Abstract
Calculation of the shortest path between two nodes in a graph is a popular operation used in graph queries in applications such as map information systems, social networking services, and biotechnology. Recent shortest-path search techniques based on graphs stored in relational databases are able to calculate the shortest path efficiently, even in large data using frontier-expand-merge operations. However, previous approaches used a sequential bidirectional search method that causes a bottleneck, thus degrading performance. The repeated use of an aggregate SQL function also degrades performance. This paper proposes a parallel bi-directional search method using multithreading. In addition, an efficient optimization method is proposed that uses B-tree indexing instead of an aggregate SQL function. Various experiments using synthetic and real data reveal that the proposed optimization technique performs more efficiently than conventional methods. As the size of data in practical applications continues to grow, these optimizations will enable the shortest path in a graph to be found quickly and accurately.
1. Introduction
Graph models are used in various fields for data that can be expressed using edges, which represent relationships between nodes (which indicate a single point). For instance, graph models can be used in map information systems, web page links, social networking services, and protein networks [1]. With the advancements in technology in fields that use graphs, the typical size of graph data is increasing. However, graph databases and the accompanying in-memory solution are unsuitable for large graphs in map information systems. They require ample memory to retain all nodes and edges in the graph. Moreover, conventional graph analysis requires transferring data out of the database into places where an analytic service (shortest-path search) is performed. For these cases, the user must know the database and the analytic framework. Therefore, recent studies have focused on performing various graph algorithms using SQL on graph data that has been stored and processed using a relational database management system (RDBMS). The advantages of an RDBMS lie in its scalability, stability, and ease of programming for graph management [2].
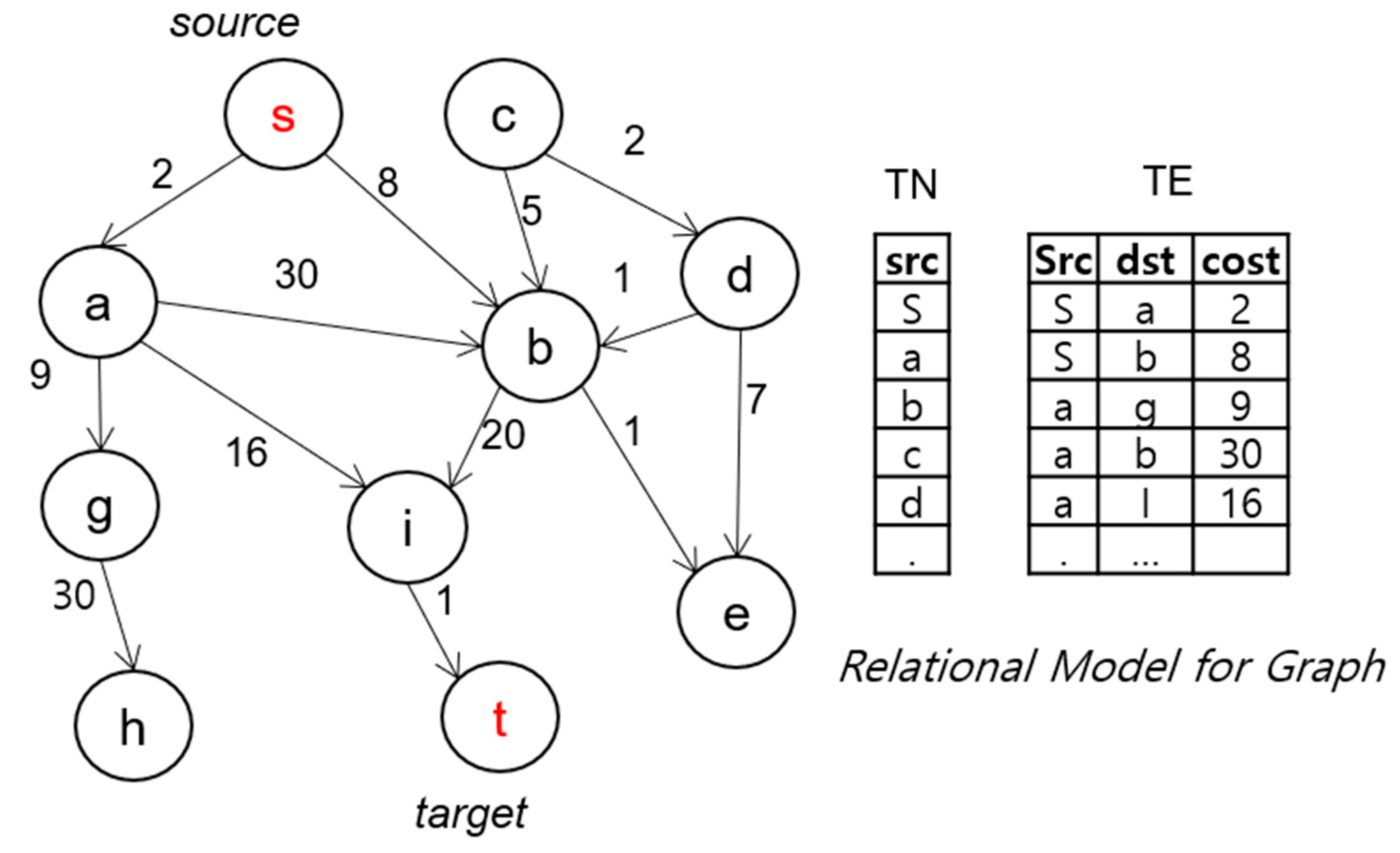
Relational database-based studies on search algorithms to find the shortest path between two nodes, which is a typical graph search query, are also actively underway [2,3]. The frontier–expand–merge (FEM) approach stores graph data in relational database tables, as illustrated in Figure 1. The nodes and edges of a graph are stored in the TN and TE tables, respectively. The Dijkstra algorithm is implemented through FEM consisting of SQL statements for the three operations (frontier, expand, and merge). Performance is further improved using a bi-directional search [4]. This simultaneously calculates the shortest path from the starting node and target node. However, a bi-directional search using FEM uses a sequential method, which causes a processing bottleneck. Furthermore, the performance is degraded because an aggregate function with a large overhead is repeatedly used whenever the FEM is calculated.
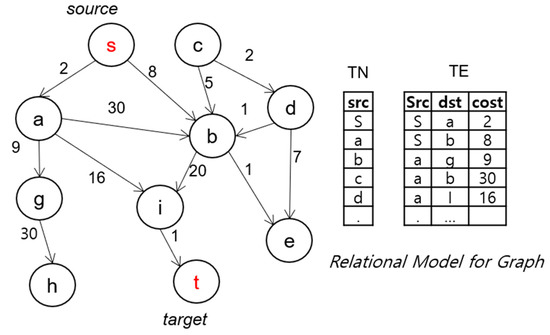
Figure 1.
Example of graph data and their storage in a relational database.
The contributions of this paper are as follows. First, this paper proposes an optimization method that efficiently calculates the shortest path for graph data using an RDBMS. The proposed method calculates the shortest path in parallel using multithreading in the bi-directional search of conventional relational-database FEM methods. Second, this paper proposes a method to effectively use B-tree indexing instead of an aggregate function that requires repeated calculations to find the minimum value. The performance of the proposed method is compared to previously proposed techniques. These results demonstrate that an appropriate proper optimization technique can greatly improve the performance of the shortest-path calculation.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows: Section 2 discusses the related work. This section discusses issues regarding calculations of the shortest path. This includes a RDBMS and other platforms for graph processing. Section 3 defines the data model and explains other background concepts and then introduces the basic FEM method. In addition, optimization techniques are proposed which are applied to the existing approaches. In Section 4, the datasets are explained and thoroughly analyzed. Section 5 summarizes and discusses the results of the experiments. Finally, the conclusions are presented in Section 6.
2. Related Work
Many studies on the application of graph-related algorithms using relational databases have been performed. Relational databases have been developed for over 40 years. The technology has developed enough to handle graph data for data storage, buffering, indexing, and optimization [2,3]. Of these studies, recent research on the shortest-path problem has made much progress. The shortest-path search algorithms in a graph are mainly divided into single-source shortest-path algorithms, which find the shortest path from one starting node to another node, and all-pairs shortest-path algorithms, which find the shortest path between all nodes. Gao et al. [2] is a typical relational database-based single-source shortest-path search method. In addition, De Leo and Boncz [5] developed SQL-based code that supports the shortest path in MonetDB, an open-source relational database, and Greco et al. [6] proposed a method for the all-pairs shortest-path problem for variable graph data using a relational database.
In contrast, research on dedicated databases that handle only graph data is actively underway [7,8]. Graph databases are advantageous insofar as they offer better performance for the structural queries and the full-text character searches [9]. However, because indexing in a graph database is based on strings, its performance for numeric queries is less than that of a relational database. Moreover, these mechanisms require ample memory to retain a large graph. For example, Neo4J—a graph database platform—suffers from performance and scalability issues with large graphs [1].
Recently, studies on handling graph-related data using distributed platforms such as Hadoop [10] and SPARK [11] have also been conducted. Aridhi et al. [12] proposed a shortest-path search method using the MapReduce platform [13]. By partitioning the original graph into several subgraphs, this method calculates the shortest path in the original graph after calculating (in parallel) the shortest path in each partition. A method to calculate the shortest path efficiently using SPARK, a parallel platform based on distributed memory, was proposed in [14]. Fan et al. [15] proposed various parallelizing sequential graph computations, including the graph shortest path, which can be migrated to an existing graph system such as a MapReduce-based implementation. Generally, MapReduce-based approaches achieve high scalability in large graphs, but they have weak support for online queries and dynamic graph updates are computationally expensive. This paper focuses on the parallelizing operation in RDB-based graphs.
