Abstract
The visual perception of streets plays an important role in urban planning, and contributes to the quality of residents’ lives. However, evaluation of the visual perception of streetscapes has been restricted by inadequate techniques and the availability of data sources. The emergence of street view services (Google Street View, Tencent Street View, etc.) has provided an enormous number of new images at street level, thus shattering the restrictions imposed by the limited availability of data sources for evaluating streetscapes. This study explored the possibility of analyzing the visual perception of an urban street based on Tencent Street View images, and led to the proposal of four indices for characterizing the visual perception of streets: salient region saturation, visual entropy, a green view index, and a sky-openness index. We selected the Jianye District of Nanjing City, China, as the study area, where Tencent Street View is available. The results of this experiment indicated that the four indices proposed in this work can effectively reflect the visual attributes of streets. Thus, the proposed indices could facilitate the assessment of urban landscapes based on visual perception. In summary, this study suggests a new type of data for landscape study, and provides a technique for automatic information acquisition to determine the visual perception of streets.
1. Introduction
Streets represent the most direct connection between urban residents and the city landscape [1]. In developed countries, the visual perception of streets often receives considerable attention in urban planning and construction [2]. Most departments in the U.S. have their own methods for assessing landscape aesthetics [3]. The U.S. National Scenic Byways Program requires byway landscape resources to be assessed using four indices: memorability, uniqueness, originality, and integrity [4]. Different schools of thought have formed various theories and methods based on urban landscape research, including visual impact assessment methods, scenic quality estimation models, landscape comparative assessment methods, and environmental assessment models [5,6]. However, at present, research on the landscapes and aesthetics of roads remains constrained by inadequate techniques and a shortage of data sources, a situation that results in complex information acquisition and landscape assessment.
The emergence of street view has shattered previous restrictions on the availability of data sources for evaluating streets [7,8]. Street views are electronic maps based on actual scenery; as the street view images provided by these maps are rich in detail and have wide coverage, they contain a large quantity of information on urban streets. Hence, these street view images have the potential to become an important form of supporting data for the evaluation of visual perceptions of urban streets. Currently, a number of Internet companies, such as Google, Microsoft, Baidu, and Tencent, have launched online street view services [9,10]. In the majority of China’s cities, most streets are already covered by the street view; thus, users in Nanjing may enjoy the charms of the alleys of the ancient city of Lijiang thousands of miles away or experience the wonders of the highlands at the foot of the Potala Palace from within the comfort of their homes. It therefore follows that the automated extraction of useful characteristics from the vast amount of street view image data taken under varying imaging conditions and photographic angles is a field that requires further investigation.
As a new source of data, street view images have become a focal point of research. A very wide range of urban studies was based on street view images, with examples including studies on three-dimensional (3D) urban reconstructions [11,12,13], specific scene recognition [14], investigations of plant and animal species [15,16,17], route selection [8,18], perceived safety evaluation [19], data extraction on alcohol consumption [20], evaluation of the visual perception of streets [21,22], and so on. In particular, the visual perception of streets serves as a basis for urban landscape planning and residential quality of life [22]. According to Lynch, the visual and sensual aspects of the present and future city should become a normal and integral part of its comprehensive plan [23]. Hence, this topic has always been a focal point of research and studies. Oh used street view images in combination with geographic information systems and computational mapping techniques to study the visual threshold carrying capacity of streetscapes [21]. Stamps studied environmental enclosures in cities through a small number of sample photographs [24]. Yang used street view images taken from four different directions to calculate the green view index by counting the proportion of green-colored pixels in four pictures and taking this proportion as the value of the green view index at a given sampling point. The mean green view index of the sampling points within the various neighborhoods of a city can then be taken as the city’s green view value [25]. Li felt that merely using street view images taken from four directions at each sampling point to calculate a city’s green view index, as proposed by Yang, was a somewhat limited approach. Consequently, Li proposed a method that analyzed 18 images captured from different vertical angles and covering a circle around the evaluated point to obtain the green view index. Li also pointed out that street view imagery has immense applicative prospects for planning future urban environments [19].
Based on our review of the studies published in the literature, there remain several unresolved issues in urban studies based on street views: (1) Some studies are based on street view images taken from a small number of angles and do not form a true panoramic image, resulting in gaps or overlaps in the visual field; and (2) visual perception has been treated as an abstract concept that requires evaluation from multiple aspects; currently, the single index is insufficient to describe the visual perception from multiple angles. In view of these issues, in our approach, we first process street view images into panoramic images that are compatible with human visual perspectives. Based on these panoramic images, we propose a technical procedure that involves a set of image processing methods, including image segmentation and the detection of salient regions, to extract the characteristics from a vast quantity of street view images. Finally, we implement four visual indices: salient region saturation (SRS), visual entropy (VE), a green view index (GVI) and a sky-openness index (SOI). These indices are used as surrogates to characterize likely perception of streets, providing a scientific form of guidance for the planning and construction of urban landscapes.
2. Study Area and Data
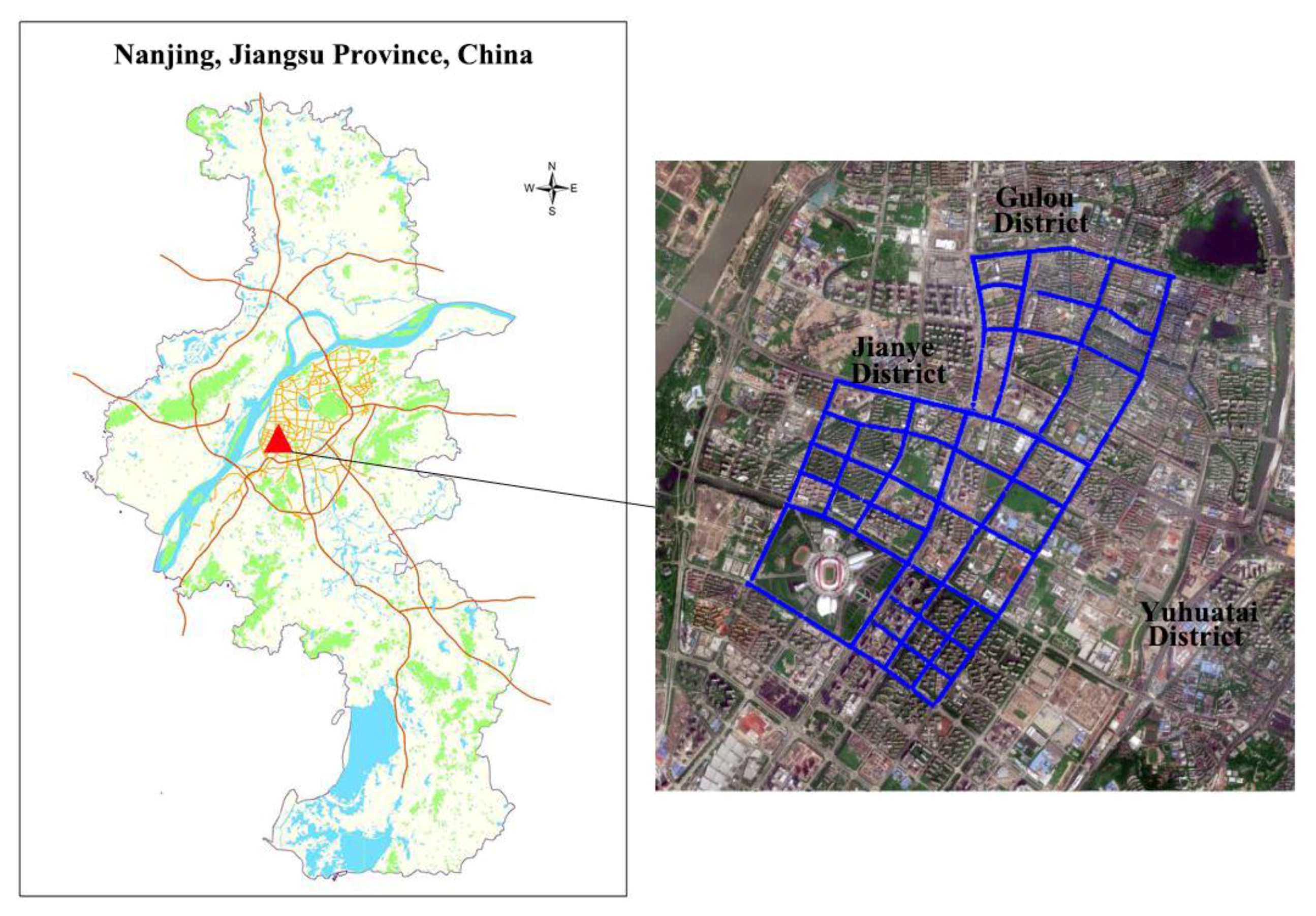
The study area is the Jianye District of Nanjing City, China, which lies to the west of the Yangtze River, and is bordered in the east and south by the Qinhuai River (Figure 1). It has a total of six streets, and had a population of 455,000 in 2015. High-rise buildings, commercial districts, and skyscrapers are found throughout the central and southern regions of the study area. A section of the northern region of the study area is an old town zone despite widespread reconstruction work carried out in recent years. Apartment blocks consisting of five to seven floors are frequently seen, with a few commercial buildings scattered between them. The Nanjing Olympic Center (referred to as the Olympic Center henceforth) is located in the southwest Jianye District, which has many parks and green areas in its surroundings as well as road widths that are significantly wider than those in the northern region of the study area. On the whole, the artificial features within the study area such as its roads, buildings, and plant cover are highly varied and complex, making it well suited for evaluative studies on the visual perception of streets.
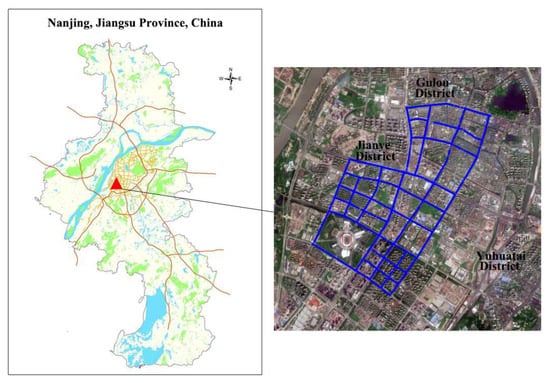
Figure 1.
Study area.
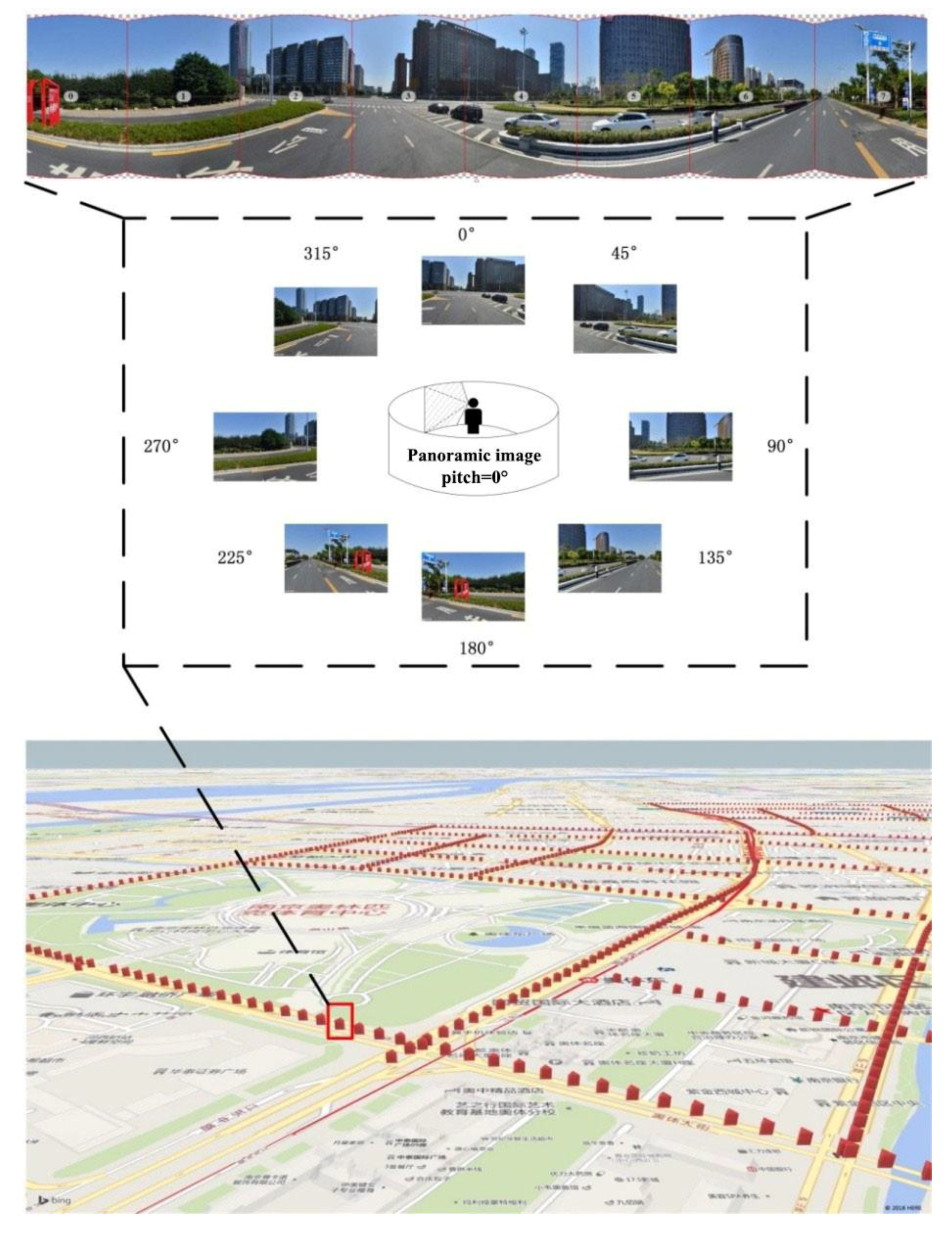
The uniform resource locator (URL) links provided by the Tencent street view application programming interface (API) include five parameters: size, location, pitch, heading, and key. The size parameter is the resolution of the street view image in units of pixels. Location corresponds to the latitude and longitude coordinates of the street view image. Heading refers to the heading angle, which is used to indicate the horizontal orientation of the camera lens when the image was taken with respect to the north. Pitch refers to the pitch angle, which is used to indicate the angle formed by the lens with respect to the horizontal reference line when the image was taken. These five parameters uniquely specify each street view image (if it exists within the Tencent Street View database).
