Meeting the Challenges of the UN Sustainable Development Goals through Holistic Systems Thinking and Applied Geospatial Ethics
Abstract
1. Introduction
Introduction of Systems Thinking Approaches
- Diversifying and decolonizing technology may include mapping and encoding meaning from diverse conceptualizations (if possible and ethical), and/or using “concept and meaning mapping” as a technological tool for engagement between knowledge systems;
- Bottom-up, community-driven initiatives have an appreciable, aggregate effect toward significant macro-economic and global environmental goals.
- Is it appropriate to encode and model all kinds of knowledge (e.g., IK)?
- How might this modeling affect knowledge access and control?
- What are the risks of appropriation, extraction, and misinterpretation?
- What are the risks in “diluting” or “reducing” relational knowledge, or other ways that might negatively transform it? [32]
- Increasing participation in the processes and policies in place to meet climate change and environmental justice challenges from those holding diverse worldviews, providing novel insights and crucial understandings that are not currently presented to meet global challenges;
- Fostering a broader acknowledgment of, and adherence to, ethical frameworks and protocols for the development of digital technologies and use of geospatial data through a critical analysis of research methods and the asserted objectivity of the practice of science;
- Pathways to revolutionizing how Western scientists and technologists consider society, culture, and the environment as integral parts of moral and ethical checks and balances in the digital age;
- Diversifying AI and ML models for better collective information gathering and decision making, privileging knowledge systems with a basis in moral and ethical obligations toward life—both natural and artificial systems—to help spur revolutionary shifts toward global sustainability goals;
- Supporting the development of sustainable and resilient polycentric techno-socio-ecological systems through a myriad of data and information from diverse knowledge systems, with geographic information systems serving as a mediator for sharing knowledge across differences.
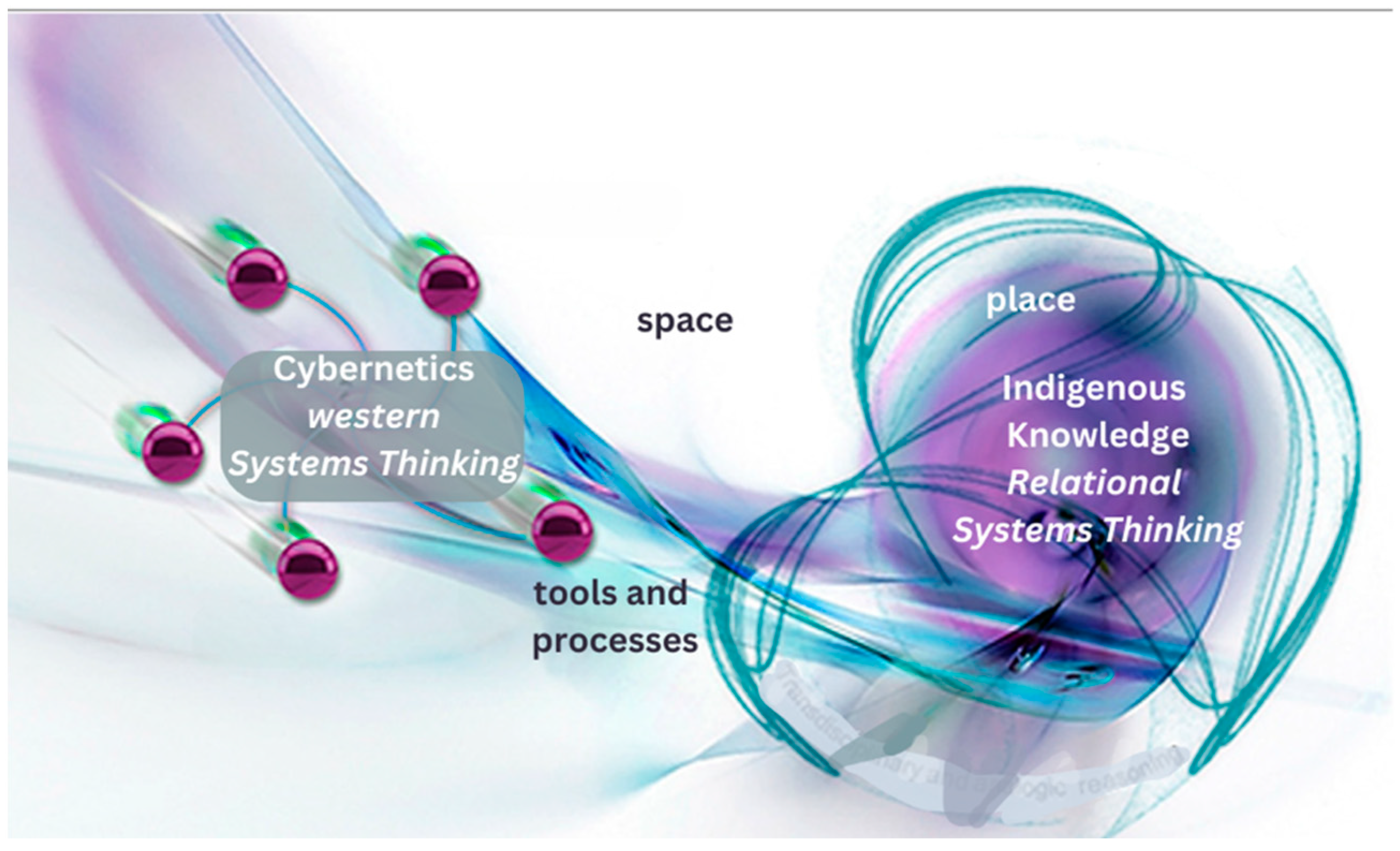
2. Semantics, Cybernetics, and the ‘Knowledge in Place’ Challenge of Big Earth Data
2.1. Semantics and Geocybernetics
2.2. Systems Thinking Theory and Background of “Knowledge in Place” Representation
