Urban Quality of Life: Spatial Modeling and Indexing in Athens Metropolitan Area, Greece
Abstract
:1. Introduction
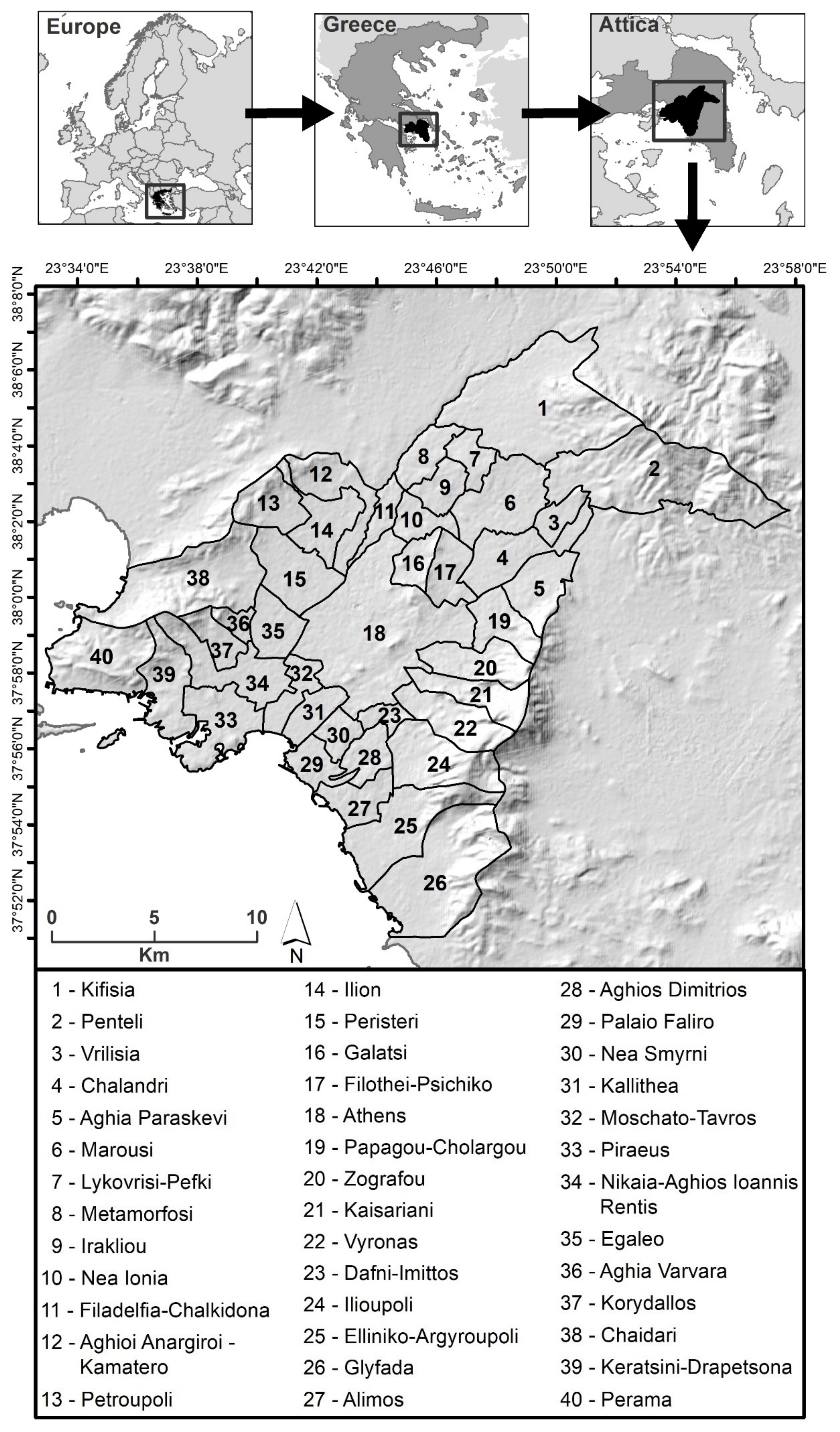
2. Study Area
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Criteria and Variables
3.2. GIS Modeling
- Ci = composite criterion
- n = number of variables
- Vi = variable.