The normal human visual field is defined as the spatial range observed by a single eye or both eyes from a fixed point of view. The boundaries of the normal human visual field are 56° upwards, 74° downwards, 65° nasally (towards the nose), and 91° temporally (away from the nose). The horizontal and vertical field of view (FOV) of cameras typically used to capture street view images ranges from 80 to 140°; when the pitch angle of the street view camera is 0°, its visual field is approximately equal to that of the normal human visual field. We sampled points at 30-m intervals according to the sampling points indicated in Figure 2 and obtained a total of 1669 sampling points. We downloaded a total of eight images (each with a pitch angle of 0° and headings of 0°, 45°, 90°, 135°, 180°, 225°, 270°, and 315°) to form panoramic images that simulate the 360° view that surrounds a person standing at a fixed point, as shown in Figure 2. All of the street view images taken in the study area were acquired during October 2014.
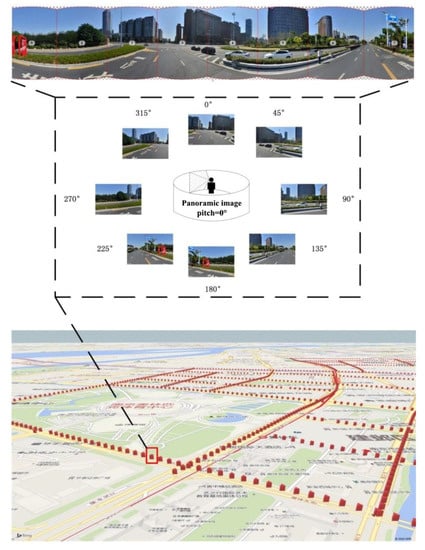
Figure 2.
Schematic of the locations at which panoramic images were generated.
3. Methods
3.1. Salient Region Saturation
Intense feelings may be expressed by color through associative thoughts, and saturation is the factor that is the most attractive to human attention [26]. Saturation refers to the degree of brilliance or purity of a hue. In this respect, brilliant flowers and gorgeous billboards in the street all have high saturation. Hence, calculations of the saturation of a panoramic image reflect on the color perception of a street to a certain degree. Furthermore, in order to achieve more effective saturation for reflecting the feelings, we propose SRS. The salient regions within a panoramic image are indicative of the features that attract attention when a person walks along a street to a certain extent. Some examples may include an advertisement board with bright and vivid colors or a single fresh and delicate flower in a clump of bushes, or a straight walkway that suddenly becomes a winding trail. An analysis of the lightness and saturation in these salient regions can enable more accurate and objective reflections of the feelings of pedestrians walking along a street. In this work, we use the algorithm of saliency detection by combining simple priors (SDSP) proposed by Zhang et al. to extract the salient regions from panoramic images of streets [27]. The specific procedure of this algorithm is as follows:
Step (1) calculates the saliency of the frequencies. The use of HSV (hue, saturation and value) values to capture the salient features within a scene can be modeled using a band-pass filter. A log-Gaber filter is constructed to perform filtering in the frequency domain of a native panoramic image, and its equation is as follows:
In this equation, is the coordinate in the frequency domain, is the central frequency, and determines the bandwidth of the filter. Let represent the panoramic image, with representing the spatial domain of the image. is a one-dimensional vector, containing three values representing the red (R), green (G), and blue (B) intensities at position . The panoramic image is first converted from the RGB color space to the L*a*b* color space; then the above filter is used to filter the , , and channels of the panoramic image within the L*a*b* space. , , and represent the L*-channel, a*-channel, and b*-channel, respectively. The frequency domain saliency map of a panoramic image is defined as follows:
where indicates the convolution operation.
Step (2) calculates the saliency of the colors. Some studies have shown that warm color tones such as red or yellow more easily attract the attention of the human visual system than cold color tones such as green or blue [28]. In Step (1), a native panoramic image is converted from the RGB color space to the L*a*b* color space. The higher the a* value of a pixel, the redder it seems; conversely, the lower the a* value, the greener it seems. Similarly, the higher the b* value of a pixel, the yellower it seems; and the lower the b* value, the bluer it seems. Therefore, when a pixel has high values of either a* or b*, it appears “warmer”, and the inverse results in a “colder” appearance. Based on the above analysis, we may design a quantitative indicator for the color saliency of each pixel. The a*-channel and b*-channel of the panoramic image in the L*a*b* color space are linearly converted according to and , respectively, with the equations governing the conversions being:
In the above equation, ( ) is the minimum (maximum) value of , and ( ) is the minimum (maximum) value of . After the above conversion, every pixel can be defined as a coordinate within the color coordinate plane, . Intuitively, is the “coldest point” on this plane, thus being the least salient. Based on the above, the color saliency of pixel is as follows:
where is a control parameter.
Step (3) calculates the positional saliency of each pixel. Some researchers have found that centrally located features tend to attract human attention more strongly [29]. In other words, regions closer to the photographic center of an image are more salient than regions located far away from the central region. In the panoramic image , the photographic centers are a point set as , where is half of the height of image . Then, the positional saliency of an arbitrary pixel can be expressed by a Gaussian map of the panoramic image:
where is a control parameter.
The saliency map of the panoramic image is calculated in Step (4). After the frequency, color, and positional saliency of each of the pixels within a panoramic image have been obtained via Steps (1)–(3), we then have three saliency maps of the panoramic image, i.e., the frequency saliency map , the color saliency map , and the positional saliency map . The saliency map of the panoramic image can then be obtained via Equation (7):
The saliency map of the panoramic image that we finally obtain is a greyscale image in which the saliency of a pixel increases as its greyscale value decreases. Next, we obtain the binarization saliency map using Otsu’s method (implemented using GRAYTHRESH in MATLAB) [30], which selects the threshold that minimizes the variance within the two bins. Then, we mask the original panoramic image and provide the salient regions within a panoramic image, i.e., the regions that are of interest to the human visual system. Finally, the SRS can be directly obtained by converting the salient regions from the RGB color space to the HSV color space:
3.2. Visual Entropy
To measure the amount of information within an image and the sensitivity of the human visual system to the image, Fan et al. proposed the concept of VE [31]. Visual entropy is the result of combining the concepts of information entropy with the characteristics of the human visual system. The magnitude of the visual entropy value can reflect the visual complexity and richness of an urban streetscape to an extent. Since an aesthetically pleasing streetscape often has multiple layers of complexity, it should have a correspondingly high value of visual entropy. The definition of visual entropy is as follows: for some specified area within an image, if we assume that the encoded image and the original image are not significantly different in terms of visual perception, then the visual entropy is the minimum number of bits obtained for each encoded pixel. However, the theory of visual entropy remains at the developmental stage, and its mathematical description continues to be incomplete.
The calculation of the visual entropy of each panoramic image uses the following strategy: image segmentation is first performed on each panoramic image to obtain regions with distinct boundaries in which the probability for the emergence of the th region is , with the quantity of information within this region being . For a panoramic image composed of regions, the total amount of information is calculated according to Equation (9):
From the calculation of visual entropy shown above, it may be inferred that the accuracy of this calculation can be increased by improving the image segmentation. As a very large quantity of street view image data needs to be processed, the efficiency of the algorithm is also an important consideration. Hence, we decided to apply the segmentation algorithm for color images proposed by Ye [32] to segment panoramic images for visual entropy calculations. The segmentation process is as follows:
Step (1) quantifies the colors within the image. Suppose that each image contains windows that are wide, and each window contains pixels. is defined as the color coarseness within the window, and is the mean color coarseness of the panoramic image; the more intense the color changes, the higher the color coarseness. The mean color coarseness is also used to determine the number of color quantization steps in the image. The definitions of and are as follows:
In these equations, is the color of the th pixel within this window. After the color coarseness has been determined, the number of color quantizations in the panoramic image can be calculated by:
where is separately set according to the specific level of accuracy required. After the number of colors has been calculated, vector quantization is performed to segment the pixels within the color space, thus completing the quantization of color.
The initial segmentation of the image is performed in Step (2) using the region-growing method. The rules for the selection of seed regions are as follows: (1) the pixels in the region must have similar color; (2) adjacent pixels in the region must have the topological relation of a 4-neighborhood; (3) the seed regions must reach the specified area threshold (also known as the number of pixels), which is set to 0.01% of the area of the image. Nearby pixels are then searched for, and the pixels with the most similar colors amongst these are added to the seed regions.
The regions are then consolidated in Step (3). After the initial segmentation of the panoramic image, numerous regions have been formed; but some of these regions continue to have a very high level of similarity, which necessitates another step to consolidate these highly similar regions. Regions that have small gaps in space and color are merged if distinct boundary regions are not present within their interfaces. The inter-region distance , color distance , and boundary distance are calculated as follows:
In these equations, and are the pixels contained in regions and , whereas and represent the mean color values of these two regions, respectively. is a pixel that lies within the boundary of two neighboring regions that are to be merged, with representing the number of pixels on the boundary, whereas and are the color values of the and points at the two edges of the boundary, and indicates whether the regions i and j are connected. If the regions are connected, then ; if they are not connected, then .
Step (4) sets the rules for terminating the consolidation of regions. The degree of color inhomogeneity in the various regions can be measured by a function that characterizes the color dispersion of the image regions. When the regions of a panoramic image have been consolidated, its color dispersion is defined as follows:
where represents the total number of pixels, represents the number of pixels in the th region, represents the color value of the th pixel in the th region, and represents the mean color value of the th region. grows continuously with each iterative cycle of the region consolidation process, whereas the number of regions in the entire panoramic image, , decreases continuously. When reaches its minimum value, the region consolidation process is terminated, and we then obtain the final segmentation result.
After we have obtained the final segmentation of the image, the surface area of each region as a proportion of the total area is substituted into Equation (9) to calculate the visual entropy of the panoramic image.
3.3. Green View Index
The level of greenery of a street has a significant impact on its attractiveness and walkability [33]. The presence of plant cover usually increases the number of positive evaluations that an urban streetscape receives [34]. The “green-looking ratio” theory proposed by Japanese environmental psychology expert Ryuzo Ohno has been recognized in a number of countries. This theory uses photographs to determine the composite ratio of green spaces such that people’s feelings towards shades of green can be reflected in terms of visual perception. The “green-looking ratio” refers to the proportion of green areas within the circular area of the human visual field. In this work, street view images taken from a set perspective are combined to create panoramic images that simulate the visual field of a person, and the green areas are extracted from the panoramic images to give the GVI.
The GVI is defined as the proportion of green regions within the area of an image, and the equation for calculating its value is as follows:
In this equation, is the total number of pixels occupied by green areas within the panoramic image, whereas is the total number of pixels within the panoramic image. The procedures of extracting green regions are as follows:
Step (1) segments the image based on color. The three components of the RGB space are normalized to minimize the impact of illumination. The red component r, green component g, and blue component b are extracted from the image and normalized according to Equation (18) as R, G, and B, respectively. The [−1, 2, −1] template is used to process the (R, G, B) components of each pixel within the panoramic image, as shown in Equation (19), to suppress the red and blue components while emphasizing the green component. Thereby, the green regions of interest (ROI) are obtained.
Step (2) removes spurious points. Each pixel in the image obtained from Step (1) is thresholded by 0 to produce a binary image. The resulting foreground represents the green region. At this point, the opening operator of mathematical morphology is required to remove the spurious points generated during the binarization process. The use of structural element to conduct the opening operation of image is denoted as , as in Equation (20). This operation first erodes the image before dilating it. Spurious points can be removed via erosion, but this also causes the green regions to become smaller, which is why the dilation operation is required to restore its size. The erosion operation is denoted as , and is represented by Equation (21). In this equation, is the complement of . Dilation is denoted as , as in Equation (22), in which is the symmetrical image of about the origin.