Instead of searching for paths with the exact distances specified in graphs, there have been studies on calculating the shortest paths using heuristic methods. The A* algorithm is a typical method. It not only considers the distance from a starting node to an intermediate node but also estimates the heuristic distance from the intermediate node to an arrival node to consider two distances comprehensively [16]. Goldberg et al. [17,18] proposed the ALT algorithm, which applies the triangle inequality theorem to the A* algorithm by defining a node between the starting node and target node as a landmark node. However, the ALT algorithm requires preprocessing that calculates the distances and paths from the landmark node to all other nodes. Thus, if the graph changes over time, the overhead for updating the distance and paths can be expensive.
3. Shortest-Path Search in RDBMS
3.1. Basic Concept
This section describes a graph data model and some basic shortest path methods that are used throughout this paper.
3.1.1. Graph Data Model and Concept Definition
Definition 1.
(Weighted graph) A graph is made up of a set of vertices or nodes and edges and is represented by the ordered pair G = (V, E). A weighted graph is a graph in which an edge generally has a weight given by the weight function w: E → R, which assigns a real number weight to each edge.
Definition 2.
(Graph path) If a weighted graph G = (V, E) and a weight function w: E → R are given, the graph path is P = <v0, v1, …, vk>.
Definition 3.
(Shortest path) If a weighted graph and two vertices (v0, vk) are given, the sum of the path weights between the two vertices W(P) is as follows.
Here, the weight of the shortest path from v0 to vk is as follows.
3.1.2. Basic FEM
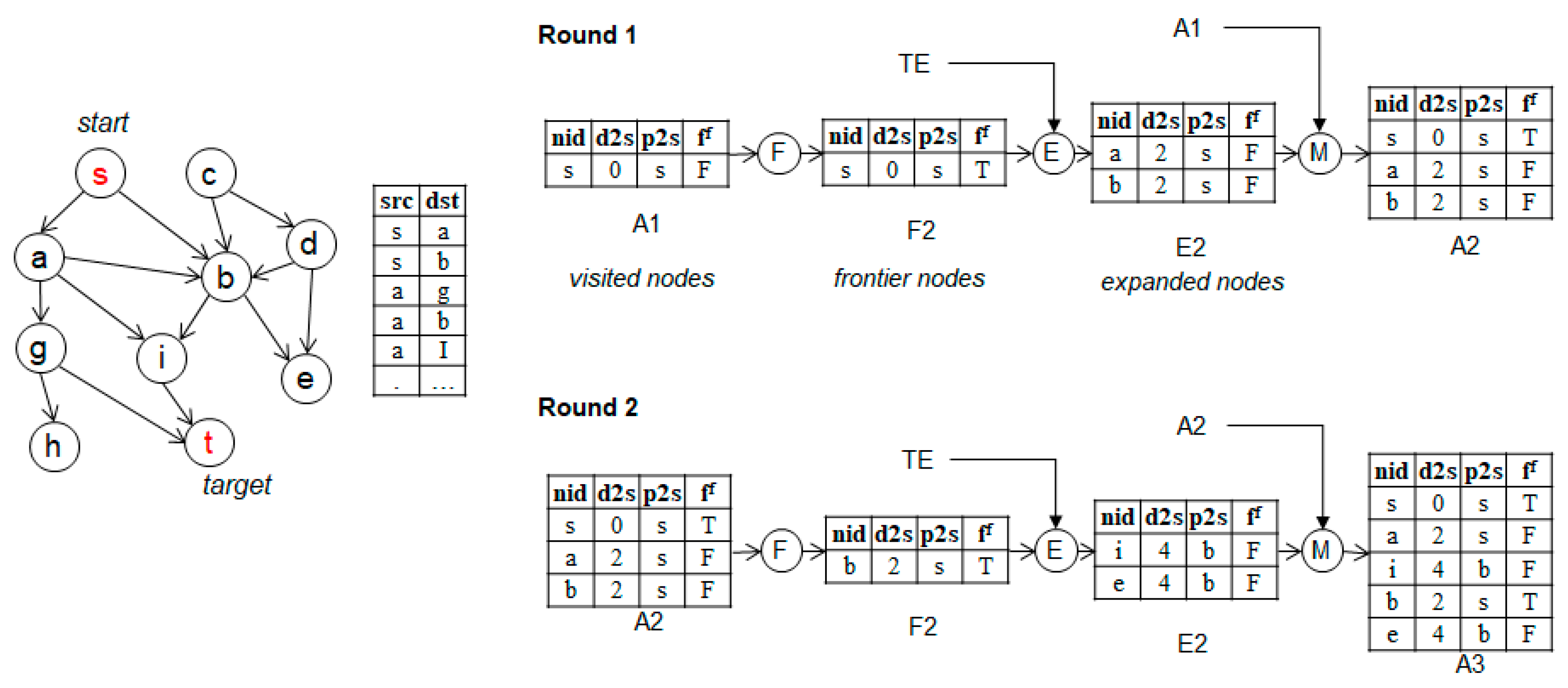
Gao et al. [2] extended the Dijkstra algorithm, a typical shortest path search algorithm, to FEM using an RDBMS [2]. In FEM, all operations are processed as SQL statements and the meaning of each operation (frontier, expand, and merge) is as follows. The frontier operator selects some already-visited nodes to be expanded as frontier nodes. The expand operator expands frontier nodes by searching for the neighboring nodes of the selected frontier nodes. The merge operator incorporates the neighboring nodes of the expanded frontier nodes into the set of already-visited nodes. Figure 1 shows this process, which can be viewed as a single iteration. The iteration is repeated until the target node is found. By repeatedly applying the above FEM process, they were able to implement the Dijkstra algorithm in an RDBMS.
The schema of the table used in FEM consists of nid, d2s, p2s, and ff, as shown in Figure 2. The term nid refers to a node ID, d2s refers to the distance from the starting node to the current node (the sum of the path weights W(p) in Definition 2), p2s refers to the ID of the previous node in the path to the current node, and ff indicates whether the calculated path is the shortest path. For example, in Round 1 of Figure 2, the current node is s and the distance from the starting node to node s is 0. Hence, the value of d2s is 0 and the previous node is also s. Here, once the FEM process has been applied, the node s is confirmed to be on the shortest path and the value of ff becomes true. In the same way, in Round 2, b is selected as the frontier node and the FEM process is repeated.
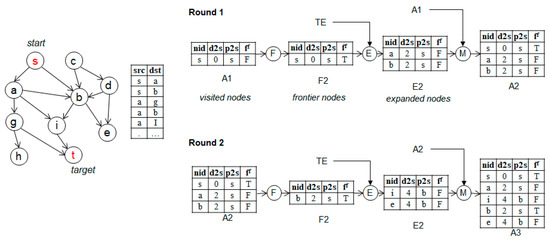
Figure 2.
Example of a frontier–expand–merge (FEM) framework.
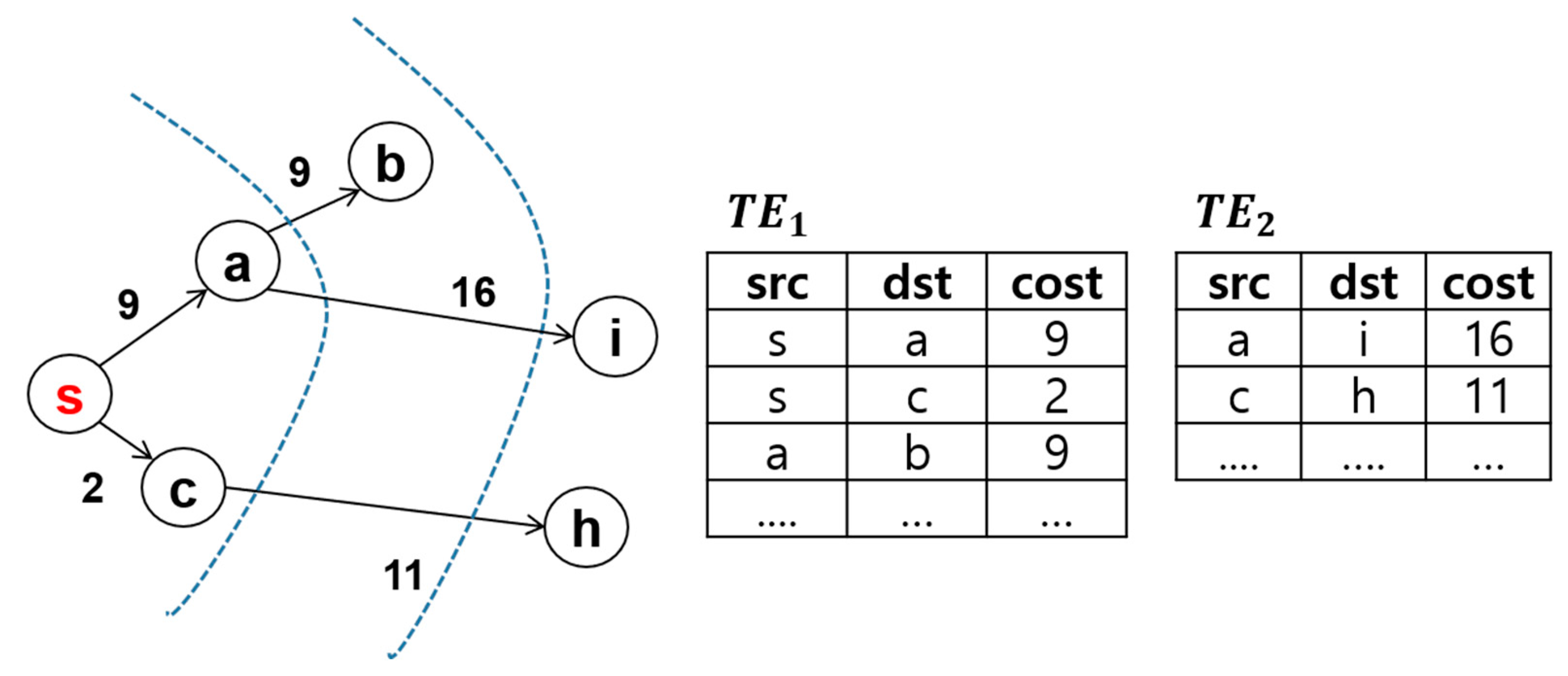
In FEM, a heuristic breadth-first search called BRBFS is additionally applied to improve performance. BRBFS partitions all edges according to a weight criterion, creates as many tables as needed to partition the data, and then conducts a search using the algorithm. Tables are partitioned according to two variables: the weight partition unit and the number of partition tables. Figure 3 illustrates the two tables created based on a weight partition unit of 10. The difference between the basic FEM and BRBFS method is that the FEM method sets node s as the starting point of the search order, expands nodes a and c, and then selects node c because it has the lowest weighted sum. Meanwhile, the search order of the BRBFS method expands nodes a and c and then selects node b. This is because BRBFS refers to the partitioned nodes in ascending order according to weight in the node expansion step. For instance, edge a → b with a weight of 9 (see table TE1) is selected rather than edge c → h with a weight of 11 (in table TE2). This approach has the advantage of reducing the number of adjacent nodes and performs better than the basic FEM [2].