- QoL = overall urban quality of life
- n = number of criteria
- Ci = composite criterion.
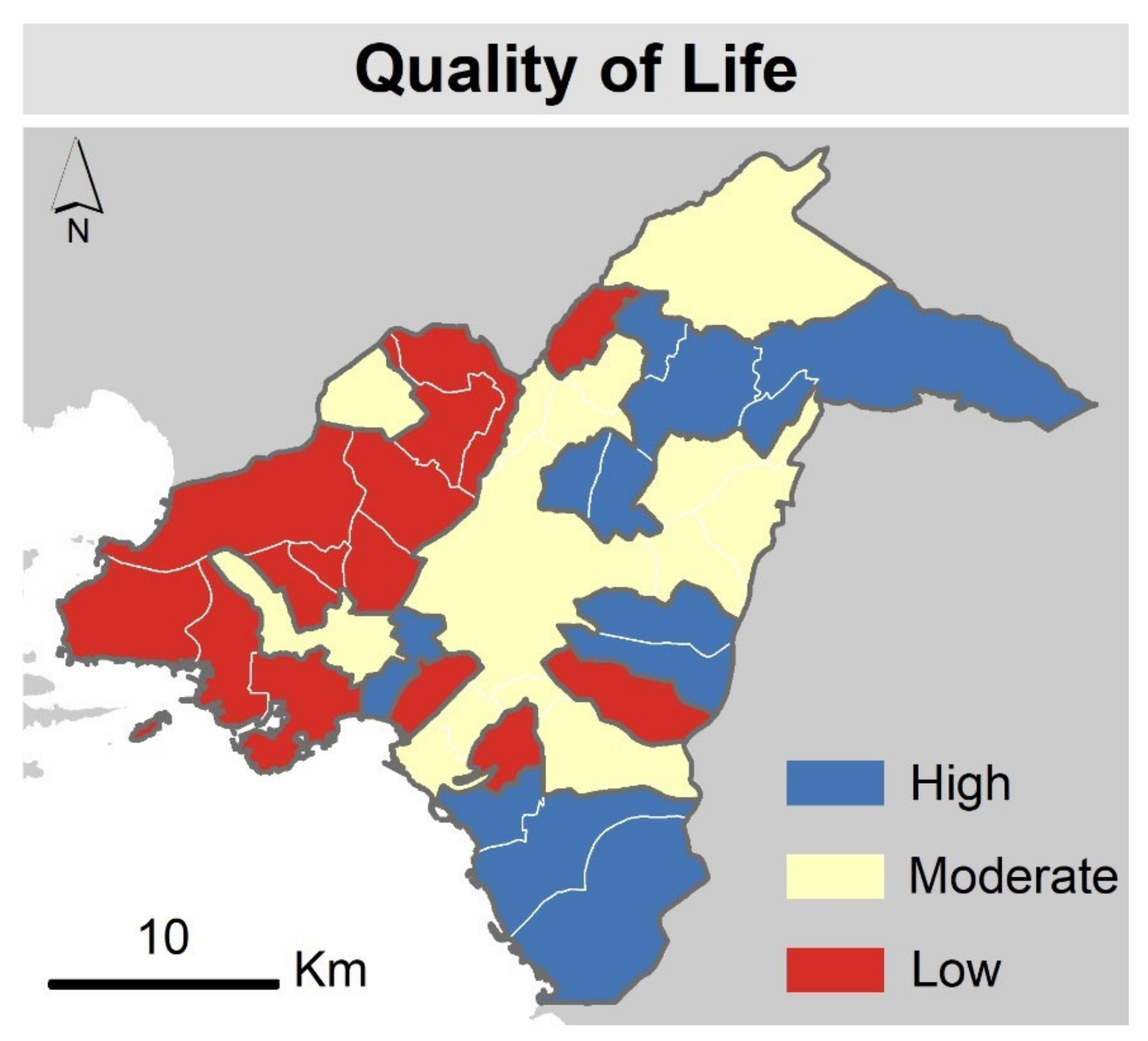
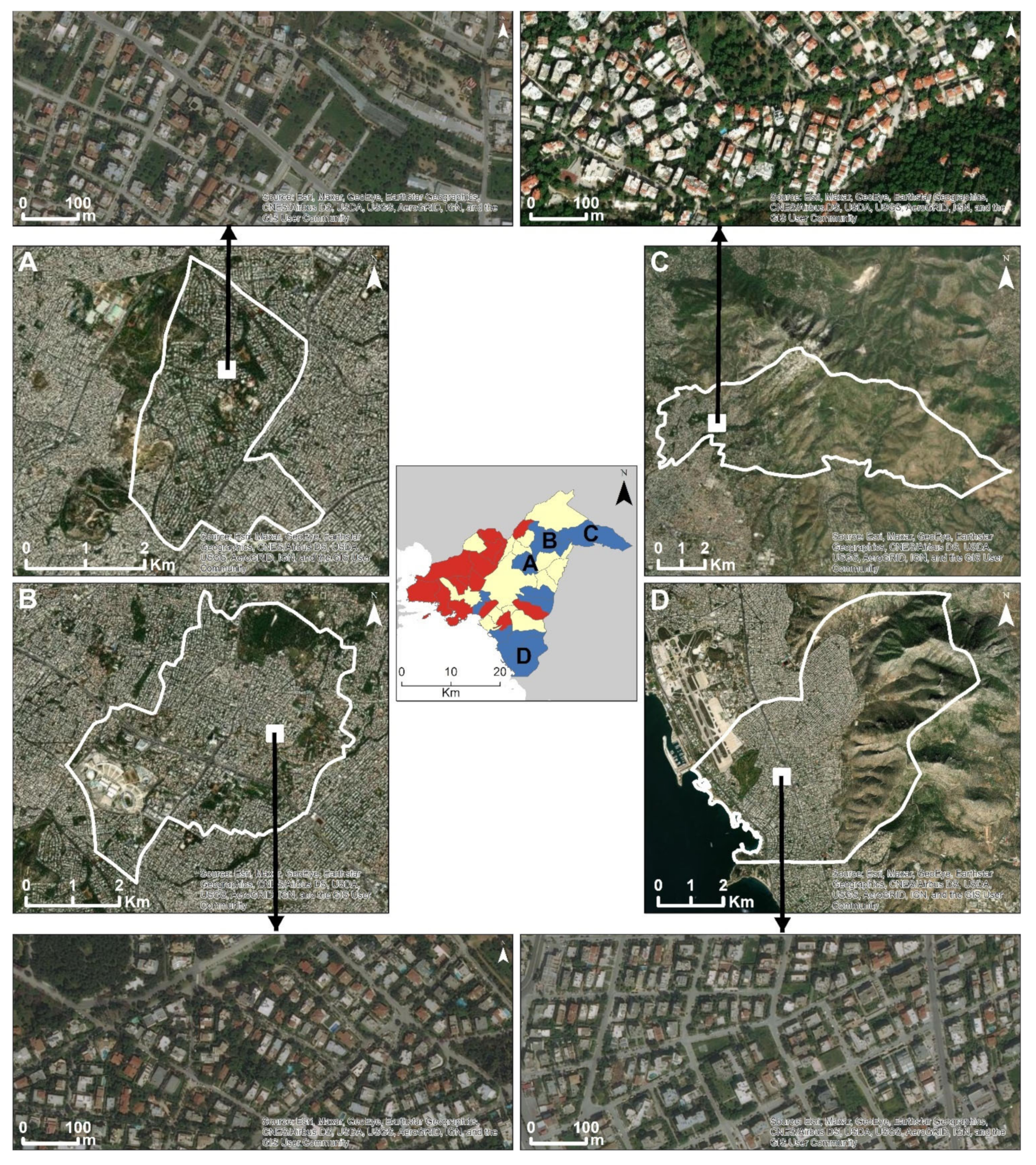
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schalock, R.L. Three Decades of Quality of Life. Focus Autism Other Dev. Disabil. 2000, 15, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farquhar, M. Definitions of quality of life: A taxonomy. J. Adv. Nurs. 1995, 22, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maggino, F.; Zumbo, B.D. Measuring the Quality of Life and the Construction of Social Indicators. In Handbook of Social Indicators and Quality of Life Research; Land, K.C., Michalos, A.C., Sirgy, M.J., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2012; pp. 201–238. [Google Scholar]
- Sirgy, M.J.; Michalos, A.C.; Ferriss, A.L.; Easterlin, R.A.; Patrick, D.; Pavot, W. The quality-of-life (QOL) research movement: Past, present, and future. Soc. Indic. Res. 2006, 76, 343–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, T.M. A Critical Appraisal of the Quality of Quality-of-Life Measurements. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 1994, 272, 619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHOQOL. User Manual. In Division of Mental Health and Prevention of Substance Abuse; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Faka, A. Assessing Quality of Life Inequalities. A Geographical Approach. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eurofound. Quality of Life in Europe—First European Quality of Life Survey; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Eurofound. Second European Quality of Life Survey-Overview; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Eurofound. Third European Quality of Life Survey—Quality of Life in Europe: Impacts of the Crisis; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Eurofound. European Quality of Life Survey 2016: Quality of Life, Quality of Public Services, and Quality of Society; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- European Commission. Quality of Life in European Cities 2015; Office for Official Publications of the European Communities: Luxembourg, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- EEA—European Environment Agency. Ensuring Quality of Life in Europe’s Cities and Towns, EEA Report