Abstract
Cartographic design is fundamental to effective mapmaking, requiring adherence to principles such as visual hierarchy, symbolization, and color theory to convey spatial information accurately and intuitively, while Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Large Language Models (LLMs) have transformed various fields, their application in cartographic design remains underexplored. This study assesses the capabilities of a multimodal advanced LLM, GPT-4o, in understanding and suggesting cartographic design elements, focusing on adherence to established cartographic principles. Two assessments were conducted: a text-to-text evaluation and an image-to-text evaluation. In the text-to-text assessment, GPT-4o was presented with 15 queries derived from key concepts in cartography, covering classification, symbolization, visual hierarchy, color theory, and typography. Each query was posed multiple times under different temperature settings to evaluate consistency and variability. In the image-to-text evaluation, GPT-4o analyzed maps containing deliberate cartographic errors to assess its ability to identify issues and suggest improvements. The results indicate that GPT-4o demonstrates general reliability in text-based tasks, with variability influenced by temperature settings. The model showed proficiency in classification and symbolization tasks but occasionally deviated from theoretical expectations. In visual hierarchy and layout, the model performed consistently, suggesting appropriate design choices. In the image-to-text assessment, GPT-4o effectively identified critical design flaws such as inappropriate color schemes, poor contrast and misuse of shape and size variables, offering actionable suggestions for improvement. However, limitations include dependency on input quality and challenges in interpreting nuanced spatial relationships. The study concludes that LLMs like GPT-4o have significant potential in cartographic design, particularly for tasks involving creative exploration and routine design support. Their ability to critique and generate cartographic elements positions them as valuable tools for enhancing human expertise. Further research is recommended to enhance their spatial reasoning capabilities and expand their use of visual variables beyond color, thereby improving their applicability in professional cartographic workflows.
1. Introduction
Cartographic design is the backbone of effective mapmaking, transforming raw geographical data into meaningful, accessible, and visually compelling information [1,2]. The application of principles such as visual hierarchy, layout, symbolization, scale, color choices, symbol sizes, and data classification ensures that maps convey accurate spatial information in an intuitively understandable manner [3,4]. A well-designed map not only distills complex spatial data into clear insights but also anticipates the needs of diverse audiences—including scientists, policymakers, and the general public—thereby facilitating informed decision-making [5,6]. Without proper attention to these cartographic principles, maps may become unclear, misleading, or overly complex, thus failing in their fundamental goal of effective communication. As geographic data continues to grow in volume and complexity, adherence to these principles becomes increasingly critical to prevent information overload and to ensure that maps remain usable tools [7].
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Large Language Models (LLMs) have rapidly transformed numerous fields, from healthcare and finance to entertainment and education [8,9]. Among these, Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT) models, such as GPT-3 and GPT-4, exemplify the sophisticated capabilities of LLMs in understanding and generating human-like language. These advances have been driven by the increased availability of data and computational power, alongside the development of transformative architectures like the Transformer model [10], which underpins many LLMs, including GPT. In areas such as natural language processing, pattern recognition, and automated content creation, AI technologies, particularly GPT-based models, have demonstrated exceptional capabilities, expanding what was once thought possible for machine-assisted tasks [11].
LLMs, such as GPT-3 and beyond, have been impactful in domains that require interaction with language, including creative writing, automated customer service, and complex research synthesis [12,13]. Their ability to understand context, provide detailed explanations, and generate fluent text has made them valuable tools for enhancing human capabilities in both routine and intellectually demanding tasks [14]. As AI technologies grow more sophisticated, their use cases are expanding to new domains, including the traditionally human-centric field of cartography. Investigating the integration of AI into creative and technical fields like mapmaking is essential for understanding how these technologies can enhance cartographic practices and overcome current limitations [15].
While there have been GeoAI studies addressing cartographic topics like map generalization, object detection, feature extraction, expert systems, and ontologies [15,16,17,18,19], there is a noticeable lack of research on the application of LLMs in cartographic visualization and design. Existing applications rely on standard color palettes and default settings in Python libraries like Matplotlib, leading to uniform maps that may neglect essential cartographic rules. This homogenization results in maps that lack diversity and fail to communicate spatial information. Although many studies have explored the use of LLMs for spatial analysis and map production, a comprehensive examination of their capabilities and limitations in cartographic representation is still missing. The ‘black box’ nature of LLMs further complicates the understanding of the extent and scope of their knowledge, necessitating an in-depth analysis to uncover their cartographic potential. To address these challenges, researchers and practitioners in the field are developing benchmarks with diverse focuses, such as mathematics, to evaluate and enhance LLM performance. Such efforts aim to improve their spatial reasoning capabilities and expand their use of visual variables beyond color, ultimately advancing their role in professional cartographic workflows.
The primary purpose of this study is to assess and compare the capabilities of GPT-4o model in understanding and suggesting cartographic design elements. In the study, the feasibility of using GPT-4o in cartographic design processes is examined, with a focus on how well they adhere to established cartographic principles. By evaluating their ability to understand and implement key design aspects like visual hierarchy, symbolization, and color usage, this research seeks to evaluate the potential role of LLMs in enhancing cartographic workflows.
To accomplish this, two assessments were conducted using GPT-4o, selected among other LLMs through preliminary testing for its advanced capabilities and high performance in natural language processing. Leveraging its multimodal capabilities to process and integrate both textual and visual inputs, the first assessment focused on text-to-text analysis, while the second evaluated image-to-text interpretation, both influenced by well-known cartography textbooks [3,5,20]. The results were analyzed within the framework of five fundamental cartographic design principles outlined in the Geographic Information Science & Technology Body of Knowledge (GIS&T BoK), providing a systematic approach to evaluating GPT-4o’s proficiency in cartographic interpretation.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows: Section 2 reviews relevant literature on GeoAI, cartographic design principles, and LLM applications. Section 3 outlines the methodology for assessing LLM capabilities in cartographic design. Section 4 presents the study results, while Section 5 discusses the implications, limitations, and potential opportunities for LLMs in cartography. Finally, Section 6 concludes with key findings and recommendations for future research.
2. Literature Review
2.1. Overview of Large Language Models
LLMs have seen significant advancements in recent years due to improved neural network architectures, increased computational power, and the availability of massive datasets [21]. Early LLMs were focused on simple tasks like sentence completion or text classification. However, the introduction of the Transformer architecture by Vaswani et al. [10] enabled LLMs to better understand and generate complex language structures, paving the way for advanced models like GPT-3 and GPT-4 [22].
GPT-4, developed by OpenAI, is one of the most advanced LLMs available today, building on the strengths of its predecessors in natural language understanding and generation [23]. Other notable LLMs include Llama, developed by Meta [24], Gemini by Google DeepMind [25], and Claude by Anthropic [26]. With hundreds of billions of parameters, these models excel at understanding syntax, semantics, and world knowledge. They can engage in sophisticated dialogue, translate languages, summarize documents, and create content such as stories or poems. Their adaptability across domains marks a shift from task-specific models to general-purpose intelligence tools.
LLMs have demonstrated capabilities in logical reasoning and multi-step problem-solving, supported by reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF), which helps align model outputs with human expectations [27]. These capabilities are driving transformative changes across various industries by streamlining workflows, assisting professionals, and enhancing creative processes. In healthcare, they support clinical workflows, assist in analyzing medical literature, and aid in diagnosing conditions [28,29]. In education, LLMs function as adaptive tutoring systems, generate content, and provide personalized feedback, which helps both educators and students by creating lesson plans and educational materials that enrich the learning experience [30]. Creative industries also benefit, as writers, designers, and artists utilize LLMs to brainstorm ideas and collaborate on content [31]. Technical fields like software development leverage LLMs for code generation and problem-solving. Additionally, in financial and legal sectors, LLMs automate tasks such as market sentiment analysis, report generation, and legal research, making information processing more efficient [32,33,34].
An emerging frontier in LLM development is multimodality, where models can process and integrate data across diverse formats, such as text, images, audio, and video. Multimodal LLMs demonstrate remarkable capabilities by interpreting visual data and generating accurate, context-aware textual descriptions. For example, these models can analyze complex images—ranging from medical scans to infographics—and provide precise textual summaries or annotations that aid in diagnostics, accessibility, and content understanding [35,36]. This capability expands the scope of applications for LLMs, enabling cross-disciplinary workflows such as image-based documentation, enhanced accessibility tools for visually impaired individuals, and automation in creative tasks like generating captions or narratives for visual content.
