Optimizing the Spatial Location of Street Lights in Belle Isle, Michigan
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Models and Solution Methods
- Road centerlines are covered by street lights (distance between a point on a road centerline and its nearest street light not to exceed 150 ft);
- Road intersections should be covered by at least two street lights.
2.1. Street Lighting Maximal Coverage Location Problem (SLMCLP)
- (, : the index and set of potential street light locations;
- , : the index and set of points on road centerlines;
- : coverage distance (distance between a point on a road centerline and its nearest street light) threshold;
- : a binary parameter that equals 1 if the distance from potential street light to point is smaller than or equal to , 0 otherwise;
- : the number of street lights required to cover point ;
- : number of street lights to be located;
- : a binary decision variable that equals 1 if potential street light is located, 0 otherwise;
- : a binary decision variable that equals 1 if point is covered by one or more street lights located within a distance of , 0 otherwise.
2.2. Street Lighting Location Set Covering Problem (SLLSCP)
2.3. Solution Methods
3. Case Study
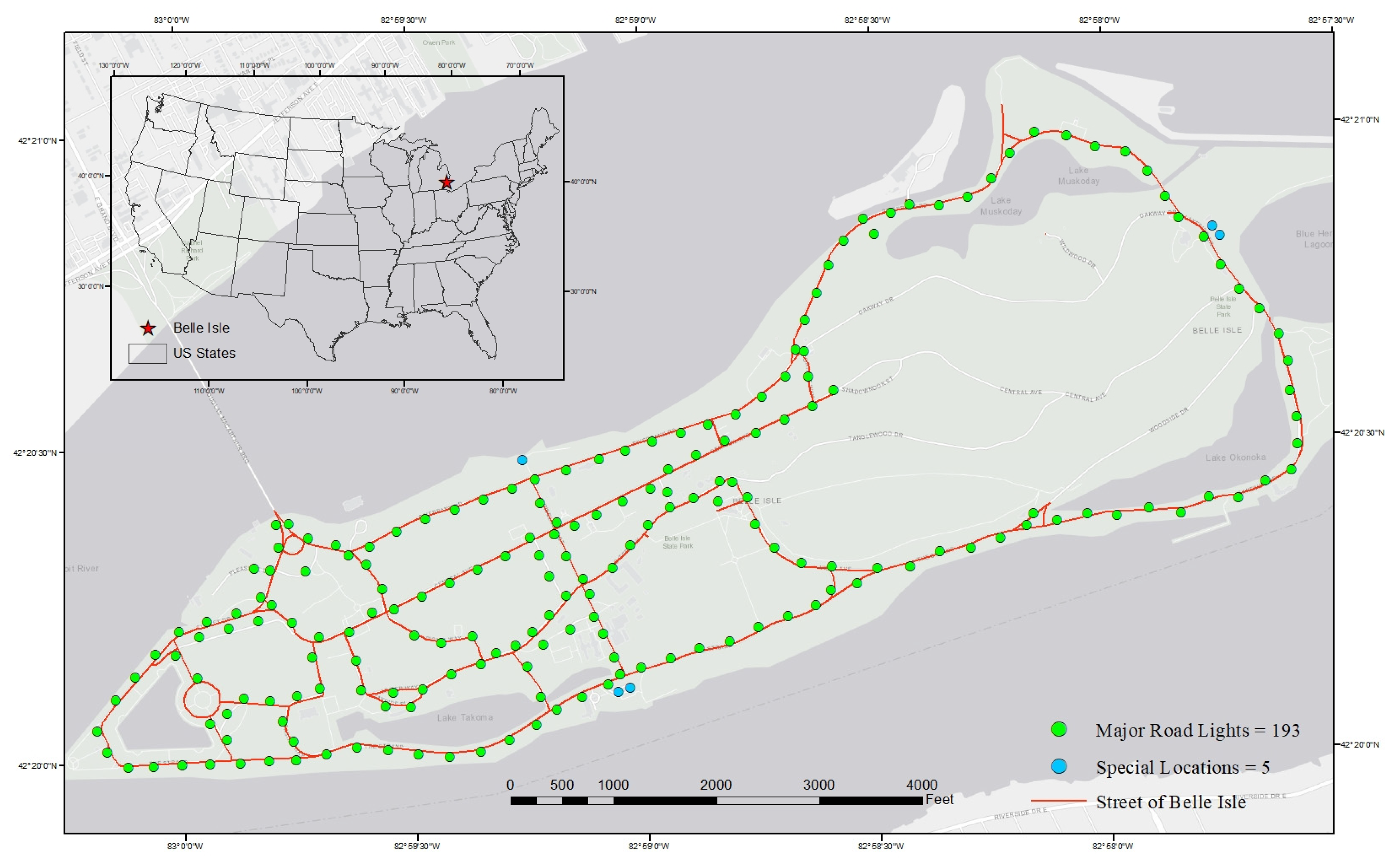
3.1. Background
3.2. Data Source
3.3. Data Preprocessing
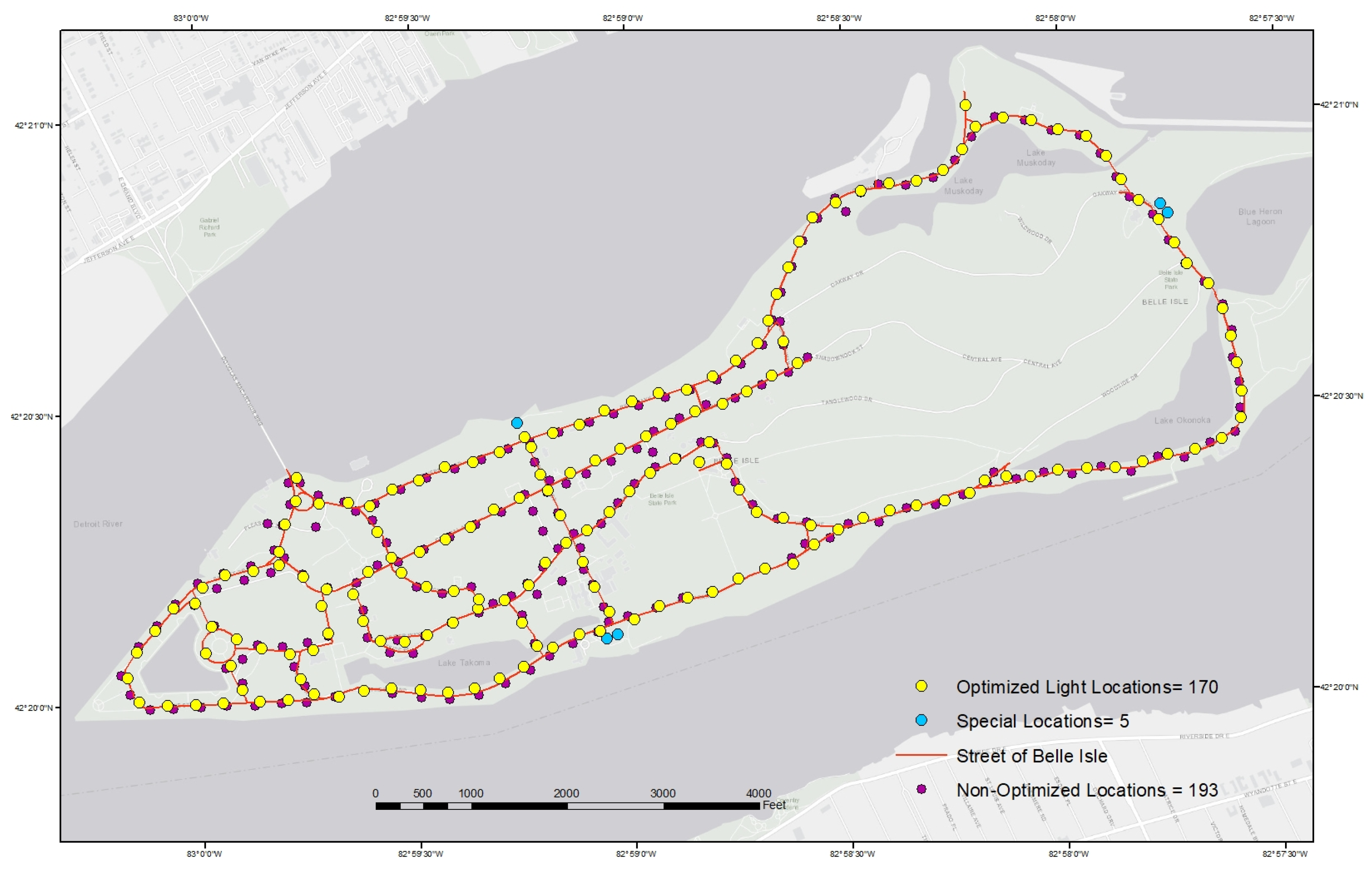
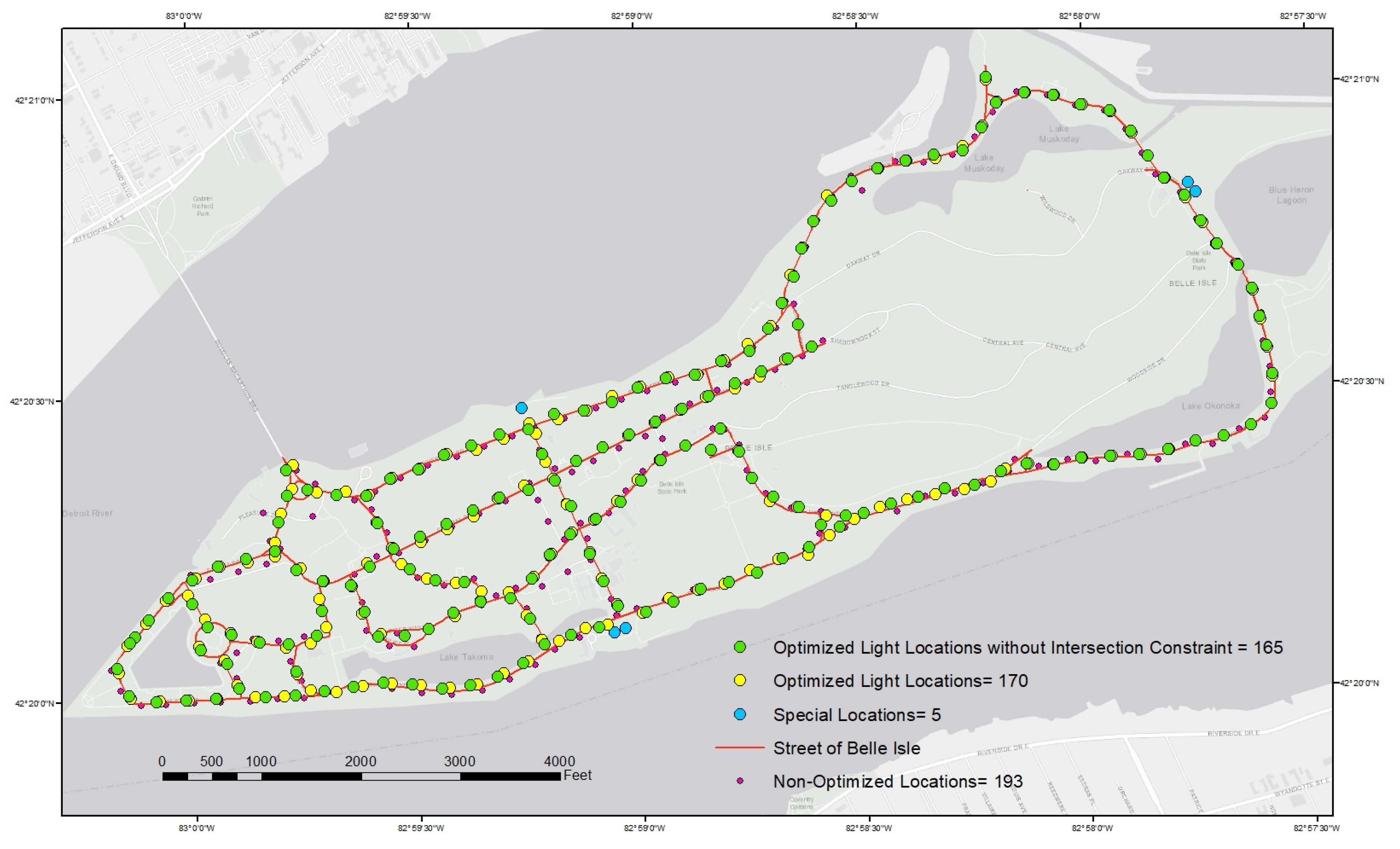
3.4. Results
3.4.1. Scenario 1: Cover All Road Centerline Points with a Minimum Number of Lights