No 5/2009; Office for Official Publications of the European Communities: Luxembourg, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Murgaš, F.; Klobučník, M. Municipalities and regions as good places to live: Index of quality of life in the Czech Republic. Appl. Res. Qual. Life 2016, 11, 553–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafpour, H.; Bigdeli Rad, V.; Lamit, H.B.; Rosley, M.S.F.B. The systematic review on quality of life in urban neighborhoods. Life Sci. J. 2014, 11, 355–364. [Google Scholar]
- Linares, S.; Mikkelsen, C.A.; Velázquez, G.A.; Celemín, J.P. Spatial Segregation and Quality of Life: Empirical Analysis of Medium-Sized Cities of Buenos Aires Province. In Indicators of Quality of Life in Latin America; Tonon, G., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2016; Volume 62, pp. 201–218. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez, J. Mapping dynamic indicators of quality of life: A case in Rosario, Argentina. Appl. Res. Qual. Life 2019, 14, 777–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCann, E.J. “Best places”: Interurban competition, quality of life and popular media discourse. Urban Stud. 2004, 41, 1909–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murgaš, F. Geographical conceptualization of quality of life. Ekol. Bratisl. 2016, 35, 309–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCrea, R.; Shyy, T.K.; Stimson, R. What is the Strength of the Link Between Objective and Subjective Indicators of Urban Quality of Life? Appl. Res. Qual. Life. 2006, 1, 79–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Weng, Q. Measuring the quality of life in city of Indianapolis by integration of remote sensing and census data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2007, 28, 249–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmahdi, A.; Afify, A. Development of a GIS tool for qualitative assessment of the Egyptian’s quality of life. Environmentalist 2007, 27, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemzadeh-Zow, A.; Darvishi Boloorani, A.; Samany, N.N.; Toomanian, A.; Pourahmad, A. Spatiotemporal modelling of urban quality of life (UQoL) using satellite images and GIS. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2018, 39, 6095–6116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Zhang, L.; Tao, S.; Xie, B. Spatial Accessibility to Healthcare Services in Metropolitan Suburbs: The Case of Qingpu, Shanghai. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 2019, 16, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, C.; Jin, S.; Tang, X.; Lu, C.; Li, H.; Pang, J. Spatio-Temporal Comprehensive Measurements of Chinese Citizens’ Health Levels and Associated Influencing Factors. Healthcare 2020, 8, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merschdorf, H.; Hodgson, M.E.; Blaschke, T. Modeling Quality of Urban Life Using a Geospatial Approach. Urban Sci. 2020, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bartoněk, D.; Bureš, J.; Švábenský, O. Evaluation of Influence of the Environment on the Choice of Buildings for Residential Living. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, T.; Lü, G.; Zhong, X.; Tang, H.; Ye, Y. Measuring Human-Scale Living Convenience through Multi-Sourced Urban Data and a Geodesign Approach: Buildings as Analytical Units. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giuffrida, N.; Le Pira, M.; Inturri, G.; Ignaccolo, M. Mapping with Stakeholders: An Overview of Public Participatory GIS and VGI in Transport Decision-Making. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abd El Karim, A.; Awawdeh, M.M. Integrating GIS Accessibility and Location-Allocation Models with Multicriteria Decision Analysis for Evaluating Quality of Life in Buraidah City, KSA. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vukmirovic, M.; Gavrilovic, S.; Stojanovic, D. The Improvement of the Comfort of Public Spaces as a Local Initiative in Coping with Climate Change. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez, J. The use of GIS and indicators to monitor intra-urban inequalities. A case study in Rosario, Argentina. Habitat Int. 2009, 33, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. How’s Life? 2017: Measuring Well-Being; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- UN-Habitat. Measurement of City Prosperity: Methodology and Metadata; United Nations Human Settlements Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Eurostat. Quality of Life Indicators. 2020. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/statistics-explained/index.php?title=Quality_of_life_indicators_-_measuring_quality_of_life (accessed on 23 December 2020).