Despite significant advancements in artificial intelligence, critical ethical and practical challenges persist. Among these are biases embedded in model outputs, which can perpetuate systemic inequalities and lead to unfair outcomes [37,38]. Additionally, the potential for misinformation dissemination raises concerns about the reliability and trustworthiness of AI-generated content [39,40]. Furthermore, the substantial environmental impact associated with training large-scale models underscores the need for sustainable practices in AI development [41,42].
2.2. GeoAI in Cartography
GeoAI, a confluence of geographic information science and artificial intelligence, has attracted considerable interest for its potential to transform cartographic design. By enabling automated processes and enhancing the efficiency of traditionally complex cartographic tasks, GeoAI has emerged as a promising tool in spatial science [43,44,45].
GeoAI models have facilitated various cartographic applications, particularly in automating labor-intensive tasks like map generalization and symbolization [17,18,46,47]. Researchers have leveraged machine learning models to streamline map production by automating repetitive design tasks, such as positioning and color schematization, which traditionally require expert input [48], while AI models have been applied to tasks ranging from spatial pattern recognition to geospatial visualization, their success depends on specific data modalities, such as raster or vector data, which suit distinct cartographic functions [19].
A promising area involves integrating GeoAI with cartographic symbolism. Some studies have explored GeoAI for “active cartographic symbolism”, where AI models assist in selecting optimal design parameters to match user contexts, moving beyond rigid rule-based frameworks to more adaptive and context-sensitive designs [49]. Specifically, LLMs enhance AI-assisted mapmaking by generating thematic elements, labeling, and interpreting spatial datasets. For instance, the development of Autonomous Geographic Information Systems (GISs) leverages LLMs’ capabilities in natural language understanding, reasoning, and coding to automate spatial data collection, analysis, and visualization [50]. Additionally, the GeoLLM framework demonstrates how LLMs can extract geospatial knowledge, contributing to tasks such as population density measurement and economic livelihood assessments [51].
Furthermore, LLMs with geospatial technologies have demonstrated potential in enhancing GIS applications and democratizing their accessibility. Zhang et al. [52] introduced BB-GeoGPT, a GIS-specific LLM that utilizes curated training data (BB-GeoPT and BB-GeoSFT) and an evaluation dataset (BB-GeoEval) to improve the model’s geospatial understanding and performance. Their findings underscore the model’s superiority over general-purpose LLMs like Alpaca-7B and Vicuna-7B but highlight limitations compared to GPT-3.5-turbo, particularly in addressing GISs’ interdisciplinary demands. Concurrently, Mansourian and Oucheikh [53] proposed ChatGeoAI, a system leveraging LLMs for translating natural language queries into geospatial analysis code, exemplifying its utility in domains like health and disaster management. Their study emphasizes the need for error correction loops and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to refine system reliability and expand its contextual scope. Zhang et al. [54] also introduced MapGPT, a framework employing GPT-4 to autonomously design maps based on natural language inputs. With 68 dedicated mapping tools, MapGPT aims to benefit both professional cartographers and non-experts, though limitations in interaction design, tool diversity, and cartographic best practices require further exploration.
Despite significant advancements in GeoAI, technical challenges persist. Notably, current GeoAI-based metrics often provide superficial evaluations that fail to capture the intricate nuances of cartographic design, thereby limiting their application. Kang et al. [55] highlight that although AI techniques like Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) can transfer multiscale map styles, they may not fully replicate the complexities inherent in traditional cartographic aesthetics. Quantitative, machine-based metrics provide scalable methods to assess map quality; however, they often fall short in evaluating the subjective aesthetic elements crucial to effective map design [56]. Another significant challenge is the interpretability of AI outputs. The opaque nature of “black-box” models obscures the understanding of how specific inputs influence cartographic decisions, thereby complicating error tracking and quality assurance processes [57].
2.3. Cartographic Design Principles
In the creation of maps, cartographers must make numerous decisions to effectively visualize geographic information. This process involves several critical steps, including the classification of data, the design of symbolization and visual variables, and the determination of visual hierarchy and layout, as well as decisions on color schemes and the appropriate use of typography. These stages are well-documented across the literature, particularly in foundational cartography textbooks. Among these resources, one stands out as particularly comprehensive: The GIS&T BoK, which provides an in-depth exploration of these mapping principles and practices.
GIS&T BoK is a foundational resource outlining the essential concepts, methodologies, and competencies within geographic information science and technology. Initially published in 2006 by the University Consortium for Geographic Information Science (UCGIS), the BoK serves as a reference framework for curriculum development, professional certification, and research in GIS&T. It organizes its content into ten Knowledge Areas, each subdivided into Units and Topics, covering diverse domains such as spatial analysis, data modeling, and cartography, which allows for a systematic understanding of geospatial science [20,58,59].
The GIS&T BoK identifies several key principles that are instrumental for cartographers: classification, visual hierarchy and layout, symbolization and visual variables, color theory, and typography. Each principle plays a unique role in organizing, displaying, and interpreting spatial data, ensuring that maps are both visually engaging and analytically informative. These cartographic principles are outlined below in five categories based on the GIS&T BoK.
Classification: Transforming raw data into structured categories through classification enhances visual interpretation in cartography. Classification is a key component within the broader category of “Statistical Mapping, Enumeration, Normalization, and Classification” as described in the GIS&T BoK. The equal interval method is ideal for uniformly distributed data with familiar ranges, as it creates classes with consistent intervals, making it easy to interpret. However, it may not account for uneven data distributions. The quantiles (equal count) method is well-suited for ordinal data or evenly distributed datasets, as it places an equal number of observations into each category, highlighting patterns clearly. This approach is intuitive for users but may obscure outliers due to the forced balance in counts. Meanwhile, the mean–standard deviation method excels with normally distributed datasets, providing meaningful distinctions around ‘averages’ and deviations, making it effective for highlighting data trends in such distributions [20].
Visual Hierarchy and Layout: Visual design principles highlights the distinctions between attributes perceived as ‘stronger’ or ‘weaker’ in a visual hierarchy. Key elements such as size, color, focus, and arrangement play a critical role in guiding viewer attention and establishing visual dominance. Larger elements naturally draw more attention than smaller ones, while warm hues and highly saturated colors are more visually prominent than cool or pale tones. Additionally, contrast in color value—such as dark on light or light on dark backgrounds—significantly enhances visibility, emphasizing the importance of contrast as a fundamental aspect of effective design [20].
Symbolization and Visual Variables: Symbolization translates data attributes into visual forms, making abstract information accessible. For nominal data, which represents categories without inherent order, variables like shape, color hue, orientation, and texture are highly effective, as they allow clear distinction between categories without implying hierarchy or progression. In contrast, ordinal data, characterized by a meaningful order among categories, benefits from variables such as size, color value, color saturation, and transparency, which intuitively convey a sense of progression or ranking. Finally, for numerical data, where precise quantities and measurable intervals are essential, variables like size, color value, color saturation, and texture excel, as they enable proportional representation and fine granularity [20].
Color Theory: The principles of color theory play a crucial role in enhancing both the aesthetics and readability of maps. To create effective maps and visualizations, the careful selection and arrangement of colors is essential to reflect the underlying data structure. A database of color palettes tailored for choropleth and qualitative maps has been developed, incorporating three types of color schemes based on the number of classes and the data’s nature [3,60]. Sequential schemes are designed to depict ordered data, progressing from light to dark hues to represent increasing values, making them ideal for data such as percentages or densities. Diverging schemes combine two sequential schemes diverging from a shared midpoint, useful for highlighting critical thresholds or contrasts, such as increases and decreases in a phenomenon. Qualitative schemes, conversely, employ distinct hues of similar lightness to differentiate between categories, ensuring visual emphasis is given to key data points, making them ideal for nominal or categorical data like land use or inventory maps [20].