Step (3) reconstructs the image. After processing in Step (2), most of the spurious points have been removed; however, as the borders have also changed as a result, morphological reconstruction algorithms need to be used to further restore the image. The image that was processed in Step (2) for spurious point removal and further processed by the opening operator of mathematical morphology is taken as marker image , and the threshold image obtained previously is taken as the masking image ; the morphological reconstruction of towards is denoted as . This is iterated until , in which , and . represents the n-times dilation of marker image about image template , with as its structural element. In other words, the dilation of the marker image is constrained to the mask image .
3.4. Sky-Openness Index
The vast sky brings a bright and relaxed feeling, therefore the sky is an important factor in landscape study [35,36]. In this section, we propose the SOI, which is defined as the proportion of the visual cone occupied by the sky from some point of observation. The panoramic images generated from street view images are an excellent simulation of the FOV of human observation. Hence, the proportion occupied by the sky in a panoramic image is a close approximation of the SOI. During the process of calculating VE, we use a method for color image segmentation based on simultaneous processing of color and spatial information; the same method can be used to accurately segment the regions occupied by the sky in panoramic images. Therefore, we may conveniently use the previously described methods to directly calculate the SOI. The equation used for calculating the SOI in this work is as follows:
In this equation is the number of regions that have been categorized as the sky within the panoramic image after image segmentation, is the number of pixels within the th sky region, and is the total number of pixels in the panoramic image.
3.5. Evaluation Method
We evaluated the experimental results by selecting 84 panoramic images that were sampled in 600-m intervals from the 1669 panoramic images for a questionnaire. The questionnaire was designed to grade the panoramic image in five classes (a score of 1 indicates the lowest or worst grade whereas a score of 5 represents the highest or best grade), and a total of 100 volunteers (50 from within the experimental area and 50 recruited online) were asked to participate. For each volunteer, the scores of SRS, VE, GVI, and SOI are based on visual brilliance, richness, the green quantity, and the sky area, respectively. Additionally, the relation between the four indices and landscape was evaluated by including the score for the general landscape in this questionnaire. For each panoramic image, the final score was the average of the scores awarded by the 100 volunteers. The accuracy of the indices was discussed based on the panoramic images and the questionnaire.
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Salient Region Saturation
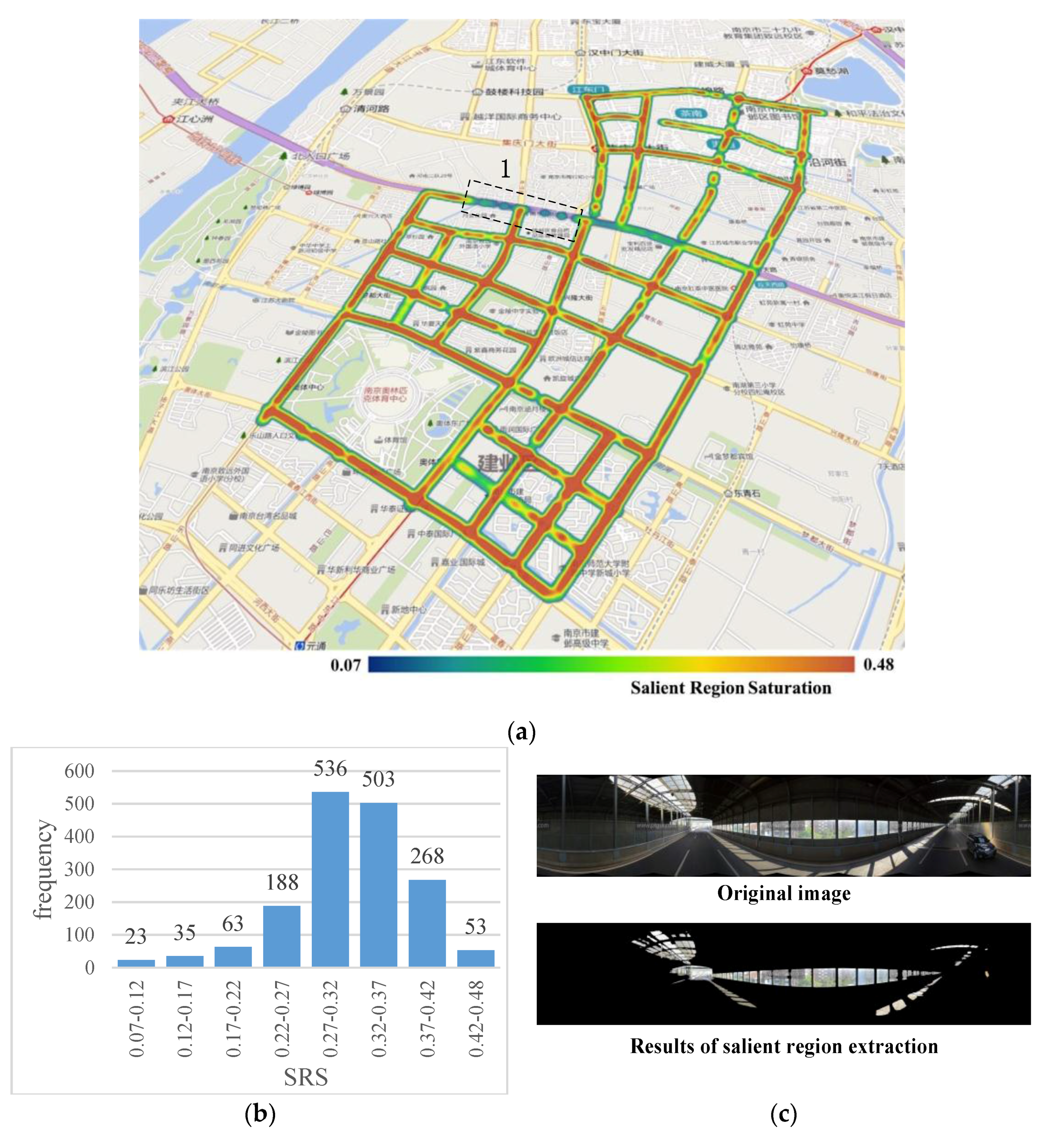
Figure 3a shows the results of the SRS calculation of 1669 panoramic images in the study area. In Figure 3b, which shows the SRS histogram comprised of all panoramic images, it is clear that most of the sampled points have SRS values in the range 0.27–0.42, with only a few points having values outside of this range. The SRS distribution map of the study area shown in Figure 3a indicates that most of the streets in the study area have a high SRS level, indicating that these streets are visually full and brightly colored on the whole, and thus easily attract the attention of pedestrians. We noticed a low SRS level for Street 1 in Figure 3a. This is because Street 1 is dome-roofed elevated road, as shown in Figure 3c, in which we observe that the regions recognized as salient regions include portions of the sky of which the colors are not saturated, potentially causing people to feel depressed and uncomfortable.
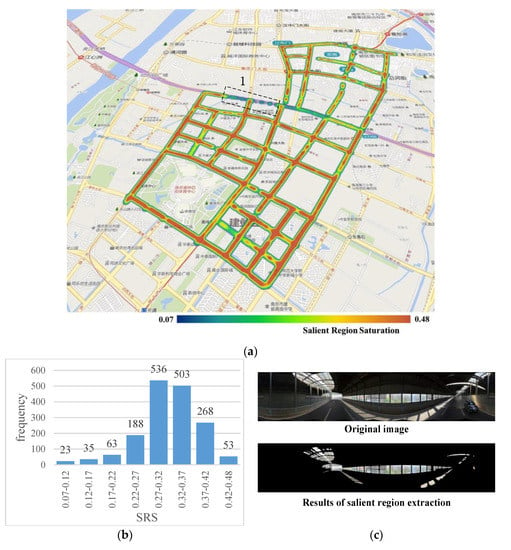
Figure 3.
Results of salient region saturation (SRS) calculation: (a) Study area (a section of Street 1, which has a low SRS level), outlined by the black dotted lines; (b) SRS histogram; (c) Image of Street 1.
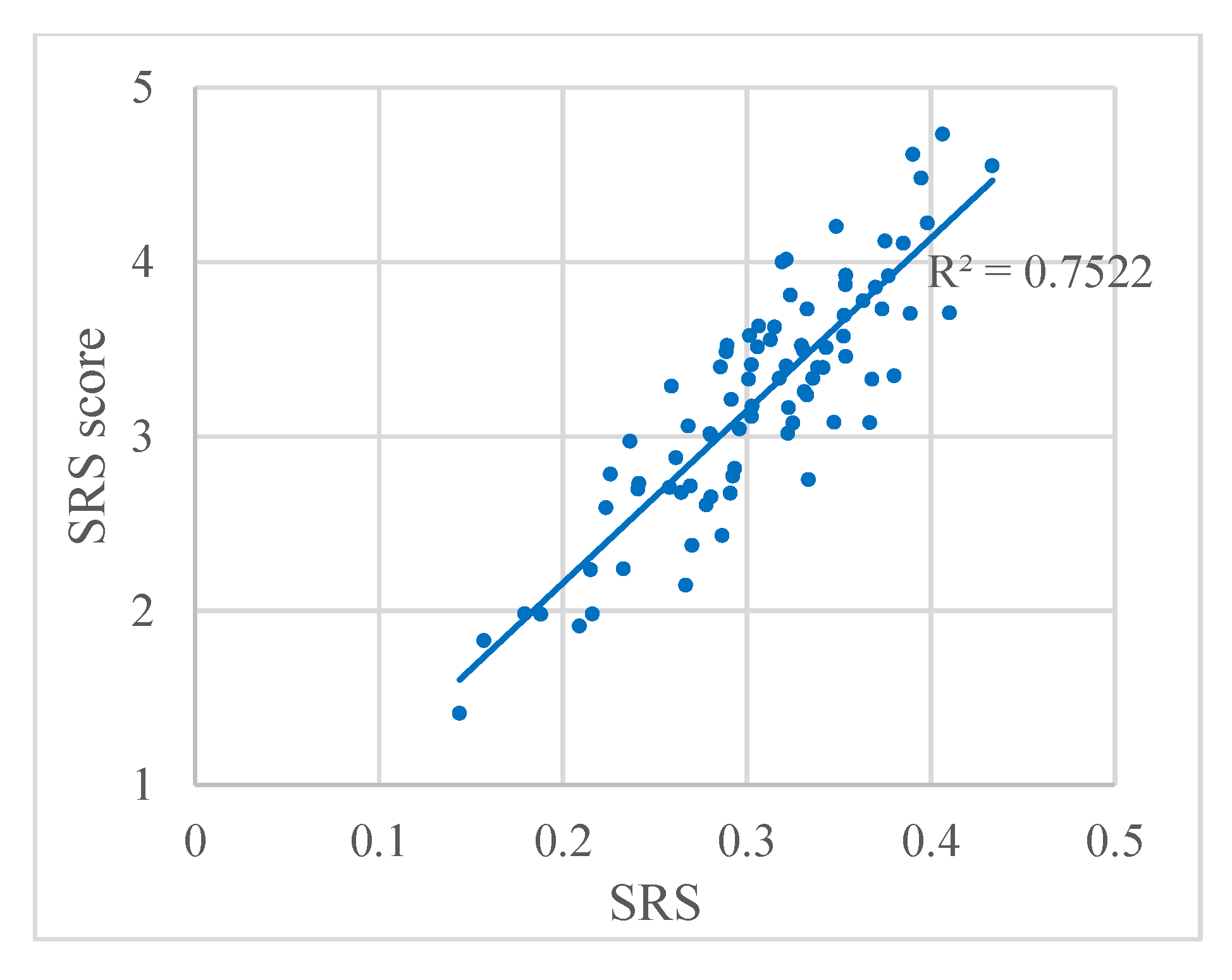
On the other hand, to compare the SRS results with the visual perception of brilliance, the relation between SRS and the SRS score from the questionnaire is plotted in Figure 4. The regression analysis performed on both sets of data yielded a correlation coefficient of R2 = 0.7522, indicating that the algorithm for the SRS obtains accurate results when used in panoramic images.
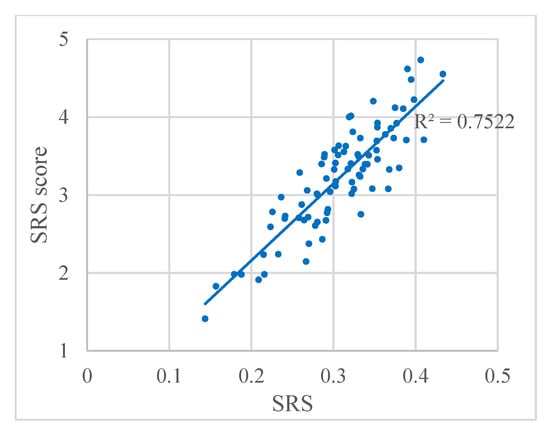
Figure 4.