“Out of our ignorance of a total system of relations and their complex functioning—and out of the selection of “individuals” (or peoples, or countries) as independent, isolatable things—we can fall into pathological patterns. We can get ourselves into “double-binds,” where destructive behaviors are reinforced by conscious efforts to mitigate them. In double-binds the message, at one level, is contradicted at a different level, and pushing the message inadvertently reinforces the pathological behavior” [19].
“Conceiving of imagination without sourcing its ecological origin contributes to and extends anthropocentrism consistent with minds unwilling to naturalize to their surroundings…Minding all things performs the spiritual conservation of all things. All things comprise the Indigenous mind and Indigenous minds are composed of all things.”
2.3. GeoSemantics: Space, Place, and Belonging
- The overrepresentation of digital data about space, rather than knowledge of place;
- A lack of facility in differentiating access to knowledge and enabling Indigenous data sovereignty;
- A lack of facility in supporting and sustaining relationships between Indigenous and non-Indigenous peoples [61].
- Make sense of patterns and growing volumes of information and knowledge;
- Leverage agency and the complementarity of perspectives, knowledges, and capacities to include Western and Indigenous sciences;
- Help change agents—change communities to bring knowledge of environment and place to where they are located—to contribute to the evolving knowledge of the whole;
- Realize a decentralized nodal network approach (e.g., machine-referential semantic web vocabularies) with multiple distributed leverage points that may form a coherent systemic change as an emergent outcome of aggregate agency [2].
“…if researchers and residents ignore this increasingly dominant form of knowledge representation, their voices may be silenced in key knowledge construction and information policy-making processes.”
3. Discussion
3.1. Applied Geomatics and Knowledge Co-Production
3.2. Mediation for a Shift in Worldview
3.3. Guiding Principles and Cautions for Geoethics
- Nothing About us Without us;
- Recognize Indigenous Knowledge in its Own Right;
- Practice Good Governance;
- Communicate with Intent;
- Exercise Accountability—Building Trust;
- Build Meaningful Partnerships;
- Information and Data Snaring, Ownership, and Permissions;
- Equitably Fund Inuit Representation and Knowledge.
