1. Introduction
The geographic component is a strategic attribute in digital data with respect to policy and operational planning [
1]. The geographic component of addresses is often linked to multiple data types, such as building, transport, population, marketing, delivery, safety, and health information data [
2,
3]. There is consensus in the European statistical community on the best methodology for linking statistics to a location using point-based geocoding infrastructure [
4]. The address data components on the Internet network are present on most web pages and almost 20% of users’ queries are on web browsers [
5]. In fact, network users can navigate to other well-known places or shared locations using sensors on mobile devices [
6] with location-based system (LBS) applications [
7]. For these reasons, addresses are a fundamental component of urban management, smart cities, and urban spatial analytics [
8,
9].
Addresses are a type of geographic feature that can be collected directly by users or professionals. This dataset can be stored in the spatial databases of urban cartography before use in any geographic information system (GIS). In fact, georeferencing dwellings using postal address references has historically been important for the scientific community [
10] due to the linkage between records of the geographic component and other types of information. For more than 20 years, numerous scientific papers on linking data with geocoded addresses to exploit the geographic component in other disciplines, such as epidemiology [
11,
12], environment, demography [
13], business [
14], crimes [
15], emergencies [
16], and security [
17], have been published. In fact, there are numerous academic, industrial, or commercial studies on the positional accuracy [
2,
18,
19,
20,
21,
22,
23,
24] or semantic quality of the addresses obtained using geocoders [
25,
26].
Authoritative addresses can be downloaded from government web repositories, web services, and open data web platforms (OpenAdresses [
27]). In addition, standard addresses are a key element for delivering policies at national and international levels [
28] in support of the United Nations (UN) Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Currently, data re-usability has an increasingly important place on the agendas of many open data and open government data initiatives [
29]. In fact, the European Union is implementing spatial data infrastructure (SDI) [
30] to provide harmonized datasets through web service operations (WFS or Atom) and metadata according to the INSPIRE European Directive [
31] and international standards from the Open Geospatial Consortium (OGC [
32]) and ISO/TC 211 [
33]. Nevertheless, many countries lack a government-maintained address database (demonstrated in
Section 2.2). Furthermore, addresses can be made accessible as volunteer geographic information (VGI) that is georeferenced by the users [
34,
35] of crowdsourcing map platforms, such as OpenStreetMap (OSM [
36]).
On the other hand, there are many companies that provide commercial address datasets using geocoding web services (Google [
37], Microsoft [
38], Here [
39], etc.). The geocoding process has two main ways of querying address data: 1. the direct method, which provides geographic coordinates (latitude and longitude) as a result when there is a match with the text of the requested address of the web service, and 2. the reverse geocoding method, which is the process of extracting a text address (street and number) by providing global position coordinates.
Despite the large volume of address data produced by governments, it is sometimes necessary to improve and update the authoritative geographic information of the addresses using data produced by volunteers [
40] or data from commercial geocoding services [
19]. However, there are some related studies about the quality of authoritative and crowdsourced geospatial information [
41,
42,
43,
44]. Overall, these studies analyzed residential address datasets compared with commercial addresses obtained from global geocoding web services [
19,
20,
25,
26].
Nevertheless, there is no research about automated algorithms that can be used to check the quality and reliability of large authoritative or volunteered address datasets [
45] from several countries that are stored on different platforms (public repositories or SDI web services) against commercial addresses using both methods of geocoding. The methodology developed focuses on residential addresses that are used as spatial and semantic references in LBSs to locate buildings, dwellings, businesses, or recreation and leisure venues. The results show statistics about the spatial and semantical quality components of addresses of authoritative, commercial, or crowdsourced datasets. Thus, this paper aims to develop an algorithm to determine the quality of address data from urban areas and several datasets using geocoding web services.