- Pacione, M. Urban Environmental Quality and Human Well-Being—A Social Geographical Perspective. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2003, 65, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, R.B.; Noll, H. Conceptual Framework and Structure of a European System of Social Indicators, EU Reporting Paper No 9; Centre for Survey Re-Search and Methodology (ZUMA)—Social Indicators Department: Mannheim, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Hagerty, M.R.; Land, K.C. Constructing Summary Indices of Quality of Life: A Model for the Effect of Heterogeneous Importance Weights. Sociol. Methods Res. 2007, 35, 455–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eurofound. Monitoring Quality of Life in Europe; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Van Kamp, I.; Leidelmeijer, K.; Marsman, G. Urban environmental quality and human well-being: Towards a conceptual framework and demarcation of concepts; a literature study. Landsc. Urban. Plan. 2003, 65, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biagi, B.; Ladu, M.G.; Meleddu, M. Urban Quality of Life and Capabilities: An Experimental Study. Ecol. Econ. 2018, 150, 137–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabello Eras, J.J.; Covas Varela, D.; Hernández Pérez, G.D.; Sagastume Gutiérrez, A.; García Lorenzo, D.; Vandecasteele, C.; Hens, L. Comparative study of the urban quality of life in Cuban first-level cities from an objective dimension. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2014, 16, 195–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D. Urban quality of life: A case study of Guwahati. Soc. Indic. Res. 2008, 88, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feneri, A.M.; Vagiona, D.; Karanikolas, N. Measuring Quality of Life (QoL) in Urban Environment: An Integrated Approach. In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Environmental Science and Technology, Athens, Greece, 5–7 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Garau, C.; Pavan, V.M. Evaluating Urban Quality: Indicators and Assessment Tools for Smart Sustainable Cities. Sustainability 2018, 10, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peach, N.D.; Petach, L.A. Development and Quality of Life in Cities. Econ. Dev. Q. 2016, 30, 32–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Psatha, E.; Deffner, A.; Psycharis, Y. Defining the Quality of Urban Life: Which Factors Should Be Considered? In Proceedings of the 51st Congress of the European Regional Science Association: New Challenges for European Regions and Urban Areas in a Globalised World, Barcelona, Spain, 30 August 2011–3 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Blomquist, G.C. Measuring Quality of Life. In A Companion to Urban Economics; Arnott, R.J., McMillen, D.P., Eds.; Blackwell Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2006; pp. 479–482. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, L.D.; Martins, I. Monitoring urban quality of life: The porto experience. Soc. Indic. Res. 2007, 80, 411–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serag El Din, H.; Shalaby, A.; Farouh, H.E.; Elariane, S.A. Principles of urban quality of life for a neighborhood. HBRC J. 2013, 9, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Longley, P.A.; Goodchild, M.F.; Maguire, D.J.; Rhind, D.W. Geographic Information Systems and Science, 2nd ed.; John Wiley and Sons: Chichester, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Zunino, A.; Velázquez, G.; Celemín, J.P.; Mateos, C.; Hirsch, M.; Rodriguez, J.M. Evaluating the Performance of Three Popular Web Mapping Libraries: A Case Study Using Argentina’s Life Quality Index. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feneri, A.M.; Vagiona, D.; Karanikolas, N. Multi-criteria decision making to measure quality of life: An Integrated approach for implementation in the urban area of Thessaloniki, Greece. Appl. Res. Qual. Life 2015, 10, 573–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivaldi, E.; Bonatti, G.; Soliani, R. Composite index for quality of life in Italian cities: An application to URBES indicators. Rev. Econ. Financ. 2014, 4, 18–32. [Google Scholar]
- Mizgajski, A.; Walaszek, M.; Kaczmarek, T. Determinants of the quality of life in the communes of the poznań agglomeration: A quantitative approach. Quaest. Geogr. 2014, 33, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eurostat—Spatial Units. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/web/cities/spatial-units (accessed on 25 April 2021).