Relation between SRS and the SRS score from the questionnaire. Each dot represents a panoramic image.
4.2. Visual Entropy
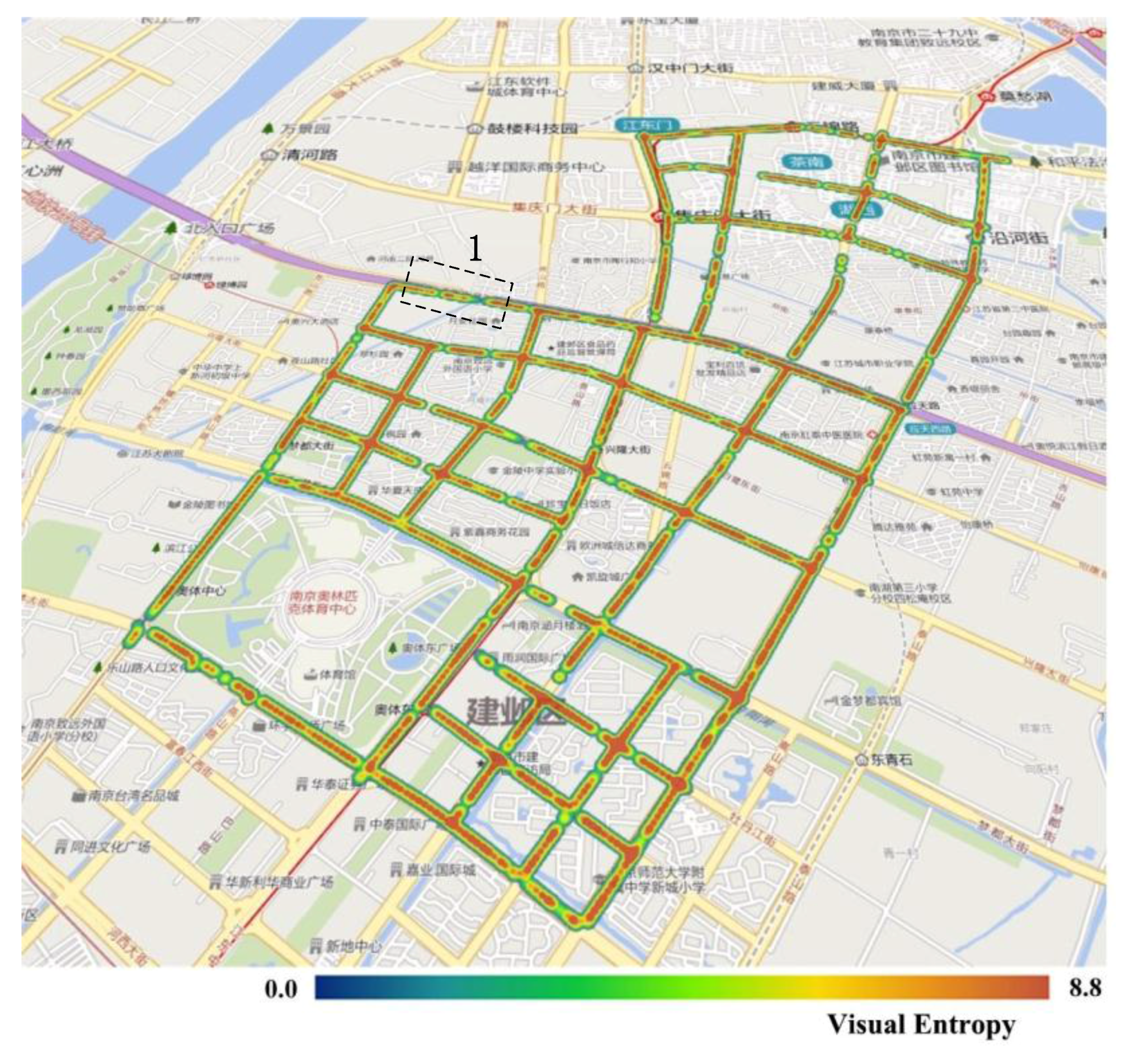
The VE of all panoramic images in the experimental area is shown in Figure 5. The results in the figure indicate that, although the visual entropy has a range of (0, 8.8), most of the streets in the study area have high levels of visual entropy, with these levels being relatively homogeneous throughout. As a whole, this indicates that the urban streetscapes within the study area are richly layered. A more detailed inspection reveals that Street 1 (Figure 5) has a lower-than-average level of visual entropy. This is because this road is an elevated road with a domed roof, as described by the analysis in Section 4.1. As shown in Figure 3c, much of the visual field is blocked by the domed roof, which results in only a few visual layers and a correspondingly low value of visual entropy.
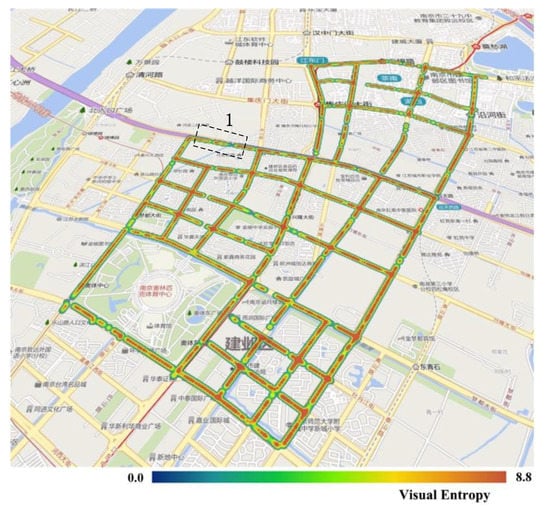
Figure 5.
Visual entropy (VE) results in the study area. The section outlined by the black dotted lines is a section of Street 1, which has a lower-than-average level of visual entropy.
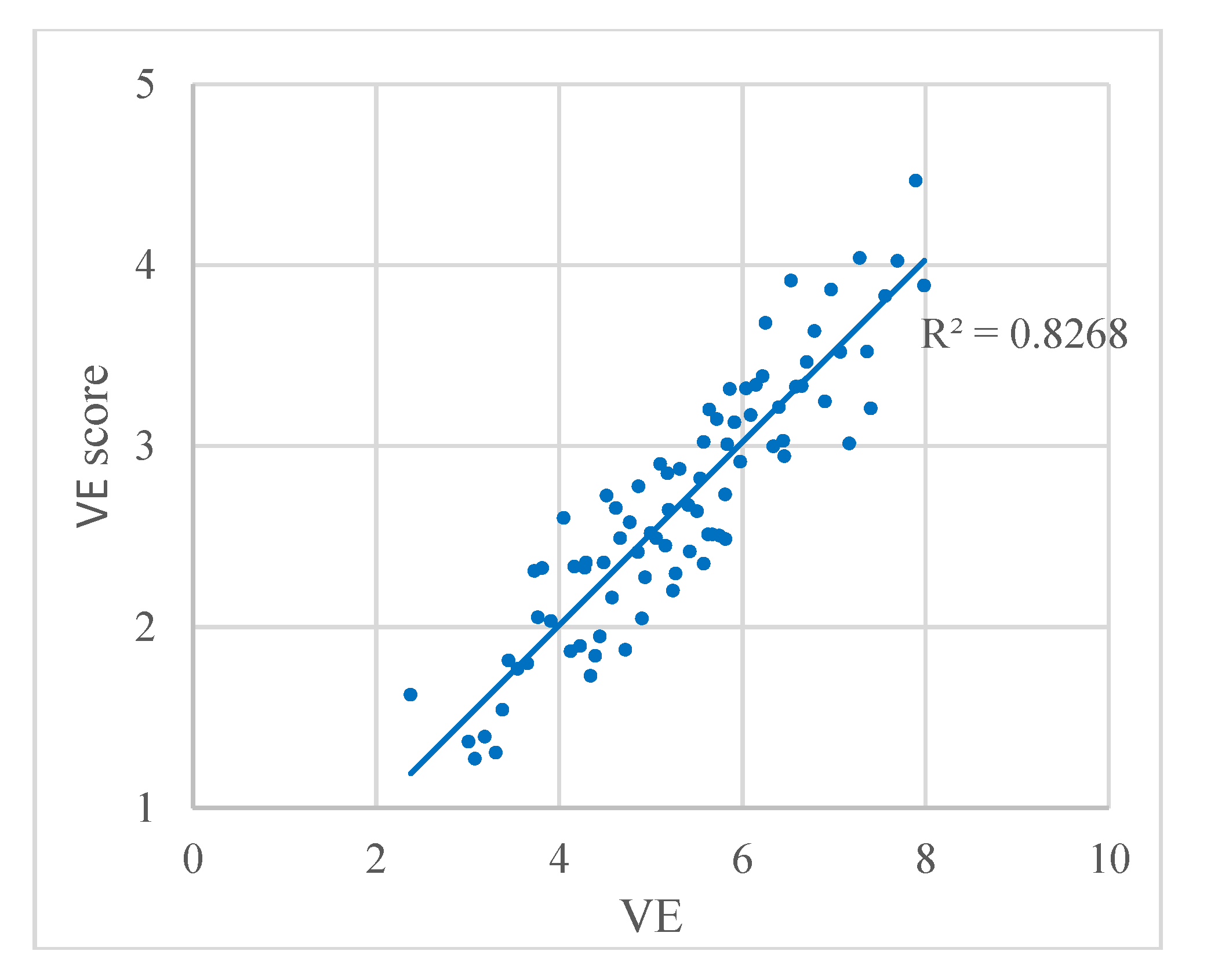
The VE results are compared with the visual perception of richness in Figure 6, where the relation between VE and the VE score from the questionnaire is plotted. We found a strong correlation with a correlation coefficient of R2 = 0.8268, which indicates that the result of VE accords well with the visual perception.
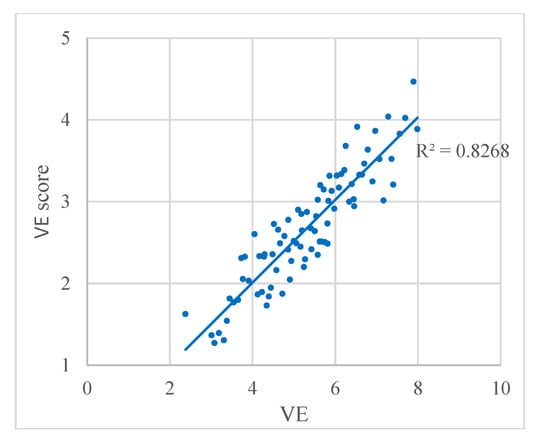
Figure 6.
Relation between VE and the VE score from the questionnaire. Each dot represents a panoramic image.