3.4.2. Scenario 2: Cover All Road Centerline Points with a Minimum Number of Lights without the Intersection Constraint
3.5. Sensitivity Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Painter, K.A.; Farrington, D.P. The influence of street lighting improvements on crime, fear and pedestrian street use, after dark. Landsc. Urban Plan. 1996, 35, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaston, K.J.; Gaston, S.; Bennie, J.; Hopkins, J. Benefits and costs of artificial nighttime lighting of the environment. Environ. Rev. 2014, 23, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rabaza, O.; Gómez-Lorente, D.; Pérez-Ocón, F.; Peña-García, A. A simple and accurate model for the design of public lighting with energy efficiency functions based on regression analysis. Energy 2016, 107, 831–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beccali, M.; Bonomolo, M.; Leccese, F.; Lista, D.; Salvadori, G. On the impact of safety requirements, energy prices and investment costs in street lighting refurbishment design. Energy 2018, 165, 739–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Painter, K.A.; Farrington, D.P. The financial benefits of improved street lighting, based on crime reduction. Trans. Illum. Eng. Soc. 2001, 33, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisenbeis, G. Artificial night lighting and insects: Attraction of insects to streetlamps in a rural setting in Germany. Ecol. Conseq. Artif. Night Lighting 2006, 2, 191–198. [Google Scholar]
