-Like Behavior in Bdnf-HA Generated Transgenic (TG) Mice
2.5. Anxiolytic-Like Behavior of Sialoadenectomized Bdnf-HA TG Mice
2.6. Metabolome Analysis in the Hippocampus
2.7. Glutamate Decarboxylase 1 (Gad1) mRNA Expression in the Hippocampus
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Generation of Transgenic Mice
4.2. Sialoadenectomy Model
4.3. Sample Collection
4.4. RNA Isolation and RT-PCR
4.5. Immunoblotting
4.6. Immunohistochemistry
4.7. ELISA Analysis
4.8. Behavioral Tests
4.9. Metabolic Analyses of the Hippocampus
4.9.1. Metabolomic Analyses
4.9.2. Processing of Tissue
4.9.3. Data Analysis for Metabolomic Data
4.10. Real-Time PCR
4.11. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Ab | Antibody |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| BDNF | Brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| GABA | γ-Aminobutyric acid |
| GAD1 | Glutamate decarboxylase 1 |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| HA | Hemagglutinin |
| HRP | Horseradish peroxidase |
| OF | Open field |
| SEM | Standard error of the mean |
| TG | Transgenic |
| TrkB | Tyrosine kinase B |
| UDP | Uridine diphosphate |
References
- Monteggia, L.M.; Barrot, M.; Powell, C.M.; Berton, O.; Galanis, V.; Gemelli, T.; Meuth, S.; Nagy, A.; Greene, R.W.; Nestler, E.J. Essential role of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in adult hippocampal function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 10827–10832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpova, N.N. Role of BDNF epigenetics in activity-dependent neuronal plasticity. Neuropharmacology 2014, 76 Pt C, 709–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziemlinska, E.; Kugler, S.; Schachner, M.; Wewior, I.; Czarkowska-Bauch, J.; Skup, M. Overexpression of BDNF increases excitability of the lumbar spinal network and leads to robust early locomotor recovery in completely spinalized rats. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, H.D.; Duman, R.S. Peripheral BDNF produces antidepressant-like effects in cellular and behavioral models. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010, 35, 2378–2391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nibuya, M.; Nestler, E.J.; Duman, R.S. Chronic antidepressant administration increases the expression of cAMP response element binding protein (CREB) in rat hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 2365–2372. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gil-Ad, I.; Portnoy, M.; Tarasenko, I.; Bidder, M.; Kramer, M.; Taler, M.; Weizman, A. A novel analog of olanzapine linked to sarcosinyl moiety (PGW5) demonstrates high efficacy and good safety profile in mouse models of schizophrenia. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014, 24, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydemir, C.; Yalcin, E.S.; Aksaray, S.; Kisa, C.; Yildirim, S.G.; Uzbay, T.; Goka, E. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) changes in the serum of depressed women. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2006, 30, 1256–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castren, E.; Voikar, V.; Rantamaki, T. Role of neurotrophic factors in depression. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2007, 7, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson Ray, M.; Weickert, C.S.; Wyatt, E.; Webster, M.J. Decreased BDNF, trkB-TK+ and GAD67 mRNA expression in the hippocampus of individuals with schizophrenia and mood disorders. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2011, 36, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenalti, G.; Law, R.H.; Buckle, A.M.; Langendorf, C.; Tuck, K.; Rosado, C.J.; Faux, N.G.; Mahmood, K.; Hampe, C.S.; Banga, J.P.; et al. GABA production by glutamic acid decarboxylase is regulated by a dynamic catalytic loop. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2007, 14, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makinson, R.; Lundgren, K.H.; Seroogy, K.B.; Herman, J.P. Chronic social subordination stress modulates glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) 67 mRNA expression in central stress circuits. Physiol. Behav. 2015, 146, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duman, C.H.; Schlesinger, L.; Terwilliger, R.; Russell, D.S.; Newton, S.S.; Duman, R.S. Peripheral insulin-like growth factor-I produces antidepressant-like behavior and contributes to the effect of exercise. Behav. Brain Res. 2009, 198, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabel, K.; Fabel, K.; Tam, B.; Kaufer, D.; Baiker, A.; Simmons, N.; Kuo, C.J.; Palmer, T.D. VEGF is necessary for exercise-induced adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2003, 18, 2803–2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govindarajan, A.; Rao, B.S.; Nair, D.; Trinh, M.; Mawjee, N.; Tonegawa, S.; Chattarji, S. Transgenic brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression causes both anxiogenic and antidepressant effects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 13208–13213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpova, N.N.; Lindholm, J.S.; Kulesskaya, N.; Onishchenko, N.; Vahter, M.; Popova, D.; Ceccatelli, S.; Castren, E. TrkB overexpression in mice buffers against memory deficits and depression-like behavior but not all anxiety- and stress-related symptoms induced by developmental exposure to methylmercury. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ping, G.; Qian, W.; Song, G.; Zhaochun, S. Valsartan reverses depressive/anxiety-like behavior and induces hippocampal neurogenesis and expression of BDNF protein in unpredictable chronic mild stress mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2014, 124, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukinoki, K.; Saruta, J. Role of stress-related brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in the rat submandibular gland. Acta Histochem.Cytochem. 2012, 45, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saruta, J.; Tsukinoki, K.; Sasaguri, K.; Ishii, H.; Yasuda, M.; Osamura, Y.R.; Watanabe, Y.; Sato, S. Expression and localization of chromogranin A gene and protein in human submandibular gland. Cells Tissues Organs 2005, 180, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bigi, S.; Maestripieri, D.; Aloe, L.; Alleva, E. NGF decreases isolation-induced aggressive behavior, while increasing adrenal volume, in adult male mice. Physiol. Behav. 1992, 51, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzozowski, T.; Konturek, S.J.; Pytko-Polonczyk, J.; Warzecha, Z. Gastric adaptation to stress: Role of sensory nerves, salivary glands, and adrenal glands. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 1995, 30, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorita, J.; Camprecios, G.; Soley, M.; Ramirez, I. ErbB receptors protect the perfused heart against injury induced by epinephrine combined with low-flow ischemia. Growth Factors 2009, 27, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamano, S.; Huang, L.Y.; Ding, C.; Chiorini, J.A.; Goldsmith, C.M.; Wellner, R.B.; Golding, B.; Kotin, R.M.; Scott, D.E.; Baum, B.J. Recombinant adeno-associated virus serotype 2 vectors mediate stable interleukin 10 secretion from salivary glands into the bloodstream. Hum. Gene Ther. 2002, 13, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radka, S.F.; Holst, P.A.; Fritsche, M.; Altar, C.A. Presence of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in brain and human and rat but not mouse serum detected by a sensitive and specific immunoassay. Brain Res. 1996, 709, 122–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vicente, J.C.; Garcia-Suarez, O.; Esteban, I.; Santamaria, J.; Vega, J.A. Immunohistochemical localization of neurotrophins and neurotrophin receptors in human and mouse salivary glands. Ann. Anat. 1998, 180, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsubota, K.; Nishiyama, T.; Mishima, K.; Inoue, H.; Doi, T.; Hattori, Y.; Kodama, T.; Higuchi, A.; Hayashi, Y.; Saito, I. The role of fractalkine as an accelerating factor on the autoimmune exocrinopathy in mice. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 4753–4760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, I.; Haruta, K.; Shimuta, M.; Inoue, H.; Sakurai, H.; Yamada, K.; Ishimaru, N.; Higashiyama, H.; Sumida, T.; Ishida, H.; et al. Fas ligand-mediated exocrinopathy resembling Sjogren’s syndrome in mice transgenic for IL-10. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 2488–2494. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shirayama, Y.; Chen, A.C.; Nakagawa, S.; Russell, D.S.; Duman, R.S. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor produces antidepressant effects in behavioral models of depression. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 3251–3261. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Siuciak, J.A.; Lewis, D.R.; Wiegand, S.J.; Lindsay, R.M. Antidepressant-like effect of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 1997, 56, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirulli, F.; Berry, A.; Chiarotti, F.; Alleva, E. Intrahippocampal administration of BDNF in adult rats affects short-term behavioral plasticity in the Morris water maze and performance in the elevated plus-maze. Hippocampus 2004, 14, 802–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koponen, E.; Voikar, V.; Riekki, R.; Saarelainen, T.; Rauramaa, T.; Rauvala, H.; Taira, T.; Castren, E. Transgenic mice overexpressing the full-length neurotrophin receptor trkB exhibit increased activation of the trkB-PLCgamma pathway, reduced anxiety, and facilitated learning. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2004, 26, 166–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterhouse, E.G.; An, J.J.; Orefice, L.L.; Baydyuk, M.; Liao, G.Y.; Zheng, K.; Lu, B.; Xu, B. BDNF promotes differentiation and maturation of adult-born neurons through GABAergic transmission. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 14318–14330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subburaju, S.; Benes, F.M. Induction of the GABA cell phenotype: An in vitro model for studying neurodevelopmental disorders. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croll, S.D.; Suri, C.; Compton, D.L.; Simmons, M.V.; Yancopoulos, G.D.; Lindsay, R.M.; Wiegand, S.J.; Rudge, J.S.; Scharfman, H.E. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor transgenic mice exhibit passive avoidance deficits, increased seizure severity and in vitro hyperexcitability in the hippocampus and entorhinal cortex. Neuroscience 1999, 93, 1491–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunha, C.; Angelucci, A.; D’Antoni, A.; Dobrossy, M.D.; Dunnett, S.B.; Berardi, N.; Brambilla, R. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) overexpression in the forebrain results in learning and memory impairments. Neurobiol. Dis. 2009, 33, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikkelsen, T.R.; Brandt, J.; Larsen, H.J.; Larsen, B.B.; Poulsen, K.; Ingerslev, J.; Din, N.; Hjorth, J.P. Tissue-specific expression in the salivary glands of transgenic mice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992, 20, 2249–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saruta, J.; Lee, T.; Shirasu, M.; Takahashi, T.; Sato, C.; Sato, S.; Tsukinoki, K. Chronic stress affects the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in rat salivary glands. Stress 2010, 13, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saruta, J.; Kondo, Y.; Sato, C.; Shiiki, N.; Tsukinoki, K.; Sato, S. Salivary glands as the source of plasma brain-derived neurotrophic factor in stressed rats engaged in biting behavior. Stress 2010, 13, 238–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, Y.; To, M.; Saruta, J.; Hayashi, T.; Sugiyama, H.; Tsukinoki, K. Role of TrkB expression in rat adrenal gland during acute immobilization stress. J. Neurochem. 2013, 124, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- To, M.; Kamata, Y.; Saruta, J.; Shimizu, T.; Sato, T.; Kondo, Y.; Hayashi, T.; Hamada, N.; Tsukinoki, K. Induction of β-defensin expression by porphyromonas gingivalis-infected human gingival graft transplanted in nu/nu mouse subdermis. Acta Histochem. Cytochem. 2013, 46, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saruta, J.; Fujino, K.; To, M.; Tsukinoki, K. Expression and localization of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) mRNA and protein in human submandibular gland. Acta Histochem. Cytochem. 2012, 45, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukinoki, K.; Saruta, J.; Sasaguri, K.; Miyoshi, Y.; Jinbu, Y.; Kusama, M.; Sato, S.; Watanabe, Y. Immobilization stress induces BDNF in rat submandibular glands. J. Dent. Res. 2006, 85, 844–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, Y.; Saruta, J.; To, M.; Shiiki, N.; Sato, C.; Tsukinoki, K. Expression and role of the BDNF receptor-TrkB in rat adrenal gland under acute immobilization stress. Acta Histochem. Cytochem. 2010, 43, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chourbaji, S.; Hellweg, R.; Brandis, D.; Zorner, B.; Zacher, C.; Lang, U.E.; Henn, F.A.; Hortnagl, H.; Gass, P. Mice with reduced brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression show decreased choline acetyltransferase activity, but regular brain monoamine levels and unaltered emotional behavior. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 2004, 121, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawahata, M.; Ono, Y.; Ohno, A.; Kawamoto, S.; Kimoto, K.; Onozuka, M. Loss of molars early in life develops behavioral lateralization and impairs hippocampus-dependent recognition memory. BMC Neurosci. 2014, 15, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, M.; Ikeda, S.; Niigata, K.; Tomita, M.; Sato, H.; Soga, T. MMMDB: Mouse multiple tissue metabolome database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D809–D814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soga, T.; Igarashi, K.; Ito, C.; Mizobuchi, K.; Zimmermann, H.P.; Tomita, M. Metabolomic profiling of anionic metabolites by capillary electrophoresis mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 6165–6174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, S.; Sugimoto, M.; Kitabatake, K.; Sugano, A.; Nakamura, M.; Kaneko, M.; Ota, S.; Hiwatari, K.; Enomoto, A.; Soga, T.; et al. Identification of salivary metabolomic biomarkers for oral cancer screening. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, M.; Wong, D.T.; Hirayama, A.; Soga, T.; Tomita, M. Capillary electrophoresis mass spectrometry-based saliva metabolomics identified oral, breast and pancreatic cancer-specific profiles. Metabolomics 2010, 6, 78–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimoto, M.; Kawakami, M.; Robert, M.; Soga, T.; Tomita, M. Bioinformatics tools for mass spectroscopy-based metabolomic data processing and analysis. Curr. Bioinform. 2012, 7, 96–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saruta, J.; To, M.; Sugimoto, M.; Yamamoto, Y.; Shimizu, T.; Nakagawa, Y.; Inoue, H.; Saito, I.; Tsukinoki, K. Salivary Gland Derived BDNF Overexpression in Mice Exerts an Anxiolytic Effect. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1902. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091902
Saruta J, To M, Sugimoto M, Yamamoto Y, Shimizu T, Nakagawa Y, Inoue H, Saito I, Tsukinoki K. Salivary Gland Derived BDNF Overexpression in Mice Exerts an Anxiolytic Effect. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(9):1902. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091902
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaruta, Juri, Masahiro To, Masahiro Sugimoto, Yuko Yamamoto, Tomoko Shimizu, Yusuke Nakagawa, Hiroko Inoue, Ichiro Saito, and Keiichi Tsukinoki. 2017. "Salivary Gland Derived BDNF Overexpression in Mice Exerts an Anxiolytic Effect" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 9: 1902. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091902
APA StyleSaruta, J., To, M., Sugimoto, M., Yamamoto, Y., Shimizu, T., Nakagawa, Y., Inoue, H., Saito, I., & Tsukinoki, K. (2017). Salivary Gland Derived BDNF Overexpression in Mice Exerts an Anxiolytic Effect. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(9), 1902. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091902