4.3. Green View Index
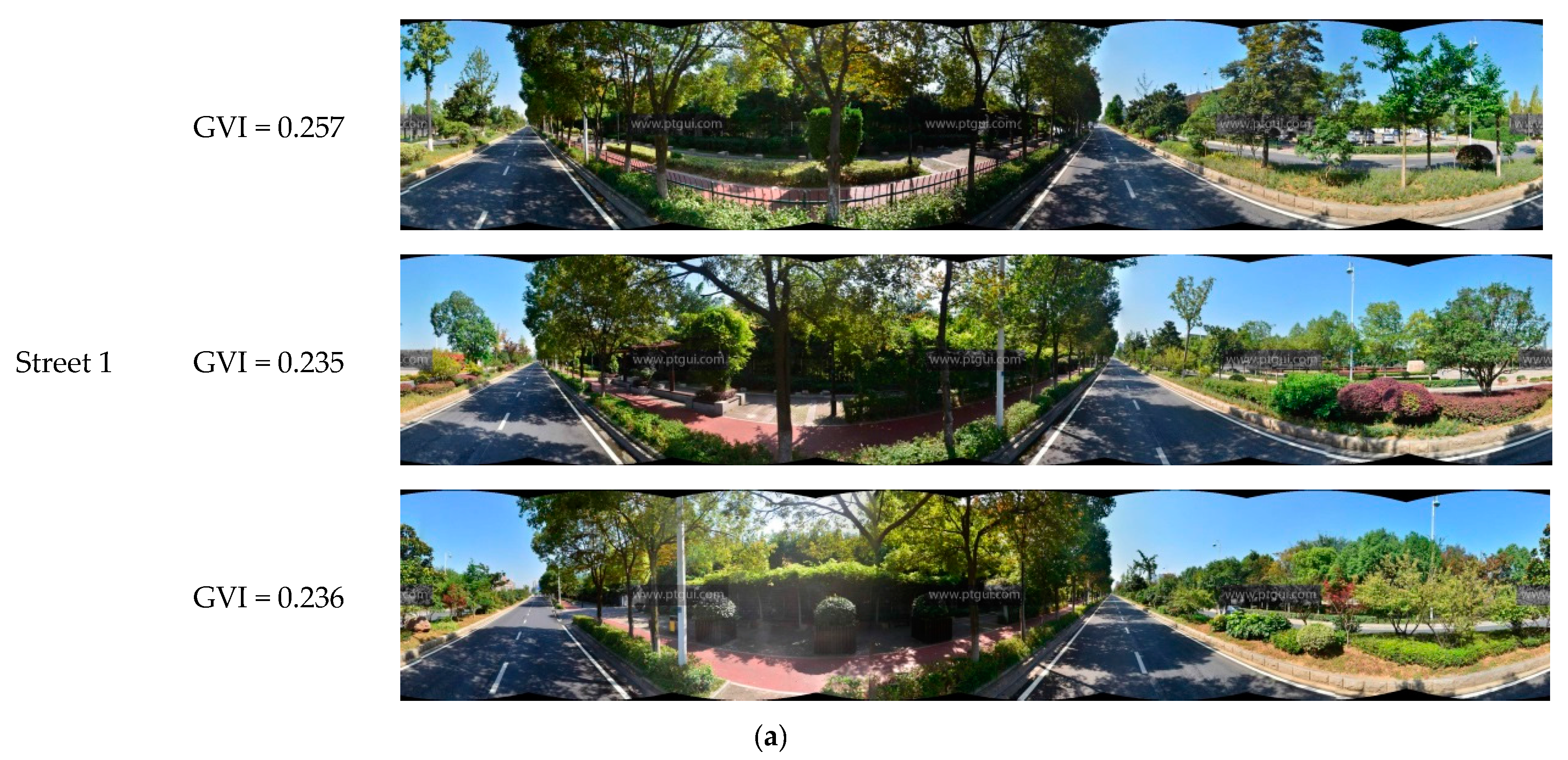
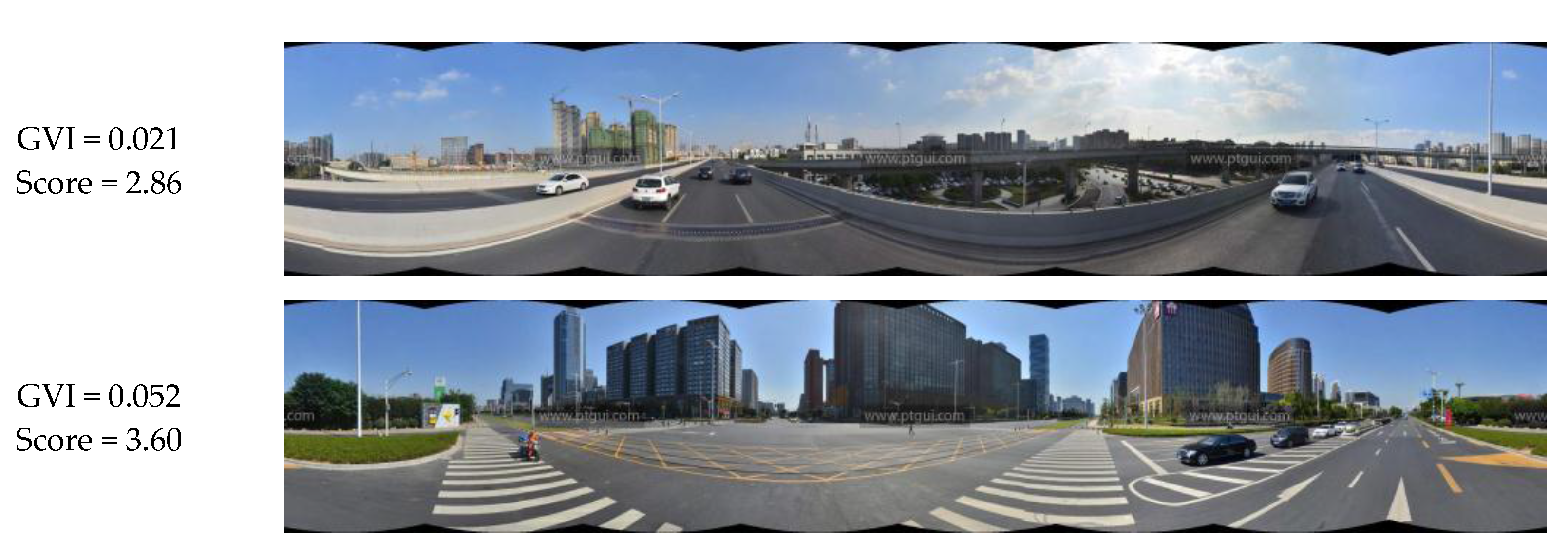
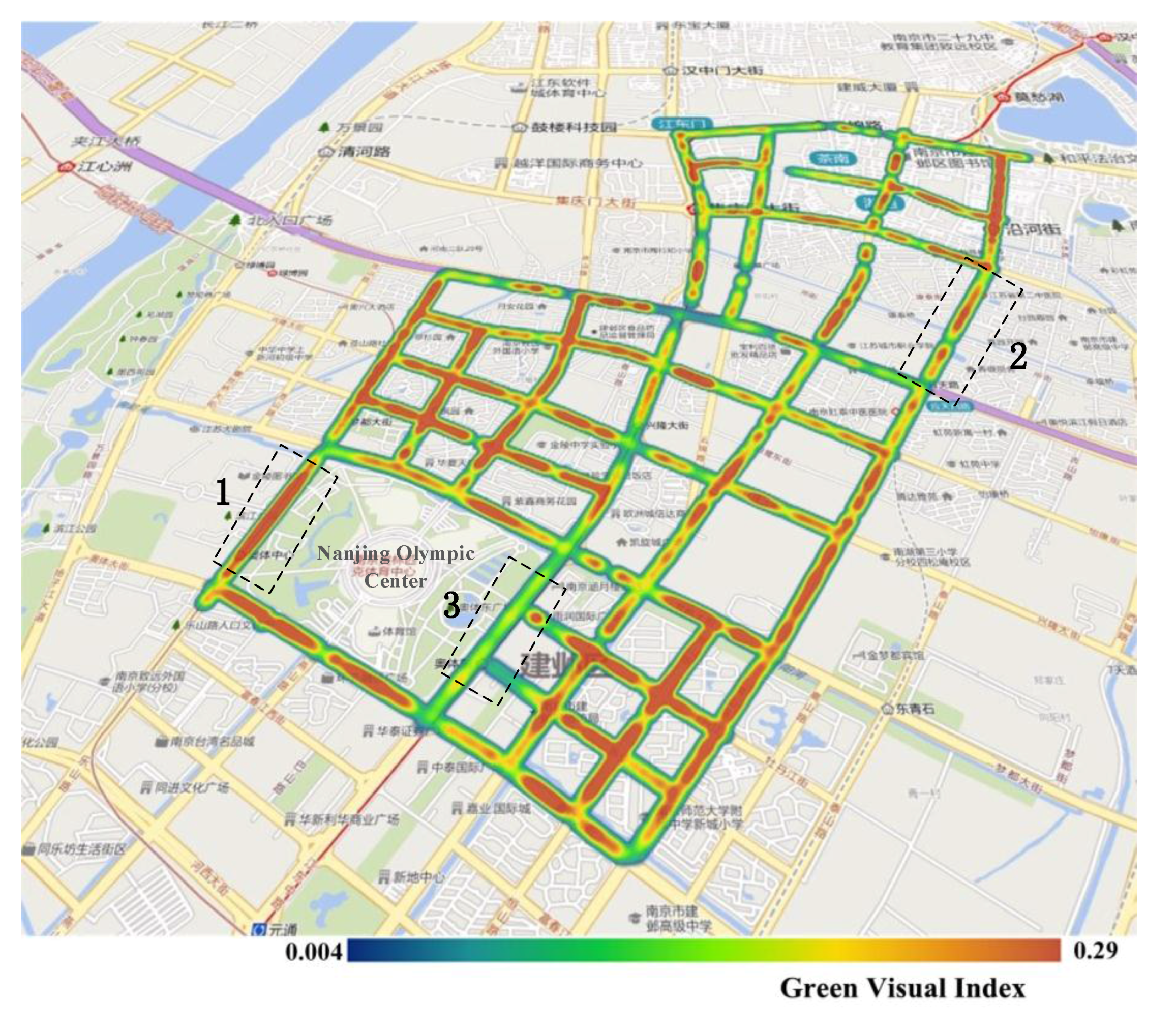
Figure 7 shows the results of the calculation of the GVI of 1669 panoramic images in the experimental area. The figure shows that, in terms of the overall distribution of the GVI within the study area, the GVI of the streets located in the southern part was higher than that of the streets in the northern part. These results are consistent with the fact that residential areas and a science and technology park are located in the northern part of the study area, whereas the southern part comprises the new town, the Nanjing Olympic Center, and its surrounding areas. It may also be observed from this figure that the western and southern sides of the Olympic Center have a higher GVI than the northern and eastern sides. The specific states of green regions along these streets are shown in Figure 8. Street 1 had the highest GVI and Street 2 had a moderate GVI, whereas Street 3 had the lowest GVI. Street 1 is a section of Leshan Road west of the Olympic Center, and one may observe that the panoramic image is almost entirely covered by trees, shrubs, and grassy areas. Street 2, which is a section of Nanhu road with many residential suburbs in its surroundings, has a moderate level of greenery. Street 3 is a section of Central Jiangdong road to the east of the Olympic Center. This street is an expressway that was opened for use fairly recently, and the trees on the sides of this road are still relatively young; hence, this road has the lowest level of greenery among these three streets. In general, streets with higher GVI such as Street 1 are likely to enhance the vivifying and refreshing visual perception, rather than Streets 2 and 3.
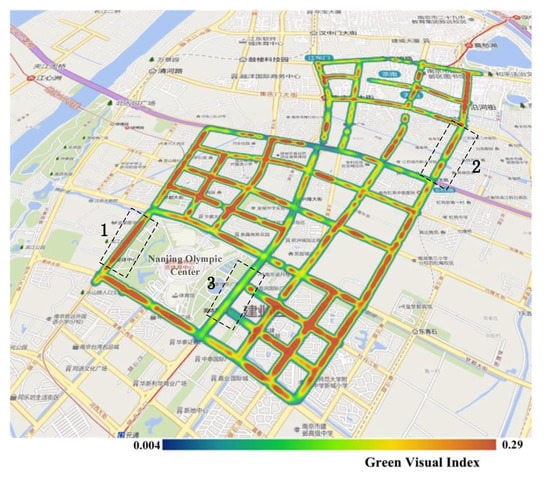
Figure 7.
Green view index (GVI) results in the study area. The streets outlined by black dotted lines are denoted as Street 1, Street 2, and Street 3, respectively, and the GVI from high to low is: Street 1, Street 2, and Street 3.


Figure 8.
Streets with different GVI levels. (a) Street 1; (b) Street 2; (c) Street 3.
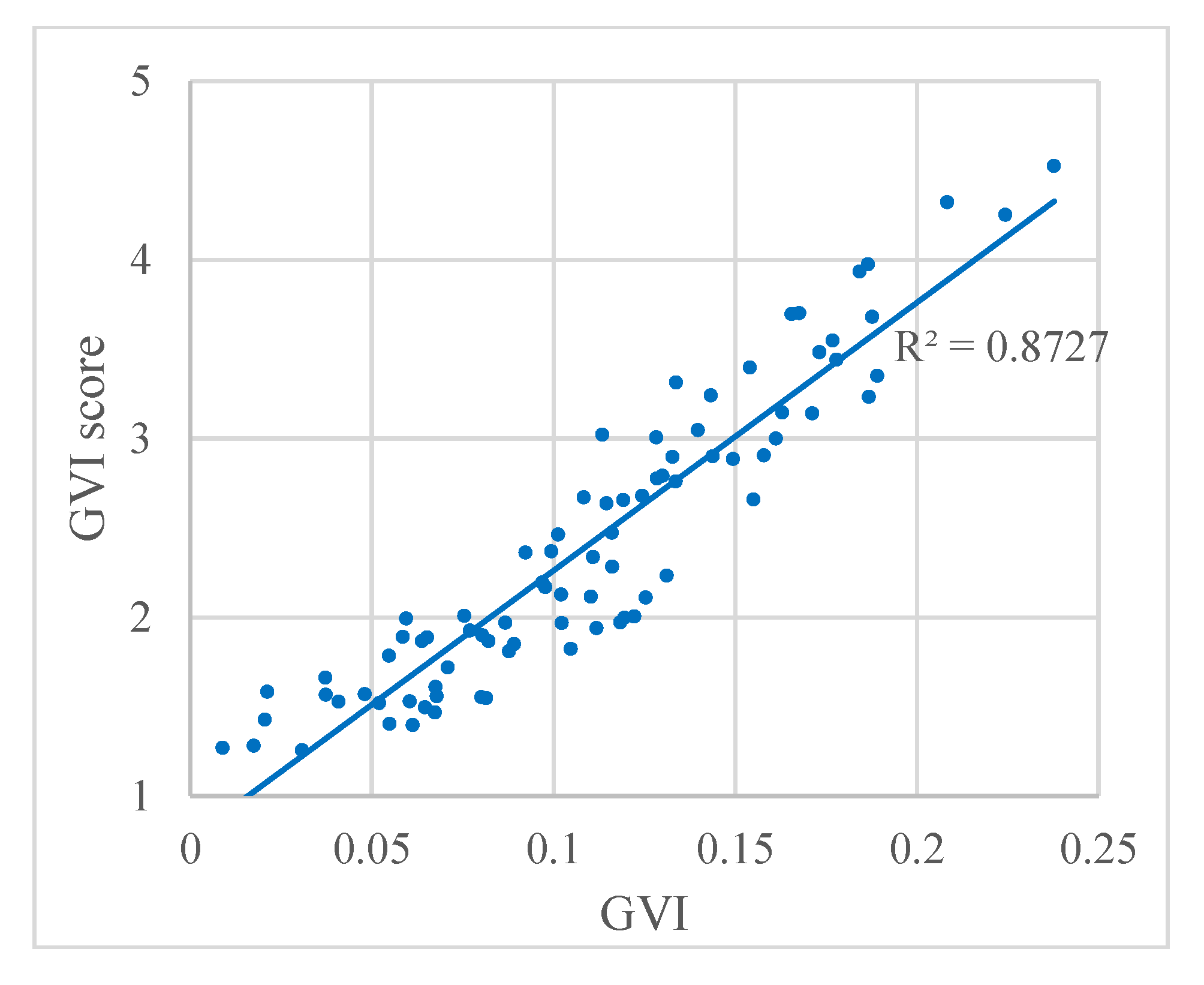
In addition, Figure 9 shows the relationship between the GVI and the GVI score from the questionnaire. We found a strong correlation between the two scores with a correlation coefficient of R2 = 0.8727. These results indicate that the GVI calculated based on the proposed automatic classification method is of high quality, and the GVI values are in accord with the visual perception. Although the GVI performs well, this index cannot differentiate among pixels that appear green because of vegetation and other green pixels, such as green signs and buildings. This problem may be solved by adding multi-temporal data in future studies. Multi-temporal images could show the different vegetation colors during different seasons to identify the vegetation, and further improve the correlation coefficient.