- Kandylis, G.; Maloutas, T.; Sayas, J. Immigration, inequality and diversity: Socio-ethnic hierarchy and spatial organization in Athens, Greece. Eur. Urban Reg. Stud. 2012, 19, 67–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pukeliene, V.; Starkauskiene, V. Quality of life: Factors determining its measurement complexity. Eng. Econ. 2011, 22, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Başkan, A.H.; Zorba, E.; Bayrakdar, A. Impact of the population density on quality of life. J. Hum. Sci. 2017, 14, 506–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Winters, J.V.; Li, Y. Urbanisation, natural amenities and subjective well-being: Evidence from US counties. Urban Stud. 2017, 54, 1956–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, V.; Torgersen, S.; Kringlen, E. Quality of life in a city: The effect of population density. Soc. Indic. Res. 2004, 69, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Science for Environment Policy. What Are the Health Costs of Environmental Pollution? Future Brief 21. Brief Produced for the European Commission DG Environment by the Science Communication Unit; UWE: Bristol, UK, 2018; Available online: http://ec.europa.eu/science-environment-policy (accessed on 17 December 2020).
- Eurofound. Third European Quality of Life Survey—Quality of Life in Europe: Social Inequalities; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2013; Available online: https://www.eurofound.europa.eu/sites/default/files/ef_publication/field_ef_document/ef1362en.pdf (accessed on 17 December 2020).
- OECD. How’s Life? 2013: Measuring Well-Being; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2013; Available online: http://www.oecd.org/sdd/3013071e.pdf (accessed on 17 December 2020).
- Rose, R.; Munro, N.; Wallace, C. Second European Quality of Life Survey: Quality of Life in Europe 2003–2007; European Foundation for the Improvement of Living and Working Conditions: Dublin, Ireland, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- UNESCO Institute for Statistics. International Standard Classification of Education ISCED 2011; UNESCO Institute for Statistics: Montréal, QC, Canada, 2012; Available online: http://uis.unesco.org/sites/default/files/documents/international-standard-classification-of-education-isced-2011-en.pdf (accessed on 17 December 2020).
- Sirgy, M.J.; Cornwell, T. How neighborhood features affect quality of life. Soc. Indic. Res. 2002, 59, 79–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witten, K.; Exeter, D.; Field, A. The quality of urban environments: Mapping variation in access to community resources. Urban Stud. 2003, 40, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weziak-Białowolska, D. Quality of life in cities—Empirical evidence in comparative European perspective. Cities 2016, 58, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apparicio, P.; Séguin, A.M.; Naud, D. The quality of the urban environment around public housing buildings in Montréal: An objective approach based on GIS and multivariate statistical analysis. Soc. Indic. Res. 2008, 86, 355–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzi, F.; Türkoğlu, H.D.; Bölen, F.; Baran, P.K.; Salihoğlu, T. Residents’ Perception of Cultural Activities as Quality of Life in Istanbul. Soc. Indic. Res. 2015, 122, 211–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marans, R.W.; Kweon, B. The quality of life in metro Detroit at the beginning of the millennium. In Investigating Quality of Urban Life; Marans, R.W., Stimson, R., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Beggs, B.A.; Elkins, D.J.; The influence of leisure motivation on leisure satisfaction. LARNet; The Cyber Journal of Applied Leisure and Recreation Research. 2010. Available online: http://larnet.org/2010-02.html (accessed on 23 December 2020).