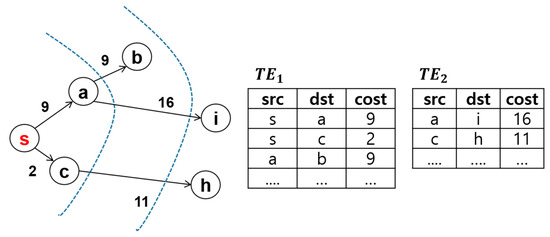
Figure 3.
Example of BRBFS (a heuristic breadth-first search).
3.1.3. Limitations of Basic FEM
FEM methods adopt the bi-directional search used in [4,19] to optimize performance [1]. A bi-directional search in FEM alternates between the starting point and target point and performs forward and backward searches, respectively. After a common node is found, the path is extended to this node.
However, a bottleneck occurs when checking the termination condition because it takes a sequential approach. The sequential method joins data calculated at the time of the search with an aggregate function. The execution time increases linearly as the number of FEM executions increases, which degrades the overall performance. Moreover, the data derived from the FEM bi-directional search are independent, yet idle processing time occurs because of the sequential processing approach.
Another problem is that an aggregate function should be used whenever a frontier node that is connected to the node with the lowest path weight is selected in a FEM operation. An aggregate function is an operation that causes overhead in an RDBMS. The frequent use of such a function can degrade the performance of FEM.
Considering all these limitations, an optimization technique is suggested that efficiently calculates the shortest path while including the advantages of both the conventional FEM and bi-directional search. The proposed technique performs a bi-directional search in parallel using multithreading and can run efficiently by removing the overhead computation that arises from repeatedly using an aggregate function in the indexing.
3.2. Optimization Techniques for Improving the Shortest Path Search
3.2.1. Multithread Bi-Directional Search
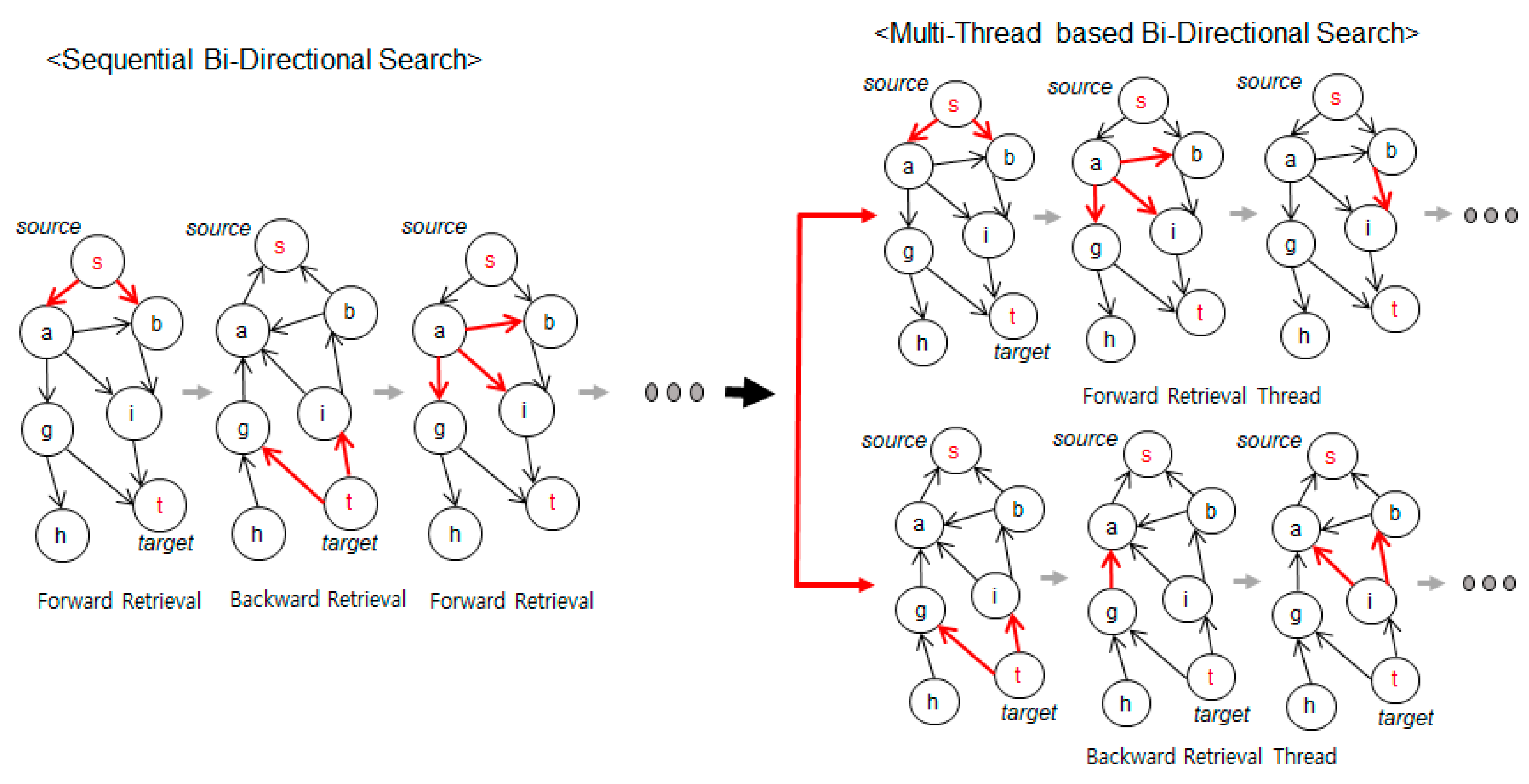
In this paper, the performance of the bi-directional search used in the conventional FEM is improved using a thread-based parallel search. As shown in Figure 4, if a parallel search is possible, the problem of an unbalanced search, in which the forward or reverse search is biased to one side, can be avoided.
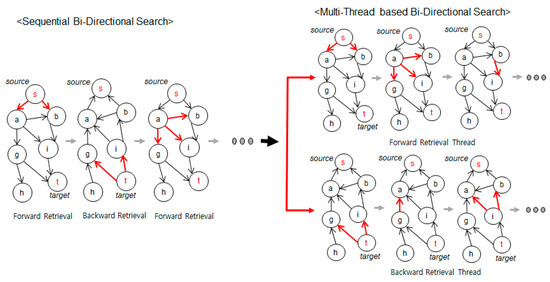
Figure 4.
Sequential and multithread bi-directional search.
A thread is a unit of execution in a program or a process. In general, a program can execute one or more threads [20]. In this paper, threads are used to perform bi-directional searches in parallel. The proposed technique uses a total of three threads: one thread per direction and another thread responsible for synchronization.
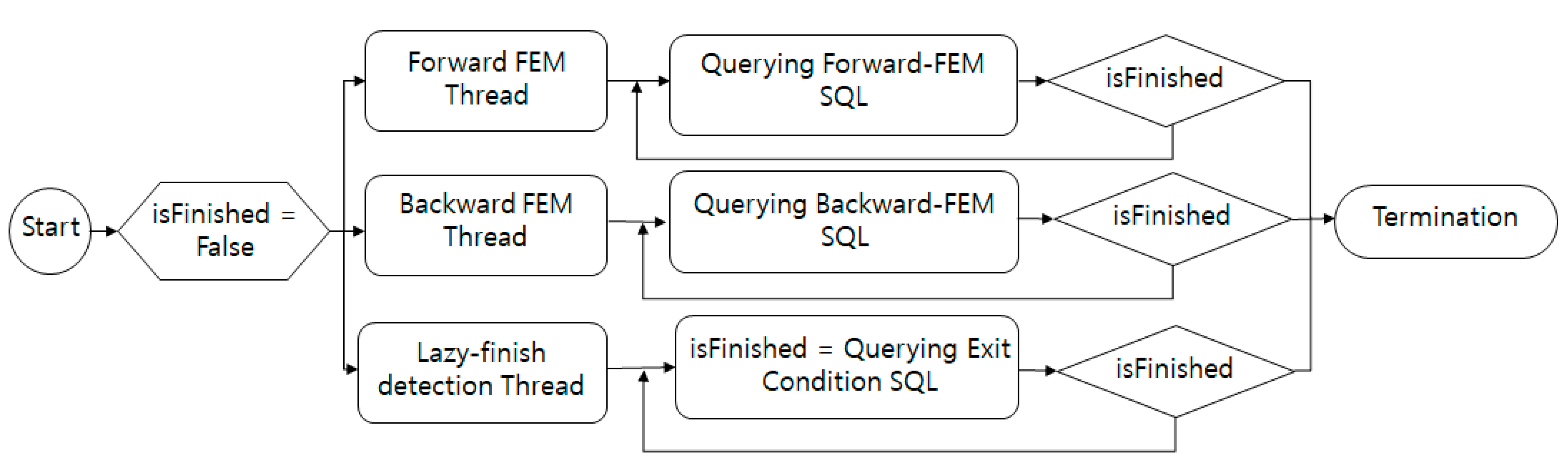
As shown in Figure 5, the three threads play independent roles. The forward and backward FEM threads perform the search in each direction independently through repeated SQL commands. The lazy-finish detection thread that oversees the execution of these two threads controls the isFinished variable.
