Building Virtual 3D City Model for Smart Cities Applications: A Case Study on Campus Area of the University of Novi Sad
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Background and Related Work
2.1. CityGML
2.2. Applicability of 3D City Models
3. Study Area and Methods
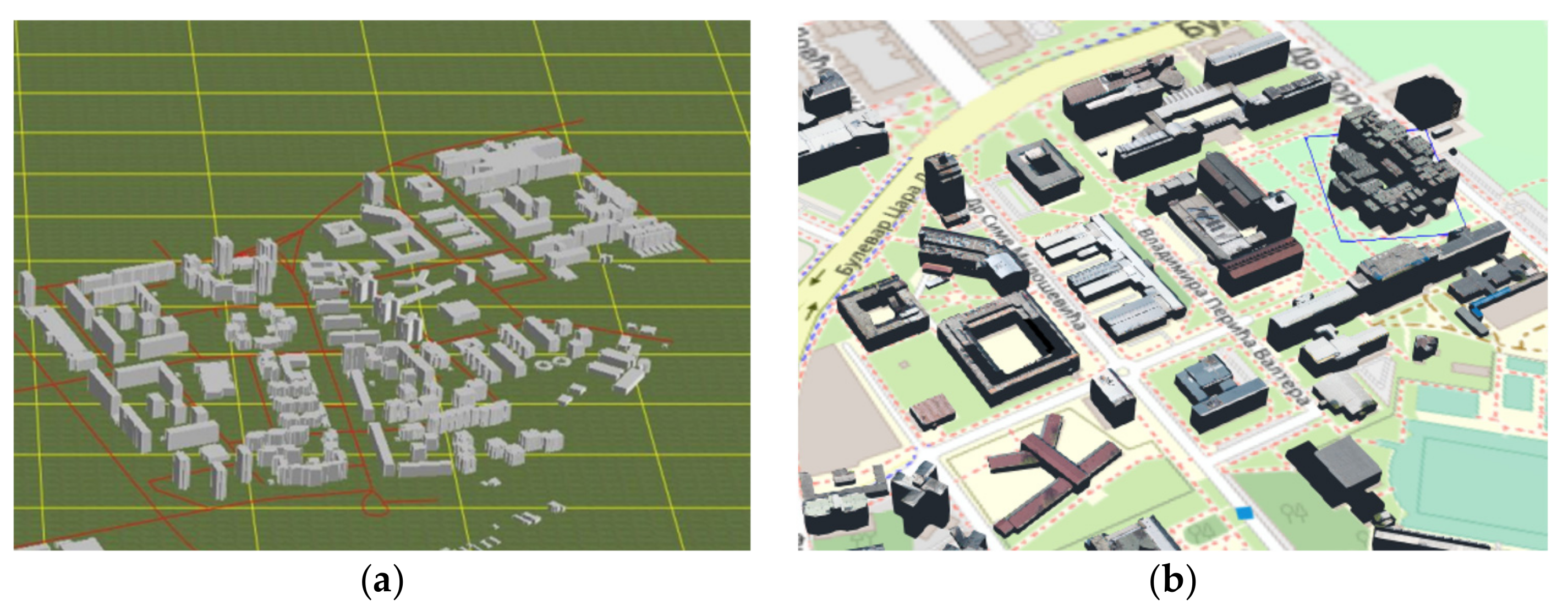
3.1. Study Area
3.2. Acquisition Parameters and Basic Processing
- Download and backup of the raw images
- Camera trajectory output
- Raw data processing
- Frames georeferencing, mosaicking, and orthorectifying.
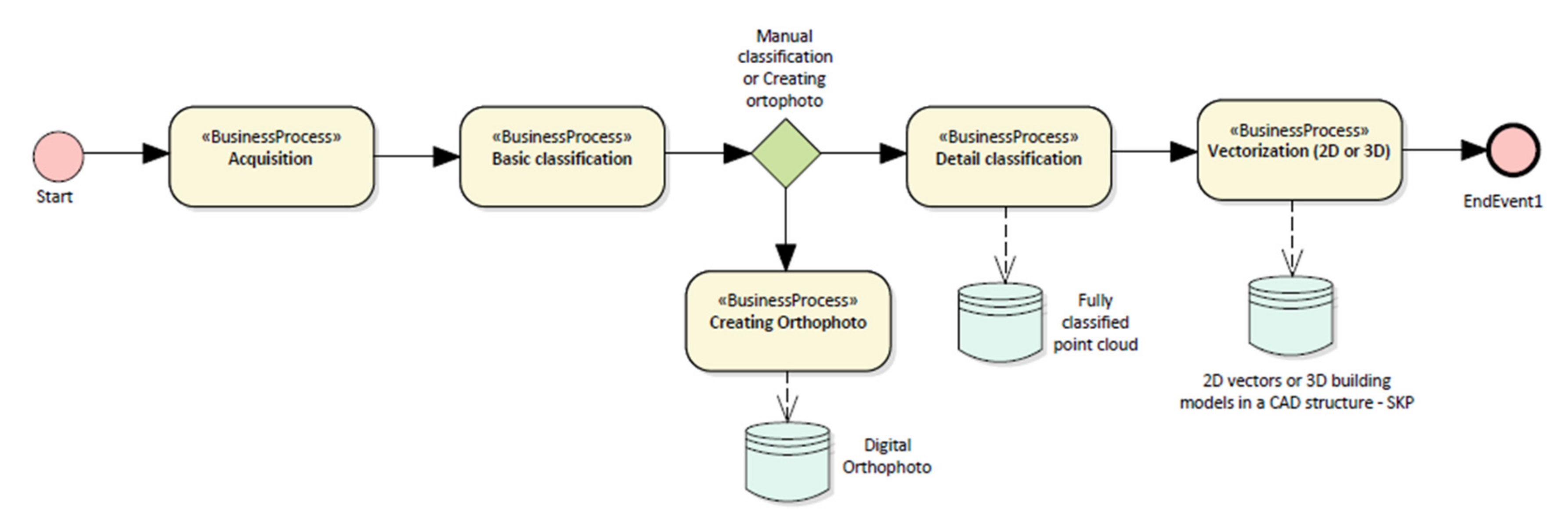
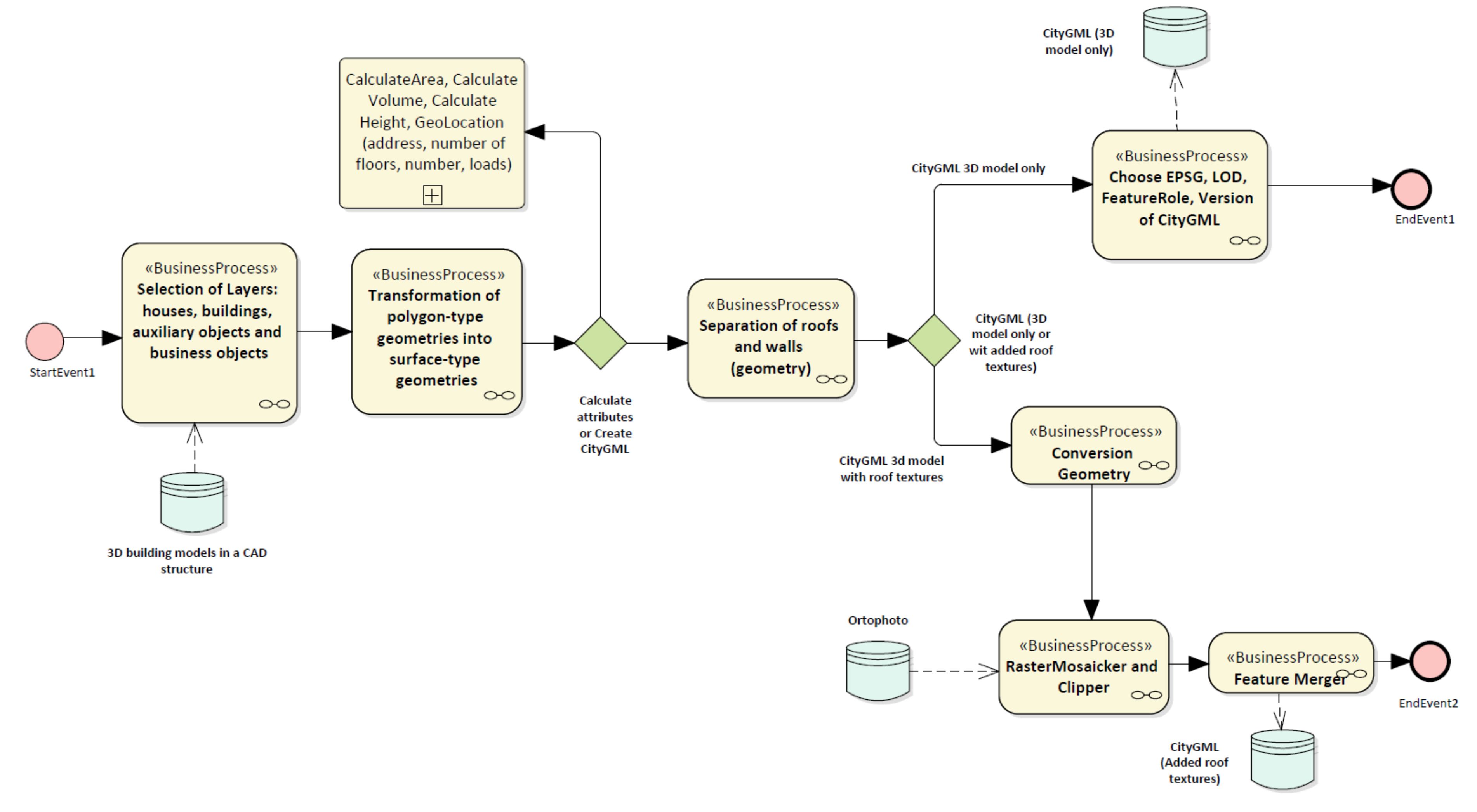
4. Results—Development of Virtual 3D City Model