4. Conclusions
Future Work
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Global Assessment Report on Disaster Risk Reduction 2022 (GAR2022) and Contributing Papers. Available online: https://www.undrr.org/gar2022-our-world-risk/contributing-papers (accessed on 19 April 2023).
- Finidori, H. Patterns that connect: Exploring the potential of patterns and pattern languages in systemic interventions towards realizing sustainable futures. In Proceedings of the 60th Annual Meeting of the International Society for the Systems Sciences (ISSS), Boulder, CO, USA, 23–30 July 2016; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- IPBES. Summary for Policymakers of the Global Assessment Report on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services of the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services; Díaz, S., Settele, J., Brondízio, E., Ngo, H., Guèze, M., Agard, J., Arneth, A., Balvanera, P., Brauman, K.A., Butchart, S., et al., Eds.; IPBES Secretariat: Bonn, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Pörtner, H., Roberts, D., Tignor, M., Poloczanska, E., Mintenbeck, K., Alegría, A., Craig, M., Langsdorf, S., Löschke, S., Möller, C., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Ripple, W.; Wolf, C.; Newsome, T.M.; Galetti, M.; Alamgir, M.; Crist, E.; Mahmoud, M.; Laurance, W. World scientists’ warning to humanity: A second notice. BioScience 2017, 67, 1026–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBean, G.A. Integrating Global Science to Address the Global Agenda 2030. Environ. Sci. Policy Sustain. Dev. 2018, 60, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bray, D.; Velázquez, A. From Displacement-Based Conservation to Place-Based Conservation. Conserv. Soc. 2009, 7, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jessen, T.D.; Ban, N.C.; Claxton, N.X.; Darimont, C.T. Contributions of Indigenous Knowledge to ecological and evolutionary understanding. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2021, 20, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atleo, E.R. Principles of Tsawalk: An Indigenous Approach to Global Crisis; University of British Columbia Press: Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Berkes, F. Sacred Ecology; Routledge: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Cajete, G. Native Science: Natural Laws of Interdependence; Clear Light Publishing: Santa Fe, NM, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Whyte, K.P.; Brewer, J.P.; Johnson, J.T. Weaving Indigenous science, protocols and sustainability science. Sustain. Sci. 2016, 11, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz, D. Geographical Information Systems (GIS) in Humanitarian Assistance: A Meta-Analysis. J. Humanist. Soc. Inq. 2020, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Tengo, M.; Austin, B.J.; Danielsen, F.; Fernandez-Llamarzares, A. Creating Synergies between Citizen Science and Indigenous and Local Knowledge. BioScience 2021, 71, 503–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasher, J.; Mitchell, S.W.; King, D.J.; Fahrig, L.; Smith, A.C.; Lindsay, K.E. Optimizing Landscape Selection for Estimating Relative Effects of Landscape Variables on Ecological Responses. Landsc. Ecol. 2013, 28, 371–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pause Giant AI Experiments: An Open Letter. March 2023. Future of Life Institute. Available online: https://futureoflife.org/open-letter/pause-giant-ai-experiments/?utm_source=newsletter&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=newsletter_axiosam&stream=top (accessed on 24 August 2023).