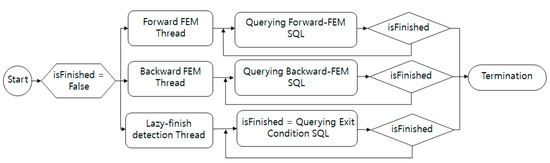
Figure 5.
Bi-directional search based on multithreading.
Algorithm 1 shows the shortest path search through multithreading in FEM. First, the starting and target nodes are initialized through SQL#1 and create threads to search for each direction through the async() function. The created search threads repeatedly select a frontier node for each direction using SQL#2 and add them to the visited-node table by expanding and merging the paths. A thread termination condition is checked repeatedly through SQL#4. When the condition is met, the terminate() function sends a termination signal to the threads and each subpath is merged at the node at which the forward and backward paths meet. The four SQL commands used in the algorithm (SQL command 1, SQL command 2, SQL command 3, and SQL command 4) are described in detail in the Appendix A.
| Algorithm 1. Multithread Bi-directional Shortest Path Search |
| Input: starting node s, target node t, graph G = (V, E) Output: The shortest path between s and t. Initialize using SQL command 1 asyncCall(ForwardFEM) asyncCall(BackwardFEM) while ForwardFEM.dist + BackwardFEM.dist <= minCost do Compute minCost using SQL command 4 terminate(ForwardFEM) terminate(BackwardFEM) Return restore path Procedure ForwardFEM() while true do Find the frontier node in Forward using SQL command 2 if frontier == null then Break Dist = frontier.d2s Expand and Merge paths using SQL command 3 Procedure BackwardFEM() while true do Find the frontier node in Backward using SQL command 2 if frontier == null then Break Dist = frontier.d2s Expand and Merge paths using SQL command 3 Procedure asynchCall(Method) |
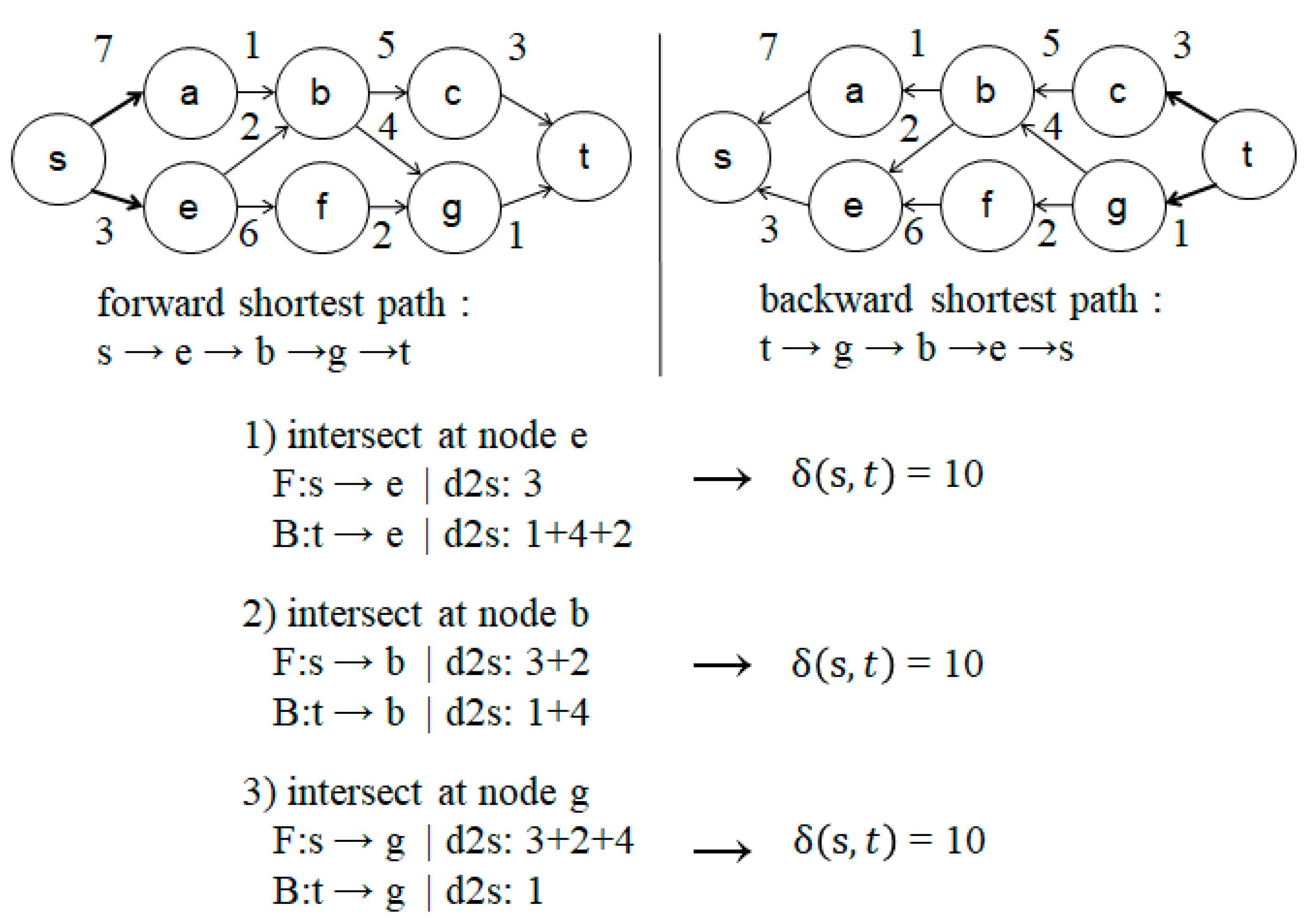
An example is shown in Figure 6 where the proposed method performs the forward search starting from node s and the backward search starting from node t. Once the searches in both directions find the same node, the termination condition is checked. When the paths intersect at node e, the forward search has path s → e and the reverse search has path t → g → b → e. The shortest path, that is, s → e → b → g → t, is determined by adding the result of the forward search to the result of the backward search in reverse order. Here, the weight is 10, which is the result of adding the forward search value (3) and the backward search value (7).
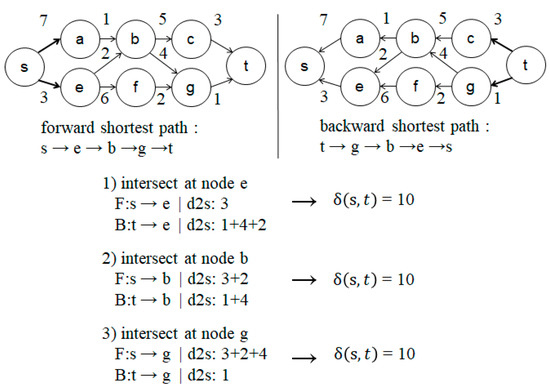
Figure 6.
Example of calculating the shortest path using multithread bi-directional search.
3.2.2. B-Tree Indexing on the Visited-Node Table
Each operation of the FEM algorithm is made up mostly of SQL operations. In addition, the SQL execution time is mostly spent on repeated FEM operations. As the number of SQL queries increases, the overall execution time also increases accordingly. This paper focuses on the SQL query that performs the frontier operation. The SQL operation below executes the frontier operation for finding the frontier node.
| SELECT top 1 nid from TA where ff = 0 and d2s = (SELECT min(d2s) from TA where ff = 0) |
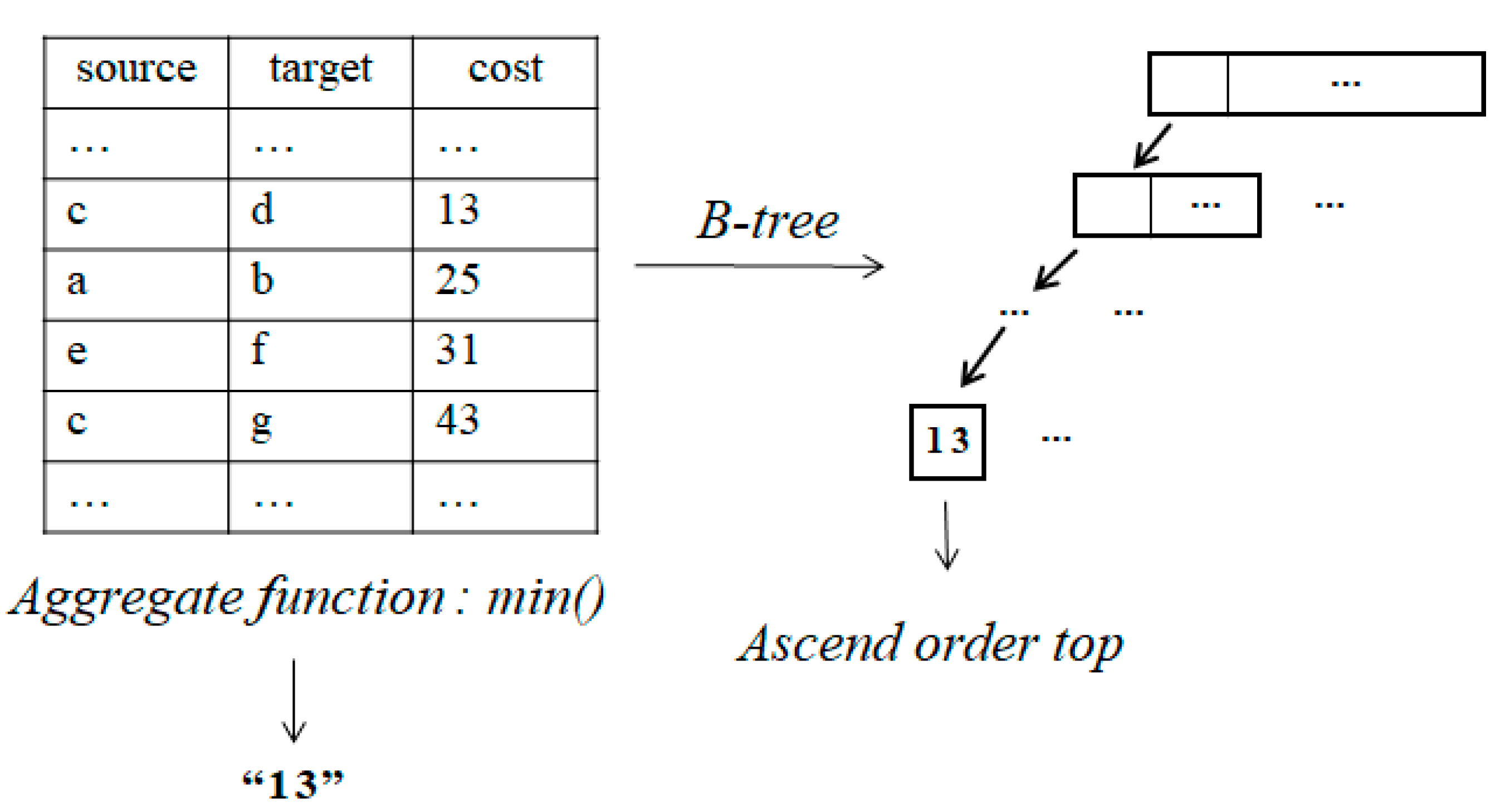
Here, TAn is a table that contains information on the nodes that have been searched (or visited) so far. This table is referred to in the FEM process constantly and is the main cause of disk I/O. In addition, the min() function in the nested query is an aggregate function. This function uses the group-by clause to group rows, calculates the minimum value between the grouped rows, and returns the value. In this paper, a method is proposed that reduces the computation time because it does not use the aggregate function to calculate the smallest d2s value.