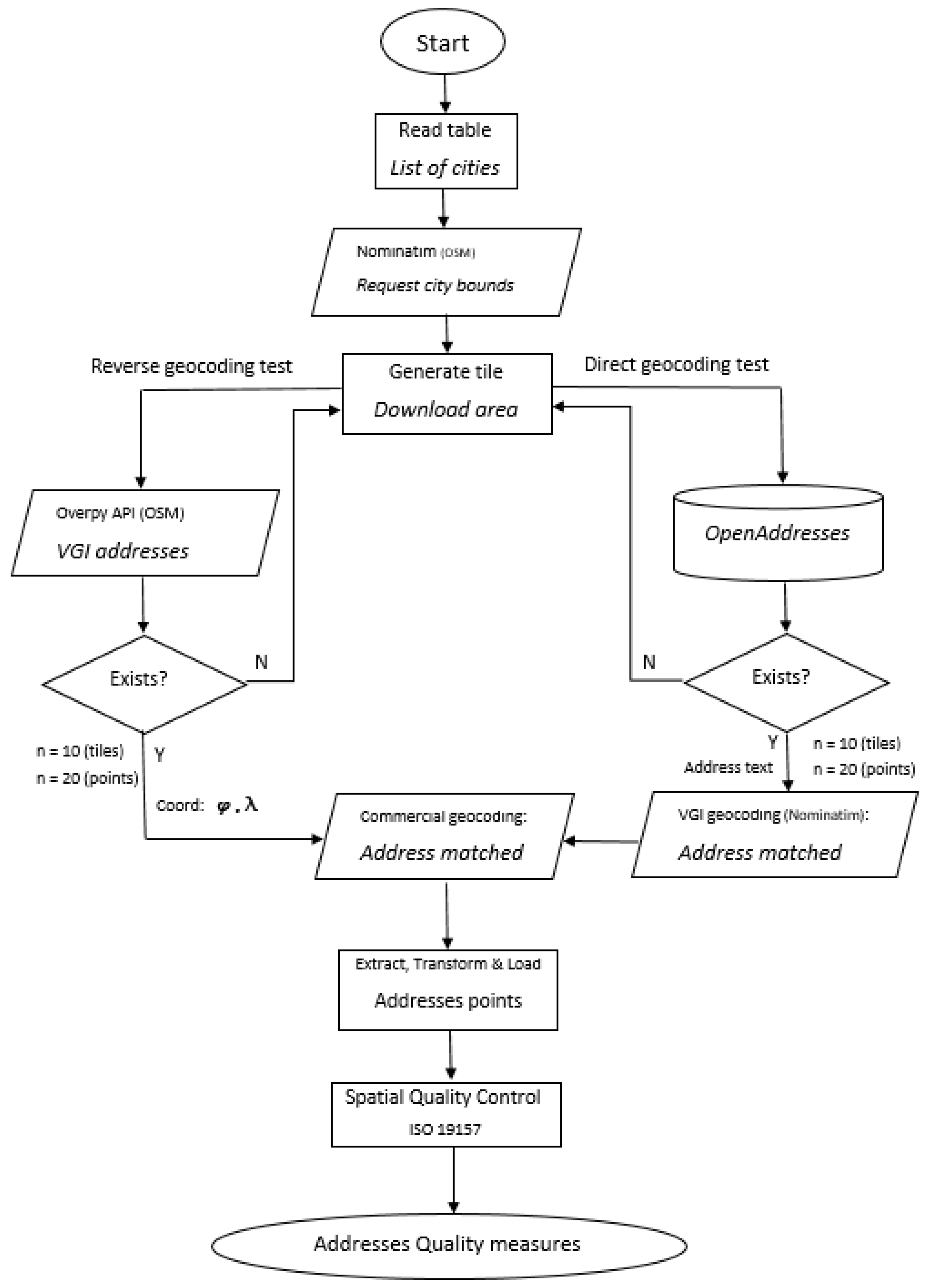
The algorithm extracts well-known random samples of authoritative and VGI addresses as reference data in the main urban areas of Europe; these were automatically requested from commercial geocoding web services. The responses are stored on spatial databases in order to analyze the quality elements (positional and thematic accuracy, completeness, or logical consistency) according to ISO 19157:2013 [
46] (“International Standard Geographic information—Data quality,” 2013). The spatial and semantic algorithms are developed with the Python language, using libraries for data mining [
47,
48], machine learning [
8], and big data [
49] management in cloud computing systems in order to evaluate different address-matching methods [
50].
Therefore, the algorithm contributes to checking the quality components of commercial, crowdsourced, and authoritative addresses within the user-defined geographical urban area. The main goal is to automatically evaluate whether the quality of voluntary or commercial geographic information relative to postal addresses in any given area is good enough to improve authoritative address datasets. However, this tool can be also used to design any future geolocated urban data in a GIS using several geocoding address datasets. Finally, the results allow for enhancing strategic address datasets for the benefit of public administration, companies, and citizens.
2. Data
Analyzing the components of an address is an essential preliminary step prior to designing quality control. The developed methodology needs to be able to automatically compare several datasets with different data schema, texts, and positions with respect to whether they are commercial, voluntary, or authorized addresses, and they must necessarily represent the same concepts and similar values.
There are two different techniques for determining the positional component of addresses in geocoding web services: street (linear network analysis) or rooftop (points). Some publications analyze differences in the quality of georeferenced geocoding techniques [
19,
51], but in this study, the positional origin of addresses is not evaluated because the algorithm does not discriminate between geocoding web service responses. Furthermore, the street method is mainly applied in the USA, and it is important to have a well-defined transport network in order to correctly interpolate the input number. On the other hand, the point method is mainly applied to addresses that are authorized in European countries (the UK, France, Spain, etc.), although, depending on the type of land use, addresses can be georeferenced on a roof, the centroid of a parcel, the entrance to a house, or on a public road in front of a building.
The semantic component of address data basically consists of text (usually the street name), building or door numbers, postal codes, and administrative units. In some cases, addresses provided by government agencies may add other identifiers that may be linked to cadastral parcels, statistical units, demographic censuses, and other types of urban surveys [
51].
In addition, the components of semantic addresses for administrative units and settlements must particularly follow a complete common structure and order relative to a hierarchy (settlement or district, municipality, province, state, region, and country). Thus, geocoders can distinguish similar addresses from different areas in the same region or municipality. Some countries use a postal, census, or zip code, which relates to a specific geographical area. In fact, the geographical boundaries of administrative units or urban areas are important in this algorithm in order to extract reference address samples for quality analysis. The datasets used to test the algorithm in European countries are detailed in the following sections.
2.1. Authoritative Dataset from the OpenAddresses Web Platform
The authoritative address datasets must be free and open and obtained from the governments’ web portals because they are the most reliable reference source for text address components [
52].
The OpenAddresses web platform gathers this information and normalizes it in order to distribute the information in text files with plain format, comma-separated values (CSVs) or geographic formats (GEOJSON and shapefiles) with the following structure: lon, lat, number, street, unit, city, district, region, postcode, id, and hash. Moreover, this open repository has one folder per country with several address files in CSV text format and metadata files in JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) text format.