- Bowen, G.A. Grounded Theory and Sensitizing Concepts. Int. J. Qual. Methods 2006, 5, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Puy, W.; Weger, J.; Foster, K.; Bonanno, A.M.; Kumar, S.; Lear, K.; Basilio, R.; German, L. Environmental governance: Broadening ontological spaces for a more livable world. EPE Nat. Sci. 2022, 5, 947–975. [Google Scholar]
- Bateson, G. Steps to an Ecology of Mind: Collected Essays in Anthropology, Psychiatry, Evolution, and Epistemology; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Wiener, N. The Human Use of Human Beings: Cybernetics and Society; Da Capo Press: Boston, MA, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Ashby, W.R. An Introduction to Cybernetics; Chapman & Hall: London, UK, 1956. [Google Scholar]
- McCulloch, W. What is a number, that a man may know it, and a man, that he may know a Number. Gen. Semant. Bull. 1961, 26, 7–18. [Google Scholar]
- del Carmen Reyes, M.; López-Caloca, A.A.; López-Caloca, F.; Sánchez-Sandoval, R. Geocybernetics as a Tool for the Development of Transdisciplinary Frameworks. In Developments in the Theory and Practice of Cybercartography: Applications and Indigenous Mapping; Modern Cartography Series: Volume 5, Chapter 3; Taylor, D.R.F., Lauriault, T.P., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- López-Caloca, F.; Sánchez-Sandoval, R.; del Carmen Reyes, M.; López-Caloca, A.A. From Cybercartography to the Paradigm of Geocybernetics: A Formal Perspective. In Developments in the Theory and Practice of Cybercartography: Applications and Indigenous Mapping; Modern Cartography Series: Volume 5, Chapter 2; Taylor, D.R.F., Lauriault, T.P., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Berkes, F. Sacred Ecology, 4th ed.; Routledge: London, UK, 2017; 394p, ISBN 9781138071490. [Google Scholar]
- Barnhardt, R.; Kawagley, A.O. Culture, Chaos and Complexity: Catalysts for Change in Indigenous Education. Cultural Survival Quarterly, Winter, 2003. Available online: https://www.uaf.edu/ankn/publications/collective-works-of-angay/Culture_-Chaos-_-Complexity.pdf (accessed on 16 March 2024).
- Marshall, A.; Bartlett, C. Two-Eyed Seeing. Integrative Science, 2004. Available online: http://integrativescience.ca/ (accessed on 8 September 2023).
- Hill, R. Talking Points on History and Meaning of the Two Row Wampum Belt; Deyohahá:ge: Indigenous Knowledge Centre: Ohsweken, ON, Canada, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, J. Resisting reduction: A manifesto. J. Des. Sci. 2017, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glanville, R. Second order cybernetics. In Systems Science and Cybernetics; Encyclopaedia of Life Support Systems (EOLSS); Parra-Luna, F., Ed.; EoLSS: Oxford, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Slavin, K. Design as Participation. J. Des. Sci. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulsifer, P.L.; Taylor, D.R.F. The Cartographer as Mediator: Cartographic Representation from Shared Geographic Information; Chapter 7, Modern Cartography Series; Fraser Taylor, D.R., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2005; Volume 4, pp. 149–179. ISSN 1363–0814. ISBN 9780444516299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodchild, M. Relational Systems Thinking: That’s How Change Is Going to Come, from Our Earth Mother. J. Aware. Based Syst. Change 2021, 1, 75–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senge, P.; Scharmer, C.O.; Jaworski, J.; Flowers, B.S. Presence: Human Purpose and The Field of the Future; Society for Organizational Learning; Crown Currency: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, S Research Is Ceremony: Indigenous Research Methods; Fernwood Publishing: Halifax, NS, Canada, 2008.
- Goodchild, M. Relational Systems Thinking: The Dibaajimowin (Story) of Re-Theorizing “Systems Thinking” and “Complexity Science”. J. Aware. -Based Syst. Chang. 2021, 2, 53–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.A.; Abdilla, A.; Arista, N.; Baker, K.; Benesiinaabandan, S.; Brown, M.; Cheung, M.; Coleman, M.; Cordes, A.; Davison, J.; et al. Indigenous Protocol and Artificial Intelligence Position Paper. Aboriginal Territories in Cyberspace Edited by Jason Edward Lewis. English Language Version of “Kaʻina Hana. 2020. Spectrum Research Repository, Concordia University. Available online: https://www.indigenous-ai.net/position-paper/ (accessed on 22 May 2023).
- AI Decolonial Manifesto. Available online: https://manyfesto.ai/ (accessed on 22 May 2023).