- Oldenburg, R. The Great Good Place; Marlowe & Co.: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd, K.M.; Auld, C.J. The role of leisure in determining quality of life: Issues of content and measurement. Soc. Indic. Res. 2002, 57, 43–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenks, G.F. Optimal Data Classification for Choropleth Maps. In University of Kansas Occasional Paper; University of Kansas: Lawrence, KS, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Dent, B. Cartography, Thematic Map Design, 5th ed.; McGraw Hill: Boston, MA, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Chalkias, C.; Papadopoulos, A.G.; Kalogeropoulos, K.; Tambalis, K.; Psarra, G.; Sidossis, L. Geographical heterogeneity of the relationship between childhood obesi-ty and socio-environmental status: Empirical evidence from Athens, Greece. Appl. Geogr. 2013, 37, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmanuel, D. Socio-economic inequalities and housing in Athens: Impacts of the monetary revolution of the 1990s. Greek Rev. Soc. Res. 2004, 113, 121–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maloutas, T. Segregation and residential mobility. Spatially entrapped socialmobility and its impact on segregation in Athens. Eur. Urban Reg. Stud. 2004, 11, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arapoglou, V.; Karadimitriou, N.; Maloutas, T.; Sayas, J. Multiple deprivation in Athens: A legacy of persisting and deepening spatial divisions. In Hellenic Observatory Discussion Papers on Greece and Southeast Europe (157); Hellenic Observatory; European Institute; LSE: London, UK, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Karadimitriou, N.; Maloutas, T.; Arapoglou, V.P. Multiple Deprivation and Urban Development in Athens, Greece: Spatial Trends and the Role of Access to Housing. Land 2021, 10, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram Mohan Rao, K.; Kant, Y.; Gahlaut, N.; Roy, P.S. Assessment of quality of life in Uttarakhand, India using geospatial techniques. Geocarto Int. 2012, 27, 315–328. [Google Scholar]
- Shyy, T.K.; Stimson, R.; Chhetri, P.; Western, J. Mapping quality of life in the south east Queensland region with a web-based application. J. Spat. Sci. 2007, 52, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Indicators | Dataset, Year | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Population density | Population, 2011 | Hellenic Statistical Authority |
| Spatial layer (polygon) of municipalities, 2011 | Hellenic Statistical Authority | |
| % Open spaces | Spatial layer (polygon) of open spaces, including cultivations, forests, green urban areas, herbaceous vegetation, pastures, crops, water, land without current use, 2012 | Urban Atlas—European Environment Agency |
| Spatial layer (polygon) of municipalities, 2011 | Hellenic Statistical Authority | |
| Mean distance to industrial units | Spatial layer (points) of industrial units, 2020 | Google Maps |
| Spatial layer (polygon) of municipalities, 2011 | Hellenic Statistical Authority | |
| Indicators | Dataset, Year | Source |
| Density of high-traffic roads and highways | Spatial layer (polyline) of high-traffic roads and highways, including motorways, trunks, primary, secondary and tertiary road network, 2020 | OpenStreetMap.org |
| Spatial layer (polygon) of municipalities, 2011 | Hellenic Statistical Authority | |
| % Green urban areas | Spatial layer (polygon) of green urban areas, 2012 | Urban Atlas—European Environment Agency |
| Spatial layer (polygon) of municipalities, 2011 | Hellenic Statistical Authority | |
| % Unemployment | Unemployed population, 2011 | Hellenic Statistical Authority |
| Economically active population, 2011 | Hellenic Statistical Authority | |
| % Higher educated population | Population of ISCED level 8, 7, 6, and 5, 2011 | Hellenic Statistical Authority |
| Total population (population born after 2005 was excluded), 2011 | Hellenic Statistical Authority | |
| % Illiterate population | Population of ISCED level 0, 2011 | Hellenic Statistical Authority |
| Total population (population born after 2005 was excluded), 2011 | Hellenic Statistical Authority | |
| Mean income | Mean income in euro, 2016 | General Secretariat for Information Systems (GSIS) of the Greek Ministry of Economy and Finance |