- Beyer, F.R.; Ker, K. Street lighting for preventing road traffic injuries. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2009, 1, CD004728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murray, A.T.; Matisziw, T.C.; Wei, H.; Daoqin, T. A Geocomputational Heuristic for Coverage Maximization in Service Facility Siting. Trans. GIS 2008, 12, 757–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachamanov, A.; Pachamanova, D. Optimization of the light distribution of luminaries for tunnel and street lighting. Eng. Optim. 2008, 40, 47–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, A.T. Advances in location modeling: GIS linkages and contributions. J. Geogr. Syst. 2010, 12, 335–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hale, J.D.; Davies, G.; Fairbrass, A.J.; Matthews, T.J.; Rogers, C.D.; Sadler, J.P. Mapping lightscapes: Spatial patterning of artificial lighting in an urban landscape. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaundinya, D.P.; Balachandra, P.; Ravindranath, N.H.; Ashok, V. A GIS (geographical information system)-based spatial data mining approach for optimal location and capacity planning of distributed biomass power generation facilities: A case study of Tumkur district, Indi. Energy 2013, 52, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pain, R.; MacFarlane, R.; Turner, K.; Gill, S. ‘When, where, if, and but’: Qualifying GIS and the effect of streetlighting on crime and fear. Environ. Plan. A 2006, 38, 2055–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Welsh, B.C.; Farrington, D.P. Effects