Most RDBMSs provide various indexing capabilities for tables. In a DBMS, a specific attribute value can be specified when creating an index. That is, an index for the d2s attribute can be created to find its minimum value. If the B-tree [21] index is created in descending order for the d2s attribute of the TAn table containing the visited nodes, the values are automatically stored in descending order. In other words, the smallest d2s value is placed in the leftmost node of an indexed tree. If they are assorted in ascending order and the top keyword is then returned (selection of the top tuple), the same minimum d2s value can be obtained without using an aggregate function. Figure 7 compares the two processes.
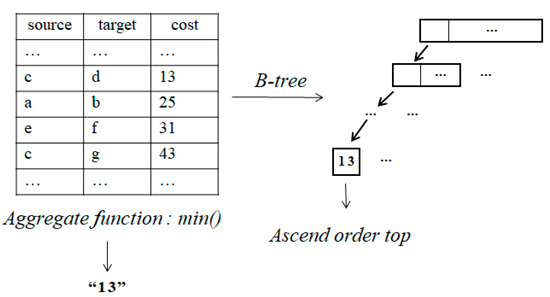
Figure 7.
Aggregate function versus B-tree index.
4. Evaluation Methodology
The proposed method was compared with the other shortest path search techniques described above to evaluate the performance. Specifically, the proposed technique was compared with the bi-directional FEM (BFEM) [2], the heuristic-based FEM (BRBFS) [2], the graph-model database Neo4J [7](graph-algorithm-algo-3.4.0.0), and the SPARK platform(version 2.3.1). The techniques proposed in this paper were divided into bi-directional FEM (Bi-Thread) based on multithreading and the optimization technique adding B-tree (Bi-Thread Indexed) for the analysis.
Experiments were conducted using an Intel (R) Xeon (R) CPU E3-1220 V2 3.10GHz (cores = 4, threads = 4) and Ubuntu 14.04.5 LTS (3.16.0-77-generic Kernel) with 24 GB of RAM memory. The database platform used for the experiments was PostgreSQL version 10 and the database was controlled by a JDBC connection based on JDK 10. For the sake of fairness, the experiments were performed in the same PC environment.
The datasets used in the experiments, detailed in Table 1, consisted of experimental data and real data(9th DIMACS Implementation Challenge-Shortest Paths) [22]. All graph search algorithms were applied to each dataset. A weighted directed graph was randomly generated to create the synthetic datasets 10K-nodes and 50K-nodes. In addition, one edge was represented as a triplet (start node, target node, and weight).

Table 1.
Statistics of the experimental graph datasets.
The names of the real datasets, NY, COL, FLA, and WEST, correspond to graph datasets representing actual road conditions in New York, Colorado, Florida, and the western USA, respectively [22]. In addition, a point that is a weighted graph has the same characteristics as the synthetic dataset graph but is directed. The real dataset is much larger than the virtual dataset and represents one edge as the set (arc, start node, target node, and weight). Table 2 shows a sample from both datasets.

Table 2.
Samples of real and synthetic data used in the experiments.