- Fraser Taylor, D.R.; Cowan, C.; Ljubicic, G.J.; Sullivan, C. Cybercatrography for Education: The Application of Cybercartography to Teaching and Learning in Nunavut, Canada. In Developments in the Theory and Practice of Cybercartography: Applications and Indigenous Mapping; Modern Cartography Series: Volume 5, Chapter 20; Taylor, D.R.F., Lauriault, T.P., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Pyne, S.; Fraser Taylor, D.R. Cybercartography in a Reconciliation Community: Engaging Intersecting Perspectives, 1st ed.; Stephanie Pyne, D.R., Ed.; Modern Cartography Series; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; Fraser Taylor eBook; ISBN 9780128157060. [Google Scholar]
- Zamenopoulos, T.; Alexiou, K. Co-Design as Collaborative Research; Connected Communities Foundation Series; Bristol University/AHRC Connected Communities Programme: Bristol, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Pyne, S. The Role of Experience in the Iterative Development of the Lake Huron Treaty Atlas. In Developments in the Theory and Practice of Cybercartography: Applications and Indigenous Mapping; Modern Cartography Series: Volume 5, Chapter 17; Taylor, D.R.F., Lauriault, T.P., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Pulsifer, P.; Caquard, S.; Taylor, D.R.F. Toward a New Generation of Community Atlases—The Cybercartographic Atlas of Antarctica (195–216), Multimedia Cartography; Cartwright, W., Peterson, M., Gartner, G., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Browne, T.D.L.; Ljubicic, G.J. Considerations for informed consent in the context of online, interactive, atlas creation. In Further Developments in the Theory and Practice of Cybercartography: International Dimensions and Language Mapping; Taylor, D.R.F., Anonby, E., Murasugi, K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Eades, G.L.; Seiber, R.; Wellen, C. Geospatial Technologies and the Representation of Cree Knowledge. In Finding Our Way to Respect and Relationship; Scott, C., Labrecque, J., Eds.; UBC Press: Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2022; p. 32. [Google Scholar]
- Di Leo Browne, T.; Ljubicic, G.J. Considerations for Informed Consent in the Context of Online, Interactive, Atlas Creation. In Developments in the Theory and Practice of Cybercartography: Applications and Indigenous Mapping, 2nd ed.; Taylor, D.R.F., Lauriault, T.P., Eds.; Elsevier Science: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 263–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indigenous Peoples’ Rights and the 2030 Agenda, Briefing Note, Office of the High Commission for Human Rights (OHCHR) and the Secretariat of the Permanent Forum on Indigenous Issues, Division for Social Policy and Development, Prepared and Published by United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs, 2017. pp. 1–15. Available online: https://www.un.org/development/desa/indigenouspeoples/wp-content/uploads/sites/19/2016/10/Briefing-Paper-on-Indigenous-Peoples-Rights-and-the-2030-Agenda.pdf (accessed on 8 June 2023).
- Greenough, P.G.; Nelson, E.L. Beyond mapping: A case for geospatial analytics in humanitarian health. Confl. Health 2019, 13, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexopoulos, P. Semantic Modeling for Data: Avoiding Pitfalls and Breaking Dilemmas, 1st ed.; O’Reilly Media: Sebastopol, CA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- López, A.; Muñoz, E. Aportaciones Desde la Geocibernética y la Percepción Remota a la Política Pública de Áreas Verdes Urbanas. GEOcibernética: I+G+S (Año 1, Número 1). 2012. Available online: www.geocybernetics.org (accessed on 5 June 2023).
- Kuhn, W.; Raubal, M.; Gärdenfors, P. Editorial: Cognitive Semantics and Spatio-Temporal Ontologies. Spat. Cogn. Comput. 2007, 7, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, G.; Sieber, R. Do geospatial ontologies perpetuate Indigenous assimilation? Prog. Hum. Geogr. 2020, 44, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montréal Declaration for a Responsible Development of Artificial Intelligence. 2018. Available online: https://montrealdeclaration-responsibleai.com/#:~:text=The%20Montr%C3%A9al%20Declaration%20is%20a,recommendations%20with%20strong%20democratic%20legitimacy (accessed on 8 June 2023).