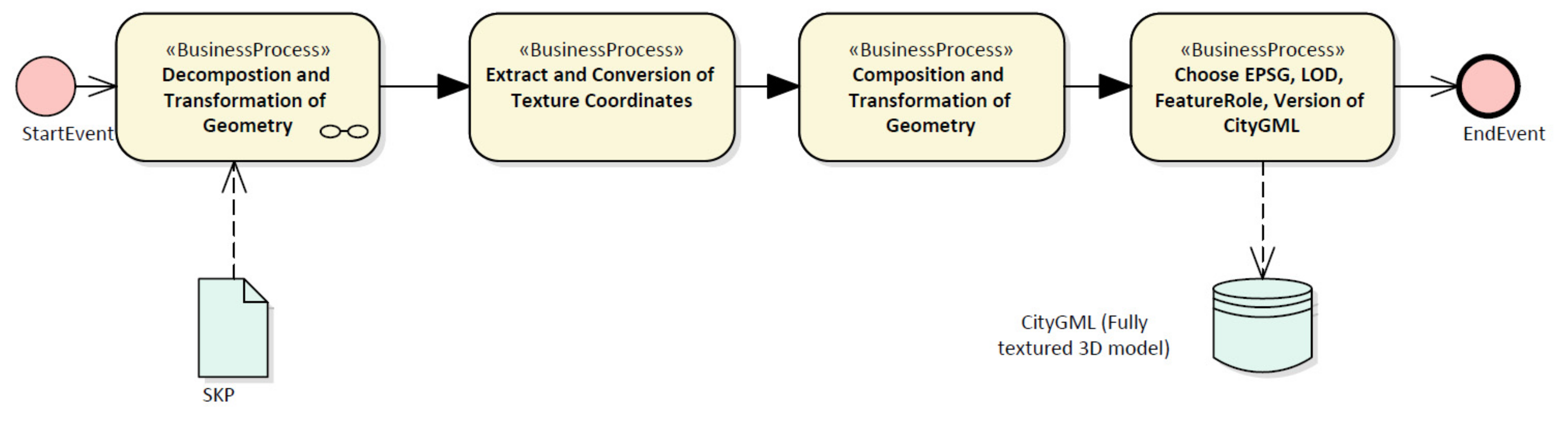
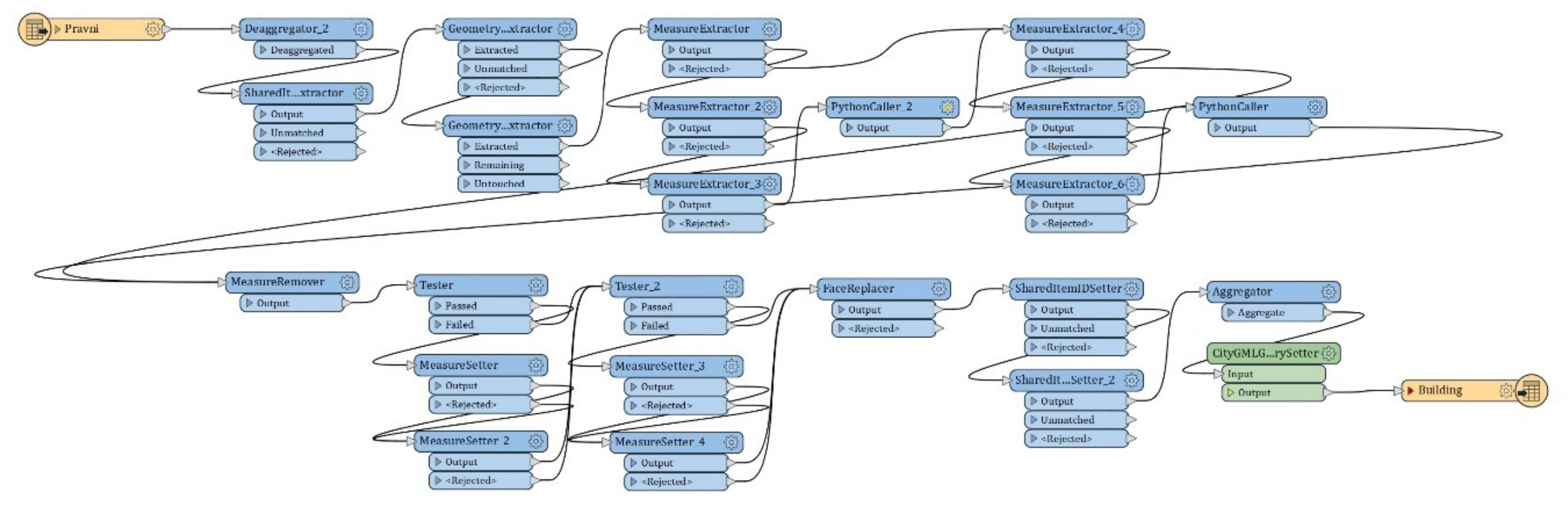
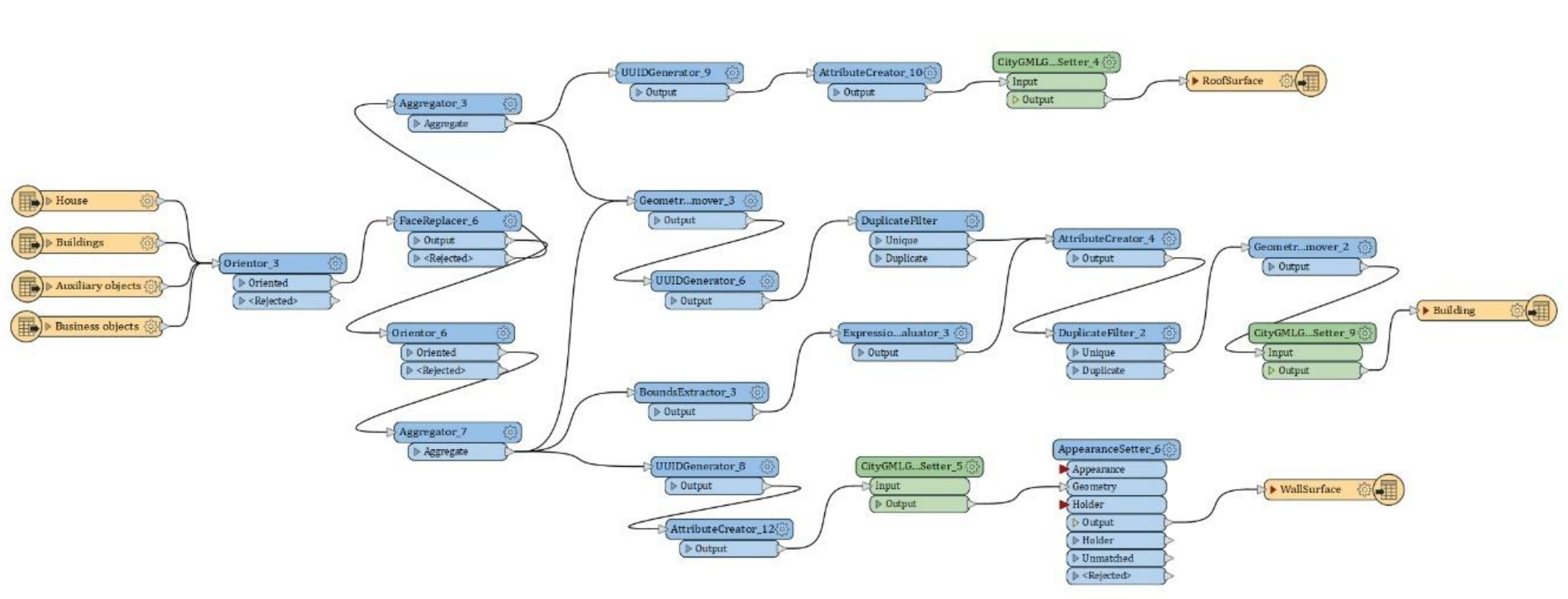
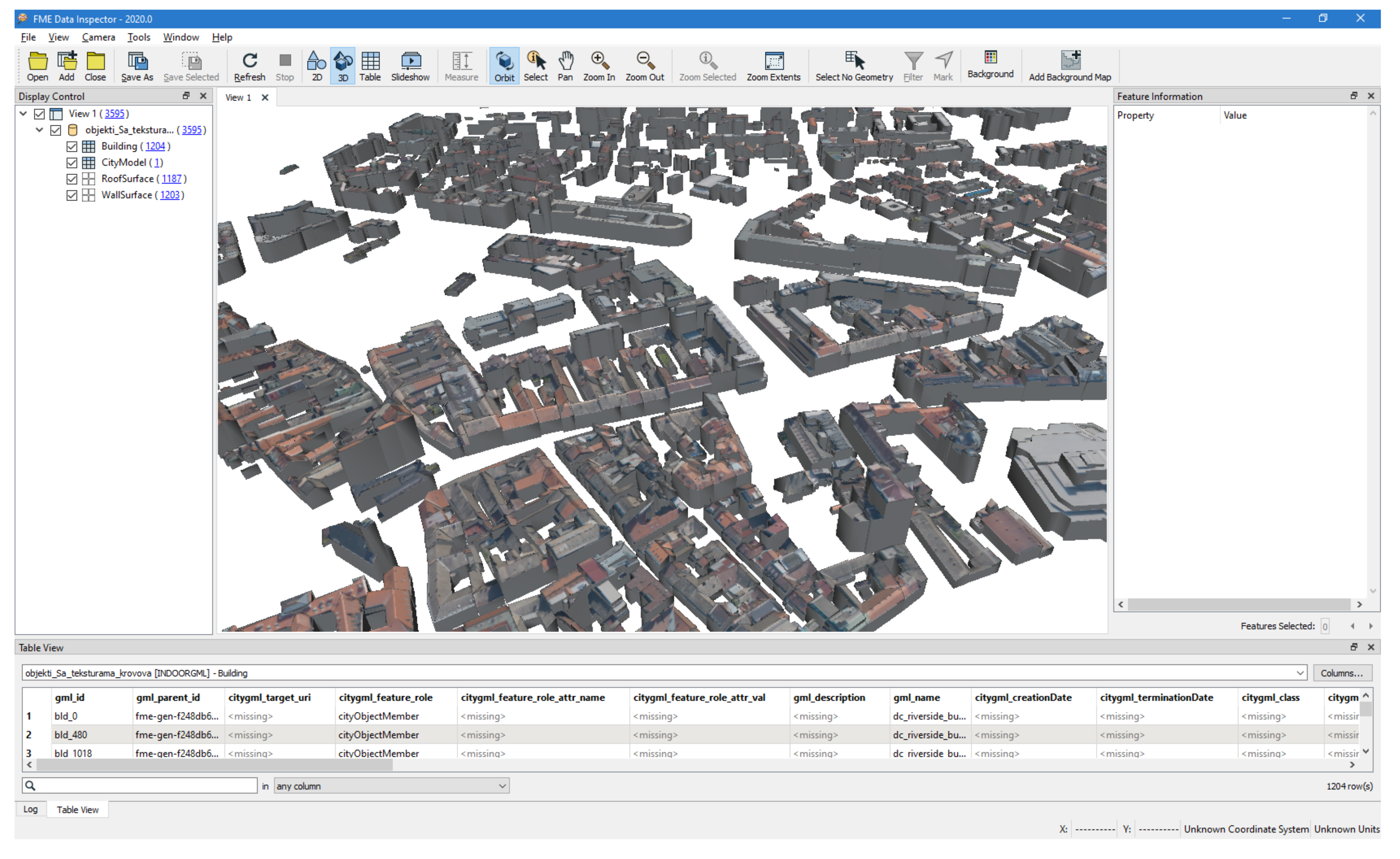
4.1. Data Transformation
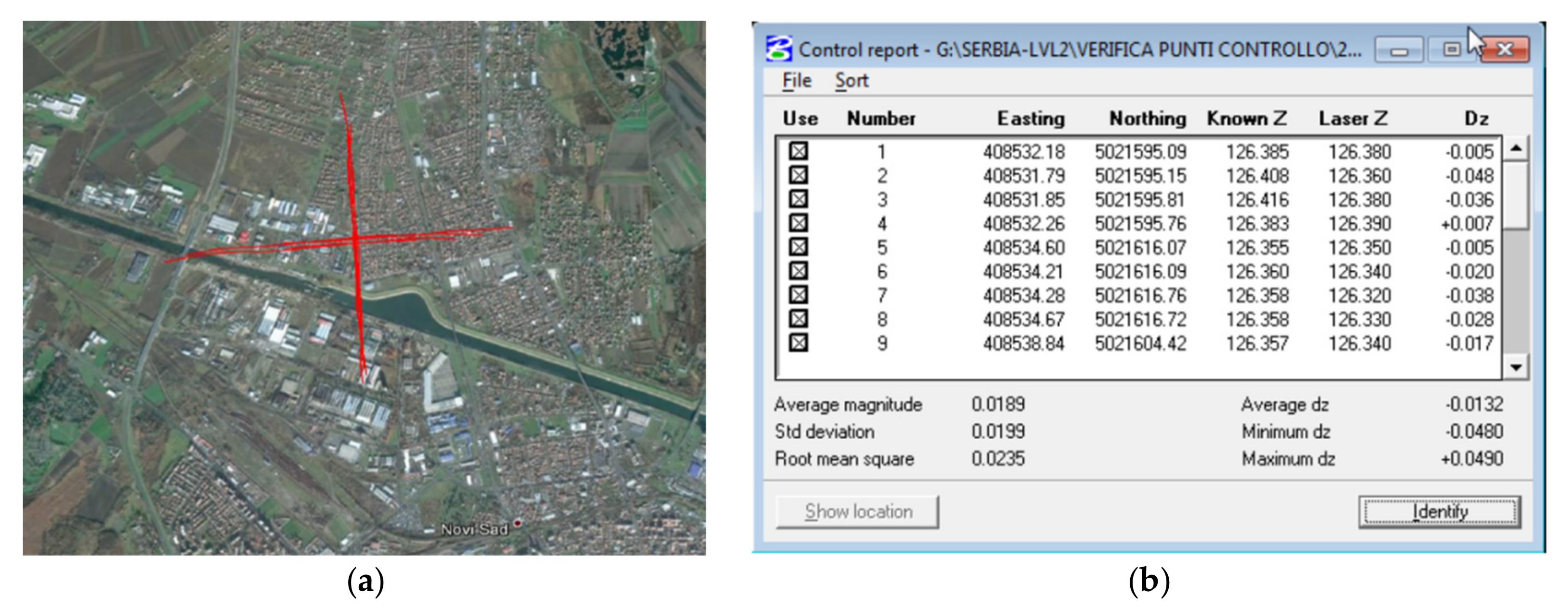
4.2. Data Accuracy Assement
5. Discussion and Future Developments
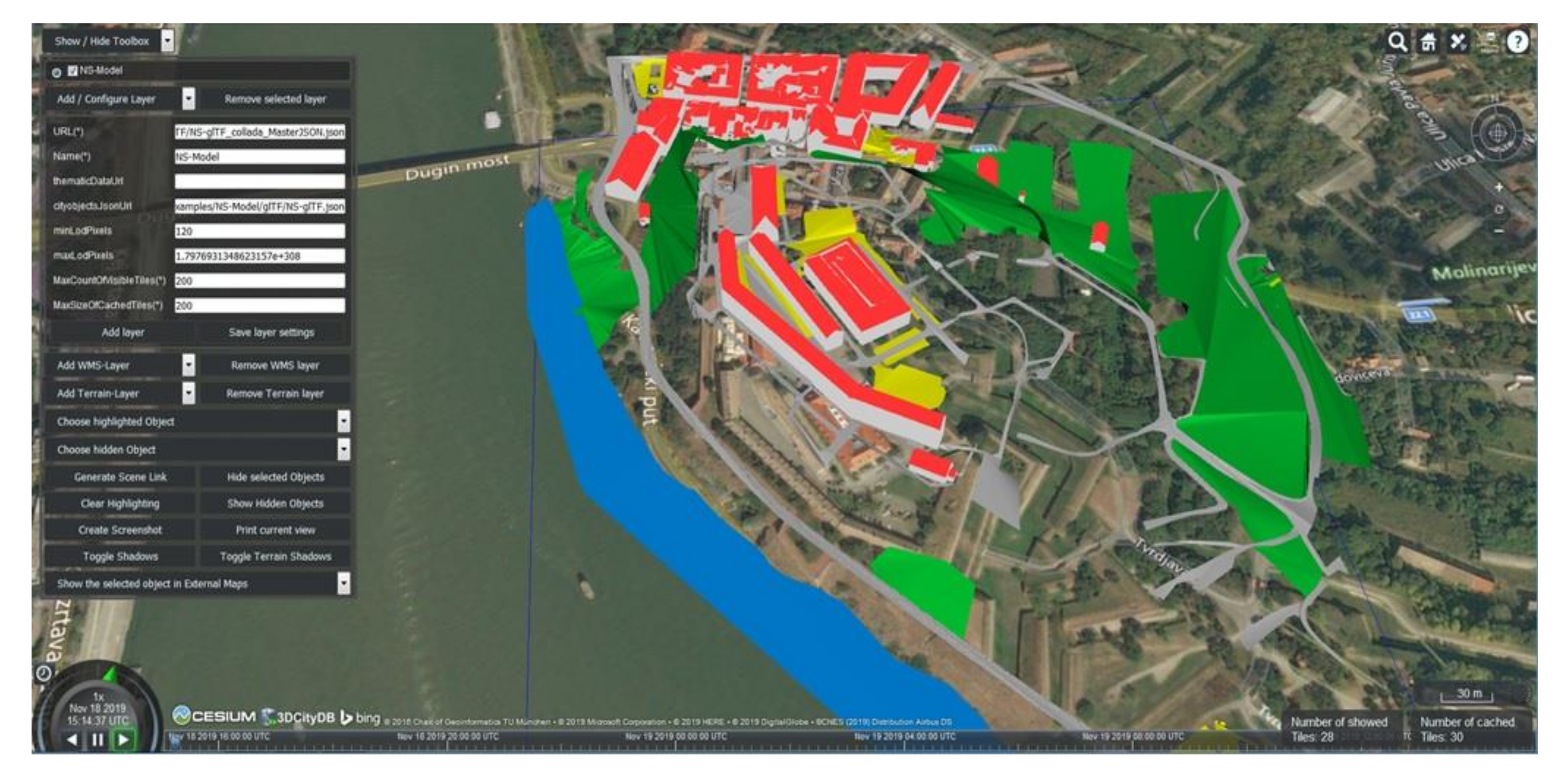
5.1. Virtual 3D City Model and Urban Planning
5.2. Virtual 3D City Model and 3D Cadastre
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Peris-Ortiz, M.; Bennett, D.R.; Yábar, D.P.-B. Sustainable Smart Cities: Creating Spaces for Technological, Social and Business Development; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016; ISBN 9783319408958. [Google Scholar]