of improved street lighting on crime. Campbell Syst. Rev. 2008, 13, 1–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, T.; Rogerson, R.; Barnacle, M. A comparison between the cost effectiveness of CCTV and improved street lighting as a means of crime reduction. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2018, 68, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Y.; Fu, C.; Kennedy, E.; Jiang, S.; Owusu-Agyemang, S. The impact of street lights on spatial-temporal patterns of crime in Detroit, Michigan. Cities 2018, 79, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotios, S.; Gibbons, R. Road lighting research for drivers and pedestrians: The basis of luminance and illuminance recommendations. Lighting Res. Technol. 2018, 50, 154–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullough, J.D.; Donnell, E.T.; Rea, M.S. To illuminate or not to illuminate: Roadway lighting as it affects traffic safety at intersections. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2013, 53, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, T.W.; Bennie, J.; Gaston, K.J. Street lighting changes the composition of invertebrate communities. Biol. Lett. 2012, 8, 764–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IDSA. 15 Million Tons of Carbon Dioxide Emitted Each Year On Residential Outdoor Lighting in the U.S. 2016. Available online: https://www.darksky.org/15-million-tons-of-carbon-dioxide-emitted-each-year-on-residential-outdoor-lighting-in-the-u-s/ (accessed on 21 December 2016).