| Proximity to medical services/hospitals | Spatial layer (points) of public hospitals, 2020 | Google Maps |
| Spatial layer (polyline) of road network, 2020 | OpenStreetMap.org | |
| Spatial layer (polygon) of municipalities, 2011 | Hellenic Statistical Authority | |
| Schools per 10,000 population | Spatial layer (points) of public primary schools, 2019 | Greek Ministry of Education and Religious Affairs |
| Spatial layer (points) of public secondary schools, 2019 | Greek Ministry of Education and Religious Affairs | |
| Population, 2011 | Hellenic Statistical Authority | |
| Proximiy to sport facilities | Spatial layer (polygon) of sports facilities, 2012 | Urban Atlas—European Environment Agency |
| Spatial layer (polyline) of road network, 2020 | OpenStreetMap.org | |
| Spatial layer (polygon) of municipalities, 2011 | Hellenic Statistical Authority | |
| % Population living in houses without basic facilities | Population living in dwellings without heating, WC, bathroom, kitchen, 2011 | Hellenic Statistical Authority |
| Total population (population living in collective dwellings and non-classified was excluded), 2011 | Hellenic Statistical Authority | |
| Indicators | Dataset, Year | Source |
| % Population living in detached houses | Population living in detached dwelling units, 2011 | Hellenic Statistical Authority |
| Total population (population living in collective dwellings and non-classified was excluded), 2011 | Hellenic Statistical Authority | |
| % Population living in newly built units | Population living in dwellings constructed after 2005, 2011 | Hellenic Statistical Authority |
| Total population (population living in irregular dwellings, collective dwellings, and non-classified was excluded), 2011 | Hellenic Statistical Authority | |
| Housing space (m2) per person | Dwelling size per person, 2011 | Hellenic Statistical Authority |
| Total population (population living in collective dwellings and non-classified was excluded), 2011 | Hellenic Statistical Authority | |
| Proximity to recreational facilities | Spatial layer (points) of theaters, cinemas, cultural centers, recreational parks, 2020 | Google Maps and other sites of related infrastructures (www.tripadvisor.gr, www.vrisko.gr, www.xo.gr (accessed on 17 May 2021)) |
| Spatial layer (polyline) of road network, 2020 | OpenStreetMap.org (accessed on 17 May 2021) | |
| Spatial layer (polygon) of municipalities, 2011 | Hellenic Statistical Authority | |
| Proximity to cultural facilities | Spatial layer (points) of archeological sites, museums and libraries, 2020 | Google Maps and other sites of related infrastructures (odysseus.culture.gr, museumfinder.gr, www.eebep.gr, www.network.nlg.gr, www.library4you.weebly.com, www.visitgreece.gr, www.vrisko.gr (accessed on 17 May 2021)) |
| Spatial layer (polyline) of road network, 2020 | OpenStreetMap.org (accessed on 17 May 2021) | |
| Spatial layer (polygon) of municipalities, 2011 | Hellenic Statistical Authority |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Faka, A.; Kalogeropoulos, K.; Maloutas, T.; Chalkias, C. Urban Quality of Life: Spatial Modeling and Indexing in Athens Metropolitan Area, Greece. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2021, 10, 347. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi10050347
Faka A, Kalogeropoulos K, Maloutas T, Chalkias C. Urban Quality of Life: Spatial Modeling and Indexing in Athens Metropolitan Area, Greece. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2021; 10(5):347. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi10050347
Chicago/Turabian StyleFaka, Antigoni, Kleomenis Kalogeropoulos, Thomas Maloutas, and Christos Chalkias. 2021. "Urban Quality of Life: Spatial Modeling and Indexing in Athens Metropolitan Area, Greece" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 10, no. 5: 347. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi10050347
APA StyleFaka, A., Kalogeropoulos, K., Maloutas, T., & Chalkias, C. (2021). Urban Quality of Life: Spatial Modeling and Indexing in Athens Metropolitan Area, Greece. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 10(5), 347. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi10050347