- Hunt, D.; Rogers, C.; Cavada, M. Smart Cities: Contradicting Definitions and Unclear Measures; MDPI Sciforum: Basel, Switzerland, 2014; p. f004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaturvedi, K.; Matheus, A.; Nguyen, S.H.; Kolbe, T.H. Securing Spatial Data Infrastructures for Distributed Smart City applications and services. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 101, 723–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Open Geospatial Consortium. Available online: https://www.ogc.org/ (accessed on 1 April 2020).
- OGC SmartCity DWG. Available online: https://www.ogc.org/projects/groups/smartcitiesdwg (accessed on 1 April 2020).
- Ullah, Z.; Al-Turjman, F.; Mostarda, L.; Gagliardi, R. Applications of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Smart Cities. Comput. Commun. 2020, 154, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathore, M.; Paul, A.; Hong, W.; Seo, H.; Awan, I.; Saeed, S. Exploiting IoT and Big Data Analytics: Defining Smart Digital City Using Real-Time Urban Data. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 40, 600–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahad, M.A.; Paiva, S.; Tripathi, G.; Feroz, N. Enabling Technologies and Sustainable Smart Cities. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninčević Pašalić, I.; Ćukušić, M.; Jadrić, M. Smart city research advances in Southeast Europe. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2020, 102127, in press. [Google Scholar]
- OGC City Geography Markup Language (CityGML) Encoding Standard; Open Geospatial Consortium: Wayland, MA, USA, 2012.
- OGC IndoorGML-with Corrigendum; Open Geospatial Consortium: Wayland, MA, USA, 2018.
- OGC CityGML 3.0 Conceptual Model. Available online: https://github.com/opengeospatial/CityGML-3.0CM (accessed on 14 June 2020).