Typography: Effective typography is essential for map legibility, as it influences the clarity and hierarchy of information. According to GIS&T BoK, primary labels (e.g., place names) should stand out, while secondary labels remain subdued to create a clear information structure. Typeface choices can also reflect the map’s tone, with sans-serif fonts often suggesting modernity and serif fonts tradition. Well-designed typography avoids clutter, guiding users through textual and graphical elements fluidly. Furthermore, it is essential to acknowledge the concept of the “semantic effect” of typefaces, a phenomenon extensively explored in prior research. Empirical evidence indicates that typefaces possess distinct personalities that can evoke specific emotional or cognitive associations in viewers [61,62]. This inherent personality of typefaces influences how textual content is perceived, interpreted, and understood. The “semantic effect”, as defined by Childers and Jass [63], refers to this ability of typefaces to convey meaning or evoke impressions beyond the literal content of the text they display [20].
3. Methodology
3.1. Research Design
This research employs a mixed-methods approach, combining qualitative and quantitative methodologies to comprehensively evaluate the capabilities of a large language model, GPT-4o, in the context of cartographic design. The study involves two distinct assessments—a text-to-text evaluation and an image-to-text evaluation—designed to gauge GPT-4o’s proficiency in cartographic tasks and to understand the potential of LLMs for AI-assisted mapmaking.
The text-to-text assessment focused on the model’s ability to understand and apply cartographic theory, terminologies, and best practices. A set of 15 direct questions—three dedicated to each of five different categories—was developed, primarily derived from key concepts in the GIS&T BoK. The questions followed a consistent structure, such as: “As a cartographer tasked with creating a map to [task], which [method] would you choose? Provide only a short answer, without explanation”. These queries required the model to identify the most suitable cartographic method for various tasks, ensuring responses were succinct to facilitate quantitative evaluation.
Each text-based query was posed 100 times using OpenAI’s API with Python, ensuring a zero-shot mode with a clear history and memory reset between each attempt. This approach provided quantitative metrics to assess the consistency and reliability of GPT-4o’s responses. The distribution of the results was analyzed both qualitatively and quantitatively, offering in-depth insights into the model’s interpretative abilities and examining how well it aligns with cartographic conventions and standards.
The image-to-text evaluation tested GPT-4o’s ability to analyze and interpret visual cartographic elements. Stimuli were drawn from established cartography textbooks to ensure that the maps and design elements represented cartographic norms. Each image contained deliberate cartographic errors, such as typographic issues or improper symbolization, to gauge the model’s ability to identify these mistakes and provide suitable corrections. A set of five image-based queries was created, each featuring basic maps or map components with specific intentional errors. The model was asked questions like: “Is this [method] correct on this map? Briefly critique it and suggest a new one if applicable”.
Using the GPT-4o user interface, each image-based query was presented 10 times in a zero-shot mode with memory reset between attempts. The results were analyzed qualitatively in depth, incorporating information from textbooks and leveraging the authors’ domain knowledge. This combination allowed for both in-depth qualitative insights into the model’s interpretative abilities and quantitative assessment of its consistency and reliability.
Both assessments were structured to provide a systematic evaluation of GPT-4o’s performance using fundamental cartographic design principles, which serve as ideal benchmarks for evaluating AI capabilities in mapmaking. Qualitative and quantitative methodologies were combined, and the distribution of responses was analyzed to comprehensively assess the model’s proficiency in cartographic tasks and to understand the potential of LLMs for AI-assisted mapmaking.
3.2. LLM Selection and Temperature Settings
GPT-4o was selected for this study following a preliminary testing phase due to its advanced multimodal capabilities and consistently high performance in natural language processing, contextual understanding, and cartographic interpretation. Several key criteria informed the decision to use GPT-4o over other LLMs, such as Llama and Gemini. These criteria included the model’s parameter size, benchmark test results, and specific performance in geography-related studies [64,65].
The temperature parameter in LLMs controls the randomness of the generated output, affecting the balance between creativity and consistency. Lower temperatures (close to 0) make the output more predictable, producing responses that align closely with common patterns and established knowledge. Higher temperatures (approaching 1 or beyond) introduce more variability, encouraging the model to take creative or less conventional approaches. In our text-to-text experiments, three temperature settings were tested: 0.4 (less creative), 0.7 (default), and 1.0 (most creative), allowing us to observe and discuss the variability in responses across these levels. For our image-to-text experiments, the default temperature value of 0.7 was used to maintain a balanced approach, as high levels of creativity were not required in this context. This approach helped us evaluate how temperature adjustments impact both the consistency and creativity of the model’s output.
4. Results
4.1. Text-to-Text Assessment
The results are presented using a structured approach that combines tables and visualizations to enhance clarity and accessibility. An initial summary table highlights the categories and corresponding queries, offering a quick overview. This is followed by detailed sub-tables organized by category, allowing for focused analysis within each thematic area. Variability in responses across temperature settings of 0.4, 0.7, and 1.0 is illustrated, demonstrating how the distribution of answers shifts with different settings. Finally, a heatmap provides a comprehensive view of response consistency across all questions and temperature settings, highlighting areas where the model’s reliability varies.
Table 1 provides a summary of the various categories and corresponding queries used in the text-to-text assessment. The table organizes the queries into distinct thematic categories that reflect key aspects of cartographic design, allowing for a systematic evaluation of the model’s capabilities.

Table 1.
Thematic Categorization of Queries for Text-to-Text Assessment in Cartographic Design Evaluation.
In the Classification category, queries are designed to assess the model’s suggestions for classifying data types based on their distribution (e.g., uniform, normal, or evenly distributed ordinal data). Expected responses include the use of equal intervals for uniform distributions, standard deviation for normal distributions, and quantiles for evenly distributed ordinal data [20].
Visual Hierarchy and Layout includes questions regarding color choices to establish different levels of visual importance. Expected contrasts include the following: strong contrast is achieved through large size, warm hues, intense saturation, and bold transitions between dark and light values; conversely, weak contrast is characterized by small size, cool hues, pale saturation, and subtle transitions between dark and light values [20].
The Symbolization and Visual Variables category focuses on determining which visual variables should be used for nominal, ordinal, or numerical data representation. For nominal data, expected variables include shape, color hue, orientation, and texture. Ordinal data should utilize size, color value, color saturation, transparency, crispness, and resolution, while numerical data primarily relies on size as a visual variable [20].
Color Theory examines the use of color schemes appropriate for various types of data. Sequential color schemes are expected for ratio data, qualitative schemes for land use/land cover data, and diverging schemes for cheapest and costliest locations [20].
Lastly, the Typography category tests the model’s recommendations for suitable typefaces for different types of maps, ranging from property maps to entertainment-focused depictions. Unlike other categories, Typography does not have a single correct answer, as multiple fonts can effectively fulfill the same purpose among the thousands of available options [20].
4.1.1. Classification
Table 2 presents the distribution of responses generated under different temperature settings, focusing on nominal data, normally distributed data, and evenly distributed ordinal data. Bolded entries in the table denote the expected optimal responses for each data type, serving as a benchmark against cartographic best practices.

Table 2.
Distribution of Response Rates Across Temperature Settings for Uniform Distribution, Normal Distribution, and Evenly Distributed Ordinal Data.
For uniform distribution, the model consistently recommended the ‘Equal Intervals’ method across all temperature settings, demonstrating reliability even with increased randomness, though some minor variations appeared at higher temperatures. In the case of normally distributed data, the model’s responses diversified as temperature increased, with ‘Natural Breaks’ becoming more prominent. Conversely, the expected response, ‘Standard Deviation’, was rarely observed at higher temperatures, suggesting that the observed shift might stem from amplified variability rather than the appropriateness of the response. Similarly, for evenly distributed ordinal data, the model predominantly suggested ‘Equal Intervals’ rather than the desired ‘Quantiles’, while the model’s recommendations cannot be deemed entirely incorrect given the nuanced dependence on specific data characteristics, they are not fully aligned with theoretical expectations.
4.1.2. Visual Hierarchy and Layout
Table 3 highlights the distribution of responses across temperature levels for design prompts targeting contrast and background emphasis. Bolded responses in the table indicate optimal answers based on GIS&T BoK, serving as benchmarks for evaluation.

Table 3.
Distribution of Response Rates Across Temperature Settings for Contrast and Background Emphasis Prompts.