- Statement on AI Risk: AI Experts and Public Figures Express Their Concern about AI Risk. Center for AI Safety. 2023. Available online: https://www.safe.ai/statement-on-ai-risk (accessed on 6 January 2024).
- Sullivan, S. What’s ontology got to do with it? On nature and knowledge in a political ecology of ‘the green economy’. J. Political Ecol. 2017, 24, 217–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.E.; Arista, N.; Pechawis, A.; Kite, S. Making kin with the machines. J. Des. Sci. 2018, 3, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Cadena, M. Indigenous cosmopolitics in the Andes: Conceptual reflections beyond “politics”. Cult. Anthropol. 2010, 25, 334–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn, E. How Forests Think: Towards an Anthropology beyond the Human; University of California Press: Oakland, CA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chaney, A. Runaway: Gregory Bateson, the Double Bind, and the Rise of Ecological Consciousness, University of North Carolina Press, JSTOR. 2017. Available online: https://www.jstor.org/stable/10.5149/9781469631745_chaney (accessed on 12 September 2023).
- Sheridan, J.; Longboat, R. The Haudenosaunee Imagination and the Ecology of the Sacred. Space Cult. 2006, 9, 365–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, C.; Burfurd, I.; Duckham, M.; Guntarik, O.; Kerr, D.; McMillan, M.; Matrin Saldias, D. Bridging the geospatial gap: Data about space and indigenous knowledge of place. Geogr. Compass 2020, 14, e12542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulsifer, P.L.; Brauen, G.; Furgal, C.; Sherar, M.; Sheldon, T.; Nickels, S. Sharing Nunatsiavimmiut Knowledge in Support of Regional Land Use Planning and Policy Development: Visualization of complex concept models. 2015. ArcticNet Annual Scientific Meeting (ASM 2015), 7-11/12/2015, Vancouver, BC, Canada. Available online: http://www.arcticnetmeetings.ca/asm2015/docs/posters-abstracts.pdf (accessed on 5 September 2023).