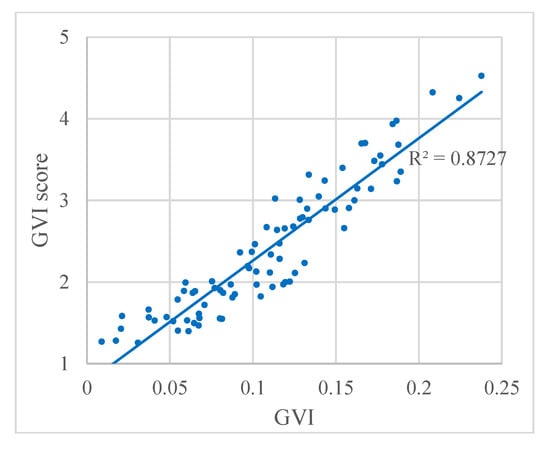
Figure 9.
Relation between the GVI and the GVI score from the questionnaire. Each dot represents a panoramic image.
4.4. Sky-Openness Index
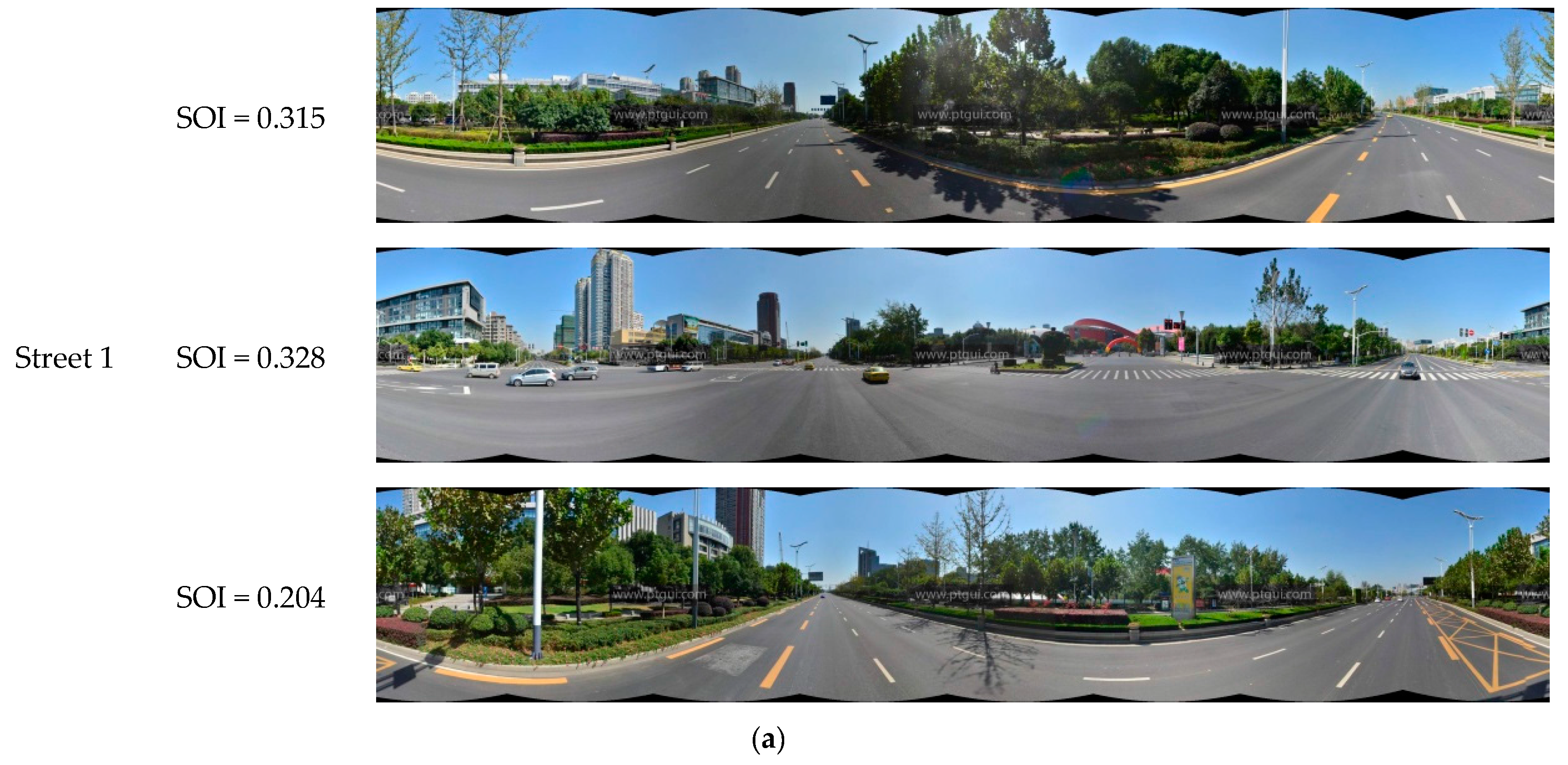
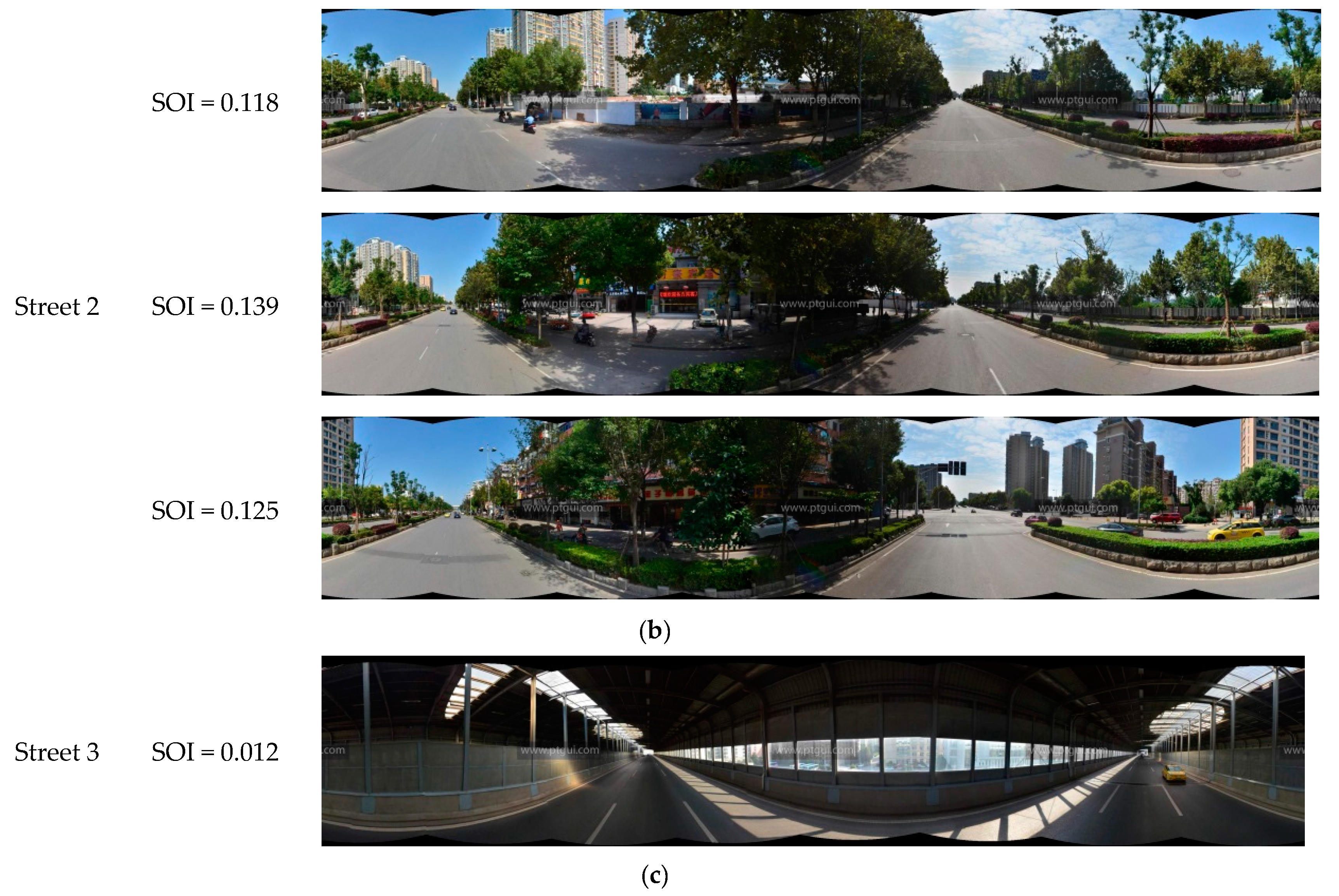
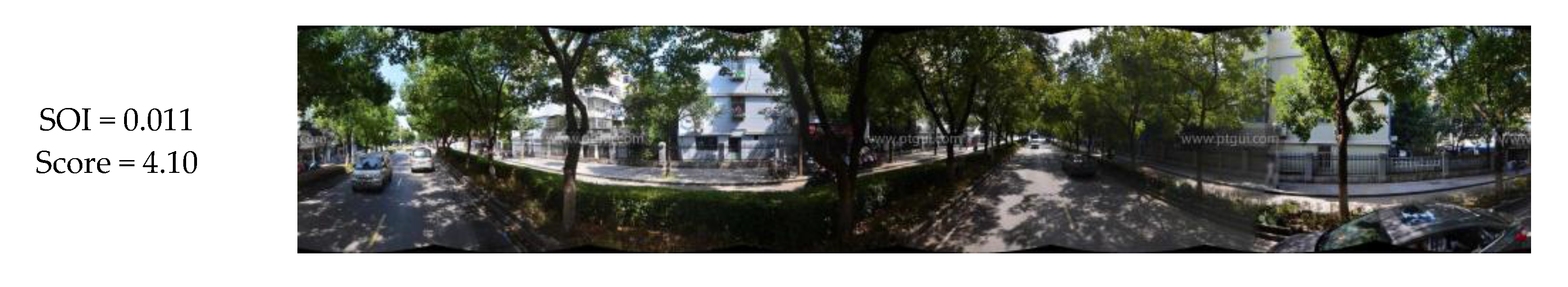
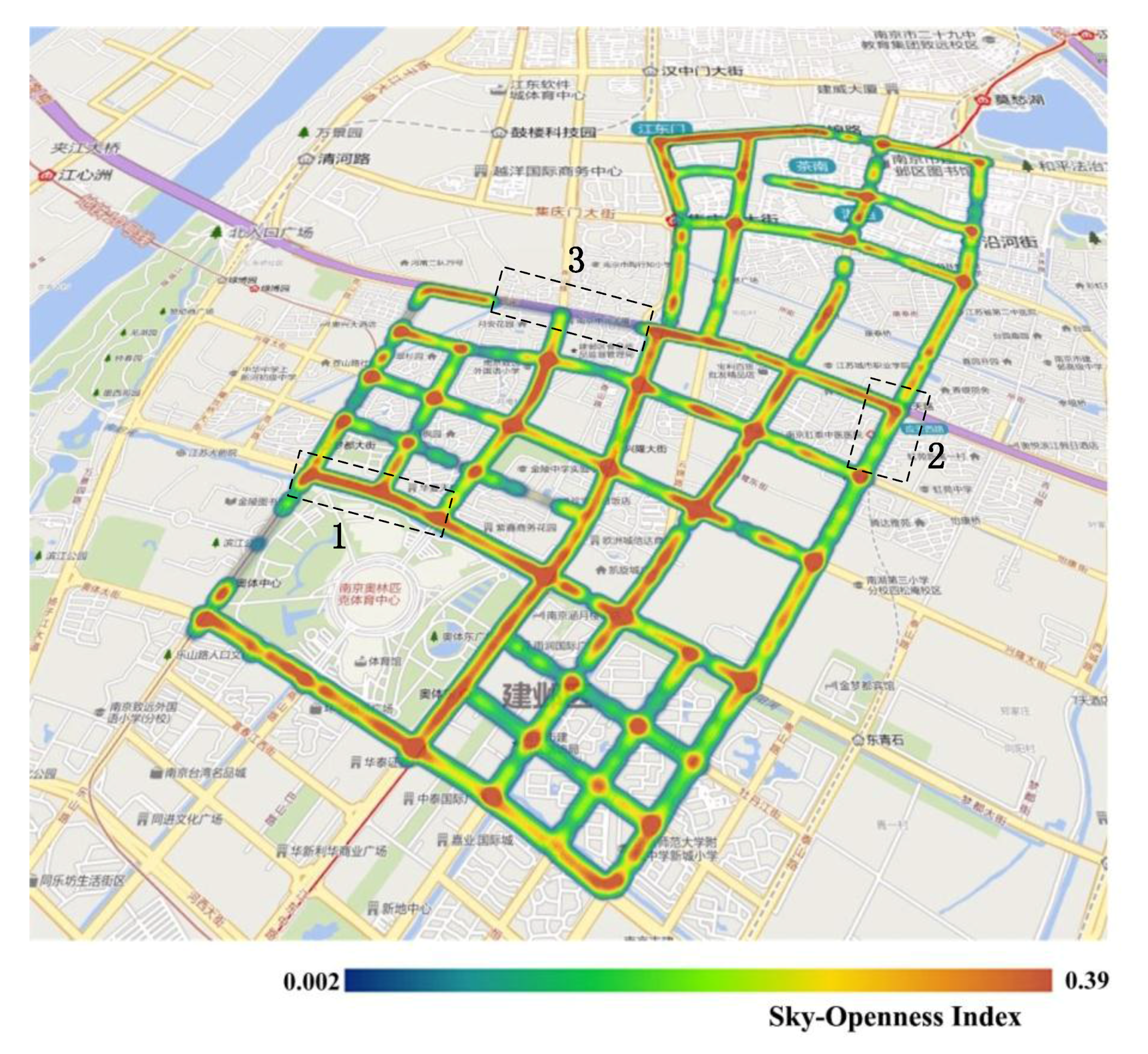
The SOI of all panoramic images in the experimental area are shown in Figure 10. The figure clearly shows that most of the road junctions have high SOI values. As the visual field at road junctions is very wide, the portion of the sky that is visible from these points is also correspondingly large. This indicates that the SOI values calculated in this work are consistent with real-life observations. Other than street intersections, streets passing through residential areas generally have lower SOI values than main roads. This is because residential buildings are situated close to both sides of these roads, and the narrowness of these roads results in lower SOI values. The panoramic images taken from the sampling points on the three streets highlighted in Figure 10 are analyzed in Figure 11. Street 1 is a main road, and has the highest SOI value; Street 2 is a residential street, and has a relatively high SOI value; and