For strong contrast, the model consistently selected ‘Complementary’ colors across all temperatures, demonstrating a stable application of color hue principles, with warmer colors used effectively for stronger contrasts. In weak contrast scenarios, the model primarily leaned towards gray tones, incorporating only a single color from the range of cooler hues on the opposite side of the color wheel. Higher temperatures introduced slightly more variety, with muted and pastel tones appearing 10% more frequently. For background receding effects, the model reliably adhered to expectations, selecting soft, muted colors such as light gray, pale blue, and soft green, regardless of temperature.
4.1.3. Symbolization and the Visual Variables
In this section, the model’s capability to assign appropriate visual variables to different types of cartographic data—nominal, ordinal, and numerical—based on text-to-text queries was evaluated, as presented in Table 4.

Table 4.
Distribution of Response Rates Across Temperature Settings for Visual Variables to Nominal, Ordinal, and Numerical Data.
For nominal data, the model consistently selects ‘Color Hue’ as the primary visual variable, aligning with expected preferences. However, as the temperature increases, a slight expansion of choices is observed, though the model generally overlooks other suitable variables namely shape, orientation, and texture outlined in the GIS&T BoK. For ordinal data, the model predominantly assigns ‘Color Hue’, while occasionally incorporating ‘Color Value’ (a combination of the original responses ‘Choropleth Shading’ and ‘Graduated Colors’) as the temperature rises, while ‘Color Value’ aligns with the expected response, the predominant attribute, ‘Color Hue’, is not recommended as a good practice for ordinal data according to the GIS&T BoK. Despite the GIS&T BoK listing multiple viable visual variables for ordinal data, such as size, transparency, and crispness, the model’s responses remain narrowly focused on color-based solutions. For numerical data, the results are notably diverse. At lower temperatures, the model demonstrates a preference for ‘Color Value’ and ‘Color Hue’. As the temperature increases, the responses broaden significantly, encompassing ‘Color Gradients’, ‘Color Saturation’, and occasionally the expected ‘Size’ variable, which aligns better with GIS&T BoK recommendations.
4.1.4. Color Theory
Table 5 outlines the distribution of the model’s responses for prompts addressing the use of color schemes in three scenarios: ratio data, land use/land cover, and thematic representation of economic data, such as the cheapest and costliest places.

Table 5.
Distribution of Response Rates Across Temperature Settings for Color Scheme Selection in Ratio Data, Land Use/Land Cover, and Economic Thematic Mapping.
For ratio data, the model consistently suggests a sequential color scheme, reflecting an appropriate approach for ordered data, regardless of temperature. In the case of land use/land cover data, where a qualitative scheme is expected, the model demonstrates a nuanced understanding of color theory. It predominantly suggests custom color palettes, a subset of qualitative schemes, including greens for vegetation, browns for urban areas, and blues for water bodies, aligning with traditional cartographic practices, while temperature variations introduce slight changes (e.g., gray for urban areas or brown for barren land), the underlying recommendations remain aligned with established principles. For thematic representations of economic extremes, such as the cheapest and costliest locations, the model consistently opts for a diverging scheme, often suggesting shades of green for the cheapest areas and shades of red for the most expensive. This adherence to the expected diverging color scheme persists across all temperature levels, with no alternative color combinations offered.
4.1.5. Typography
Table 6 illustrates the distribution of the model’s typographic suggestions across different temperature settings (0.4, 0.7, and 1.0) within the Typography category, showcasing its ability to adapt to various cartographic contexts: ‘Property Legal Designations’, ‘Visited Entertainment Venues’, and ‘Star Wars Planets & Colonies’.

Table 6.
Distribution of Response Rates Across Temperature Settings for Divers Cartographic Contexts.
The results demonstrate the influence of temperature on creativity and variability in font selection. Lower temperatures tend to favor stable and conventional typeface choices, while higher temperatures introduce greater diversity and creativity. For instance, in the ‘Property Legal Designations’ context, Helvetica was the dominant choice across all settings, reflecting its clean and professional semantic effect. Although higher temperatures introduced alternatives like Garamond and Gotham, the overall variability remained limited, aligning with the semantic needs of this context.
In contrast, the ‘Visited Entertainment Venues’ queries displayed greater sensitivity to temperature changes. At lower temperatures, the model preferred Helvetica, but higher temperatures expanded the range to include fonts like Avenir and Futura, suggesting that context and word choice significantly influence typographic diversity. For example, some queries featured up to eight fonts even at low temperatures, while others exhibited minimal variability. This variability underscores the importance of thematic alignment in achieving creative outputs. Similarly, for ‘Star Wars Planets & Colonies’, the model consistently suggested futuristic and bold typefaces such as Eurostile, which aligns with the semantic expectations of the theme. Higher temperatures further diversified the output, introducing imaginative fonts like Aurebesh and Star Jedi, reinforcing the model’s ability to adapt to stylistic and thematic demands.
4.1.6. Response Consistency of GPT-4o Across Temperature Settings
Figure 1 presents a heatmap showcasing the response consistency of GPT-4o across questions under three different temperature settings (0.4, 0.7, and 1). The heatmap provides a comparative visual analysis of response distributions, with darker shades indicating higher consistency and lighter shades highlighting areas of variability.
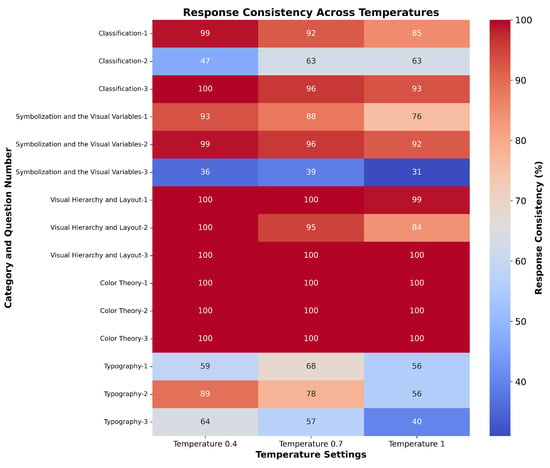
Figure 1.
Heatmap illustrating the response consistency of GPT-4o across 15 cartographic design questions under three temperature settings.
Categories like ‘Color Theory’ and ‘Visual Hierarchy and Layout’ demonstrate near-perfect consistency across all temperature settings, suggesting a robust understanding of these design principles. In contrast, the variability observed in responses to questions involving more nuanced or subjective elements, such as ’Symbolization and the Visual Variables’ and ’Typography’, indicates potential limitations in the model’s ability to consistently align with specific design conventions.
4.2. Image-to-Text Assessment
This section focuses on evaluating the model’s capability to interpret and critique visual cartographic elements through image-based queries. In this part of the study, a series of five different map images, each designed with specific, deliberate errors, was presented to the language model. The goal was to assess how effectively the model could identify inaccuracies and provide constructive feedback or suggestions for improvement. These images showcased basic maps or individual cartographic components, allowing us to examine whether the model could discern principles of cartographic design from visual input.
4.2.1. Map Scenario 1—Misleading Color Scheme
The model’s ability to interpret and critique visual cartographic elements was evaluated using an illustrative map that visualized regional preferences for hotdog condiments (ketchup, mustard, relish) based on plurality opinion (Figure 2a). This map, adapted from Krygier and Wood [5], was intentionally designed with a misleading and problematic color scheme—hues of red, orange, and yellow—that violated best practices in cartographic design. These colors, being sequential and tonally similar, are neither colorblind-friendly nor sufficiently distinct, creating confusion for viewers. When prompted, the model successfully identified the issue, noting the inappropriate use of sequential colors for categorical data. It suggested a revised color scheme with more distinct and intuitive choices: red for ketchup, yellow for mustard, and green for relish, aligning with commonly associated color conventions. An example map created based on the suggestions is shown in Figure 2b. Additionally, the model demonstrated the ability to assess the appropriateness of color schemes for individuals with visual impairments, offering alternative recommendations to enhance accessibility.
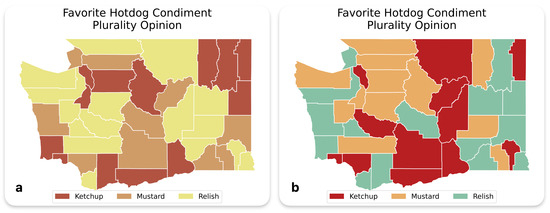
Figure 2.
(a) Example of a Misleading Cartographic Design, and (b) Improved Design Reflecting GPT-4o Suggestions for Hotdog Condiment Preferences.