- Kutzner, T.; Chaturvedi, K.; Kolbe, T.H. CityGML 3.0: New Functions Open Up New Applications. PFG J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Geoinf. Sci. 2020, 88, 43–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ślusarski, M.; Jurkiewicz, M. Visualisation of Spatial Data Uncertainty. A Case Study of a Database of Topographic Objects. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bonczak, B.; Kontokosta, C.E. Large-scale parameterization of 3D building morphology in complex urban landscapes using aerial LiDAR and city administrative data. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2019, 73, 126–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Guldmann, J.M. Creating 3D city models with building footprints and LIDAR point cloud classification: A machine learning approach. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2019, 75, 76–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henn, A.; Gröger, G.; Stroh, V.; Plümer, L. Model driven reconstruction of roofs from sparse LIDAR point clouds. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2013, 76, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abayowa, B.O.; Yilmaz, A.; Hardie, R.C. Automatic registration of optical aerial imagery to a LiDAR point cloud for generation of city models. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2015, 10, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biljecki, F. Level of Detail in 3D City Models. Ph.D. Thesis, TU Delft, Delft, The Netherlands, 2017; p. 353. [Google Scholar]
- Gröger, G.; Plümer, L. CityGML—Interoperable semantic 3D city models. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2012, 71, 12–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goebbels, S.; Pohle-Fröhlich, R. Techniques for improved CityGML models. Graph. Models 2019, 106, 101044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Luo, F.; Zhu, H.; Ying, S.; Zhao, Z. A two-level topological model for 3D features in CityGML. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2016, 59, 11–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biljecki, F.; Ledoux, H.; Stoter, J. An improved LOD specification for 3D building models. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2016, 59, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Biljecki, F.; Ledoux, H.; Stoter, J.; Zhao, J. Formalisation of the level of detail in 3D city modelling. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2014, 48, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Duan, X.Q.; Zhu, H.H.; Guo, R.Z.; Ying, S. Semantic volume texture for virtual city building model visualisation. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2015, 54, 95–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biljecki, F.; Ledoux, H.; Stoter, J. Generating 3D city models without elevation data. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2017, 64, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Ying, S.; Li, L.; Biljecki, F.; Su, F. An application-driven LOD modeling paradigm for 3D building models. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2020, 16, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biljecki, F.; Stoter, J.; Ledoux, H.; Zlatanova, S.; Çöltekin, A. Applications of 3D City Models: State of the Art Review. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2015, 4, 2842–2889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tang, L.; Li, L.; Ying, S.; Lei, Y. A Full Level-of-Detail Specification for 3D Building Models Combining Indoor and Outdoor Scenes. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Monsalvete, P.; Robinson, D.; Eicker, U. Dynamic Simulation Methodologies for Urban Energy Demand. Energy Procedia 2015, 78, 3360–3365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agugiaro, G. Open data-modeling standards for city-wide energy simulations. Urban Energy Syst. Low-Carbon Cities 2019, 1, 241–255. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Hong, T.; Luo, X.; Hooper, B. Development of city buildings dataset for urban building energy modeling. Energy Build. 2019, 183, 252–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paiho, S.; Ketomäki, J.; Kannari, L.; Häkkinen, T.; Shemeikka, J. A new procedure for assessing the energy-efficient refurbishment of buildings on district scale. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 46, 101454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, B.; Ban, Y.; Laumert, B. Dynamic Online 3D Visualization Framework for Real-Time Energy Simulation Based on 3D Tiles. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murshed, S.M.; Picard, S.; Koch, A. Modelling, Validation and Quantification of Climate and Other Sensitivities of Building Energy Model on 3D City Models. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2018, 7, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, K.; Siebers, P.O.; Robinson, D. Towards Generalized Co-simulation of Urban Energy Systems. Procedia Eng. 2017, 198, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattenbach, M.; Redweik, R.; Lüdtke, S.; Kuster, B.; Nagel, C. Uncertainties in City Greenhouse Gas Inventories. Energy Procedia 2015, 76, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jusuf, S.K.; Mousseau, B.; Godfroid, G.; Hui, V.S.J. Integrated modeling of CityGML and IFC for city/neighborhood development for urban microclimates analysis. Energy Procedia 2017, 122, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eicker, U.; Nouvel, R.; Duminil, E.; Coors, V. Assessing Passive and Active Solar Energy Resources in Cities Using 3D City Models. Energy Procedia 2014, 57, 896–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eicker, U.; Zirak, M.; Bartke, N.; Rodríguez, L.R.; Coors, V. New 3D model based urban energy simulation for climate protection concept. Energy Build. 2018, 163, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Góźdź, K.; Pachelski, W.; van Oosterom, P.; Coors, V. The Possibilities of Using CityGML for 3D Representation of Buildings in the Cadastre. In Proceedings of the 4th International Workshop on 3D Cadastres, Dubai, UAE, 9–11 November 2014; pp. 339–362. [Google Scholar]
- Rönsdorf, C.; Wilson, D.; Stoter, J. Integration of Land Administration Domain Model with CityGML for 3D Cadastre. In Proceedings of the 4th International Workshop on 3D Cadastres, Dubai, UAE, 9–11 November 2014; pp. 313–322. [Google Scholar]
- Roschlaub, R.; Batscheider, J. An INSPIRE-conform 3D model building model of Bavaria using cadastre information, Lidar and image matching. ISPRS—Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. XLI-B4 2016, 41, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmen, C.; van Oosterom, P.; Bennett, R. The Land Administration Domain Model. Land Use Policy 2015, 49, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Çağdaş, V. An Application Domain Extension to CityGML for immovable property taxation: A Turkish case study. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2013, 21, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Lei, Y.; Tang, L.; Yan, F.; Zhu, H. A 3D spatial data model of the solar rights associated with individual residential properties. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2019, 7, 88–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wu, J.; Zhu, H.; Duan, X.; Luo, F. 3D modeling of the ownership structure of condominium units. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 2016, 59, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitsakis, D.; Kalantari, M.; Rajabifard, A.; Atazadeh, B.; Dimopoulou, E. Exploring the 3rd dimension within public law restrictions: A case study of Victoria, Australia. Land Use Policy 2019, 85, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Mi, S.; Olsson, P.; Paulsson, J.; Harrie, L. Utilizing BIM and GIS for Representation and Visualization of 3D Cadastre. SPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2019, 8, 503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aien, A.; Rajabifard, A.; Kalantari, M.; Shojaei, D. Integrating Legal and Physical Dimensions of Urban Environments. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2015, 4, 1442–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Radulović, A.; Govedarica, M.; Pržulj, Đ. Recommendation for the development of 3D cadastre. In Proceedings of the Serbian Geodetic Congress, Belgrade, Serbia, 1–3 December 2011; Republic Geodetic Authority: Belgrade, Serbia, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sladić, D.; Radulović, A.; Govedarica, M. Development of process model for Serbian cadastre. Land Use Policy 2020, 22, 104273, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Eicker, U.; Weiler, V.; Schumacher, J.; Braun, R. On the design of an urban data and modeling platform and its application to urban district analyses. Energy Build. 2020, 13, 109954, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egusquiza, A.; Prieto, I.; Izkara, J.L.; Béjar, R. Multi-scale urban data models for early-stage suitability assessment of energy conservation measures in historic urban areas. Energy Build. 2018, 164, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pispidikis, I.; Dimopoulou, E. CityGML Restful Web Service: Automatic Retrieval of CityGML Data Based on their Semantics. Principles, Guidelines and Bldg Conceptual Design. ISPRS Ann. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2018, 4, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buyuksalih, G.; Baskaraca, P.; Bayburt, S.; Buyuksalih, I.; Abdul Rahman, A. 3D City Modelling of Istanbul Based on Lidar Data and Panoramic Images—Issues and Challenges. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2019, 4, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Axelsson, P. Processing of Laser Scanner Data—Algorithms and Applications. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 1999, 54, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Axelsson, P. DEM Generation from Laser Scanner Data Using Adaptive TIN Models. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2000, 33, 110–117. [Google Scholar]
- Elaksher, A.F. Using LIDAR-Based DEM to Orthorectify IKONOS Panchromatic Images. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2009, 47, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Peterson, J.; Chandra, S. LiDAR-Derived High Quality Ground Control Information and DEM for Image Orthorectification. Geoinformatica 2007, 11, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Republic Geodetic Authority of Serbia, Digital Topographic Key. 2005. Available online: https://www.grf.bg.ac.rs/p/learning/digitalni_topografski_kljuc_1463993460069.pdf (accessed on 5 April 2020).