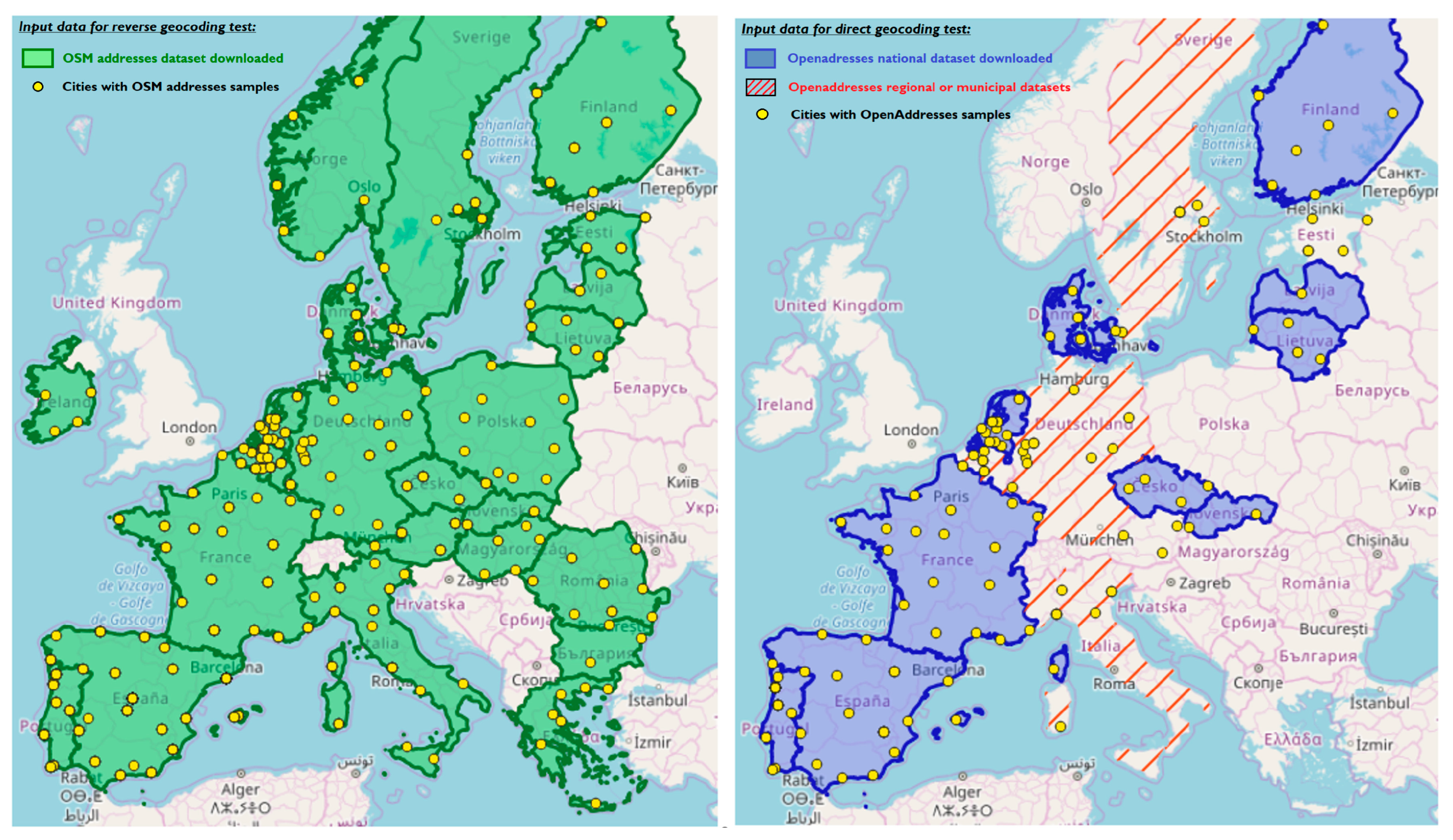
In this study, 144 datasets from OpenAddresses in the European area were used, with addresses from 21 countries: 14 country-wide, 16 regional, and 114 local datasets. The datasets were inserted into a unique spatial database (PostgreSQL with PostGIS extension) as point geometries for better quality control algorithm performance. Developed algorithm (developed in
Section 3.1) shows the geographical extent of OpenAddresses datasets, which includes the continental area of Europe, with the exception of Greece, Bulgaria, and Hungary.
Datasets need a complete revision of quality components with respect to completeness, logical consistency, and the harmonization of different data schemas across countries. Thus, an initial analysis of addresses was carried out to ensure the initial quality with respect to these measures. Some spatial queries were designed to analyze almost 100 million addresses in the initial 80 European datasets loaded into the database, with almost 1% being duplicated in terms of attributes (lon, lat, street, and house number) and 0.14% being duplicated in terms of attributes (street, house number, and city). Only 19 datasets did not contain some of the initial errors. There are also a few datasets with completeness problems with respect to semantic attributes, with most being caused by data import problems.
The OpenAddresses web portal offers information about products but could be more useful for obtaining metadata product links of authoritative address datasets.
2.2. Authoritative Datasets from INSPIRE Addresses on European SDI
The INSPIRE European Directive ensures the interoperability of European authoritative datasets using common well-known data schemas, metadata, and network service implementation that are accessible without restrictions from a unique geoportal [
53].
The INSPIRE Addresses schema [
54] is linked to other geographic feature schemas such as buildings, geographical names, administrative units, and transport networks. Address data depend on the other themes in order to be completely useful.
The European geoportal in SDI offers 60 downloadable address datasets, 217 metadata records, and 107 viewable datasets in its catalog. The address download service was implemented in 21 out of 32 countries, but only 18 countries have data in the INSPIRE common schema.
The results from downloadable web services (
Table 1) with addresses are as follows: 17 implemented the Web Feature Service and 15 implemented Atom Massive Download links (standard OpenSearch using feeds with the XML language). These data were collected by different public institutions, such as national or regional maps, agencies, cadasters, municipalities, land registries, and statistical offices (
Table 1).
Most of these addresses’ datasets are identical to those in the OpenAddresses data platform because they have the same government source. However, there are fewer authoritative address datasets in the INSPIRE schema than those provided by OpenAddresses because some countries do not distribute this formatted data in the European SDI.
2.3. Crowdsourcing Dataset from the OpenStreetMap Project
This address reference dataset was collected by volunteers of the OpenStreetMap (OSM) crowdsourcing project. Basically, this VGI comes from a collaborative map of streets, points of interest, and other geographic information principally produced by users.
These crowdsourced addresses can be collected by users on site and at the street level using a mobile device with a global navigation satellite system (GNSS) sensor or by carrying out digitalization using a map platform such as JOSM. OSM address data, such as house numbers, are collected by users and can be geometrically associated (“node”) with any geographic feature and establish relationships with another element [
55]. The semantic component of the address can then be linked to the geographic position in front of an entrance or at the top of a building, and some studies analyze the quality relation of crowdsourced information. This VGI on OSM frequently has poor information with respect to metadata in datasets and geocoding responses, although it could make a relevant contribution to evaluating address quality.