4.2.2. Map Scenario 2—Improper Monochromatic Gradient
In Figure 3a, the map, reproduced from Krygier and Wood [5], depicts farm density across a region using a monochromatic grayscale gradient, categorized into five ranges. This design, intentionally flawed, was employed to evaluate the model’s ability to critique and improve cartographic visuals. Grayscale palettes, while occasionally used in cartography, present significant challenges for interpretability, particularly for individuals with visual impairments or in low-light conditions. The minimal contrast between adjacent categories (e.g., “1.31–1.80” and “1.80–2.21”) diminishes clarity, making it difficult to discern spatial differences. Additionally, the color ramp in this map violates intuitive design principles, where darker shades typically represent higher values and lighter shades lower values. When prompted, the model successfully identified these issues, highlighting the perceptual hierarchy problem and suggesting a more effective approach (Figure 3b). It recommended replacing the grayscale scheme with a sequential multi-hue palette, such as transitioning from light blue for the lowest density to darker shades for higher ranges. Furthermore, the model demonstrated versatility by proposing texture patterns as an alternative solution for scenarios requiring grayscale, showcasing its ability to adapt visual variables for different contexts.
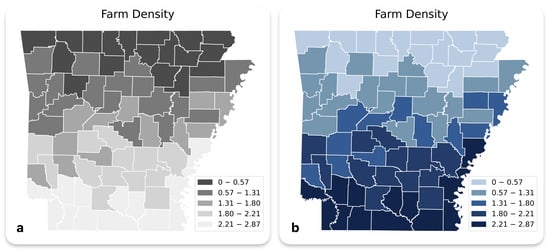
Figure 3.
(a) Example of Improper Monochromatic Gradient for Farm Density Visualization (b) Improved Design Reflecting GPT-4o Suggestions.
4.2.3. Map Scenario 3—Misleading Color Palette and Data Categorization
In Figure 4a, the map, reproduced from Krygier and Wood [5], illustrates the percent change in interest in “Worm Rooping” across a region, segmented into six data ranges. The map uses a sequential red-to-yellow color palette, intentionally flawed to assess the model’s ability to critique and propose improvements for misleading visual designs. The current color scheme assigns highly saturated red hues to minimal positive percent changes (e.g., “1% to 25%”) while using lighter yellows for significant negative changes (e.g., “−500% to −1000%”), creating a misleading visual emphasis. This design misrepresentation can bias viewers into perceiving small increases as more impactful than large decreases. Additionally, the wide data bins for negative changes (e.g., “−500% to −1000%” and “−100% to −499%”) and the use of overly similar hues for distinct categories (e.g., “0 to −99%” and “1% to 25%”) obscure the granularity and accuracy of the information, reducing interpretability. The model effectively identified these issues, categorizing them as a lack of intuitive gradient and clarity in distinguishing positive from negative changes (Figure 4b). It proposed a more suitable color scheme that introduces a clear contrast between cool tones (light blue to dark blue for positive changes) and warm tones (light orange to dark red for negative changes), improving the visualization’s ability to convey the increasing or decreasing trends across regions. However, it is important to note that the use of cool tones for positive changes and warm tones for negative changes may vary depending on the data, as well as regional and cultural differences.
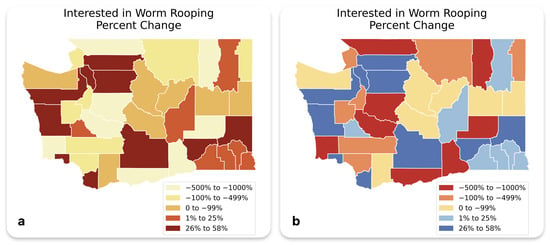
Figure 4.
(a) Example of Misleading Color Palette and Data Categorization for Percent Change in Interest in ‘Worm Rooping’ (b) Improved Design Reflecting GPT-4o Suggestions.
4.2.4. Map Scenario 4—Inappropriate Shape Symbolization
The map, reproduced from Krygier and Wood [5], in Figure 5a visualizes the distribution of active hate groups across the United States, employing geometric shapes (stars, diamonds, circles, squares, and triangles) to represent different numerical ranges by state. This map contains intentional design flaws to assess the model’s capability in identifying cartographic visualization principles. Most notably, the map employs an inappropriate visual variable—geometric shapes—to represent quantitative data, violating fundamental principles of visual hierarchy and perceptual ordering. Unlike continuous variables such as size or color intensity, geometric shapes lack natural ordinal properties, making it challenging for viewers to intuitively comprehend the relative magnitudes between states. The model demonstrated proficiency in detecting this core cartographic flaw, consistently recommending more appropriate visual variables such as color gradients or proportionally sized symbols that better align with quantitative data visualization principles (Figure 5b). Beyond identifying the primary design issue, the model exhibited sophisticated cartographic understanding by suggesting several enhancement strategies: incorporating qualitative descriptions for numerical ranges (e.g., “very high”, “moderate”, “low”), adding temporal context to track changes over time, utilizing inset maps for areas with high density, and implementing more granular category divisions to better capture spatial variations. These additional recommendations reflect the model’s capacity to not only identify problematic design choices but also propose comprehensive solutions for improving map legibility and effectiveness.
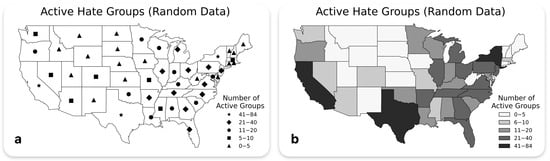
Figure 5.
(a) Example of Misleading Map Design Using Abstract Geometric Shapes to Represent Quantitative Data of Active Hate Groups (b) Improved Design Reflecting GPT-4o Suggestions.
4.2.5. Map Scenario 5—Misused Size Variable
The map, reproduced from Krygier and Wood [5], in Figure 6a depicts the spatial distribution of dominant hate groups across the United States, utilizing graduated circle symbols to represent different types of extremist organizations, including the Ku Klux Klan (KKK), Neo-Nazis, Black Separatists, Neo-Confederates, Christian Identity, and Racist Skinheads. This map incorporates deliberate cartographic flaws to evaluate the model’s understanding of visual variable selection principles. The primary design flaw lies in the inappropriate use of circle size—a quantitative visual variable—to represent qualitative categorical data. This misapplication creates an unintended hierarchical impression among the hate group categories, potentially leading viewers to incorrectly infer relative importance or magnitude where none exists. The model successfully identified this fundamental cartographic error, demonstrating consistent recognition that size variation is unsuitable for categorical data representation. It appropriately recommended the use of color hues (e.g., red for KKK, blue for Neo-Nazis, green for Black Separatists) as a more suitable visual variable for distinguishing between qualitative categories (Figure 6b). Beyond identifying the primary design flaw, the model exhibited broader cartographic awareness by suggesting additional improvements: incorporating alternative visual variables such as patterns (cross-hatching, dots, stripes), enhancing the legend with detailed explanations, and addressing the contextual ambiguity of the term “dominant” by clarifying whether it refers to numerical presence, influence, or geographic extent. These supplementary recommendations reflect the model’s capacity to consider both technical cartographic principles and the broader communicative context of sensitive thematic data.
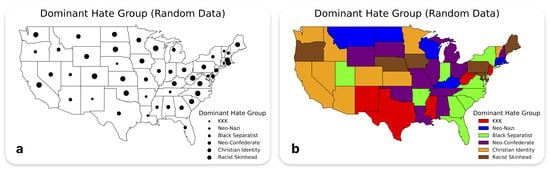
Figure 6.
(a) Example of Misleading Map Design Using Size Variation to Represent Categorical Data of Dominant Hate Groups (b) Improved Design Reflecting GPT-4o Suggestions.
4.2.6. Map Scenario 6—Improper Labeling
The map in Figure 7, reproduced from Brewer [3], depicts the Pacific coastline with three labeled locations—Cannon Beach, Pleasant Valley, and Neskowin. This map includes intentional cartographic flaws to evaluate the model’s ability to interpret and critique visual map elements. Notably, the labels for Cannon Beach and Neskowin are misaligned, positioned too far to the right of their respective points, compromising spatial accuracy. Correcting this misalignment by placing the labels in the water could better emphasize their coastal locations. Additionally, the label for Pleasant Valley inappropriately spans from water onto land, violating cartographic conventions, while the model identified some of these alignment issues, it failed to recognize the specific error in the placement of the Pleasant Valley label, highlighting a limitation in its interpretative capabilities.
