Multi-Scale Representation of Ocean Flow Fields Based on Feature Analysis
Abstract
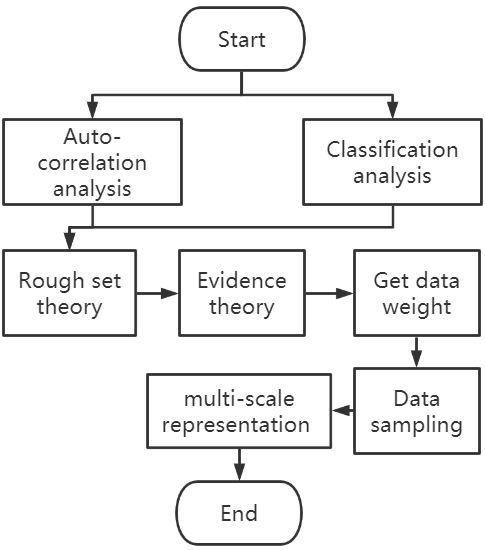
1. Introduction
2. Analysis of Attributes, Feature of Flow Fields, and Weight Allocation
2.1. Autocorrelation Analysis
2.1.1. Autocorrelation Analysis of Speed
2.1.2. Autocorrelation Analysis of Direction
2.2. Analysis of Classification
2.2.1. Classification of Speed
2.2.2. Classification of Variation Rate of Direction
3. Attribute Weight Assignment Based on Rough Set Theory and Evidence Theory
3.1. Support Degree Based on Rough Set Theory
3.2. Attribute Weight Combination Based on Evidence Theory
4. Integrated Mapping of Ocean Flow Fields
4.1. Integrated Mapping of Test Region
4.2. Integrated Mapping of Verification Region
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cai, Z.H. Rarefying and Representation of Flow Fields. Ph.D. Thesis, Capital Normal University, Beijing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Cheng, Y.; Hong, L.; Liu, X. A Novel Algorithm for Ocean Wave Direction Inversion from X-band Radar Images Based on Optical Flow Method. Acta Oceanol. Sin. 2018, 37, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, F.H.; de Leeuw, W.C.; Sadarjoen, I.A.; Reinders, F.; Van Walsum, T. Global, Geometric, and Feature-based Techniques for Vector Field Visualization. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 1999, 15, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Ai, B.; Fang, J.; Xin, W.; Zhao, X.; Lv, G. Multi-Scale Flow Field Mapping Method Based on Real-Time Feature Streamlines. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeuw, W.D.; Liere R, V. Visualization of Global Flow Structures Using Multiple Levels of Topology. In Data Visualization; Springer: Vienna, Austria, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Tricoche, X.; Wischgoll, T.; Scheuermann, G.; Hagen, H. Topology tracking for the visualization of time-dependent two-dimensional flows. Comput. Graph. 2002, 26, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, M.; Peikert, R. Spatial and Temporal Variability of The Iberian Peninsula Coastal Low-level jet. Int. J. Climatol. 2018, 38, 1605–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Machiraju, R.; Thompson, D. A Novel Approach to Vortex Core Region Detection. Data Vis. Eurograph. Assoc. 2002, 17, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricoche, X.; Garth, C.; Scheuermann, G. Fast and Robust Extraction of Separation Line Features. IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed. A Publ. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2006, 14, 1291–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinkauf, T.; Theisel, H.; Hege, H.C.; Seidel, H.P. Boundary Switch Connectors for Topological Visualization of Complex 3D vector Fields. In Proceedings of the Data Visualization, Konstanz, Germany, 19–21 May 2004; pp. 183–192. [Google Scholar]
- Theisel, H.; Weinkauf, T.; Hege, H.C.; Seidel, H.P. Stream Line and Path Line Oriented Topology for 2D Time-Dependent Vector Fields. In Proceedings of the IEEE Visualization, Austin, TX, USA, 10–15 October 2004; pp. 321–328. [Google Scholar]
- Theisel, H.; Weinkauf, T.; Hege, H.C.; Seidel, H.P. Grid-independent detection of closed stream lines in 2D vector fields. In Proceedings of the Vision, Modeling and Visualization, Stanford, CA, USA, 16–18 November 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Guenther, R.; Miklasz, K.; Carrington, E.; Martone, P.T. Macroalgal spore dysfunction: Ocean acidification delays and weakens adhesion. J. Phycol. 2017, 54, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.; Petersen, M.; Bremer, P.T.; Hecht, M.; Pascucci, V.; Ahrens, J.; Hlawitschka, M.; Hamann, B. Adaptive Extraction and Quantification of Geophysical Vortices. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2011, 17, 2088–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehler, C.; Wischgoll, T.; Dong, H.; Gaston, Z. Vortex Visualization in Ultra Low Reynolds Number Insect Flight. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2011, 17, 2071–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadlo, F.; Peikert, R. Efficient Visualization of Lagrangian Coherent Structures by Filtered AMR Ridge Extraction. IEEE Trans. Vis. Comput. Graph. 2007, 13, 1456–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipinski, D.; Mohseni, K. A ridge tracking algorithm and error estimate for efficient computation of Lagrangian coherent structures. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doleisch, H.; Gasser, M.; Hauser, H. Interactive feature specification for focus+context visualization of complex simulation data. VisSym 2003, 3, 239248. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Li, S. Intelligent Flow Feature Extraction and Multi-Resolution Visualization. J. Comput. Aided Des. Comput. Graph. 2008, 20, 571–576. [Google Scholar]