Street 3 is a section of a road within a dome-roofed viaduct, and the area of the sky that is visible in its panoramic image is very small, which is why it has the lowest SOI value of all of the streets in the study area. Streets with higher SOI such as Street 1 are likely to enhance the visual perception of brightness and warmness, when compared to Streets 2 and 3.
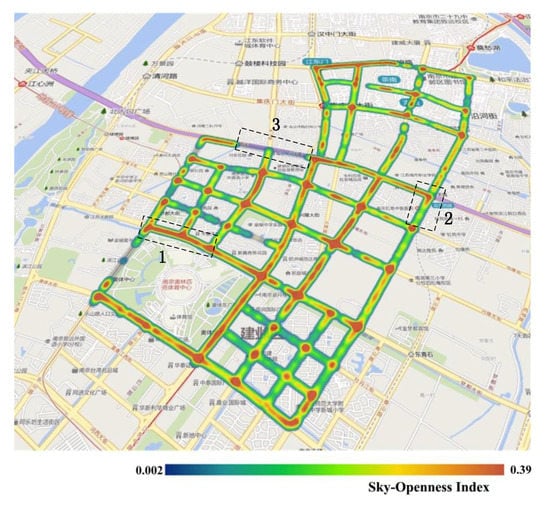
Figure 10.
The sky-openness index (SOI) results in the study area. The streets outlined by the black dotted lines are denoted Street 1, Street 2, and Street 3, respectively, and the SOI from high to low is: Street 1, Street 2, and Street 3.


Figure 11.
Streets with different SOI levels. (a) Street 1; (b) Street 2; (c) Street 3.
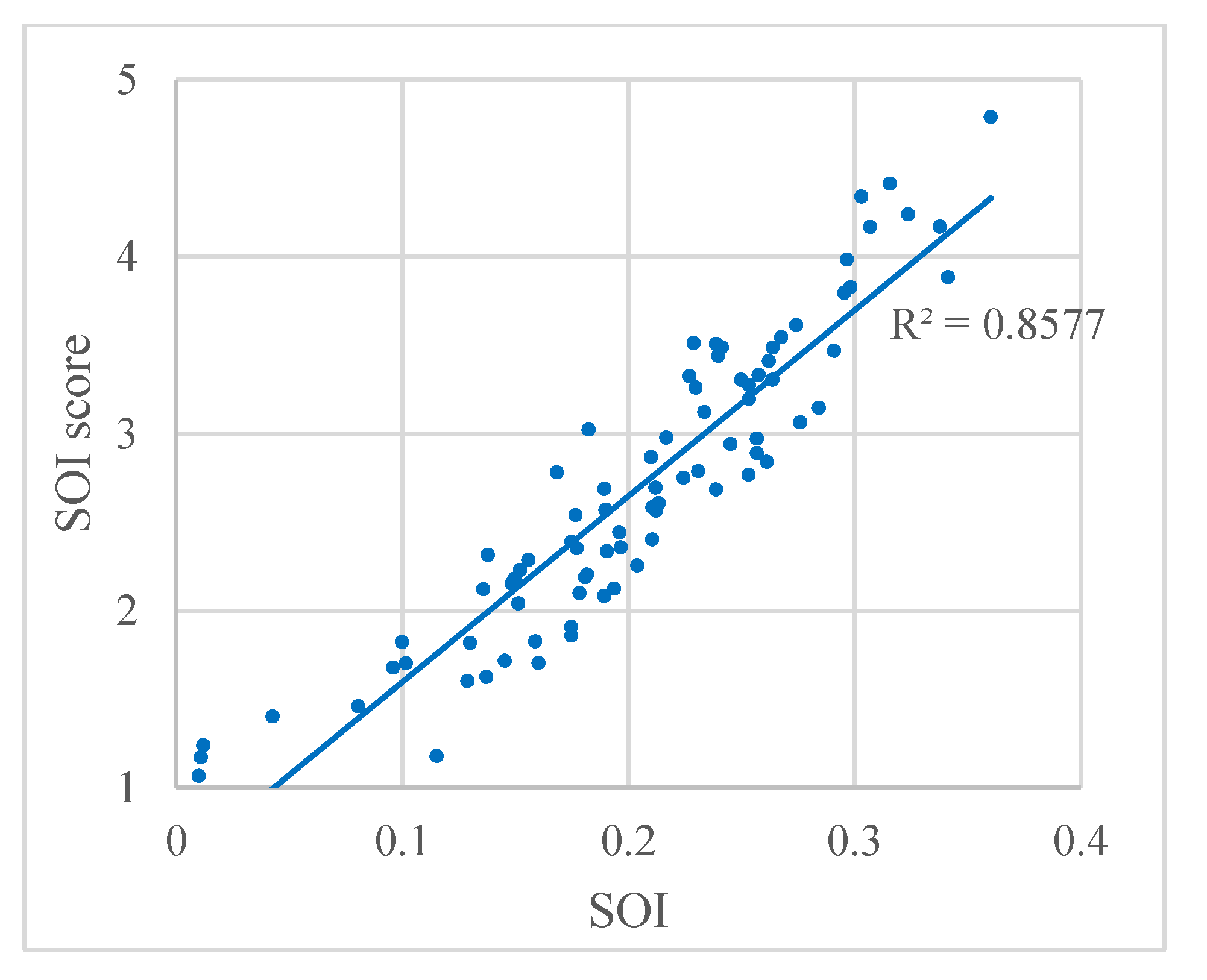
In addition, to evaluate the SOI results, the relation between the SOI and the SOI score from the questionnaire are plotted in Figure 12. The strong correlation between the SOI and the SOI score is evident, with a correlation coefficient of R2 = 0.8577. These results indicate that the SOI result accords well with the visual perception.
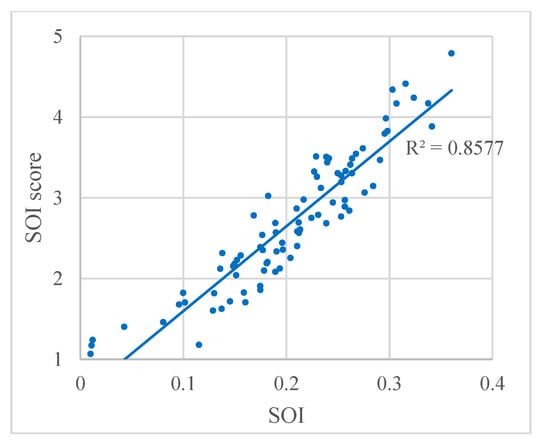
Figure 12.
Relation between SOI and the SOI score from the questionnaire. Each dot represents a panoramic images.