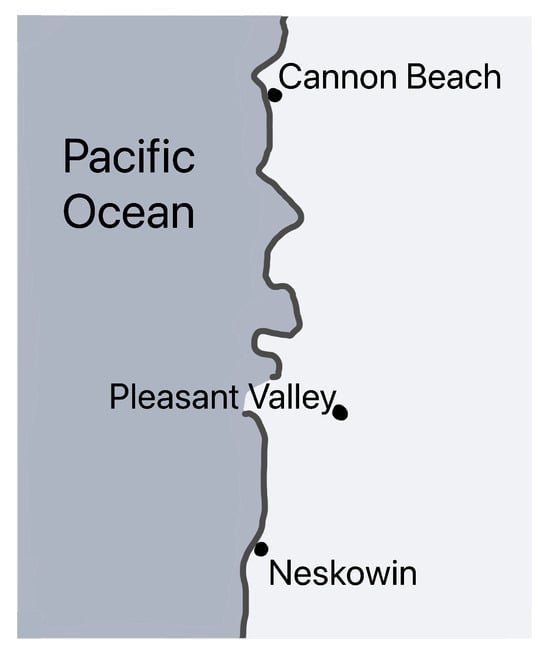
Figure 7.
Example of Intentionally Mislabeled Coastal Locations.
4.2.7. Map Scenario 7—Misleading Design for Elderly People
In Figure 8, the model was evaluated for its ability to interpret and critique visual cartographic elements of a map illustrating the percentage of the population aged 65 and older in Florida counties during Hurricane Charley in 2004, overlaid with the storm’s wind path. This map, reproduced from Krygier and Wood [5], intentionally designed with flaws to test the model’s critique capabilities. The model successfully identified issues such as poor color gradient choice and ineffective visual hierarchy—problems particularly relevant for older viewers who may experience reduced color perception or color vision deficiencies. However, while the model provided actionable suggestions to address these issues, it disproportionately relied on adjustments to color properties, despite the original source of the map (Krygier and Wood [5]) emphasizing the importance of incorporating a variety of visual variables, such as appropriately sized proportional symbols, to enhance map readability and accessibility.
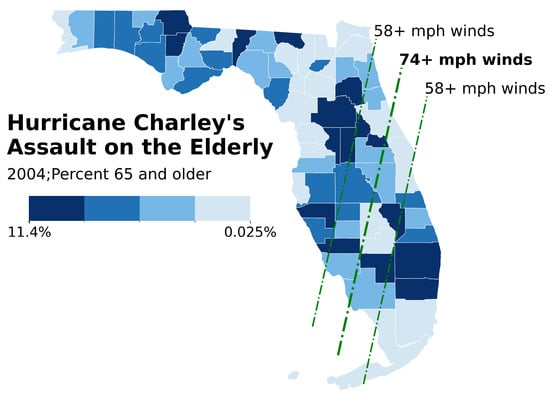
Figure 8.
Example of Misleading Map Design Using Ineffective Color Choices, Hindering Interpretation by Elderly Users.
5. Discussion
5.1. Text-to-Text Assessment
The findings from this study reveal the nuanced interplay between the GPT model’s reliability and the variability introduced through temperature tuning across diverse cartographic elements. In classification tasks, the model demonstrates general reliability; however, the influence of temperature-induced variability and the characteristics of the underlying data significantly impact the appropriateness of its classification outputs. This suggests that while the model is adept at responding to text-based queries, its choices may not always align with domain-specific expectations, particularly in dynamic or high-variability contexts.
The potential impact on cartographic workflows is notable here. The model’s ability to handle classification tasks can streamline certain processes, such as the rapid categorization of map features or labels. However, the variability introduced by temperature adjustments may require human oversight to ensure that domain-specific criteria are met, especially when dealing with complex datasets. Therefore, the integration of GPT-4o into cartographic workflows should emphasize their role in augmenting, rather than replacing, expert judgment, particularly when precision is critical.
Regarding visual hierarchy and layout, the model performs with stability and predictability under lower temperatures, maintaining coherence and professional applicability. However, higher temperatures foster a limited yet meaningful stylistic diversity, particularly in settings involving weaker contrasts. This ability to introduce variation while retaining overall structural integrity highlights the model’s potential for both routine and exploratory design scenarios. To capitalize on this, GPT-4o could be used in iterative design workflows—where initial drafts are generated automatically and refined by designers—allowing for faster prototyping while still ensuring alignment with best practices.
In tasks involving symbolization and visual variables, the model shows a capacity for exploratory variability, particularly at higher temperatures. This variability allows the model to propose diverse symbolization strategies, often favoring color variables over the theoretically preferred ‘Size’ for representing numerical data. These outcomes underline the model’s adaptability to creative or unconventional queries but also highlight constraints. Specifically, there is a gap in aligning outputs with established cartographic principles, especially at lower temperatures where more adherence to norms is expected. To integrate GPT-4o effectively, cartographers may need to develop predefined templates or training data that guide the model towards more conventional symbolization choices, reducing the manual intervention required to achieve standard outcomes.
In the domain of color theory, the model reliably adheres to established principles, maintaining consistency in its internal representation of color relationships even when variability is intentionally increased through temperature adjustments. However, constraints arise from the model’s limited ability to contextualize these color choices within a broader map design framework. For instance, while specific hues or tones may shift, the overall impact on map readability may require human evaluation. The effective integration of GPT-4o could involve coupling them with tools that simulate end-user perception, thereby enhancing the model’s ability to consider the accessibility and usability of its color choices.
Finally, in typography, the model balances consistency and creativity effectively through temperature tuning. Lower temperatures prioritize consistency and precision, making the model suitable for professional and formal design contexts. Conversely, higher temperatures enable creative exploration, offering value for thematic or imaginative design use cases. This adaptability provides practical guidance for cartographers, allowing them to calibrate temperature settings to achieve the desired balance between variability and semantic alignment. Incorporating GPT-4o into cartographic workflows here could provide significant time savings by automating typographic standardization across large-scale map projects, with flexibility for creative customization when needed.
5.2. Image-to-Text Assessment
The evaluation of the model’s capabilities in interpreting and critiquing visual cartographic elements revealed its potential to identify and address critical design flaws in seven distinct map scenarios, each emphasizing a different type of cartographic error. Across multiple tests, the model demonstrated proficiency in recognizing problematic aspects of cartographic design and suggesting actionable improvements, particularly in the domains of color schemes, accessibility, and interpretability.
Additionally, beyond detecting poorly chosen color palettes or label misalignment issues, the model recognized the misuse of geometric shapes to represent quantitative data and the flawed application of symbol size to differentiate categorical data, underscoring how mismatched visual variables can distort viewers’ perceptions—whether by obscuring ordinal relationships through shapes or by introducing artificial hierarchies among categories via size. Consistent with its overall approach, GPT-4o recommended more appropriate variables (e.g., color gradients for quantities, distinct hues or patterns for categories) to ensure visual clarity and avoid misleading interpretations.
In terms of practical impact, these capabilities could transform cartographic review processes. For instance, the model’s ability to identify issues like inappropriate color schemes, poor contrast, or the misuse of shapes and size can help streamline map design reviews, reducing the time that experts need to spend on such tasks. However, constraints affecting these results include the model’s dependency on the quality of input imagery and its limited ability to interpret nuanced spatial relationships, which can lead to occasional inaccuracies, as seen in the Pleasant Valley label misalignment, which extended onto water and created ambiguity about whether it represents a coastal or land feature. These factors imply that the use of GPT-4o in this context requires human validation to ensure spatial accuracy, especially for maps involving detailed labeling or intricate layouts.
The model’s critiques of visual cartographic elements—such as recommending accessible color palettes or identifying perceptual imbalances—suggest that GPT-4o could be integrated into mapmaking software as assistive features. By providing context-aware suggestions during the design process, these models can serve as intelligent assistants, guiding designers towards best practices while leaving final decisions to human experts. Additionally, further training on spatial alignment and layout assessment data could enhance the model’s utility in areas where current limitations exist.
