Validity of VR Technology on the Smartphone for the Study of Wind Park Soundscapes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Selection
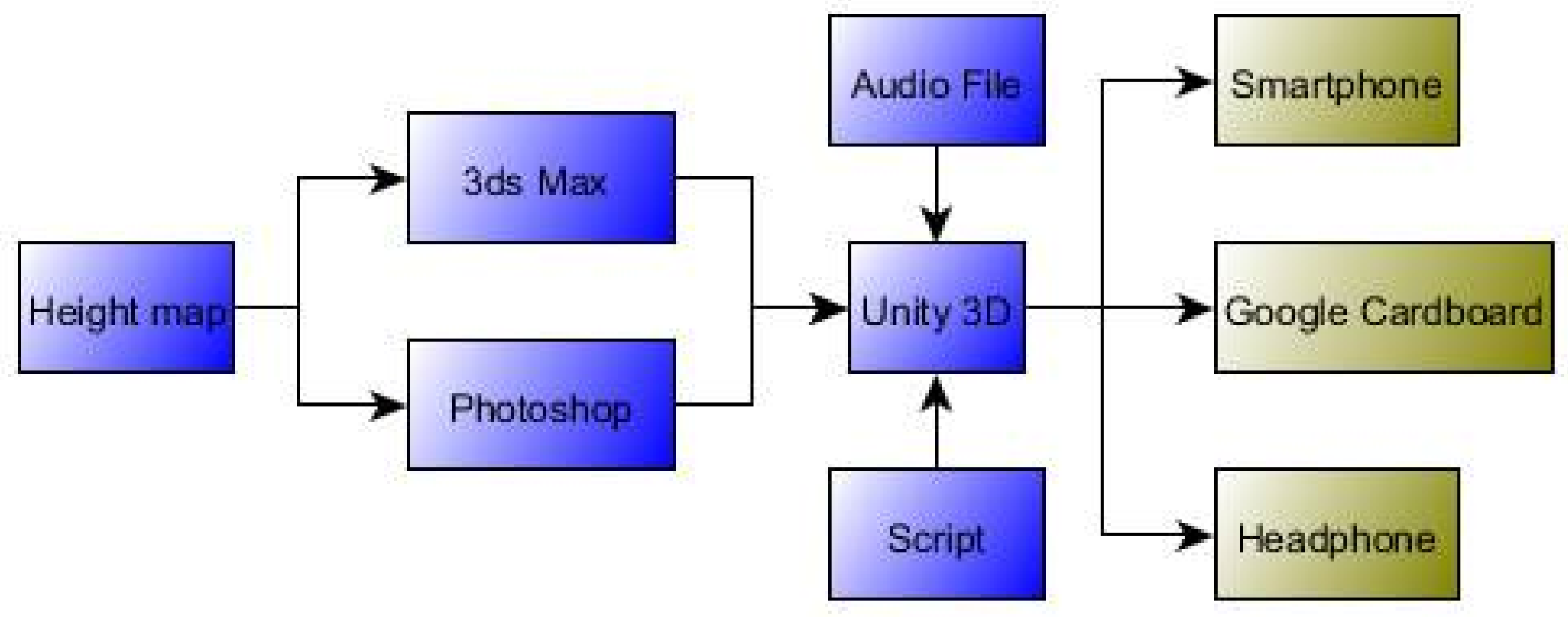
2.2. Aural and Visual Materials
2.3. Measures of Subjective Evaluations
2.4. Participants and Experimental Precedure
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Realism of VR Simulations
3.2. Aural–Visual Interactions in VR Simulations
3.3. Soundscape in Multidimensional Scales in VR Simulations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kontogianni, A.; Tourkolias, C.; Skourtos, M.; Damigos, D. Planning globally, protesting locally: Patterns in community perceptions towards the installation of wind farms. Renew. Energy 2014, 66, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertsch, V.; Hall, M.; Weinhardt, C.; Fichtner, W. Public acceptance and preferences related to renewable energy and grid expansion policy: Empirical insights for Germany. Energy 2016, 114, 465–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hills, J.M.; Michalena, E. Renewable energy pioneers are threatened by EU policy reform. Renew. Energy 2017, 108, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowell, R. Wind power, landscape and strategic, spatial planning—The construction of ‘acceptable locations’ in wales. Land Use Policy 2010, 27, 222–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.L.; Sheppard, S.R.J. Culture and communication: Can landscape visualization improve forest management consultation with indigenous communities? Landsc. Urban Plan. 2006, 77, 291–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manyoky, M. Developing a GIS-based visual-acoustic 3d simulation for wind farm assessment. Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2014, 3, 29–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Behm, H.; Bill, R.; Kang, J. Audio-visual perception of new wind parks. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 165, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iachini, T.; Maffei, L.; Ruotolo, F.; Senese, V.P.; Ruggiero, G.; Masullo, M.; Alekseeva, N. Multisensory assessment of acoustic comfort aboard metros: A virtual reality study. Appl. Cognit. Psychol. 2012, 26, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Masullo, M.; Maffei, L.; Meng, F.; Vorländer, M. A demonstrator tool of web-based virtual reality for participatory evaluation of urban sound environment. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2017, 170, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruotolo, F.; Maffei, L.; Di Gabriele, M.; Iachini, T.; Masullo, M.; Ruggiero, G.; Senese, V.P. Immersive virtual reality and environmental noise assessment: An innovative audio-visual approach. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2013, 41, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manyoky, M.; Wissen Hayek, U.; Pieren, R.; Heutschi, K.; Grêt-Regamey, A. Evaluating a visual-acoustic simulation for wind park assessment. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2016, 153, 180–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, L.; Lange, E. Getting virtual 3d landscapes out of the lab. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2015, 54, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindquist, M.; Lange, E.; Kang, J. From 3d landscape visualization to environmental simulation: The contribution of sound to the perception of virtual environments. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2016, 148, 216–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, E.; van den Berg, F.; Bakker, R.; Bouma, J. Response to noise from modern wind farms in the netherlands. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2009, 126, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torija, A.J.; Ruiz, D.P.; Ramos-Ridao, A.F. Application of a methodology for categorizing and differentiating urban soundscapes using acoustical descriptors and semantic-differential attributes. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2013, 134, 791–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plehn, M. Wind Energy in the Baltic Sea Region 2. 2012. Available online: www.windenergy-in-the-bsr.net (accessed on 12 June 2015).
- Bishop, I.D.; Miller, D.R. Visual assessment of off-shore wind turbines: The influence of distance, contrast, movement and social variables. Renew. Energy 2007, 32, 814–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Zhang, M. Semantic differential analysis of the soundscape in urban open public spaces. Build. Environ. 2010, 45, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axelsson, Ö.; Nilsson, M.E.; Berglund, B. A principal components model of soundscape perception. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2010, 128, 2836–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudarsono, A.S.; Lam, Y.W.; Davies, W.J. The effect of sound level on perception of reproduced soundscapes. Appl. Acoust. 2016, 110, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szychowska, M.; Hafke-Dys, H.; Preis, A.; Kociński, J.; Kleka, P. The influence of audio-visual interactions on the annoyance ratings for wind turbines. Appl. Acoust. 2018, 129, 190–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudarsono, A.S.; Lam, Y.W.; Davies, W.J. The validation of acoustic environment simulator to determine the relationship between sound objects and soundscape. Acta Acust. United Acust. 2017, 103, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jian, K. From dBA to soundscape indices: Managing our sound environment. Front. Eng. Manag. 2017, 4, 184–192. [Google Scholar]







| Sound Features | Visual Features | Description | LAeq [dB] | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sites | Wind Turbines | Cars | People | Stream | Road | Dwellings | Trees | Sky | |||
| Site 1 | High traffic flow | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | Main Avenue with high road traffic flow with a large number of vehicles. | 65.3 | |||
| Site 2 | Birds | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | Location situated in natural environment isolated from sounds of human activity, sounds dominated with bird sounds. | 39 | |||||
| Site 3 | Motorway | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | Location situated in the motorway. | 52.5 | |||
| Site 4 | Human sounds | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | Location situated in a residential area, sounds included people talking. | 50.2 | |||