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Performance Evaluation
In this section, the execution time is defined as the time from when a system receives two nodes (starting node, target node) until the system finishes computing the results. Ten node pairs were randomly selected from the datasets and the experimental results were averaged over five runs.
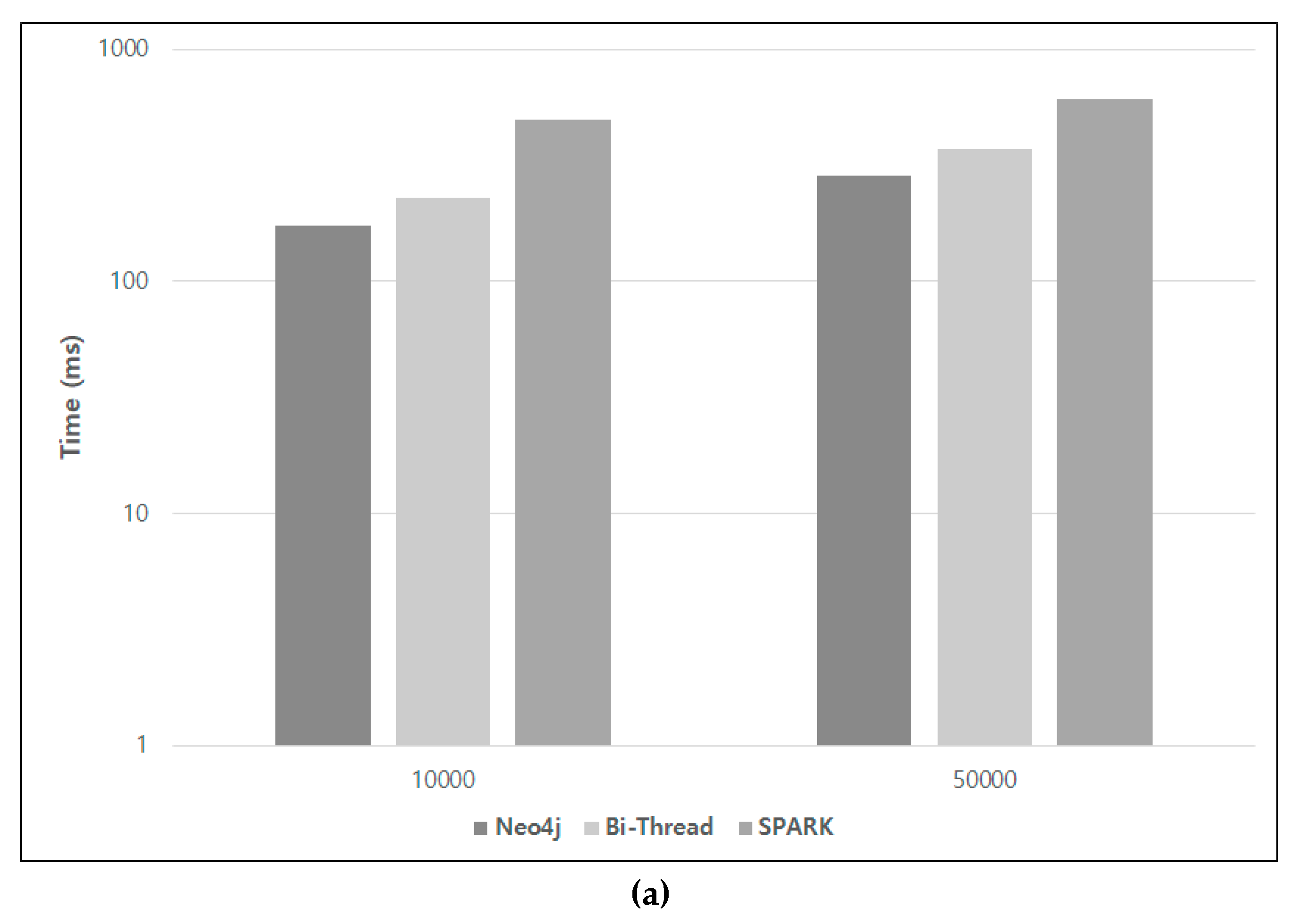
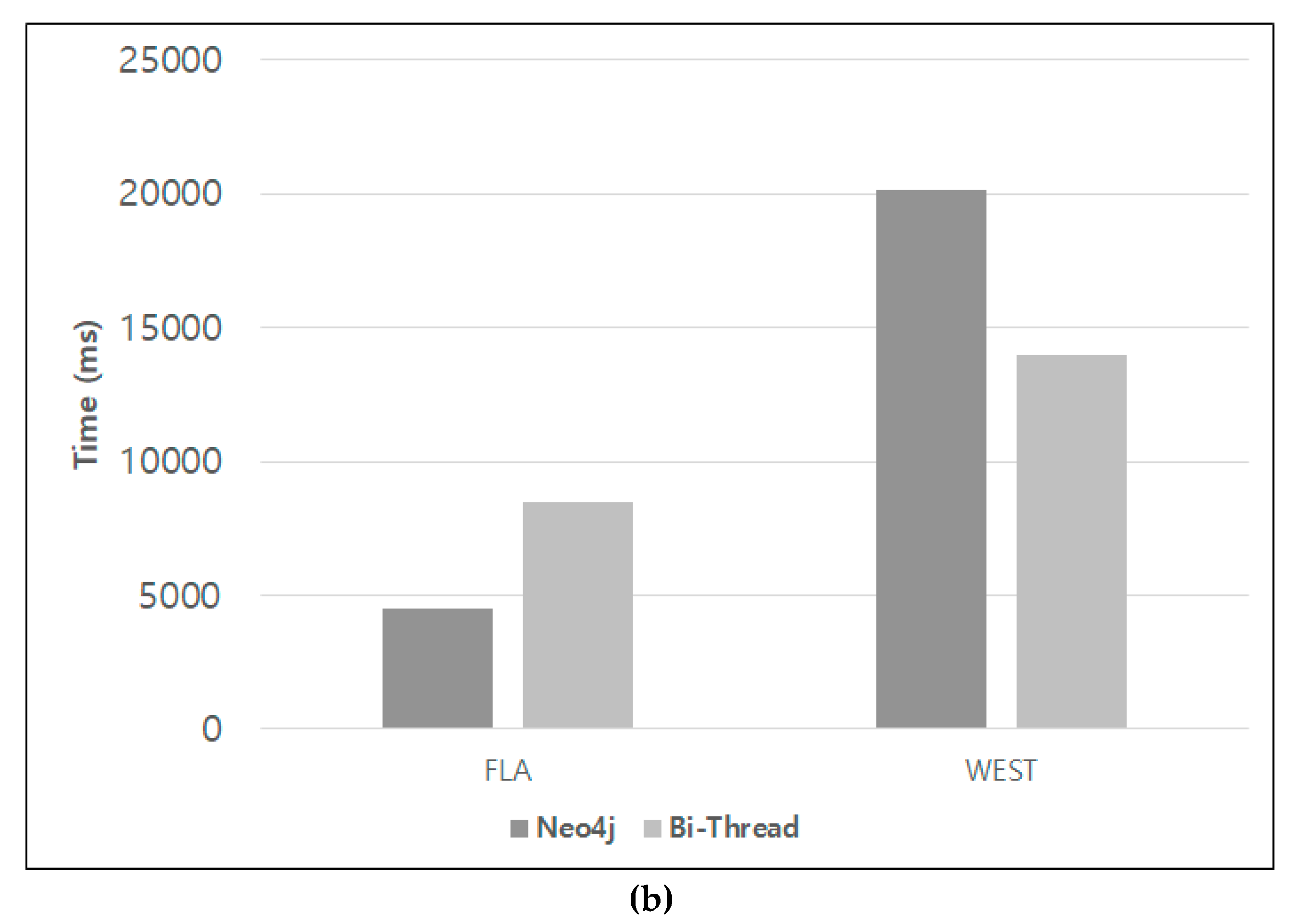
Figure 8 compares the execution time in the log scale of Neo4J, SPARK, and Bi-Thread on the experimental data. To make comparisons fair, the size of memory in Neo4J and SPARK was the same as RDBMS. As shown in Figure 8a, Neo4J yields better performance for small data (10K-nodes). SPARK requires more time to operate. Figure 8b compares the results of the relatively large real data. As seen in Figure 8, Neo4J performs better on the 2M-edge FLA data, but the proposed Bi-Thread performs better for graphs with more than 8M edges. In particular, errors occur often for some paths during the Neo4J execution while SPARK runs out of memory for all real data sets. The queries used in this experiment are described in Table 3. Q1, Q2, Q3, Q4, and Q5 are the queries for a short path using WEST data. For these queries, both approaches can be operated without errors and the Bi-Thread algorithm is faster than the other. However, the Bi-Thread approach is superior in queries Q6, Q7, and Q8. All of these queries require the computation for over 2000 nodes in a path. Additionally, the Neo4J could not be performed with these queries due to limitations with the memory. Although the performance of Neo4J degrades with large data, Neo4J is faster with small data compared to an RDBMS-based method such as Bi-Thread, which must perform a join operation insofar as it stores the relationships among the data along with the data. As a result, memory-based approaches, including Neo4J and SPARK, are not good for scalability and stability.
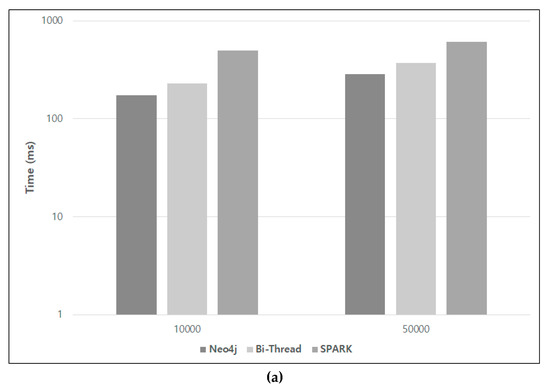
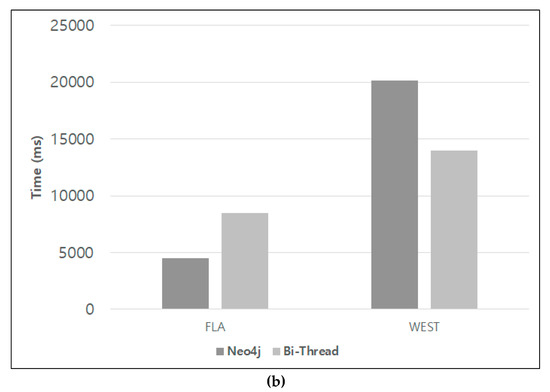
Figure 8.
Performance comparison of Neo4J, BFEM, and Bi-Thread: (a) experiments for synthetic data; (b) experiments for real data.

Table 3.
Performance analysis for sample queries for WEST data.
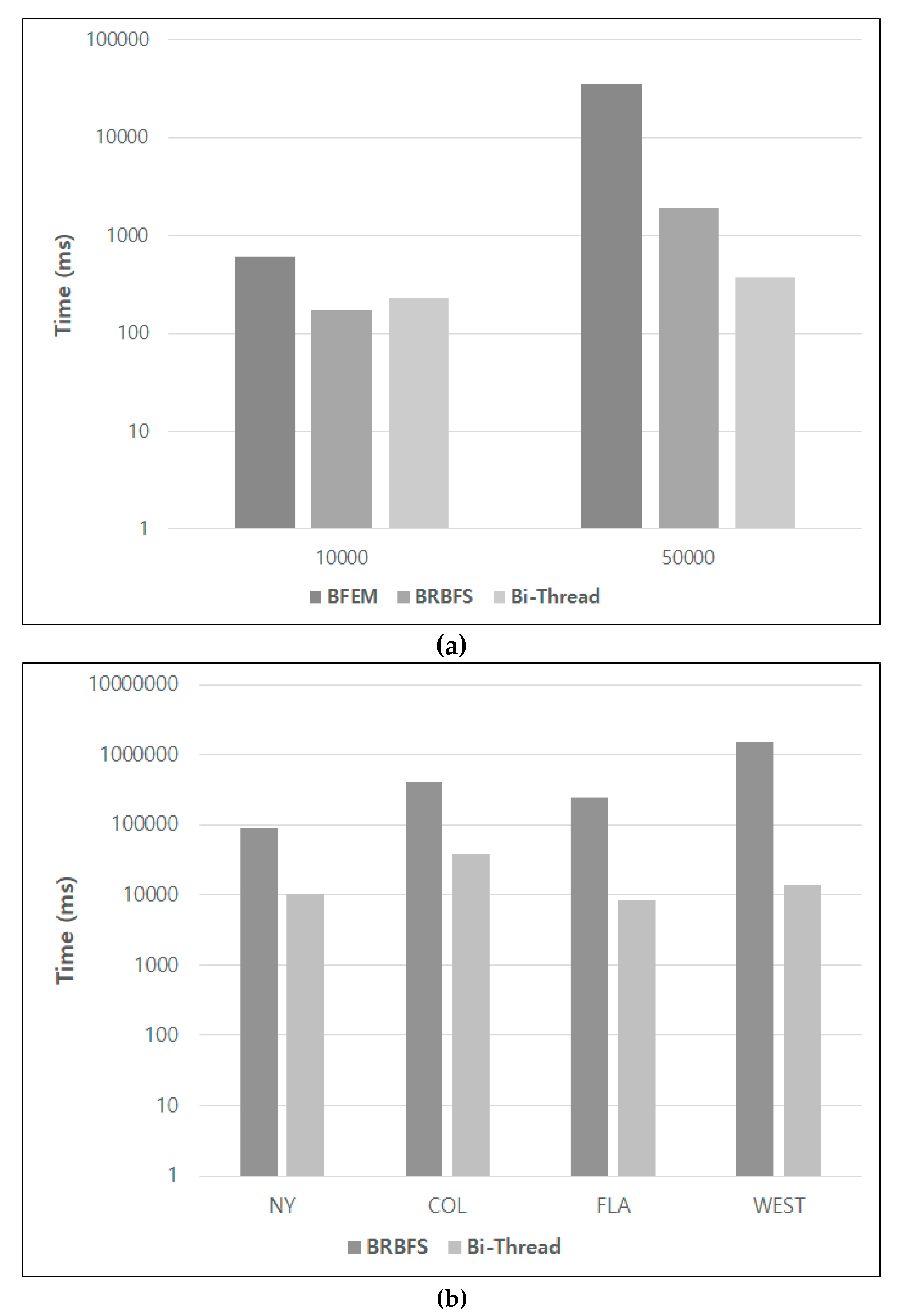
Figure 9 compares the execution time (log-scale) of BFEM, BRBFS, and Bi-Thread by calculating the average execution time of each algorithm for the same path. The difference between the two techniques is not very significant on the small-size synthetic datasets, as shown in Figure 9a, but Bi-Thread performs better on the real data, as shown in Figure 9b. BFEM was excluded from Figure 9b due to its very slow execution speed. Considering that the runtime for the real data is shown in the log scale, the performance difference is quite substantial.