In this study, 35 million OSM addresses were downloaded using queries in the osmosis application. Principally, building nodes contain house numbers, but there are some point-of-interest tags with addresses (1.8% amenity; 1.4% shops; 0.1% tourism; 0.02% public transport). In addition, a preliminary quality analysis of OSM addresses identified serious problems with respect to completeness (17%—street without a name or code; 2%—house number without text) and logical consistency (3%—duplicated addresses). Nevertheless, the algorithm using the reverse method will use the spatial component of OSM data to locate nearby addresses via commercial geocoding web services.
On the other hand, OSM’s geocoding web service, Nominatim, can geocode addresses and place names using direct and inverse methods. Nominatim has been used to develop algorithms with direct methods in order to obtain 10 semantic address components in the GeoJSON geographic format (house number, road, hamlet, town, village, city, state district, state, postcode, and country). The returned addresses are parsed and compared with authoritative addresses. This can be useful for public administrations in order to improve upkeep. In fact, some parts of the OSM database were massively imported from authoritative sources such as the TIGER database of the U.S. Census Bureau [
56].
2.4. Commercial Datasets from Geocoding Web Services
These datasets were obtained in response to requests made to geocoding web services. Hence, they have no availability with respect to examining the complete features of address data in a specific urban area to discover their density, geographic coverage, or data quality. However, these geocoding services are quite reliable as they are consulted by two of the world’s leading web service, LBS, and software providers, i.e., Google and Microsoft (Bing), and by long-standing address data providers such as Here (Nokia, formerly Navteq).
Commercial geocoding companies were also chosen following the criteria of intensive use or demand from users. Moreover, we queried some of the literature that reviewed quality analysis using some geocoders [
57,
58] in order to choose free geocoders that have the most responses and matches and the highest accuracy. However, it might be interesting to compare their data against other LBS address data with respect to accurate commercial geocoding systems because they usually use multiple sources of reference datasets [
59].
Basically, all chosen geocoders have REST architecture and are limited in use because they must be paid for and return data in XML and JSON formats. In addition, in all of them, the number of possible responses per request can be limited. Currently, the algorithm only works when using a single option as a response from the geocoder in JSON format, which is similar to plain texts with JavaScript codes chosen for their simplicity in parsing the data contained in lists within the Python library. These data are not completely validated by a data schema, such as the XML INSPIRE schema, but this is not necessary as the algorithm is developed to automate structure and check data responses:
Google: The Geocoding API is requested by the algorithm. The response is a JSON list with seven semantic components (street number, route, locality, two administrative areas, country, and postal code), locations (latitude and longitude), and geocoding type (rooftop).
Bing (Microsoft): The REST location service by address provides six semantic components (address line, two administrative districts, country region, locality, and postal code), locations (latitude and longitude), and usage type (route).
Here: The Geocoding & Search API returns nine semantic components (street, house number, city, postal code, district, subdistrict, county, state, and country), positions (latitude and longitude), and house number type (PA or building, interpolated along street).
4. Results
The application of the algorithm to the European region shows that the number of responses from geocoding web services was over 83% for the direct method and 74% for the reverse method. Spatial accuracy is one of the most important spatial quality elements, and the results confirm our initial expectations: Geocoders have similar spatial magnitudes within a range of 10 m. However, it is necessary to filter the responses of outliers using an estimated threshold: 45% in the direct method and 5% in the reverse method.
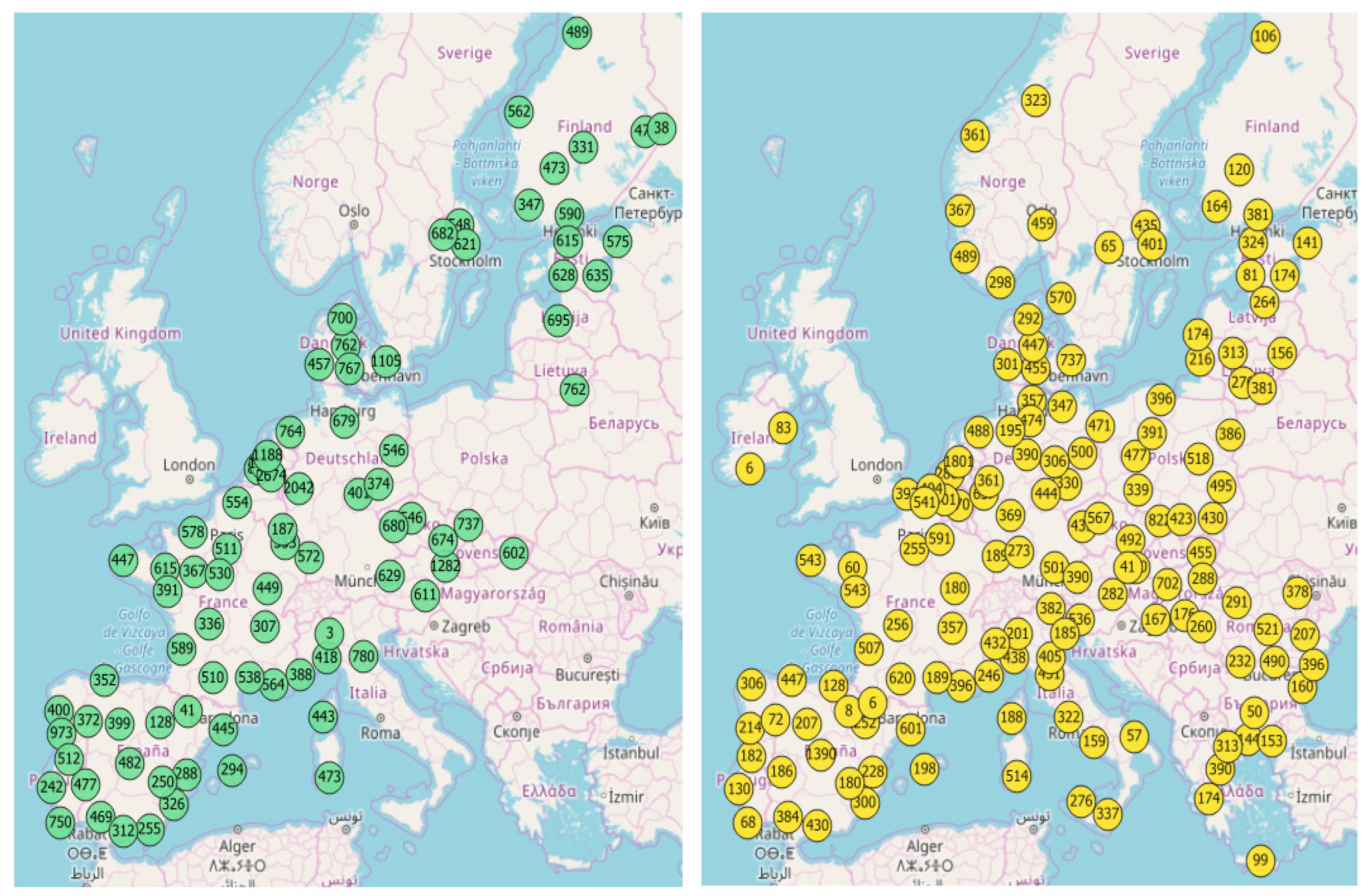
The case study was designed to test the algorithm, where both geocoding methods extract random address samples inside random geographic areas (tiles) in some urban zones of European cities. Then, if the algorithm does not find any addresses inside their bounds, it continues to search for addresses inside the tiles for up to 10 tiles. Thus, the number of tiles is a good indicator of the available geographic reference address datasets in both OpenAddresses and OSM. Above all, the number of address samples in every city can demonstrate the availability of address data within this area (
Figure 6).