4.5. General Discussion
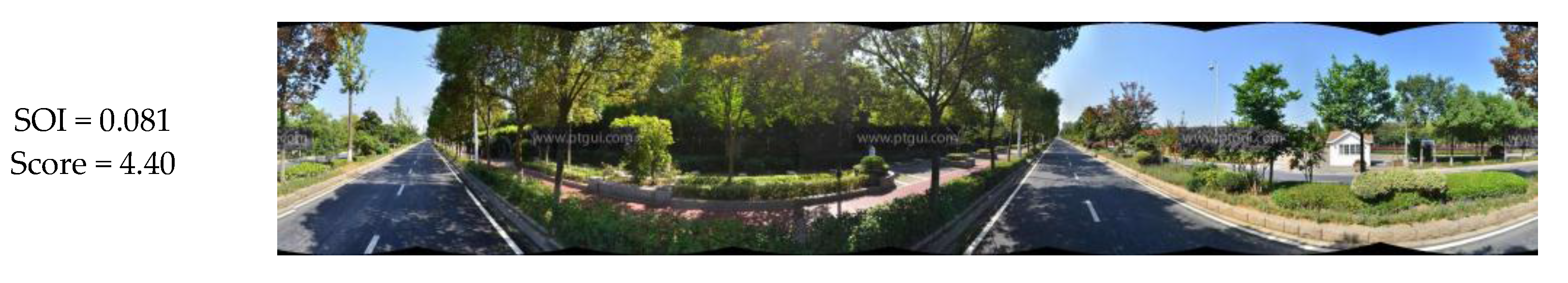
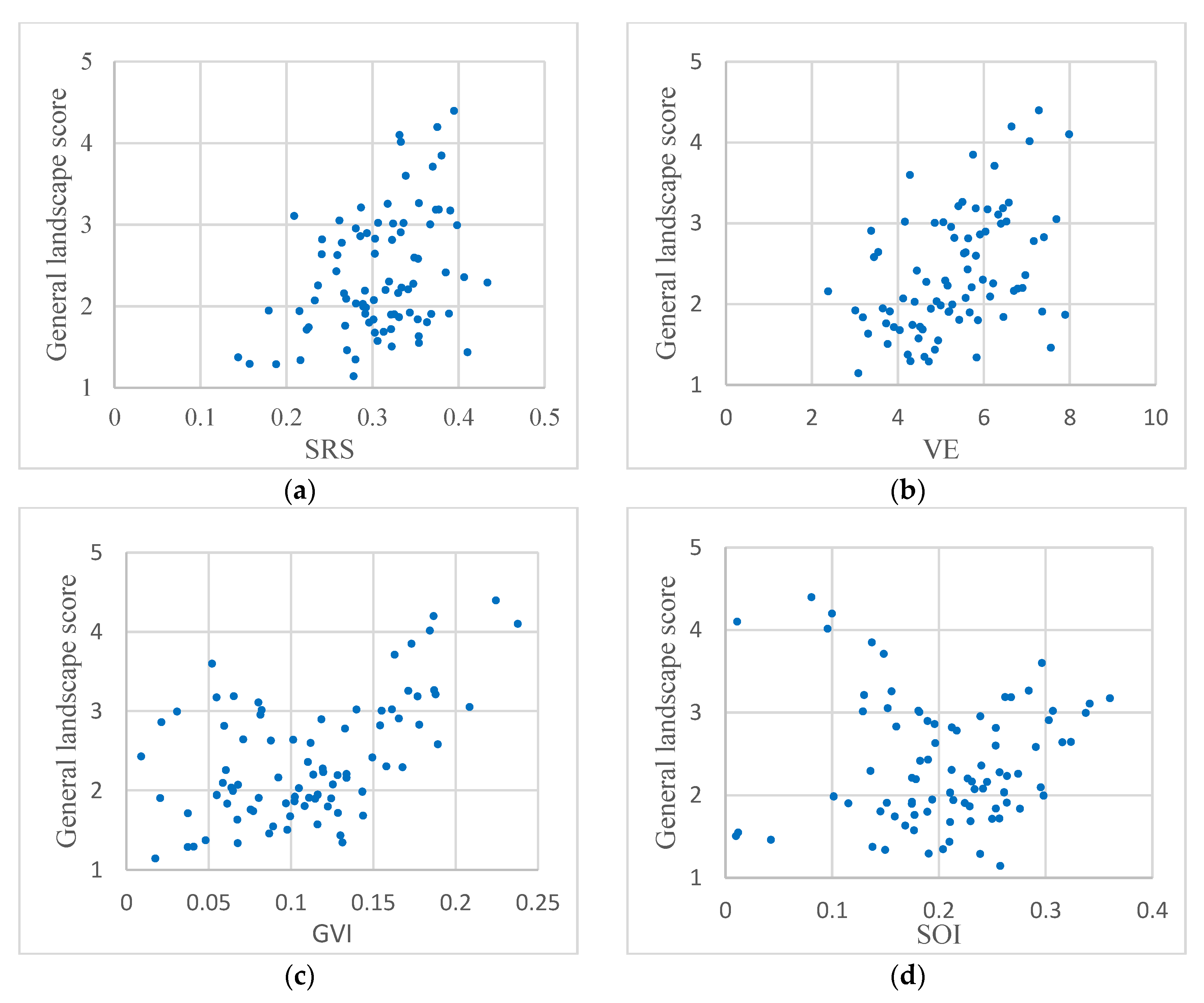
In this study, four indices, namely, SRS, VE, GVI, and SOI were employed to effectively reflect visual perception. This suggests that there may be some relationships between these indices and the general landscape. The relationships between the four indices and the general landscape score from the questionnaire are plotted in Figure 13. Figure 13a,b indicate that the SRS and VE have a positive correlation with the general landscape score, although it is not particularly strong. This indicates that additional SRS and VE would be expected to result in a more pleasing landscape. Further, in Figure 13c,d, a fairly interesting observation is that the overall score shows a “V” distribution with an increase in GVI and SOI. This means that some points have a low GVI or SOI but a high score. In the case of Figure 13c, this is because some streets do not contain much green vegetation but are characterized by beautiful sky, buildings, and billboards. As shown in Figure 14, panoramic images have broad sections of sky and tall buildings, which create princely visual perception, thus the score from the questionnaire is relatively high. For Figure 13d, as shown in Figure 15, some streets are lined by many trees, which obstruct the sky and result in a low SOI. However, the proliferation of trees can form a landscape of vegetation and hence the best visual perception and result in a high score. Therefore, ways in which to combine the GVI and SOI, or allocate weights to them should be considered carefully under different requirements for visual perception.
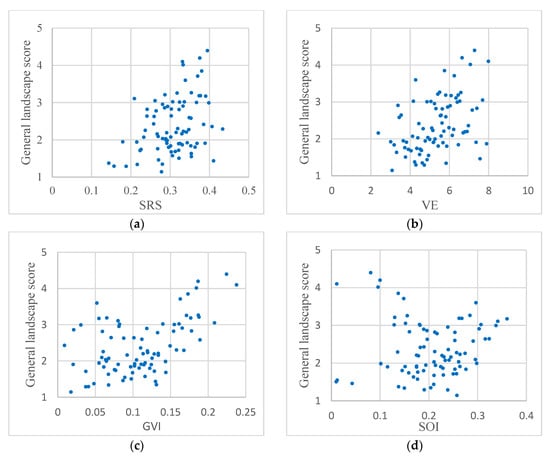
Figure 13.
Relation between the general landscape score and the four respective indices: (a) SRS; (b) VE; (c) GVI; (d) SOI.

Figure 14.
Panoramic images with low GVI but high score.


Figure 15.
Panoramic images with low SOI but high score.
Each index has a stronger or weaker relationship with the general landscape score. However, in urban planning and construction, the visual perception requirement varies considerably. Different local residents and different climatic conditions are expected to make a great difference in the visual assessment of the landscape. Therefore, the four indices were introduced to practically assess street view imagery for urban planning. However, it is necessary to determine an appropriate combination of these indices by taking into account the differences in local history, culture, and climate, etc.
5. Conclusions
This paper proposes an automated technical procedure to quantify the visual perception of streets. The procedure is based on panoramic images formed by merging street view imagery. The image processing techniques integrated within this procedure include color space conversions, image segmentation, and the detection of salient regions. Four types of indices that reflect the visual perception of streets were thus generated: SRS, VE, GVI, and SOI. The Jianye District of Nanjing, China was selected as the study area. The results of our experiments indicated that the proposed indices can accurately evaluate the visual perception of urban streets, as the specific numerical values of the various indices are supported by experimentally obtained data and are objective in nature. The results of evaluations based on these indices are consistent with real-life observations, indicating a high level of reliability. The SRS, VE, GVI, and SOI can effectively characterize the visual perception of brilliance, richness, green quantity, and the sky-openness degree, respectively. These indices can describe the visual perception from multiple angles, and enrich this visual perception based on computer-generated results in an urban landscape study. As this algorithm is highly automated, in the future, these four indices may be added to Tencent Street View and may also be extended to Google Street View, Baidu Street View, and so on. These indices can provide scientific guidance for planners of urban landscapes, thus improving the quality of urban residents’ lives.
In these experiments, the study area was the Jianye District of Nanjing, China. However, many factors such as the location of the city, the time of taking pictures, degree of sunlight, history and culture have a stronger or weaker effect on the transferability of these indices. Therefore, determining how to combine these indices effectively and popularizing the results requires further study.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41622109, 41371017) and the National Key Research and Development Plan (Grant No. 2017YFB0504205).
Author Contributions
Liang Cheng and Sensen Chu conceived the research idea and designed the experiments. Wenwen Zong, Shuyi Li and Jie Wu collected the questionnaires and analyzed the data. Sensen Chu wrote the manuscript. Liang Cheng and Manchun Li edited the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Strom, E. The Street: A quintessential social public space. J. Urban Technol. 2015, 22, 139–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozkan, U.Y. Assessment of visual landscape quality using IKONOS imagery. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clay, G.R.; Smidt, R.K. Assessing the validity and reliability of descriptor variables used in scenic highway analysis. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2004, 66, 239–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swimmer, E.; Whiteman, J.; Taintor, R. Byway Beginnings: Understanding, Inventorying, and Evaluating a Byway's Intrinsic Qualities; National Scenic Byways Program Publication: Washington, DC, USA, 1999.
- Antrop, M.; Stobbelaar, D.J.; Mansvelt, J.D.V. Background concepts for integrated landscape analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2000, 77, 17–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, T.C. Whither scenic beauty? Visual landscape quality assessment in the 21st century. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2001, 54, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Cheng, Q.; Wang, Z.; Shao, Z. ‘Big data’ for pedestrian volume: Exploring the use of Google Street View images for pedestrian counts. Appl. Geogr. 2015, 63, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Runge, N.; Samsonov, P.; Degraen, D.; Schoning, J. No more autobahn: Scenic route generation using Googles Street View. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Intelligent User Interfaces, Sonoma, CA, USA, 7–10 March 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kopf, J.; Chen, B.; Szeliski, R.; Cohen, M. Street Slide: Browsing Street Level Imagery. In Proceedings of the 37th ACM SIGGRAPH Conference and Exhibition on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques, Los Angeles, CA, USA, 26–30 July 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hoelzl, I.; Marie, R. Google Street View: Navigating the operative image. Vis. Stud. 2014, 29, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torii, A.; Havlena, M. From google street view to 3d city models. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Kyoto, Japan, 29 September–2 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Anguelov, D.; Dulong, C.; Filip, D.; Frueh, C.; Lafon, S.; Lyon, R.; Ogale, A.; Vincent, L.; Weaver, J. Google street view: Capturing the world at street level. Computer 2010, 43, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstockt, S.; Gerke, M.; Kerle, N. Geolocalization of Crowdsourced Images for 3-D Modeling of City Points of Interest. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 1670–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, K.; Azenkot, S.; Campbell, M.; Bennett, C.L.; Le, V.; Pannella, S.; Moore, R.; Minckler, K.; Ng, R.H.; Froehlich, J.E. Improving Public Transit Accessibility for Blind Riders by Crowdsourcing Bus Stop Landmark Locations with Google Street View. In Proceedings of the 15th International ACM SIGACCESS Conference on Computers and Accessibility, Washington, DC, USA, 21–23 October 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Olea, P.P.; Mateo-Tomás, P. Assessing species habitat using Google Street View: A case study of cliff-nesting vultures. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousselet, J.; Imbert, C.; Dekri, A.; Garcia, J.; Goussard, F.; Vincent, B.; Denux, O.; Robinet, C.; Dorkeld, F.; Roques, A.; et al. Assessing species distribution using Google Street View: A pilot study with the pine processionary moth. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berland, A.; Lange, D.A. Lange Google Street View shows promise for virtual street tree surveys. Urban For. Urban Green. 2017, 21, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanwolleghem, G.; Dyck, D.V.; Ducheyne, F.; Bourdeaudhuij, I.D.; Cardon, G. Assessing the environmental characteristics of cycling routes to school: A study on the reliability and validity of a Google Street View-based audit. Int. J. Health Geogr. 2014, 13, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, W. Does the visibility of greenery increase perceived safety in urban areas? Evidence from the place pulse 1.0 dataset. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2015, 4, 1166–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clews, C.; Brajkovich-Payne, R.; Dwight, E.; Fauzul, A.A.; Burton, M.; Carleton, O.; Cook, J.; Deroles, C.; Faulkner, R.; Furniss, M.; et al. Alcohol in urban streetscapes: A comparison of the use of Google Street View and on-street observation. BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, K. Visual threshold carrying capacity (VTCC) in urban landscape management: A case study of Seoul, Korea. Landsc. Urban Plan. 1998, 39, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, W.; Ricard, R.; Meng, Q.; Zhang, W. Assessing street-level urban greenery using Google Street View and a modified green view index. Urban For. Urban Green. 2015, 14, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, K. The Image of the City; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Stamps, A.E.; Smith, S. Environmental enclosure in urban settings. Environ. Behav. 2002, 34, 781–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhao, L.; Mcbride, J.; Gong, P. Can you see green? Assessing the visibility of urban forests in cities. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2009, 91, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayad, Y.M. Remote Sensing and GIS in Modeling Visual Landscape Change: A Case Study of the Northwestern Arid Coast of Egypt. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2005, 73, 307–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Gu, Z.; Li, H. Sdsp: A Novel Saliency Detection Method by Combining Simple Priors. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, Melbourne, Australia, 15–18 September 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, X.; Wu, Y. A Unified Approach to Salient Object Detection via Low Rank Matrix Recovery. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Providence, RI, USA, 16–21 June 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Judd, T.; Ehinger, K.; Durand, F.; Torralba, A. Learning to Predict Where Humans Look. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Kyoto, Japan, 29 September–2 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Otsu, N. A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.L.; Zhou, L. Visual Entropy-Based Classified Bath Fractal Transform for Image Coding. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Beijing, China, 18 October 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Q.X.; Gao, W.; Wang, W.Q.; Huang, T.J. A Color Image Segmentation Algorithm by Using Color and Spatial Information. J. Softw. 2004, 15, 522–530. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bain, L.; Gray, B.; Rodgers, D. Living Streets: Strategies for Crafting Public Space; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Camacho-Cervantes, M.; Schondube, J.E.; Castillo, A.; MacGregor-Fors, L. How Do People Perceive Urban Trees? Assessing Likes and Dislikes in Relation to the Trees of a City. Urban Ecosyst. 2014, 17, 761–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garré, S.; Meeus, S.; Gulinck, H. The dual role of roads in the visual landscape: A case-study in the area around Mechelen (Belgium). Landsc. Urban Plan. 2009, 92, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.; Wang, Z. Measuring visual enclosure for street walkability: Using machine learning algorithms and Google Street View imagery. Appl. Geogr. 2016, 76, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).