Different Sourcing Point of Interest Matching Method Considering Multiple Constraints
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Related Work
2.1. Existing POI Matching Methods Integrating Dpatial and Nonspatial Attributes
2.2. Shortcomings of the Existing Methods
3. POI Matching Method Considering Multiple Constraints
3.1. Multiattribute Constraint Calculation
3.1.1. Name Similarity Calculation
3.1.2. Address Similarity Calculation
3.1.3. Class Similarity Calculation
3.1.4. Spatial Constraint Calculation Considering Spatial Topological Relationships
3.2. Determination of the Constraint Thresholds
3.2.1. Determination of the Name Similarity Threshold
3.2.2. Determination of the Address Similarity Threshold
3.2.3. Determination of the Spatial Distance Threshold
3.3. Multiple Determination Constraints
4. Experiments and Analyses
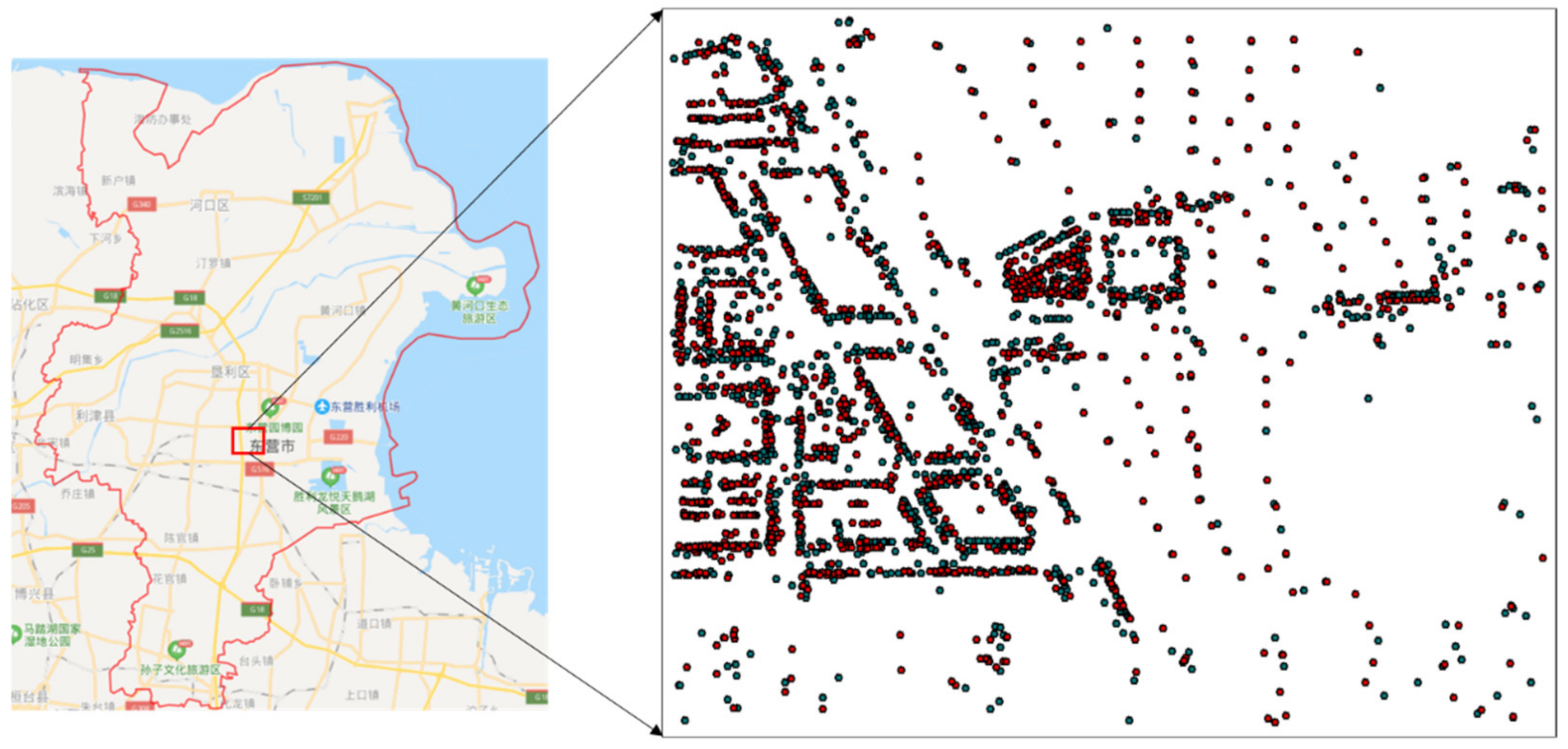
4.1. Experimental Data
4.2. Overall Accuracy Analysis
4.3. Superiority Analysis
4.4. Citywide Validation
5. Conclusions and Discussions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aliannejadi, M.; Crestani, F. Personalized Context-Aware Point of Interest Recommendation. ACM Trans. Inf. 2018, 36, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, Y.; Xiong, H.; Leach, K.; Zhang, Y.; Chow, P.; Fua, K.; Barnes, L.E. Assessing social anxiety using gps trajectories and point-of-interest data. In Proceedings of the 2016 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing, Heidelberg, Germany, 12–16 September 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, S.; Alves, A.; Rodrigues, F.; Ferreira, J., Jr.; Pereira, F.C. Mining point-of-interest data from social networks for urban land use classification and disaggregation. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2015, 53, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Long, Y. Automated identification and characterization of parcels with OpenStreetMap and points of interest. Environ. Plan. B Urban Anal. City Sci. 2015, 43, 341–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Liu, L.; Li, L.; Zhang, X. A point of interest recommendation method using user similarity. Web Intell. 2018, 16, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Vasardani, M.; Winter, S. Similarity matching for integrating spatial information extracted from place descriptions. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2016, 31, 56–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamprianidis, G.; Skoutas, D.; Papatheodorou, G.; Pfoser, D. Extraction, integration and analysis of crowdsourced points of interest from multiple web sources. In Proceedings of the 3rd ACM SIGSPATIAL International Workshop on Crowdsourced and Volunteered Geographic Information, Dallas, TX, USA, 4–7 November 2014; Volume 11, pp. 16–23. [Google Scholar]
- Scheffler, T.; Schirru, R.; Lehmann, P. Matching Points of Interest from Different Social Networking Sites; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2012; pp. 245–248. [Google Scholar]
- Hochmair, H.; Juhász, L.; Cvetojevic, S. Data Quality of Points of Interest in Selected Mapping and Social Media Platforms. In Proceedings of the LBS 2018: 14th International Conference on Location Based Services, Zurich, Switzerland, 15–17 January 2018; pp. 293–313. [Google Scholar]