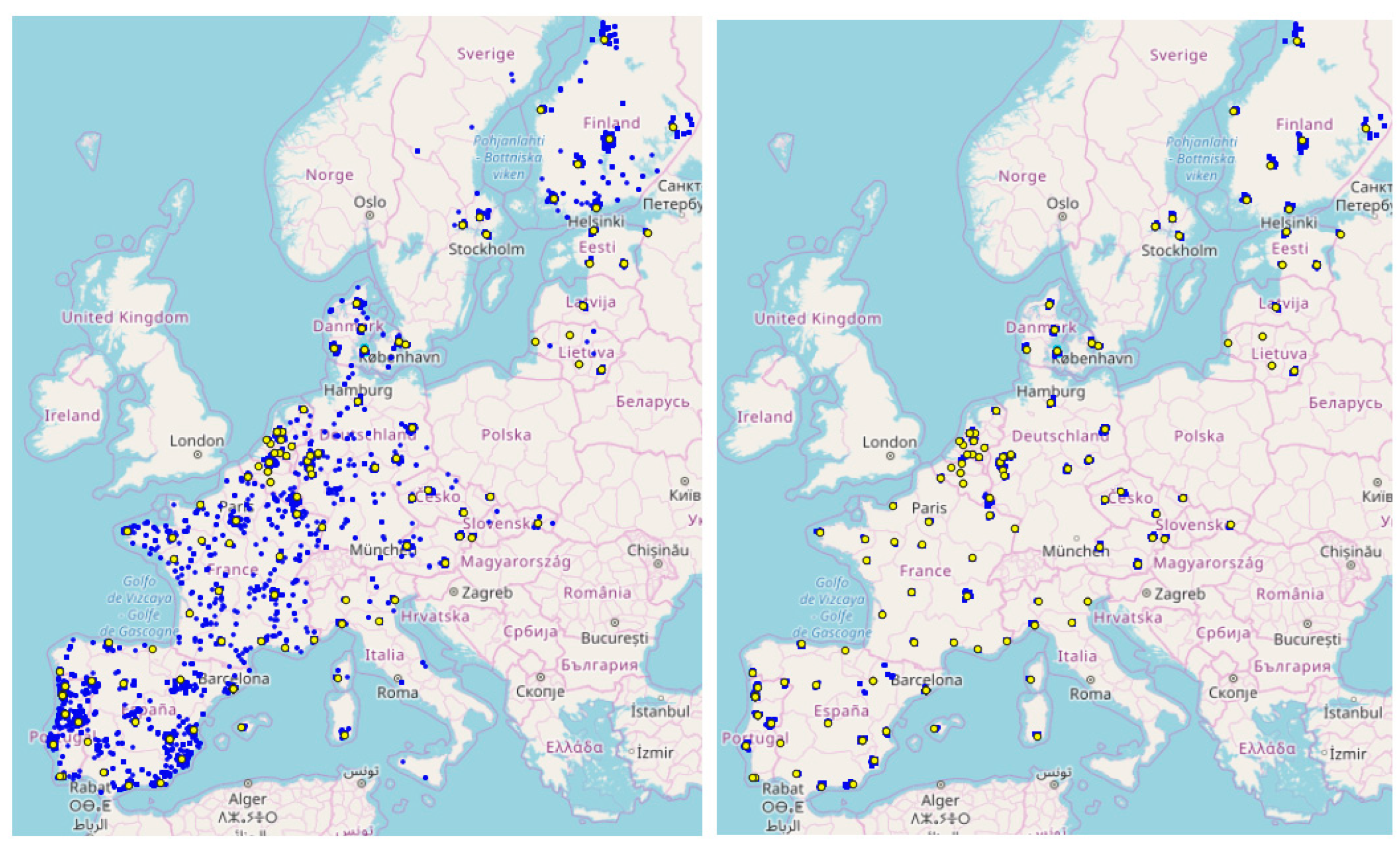
The first obtained result is the influence of semantic quality on the text components in address datasets. If some components are incomplete (street name, number, city, region, postcode, etc.), the match rate will be low with respect to any geocoding method. If the web service finds a matching address but its associated spatial coordinates are far from the real ones, then an outlier is introduced in the spatial data quality sample (
Figure 7).