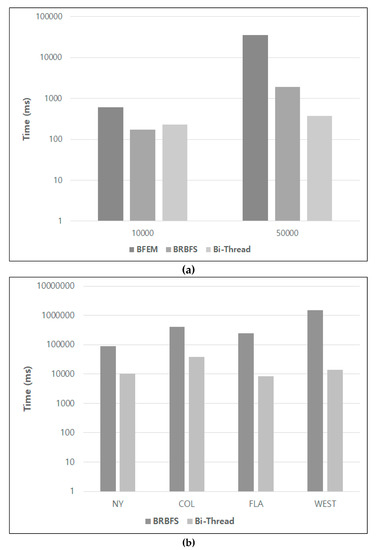
Figure 9.
Performance comparison of BRBFS and Bi-Thread: (a) results for synthetic data; (b) results for real data.
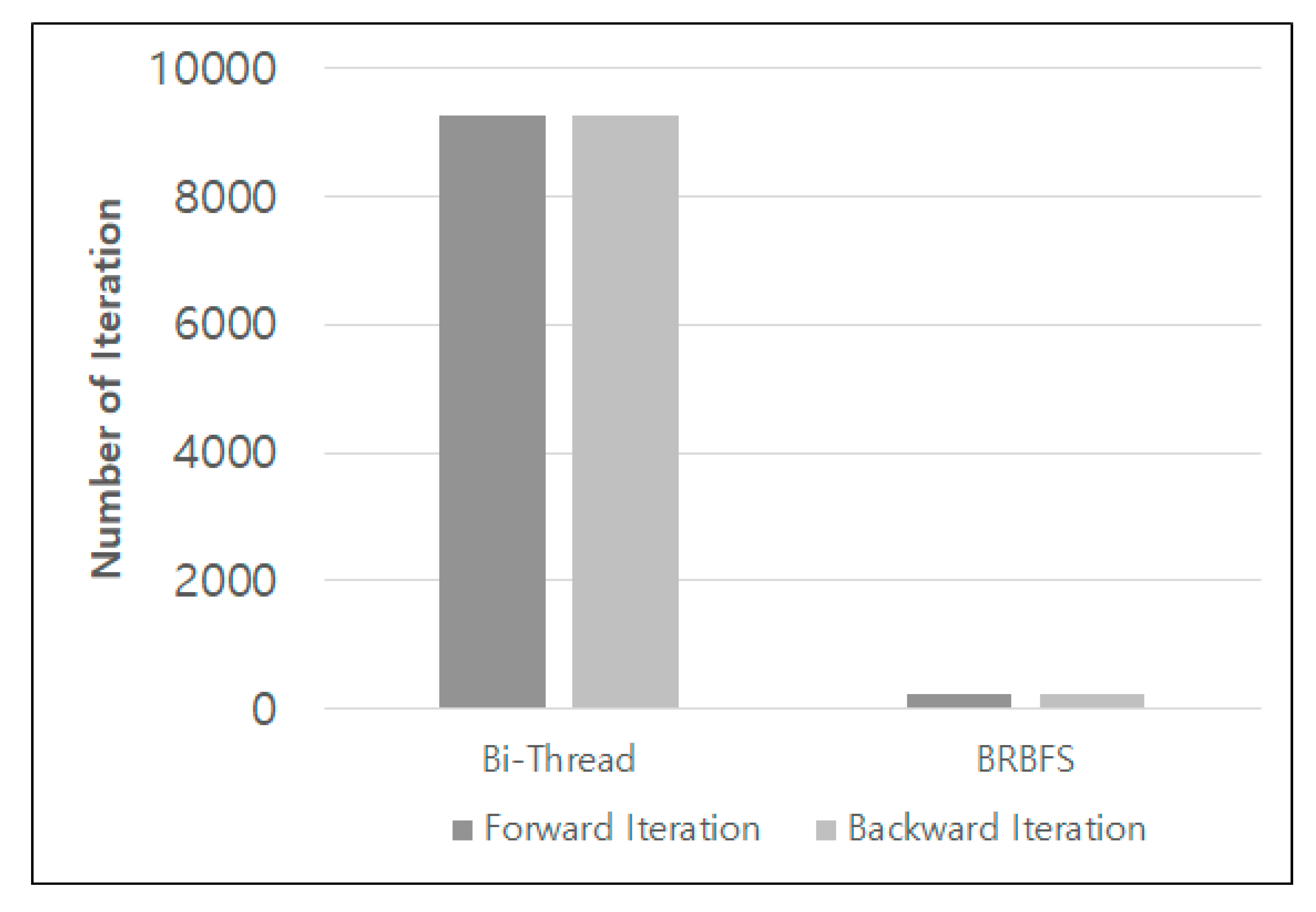
Figure 10 shows the average number of repeated FEM operations during the shortest path search for the WEST data in order to analyze the difference between BRBFS and Bi-Thread. As seen in the figure, the comparison of directions is relatively even for both techniques. Because the proposed method simultaneously performs forward and backward iterations and checks the results of the threads corresponding to the termination condition, the number of iterations increases; thus, increasing the throughput. This reduces the overall execution time.
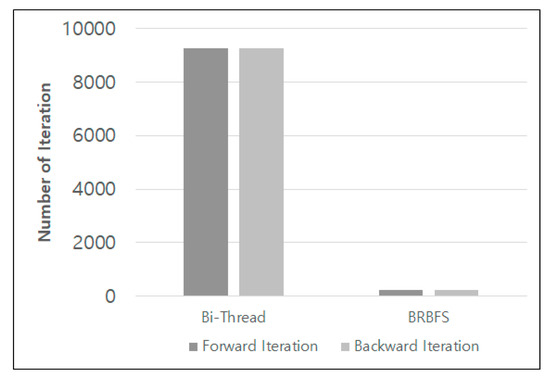
Figure 10.
Average number of repeated FEM operations.
A deep analysis was made on the detailed query plan. The EXPLAIN keyword [23] provided by PostgreSQL can be used to SQL the query analysis. With the ANALYZE option, EXPLAIN SQL query executes the query and then shows the results. The total cost is calculated by the formula below (http://postgresql.org/docs/10/using-explain.html).
Total cost = (Disk pages read * Seq_page_cost) + (Row scanned * CPU_tuple_cost)
The Seq_page_cost is the planner’s estimate of the cost of a disk page fetch that is part of a series of sequential fetches. The PostgreSQL sets the default value as 1.0. The CPU_tuple_cost is the planner’s estimate of the cost of processing each row during a query. This value was set to 0.01 as a default value. The total cost includes disk pages read and rows scanned. Thus, this value can be used as the cost amount of the disk I/O and the approximate CPU. Table 4 shows the total cost of BRBFS and Bi-Thread by calculating the average over three queries for synthetic data (10000, 50000) and real data (WEST). The results indicate that Bi-Thread costs less for the amounts of disk I/O and CPU than BRBFS for 50000 and WEST data. Note that the numbers of Bi-Thread’s FEM iteration are larger than the BRBFS.

Table 4.
Query analysis.
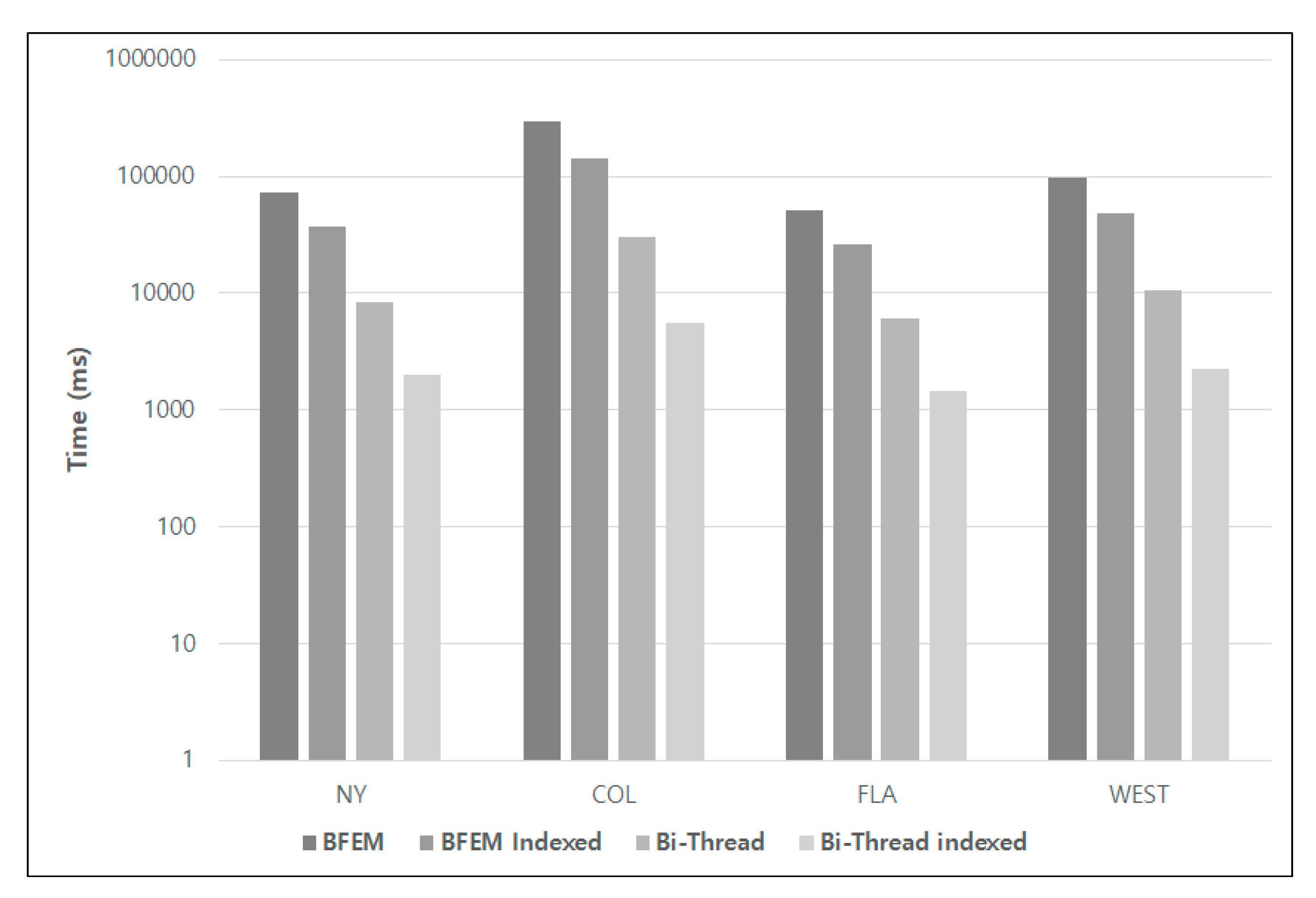
Figure 11 shows the experimental results in a log scale for indexing the visited-node table proposed in this paper. The indexing technique was implemented in both BFEM and Bi-Thread techniques. As shown in Figure 11, the methods that use indexing can effectively handle the shortest path search. The other techniques use the aggregate function min() for each iteration to determine the output of the frontier operator, that is, the frontier node. In contrast, the use of indexing can significantly reduce the execution time of the frontier operator.