Finally, while the model effectively recommended improvements for color gradients and visual hierarchy, its over-reliance on color as a corrective measure indicates a need for more robust multi-variable strategies. To integrate GPT models effectively, it would be beneficial to augment their training with diverse visual examples that emphasize the use of alternative variables, such as orientation or texture, ensuring that their recommendations encompass a wider range of design tools. This would enable more comprehensive design support, particularly for audiences with specific accessibility needs, such as older viewers or those with visual impairments.
5.3. Limitations
Several limitations should be noted for this study. First, GPT-4o was selected according to criteria derived from geographic studies, which may not fully address the details required for visualization tasks. The assumption that success in text-based tasks directly translates to success in visualization-based tasks may not always be valid. Additionally, multiple responses from GPT-4o were analyzed to gauge the model’s handling of map knowledge, a subject influenced by subjective interpretations. Designing a purely quantitative method to evaluate map designs remains challenging, as cartography involves complex, context-driven principles alongside artistic and perceptual elements that are difficult to measure.
Another limitation arises from the prompt design strategy. Variations in prompt design can significantly affect how models like GPT-4o perform, particularly in image-to-text tasks and map design. However, different prompt designs were not systematically examined, since open-ended responses were used instead of a multiple-choice format, while this approach provides richer qualitative insights—especially in creative tasks—it limits the ability to determine the most effective prompt designs.
Lastly, the image-to-text experiments focused mainly on color, size, and shape, leaving out other important visual variables such as orientation, density, and texture. This focus was guided by map designs recommended in standard cartography textbooks, which emphasize best practices for color use and labeling. Although this method made it possible to evaluate certain cartographic conventions, it constrained the scope of how GPT-4o’s performance is understood in relation to the full range of visual factors.
6. Conclusions
This study evaluated the capabilities of LLMs, specifically GPT-4o, in cartographic design through text-to-text and image-to-text tasks, revealing both strengths and limitations. In text-based tasks, GPT-4o demonstrated adaptability, offering creative variability through temperature tuning, yet struggled to consistently align with established cartographic principles in dynamic or domain-specific contexts. Their critiques of visual elements highlighted strong performance in identifying and addressing issues related to color schemes, accessibility, and interpretability, while limitations in spatial accuracy and over-reliance on color-based solutions were noted. These findings position GPT-4o as reliable yet evolving tools for cartographic workflows.
This research contributes to the emerging field of AI-assisted mapmaking by systematically evaluating GPT-4o’s performance across diverse cartographic design elements. It highlights the nuanced interplay between model variability, task requirements, and cartographic principles, offering practical insights into their application. The study underscores the adaptability of GPT-4o in creative tasks, such as symbolization and typography, while also pinpointing areas where domain-specific alignment is needed. These insights advance understanding of how GPT-4o can complement human expertise in cartography and inform their calibration for optimal results.
While GPT-4o show promise, this study identifies key areas for further research. Enhancing spatial reasoning capabilities, such as improving accuracy in label placement and alignment tasks, is critical for integrating these models into professional cartographic workflows. Additionally, exploring their ability to leverage alternative visual variables, such as size and texture, could reduce reliance on color-based solutions and expand their versatility. Investigating the impact of training data characteristics and refining model prompts to better align with domain-specific conventions also merit deeper exploration.
The findings illustrate the transformative potential of LLMs in cartography, particularly in tasks requiring creative exploration or routine design support. Their ability to critique and generate cartographic elements positions them as valuable tools for augmenting human expertise. Notably, the study underscores two key applications: the system’s proficiency in recommending color schemes aligned with color theory principles, aiding in the creation of clear and aesthetically balanced maps, and its role as a supportive critique tool for less experienced users, fostering the development of higher-quality maps. While challenges remain in achieving domain-specific precision and expanding their repertoire of visual strategies, their adaptability and scalability offer a promising foundation for future innovation. With continued refinement and integration, LLMs have the potential to reshape the landscape of cartographic design, enabling more accessible, inclusive, and effective mapmaking practices.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Dent, B.D.; Torguson, J.S.; Hodler, T.W. Cartography: Thematic Map Design, 6th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Robinson, A.H.; Sale, R.D.; Morrison, J.L.; Muehrcke, P.C. Elements of Cartography, 6th ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Brewer, C.A. Designing Better Maps: A Guide for GIS Users, 2nd ed.; ESRI Press: Redlands, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Slocum, T.A.; McMaster, R.B.; Kessler, F.C.; Howard, H.H. Thematic Cartography and Geovisualization, 4th ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krygier, J.B.; Wood, D. Making Maps: A Visual Guide to Map Design for GIS, 2nd ed.; Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Monmonier, M. How to Lie with Maps; University of Chicago Press: Chicago, IL, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- MacEachren, A.M. How Maps Work: Representation, Visualization, and Design; Guilford Press: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, S.; Norvig, P. Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach, 3rd ed.; Pearson: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jordan, M.I.; Mitchell, T.M. Machine Learning: Trends, Perspectives, and Prospects. Science 2015, 349, 255–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, T.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is All You Need. In Proceedings of the 31st Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS 2017), Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Goodfellow, I.; Bengio, Y.; Courville, A. Deep Learning; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, T.B.; Mann, B.; Ryder, N.; Subbiah, M.; Kaplan, J.; Dhariwal, P.; Neelakantan, A.; Shyam, P.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; et al. Language Models Are Few-Shot Learners. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 1877–1901. [Google Scholar]
- Bommasani, R.; Hudson, D.A.; Adeli, E.; Altman, R.; Arora, S.; von Arx, S.; Bernstein, M.S.; Bohg, J.; Bosselut, A.; Brunskill, E.; et al. On the Opportunities and Risks of Foundation Models. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.07258. [Google Scholar]
- Bubeck, S.; Chandrasekaran, V.; Eldan, R.; Gehrke, J.; Horvitz, E.; Kamar, E.; Lee, P.; Tandon, N.; Zhang, Y. Sparks of Artificial General Intelligence: Early Experiments with GPT-4. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.12712. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Y.; Gao, S.; Roth, R.E. Artificial Intelligence Studies in Cartography: A Review and Synthesis of Methods, Applications, and Ethics. Cartogr. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2024, 51, 599–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brus, J.; Dobešová, Z.; Kanok, J. Utilization of expert systems in thematic cartography. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Conference on Intelligent Networking and Collaborative Systems, Barcelona, Spain, 4–6 November 2009; pp. 285–289. [Google Scholar]
- Roussel, C. Visualization of Explainable Artificial Intelligence for GeoAI. Front. Comput. Sci. 2024, 6, 1414923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usery, E.L.; Arundel, S.T.; Shavers, E.; Stanislawski, L.; Thiem, P.; Varanka, D. GeoAI in the US Geological Survey for Topographic Mapping. Trans. GIS 2021, 1, 25–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrie, L.; Touya, G.; Oucheikh, R.; Ai, T.; Courtial, A.; Richter, K.F. Machine Learning in Cartography. Cartogr. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2024, 51, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- University Consortium for Geographic Information Science. GIS&T Body of Knowledge. 2023. Available online: https://ucgis.org (accessed on 10 December 2024).
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-training of Deep Bidirectional Transformers for Language Understanding. In Proceedings of the NAACL-HLT 2019, Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–7 June 2019; pp. 4171–4186. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Wu, J.; Child, R.; Luan, D.; Amodei, D.; Sutskever, I. Language Models Are Unsupervised Multitask Learners. OpenAI Blog 2019, 1, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Achiam, J.; Adler, S.; Agarwal, S.; Ahmad, L.; Akkaya, I.; Aleman, F.L.; McGrew, B. GPT-4 Technical Report. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.08774. [Google Scholar]
- Touvron, H.; Lavril, T.; Izacard, G.; Martinet, X.; Lachaux, M.A.; Lacroix, T.; Lample, G. Llama: Open and Efficient Foundation Language Models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.13971. [Google Scholar]
- Team, G.; Anil, R.; Borgeaud, S.; Alayrac, J.B.; Yu, J.; Soricut, R.; Blanco, L. Gemini: A Family of Highly Capable Multimodal Models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2312.11805. [Google Scholar]
- Anthropic. Claude 3 Model Card. 2024. Available online: https://www.anthropic.com/claude-3-model-card (accessed on 10 December 2024).