The case study shows that the high number of positional accuracy outliers in the direct method is due to the high coincidence response rate of commercial geocoders (82%
Table 4) with respect to incomplete text addresses in OpenAddresses, which often lack correct information for settlements, residential districts, or municipalities in the requests to geocoders. However, this algorithm does not analyze the confidence or quality of address data references. Sometimes, this information is a unique source for locating any feature in the world. In addition, a possible cause of the large positional error results could be that a random assessment area may contain addresses in rural areas adjacent to large cities, which are not assessed in this study (lower spatial resolution). Once filtered by geocoding error distances and the number of matches using geocoders, this problem could be identified and solved. Sometimes, placing an address on a roof or street can also change the degree of positional accuracy of the product. Moreover, sometimes, the cause of positional issues is building typology and the type of urban planning, as open areas with large plots and single-family construction units can generate a higher number of positional errors.
For this reason, the quality algorithm begins with an analysis of completeness or logical consistency for every measure of quality in both geocoding methods. These measures must be indicated by the number of errors according to ISO 19157.
Table 3 lists an average of errors, but it may not be a good method for explaining the lack of reliability in some elements for readers.
In the original sample for the direct geocoding method, 19,957 address samples were randomly selected to analyze downloaded data from OpenAddresses in order to match their address text. We obtained 66,324 responses, which accounted for 82% of responses on geocoders. For the reverse geocoding method, 17,463 samples were extracted from the OSM “overpass” API, with 74% of responses from commercial geocoders. Using the reverse method, we found OSM addresses in 89% of tiles, and authoritative addresses were extracted from OpenAddresses, making up 71%. The mean response time of the geocoders was 0.54 s using the direct method and 0.65 s using the reverse geocoding method with a 4G broadband connection.
Overall, a lack of consistency in geocoding address data was detected in the attributes related to administrative units. In particular, a different representation of their scope was detected at the population, neighborhood, district, and municipality levels. Reaching such a level is essential because there are streets with the same name within the same municipal administrative area, and it is necessary to know the actual name of a settlement in order to be able to geocode it correctly.
Sometimes, errors are a result of uncertainties in abbreviated street names and the lack of residential district or settlement names in the addresses’ data reference (OpenAddresses). Incomplete text components with respect to addresses can produce significant errors during geocoding because geocoding web services try to provide some response to the candidate, while the Nominatim matching algorithm (OSM geocoder) does not force responses to any candidate when requests are incomplete.
This methodology was carried out to extract the average semantic match for each address request made to the geocoding web service using both methods. Aggregating these results, the algorithm allows for obtaining quality measures with thematic accuracy
Table 5 for address datasets from different countries, cities, or areas.
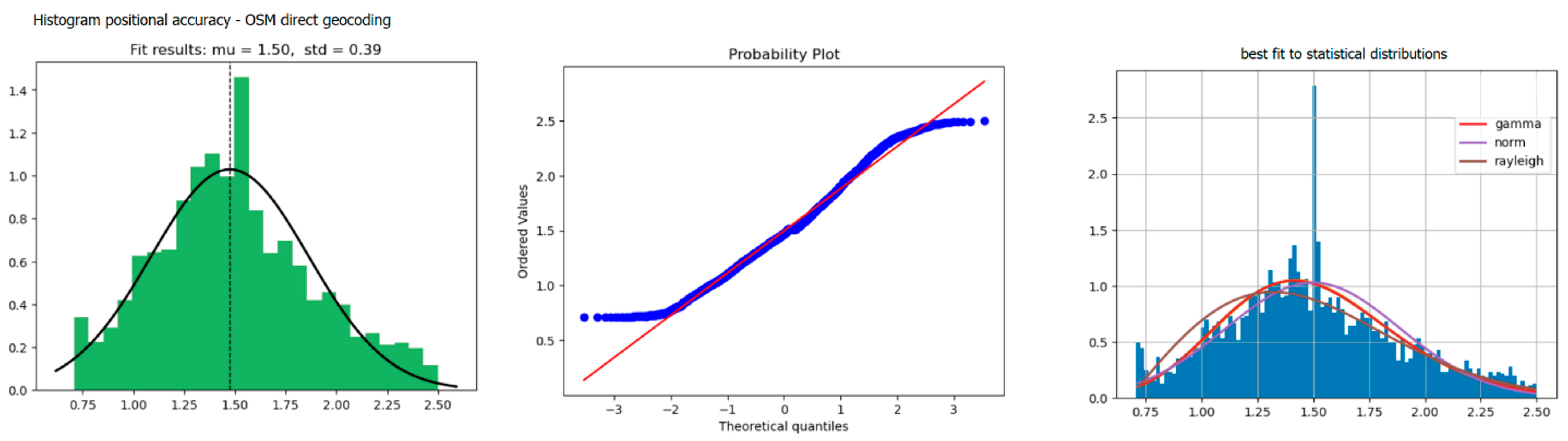
The statistical distribution of geocoding positional accuracies (error distance) in the raw data was positively skewed to the right (around cero), as shown in descriptive statistics and in studies published by other authors [
18,
19]. Despite the evidence of non-normal behavior [
21] with respect to geocoding positional errors, most existing results follow a log-normal distribution [
24,
26].
The algorithm assumes a non-normal distribution of spatial errors but carries out statistical evaluations with an adjustment using the least squares method to fit distance values and extract the statistical parameters of positional errors. In the future, these spatial accuracy values can be used to filter the spatial matching of the address responses of geocoders, datasets, or subdatasets (regions, cities, etc.). In the case study, we reduced previously filtered commercial geocoder data responses by 30%, applying a transformation with least squares, and we estimated outliers from 6 m, as shown in
Figure 6. The results for commercial geocoder positional accuracy values had a median of 1–2 m without ambiguity and an RMSE of 4–5 m, with 99.8% positional feasibility (2.5 sigma) upon matches. However, with respect to the crowdsourced geocoder, the median value was similar, but a better RMSE of 2.44 m was observed, as shown in
Figure 8.
OSM positional errors exhibited a better fit relative to the normal distribution, and there were fewer spatial position coincidences. Moreover, this test demonstrated that the OSM spatial data source is unique and does not share address data with geocoders. However, sometimes, OSM can be completed using authoritative address data from some governmental organizations.