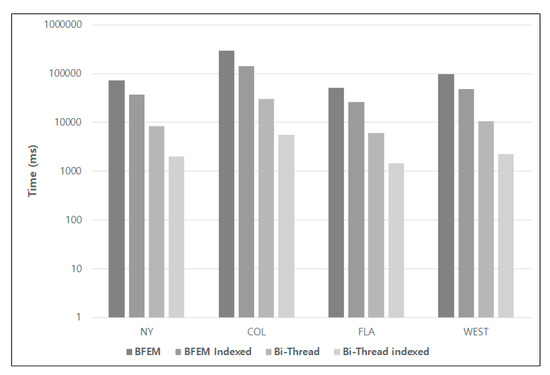
Figure 11.
Performance analysis for B-tree indexing.
5.2. Discussion
From the experimental results, the following conclusions were developed. State-of-the-art shortest path algorithms were performed (namely, BFEM, and BRBFS) in an RDBMS-based graph over two synthetic and four real-world datasets. The results indicate that their sequential bi-directional search and aggregate function degrade the performance of the shortest-path search. This suggests the need for optimization techniques. In all cases, the multi-thread algorithm notably outperformed the BFEM and BRBFS algorithms proposed in [1]. This is because the Bi-Thread processes many more iterations than BRFBS and increases the throughput of the shortest-path search. Further, the use of B-tree indexing instead of the aggregate function min() can improve the performance of all methods for RDBMS-based graphs. In summary, combining the multi-thread and B-tree indexing can improve the performance.
6. Conclusions
Algorithms to find the shortest path in a graph are an area of active research. This paper proposed optimization methods based on RDBMSs for finding a single source shortest path. In the first proposed method, a sequential search method was converted to a parallel search method to avoid the bottleneck caused by search imbalance. In the second method, the performance was improved by replacing an aggregate function that is performed repeatedly whenever a path is searched with B-tree indexing. As a result, this method is able to reduce the size of the data search space considerably. The proposed method performs more quickly than the basic FEM and its extensions (i.e., BFEM, Neo4J, and BRBFS).
In future research, the search space will be reduced using trees and graph reachability [24,25]. When calculating the shortest path, if we know in advance whether a path exists between two points, then the number of candidate nodes used can be reduced for the shortest path search. There is also the need to research the use of several conventional query optimization techniques that quickly calculate the existence of a path between two points in the shortest path search. In addition, the scaling performance with respect to diverse configurations, such as the number of threads, will be examined to validate the proposed approach. Finally, we plan to design and implement an efficient mechanism to address any updated issues that involve insertions and deletions of nodes in a graph.
Author Contributions
Dong-Hyuk Im conceived the problem and supervised the overall research; Jinhyun Ahn clarified some points that helped Dong-Hyuk Im write the algorithm; Kwangwon Seo implemented the algorithm and performed the experiments; Kwangwon Seo, Jinhyun Ahn, and Dong-Hyuk Im wrote the paper.
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Korean government (No. NRF-2017R1C1B1003600), and supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT), Korea, with a program at the Information Technology Research Center (IITP-2019-2018-0-01417) supervised by the Institute for Information & Communications Technology Promotion (IITP). Further, this work was supported by an IITP grant funded by the Korean government (MSIP) (No. R0113-15-0005, Development of a Unified Data Engineering Technology for Largescale Transaction Processing and Real-Time Complex Analytics) and by the Basic Science Research Program through NRF funded by the Ministry of Education (No. NRF-2018R1D1A1B07048380).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A
The SQL statements used in Algorithm 1 in Section 4 are as follows.
| // SQL command 1 insert into ta(nid,d2s,p2s,fwd,f) values (s,0,s,1,false) insert into ta2(nid,d2s,p2s,fwd,f) values (t,0,t,1,false) // SQL command 2 nid,d2s := select nid,d2s from ta WHERE ta.d2s=(select min(d2s) from ta where f=false) and f=false update ta set f = true where ta.nid = nid // SQL command 3 INSERT INTO ta(nid, d2s, p2s, fwd, f) (SELECT tid as nid, cost+? as d2s, ? as p2s, ? as fwd, false as f FROM TE WHERE fid=?) ON CONFLICT(nid) DO UPDATE SET d2s=excluded.d2s, p2s=excluded.p2s, fwd=excluded.fwd,f=excluded.f WHERE ta.d2s>excluded.d2s // SQL command 4 select min(TF.d2s+TB.d2s) from ta as TF, ta2 as TB where TF.nid = TB.nid |
References
- Dijkstra, E.W. A note on two problems in connection with graphs. Numer. Math. 1959, 1, 269–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Zhou, J.; Yu, J.X.; Wang, T. Shortest path computing in relational DBMSs. IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng. 2013, 26, 997–1011. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, J.; Park, K.; Han, Y.; Rasel, M.K.; Vonvou, D.; Lee, Y.K. Disk-based shortest path discovery using distance index over large dynamics graphs. Inf. Sci. 2017, 382, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, D.; Willhalm, T. Speed-up techniques for shortest-path computations. In Annual Symposium on Theoretical Aspects of Computer Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- De Leo, D.; Boncz, P. Extending SQL for computing shortest paths. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Workshop on Graph Data-management Experiences and Systems, Chicago, IL, USA, 14–19 May 2017; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Greco, S.; Molinaro, C.; Pulice, C.; Quintana, X. All-pairs shortest distances maintenance in relational DBMSs. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining (ASONAM), San Francisco, CA, USA, 18–21 August 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 215–222. [Google Scholar]
- Neo4J. Available online: http://neo4j.org/ (accessed on 28 August 2019).
- Miller, J.J. Graph database applications and concepts with Neo4J. In Proceedings of the Southern Associations for Information Systems Conference, Atlanta, GA, USA, 23–24 March 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Vicknair, C.; Macias, M.; Zhao, Z.; Nan, X.; Chen, Y.; Wilkins, D. A comparison of a graph database and a relational database: A data provenance perspective. In Proceedings of the 48th Annual Southeast Regional Conference, Oxford, MS, USA, 15–17 April 2010; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Apache Hadoop. Available online: http://hadoop.apache.org (accessed on 28 August 2019).
- Apache SPARK. Available online: http://spark.apache.org (accessed on 28 August 2019).
- Aridhi, S.; Lacomme, P.; Ren, L.; Vincent, B. A MapReduce-based approach for shortest path problem in large-scale networks. Eng. Appl. Artif. Intell. 2015, 41, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, J.; Ghemawat, S. MapReduce: Simplified data processing on large clusters. Commun. ACM 2008, 51, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfat, Y.; Mehmood, R.; Albeshri, A. Parallel shortest path graph computations of United States road network data on Apache Spark. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Smart Cities, Infrastructure, Technologies and Applications, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia, 27–29 November 2017; Springer: Chamonix, France, 2017; pp. 323–336. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, W.; Yu, W.; Xu, J.; Zhou, J.; Luo, X.; Yin, Q.; Lu, P.; Cao, Y.; Xu, R. Parallelizing sequential graph computations. ACM Trans. Database Syst. 2018, 43, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, H. Pathfinding—Dijkstra’s and A* algorithm’s. Int. J. IT Eng. 2013, 1–15. Available online: http://cs.indstate.edu/hgopireddy/algor.pdf (accessed on 27 August 2019).
- Goldberg, A.V.; Harrelson, C. Computing the shortest path: A search meets graph theory. In Proceedings of the 16th Annual ACM-SIAM Symposium on Discrete Algorithms, Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 23–25 January 2005; pp. 156–165. [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg, A.V.; Werneck, R.F.F. Computing point-to-point shortest path from external memory. In Proceedings of the ALENEX/ANALCO, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 22 January 2005; pp. 26–40. [Google Scholar]
- Vaira, G.; Kurasova, O. Parallel bidirectional Dijkstra’s shortest path algorithm. In Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence and Applications; IOS Press: Amsterdam, The Nederlands, 2011; pp. 422–435. [Google Scholar]
- Powel, M.L.; Kleiman, S.R.; Barton, S.; Shan, D.; Stein, D.; Weeks, M. SunOS multi-thread architecture. In The SPARC Technical Papers; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 339–372. [Google Scholar]
- Comer, D. Ubiquitous B-tree. ACM Comput. Surv. 1979, 11, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demetrescu, C.; Goldberg, A.V.; Johnson, D.S. Ninth DIMACS Implementation Challenge-Shortest Paths. Available online: http://www.dis.uniromal.it/~challenge9 (accessed on 30 January 2018).
- Available online: http://www.postgresql.org/docs/10/sql-explain.html (accessed on 9 October 2019).
- Ahn, J.; Lee, T.; Im, D.-H. Efficiently Answering Reachability Queries for Tree-Structured Data in Repetitive Prime Number Labeling Schemes. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J. Optimization Techniques for 2-hop Labeling of Dynamic Directed Acyclic Graphs. In Proceedings of the DC@ISWC, Kobe, Japan, 18 October 2016; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).