- Christiano, P.F.; Leike, J.; Brown, T.; Martic, M.; Legg, S.; Amodei, D. Deep Reinforcement Learning from Human Preferences. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Long Beach, CA, USA, 4–9 December 2017; Volume 30. [Google Scholar]
- Cascella, M.; Montomoli, J.; Bellini, V.; Bignami, E. Evaluating the Feasibility of ChatGPT in Healthcare: An Analysis of Multiple Clinical and Research Scenarios. J. Med. Syst. 2023, 47, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteva, A.; Robicquet, A.; Ramsundar, B.; Kuleshov, V.; DePristo, M.; Chou, K.; Dean, J. A Guide to Deep Learning in Healthcare. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 24–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajja, R.; Sermet, Y.; Cikmaz, M.; Cwiertny, D.; Demir, I. Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Intelligent Assistant for Personalized and Adaptive Learning in Higher Education. Information 2024, 15, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moura, F.T. (Ed.) Artificial Intelligence, Co-Creation and Creativity: The New Frontier for Innovation; Taylor & Francis: Abingdon, UK, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Guha, N.; Nyarko, J.; Ho, D.; Ré, C.; Chilton, A.; Chohlas-Wood, A.; Li, Z. Legalbench: A Collaboratively Built Benchmark for Measuring Legal Reasoning in Large Language Models. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 9–15 December 2024; Volume 36. [Google Scholar]
- Kwon, O.H.; Vu, K.; Bhargava, N.; Radaideh, M.I.; Cooper, J.; Joynt, V.; Radaideh, M.I. Sentiment Analysis of the United States Public Support of Nuclear Power on Social Media Using Large Language Models. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024, 200, 114570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Canli, I.; Shah, J.; Zhang, X.; Dino, I.G.; Kalkan, S. Perspectives of Machine Learning and Natural Language Processing on Characterizing Positive Energy Districts. Buildings 2024, 14, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alayrac, J.B.; Donahue, J.; Luc, P.; Miech, A.; Barr, I.; Hasson, Y.; Lenc, K.; Mensch, A.; Millican, K.; Reynolds, M.; et al. Flamingo: A Visual Language Model for Few-Shot Learning. In Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, New Orleans, LO, USA, 28 November–9 December 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Saharia, C.; Chan, W.; Saxena, S.; Li, L.; Whang, J.; Zhai, S.; Kan, H.; Salimans, T.; Norouzi, M.; Fleet, D.J. ImageBind: One Embedding Space to Bind Them All. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2305.05665. [Google Scholar]
- Pressman, S.M.; Borna, S.; Gomez-Cabello, C.A.; Haider, S.A.; Haider, C.; Forte, A.J. AI and Ethics: A Systematic Review of the Ethical Considerations of Large Language Model Use in Surgery Research. Healthcare 2024, 12, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, S.; Xu, C.; Xu, S.; Pang, L.; Dong, Z.; Xu, J. Bias and Unfairness in Information Retrieval Systems: New Challenges in the LLM Era. In Proceedings of the 30th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Barcelona, Spain, 25–29 August 2024; pp. 6437–6447. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, Q.; Parker, A.G.; De Choudhury, M. Synthetic Lies: Understanding AI-Generated Misinformation and Evaluating Algorithmic and Human Solutions. In Proceedings of the 2023 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Hamburg, Germany, 23–28 April 2023; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Bender, E.M.; Gebru, T.; McMillan-Major, A.; Shmitchell, S. On the Dangers of Stochastic Parrots: Can Language Models Be Too Big? In Proceedings of the 2021 ACM Conference on Fairness, Accountability, and Transparency, Virtual, 3–10 March 2021; pp. 610–623. [Google Scholar]
- Weidinger, L.; Mellor, J.; Rauh, M.; Griffin, C.; Uesato, J.; Huang, P.S.; Gabriel, I. Ethical and Social Risks of Harm from Language Models. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.04359. [Google Scholar]
- Rillig, M.C.; Ågerstrand, M.; Bi, M.; Gould, K.A.; Sauerland, U. Risks and Benefits of Large Language Models for the Environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 3464–3466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Claramunt, C.; Çöltekin, A.; Liu, X.; Peng, P.; Robinson, A.C.; Wang, D.; Strobl, J.; Wilson, J.P.; Batty, M.; et al. Artificial Intelligence and Visual Analytics in Geographical Space and Cyberspace: Research Opportunities and Challenges. Earth Sci. Rev. 2023, 241, 104438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Hu, Y.; Li, W. (Eds.) Handbook of Geospatial Artificial Intelligence, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janowicz, K.; Gao, S.; McKenzie, G.; Hu, Y.; Bhaduri, B. GeoAI: Spatially Explicit Artificial Intelligence Techniques for Geographic Knowledge Discovery and Beyond. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2020, 34, 625–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Zhou, Z.; Xin, Y.; Weibel, R. Reasoning Cartographic Knowledge in Deep Learning-Based Map Generalization with Explainable AI. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2024, 38, 2061–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Thiemann, F.; Sester, M. Learning Cartographic Building Generalization with Deep Convolutional Neural Networks. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Hsu, C.Y. GeoAI for Large-Scale Image Analysis and Machine Vision: Recent Progress of Artificial Intelligence in Geography. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2022, 11, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, M.P. Active Symbolism: Toward a New Theoretical Paradigm for Statistical Cartography. Cartogr. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2019, 46, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ning, H. Autonomous GIS: The Next-Generation AI-Powered GIS. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2023, 16, 4668–4686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, S. A Systematic Review of Geospatial Location Embedding Approaches in Large Language Models: A Path to Spatial AI Systems. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.10279. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; He, Z.; Li, J.; Mai, G.; Lin, J.; Yu, W. BB-GeoGPT: A Framework for Learning a Large Language Model for Geographic Information Science. Inf. Process. Manag. 2024, 61, 103808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansourian, A.; Oucheikh, R. ChatGeoAI: Enabling Geospatial Analysis for Public through Natural Language, with Large Language Models. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2024, 13, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; He, Z.; Li, J.; Lin, J.; Guan, Q.; Yu, W. MapGPT: An Autonomous Framework for Mapping by Integrating Large Language Model and Cartographic Tools. Cartogr. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2024, 51, 717–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.; Gao, S.; Roth, R.E. Transferring Multiscale Map Styles Using Generative Adversarial Networks. Int. J. Cartogr. 2019, 5, 115–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kent, A.J. Aesthetics: A Lost Cause in Cartographic Theory? Cartogr. J. 2005, 42, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, G.; Huang, W.; Sun, J.; Song, S.; Mishra, D.; Liu, N.; Lao, N. On the Opportunities and Challenges of Foundation Models for Geospatial Artificial Intelligence. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.06798. [Google Scholar]
- Penn State. Introduction to the GIS&T Body of Knowledge. 2023. Available online: https://e-education.psu.edu (accessed on 10 December 2024).
- Kemp, K.; Goodchild, M.F.; Dodson, R. The GIS&T Body of Knowledge 2.0: A New Content Model. In Advances in Spatial Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 3–22. [Google Scholar]
- Brewer, C.A. Color Use Guidelines for Mapping and Visualization. In Visualization in Modern Cartography; MacEachren, A.M., Taylor, D.R.F., Eds.; Elsevier Science: Tarrytown, NY, USA, 1994; pp. 123–147. [Google Scholar]
- Brumberger, E.R. The Rhetoric of Typography: The Persona of Typeface and Text. Tech. Commun. 2003, 50, 206–223. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, C.; Walker, P. Typographic Influences on Reading. Br. J. Psychol. 1989, 80, 241–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Childers, T.L.; Jass, J. All Dressed Up with Something to Say: Effects of Typeface Semantic Associations on Brand Perceptions and Consumer Memory. J. Consum. Psychol. 2002, 12, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulman, N.; Memduhoglu, A.; Zipf, A. Evidence for Systematic Bias in the Spatial Memory of Large Language Models. In Proceedings of the GeoExT@ECIR, Glasgow, Scotland, 24–28 March 2024; pp. 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Fulman, N.; Memduhoğlu, A.; Zipf, A. Distortions in Judged Spatial Relations in Large Language Models. Prof. Geogr. 2024, 76, 703–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Published by MDPI on behalf of the International Society for Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).