However, some studies with respect to geocoding quality characterized this non-normal distribution using statistics such as the mean, median, standard deviation, or percentiles. Therefore, the following case study, which tests the algorithm using some geocoders, datasets, and different spatial domains, shows positional errors, comparing raw data, threshold filtering, and interquartile values.
The address geocoding response data from the experiment using the algorithm are listed in
Table 4. The results show raw positional accuracy values such as distance and the length or distance between the real position and that provided by the geocoding web service.
Figure 5 and
Table 5 show how the raw positional data had outliers (atypical values) that introduced distortions in our descriptive statistics and probabilistic results. These atypical values can be observed in the box plots, scatter graphics, and histograms shown in
Figure 4 and
Figure 5.
The spatial accuracy obtained using all datasets falls within the expected range of values for this geographical data type, which is obtained from urban areas. Following this study and previous studies [
2,
23,
74], we estimate that the acceptable positional error of geocoding responses must not be around 50 m in urban areas because, in most cases, the distance values between geocoded global positions are around 5–20 m.
An interesting result of this study can be observed in
Table 3, which demonstrates that the median can be used as a more robust centrality measure in this type of positional analysis. In fact, there is a positional coincidence rate of 33% in 19,957 geocoded text addresses using the direct method. Analyzing the results in depth (
Table 5), Google Places has incorrect locations relative to 1837 addresses (9.2%), while the other geocoding services have better results. The positional errors found in geocoders comprised: Bing Maps—123 incorrect addresses (0.6%); Here—776 incorrect addresses (3.8%); and Nominatim (3.2%). VGI yields fewer requests, with no uncertainties in 23% of cases (4632 addresses), but commercial geocoders have errors that amount to more than 50 m compared with OpenAddresses. On the other hand, the reverse geocoding method has a positional matching rate of 90%, without uncertainties relative to the 17,463 addresses requested from the coordinates. In this case, nearly 2% of the geocoding errors originate from Google Places and Here, while the rest obtain correct positions. Bing Maps yields 0.3% of the errors, while the other geocoders provide correct global positions (
Table 6).
However, Bing has similar accuracies and responses compared to Here using the direct method, but when using the reverse method, the results have more spatial differences (
Table 6). The reason for this similar magnitude of errors is because Here is a provider of geographic data and LBS data to Microsoft. OSM has better accuracy than Bing Maps because OSM has fewer filtered address responses and because the Nominatim geocoder does not always try to find responses to the requested addresses.
In addition, the direct method algorithm (identifying text addresses from OpenAddresses) obtains a higher average of outliers in terms of absolute positional accuracy compared with the reverse method (matching location with OpenStreetMap) (
Table 7). These results show geocoder problems when matching the semantic components of addresses. Furthermore, this observation explains the relationship between the high number of geocoding responses (95%) and the substantial number of matching errors (providing addresses far from the requested urban area).
Moreover, the developed algorithm allows for controlling the relative errors in the positional accuracy between geocoders. The results allow for an analysis of geographical relationships or correlations in the spatial positions of address data responses between one geocoder and another geocoder.
Table 8 shows that Bing Maps often uses Here address data to reference their address in the geocoding web service.
Although no data on temporal quality were measured directly, we considered how often dataset updating can affect the matching rate of semantic address data. These results show a lack of harmonization with respect to the addresses’ data attributes, which comprise the type of values and order and the form of representation in different geocoders; moreover, the language or codification of text characters can also generate errors during geocode matching in some cases.
5. Discussion
The quality of an address dataset affects the hit rate in geocoding web services [
17,
75] and the geospatial subproducts made using geocoded data. The developed algorithm allows for analyzing quality following the standard rules denoted in ISO 19157, evaluating specific aspects with respect to geographic information products such as addresses. Therefore, the developed algorithm allows for assessing the quality of any address dataset before its use in georeferencing any spatial information.
Concretely, this paper examines the quality of authoritative and crowdsourced address datasets in urban areas across Europe, including datasets with different languages and schemas. There are similar studies using crowdsourced data from OSM, but they have other themes, such as land use [
76], road networks [
77], and similar specially made experiments [
78] with respect to buildings. These were published years before this algorithm was used to extract results. Furthermore, the algorithm is implemented to automatically compare geographic information with commercial datasets from geocoding web services, which is carried out in other studies [
19,
25,
49]. However, the implemented algorithm allows for automatically choosing random sampling areas inside urban zones, as requested by a city relative to crowdsourced datasets (OSM). However, in order to improve analyses, the number of samples for extraction can be chosen by users, and the geographical data reference can be chosen to define specific urban sample areas or city bounds.
The responses of geocoding web services from principal companies using geospatial data (Google, Microsoft, and Here) were stored in a spatial database in order to check spatial quality. In general, there is a considerable number of web service responses (98% matching) that agree with other authors [
19], but these have a high number of mistakes. This is due to the incorrect behavior of the geocoder as it tries to provide possible answers for unknown addresses. Sometimes, the problem is caused by a position error in the reference dataset or an incomplete text component in the reference dataset. However, the results show that common errors are mainly present in the names of administrative units, small residential districts, and settlements, and sometimes, these errors are a result of the multilingualism present in their texts. Most addresses from geocoders need to normalize the parsed components, which agrees with [
79]. Other related studies [
54,
80,
81,
82] use applications that implement the requested geocoders (ArcGIS, MMQGIS, and Batch; Easergeocoder), but they do not examine the raw data from providers compared to the developed algorithm.
In fact, the broad geographic scope used in this study is not used in other relevant and similar studies [
13,
18,
24,
45,
83,
84,
85,
86], as these studies focus on specific urban areas inside one country or region. Furthermore, our approach analyzes the implemented algorithm by forcing the automatic extraction of about 40,000 sample addresses for geocoding. In contrast, similar research studies developed their work using fewer sampling data and the same reference dataset source [
19,
57,
72].