- Enya, S.; Liang, Z.; Huaxun, X.; Sikun, L. Fuzzy-based Interactive Feature Description and Extraction of 3D Flows. J. Image Graph. 2011, 16, 1121–1126. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Yang, S.; Li, H.; Zhang, B.; Lv, J. Research on Geographical Environment Unit Division Based on the Method of Natural Breaks (Jenks). ISPRS Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2013, XL-4/W3, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, L. Research and Implementation of Visualization Method for Marine Environment Early Warning Data; Capital Normal University: Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bin, X. Simulation Analysis of the Influence of Spatial Weight Matrix on Moran’s I; Nanjing Normal University: Nanjing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Basir, O.; Yuan, X. Engine fault diagnosis based on multi-sensor information fusion using Dempster–Shafer evidence theory. Inf. Fusion 2007, 8, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L. Improved Method of Attribute Weight Based on Rough Theory. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2014, 50, 43–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangavel, K.; Pethalakshmi, A. Dimensionality reduction based on rough set theory: A review. Appl. Soft Comput. 2009, 9, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlak, Z. Rough set. Int. J. Comput. Inf. Sci. 1982, 11, 1655–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, B.S.; Cho, S.S.; Kim, C.Y. The integrated methodology of rough set theory and artificial neural network for business failure prediction. Expert Syst. Appl. Expert Syst. Appl. 2000, 18, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suo, Y.Q.; Ma, L.; Tan, W. A Modified Heuristic Algorithm of Attribute Reduction in Rough Set. J. Xi’an Univ. Post Telecommun. 2009, 14, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Cao, L.; Liu, B.; Li, H.; Zhou, Y. The Method of Attribute Weight Distribution in Multi-attribute System. Trans. China Electrotech. Soc. 2015, S1, 422–427. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Qian, Y. Evaluation of Simulation Credibility Based on Rough Set and Gray Correlation Analysis. J. Syst. Simul. 2018, 30, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yao, B.; Hu, H. Weight determination method based on rough set theory. Comput. Eng. Appl. 2003, 39, 20–21. [Google Scholar]
- Ai, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Sun, D. Evaluation of multi-scale representation of ocean flow fields using the Euler method based on map load. J. Spat. Sci. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]















| No. of U | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | D |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | Y1 |
| 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | Y2 |
| 3 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | Y2 |
| 4 | 1 | 2 | 4 | 1 | Y1 |
| 5 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 2 | Y1 |
| 6 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | Y2 |
| ……. | ……. | ……. | |||
| 13698 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 4 | Y1 |
| C | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.38 | 0.06 | 0.26 | 0.01 | |
| 0.49 | 0.58 | 0.59 | 0.52 | |
| 0.52 | 0.08 | 0.36 | 0.03 | |
| 0.33 | 0.19 | 0.31 | 0.15 |
| C | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.34 | 0. 2 | 0.31 | 0.15 |
| C | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.29 | 0.19 | 0.34 | 0.18 |
| C | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.42 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 0.22 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ai, B.; Sun, D.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Yang, F.; Yin, Y.; Tian, H. Multi-Scale Representation of Ocean Flow Fields Based on Feature Analysis. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi9050307
Ai B, Sun D, Liu Y, Li C, Yang F, Yin Y, Tian H. Multi-Scale Representation of Ocean Flow Fields Based on Feature Analysis. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2020; 9(5):307. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi9050307
Chicago/Turabian StyleAi, Bo, Decheng Sun, Yanmei Liu, Chengming Li, Fanlin Yang, Yong Yin, and Huibo Tian. 2020. "Multi-Scale Representation of Ocean Flow Fields Based on Feature Analysis" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 9, no. 5: 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi9050307
APA StyleAi, B., Sun, D., Liu, Y., Li, C., Yang, F., Yin, Y., & Tian, H. (2020). Multi-Scale Representation of Ocean Flow Fields Based on Feature Analysis. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 9(5), 307. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi9050307