- Kolbe, T.H.; Gröger, G.; Plümer, L. CityGML: Interoperable Access to 3D City Models. In Geo-information for Disaster Management; Van Oosterom, P., Zlatanova, S., Fendel, E.M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; pp. 883–899. [Google Scholar]
- Biljecki, F.; Ledoux, H.; Stoter, J.; Vosselman, G. The Variants of an LOD of a 3D Building Model and Their Influence on Spatial Analyses. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 116, 42–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rutzinger, M.; Rottensteiner, F.; Pfeifer, N. A Comparison of Evaluation Techniques for Building Extraction from Airborne Laser Scanning. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2009, 2, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrowski, W.; Pilarska, M.; Charyton, J.; Bakuła, K. Analysis of 3D Building Models Accuracy Based on the Airborne Laser Scanning Point Clouds. ISPRS Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2018, 2, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saraf, N.M.; Hamid, J.R.A.; Halim, M.A.; Rasam, A.R.A.; Lin, S. Accuracy Assessment of 3-Dimensional LiDAR Building Extraction. In Proceedings of the IEEE 14th International Colloquium on Signal Processing and Its Applications, Penang, Malaysia, 9 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rottensteiner, F.; Sohn, G.; Gerke, M.; Wegner, J.D. ISPRS Test Project on Urban Classification and 3D Building Reconstruction. In ISPRS—Commission III—Photogrammetric Computer Vision and Image Analysis Working Group III/4 -3D Scene Analysis; ISPRS: Paris, France, 2013; pp. 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Truong-Hong, L.; Laefer, D.F. Quantitative Evaluation Strategies for Urban 3D Model Generation from Remote Sensing Data. Comput. Graph. 2015, 49, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dorninger, P.; Pfeifer, N. A Comprehensive Automated 3D Approach for Building Extraction, Reconstruction, and Regularization from Airborne Laser Scanning Point Clouds. Sensors 2008, 8, 7323–7343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- ASPRS Guidelines Vertical Accuracy Reporting for Lidar Data. Available online: https://www.asprs.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/01/Vertical_Accuracy_Reporting_for_Lidar_Data.pdf (accessed on 15 July 2020).
- Pang, G. Outlier Detection and Data Filtering in LiDAR Data with Multiple Attributes. Ph.D. Thesis, Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Matkan, A.; Hajeb, M.; Mirbagheri, B.; Sadeghian, S.; Ahmadi, M. Spatial Analysis for Outlier Removal from LiDAR Data. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. ISPRS Arch. 2014, 40, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dorić, B. Urban and Spatial Planning Institute of Vojvodina 1950–2004, Monograph; Urban and Spatial Planning Institute of Vojvodina: Novi Sad, Serbia, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Official Gazette of the Republic of Serbia, No. 72/2009, The Law on Planning and Construction. Available online: http://www.zavurbvo.co.rs/doc/Zakon_o_planiranju_i_izgradnji.pdf (accessed on 5 April 2020).
- Sladić, D.; Govedarica, M.; Radulović, A. A Solution for Efficient Management of GIS Data in Urban Planning. In Proceedings of the 11th International Multidisciplinary Scientific GeoConference SGEM, Albena, Bulgaria, 1 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- The Environmental Noise Directive (2002/49/EC). Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/environment/archives/noise/directive.htm (accessed on 5 April 2020).