- Stone, E.L.; Jones, G.; Harris, S. Street lighting disturbs commuting bats. Curr. Biol. 2009, 19, 1123–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murray, A.T.; Feng, X. Public street lighting service standard assessment and achievement. Socio-Econ. Plan. Sci. 2016, 53, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Murray, A.T. Spatial analytics for enhancing street light coverage of public spaces. Leukos 2018, 14, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.; Jeong, H.; Choi, A.; Sung, M. Design of a Connected Security Lighting System for Pedestrian Safety in Smart Cities. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daskin, M.S. A maximum expected covering location model: Formulation, properties and heuristic solution. Transp. Sci. 1983, 17, 48–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Drezner, Z.; Hamacher, H.W. Facility Location: Applications and Theory; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Eiselt, H.A.; Marianov, V. Applications of Location Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015; Volume 232. [Google Scholar]
- ReVelle, C.S.; Eiselt, H.A. Location analysis: A synthesis and survey. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2005, 165, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakimi, S.L. Optimum locations of switching centers and the absolute centers and medians of a graph. Oper. Res. 1964, 12, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahani, R.Z.; Asgari, N.; Heidari, N.; Hosseininia, M.; Goh, M. Covering problems in facility location: A review. Comput. Ind. Eng. 2012, 62, 368–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.-H. Recent applications of the maximal covering location planning (MCLP) model. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 1986, 37, 735–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, R.L.; ReVelle, C.S. Theoretical and computational links between the p-median, location set-covering, and the maximal covering location problem. Geogr. Anal. 1976, 8, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Current, J.; Daskin, M.; Schilling, D. Discrete network location models. Facil. Locat. Appl. Theory 2002, 1, 81–118. [Google Scholar]
- Zarandi, M.H.F.; Davari, S.; Sisakht, S.A.H. The large-scale dynamic maximal covering location problem. Math. Comput. Model. 2013, 57, 710–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajagopalan, H.K.; Saydam, C.; Xiao, J. A multiperiod set covering location model for dynamic redeployment of ambulances. Comput. Oper. Res. 2008, 35, 814–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toregas, C.; ReVelle, C. Optimal location under time or distance constraints. Pap. Reg. Sci. 1972, 28, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandris, G.; Giannikos, I. A new model for maximal coverage exploiting GIS capabilities. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2010, 202, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderín, J.F.; Nodarse, C.P.; Yera, L.S.; Rodríguez, D.E.E. Software tool for model and solve the maximum coverage location problem, a case study: Locations police officers. Investig. Oper. 2018, 38, 141–149. [Google Scholar]
- Lutkevich, P.; McLean, D.; Cheung, J. FHWA Lighting Handbook; Office of Safety, Federal Highway Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- City of San José. Public Strettlight Design Guide; Alta Planning + Design: Portland, OR, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- NES Street Lighting. Nashville Electric Service Street Lighting Guidelines; NES Street Lighting: Nashville, TN, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- City of Los Angeles. Design Standards and Guildlines; Bureau of Street Lighting: Los Angeles, CA, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- City of Santa Barbara. Outdoor Lighting & Streetlighting Design Guidelines; The Planning Counter: Santa Barbara, CA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- City and County of Denver. City and County of Denver Street Lighting Design Guidelines; Engineering Division: Denver, CO, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- District of Columbia. District of Columbia Streetlight Policy and Design Guildlines; District of Columbia: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kinzey, B. Restoring Detroit’s Street Lighting System; Prepared for the U.S. Department of Energy under Contract DE-AC05-76RL01830; Pacific Northwest National Laboratory: Richland, WA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Sinha, S.M. Mathematical Programming: Theory and Methods; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Glover, F.; Kochenberger, G.A. Handbook of Metaheuristics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2003; Volume 57. [Google Scholar]
- Austin, D.; Berg, B. Public Lighting Authority Completes Relighting of Detroit; Public Lighting Authority: Detroit, MI, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Public Lighting Authority. 2016: The Lights Are on! Relighting Detroit; Anual Report of the Public Lighting Authority; Public Lighting Authority: Detroit, MI, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, C.; Deng, X.; Yang, Y. Optimizing the Spatial Location of Street Lights in Belle Isle, Michigan. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2022, 11, 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi11020115
Xu Y, Zhang Y, Fu C, Deng X, Yang Y. Optimizing the Spatial Location of Street Lights in Belle Isle, Michigan. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2022; 11(2):115. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi11020115
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Yanqing, Yue Zhang, Cong Fu, Xiyue Deng, and Yihe Yang. 2022. "Optimizing the Spatial Location of Street Lights in Belle Isle, Michigan" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 11, no. 2: 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi11020115
APA StyleXu, Y., Zhang, Y., Fu, C., Deng, X., & Yang, Y. (2022). Optimizing the Spatial Location of Street Lights in Belle Isle, Michigan. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 11(2), 115. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi11020115