| Site 5 | Leisure activities | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | Location situated near residential area, with sounds of outdoor activities. | 53.6 | ||||
| Site 6 | Medium traffic flow | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | Location situated in a residential area with medium road traffic flow. | 41.2 | |||
| Site 7 | Water | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | ✕ | Location situated in natural environment, with sounds from stream. | 43.7 | |||
| Sites | Aspects | Realism | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | ||
| Site 1 | Light | 5.1 | 1.03 |
| Color | 4.75 | 1.26 | |
| Vegetation | 4.65 | 1.39 | |
| Total realism | 5.18 | 1.28 | |
| Site 2 | Light | 5.03 | 1.16 |
| Color | 4.78 | 1.37 | |
| Vegetation | 4.48 | 1.60 | |
| Total realism | 4.63 | 1.50 | |
| Site 3 | Light | 4.88 | 1.32 |
| Color | 4.75 | 1.45 | |
| Vegetation | 4.55 | 1.71 | |
| Total realism | 4.88 | 1.51 | |
| Site 4 | Light | 4.83 | 1.38 |
| Color | 4.75 | 1.30 | |
| Vegetation | 4.58 | 1.52 | |
| Total realism | 4.08 | 1.78 | |
| Site 5 | Light | 5.1 | 1.17 |
| Color | 4.8 | 1.24 | |
| Vegetation | 4.68 | 1.53 | |
| Total realism | 5.05 | 1.15 | |
| Site 6 | Light | 4.9 | 1.32 |
| Color | 4.63 | 1.46 | |
| Vegetation | 4.3 | 1.60 | |
| Total realism | 4.83 | 1.38 | |
| Site 7 | Light | 5.05 | 1.22 |
| Color | 4.8 | 1.26 | |
| Vegetation | 4.43 | 1.68 | |
| Total realism | 4.38 | 1.69 | |
| Component | Component 1 (42.4%) | Component 2 (15.6%) | Component 3 (11.4%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Smooth–rough | 0.874 | ||
| Distinct–ordinary | 0.858 | ||
| Quite–loud | 0.841 | ||
| Order–disorder | 0.692 | ||
| Comfortable–uncomfortable | 0.679 | 0.468 | |
| Calming–agitating | 0.659 | 0.451 | |
| Open–closed | 0.836 | ||
| Natural–artificial | 0.695 | ||
| Pleasant–unpleasant | 0.458 | 0.601 | |
| Various–monotonous | 0.919 |
| Factor | Calmness/Relaxation | Naturality/Pleasantness | Diversity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Perceived realism | 0.401 | 0.339 | 0.759 * |
| Loudness | 0.841 * | 0.790 * | 0.561 |
| Fluctuation strength | 0.756 * | 0.672 | 0.294 |
| Roughness | 0.916 ** | 0.843 * | 0.571 |
| LAeq | 0.782 * | 0.794 * | 0.431 |
| Annoyance | 0.964 ** | 0.971 ** | 0.594 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
YU, T.; Behm, H.; Bill, R.; Kang, J. Validity of VR Technology on the Smartphone for the Study of Wind Park Soundscapes. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi7040152
YU T, Behm H, Bill R, Kang J. Validity of VR Technology on the Smartphone for the Study of Wind Park Soundscapes. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2018; 7(4):152. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi7040152
Chicago/Turabian StyleYU, Tianhong, Holger Behm, Ralf Bill, and Jian Kang. 2018. "Validity of VR Technology on the Smartphone for the Study of Wind Park Soundscapes" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 7, no. 4: 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi7040152
APA StyleYU, T., Behm, H., Bill, R., & Kang, J. (2018). Validity of VR Technology on the Smartphone for the Study of Wind Park Soundscapes. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 7(4), 152. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi7040152