- Iliadis, A.; Pulsifer, P.; Lauriault, T.; Couldry, N.; Mejias, U.A. Social ontology in big data organizing. In Proceedings of the Panel presented at AoIR 2018: The 19th Annual Conference of the Association of Internet Researchers, Montréal, QC, Canada, 10–13 October 2018; AoIR. Available online: http://spir.aoir.org (accessed on 5 September 2023).
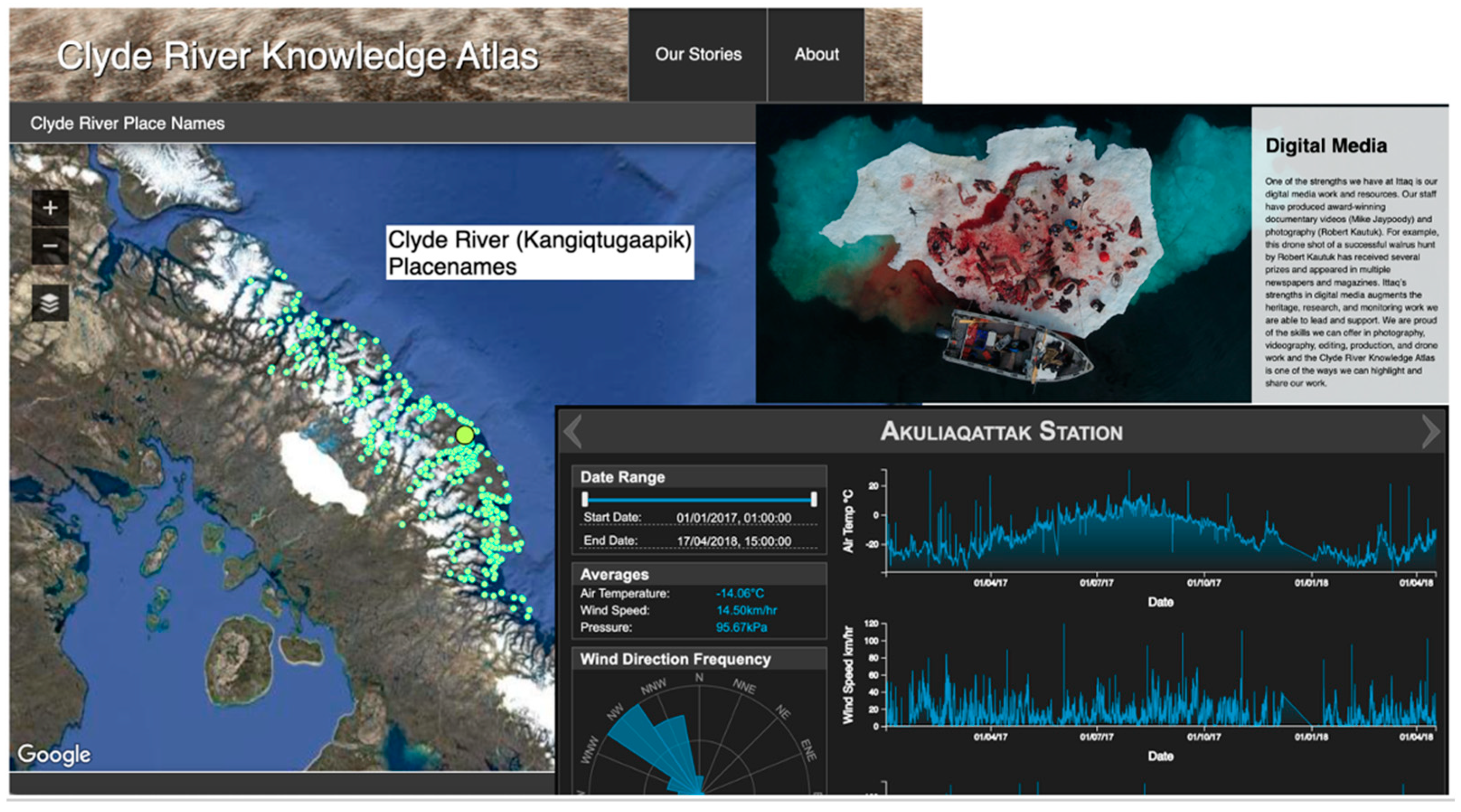
- Clyde River Atlas. Available online: https://clyderiveratlas.ca/index.html (accessed on 12 March 2023).
- 2015 to 2020—SSHRC Insight Grant: Aboriginal Research: Residential Schools Land Memory Mapping Project. Principal Investigator, Dr. Fraser Taylor; Post-Doctoral Researcher, Dr. Stephanie Pyne; et al. This Project Involves a Host of Collaborators and Participants Nationwide, and Builds on Previous SSHRC-funded Research to Produce the Lake Huron Treaty Atlas by Extending Its Residential Schools Component. Available online: https://geomedialab.org/mapping_residential_schools.html (accessed on 31 December 2023).
- 2009 to 2012—SSHRC Standard Research Grant: A Cybercartographic Case Study of the Lake Huron Treaty Relationship Process. D.R. Fraser Taylor, Principal Investigator, and PhD Researcher, Stephanie Pyne; with Co-Applicants: Nancy Doubleday (Geography and Environmental Studies, Carleton University and Sebastien Caquard (Universite de Montreal). This research Had the Broad Objective to Increase the Understanding of the Requirements for Improved Treaty-Based Relationships with Canada’s Indigenous Peoples and in Particular, the Anishinaabeg (or Anishinaabe peoples), through the Development of an Online Cybercartographic Atlas of the Lake Huron Treaty Relationship. Available online: https://gcrc.carleton.ca/index.html?module=module.gcrcatlas_indigenousknowledge#eyJ0IjoieCIsImkiOiI1ZGM1MGY1YjcwOTcxOTkyNGJmOWQ3YWY5NTZhNjRmNSIsInMiOjE3MTEwMTA0MjE3NDZ9 (accessed on 31 December 2023).