- Official Gazette of Republic of Serbia, No. 36/09, 88/10. The Law on Protection against Noise in Environment. Available online: https://www.paragraf.rs/propisi/zakon_o_zastiti_od_buke_u_zivotnoj_sredini.html (accessed on 5 April 2020).
- Official Gazette of the Republic of Serbia, No. 80/10, Rulebook on the Content and Methods of Developing Strategic Noise Maps and How They Are Presented to the Public. Available online: http://www.pravno-informacioni-sistem.rs/SlGlasnikPortal/eli/rep/sgrs/ministarstva/pravilnik/2010/80/2/reg (accessed on 5 April 2020).
- Strategic Noise Map for Part of Novi Sad-Liman; JP Urbanizam: Novi Sad, Serbia, 2014.
- Radulović, A.; Sladić, D.; Govedarica, M. Towards 3D Cadastre in Serbia: Development of Serbian Cadastral Domain Model. ISPRS Int. J. GeoInf. 2017, 6, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
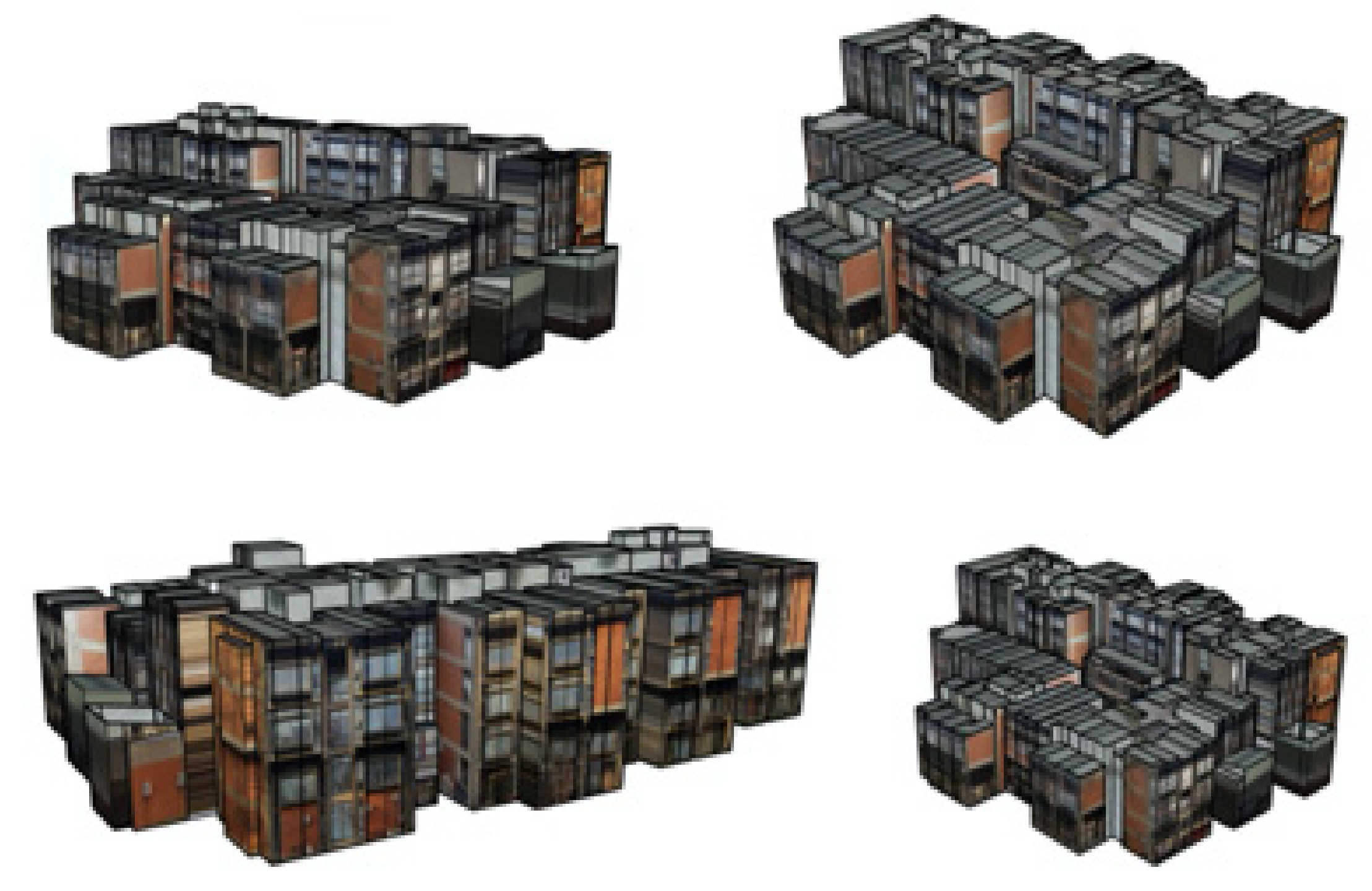
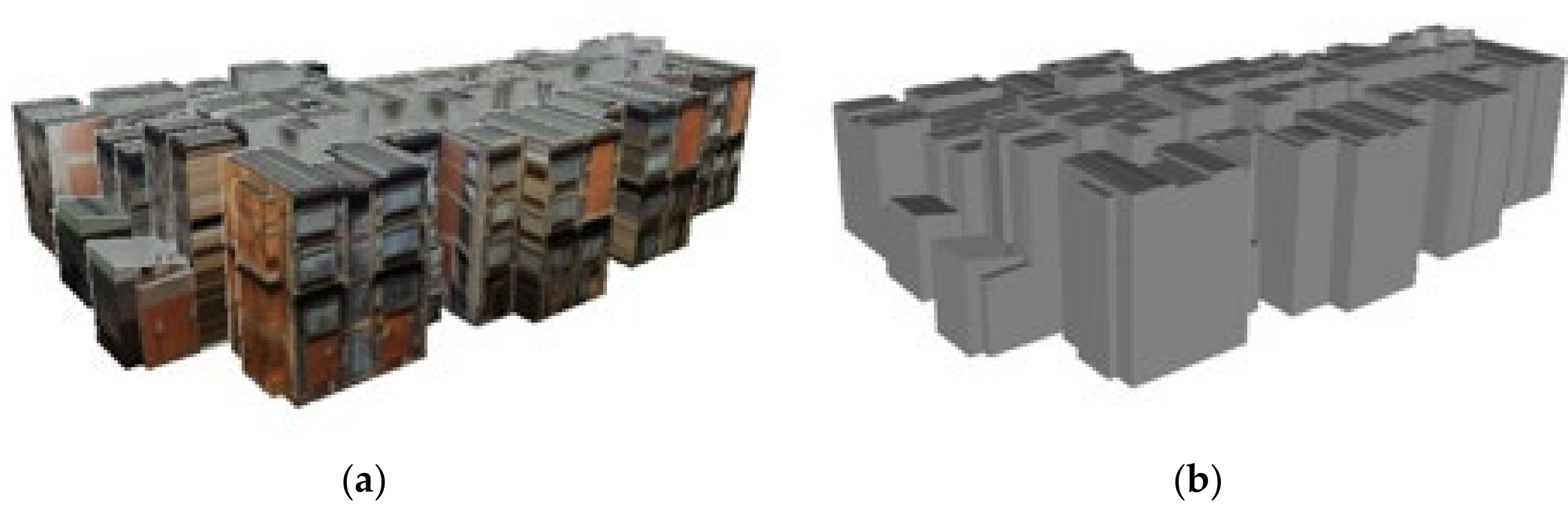






| 2D CAD/Vector Layers | 3D CAD/Vector Layers |
|---|---|
| Asphalt road, field road, pedestrian road, forest, park, isolated trees, bush, terrace, river, stream, water, canal, fence, railway, bridge, parking, bench, bus stops | House, building, residential and commercial building, auxiliary building, lighting, pole, power lines, traffic sign |
| CAD Layers | CityGML Features |
|---|---|
| House, building, auxiliary object, residential and commercial object | Building, RoofSurface, WallSurface |
| Breaklines, grid | TINRelief |
| Forest, thicket | PlantCover |
| Road, field road, pedestrian road | Road |
| Parking, other | LandUse |
| Water | WaterBody |
| External Reference | Name | URI |
|---|---|---|
| informationSystem | http://www.nsurbanizam.rs/pgr | |
| externalObject.name | 142-p-public green area |
| External Reference | Name | URI |
|---|---|---|
| informationSystem | https://katastar.rgz.gov.rs/eKatastarPublic | |
| externalObject.name | 89010-1124-0-1-1 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jovanović, D.; Milovanov, S.; Ruskovski, I.; Govedarica, M.; Sladić, D.; Radulović, A.; Pajić, V. Building Virtual 3D City Model for Smart Cities Applications: A Case Study on Campus Area of the University of Novi Sad. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2020, 9, 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi9080476
Jovanović D, Milovanov S, Ruskovski I, Govedarica M, Sladić D, Radulović A, Pajić V. Building Virtual 3D City Model for Smart Cities Applications: A Case Study on Campus Area of the University of Novi Sad. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information. 2020; 9(8):476. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi9080476
Chicago/Turabian StyleJovanović, Dušan, Stevan Milovanov, Igor Ruskovski, Miro Govedarica, Dubravka Sladić, Aleksandra Radulović, and Vladimir Pajić. 2020. "Building Virtual 3D City Model for Smart Cities Applications: A Case Study on Campus Area of the University of Novi Sad" ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information 9, no. 8: 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi9080476
APA StyleJovanović, D., Milovanov, S., Ruskovski, I., Govedarica, M., Sladić, D., Radulović, A., & Pajić, V. (2020). Building Virtual 3D City Model for Smart Cities Applications: A Case Study on Campus Area of the University of Novi Sad. ISPRS International Journal of Geo-Information, 9(8), 476. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijgi9080476