Furthermore, the implementation of the developed algorithm assists in evaluating the availability and completeness of the VGI dataset within the European Territory. If this is consistent with other studies in the European Union with respect to crowdsourced data quality compared with authoritative datasets [
43,
44,
76,
87], then the OpenAddresses dataset can be concretely [
62] used. An analysis of semantic similarity in address text components could improve the testing of new word-matching techniques. The algorithm implements a variant of the Levenhstein distance, similar to other authors [
25], but it improves the analysis because it discriminates the order of words. Some studies introduced other specific algorithms that were derived from the Levenshtein algorithm [
88]. Other studies [
89] implemented other similar text algorithms and deep learning algorithms for words (Word2Vec), which demonstrated that the improvements did not benefit developments or increase implementation costs.
On the other hand, the positional accuracy results obtained using the OSM geocoder, i.e., Nominatim, are similar to the results of [
89]. However, the results have poor semantic quality, as demonstrated by [
44], and there are a high number of omissions, as [
90] and [
18] reported. Other studies [
91] reveal the impacts of demographic biases, voluntary response, and community contribution. Nevertheless, the Nominatim geocoding OSM service has better positional accuracy with respect to geocoding responses upon this algorithm’s implementation compared with a similar test [
80]. Furthermore, most related papers that analyze geocoding responses in the USA have good performance due to the normalization of the data reference TIGER/Line from the U.S. Census Bureau [
13,
24,
51,
57,
81,
92,
93]. In fact, other papers that examine geocoding address quality in European countries have worse positional accuracy results [
80,
86,
87,
94] than those obtained using our algorithm. However, experiments on positional accuracy in specific datasets must consider estimating the sampling size for a given population [
64] and check the results relative to the product’s specifications.
Moreover, the positional accuracy obtained in geocoding responses does not conform to the normal distribution as required to extract common statistical values. The designed algorithm transforms accuracy values to fit the Gaussian function and extracts the probability of spatial errors for an empirical evaluation of address matching. However, the results with respect to transformed positional error probabilities are estimated for algorithm users because they did not pass the normality test (Kolmogorov–Smirnov, D’Agostino’s K-squared, and Anderson–Darling) and thus rejected the null hypothesis. Therefore, the positional accuracy measures of the quality extracted with the algorithm comprise descriptive statistics, such as the median and percentiles (figures), which are filtered by the spatial threshold, similar to other related studies. Thus, the algorithm can be used to compare statistics with a non-parametric test based on ranks such as Wilcoxon or Friedman [
19]. Other studies apply a spatial Monte Carlo simulation [
95,
96] to find spatial patterns for points in area-based tests. In the future, the algorithm could be implemented to extract non-parametric statistics, or improved technologies could be used in machine learning processes. However, the relative cost of the algorithm’s computation must be considered before quality control datasets.
The results of our algorithm’s implementation could show the EU’s effort toward authoritative data standardization and distribution using the common INSPIRE SDI platform. Currently, there are many geocoding applications from the European Public Administration, and only QGIS 3.28 LTR software has geocoding complements from different countries, such as France, Finland, Norway, Germany, and the Netherlands, and cities, such as Barcelona. In the future, this methodology can be implemented as a QGIS complement to benefit community users.
Finally, the statistical results show sufficient positional accuracy (about 10–40 m) when there is a match between address datasets. This positional accuracy value is similar to other related studies [
18,
69,
72,
81,
83] that confirm accuracy values. The reverse method produced better positional results with respect to its raw address responses without a positional threshold, but the results were slightly worse within 50 m. The accuracy of addresses obtained with geocoding is essential because errors can be propagated to geospatial subproducts [
97].
6. Conclusions
An algorithm that evaluates the quality of geolocated addresses in urban areas was developed and tested, and we obtained good results. The developed address quality algorithm was tested using VGI and authoritative datasets from repositories in some European countries as inputs in order to compare the results with crowdsourced (OSM—Nominatim) and commercial (Google, Microsoft, and Here) geocoding web services. In fact, the developed algorithm allows for choosing either geocoding method, whether direct or reverse, to check the spatial quality of a reference address dataset.
In addition, the spatial quality of address datasets and the geocoders’ usability were examined. User-configurable input parameters were included so that the address quality analysis could be performed according to data size, the number of areas to be checked (tiles), the number of points per sample, a priori errors, and control points. The implementation with open technologies, such as the Python language and PostGIS spatial database, allows for including third-party developments or packages, easy sharing or updating procedures by the developer’s community, optimal processing times, and integration in main GIS applications.
The quality output measures are useful for checking the reliability of the semantic and spatial components in authoritative address datasets for any selected urban area. In addition, the algorithm can provide estimated probability parameters relative to semantic and positional accuracy, and it can be used for future address-matching processes.
The normalization of the quality analysis based on ISO 19157 was ensured in the algorithm’s development. The normalization allows for the reproduction of different analyses to establish similar comparisons between several datasets and territories. In this respect, the methodology proposed by INSPIRE via SDI can greatly improve the quality of postal addresses. INSPIRE’s geographic data rules propose a complete address data schema linked to other spatial data themes using a common system to structure, distribute, share, and maintain information. The algorithm also includes the possibility of obtaining authoritative data from standard web services (WFSs) implemented following the OGC and INSPIRE European directive, but this methodology is not appropriate for testing the algorithm’s performance in this research study. However, SDI and OGC technologies are starting to use modern technologies and simpler formats in order to collect geographical information from web services using cloud computing systems.
Finally, the quality results of the implementation confirm that crowdsourced addresses could be integrated to improve and update authoritative datasets. On the other hand, the results confirm that the address datasets of geospatial companies have sufficient accuracy for the quality control of authoritative data, but filtering some responses is necessary. Therefore, this algorithm, which uses geocoding web services in order to check authoritative addresses, could optimize spatial data quality control in public administration. In fact, the automatic evaluation of address correspondence using this algorithm could increase and link thematic data (health, energy, demographics, housing, etc.) to public spatial databases. Thus, the developed algorithm can test the reliability of an address dataset in an urban area, city, or region using commercial or collaborative data, and the results can be used to detect semantic or positional errors and complete or update any address dataset.