- 2009 to 2012—SSHRC Northern Communities Grant: Views from the North: A Collaborative Visual Repatriation Project with Inuit in Nunavut. Principal Investigator: Carol Payne, Co-Applicant: D. R. F. Taylor. This Project is Part of GCRC Northern Research. Available online: https://gcrc.carleton.ca/index.html?module=module.gcrcatlas_northernresearch (accessed on 31 December 2023).
- Ljubicic, G.J.; Pulsifer, P.L.; Hayes, A.; Taylor, D.R.F. The Creation of the Inuit siku (Sea Ice) Atlas. In Developments in the Theory and Practice of Cybercartography: Applications and Indigenous Mapping, 2nd ed.; Taylor, D.R.F., Lauriault, T.P., Eds.; Elsevier Science: Oxford, UK, 2014; pp. 201–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulsifer, P.L.; Laidler, G.J.; Taylor, D.R.F.; Hayes, A. Towards an Indigenist Data Management Program: Reflections on Experiences Developing an Atlas of Sea Ice Knowledge and Use. Can. Geogr. 2011, 55, 108–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ittaq Heritage and Research Centre. Available online: https://ittaq.ca/ (accessed on 12 January 2024).
- Taylor, D.R.F.; Thumbadoo, R.V. Editorial Commentary on the IJGI Special Issue “Mapping Indigenous Knowledge in the Digital Age”. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2022, 11, 363. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade-Sanchez, J.A.; Eaton-González, R. Cybercartography as a transdisciplinary approach to solve complex environmental problems: A case study of the Kumeyaay Peoples of Baja California and the conservation of oak trees. In Further Developments in the Theory and Practice of Cybercartography: International Dimensions and Language Mapping; Taylor, D.R.F., Anonby, E., Murasugi, K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES). Available online: https://ipbes.net/ (accessed on 16 March 2024).
- Lentz, C. Indigenous theories of landownership. In Land and the Politics of Belonging in West Africa; Kuba, R., Lentz, C., Eds.; Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 35–56. [Google Scholar]
- Shipton, P.M. Mortgaging the Ancestors: Ideologies of Attachment in Africa; Yale University Press: New Havenb, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- UNESCO Recommendation on Open Science, Adopted by UN Member States in 2021; 40 C/Resolution 24. Available online: https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000372579.page=35 (accessed on 6 June 2023).
- Policy Brief, 2023 Data Ethics and the UNESCO Recommendation on Open Science Data Ethics Working group of CODATA. Available online: https://bit.ly/WG-Data-Ethics-DRAFT-Policy-Briefs (accessed on 12 January 2024).
- Merodio Gómez, P.; Ramírez Santiago, A.; García Seco, G.; Casanova, R.; MacKenzie, D.; Tucker, C. Ethics in the use of geospatial information in the Americas. Technol. Soc. 2022, 69, 101964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Caudill, C.M.; Pulsifer, P.L.; Thumbadoo, R.V.; Taylor, D.R.F. Meeting the Challenges of the UN Sustainable Development Goals through Holistic Systems Thinking and Applied Geospatial Ethics. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2024, 13, 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi13040110
Caudill CM, Pulsifer PL, Thumbadoo RV, Taylor DRF. Meeting the Challenges of the UN Sustainable Development Goals through Holistic Systems Thinking and Applied Geospatial Ethics. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2024; 13(4):110. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi13040110
Chicago/Turabian StyleCaudill, Christy M., Peter L. Pulsifer, Romola V. Thumbadoo, and D. R. Fraser Taylor. 2024. "Meeting the Challenges of the UN Sustainable Development Goals through Holistic Systems Thinking and Applied Geospatial Ethics" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 13, no. 4: 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi13040110
APA StyleCaudill, C. M., Pulsifer, P. L., Thumbadoo, R. V., & Taylor, D. R. F. (2024). Meeting the Challenges of the UN Sustainable Development Goals through Holistic Systems Thinking and Applied Geospatial Ethics. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 13(4), 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi13040110