- Novack, T.; Peters, R.; Zipf, A. Graph-Based Matching of Points-of-Interest from Collaborative Geo-Datasets. ISPRS Int. J. Geo Inf. 2018, 7, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mckenzie, G.; Janowicz, K.; Adams, B. Weighted multi–attribute matching of user–generated points of interest. In Proceedings of the 21st ACM SIGSPATIAL International Conference on Advances in Geographic Information Systems, Orlando, FL, USA, 5–8 November 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, Y.; Luo, S.; Zhang, X.; Bae, H.Y. Organization and Retrieval Method of Multimodal Point of Interest Data Based on Geo-ontology. Adv. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2014, 45, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, F. Geometric-based approach for integrating vgi pois and road networks. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2014, 28, 126–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Gao, X.; Li, R. Multi-Source POI data fusion based on the spatial location information. Period. Ocean Univ. China 2014, 44, 111–116. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M. Multi-source POI Duplication Detection Method in Map World Fujian Based on Word Segmentation. Geospat. Inf. 2018, 16, 51–53. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Zhang, Y. Pattern-mining approach for conflating crowdsourcing road networks with POIs. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2015, 29, 786–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mckenzie, G.; Janowicz, K.; Adams, B. A weighted multi–attribute method for matching user–generated Points of Interest. Cartogr. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2014, 41, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xing, X.; Xia, H.; Huang, X. Entropy-Weighted Instance Matching Between Different Sourcing Points of Interest. Entropy 2016, 18, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, Y.; Luo, A.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y. Point of Interest Matching between Different Geospatial Datasets. ISPRS Int. J. Geo Inf. 2019, 8, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Wang, J.; Cheng, H.M. An approach for spatial index of text information based on cosine similarity. Comput. Sci. 2005, 32, 160–163. [Google Scholar]












| Method | Number of Successful Matches | Number of Incorrect Matches | Number of Missing Matches | Precision | Recall | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| the existing method | 1,245 | 97 | 47 | 96.1% | 92.2% | 0.941 |
| the proposed method | 1,159 | 28 | 41 | 96.4% | 97.5% | 0.969 |
| manual discrimination | 1,162 | 0 | 0 | 100% | 100% | 1 |
| Method | Scenario 1 | Scenario 2 | Scenario 3 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Incorrect Matches | Missing Matches | Incorrect Matches | Missing Matches | Incorrect Matches | Missing Matches | |
| existing method | 63 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 5 |
| proposed method | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, C.; Liu, L.; Dai, Z.; Liu, X. Different Sourcing Point of Interest Matching Method Considering Multiple Constraints. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi9040214
Li C, Liu L, Dai Z, Liu X. Different Sourcing Point of Interest Matching Method Considering Multiple Constraints. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2020; 9(4):214. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi9040214
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Chengming, Li Liu, Zhaoxin Dai, and Xiaoli Liu. 2020. "Different Sourcing Point of Interest Matching Method Considering Multiple Constraints" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 9, no. 4: 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi9040214
APA StyleLi, C., Liu, L., Dai, Z., & Liu, X. (2020). Different Sourcing Point of Interest Matching Method Considering Multiple Constraints. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 9(4), 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi9040214






